Multiresidue Determination of 26 Quinolones in Poultry Feathers Using UPLC-MS/MS and Their Application in Residue Monitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
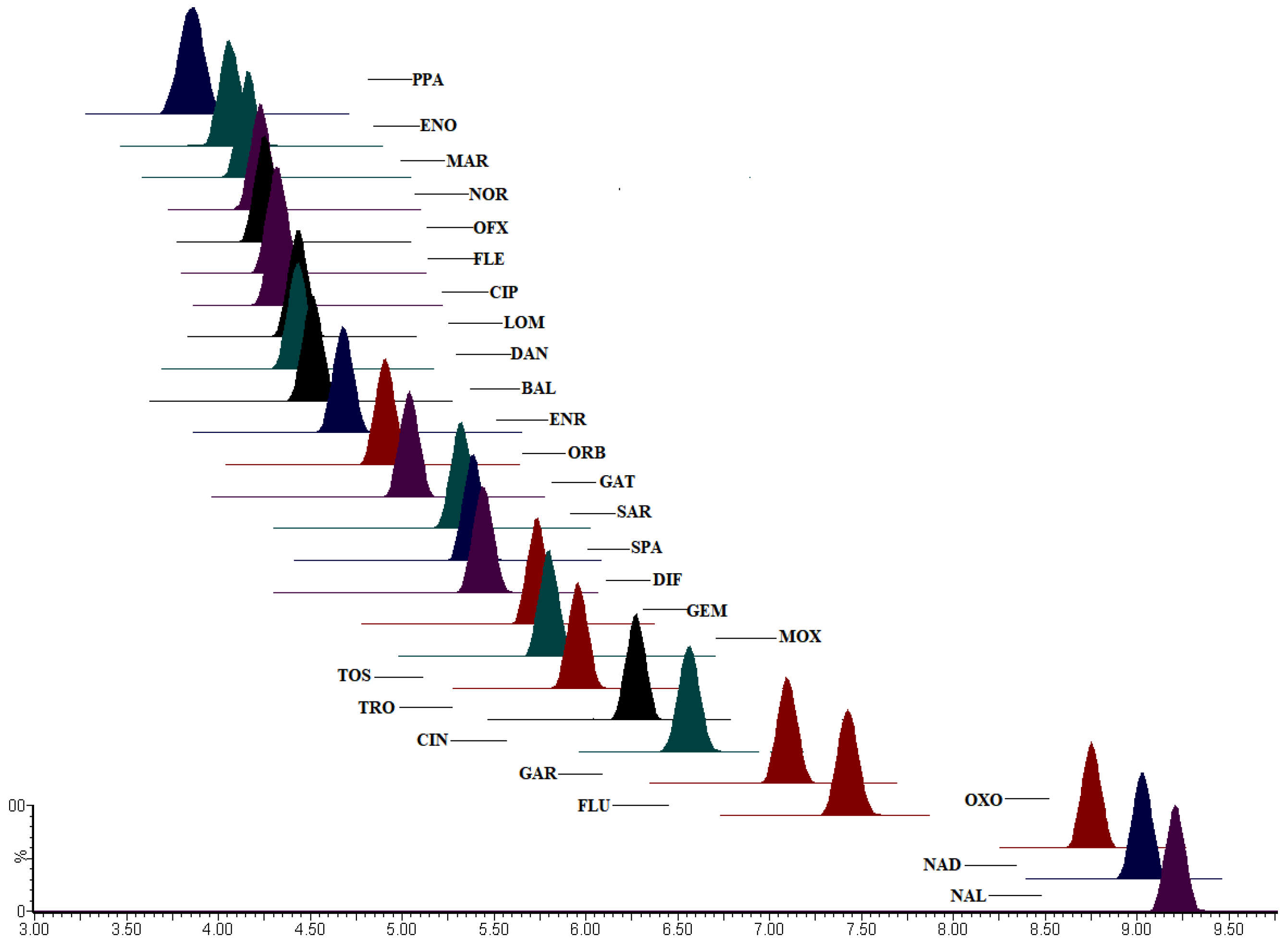
2.1. Chromatographic Condition Optimization
2.2. Extraction Optimization
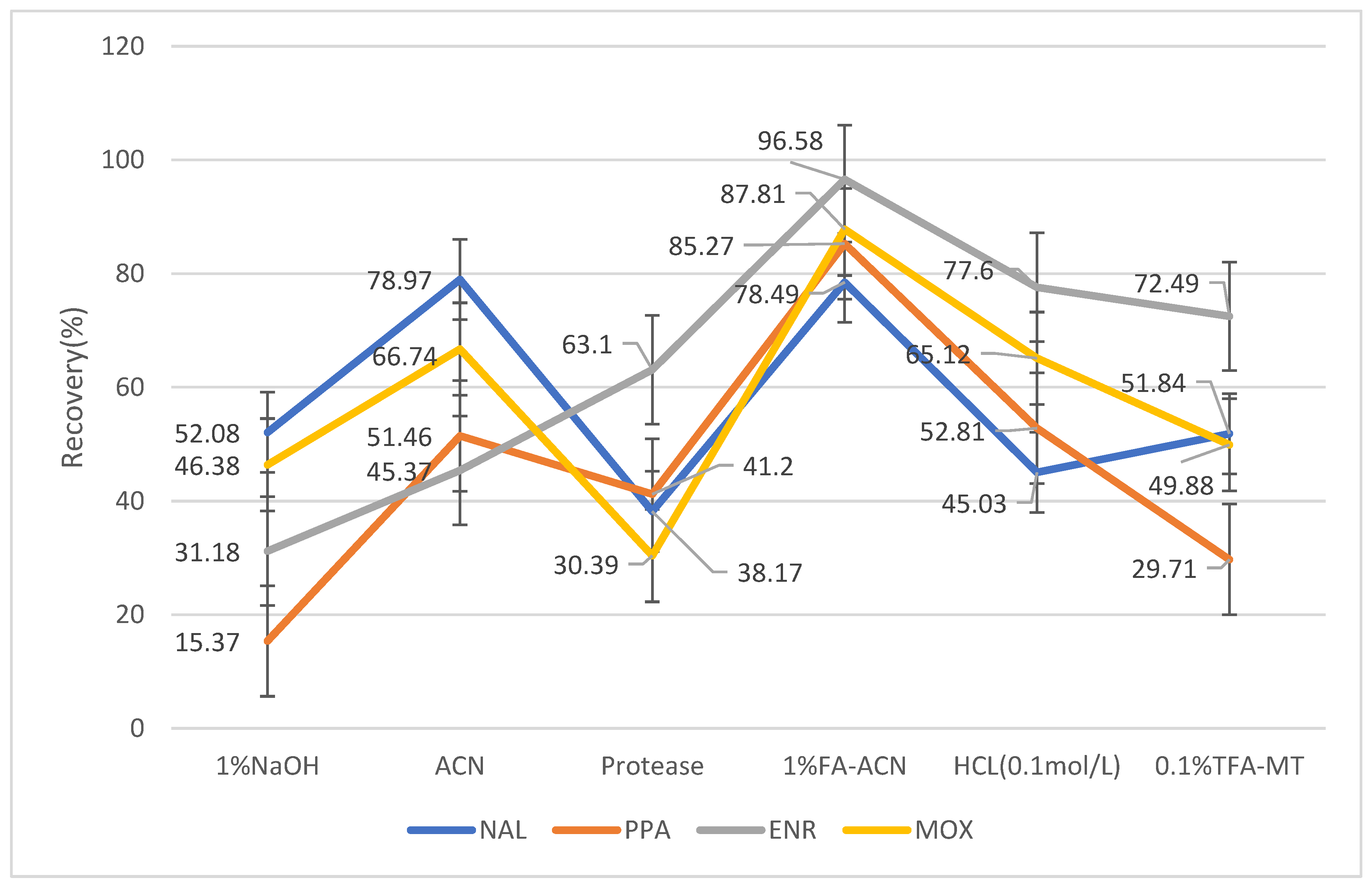
2.3. Selection of Purification Methods
2.4. Selection of Adsorbent Dosage
2.5. Matrix Effect
2.6. Methodological Validation
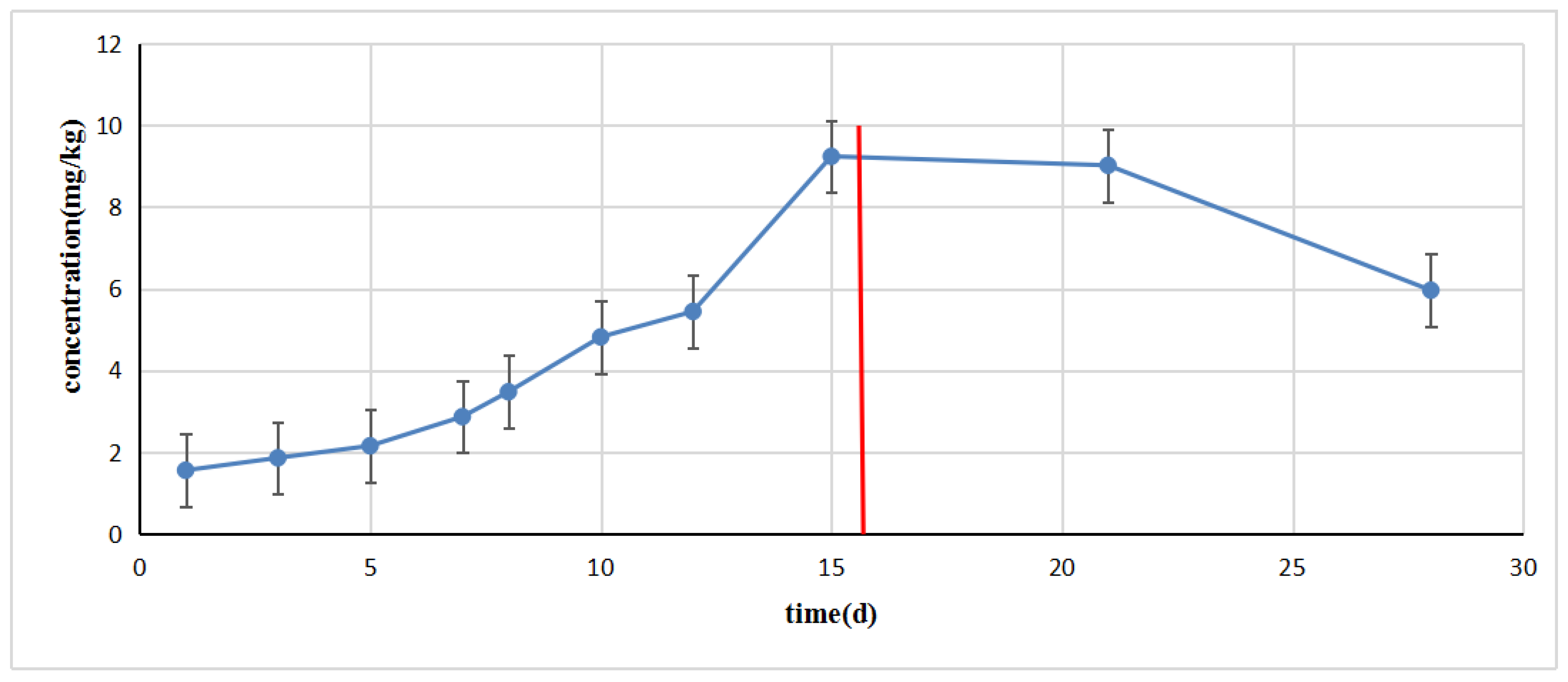
2.7. Quinolone Residue Accumulation in Laying Hens
2.8. Application
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Standard Solution Preparation
3.3. Animal Treatment
3.4. Sample Collection
3.5. Sample Pretreatment
3.6. Instrumental Analysis
3.7. Parameters for Validation of the Analytical Methodology
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Abbreviations
| Quinolones | QNS |
| Norfloxacin | NOR |
| Nadifloxacin | NAD |
| Gemifioxacin Mesylate | GEM |
| Tosufloxacin Tosilate | TOS |
| Pipemidic Acid | PPA |
| Balofloxacin | BAL |
| Fleroxacin | FLE |
| Difloxacin | DIF |
| Nalidixic Acid | NAL |
| Lomefloxacin | LOM |
| Ofloxacin | OFX |
| Sparfloxacin | SPA |
| Flumequine | FLU |
| Enoxacin | ENO |
| Enrofloxacin | ENR |
| Sarafloxacin | SAR |
| Trovafloxacin | TRO |
| Oxolinic Acid | OXO |
| Danofloxacin | DAN |
| Gatifloxacin | GAT |
| Moxifloxacin | MOX |
| Cinoxacin | CIN |
| Ciprofloxacin | CIP |
| Marbofloxacin | MAR |
| Orbifloxacin | ORB |
| Garenoxacin | GAR |
References
- Toussaint, B.; Chedin, M.; Vincent, U.; Bordin, G.; Rodriguez, A. Determination of (fluoro) quinolone antibiotic residues in pig kidney using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: Part II: Intercomparison exercise. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Arteseros, J.; Barbosa, J.; Compañó, R.; Prat, M. Analysis of quinolone residues in edible animal products. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 945, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCluskey Seánín, M.; Knapp Charles, W. Predicting antibiotic resistance, not just for quinolones. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China Announcement No. 2292. Available online: http://www.moa.gov.cn/nybgb/2015/jiuqi/201712/t20171219_6103873.htm (accessed on 28 January 2023).
- Smith, J.L.; Fratamico, P.M. Fluoroquinolone Resistance in Campylobacter. J. Food Prot. 2010, 73, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidi, L.R.; Santos, F.A.; Ribeiro, A.C.S.R.; Fernandes, C.; da Silva, L.H.M.; Gloria, M.B.A. Quinolones and tetracyclines in aquaculture fish by a simple and rapid LC-MS/MS method. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 1232–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karageorgou, E.; Myridakis, A.; Stephanou, E.G.; Samanidou, V. Multiresidue LC-MS/MS analysis of cephalosporins and quinolones in milk following ultrasound-assisted matrix solid-phase dispersive extraction combined with the quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged, and safe methodology. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 2020–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.T.; Barreto, F.; Hoff, R.B.; Jank, L.; Arsand, J.B.; Feijó, T.C.; Schapoval, E.E.S. Determination of quinolones and fluoroquinolones, tetracyclines and sulfonamides in bovine, swine and poultry liver using LC-MS/MS. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control. Expo. Risk Assess. 2015, 32, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junza, A.; Amatya, R.; Barrón, D.; Barbosa, J. Comparative study of the LC–MS/MS and UPLC–MS/MS for the multi-residue analysis of quinolones, penicillins and cephalosporins in cow milk, and validation according to the regulation 2002/657/EC. J. Chromatogr. B 2011, 25, 2601–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajda, A.; Nowacka-Kozak, E.; Gbylik-Sikorska, M.; Posyniak, A. Multi-residues UHPLC–MS/MS analysis of 53 antibacterial compounds in poultry feathers as an analytical tool in food safety assurance. J. Chromatogr. B 2019, 1104, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornejo, J.; Lapierre, L.; Iragüen, D.; Pizarro, N.; Hidalgo, H.; San, M.B. Depletion study of three formulations of flumequine in edible tissues and drug transfer into chicken feathers. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 2, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornejo, J.; Pokranta, E.; Carvalloa, C. Depletion of tylosin residues in feathers, muscle and liver from broiler chickens after completion of antimicrobial therapy. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2018, 35, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiesa, L.M.; Nobile, M.; Panseri, S. Suitability of feathers as control matrix for antimicrobial treatments detection compared to muscle and liver of broilers. Food Control. 2018, 91, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, D.C.; Halden, R.U.; Davis, M.F.; Nachman, K.E. Feather Meal: A Previously Unrecognized Route for Reentry into the Food Supply of Multiple Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products (PPCPs). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 3795–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornejo, J.; Pokrant, E.; Riquelme, R.; Briceño, C.; Maddaleno, A.; Araya-Jordán, C.; San Martin, B. Single-laboratory validation of an LC-MS/MS method for determining florfenicol (FF) and florfenicol amine (FFA) residues in chicken feathers and application to a residue-depletion study. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2017, 34, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campoli-Richards, D.M.; Monk, J.P.; Price, A.; Benfield, P.; Todd, P.A.; Ward, A. Ciprofloxacin. A review of its antibacterial activity, pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic use. Drugs 1988, 35, 373–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinquina, A.; Roberti, P.; Giannetti, L.; Longo, F.; Draisci, R.; Fagiolo, A.; Brizioli, N. Determination of enrofloxacin and its metabolite ciprofloxacin in goat milk by high performance liquid chromatography with diode-array detection: Optimization and validation. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 987, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maraschiello, C.; Cusido, E.; Abellán, M.; Vilageliu, J. Validation of an analytical procedure for the determination of the fluoroquinilone ofloxacin in chicken tissues. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 2001, 754, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Yuan, Z. Development of an indirect competitive ELISA for ciprofloxacin residues in food animal edible tissues. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 3, 1087–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucknall, S.; Silverlight, J.; Coldham, N.; Thorne, L.; Jackman, R. Antibodies to the quinolones and fluoroquinolones for the development of generic and specific immunoassays for detection of these residues in animal products. Food Addit. Contam. 2003, 20, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, R.B.; Magnani, M.; Ferrari, R.; Kottwitz, L.B.M.; Sartori, D.; Tognim, M.C.B.; De Oliveira, T.C.R.M. Detection of quinolone-resistance mutations in Salmonella spp. strains of epidemic and poultry origin. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2011, 1, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, L.J.M.; Bolck, Y.J.C.; Rademaker, J.; Zuidema, T.; Berendsen, B.J.A. The analysis of tetracyclines, quinolones, macrolides, lincosamides, pleuromutilins, and sulfonamides in chicken feathers using UHPLC-MS/MS in order to monitor antibiotic use in the poultry sector. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 21, 4927–4941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- San Martin, B.; Cornejo, J.; Iragüen, D.; Hidalgo, H.; Anadón, A. Depletion study of enrofloxacin and its metabolite ciprofloxacin in edible tissues and feathers of white leghorn hens by liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. J. Food Prot. 2007, 70, 1952–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berendsen, B.J.A.; Bor, G.; Gerritsen, H.W.; Jansen, L.J.M.; Zuidema, T. The disposition of oxytetracycline to feathers after poultry treatment. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2013, 30, 2102–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Jiang, H.; Li, X.; Mi, T.; Li, C.; Shen, J. Simultaneous Determination of Trace Levels of 10 Quinolones in Swine, Chicken, and Shrimp Muscle Tissues Using HPLC with Programmable Fluorescence Detection. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 3829–3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajda, A.; Nowacka-Kozak, E.; Gbylik-Sikorska, M.; Posyniak, A. Feather analysis as a non-invasive alternative to tissue samplingfor surveillance of doxycycline use on poultry farms. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 5971–5980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, D.; Wang, P.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhuang, H.; Li, Y.; Su, X. Multiresidue Determination of 27 Sulfonamides in Poultry Feathers Its Application to a Sulfamethazine Pharmacokinetics Study on Laying Hen Feathers Sulfonamide Residue Monitoring on Poultry, Feathers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 67, 1236–11243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, L.J.; Bolck, Y.J.; Berendsen, B.J. Berendsen. Feather segmentation to discriminate between different enrofloxacin treatments in order to monitor off-label use in the poultry sector. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena, A.; Silva, L.J.G.; Pereira, A.M.P.T.; Meisel, L.; Lino, C.M. Determination of fluoroquinolone residues in poultry muscle in Portugal. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 2615–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, E.; Moreno-Bondi, M.; Marazuela, M. Development and validation of a solid-phase extraction method coupled to liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection for the determination of fluoroquinolone residues in powdered infant formulae. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 9, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Huang, R.; Liu, G.; Wang, P.; Wang, C. Studies on the Residues of Sulfamethazinum in Eggs. China Poult. 2004, 26, 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Ding, S.; Jiang, H.; Shen, J.; Xia, X. Multiresidue analysis of sulfonamides, quinolones, and tetracyclines in animal tissues by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2016, 204, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slana, M.; Pahor, V.; Cvitkovič Maričič, L.; Sollner-Dolenc, M. Excretion pattern of enrofloxacin after oral treatment of chicken broilers. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 37, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, K.; Chan, D.; Fussell, R.J.; Kay, J.F.; Sharman, M. Can the unauthorised use of ceftiofur be detected in poultry? Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2013, 30, 1733–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokrant, E.; Medina, F.; Maddaleno, A.; Martín, B.S.; Cornejo, J. Determination of sulfachloropyridazine residue levels in feathers from broiler chickens after oral administration using liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. PLoS ONE 2018, 7, e0200206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huet, A.C.; Charlier, C.; Tittlemier, S.A.; Singh, G.; Benrejeb, S.; Delahaut, P. Simultaneous Determination of (Fluoro)quinolone Antibiotics in Kidney, Marine Products, Eggs, and Muscle by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 2822–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speltini, A.; Sturini, M.; Maraschi, F.; Viti, S.; Sbarbada, D.; Profumo, A. Fluoroquinolone residues in compost by green enhanced microwave-assisted extraction followed by ultra performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1410, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastassiades, M.; Lehotay, S.J.; Štajnbaher, D.; Schenck, F.J. Fast and easy multiresidue method employing acetonitrile extraction partitioning and “dispersive solid-phase extraction” for the determination of pesticide residues in produce. J. AOAC Int. 2003, 86, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Su, X. Development of “one-pot” method for multi-class compounds in porcine formula feed by multi-mechanism impurity adsorption cleaning followed ultra-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 947–948, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMullen, S.E.; Schenck, F.J.; Vega, V.A. Rapid method for the determination and confirmation of fluoroquinolone residues in catfish using liquid chromatography/fluorescence detection and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. AOAC Int. 2009, 92, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vessman, J.; Stefan, R.I.; van Staden, J.F.; Danzer, K.; Lindner, W.; Burns, D.T.; Fajgelj, A.; Müller, H. Selectivity in analytical chemistry (IUPAC Recommendations 2001). Pure Appl. Chem. 2001, 73, 1381–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Names and Types of Adsorption Materials | |
|---|---|
| Name | Requirement for Material Type |
| ALUMINA | Aluminum oxide |
| SCX | Sodium sulfonate bonded to silica gel |
| C18 | Octadecyl is bonded to silica gel, and the bond end has been treated. |
| PSA | Silica gel bonded N-propyl ethylenediamine |
| NONOCARB | activated carbon and zeolite |
| FLORISIL | Magnesium oxide composite silica gel adsorbent |
| PESTICARB | Graphite carbon |
| SAX | Quaternary ammonium halide bonded to silica gel |
| CARBON NANOTUBE | Multi-walled carbon nanotubes |
| Standard Curve, Correlation Coefficient, Detection Limit, and Quantitative Limit of 26 QNs | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug | Linear Equation | R2 | Concentration Range (ng/mL) | LOD (μg/kg) | LOQ (μg/kg) |
| NAL | y = 2927.6 (±0.05) x − 8767.8 (±1.07) | 0.994 | 0.5–50 | 0.16 | 1.08 |
| OXO | y = 37.002 (±0.025) x − 166.02 (±0.31) | 0.997 | 0.5–50 | 0.54 | 1.8 |
| NOR | y = 28.576 (±0.019) x + 251.17 (±0.25) | 0.992 | 1–100 | 0.27 | 1.23 |
| LOM | y = 191.87 (±0.008) x + 330.79 (±0.03) | 0.993 | 1–100 | 0.17 | 1.32 |
| DAN | y = 39.122 (±0.008) x − 98.238 (±0.04) | 0.999 | 2–200 | 0.68 | 2.20 |
| NAD | y = 1126.9 (±0.52) x − 1311.2 (±1.15) | 0.997 | 1–100 | 0.22 | 1.15 |
| OFX | y = 24.466 (±0.005) x + 38.5 (±0.03) | 0.995 | 1–100 | 0.56 | 1.87 |
| GAT | y = 17.266 (±0.004) x + 274.96 (±0.28) | 0.996 | 2–200 | 1.31 | 2.01 |
| GEM | y = 14.482 (±0.03) x + 44.762 (±0.10) | 0.998 | 2–200 | 1.20 | 2.60 |
| SPA | y = 119.28 (±0.02) x + 58.265 (±0.39) | 0.999 | 0.5–50 | 0.19 | 0.96 |
| MOX | y = 46.803 (±0.02) x − 189.76 (±0.28) | 0.995 | 1–100 | 0.34 | 1.14 |
| TOS | y = 168.78 (±0.17) x + 320.1 (±0.43) | 0.999 | 1–100 | 0.15 | 1.36 |
| FLU | y = 16.278 (±0.02) x + 54.404 (±0.15) | 0.994 | 2–200 | 0.68 | 2.2 |
| CIN | y = 236.96 (±0.12) x − 514.08 (±0.49) | 0.996 | 0.5–50 | 0.40 | 0.98 |
| PPA | y = 12.445 (±0.02) x + 79.361 (±0.23) | 0.995 | 1–100 | 0.68 | 1.73 |
| ENO | y = 60.418 (±0.007) x − 40.661 (±0.06) | 0.998 | 1–100 | 0.83 | 1.70 |
| CIP | y = 434.24 (±0.029) x + 6606.7 (±0.08) | 0.998 | 1–100 | 0.12 | 1.14 |
| BAL | y = 148.93 (±0.045) x − 271.78 (±0.65) | 0.994 | 1–100 | 0.13 | 1.44 |
| ENR | y = 154.65 (±0.023) x + 3905.2 (±0.41) | 0.993 | 2–200 | 0.30 | 1.99 |
| MAR | y = 54.164 (±0.005) x + 37.6 (±0.40) | 0.997 | 2–200 | 0.20 | 1.78 |
| FLE | y = 1069.7 (±0.058) x + 3312 (±0.41) | 0.997 | 1–100 | 0.27 | 1.12 |
| SAR | y = 541.99 (±0.027) x + 246.77 (±0.17) | 0.998 | 1–100 | 0.31 | 1.78 |
| ORB | y = 200.56 (±0.011) x − 577.78 (±0.05) | 0.995 | 2–200 | 0.58 | 2.32 |
| DIF | y = 515.72 (±0.008) x − 509.96 (±0.08) | 0.996 | 2–200 | 1.15 | 2.19 |
| TRO | y = 16.459 (±0.003) x + 33.812 (±0.09) | 0.994 | 2–200 | 0.75 | 2.50 |
| GAR | y = 111.08 (±0.088) x + 46.782 (±0.32) | 0.995 | 1–100 | 0.19 | 1.64 |
| Recovery and Precision of the Method for 26 QNs in Poultry Feathers | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drugs | Add Value | Recovery (%) | Intraday Precision (RSD, %) (n = 6, 3 Days) | Interday Precision (RSD, %) (n = 18, 3 Days) | |||
| Chicken | Duck | Chicken | Duck | Chicken | Duck | ||
| NAL | 10 | 97.8 | 89.6 | 5.0 | 5.8 | 10.5 | 2.4 |
| 100 | 99.6 | 97.6 | 6.2 | 8.9 | 9.4 | 12.7 | |
| 200 | 102 | 102 | 6.2 | 4.8 | 6.8 | 10.1 | |
| OXO | 10 | 79.2 | 82.0 | 7.3 | 1.3 | 11.3 | 2.4 |
| 100 | 88.3 | 80.8 | 1.6 | 3.0 | 5.8 | 3.1 | |
| 200 | 90.1 | 107 | 7.6 | 7.5 | 2.7 | 5.7 | |
| NOR | 10 | 83.3 | 89.7 | 4.5 | 2.9 | 7.9 | 9.9 |
| 100 | 91.2 | 91.8 | 8.8 | 3.5 | 4.2 | 7.9 | |
| 200 | 99.7 | 98.1 | 6.8 | 6.0 | 8.6 | 11.0 | |
| LOM | 10 | 78.9 | 93.7 | 9.7 | 8.4 | 5.9 | 3.4 |
| 100 | 89.6 | 105 | 8.7 | 8.4 | 6.8 | 11.2 | |
| 200 | 94.8 | 107 | 6.9 | 6.9 | 5.4 | 4.6 | |
| DAN | 10 | 96.7 | 90 | 2.9 | 6.8 | 9.9 | 6.1 |
| 100 | 98.2 | 95.4 | 1.3 | 9.5 | 13.2 | 7.5 | |
| 200 | 101 | 95.1 | 1.8 | 2.0 | 10.3 | 12.1 | |
| NAD | 10 | 87.1 | 81.1 | 5.4 | 1.6 | 8.8 | 10.2 |
| 100 | 103 | 94.2 | 6.2 | 10.8 | 7.6 | 3.3 | |
| 200 | 102 | 110 | 8.4 | 5.2 | 6.6 | 4.5 | |
| OFX | 10 | 92.3 | 89.7 | 9.3 | 3.7 | 9.4 | 6.6 |
| 100 | 97.6 | 99.5 | 8.9 | 8.2 | 11.3 | 6.7 | |
| 200 | 96.1 | 98.4 | 6.7 | 7.6 | 6.1 | 7.2 | |
| GAT | 10 | 90.9 | 91.0 | 7.5 | 1.11 | 8.6 | 1.6 |
| 100 | 96.2 | 101 | 1.68 | 1.85 | 7.1 | 12.1 | |
| 200 | 97.7 | 104 | 1.9 | 7.5 | 9.2 | 4.5 | |
| GEM | 10 | 89.1 | 87.5 | 1.6 | 0.6 | 7.7 | 7.6 |
| 100 | 93.2 | 101 | 0.8 | 5.6 | 11.9 | 9.3 | |
| 200 | 98.6 | 99.4 | 2.3 | 3.9 | 5.3 | 10.0 | |
| SPA | 10 | 87.6 | 92.7 | 4.3 | 9.8 | 4.4 | 8.5 |
| 100 | 90.8 | 95.1 | 2.6 | 4.8 | 3.7 | 4.9 | |
| 200 | 91 | 94.9 | 1.7 | 1.1 | 5.2 | 6.7 | |
| MOX | 10 | 97.0 | 86.8 | 3.8 | 0.45 | 1.7 | 5.3 |
| 100 | 98.9 | 91.3 | 8.2 | 2.96 | 9.5 | 3.7 | |
| 200 | 99.6 | 99.2 | 0.22 | 1.9 | 4.2 | 12.8 | |
| TOS | 10 | 86.4 | 89.9 | 10.1 | 5.7 | 7.0 | 4.9 |
| 100 | 88.8 | 92 | 5.9 | 4.3 | 1.1 | 6.7 | |
| 200 | 90.1 | 87.5 | 3.8 | 3.7 | 3.6 | 2.2 | |
| FLU | 10 | 97.3 | 99.4 | 0.15 | 10.2 | 12.6 | 3.1 |
| 100 | 103 | 103 | 8.4 | 0.6 | 13.7 | 7.9 | |
| 200 | 98.5 | 97.1 | 0.4 | 4.9 | 7.9 | 4.5 | |
| CIN | 10 | 91.8 | 92.3 | 1.9 | 2.8 | 2.6 | 5.1 |
| 100 | 92.4 | 96.8 | 6.4 | 7.5 | 5.6 | 7.3 | |
| 200 | 97.6 | 89.8 | 7.1 | 1.3 | 8.9 | 12.4 | |
| PPA | 10 | 88.4 | 90 | 1.7 | 5.2 | 9.8 | 3.9 |
| 100 | 89.7 | 93.3 | 8.6 | 8.4 | 12.4 | 9.3 | |
| 200 | 92.6 | 91.2 | 0.8 | 5.4 | 6.1 | 4.6 | |
| ENO | 10 | 87.1 | 89.7 | 6.5 | 1.9 | 12 | 7.2 |
| 100 | 90.2 | 93.2 | 4.2 | 2.3 | 1.1 | 1.8 | |
| 200 | 98.3 | 85.1 | 8.8 | 2.9 | 5.0 | 2.0 | |
| CIP | 10 | 92.7 | 93.8 | 3.8 | 0.1 | 14.6 | 3.7 |
| 100 | 95.6 | 99.8 | 9.8 | 1.2 | 7.8 | 8.6 | |
| 200 | 94.6 | 95.9 | 7.1 | 8.9 | 8.9 | 9.4 | |
| BAL | 10 | 88.7 | 99.5 | 8.8 | 4.9 | 8.0 | 10.1 |
| 100 | 96.6 | 103 | 3.7 | 2.7 | 2.5 | 3.6 | |
| 200 | 96.2 | 93.2 | 8.1 | 9.1 | 2.7 | 6.4 | |
| ENR | 10 | 94.5 | 88.8 | 3.3 | 1.7 | 8.2 | 1.3 |
| 100 | 98.3 | 92.7 | 9.1 | 2.1 | 4.6 | 7.8 | |
| 200 | 96.9 | 89.5 | 7.8 | 6.2 | 7.1 | 8.4 | |
| MAR | 10 | 96.7 | 99.2 | 2.5 | 5.7 | 5.6 | 4.3 |
| 100 | 97.5 | 101 | 8 | 1.2 | 13.3 | 2.1 | |
| 200 | 98.7 | 97.9 | 8.3 | 3.4 | 7.8 | 6.6 | |
| FLE | 10 | 95.3 | 97.3 | 3.4 | 3.3 | 8.1 | 9.7 |
| 100 | 98.2 | 97.6 | 9.4 | 5.4 | 9.4 | 7.4 | |
| 200 | 97.3 | 97.7 | 1.5 | 8.7 | 12.6 | 5.9 | |
| SAR | 10 | 100.2 | 96.7 | 7.1 | 2.7 | 3.7 | 11.3 |
| 100 | 97.6 | 88.3 | 8.2 | 3.4 | 11.9 | 5.8 | |
| 200 | 102 | 89.6 | 8.5 | 5.9 | 9.0 | 9.6 | |
| ORB | 10 | 89.9 | 89.6 | 2.7 | 2.1 | 13.7 | 8.7 |
| 100 | 93.7 | 87.8 | 7.8 | 4.9 | 8.6 | 6.4 | |
| 200 | 98.1 | 88.7 | 6.6 | 3.7 | 11.7 | 5.3 | |
| DIF | 10 | 91.3 | 87.6 | 5.1 | 1.7 | 10.4 | 5.5 |
| 100 | 98.2 | 92.7 | 1.1 | 2.4 | 5.7 | 6.7 | |
| 200 | 90.8 | 87.5 | 8.3 | 0.6 | 3.6 | 11.4 | |
| TRO | 10 | 95.7 | 91.4 | 5.9 | 1.4 | 10.0 | 9.7 |
| 100 | 97.2 | 96.5 | 9.8 | 3.3 | 5.8 | 10.7 | |
| 200 | 98.9 | 99.2 | 3.7 | 8.9 | 5.6 | 3.8 | |
| GAR | 10 | 91.3 | 90.7 | 1.3 | 8.7 | 7.2 | 2.6 |
| 100 | 90.7 | 85.4 | 6.7 | 5.5 | 2.1 | 5.8 | |
| 200 | 91.4 | 91.3 | 2.6 | 7 | 3.8 | 6.9 | |
| Retention Time and MS Condition of 26 QNs and IS | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug | Time (min) | Qualitative ion Pair (m/z) | Quantitative ion Pair (m/z) | Cone (V) | CE (eV) |
| NAL | 8.99 | 233 > 187 233 > 215 a | 233 > 215 | 24 | 25 |
| OXO | 7.38 | 262 > 160 262 > 215.9 a | 262 > 215.9 | 24 | 25 |
| NOR | 4.17 | 320.2 > 275 320.2 > 302 a | 320.2 > 302 | 24 | 25 |
| LOM d | 4.36 | 352.1 > 265.1 352.1 > 308.1 a | 352.1 > 308.1 | 24 | 25 |
| DAN | 4.39 | 357.9 > 283 357.9 > 340 a | 357.9 > 340 | 30 | 20 25 |
| NAD c | 8.70 | 361.14 > 283.3 361.14 > 343.2 a | 361.14 > 343.2 | 24 | 20 |
| OFX | 4.20 | 361.14 > 261.1 361.14 > 318.1 a | 361.14 > 320.2 | 24 | 25 |
| GAT d | 4.99 | 376.3 > 261.2 376.3 > 358.3 a | 376.3 > 358.3 | 24 | 25 20 |
| GEM d | 5.69 | 390.4 > 313.3 390.4 > 372.3 a | 390.4 > 313.3 | 24 | 25 20 |
| SPA b | 5.34 | 393.2 > 292.1 393.2 > 349.1 a | 393.2 > 292.1 | 24 | 25 |
| MOX | 5.75 | 402.4 > 261.1 402.4 > 384.4 a | 402.4 > 384.4 | 24 | 25 |
| TOS e | 5.91 | 405.2 > 261.2 405.2 > 387.2 a | 405.2 > 387.2 | 24 | 25 |
| FLU e | 7.37 | 262 > 160 262 > 201.9 a | 262.0 > 201.9 | 28 | 46 38 |
| CIN e | 6.52 | 263 > 189.1 263 > 217 a | 263 > 217 | 24 | 25 20 |
| PPA | 3.82 | 304.1 > 215. 304.1 > 217.4 a | 304.1 > 217.5 | 24 | 40 30 |
| ENO | 4.01 | 320.9 > 231.1 320.9 > 235.7 a | 320.9 > 231.1 | 24 | 25 20 |
| CIP | 4.28 | 332.1 > 288 332.1 > 314 a | 332.1 > 314 | 25 | 20 23 |
| BAL d | 4.39 | 357.9 > 283 357.9 > 340 a | 357.9 > 340 | 30 | 20 25 |
| ENR | 4.63 | 360.3 > 245 360.3 > 316 a | 360.3 > 316 | 45 | 30 20 |
| MAR c | 4.11 | 363.3 > 320 363.3 > 345 a | 363.3 > 345 | 32 | 16 21 |
| FLE d | 4.26 | 369.9 > 235.7 369.9 > 325.9 a | 369.9 > 325.9 | 24 | 20 25 |
| SAR | 5.27 | 386 > 299 386 > 342 a | 386 > 342 | 30 | 31 23 |
| ORB b | 4.86 | 396.4 > 295 396.4 > 352 a | 396.4 > 352 | 33 | 25 18 |
| DIF | 5.38 | 400.2 > 299 400.2 > 382 a | 400.2 > 382 | 30 | 30 |
| TRO e | 6.23 | 417.1 > 330.1 417.1 > 399.1 a | 417.1 > 370.1 | 26 | 44 46 |
| GAR e | 7.04 | 427.1 > 286 427.1 > 410 a | 427.1 > 366.2 | 12 | 44 38 |
| OXO-D5 | 266.2 > 197.4 | 266.2 > 247.9 | 10 | 20 | |
| SAR-D8 | 393.2 > 303.4 | 393.2 > 349 | 10 | 20 | |
| ENO-D8 | 329.2 > 98.9 | 329.1 > 174.9 | 10 | 20 | |
| OFX-D3 | 365.1 > 260.9 | 365.1 > 321.2 | 10 | 20 | |
| CIP-D8 | 340.2 > 296.1 | 340.2 > 322.2 | 10 | 20 | |
| DAN-D3 | 361.2 > 317.2 | 361.2 > 342.9 | 10 | 20 | |
| NOR-D5 | 325.2 > 238 | 325.2 > 281.1 | 10 | 20 | |
| NAL-D5 | 238.1 > 188.1 | 238.1 > 220 | 10 | 20 | |
| PPA-d5 | 338.16 > 274.1 | 338.2 > 293.9 | 10 | 20 30 | |
| ENR-D5 | 365.2 > 321.1 | 365.2 > 347.1 | 10 | 20 30 | |
| DIF-D3 | 392.5 > 318.4 | 392.5 > 362.1 | 10 | 20 | |
| MOX-d3 | 266.9 > 215 | 266.9 > 249.1 | 10 | 20 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Z.; Xiao, Z.; Fan, X.; Zhuang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, D.; Paerhati, M.; Suo, D. Multiresidue Determination of 26 Quinolones in Poultry Feathers Using UPLC-MS/MS and Their Application in Residue Monitoring. Molecules 2023, 28, 3738. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093738
Song Z, Xiao Z, Fan X, Zhuang H, Li Y, Zhu J, Zhao D, Paerhati M, Suo D. Multiresidue Determination of 26 Quinolones in Poultry Feathers Using UPLC-MS/MS and Their Application in Residue Monitoring. Molecules. 2023; 28(9):3738. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093738
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Zhanteng, Zhiming Xiao, Xia Fan, Hongting Zhuang, Yang Li, Jingrong Zhu, Duoyong Zhao, Maerhaba Paerhati, and Decheng Suo. 2023. "Multiresidue Determination of 26 Quinolones in Poultry Feathers Using UPLC-MS/MS and Their Application in Residue Monitoring" Molecules 28, no. 9: 3738. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093738
APA StyleSong, Z., Xiao, Z., Fan, X., Zhuang, H., Li, Y., Zhu, J., Zhao, D., Paerhati, M., & Suo, D. (2023). Multiresidue Determination of 26 Quinolones in Poultry Feathers Using UPLC-MS/MS and Their Application in Residue Monitoring. Molecules, 28(9), 3738. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28093738







