Lipid Mediators Metabolic Chaos of Asthmatic Mice Reversed by Rosmarinic Acid
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
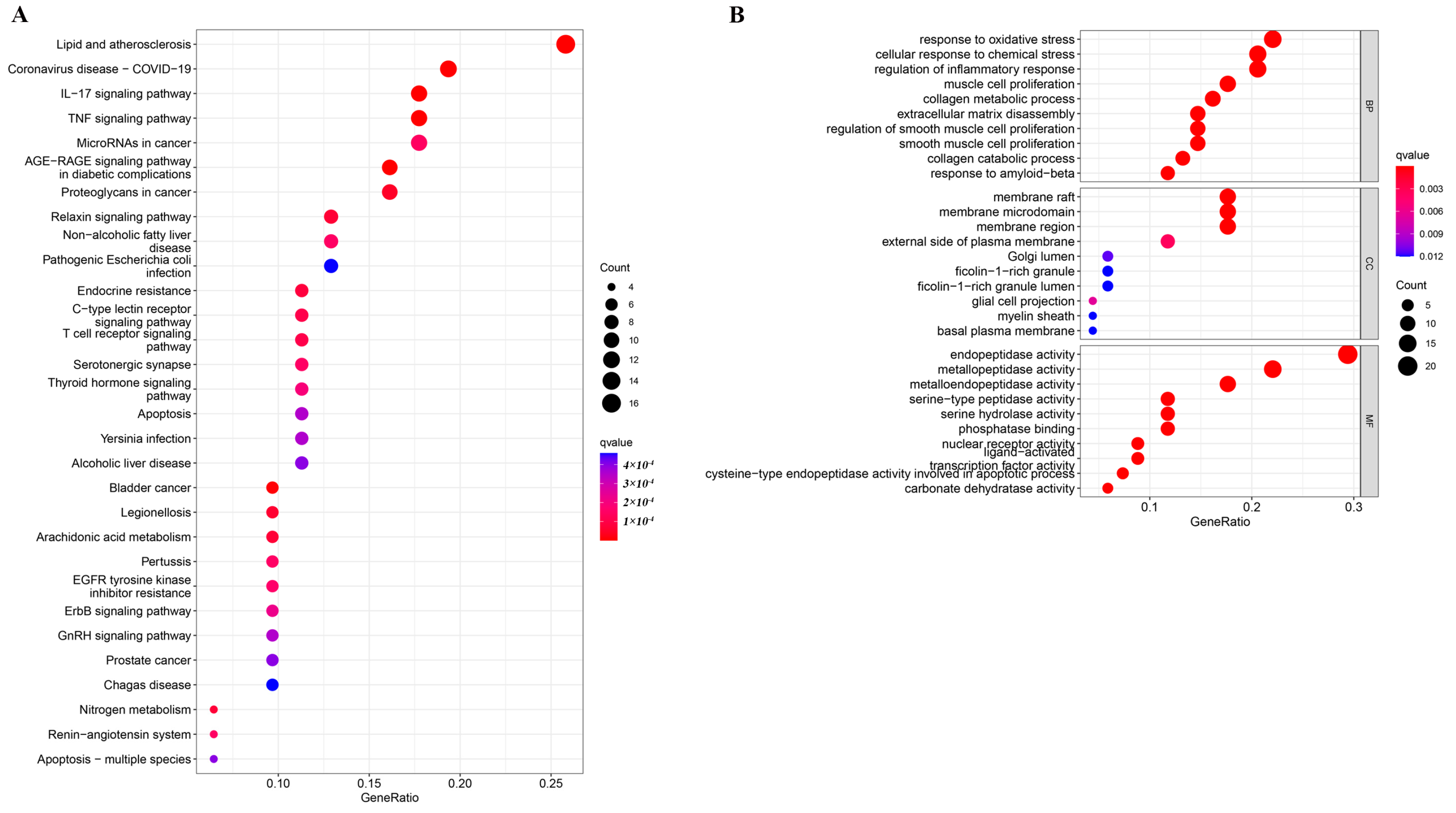
2.1. Enrichment Analysis
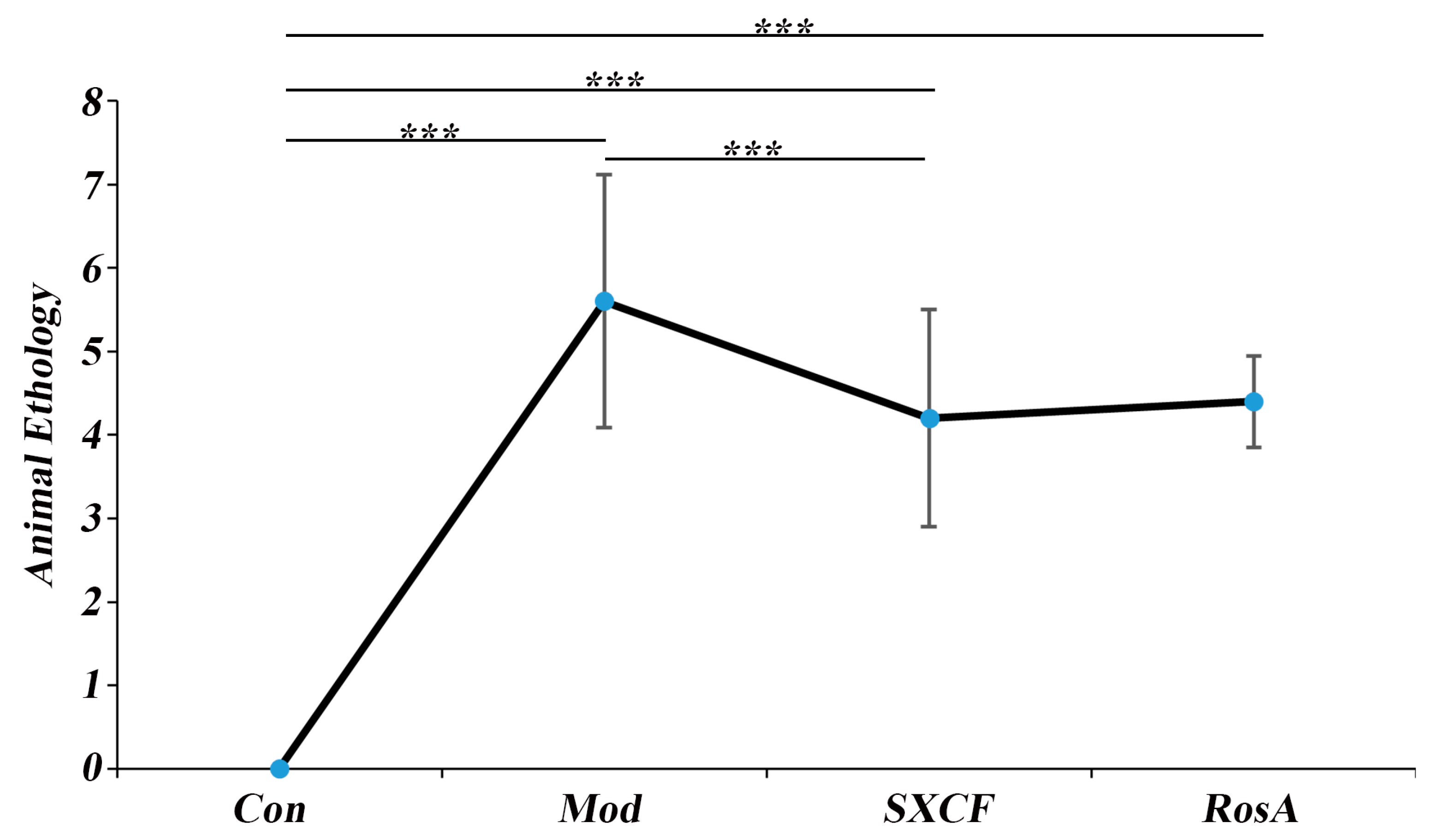
2.2. Animal Ethology
2.3. Histology and Serology
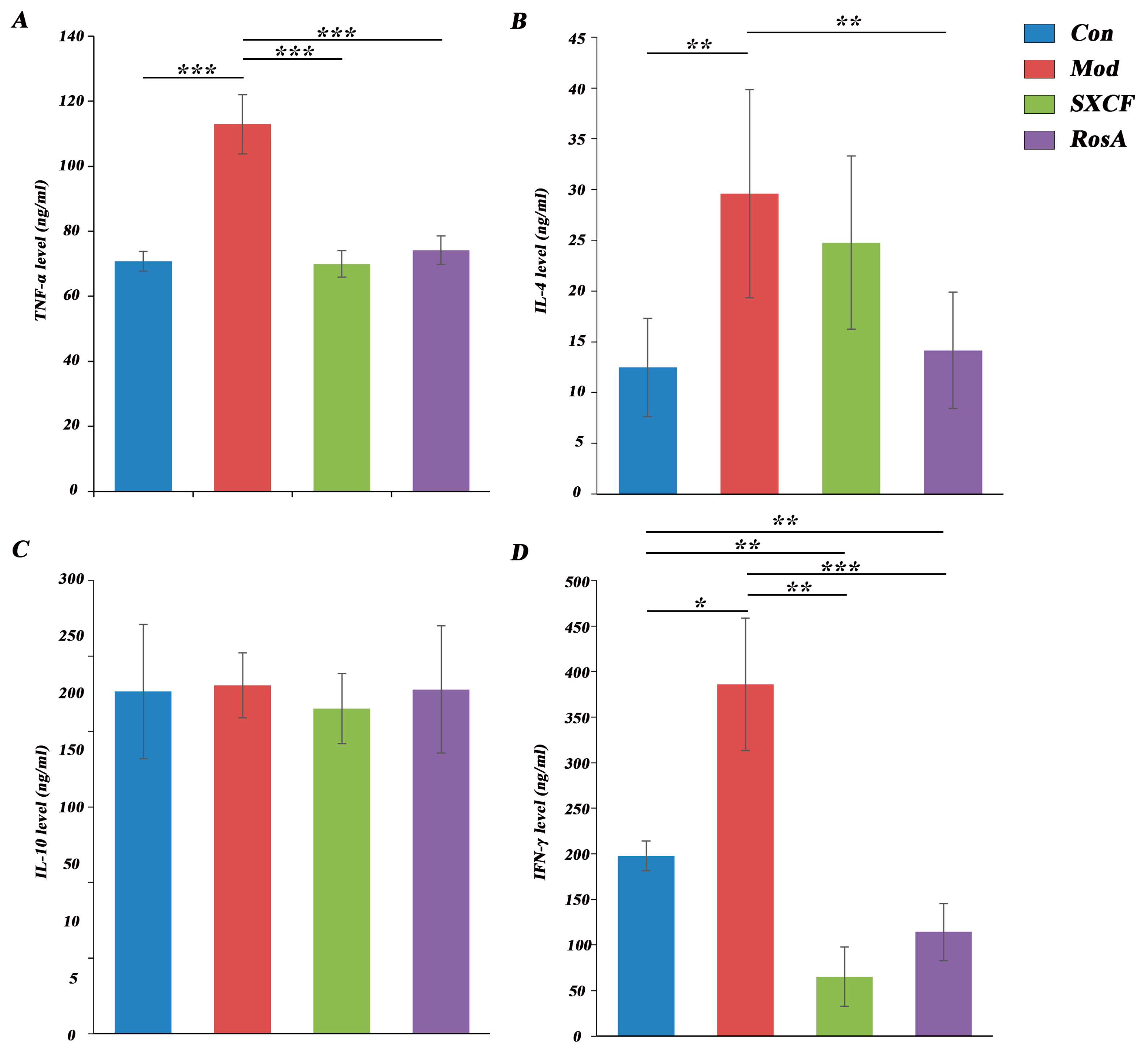
2.4. Regulated Cytokine Levels of Target Organ
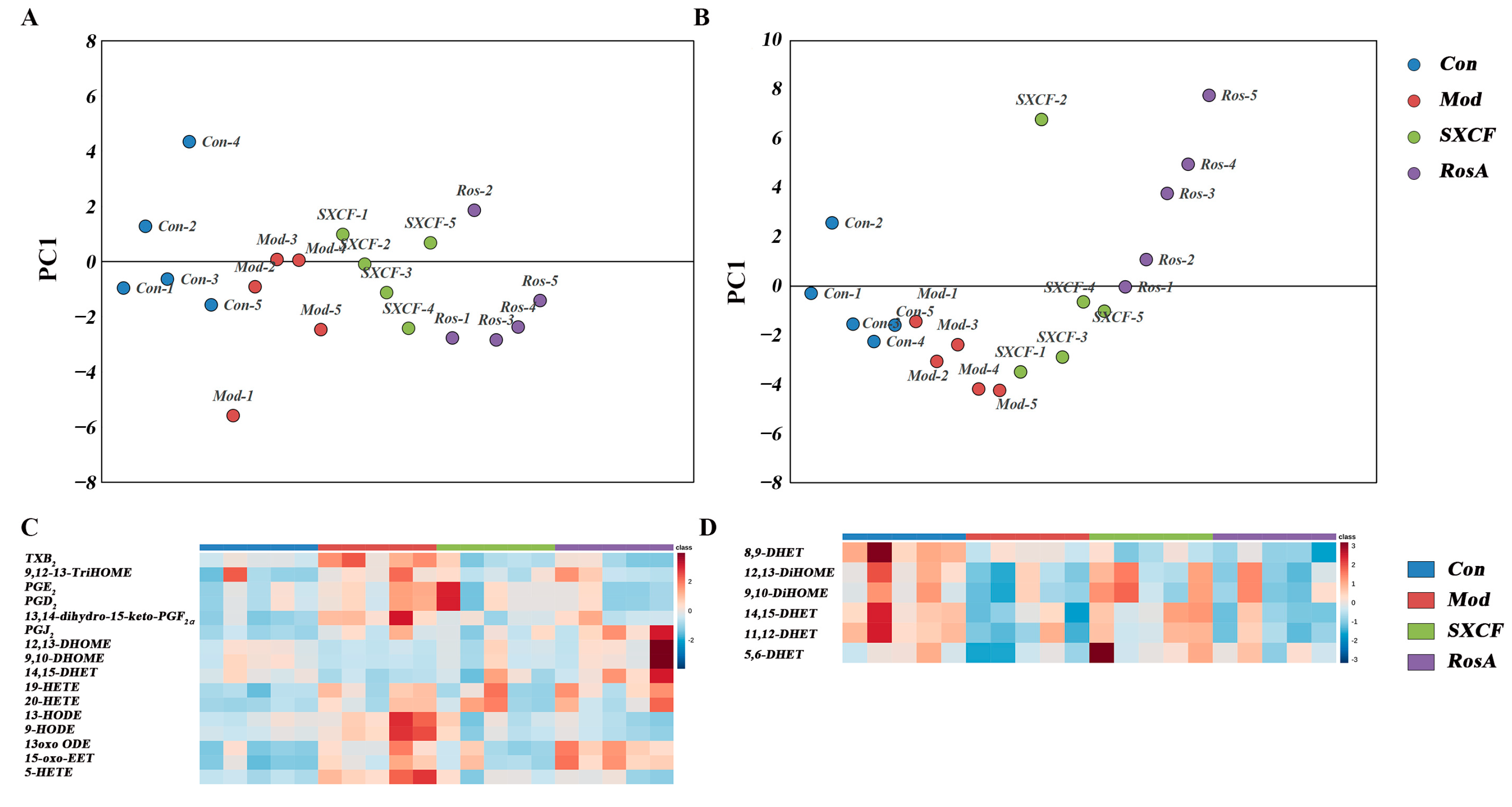
2.5. Characterization of Target Organ LMs Metabolism Network
3. Discussion
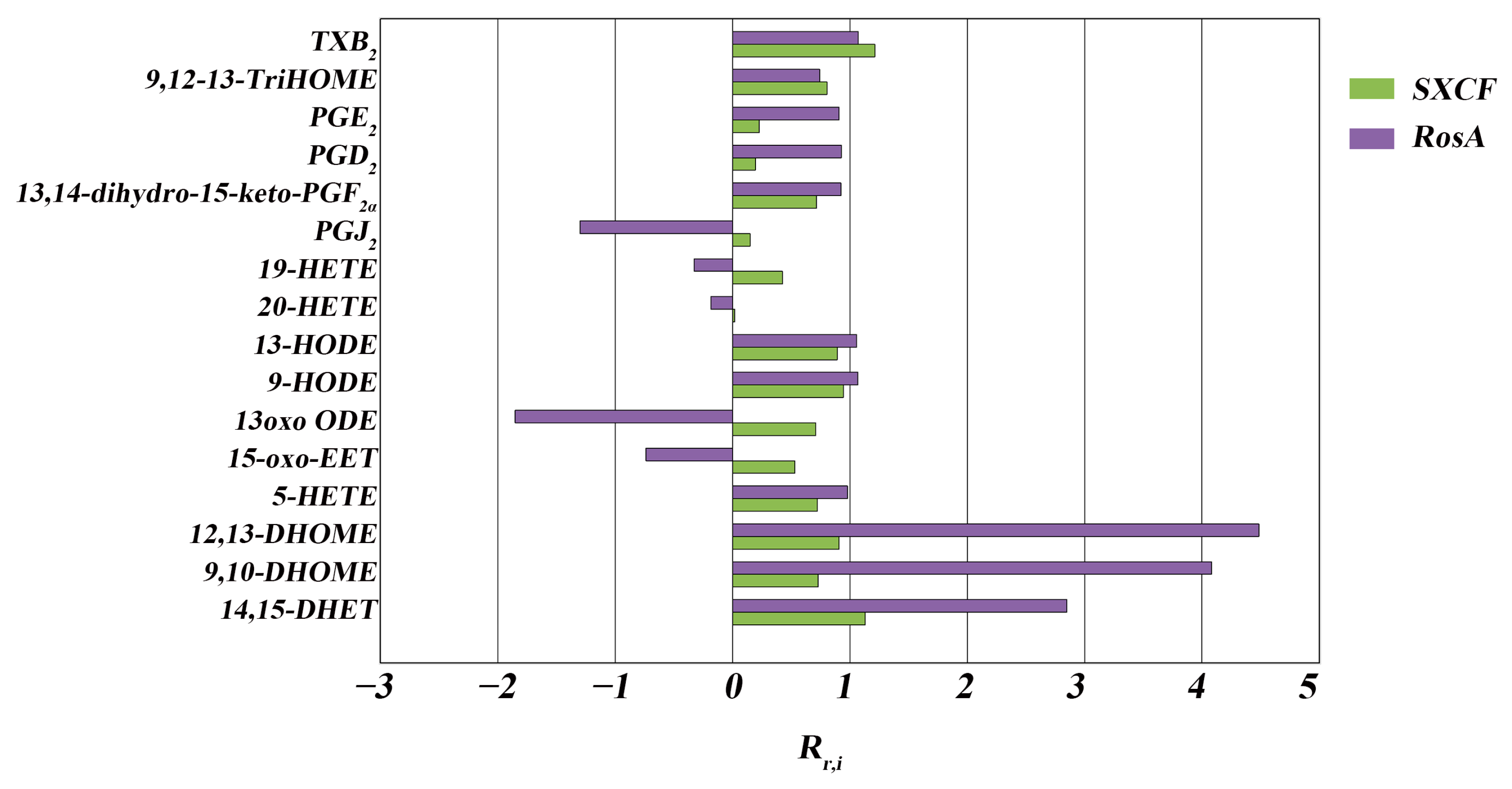
3.1. RosA Induced Equal Effects on Key-LMs as SXCF
3.2. SXCF Reduced the Side Reactions by Neutralizing Parts of RosA Regulation on LMs Metabolic Network
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Network Pharmacology
4.2.2. Animals and Preparation of Asthma Model
4.2.3. Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining
4.2.4. Cytokine Detection
4.2.5. Sample Preparation
4.2.6. UPLC-MS/MS Conditions
4.2.7. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Ray, A.; Raundhal, M.; Oriss, T.B.; Ray, P.; Wenzel, S.E. Current concepts of severe asthma. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 2394–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsumoto, T.R.; Kudo, M.; Chen, C.; Sundaram, A.; Callahan, E.C.; Zhu, J.W.; Lin, J.; Rosen, C.E.; Manz, B.N.; Lee, J.W.; et al. The phosphatase CD148 promotes airway hyperresponsiveness through SRC family kinases. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 2037–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Staa, T.-P.; Bishop, N.; Leufkens, H.G.; Cooper, C. Are inhaled corticosteroids associated with an increased risk of fracture in children? Osteoporos. Int. 2004, 15, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavoie, K.L.; Cartier, A.; Labrecque, M.; Bacon, S.L.; Lemiere, C.; Malo, J.L.; Lacoste, G.; Barone, S.; Verrier, P.; Ditto, B. Are psychiatric disorders associated with worse asthma control and quality of life in asthma patients? Respir. Med. 2005, 99, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, F.; Liu, R.; Hu, M.; Rong, X.; Bai, L.; Xu, L.; Mao, Y.; Hasimu, H.; Sun, Y.; He, J. JAX2, an ethanol extract of Hyssopus cuspidatus Boriss, can prevent bronchial asthma by inhibiting MAPK/NF-kappaB inflammatory signaling. Phytomedicine 2019, 57, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Gul, A.; Yu, H.; Huang, X.; Deng, L.; Pan, Y.; Ni, S.; Nurahmat, M.; Abduwaki, M.; Luo, Q. Integrated systems pharmacology and transcriptomics to dissect the mechanisms of Loki Zupa decoction in the treatment of murine allergic asthma. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 294, 115351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micovic, T.; Katanic Stankovic, J.S.; Bauer, R.; Nost, X.; Markovic, Z.; Milenkovic, D.; Jakovljevic, V.; Tomovic, M.; Bradic, J.; Stesevic, D.; et al. In vitro, in vivo and in silico evaluation of the anti-inflammatory potential of Hyssopus officinalis L. subsp. aristatus (Godr.) Nyman (Lamiaceae). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 293, 115201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Li, L.; Diao, J. Qualitative and quantitative analyses of labiatenic acid, apigenin and buddleoside in Hyssopus officinalis by high-performance thin-layer chromatography. JPC–J. Planar Chromatogr.–Mod. TLC 2021, 34, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, H.; Osakabe, N.; Sanbongi, C.; Yanagisawa, R.; Inoue, K.-I.; Yasuda, A.; Natsume, M.; Baba, S.; Ichiishi, E.-I.; Yoshikawa, T. Extract of Perilla frutescens Enriched for Rosmarinic Acid, a Polyphenolic Phytochemical, Inhibits Seasonal Allergic Rhinoconjunctivitis in Humans. Exp. Biol. Med. 2004, 229, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, N.; Cai, R.; Gu, J.; Xie, F.; Wei, H.; Lu, C.; Wu, D. Rosmarinic acid protects mice from imiquimod induced psoriasis-like skin lesions by inhibiting the IL-23/Th17 axis via regulating Jak2/Stat3 signaling pathway. Phytother. Res. PTR 2021, 35, 4526–4537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelm, M.; Nair, M.; Strasburg, G.; DeWitt, D. Antioxidant and cyclooxygenase inhibitory phenolic compounds from Ocimum sanctum Linn. Phytomedicine 2000, 7, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanbongi, C.; Takano, H.; Osakabe, N.; Sasa, N.; Natsume, M.; Yanagisawa, R.; Inoue, K.I.; Sadakane, K.; Ichinose, T.; Yoshikawa, T. Rosmarinic acid in perilla extract inhibits allergic inflammation induced by mite allergen, in a mouse model. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2004, 34, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Wu, L.; Deng, X.; Liang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Deng, R.; Lv, L.; Ji, M.; Hao, Z.; He, J. The Antioxidant Rosmarinic Acid Ameliorates Oxidative Lung Damage in Experimental Allergic Asthma via Modulation of NADPH Oxidases and Antioxidant Enzymes. Inflammation 2020, 43, 1902–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamid, Q.; Tulic, M. Immunobiology of Asthma. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2009, 71, 489–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.J. Th2 cytokines and asthma: An introduction. Respir. Res. 2001, 2, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, R.; Picado, C.; de Mora, F. The PGE2-EP2-mast cell axis: An antiasthma mechanism. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 63, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.; Hwang, J.J.; Kwon, B.I.; Kheradmand, F.; Corry, D.B.; Lee, S.H. Leukotriene enhanced allergic lung inflammation through induction of chemokine production. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 15, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauvreau, G.M.; Boulet, L.P.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Cockcroft, D.W.; Davis, B.E.; Leigh, R.; Tanaka, M.; Fourre, J.A.; Tanaka, M.; Nabata, T.; et al. A dual CysLT1/2 antagonist attenuates allergen-induced airway responses in subjects with mild allergic asthma. Allergy 2016, 71, 1721–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Park, Y.; Wu, J.; Chen, X.; Lee, S.; Yang, J.; Dellsperger, K.C.; Zhang, C. Role of TNF-α in vascular dysfunction. Clin. Sci. 2009, 116, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willerson, J.T.; Ridker, P.M. Inflammation as a cardiovascular risk factor. Circulation 2004, 109 (Suppl. S1), II2–II10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Y.; Bates, M.E.; Jarjour, N.N.; Busse, W.W.; Bertics, P.J.; Kelly, E.A.B. Generation of Th1 and Th2 Chemokines by Human Eosinophils: Evidence for a Critical Role of TNF-α1. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 4840–4848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, W.E. Interleukin 4: Signalling mechanisms and control of T cell differentiation. Ciba Found. Symp. 1997, 204, 208–216, discussion 216-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapsenberg, M.L. Dendritic-cell control of pathogen-driven T-cell polarization. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Lloyd, C.M.; Noble, A. Th17 responses in chronic allergic airway inflammation abrogate regulatory T-cell-mediated tolerance and contribute to airway remodeling. Mucosal Immunol. 2013, 6, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroder, K.; Hertzog, P.J.; Ravasi, T.; Hume, D.A. Interferon-gamma: An overview of signals, mechanisms and functions. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2004, 75, 163–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billiau, A.; Matthys, P. Interferon-gamma: A historical perspective. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2009, 20, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, C.P.R.; Lima, C.F.; Fernandes-Ferreira, M.; Pereira-Wilson, C. Salvia Fruticosa, Salvia Officinalis, and Rosmarinic Acid Induce Apoptosis and Inhibit Proliferation of Human Colorectal Cell Lines: The Role in MAPK/ERK Pathway. Nutr. Cancer 2009, 61, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Zou, L.; Sun, H.; Peng, J.; Gao, C.; Bao, L.; Ji, R.; Jin, Y.; Sun, S. A review of the anti-inflammatory effects of rosmarinic acid on inflammatory diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Garra, A. Cytokines induce the development of functionally heterogeneous T helper cell subsets. Immunity 1998, 8, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagihara, Y.; Ikizawa, K.; Kajiwara, K.; Koshio, T.; Basaki, Y.; Akiyama, K. Functional significance of IL-4 receptor on B cells in IL-4-induced human IgE production. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1995, 96 (Suppl. S6), 1145–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabashima, K.; Murata, T.; Tanaka, H.; Matsuoka, T.; Sakata, D.; Yoshida, N.; Katagiri, K.; Kinashi, T.; Tanaka, T.; Miyasaka, M.; et al. Thromboxane A2 modulates interaction of dendritic cells and T cells and regulates acquired immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, P.; Caraffa, A.; Gallenga, C.; Ross, R.; Kritas, S.; Frydas, I.; Younes, A.; Di Emidio, P.; Ronconi, G.; Toniato, E. IL-1 induces throboxane-A2 (TxA2) in COVID-19 causing inflammation and micro-thrombi: Inhibitory effect of the IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra). J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2020, 34, 1623–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storch, J.; MacDermot, J. IgE and IgG are synergistic in antigen-mediated release of thromboxane from human lung macrophages. Cell. Immunol. 1991, 134, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, M.; Koya, T.; Kawakami, H.; Sakagami, T.; Hasegawa, T.; Kagamu, H.; Takada, T.; Sakai, Y.; Suzuki, E.; Gelfand, E.W.; et al. A prostacyclin agonist with thromboxane inhibitory activity for airway allergic inflammation in mice. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2010, 40, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikut, J.; Komorniak, N.; Ziętek, M.; Palma, J.; Szczuko, M. Inflammation with the participation of arachidonic (AA) and linoleic acid (LA) derivatives (HETEs and HODEs) is necessary in the course of a normal reproductive cycle and pregnancy. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2020, 141, 103177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eling, T.E.; Glasgow, W.C. Cellular proliferation and lipid metabolism: Importance of lipoxygenases in modulating epidermal growth factor-dependent mitogenesis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1994, 13, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.; Wortmann, M.; Mandal, P.K.; Arpornchayanon, W.; Jannasch, K.; Alves, F.; Strieth, S.; Conrad, M.; Beck, H. Absence of Glutathione Peroxidase 4 Affects Tumor Angiogenesis through Increased 12/15-Lipoxygenase Activity. Neoplasia 2010, 12, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühn, H.; O’Donnell, V.B. Inflammation and immune regulation by 12/15-lipoxygenases. Prog. Lipid Res. 2006, 45, 334–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildreth, K.; Kodani, S.D.; Hammock, B.D.; Zhao, L. Cytochrome P450-derived linoleic acid metabolites EpOMEs and DiHOMEs: A review of recent studies. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 86, 108484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levan, S.R.; Stamnes, K.A.; Lin, D.L.; Panzer, A.R.; Fukui, E.; McCauley, K.; Fujimura, K.E.; McKean, M.; Ownby, D.R.; Zoratti, E.M.; et al. Elevated faecal 12,13-diHOME concentration in neonates at high risk for asthma is produced by gut bacteria and impedes immune tolerance. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1851–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundström, S.L.; Yang, J.; Källberg, H.J.; Thunberg, S.; Gafvelin, G.; Haeggström, J.Z.; Grönneberg, R.; Grunewald, J.; van Hage, M.; Hammock, B.D.; et al. Allergic Asthmatics Show Divergent Lipid Mediator Profiles from Healthy Controls Both at Baseline and following Birch Pollen Provocation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, B.; Liu, T.; Yao, W.; Wan, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y. Antinociception role of 14,15-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid in a central post-stroke pain model in rats mediated by anti-inflammation and anti-apoptosis effect. Neurochem. Int. 2022, 154, 105291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudhahar, V.; Shaw, S.; Imig, J.D. Epoxyeicosatrienoic acid analogs and vascular function. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 1181–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Qian, Z.-Y.; Xie, F.; Fan, W.; Nelson, J.W.; Xiao, X.; Kaul, S.; Barnes, A.P.; Alkayed, N.J. Functional screening for G protein-coupled receptor targets of 14,15-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2017, 132, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari, A.A.; Thomson, S.; Edin, M.L.; Lih, F.B.; Zeldin, D.C.; Bishop-Bailey, D. Basal and inducible anti-inflammatory epoxygenase activity in endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 446, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, G.; Yuan, S.; Tan, C.; Xie, J.; Ding, Y.; Lian, P.; Fu, L.; Hou, Q.; Xu, B.; et al. 14,15-Epoxyeicosatrienoic acid suppresses cigarette smoke condensate-induced inflammation in lung epithelial cells by inhibiting autophagy. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2016, 311, L970–L980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanRollins, M.; Kaduce, T.L.; Knapp, H.R.; Spector, A.A. 14,15-Epoxyeicosatrienoic acid metabolism in endothelial cells. J. Lipid Res. 1993, 34, 1931–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Moore, S.A.; Stoll, L.L.; Rich, G.; Kaduce, T.L.; Weintraub, N.L.; Spector, A.A. 14,15-Epoxyeicosatrienoic acid inhibits prostaglandin E2 production in vascular smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 1998, 275, H2113–H2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biliktu, M.; Senol, S.P.; Temiz-Resitoglu, M.; Guden, D.S.; Horat, M.F.; Sahan-Firat, S.; Sevim, S.; Tunctan, B. Pharmacological inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase attenuates chronic experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by modulating inflammatory and anti-inflammatory pathways in an inflammasome-dependent and -independent manner. Inflammopharmacology 2020, 28, 1509–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imig, J.D.; Zhao, X.; Capdevila, J.H.; Morisseau, C.; Hammock, B.D. Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibition Lowers Arterial Blood Pressure in Angiotensin II Hypertension. Hypertension 2002, 39, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theken, K.N.; Schuck, R.N.; Edin, M.L.; Tran, B.; Ellis, K.; Bass, A.; Lih, F.B.; Tomer, K.B.; Poloyac, S.M.; Wu, M.C.; et al. Evaluation of cytochrome P450-derived eicosanoids in humans with stable atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Atherosclerosis 2012, 222, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walkowska, A.; Červenka, L.; Imig, J.D.; Falck, J.R.; Sadowski, J.; Kompanowska-Jezierska, E. Early renal vasodilator and hypotensive action of epoxyeicosatrienoic acid analog (EET-A) and 20-HETE receptor blocker (AAA) in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 622882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemaitre, R.N.; Jensen, P.N.; Zeigler, M.; Fretts, A.M.; Umans, J.G.; Howard, B.V.; Sitlani, C.M.; McKnight, B.; Gharib, S.A.; King, I.B.; et al. Plasma epoxyeicosatrienoic acids and diabetes-related cardiovascular disease: The cardiovascular health study. eBioMedicine 2022, 83, 104189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
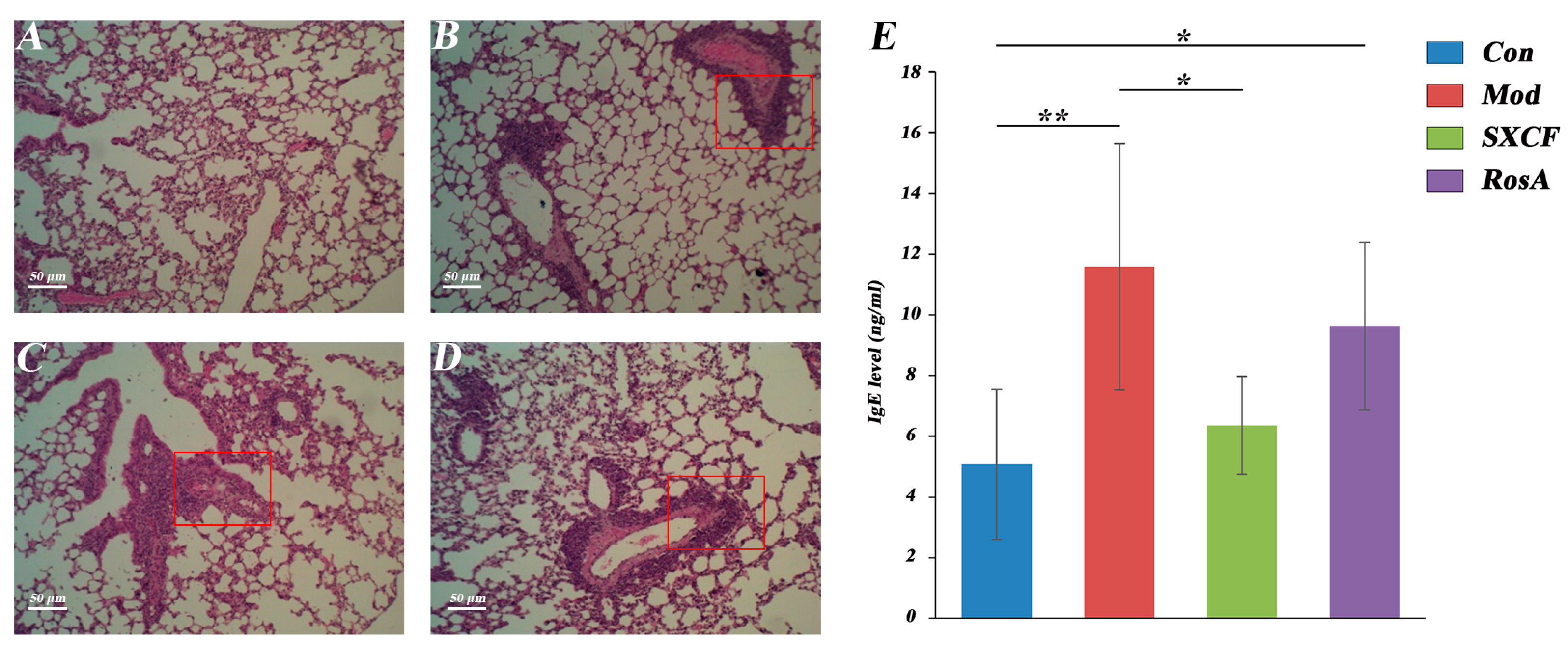

| Group (n = 5) | Grading Score for Pulmonary Injury | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| -- | + | ++ | +++ | |
| Con | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Mod | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| SXCF | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 |
| RosA | 0 | 3 | 2 | 0 |
| Group | Rr,i > 125% | 75% < Rr,i < 125% | 0 < Rr,i < 75% | Rr,i < 0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SXCF | 0 | 10 | 6 | 0 |
| RosA | 3 | 7 | 1 | 5 |
| Time/min | A% | B% |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 75 | 25 |
| 1 | 75 | 25 |
| 8 | 5 | 95 |
| 8.5 | 5 | 95 |
| 8.51 | 75 | 25 |
| 10 | 75 | 25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, T.; Rong, X.; Zhang, X.; Kong, L.; Kang, Y.; Liu, X.; Hu, M.; Liang, H.; Tie, C. Lipid Mediators Metabolic Chaos of Asthmatic Mice Reversed by Rosmarinic Acid. Molecules 2023, 28, 3827. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093827
Qin T, Rong X, Zhang X, Kong L, Kang Y, Liu X, Hu M, Liang H, Tie C. Lipid Mediators Metabolic Chaos of Asthmatic Mice Reversed by Rosmarinic Acid. Molecules. 2023; 28(9):3827. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093827
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Tuo, Xiaojuan Rong, Xiaohui Zhang, Lingfei Kong, Yutong Kang, Xuanlin Liu, Mengying Hu, Handong Liang, and Cai Tie. 2023. "Lipid Mediators Metabolic Chaos of Asthmatic Mice Reversed by Rosmarinic Acid" Molecules 28, no. 9: 3827. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093827
APA StyleQin, T., Rong, X., Zhang, X., Kong, L., Kang, Y., Liu, X., Hu, M., Liang, H., & Tie, C. (2023). Lipid Mediators Metabolic Chaos of Asthmatic Mice Reversed by Rosmarinic Acid. Molecules, 28(9), 3827. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093827





