Senkyunolide I: A Review of Its Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics, and Drug-Likeness
Abstract
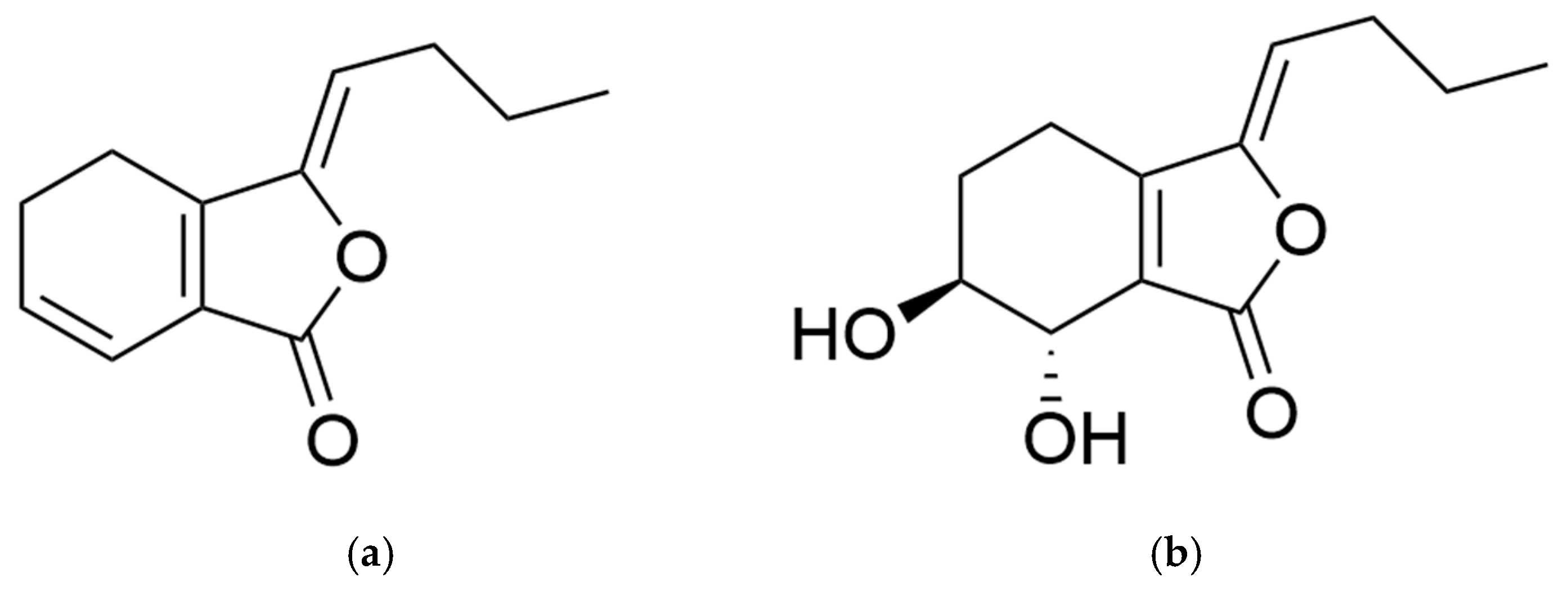
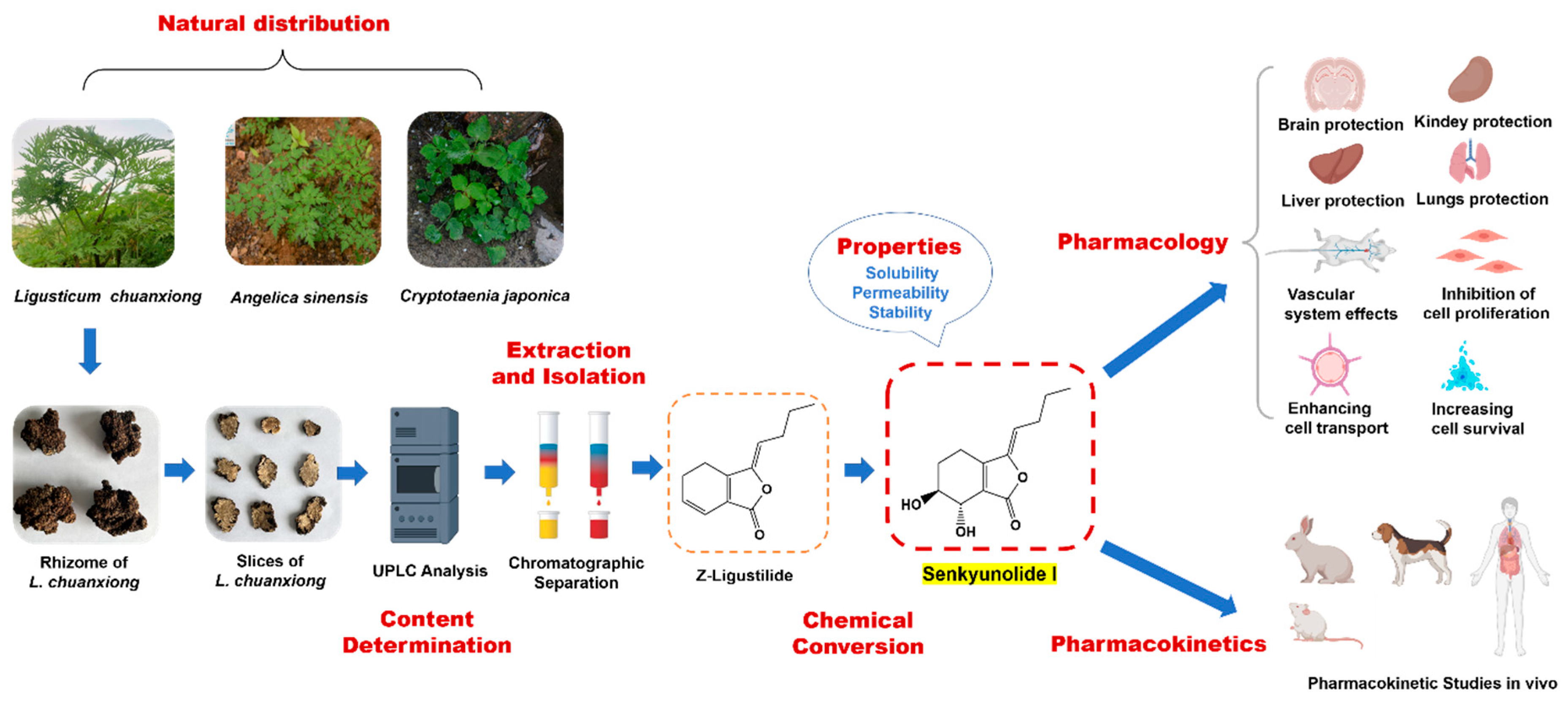
1. Introduction
2. Distribution and Production
2.1. Distribution in Nature
2.2. Production
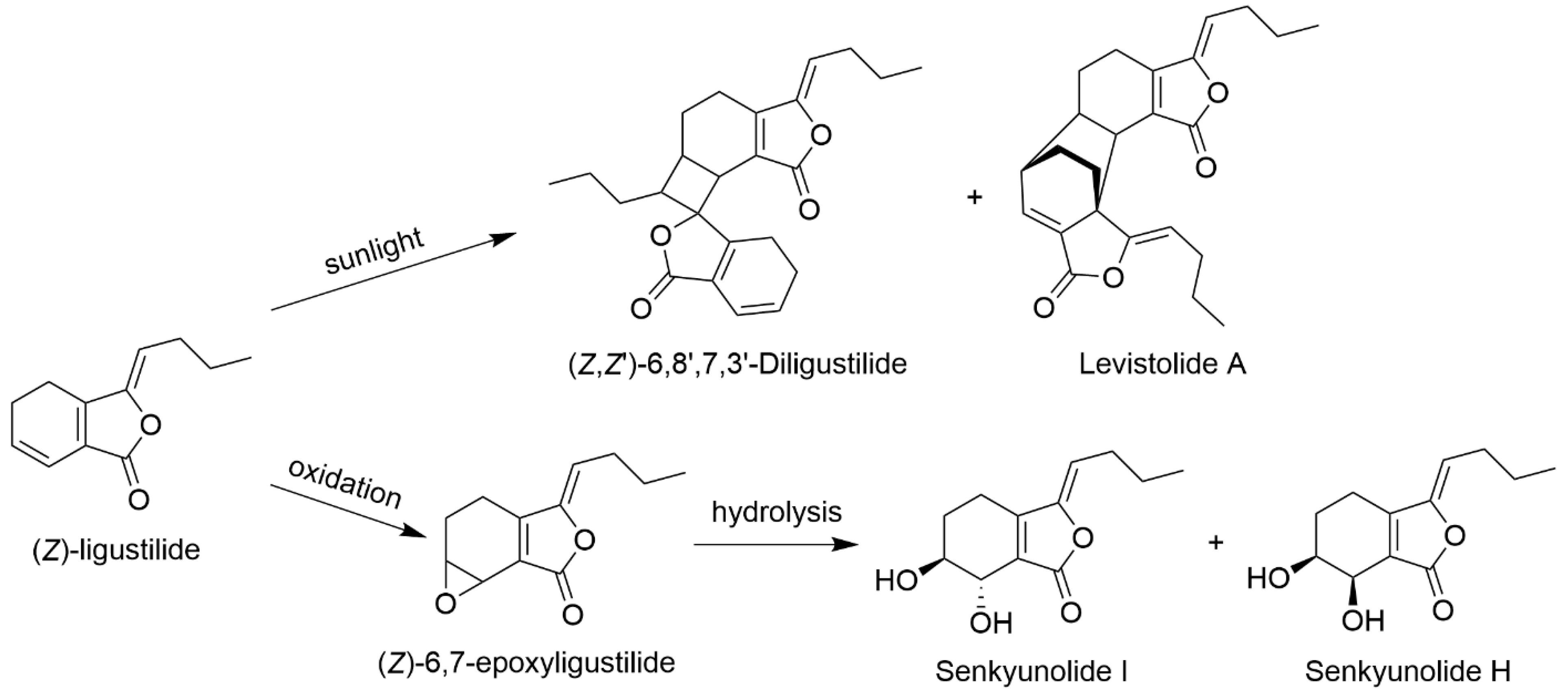
2.2.1. Chemical Transformation from LIG
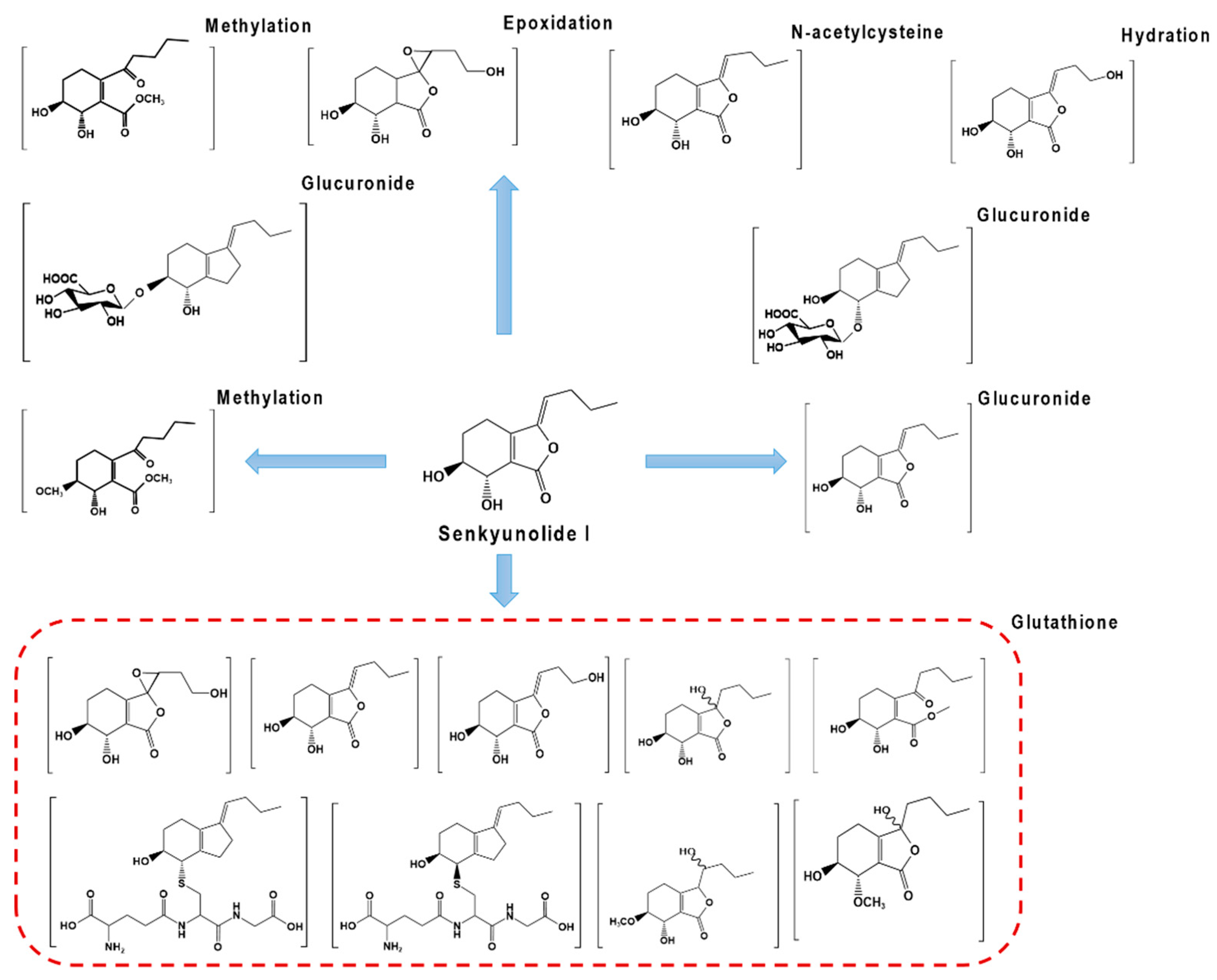
2.2.2. Metabolic Transformation of LIG
3. Chemical and Biological Properties
3.1. Stability
3.2. Permeability
4. Quantitative Analysis
4.1. Analytical Methods
4.2. Content in Medicinal Material and Preparation
5. Extraction and Isolation
| Raw Material | Extraction Solvent | Extraction Method | Separation Method | Raw Material Consumption (kg) | SI Obtained (g) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cnidium officinale rhizome | Hexane, diethyl ether, methanol | \ | Repeated elution and purification by silica gel column chromatography | 2 | 0.239 | [63] |
| Cryptotaenia japonica herba | 75% Ethanol | Cold immersion, ultrasound | Repeated elution of crude fractions by silica gel column chromatography and purification by gel column chromatography | 2 | 0.020 | [19] |
| Angelica sinensis root | Methanol | Cold immersion | Rapid silica column chromatography for crude fractionation and preparative RP-18MPC fractionation and preparative HPLC purification | 8 | 0.0038 | [16] |
| Ligusticum sinense aerial part | 95% Ethanol | \ | Repeated elution purification by flash column chromatography and silica gel column chromatography | 70 | 0.010 | [64] |
| Ligusticum chuanxiong rhizome | 90% Ethanol | Cold immersion, ultrasound | Counter current chromatography | 0.03 | 0.0064 | [39] |
| Ligusticum chuanxiong rhizome | Water | Soaking in 80 °C hot water for 1 h | Silica gel column chromatography for crude fractionation and borate affinity gel column chromatography for purification | 1 | 0.791 | [65] |
| Ligusticum chuanxiong rhizome | 80% Ethanol | Reflux | D-101 macroporous adsorption resin crude fraction and purification by silica gel column chromatography and reverse high-performance preparative liquid chromatography | 3 | 0.962 | [66] |
| Ligusticum chuanxiong rhizome | 70% Ethanol | Reflux | Crude fractionation of HPD-100 macroporous resin and purification by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography | 0.2 | 0.217 | [67] |
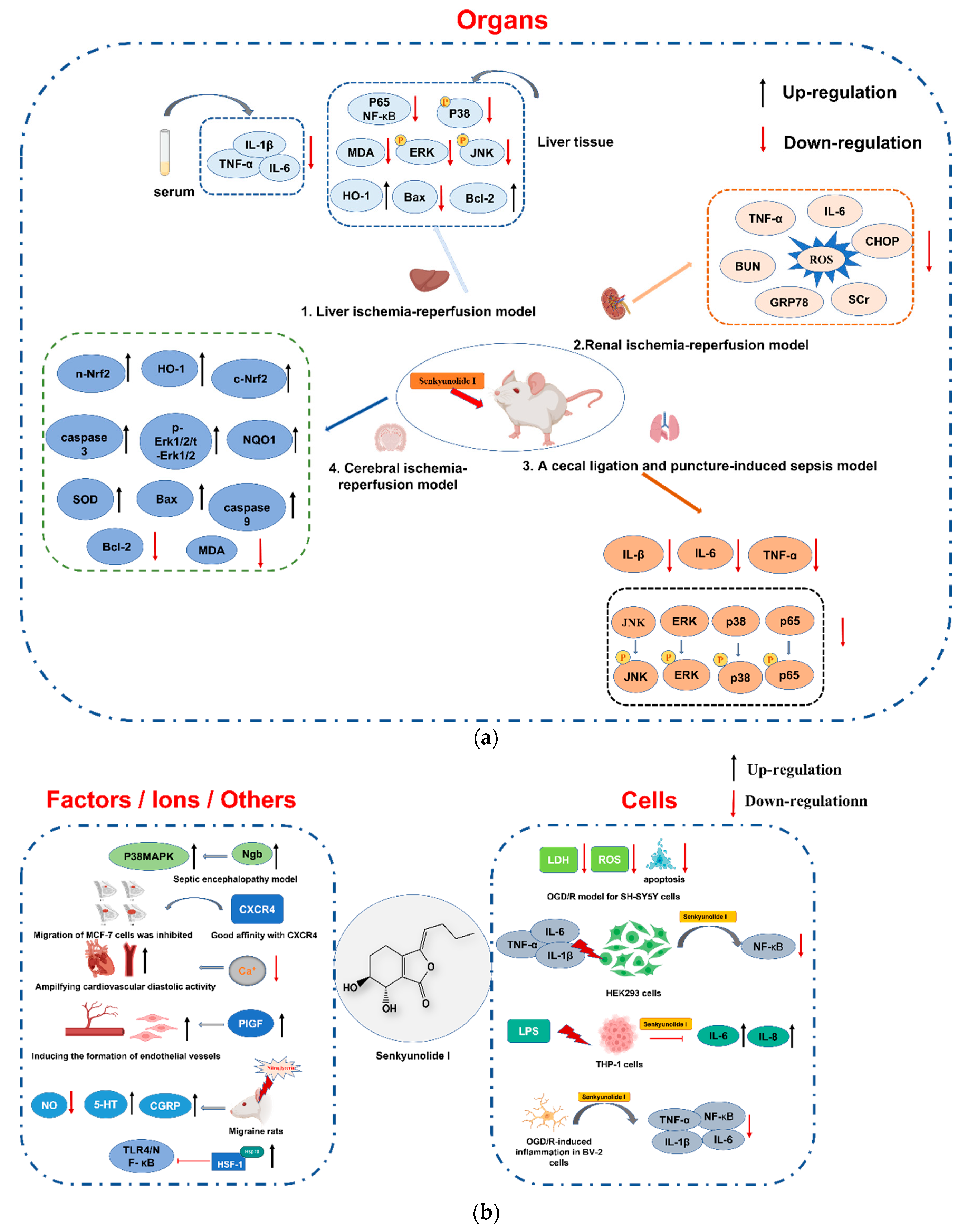
6. Pharmacology
6.1. Protection of the Brain
6.1.1. Neuroprotection of Cerebral Ischemia/Hemorrhage
6.1.2. Protection against Septic Encephalopathy
6.2. Protection of the Liver, Kidneys, and Lungs
6.3. Protection of Blood and Vascular Systems
6.3.1. Effects on the Blood System
6.3.2. Effects on the Vascular System
6.4. Other Pharmacological Effects
| Pharmacological Effect | Cell Line/Animal Model | Action Mechanism | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protection of brain | Cerebral ischemia–reperfusion model | Ameliorating neurological injury; reducing cerebral infarct volume; decreasing MDA level; increasing SOD and promoting the expression of p-Erk1/2/t-Erk1/2, c-Nrf2, n-Nrf2, HO-1, and NQO1; and deregulating the expression of Bcl-2, Bax, caspase 3, and caspase 9. | [69] |
| SH-SY5Y cells; OGD/R model | Increasing cell viability and decreasing ROS and LDH levels. | [70] | |
| ICH was induced by intracerebral injection of autologous blood | Ameliorating neurological deficit, brain edema, and neuronal injury; alleviating microglia cell and astrocyting activations; and reducing peripheral immune cell infiltration caused by ICH. | [71] | |
| Protection against septic encephalopathy | Cecal ligation and perforation were used for the sepsis model | Increasing Ngb expression and upregulating the p38 MAPK signal pathway. | [72] |
| Improving the survival rate and cognitive dysfunction of sepsis mice; ameliorating systemic inflammatory response; and inhibiting the inflammatory signaling pathway, which includes reducing the phosphorylation levels of JNK, ERK, p38, and p65. | [73] | ||
| Protection of liver | Hepatic ischemia–reperfusion; HuCCT1 cells | Decreasing TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6; inhibiting P65 NF-κB, MAPK, and MDA; increasing HO-1, SOD, and GSH-Px activities; inhibiting Bax but increasing Bcl-2; and reducing liver tissue apoptosis. It can reduce the damage of HuCCT1 cells, promote Nrf-2 nuclear translocation, and reduce the contents of ROS and MDA in vitro. | [74] |
| Protection of kidneys | Renal ischemia–reperfusion injury model was established by clipping bilateral renal pedicles; HK2 cells | Protecting renal function and structural integrity; reversing BUN, SCr, and renal pathological damage; inhibiting the secretion of TNF-α and IL-6; reducing ROS production and the expression of endoplasmic reticulum stress-related proteins GRP78 and CHOP. | [75] |
| Protection of lungs | Lung injury was induced by CLP | Inhibiting the phosphorylation of JNK, ERK, P38, and p65; downregulating the levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 in plasma and lung tissue. | [76] |
| Protection of blood system | THR (from bovine plasma) | Direct THR inhibitory activity. | [46,77] |
| ADP-induced platelet aggregation | Prolonging the PT and APTT activity. | [78] | |
| Protection of vascular system | Zebrafish thrombus model induced by phenylhydrazine | Inhibiting the expression of coagulation factor VII (f7). | [79] |
| Erythrocyte deformations induced by ConA | Reducing the deformation and orientation index. | [80] | |
| Human microvascular endothelial cells | Upregulating placental growth factor. | [82] | |
| Analgesia | Nitroglycerin induced a headache in rats | Reducing NO levels. | [83] |
| Nitroglycerin induced a headache in rats | Reducing NO and CGRP levels. | [84] | |
| Anti-inflammatory | Sepsis model induced by CLP; human embryonic kidney 293 cells | Inhibiting the NF-KB signaling pathway. | [53] |
| OGD/R model simulates stroke | Suppressing the TLR4/NF-κB pathway by up-regulating Hsp70 dependent on HSF-1. | [85] | |
| Cell transportation | Blood–brain barrier model; MDCK-MDR1 cells | Downregulating the expression of claudin-5 and occlusive zone-1. Increasing the expression of the P-glycoprotein route. | [87] |
| Antioxidation | HepG2 cells with oxidative damage induced by hydrogen peroxide | Promoting HO-1 expression and inhibiting ROS formation. | [65] |
| Calcium antagonists | Human embryonic kidney 293 cells; rat cardio myoblast cells (H9C2 cells from ATCC) | Blocking voltage-operated Ca2+ channels and ryanodine receptor antagonistic intracellular calcium accumulation. | [42,81] |
| Antitumor | MCF-7 cells | Direct binding to CXCR4 and inhibition of CXCR4-mediated migration of MCF-7 cells. | [44] |
7. Pharmacokinetics
7.1. Pharmacokinetic Properties of SI
7.2. Pharmacokinetic Properties of SI Containing Herbal Preparations
| Substance | Route of Administration and Dose | Animals/ Model | Cmax (ng/mL) | Tmax (h) | AUC(0–t) (h·ng/mL) | AUC(0–∞) (h·ng/mL) | T1/2 (h) | MRT(0–t) (h) | CL/F (L h−1kg−1) | V (L/kg) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SI | i.v. (1 mg/kg) | Normal beagle dogs | 834.12 ± 89.09 | ND | 1166.21 ± 189.42 | 1173.45 ± 134.23 | 0.62 ± 0.09 | 0.88 ± 0.05 | 2.82 ± 0.49 | 2.34 ± 0.45 | [89] |
| i.g. (1 mg/kg) | 167.45 ± 21.37 | 0.18 ± 0.02 | 578.04 ± 123.78 | 583.25 ± 145.56 | 0.69 ± 0.11 | 0.67 ± 0.11 | 6.21 ± 0.22 | 4.89 ± 1.06 | |||
| i.g (5 mg/kg) | 841.23 ± 120.34 | 0.22 ± 0.05 | 2775.98 ± 278.15 | 2777.42 ± 271.65 | 0.59 ± 0.18 | 0.84 ± 0.17 | 6.52 ± 0.45 | 5.00 ± 1.73 | |||
| i.g. (50 mg/kg) | 7034.12 ± 340.23 | 0.21 ± 0.02 | 25,590.58 ± 459.87 | 25,678.34 ± 501.54 | 0.75 ± 0.14 | 1.08 ± 0.09 | 5.48 ± 0.22 | 4.67 ± 0.34 | |||
| SI | i.g. (18 mg/kg) | Normal SD rats | 3310 ± 550 | 0.22 ± 0.07 | 10,078,200 ± 894,000 | 10,152,600 ± 836,400 | 0.51 ± 0.16 | 0.77 ± 0.16 | ND | 4.81 ± 0.1.81 | [35] |
| i.g. (36 mg/kg) | 4420 ± 1520 | 0.4 ± 0.15 | 18,046,200 ± 4,118,400 | 18,420,000 ± 3,910,200 | 0.66 ± 0.21 | 0.95 ± 0.13 | ND | 7.11 ± 3.33 | |||
| i.g. (72 mg/kg) | 8960 ± 1080 | 0.37 ± 0.14 | 35,776,200 ± 6,591,000 | 37,138,800 ± 7,714,800 | 0.75 ± 0.13 | 0.97 ± 0.11 | ND | 7.72 ± 1.37 | |||
| i.v. (18 mg/kg) | ND | ND | 269,634,000 ± 2,217,000 | 2,725,560 ± 2,503,800 | 0.64 ± 0.14 | 0.57 ± 0.07 | ND | 2.18 ± 0.37 | |||
| i.v. (36 mg/kg) | ND | ND | 47,821,200 ± 5,071,800 | 48,463,200 ± 4,962,000 | 0.73 ± 0.12 | 0.58 ± 0.04 | ND | 2.84 ± 0.71 | |||
| i.v. (72 mg/kg) | ND | ND | 106,417,800 ± 11,481,000 | 107,790,600 ± 12,061,800 | 0.66 ± 0.15 | 0.66 ± 0.12 | ND | 2.30 ± 0.49 | |||
| SI | i.v. (20 mg/kg) | Normal SD rats | 13,847,200 ± 2,732,900 | ND | 7761.1 ± 874.8 | 7902.5 ± 925.7 | 0.56 ± 0.13 | 0.55 ± 0.10 | 2.56 ± 0.29 | ND | [91] |
| i.g. (20 mg/kg) | Normal rats | 5,236,300 ± 802,800 | 0.25 ± 0.06 | 5217.5 ± 1029.5 | 5458.6 ± 1073.0 | 0.66 ± 0.19 | 0.84 ± 0.16 | 3.78 ± 0.73 | ND | ||
| 0.23 ± 0.04 | Migrainous rats | 6,049,400 ± 1,320,700 | 14,459.1 ± 2130.4 | 19,477.0 ± 4001.4 | 5.93 ± 3.61 | 3.09 ± 0.52 | 1.06 ± 0.21 | ND | |||
| i.g. (72 mg/kg) | Normal rats | 22,071,900 ± 3,456,100 | 0.38 ± 0.11 | 21,480.2 ± 3003.1 | 21,953.0 ± 3162.1 | 0.52 ± 0.12 | 0.80 ± 0.09 | 3.34 ± 0.54 | ND | ||
| Migrainous rats | 23,599,100 ± 8,052,700 | 0.416667 | 45,177.0 ± 14,366.9 | 61,810.5 ± 12,086.8 | 10.44 ± 11.64 | 2.60 ± 0.41 | 1.20 ± 0.25 | ||||
| SI | i.g. (32 g/kg) | Normal rats | 3900 ± 900 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 16,600 ± 500 | 17,800 ± 470 | 6.3 ± 2.2 | ND | ND | [43] | |
| Migrainous rats | 11,400 ± 3600 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 47,200 ± 19,200 | 49,600 ± 20,700 | 4.8 ± 2.4 | ND | ND | ||||
| L. chuanxiong | i.g. (10 g/kg) | Normal SD rats | 92.33 ± 19.69 | 0.25 ± 0.00 | 842.74 ± 16.13 | ND | 1.03 ± 0.35 | 0.78 ± 0.04 | ND | ND | [38] |
| SD rats with biliary drainage | 371.49 ± 94.10 | 0.28 ± 0.09 | 1,822,573.2 ± 638,426.4 | ND | 1.18 ± 0.45 | 1.20 ± 0.23 | ND | ND | |||
| L. chuanxiong and warfarin | i.g. (10 g/kg) | Normal SD rats | 322.36 ± 213.54 | 0.28 ± 0.09 | 1,615,385.4 ± 756,679.8 | ND | 1.45 ± 0.34 | 1.35 ± 0.19 | ND | ND | |
| SD rats with biliary drainage | 208.85 ± 80.64 | 0.47 ± 0.09 | 1,292,366.4 ± 586,936.8 | ND | 1.43 ± 0.35 | 1.26 ± 0.27 | ND | ND | |||
| Shaofu Zhuyu Decoction | i.g. (0.5 mg/kg) | Normal beagle dogs | 92.8 ± 4.9 | 0.3 | 324.9 ± 38.3 | ND | 1.3 ± 0.1 | ND | ND | [62] | |
| YiGan San | i.g. (9.1 g/kg) | Normal SD rats | 136.02 ± 39.64 | 0.94 ± 0.83 | 718.29 ± 137.86 | 898.76 ± 265.79 | 1.52 ± 0.03 | 5.66 ± 0.66 | 223.72 ± 56.06 | ND | [96] |
| Xiaoyao Powder | i.g. (4 g/kg) | Normal SD rats | 403.26 ± 201.00 | 0.36 ± 0.13 | 1582.38 ± 985.86 | 1616.46 ± 967.01 | 4.75 ± 2.78 | 5.31 ± 0.72 | ND | ND | [55] |
| Naodesheng | i.g. (4 g/kg) | Wistar rats | 6990 ± 3240 | 0.5 ± 0.15 | 9960 ± 2390 | 10,160 ± 2510 | 1.66 ± 0.63 | 1.91 ± 0.48 | ND | [99] | |
| XueBiJing injection | i.v. (100 mL/day) | Human | 313 ± 57 | ND | ND | 571 ± 115 | 0.87 ± 0.09 | 1.73 ± 0.14 | ND | [98] | |
| SI | i.v. (104 mg/kg) | Normal KM mice | 84.21 | 0.03 | 163,640,400 | 164,328,000 | 0.53 | 0.53 | 1.75 | [90] | |
| i.g. (104 mg/ kg) | 12.31 | 0.33 | 52,681,200 | 53,545,200 | 0.67 | 0.96 | 6.74 | [57] | |||
| Xian-Xiong-Gu-Kang | i.g. (1.5 mL/100g) | SD rats with osteoarthritis model | 77.15 ± 22.84 | 0.63 ± 0.14 | 441.06 ± 173.27 | ND | 6.26 ± 1.09 | 6.23 ± 1.15 | ND | ND | |
| NaoMai Tong | i.g. (6 g/kg) | Normal SD rats | 16.04 ± 9.43 | 0.50 ± 0.25 | 73.55 ± 45.87 | 90.28 ± 32.74 | 11.12 ± 35.66 | 20.93 ± 47.99 | ND | ND | [97] |
| SD rats with stroke-afflicted | 267.38 ± 164.02 | 0.45 ± 0.33 | 454.76 ± 129.26 | 487.84 ± 132.21 | 7.48 ± 4.44 | 6.05 ± 2.95 | ND | ND | |||
| Xin-Sheng-Hua Granule | i.g. (9.86 g/kg) | Normal SD rats | 86.88 ± 13.12 | 0.42 ± 0.00 | 144.41 ± 17.38 | 152.45 ± 17.21 | 2.54 ± 0.93 | 2.99 ± 0.26 | ND | ND | [56] |
| SD rats with blood deficiency | 106.09 ± 17.09 | 0.67 ± 0.00 | 191.56 ± 25.86 | 200.78 ± 25.15 | 0.67 ± 0.00 | 2.41 ± 0.41 | ND | ND |
8. Conclusions and Future Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Acronyms
| AAB | Antiplatelet aggregation biological |
| A. sinensis | Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels |
| APTT | Activated partial thromboplastin time |
| BBB | Blood–brain barrier |
| BUN | Blood urea nitrogen |
| CGRP | Calcitonin gene related peptide |
| CLP | Cecal ligation and perforation |
| CXCR4 | C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 |
| DAD | Diode array detection |
| Fxa | Factor Xa |
| HEK293 | Human embryonic kidney 293 |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS/MS | High-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry |
| I/R | Ischemia/reperfusion |
| ICH | Intracerebral hemorrhage |
| L. chuanxiong | Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort. |
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry |
| LDH | Lactate dehydrogenase |
| LIG | Ligustilide |
| MDA | Malonaldehyde |
| NBP | n-Butylphthalide |
| OGD/R | Oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation |
| PGP | P-glycoprotein |
| PMA | Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate |
| PT | Prothrombin time |
| ROS | Reactive oxidative species |
| SA | Senkyunolide A |
| SCR | Serum creatinine |
| SE | Septic encephalopathy |
| SH | Senkyunolide H |
| SI | Senkyunolide I |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| SWD | Siwu decoction |
| SX | Suxiao jiuxin pill |
| TCM | Traditional Chinese medicine |
| THR | Thrombin |
| tMCO | Transient middle cerebral artery occlusion |
| UPLC | Ultra-performance liquid chromatography |
| UPLC/Q-TOF-MS | Ultra-performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry |
| UPLC-MS/MS | Ultra-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
References
- Donkor, P.O.; Chen, Y.; Ding, L.; Qiu, F. Locally and traditionally used Ligusticum species—A review of their phytochemistry, pharmacology and pharmacokinetics. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 194, 530–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juárez-Reyes, K.; Ángeles-López, G.E.; Rivero-Cruz, I.; Bye, R.; Mata, R. Antinociceptive activity of Ligusticum porteri preparations and compounds. Pharm. Biol. 2014, 52, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- León, A.; Del-Ángel, M.; Ávila, J.L.; Delgado, G. Phthalides: Distribution in Nature, Chemical Reactivity, Synthesis, and Biological Activity. Prog. Chem. Org. Nat. Prod. 2017, 104, 127–246. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; DU, J.-R.; Wang, J.; Yu, D.-K.; Chen, Y.-S.; He, Y.; Wang, C.-Y. Z-ligustilide Extracted from Radix Angelica sinensis Decreased Platelet Aggregation Induced by ADP Ex Vivo and Arterio-venous Shunt Thrombosis In Vivo in Rats. Yakugaku Zasshi 2009, 129, 855–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, C.M.; Chen, W.Y.; Ko, W.C.; Ouyang, C. Antiplatelet effect of butylidenephthalide. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1987, 924, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao-Peng, C.H.; Wei, L.I.; Xue-Feng, X.I.; Zhang, L.L.; Chang-Xiao, L.I. Phytochemical and pharmacological studies on Radix Angelica sinensis. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2013, 11, 577–587. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, T.; Fang, J.-Y.; Zhu, L.; Tang, Y.-N.; Ji, H.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Yu, J.-C.; Zhang, X.-J.; Yu, Z.-L.; Zhao, Z.-Z.; et al. The variation in the major constituents of the dried rhizome of Ligusticum chuanxiong (Chuanxiong) after herbal processing. Chin. Med. 2016, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Zhang, L.; Xie, L.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, K.; Tang, H.; Liao, Y.; Li, X. Z-ligustilide: A review of its pharmacokinetics and pharmacology. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 1966–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Bai, L. Anti-inflammatory Effects of Z-Ligustilide Nanoemulsion. Inflammation 2012, 36, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, L.; Yu, S. Complexation of Z-ligustilide with hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin to improve stability and oral bioavailability. Acta Pharm. 2014, 64, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; He, Y.; Chen, S.; Qi, S.; Shen, J. Therapeutic targets of oxidative/nitrosative stress and neuroinflammation in ischemic stroke: Applications for natural product efficacy with omics and systemic biology. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 158, 104877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Wang, S.; Ma, F.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Xing, C.; Feng, Y.; Wang, X.; Peng, Y. From stroke to neurodegenerative diseases: The multi-target neuroprotective effects of 3-n-butylphthalide and its derivatives. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 135, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Han, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L. Novel brain-targeting 3-n-butylphthalide prodrugs for ischemic stroke treatment. J. Control. Release 2021, 335, 498–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaouadji, M.; Puech-Baronnat, M.; Mariotte, A.M. Ligustilidiol, nouveau phtalide hydroxyle isole de Ligusticum wallichii franch. Tetrahedron Lett. 1983, 24, 4675–4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Fujita, M.; Mitsuhashi, H. Components of Cnidium officinale makino: Occurrence of pregnenolone, coniferyl ferulate, and hydroxy phthalides. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1984, 32, 3770–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.; Chen, S.N.; Yao, P.; Nikolic, D.; van Breemen, R.B.; Bolton, J.L.; Fong, H.H.; Farnsworth, N.R.; Pauli, G.F. Serotonergic Activity-Guided Phytochemical Investigation of the Roots of Angelica sinensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-H.; Peng, S.-L.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, K.-B.; Ding, L.-S. Two New Phthalides from Ligusticum chuanxiong. Planta Med. 2006, 72, 652–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, S.-C.; Everngam, M.C.; Sturtz, G.; Beck, J.J. Antibacterial activity of components from Lomatium californicum. Phytotherapy Res. 2006, 20, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.H.; Niu, Y.Y. Study on chemical constituents in Cryptotaenia japonica. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2012, 43, 2365–2368. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.L.; Yan, R.; Tam, Y.K.; Lin, G. Post-Harvest Alteration of the Main Chemical Ingredients in Ligusticum chuanxiong HORT. (Rhizoma Chuanxiong). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 55, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.-Q.; Lu, G.-H.; Wei, B.-P.; Hong, Y.-L.; Li, J.-R.; Li, X. Chemical Change of Chuanxiong Raw Materials during Storage. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2013, 36, 38–41. [Google Scholar]
- Duric, K.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.-N.; Lankin, D.C.; Nikolic, D.; McAlpine, J.B.; Friesen, J.B.; Pauli, G.F. Studying Mass Balance and the Stability of (Z)-Ligustilide from Angelica sinensis Helps to Bridge a Botanical Instability–Bioactivity Chasm. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 2400–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-L.; Liu, L.-F.; Zhu, L.-Y.; Bai, Y.-J.; Mao, Q.; Li, S.-L.; Chen, S.-L.; Xu, H.-X. A high performance liquid chromatography fingerprinting and ultra high performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry chemical profiling approach to rapidly find characteristic chemical markers for quality evaluation of dispensing granules, a case study on Chuanxiong Rhizoma. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 88, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.-Z.; He, X.-G.; Lian, L.-Z.; King, W.; Elliott, J. Liquid chromatographic–electrospray mass spectrometric study of the phthalides of Angelica sinensis and chemical changes of Z-ligustilide. J. Chromatogr. A 1998, 810, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, F.; Xu, W.; Liu, J.; Jia, Z.; Chen, K.; Chen, Y.; Wang, M.; Ma, K.; Dong, J.; Chen, L.; et al. Preparing the key metabolite of Z-ligustilide in vivo by a specific electrochemical reaction. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 2799–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Ko, N.L.; Li, S.-L.; Tam, Y.K.; Lin, G. Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism of Ligustilide, a Major Bioactive Component in Rhizoma Chuanxiong, in the Rat. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2007, 36, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Li, H.; Liu, J. Metabolic profiling of ligustilide and identification of the metabolite in rat and human hepatocytes by liquid chromatography combined with high-resolution mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 4405–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, M.; Shi, L.; Hu, J. Enzyme kinetics of ligustilide metabolism in rat liver microsomes. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2009, 44, 395–400. [Google Scholar]
- Jie, G.; Weiling, P.; Xiaoliang, R.; Defei, R.; Lili, S.; Aidi, Q. Degradation kinetics of Senkyunolide I in Xuebijing injection. J. Tianjin Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2015, 34, 160–164. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, A.; Wang, L.; Xiao, H. Study on degradation products of senkyunolide A and senkyunolide I. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2012, 43, 2127–2131. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Xu, S.; Ye, L.; Yao, Y. Simultaneous Determination of Night Effective Constituents and Correlation Analysis of Multiconstituents and Antiplatelet Aggregation Bioactivity In Vitro in Chuanxiong Rhizoma Subjected to Different Decoction Times. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2019, 2019, 8970624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- YBZ-PFKL-2021029; Chuanxiong Peifangkeli. Chinese Pharmacopoeia Committee, National Drug Standards, National Medical Products Administration: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Yuan, Y.; Lin, X.; Feng, Y.; Xu, D.S.; Wang, Y.H. In Vivo Transmigration of Anti-Migrainous Compounds from Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort. Chin. Pharm. J. 2010, 45, 694–697. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, A.-H.; Cheng, M.-C.; Wang, L.; Xiao, H.-B. Analysis of chemical constituents of chuanxiong rhizoma absorbed into rat brain tissues by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2012, 37, 3647–3650. [Google Scholar]
- He, C.-Y.; Wang, S.; Feng, Y.; Liang, S.; Lin, X.; Xu, D.-S.; Ruan, K.-F. Pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution and metabolism of senkyunolide I, a major bioactive component in Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort. (Umbelliferae). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 142, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.K.; Liang, S.; Du, Y.; Tian, F.; Feng, Y. HPLC determination of equilibrium solubility and apparent oil/water partition coefficient of senkyunolide Ⅰ. Chin. J. Pharm. Anal. 2012, 32, 1644–1647. [Google Scholar]
- Ze, Y.; Hai, W.; Yaokun, X.; Xiao, L.; Shuang, L.; Yi, F. In situ Intestinal Absorption Kinetics of Senkyunolide I in Rats. Chin. Pharm. J. 2013, 48, 628–632. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.-G.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lv, H.; Xie, H.; Yang, G.; Guo, C.; Tang, J.; Tang, T. The Effects of Warfarin on the Pharmacokinetics of Senkyunolide I in a Rat Model of Biliary Drainage After Administration of Chuanxiong. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Hu, J.; Li, H.; Liu, J. Preparative isolation and purification of senkyunolide-I, senkyunolide-H and ferulic acid from Rhizoma Chuanxiong using counter-current chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2011, 34, 3426–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Ma, C.; Wu, F.; Xiong, Y.-K.; Feng, Y.; Liang, S. Preparation and structural determination of four metabolites of senkyunolide I in rats using ultra performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole-time-of-flight tandem mass and nuclear magnetic resonance spectra. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.Y.X.; Zheng, K.Y.Z.; Zhu, K.Y.; Bi, C.W.C.; Zhang, W.L.; Du, C.Y.Q.; Fu, Q.; Dong, T.T.X.; Choi, R.C.Y.; Tsim, K.W.K.; et al. Chemical and Biological Assessment of Angelicae sinensis Radix after Processing with Wine: An Orthogonal Array Design To Reveal the Optimized Conditions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 6091–6098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.X.; Yan, M.L.; Han, S.; Cong, L.F.; Wang, L.Y.; Zhang, L.; Sun, L.L.; Bai, H.Y.; Wei, G.H.; Du, H.; et al. Identification of Chemical Markers for the Discrimination of Radix Angelica sinensis Grown in Geoherb and Non-Geoherb Regions Using UHPLC-QTOF-MS/MS Based Metabolomics. Molecules 2019, 24, 3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Ma, T.; Zhang, C.; Shi, S.; Cui, S.; Bi, K.; Jia, Y. Simultaneous determination of senkyunolide I and senkyunolide H in rat plasma by LC-MS: Application to a comparative pharmacokinetic study in normal and migrainous rats after oral administration of Chuanxiong Rhizoma extract. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2015, 29, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lv, D.; Wang, S.; Wang, D.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Hong, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Cao, Y.; Chai, Y. Surface Plasmon Resonance-Based Membrane Protein-Targeted Active Ingredients Recognition Strategy: Construction and Implementation in Ligand Screening from Herbal Medicines. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 3972–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Gong, M.; Wu, S.; Qiu, F.; Ma, L. Identification and quantification of the quality markers and anti-migraine active components in Chuanxiong Rhizoma and Cyperi Rhizoma herbal pair based on chemometric analysis between chemical constituents and pharmacological effects. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 246, 112228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.-Y.; Wu, Z.-Y.; Xia, F.-B.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Gao, J.-L.; Yang, F.-Q.; Wan, J.-B. Characterization of thrombin/factor Xa inhibitors in Rhizoma Chuanxiong through UPLC-MS-based multivariate statistical analysis. Chin. Med. 2020, 15, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.X.; Ding, M.Y.; Yu, J.Y. Separation and Identification of the Phthalic Anhydride Derivatives of Liqusticum ChuanxiongHort by GC–MS, TLC, HPLC–DAD, and HPLC–MS. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2002, 40, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-J.; Cheng, Y.-Y. An HPLC/MS method for identifying major constituents in the hypocholesterolemic extracts of Chinese medicine formula ‘Xue-Fu-Zhu-Yu decoction’. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2006, 20, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Cui, W.; Zhou, W.; Duan, J.-A.; Shang, E.; Tang, Y. Chemical fingerprinting and quantitative constituent analysis of Siwu decoction categorized formulae by UPLC-QTOF/MS/MS and HPLC-DAD. Chin. Med. 2013, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.-W.; Li, P.; Li, S.-L.; Sheng, L.-H.; Li, R.-Y.; Song, Y.; Li, H.-J. Screening and identification of permeable components in a combined prescription of Danggui Buxue decoction using a liposome equilibrium dialysis system followed by HPLC and LC-MS. J. Sep. Sci. 2006, 29, 2211–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-L.; Liang, Y.-Z.; Chen, B.-M.; He, Y.-K.; Li, B.-Y.; Hu, Q.-N. LC-DAD-APCI-MS-based screening and analysis of the absorption and metabolite components in plasma from a rabbit administered an oral solution of danggui. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 383, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, M.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Luo, J.; Kong, L. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of the major constituents in Chinese medicinal preparation Guan-Xin-Ning injection by HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS(n). J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 59, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Zhou, M.; Han, Y.; Xing, L.; Zhao, H.; Dong, L.; Bai, G.; Luo, G. Identification of NF-kappaB Inhibitors in Xuebijing injection for sepsis treatment based on bioactivity-integrated UPLC-Q/TOF. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 147, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Qi, J.; Chang, Y.-X.; Zhu, D.; Yu, B. Identification and determination of the major constituents in Traditional Chinese Medicinal formula Danggui-Shaoyao-San by HPLC–DAD–ESI-MS/MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2009, 50, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Xu, Z.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Liu, M.; Geng, F.; Zhang, N. UPLC-MS/MS Method for the Determination of 14 Compounds in Rat Plasma and Its Application in a Pharmacokinetic Study of Orally Administered Xiaoyao Powder. Molecules 2018, 23, 2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, H.-Q.; Tang, Y.-P.; Cao, Y.-J.; Tan, Y.-J.; Jin, Y.; Shi, X.-Q.; Huang, S.-L.; Sun, D.-Z.; Sun, J.; Tang, Z.-S.; et al. Comparatively evaluating the pharmacokinetic of fifteen constituents in normal and blood deficiency rats after oral administration of Xin-Sheng-Hua Granule by UPLC–MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1061–1062, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chen, W.; Wang, Y.; Yin, H. An LC-MS/MS method for simultaneous quantification of 11 components of Xian-Xiong-Gu-Kang in the plasma of osteoarthritic rats and pharmacokinetic analysis. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 3386–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Yang, Y.; Feng, S.; Hu, F.; Liu, X.; Li, C. Simultaneous Determination of 10 Components in Bu-Zhong-Yi-Qi Wan by Solid Phase Extraction-High Performance Liquid Chromatography with Diode Array Detection and Evaporative Light Scattering Detection. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2015, 53, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.N.; Ye, X.; Liu, X.Q.; Feng, W.H.; Liang, Y.H.; Li, C.; Wang, Z.M. Content determination and transferring rules of seven components in Angelicae sinensis radix and its processed products. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2021, 46, 6196–6203. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Feng, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Qiu, D. Simultaneous Determination of Eight Chemical Components in Angelicae sinensis Radix and Its Herbal Products by QAMS. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2021, 2021, 7178982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Shang, E.-X.; Zhu, Y.; Qian, D.-W.; Duan, J.-A. Volatile component interaction effects on compatibility of Cyperi Rhizoma and Angelicae sinensis Radix or Chuanxiong Rhizoma by UPLC-MS/MS and response surface analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 160, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Su, S.; Cui, W.; Liu, P.; Duan, J.A.; Guo, J.; Li, Z.; Shang, E.; Qian, D.; Huang, Z. Simultaneous determination of paeoniflorin, albiflorin, ferulic acid, tetrahydropalmatine, protopine, typhaneoside, senkyunolide I in Beagle dogs plasma by UPLC-MS/MS and its application to a pharmacokinetic study after Oral Administration of Shaofu Zhuyu Decoction. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2014, 962, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, M.M.; Fujita, H. Studies on the Constituents of Umbelliferae Plants. XV.1) Constituents of Cnidium officinale: Occurrence of Pregnenolone, Coniferylferulate and Hydroxyphthalides. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1987, 35, 1427–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Yang, J.; Ren, J.; Wang, A.; Ji, T.; Su, Y. Bioactive phthalides from Ligusticum sinense Oliv cv. Chaxiong. Fitoter. 2014, 93, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, H.; Siu, S.O.; Chen, Y.; Han, Y.; Chu, I.K.; Tong, Y.; Lau, A.S.; Rong, J. Senkyunolides reduce hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative damage in human liver HepG2 cells via induction of heme oxygenase-1. Chem. Interact. 2010, 183, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ping, Z.C.; Xingnuo, L.; Yuanyi, C.; Zhiwei, G.; Jizhong, Y. Isolation and purification of senkyunolide H and I by preparative reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography. J. Zhejiang Univ. Technol. 2011, 39, 386–389. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Y.-K.; Liang, S.; Hong, Y.-L.; Yang, X.-J.; Shen, L.; Du, Y.; Feng, Y. Preparation of ferulic acid, senkyunolide I and senkyunolide H from Ligusticum chuanxiong by preparative HPLC. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2013, 38, 1947–1950. [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Harada, S.; Tokuyama, S. Sodium-glucose transporter type 3-mediated neuroprotective effect of acetylcholine suppresses the development of cerebral ischemic neuronal damage. Neuroscience 2014, 269, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Duan, M.; Liang, S.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Y. Senkyunolide I protects rat brain against focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by up-regulating p-Erk1/2, Nrf2/HO-1 and inhibiting caspase 3. Brain Res. 2015, 1605, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, W.; Mingjiang, Y.; Jianxun, L.; Yujie, W.; Pan, W.; Junguo, R.; Xiaodi, F. Study on the Active Components of Ligusticum chuanxiong for Neuroprotection. World J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. 2021, 16, 793–798. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.; Liu, D.-L.; Zeng, Q.-K.; Shi, M.-Q.; Zhao, L.-X.; He, Q.; Kuang, X.; Du, J.-R. The neuroprotective effects and probable mechanisms of Ligustilide and its degradative products on intracerebral hemorrhage in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 63, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuming, Z.; Xinfeng, L.; Li, Y.; Yuanyuan, L. Study on Cerebral Protective Effect of Senkyunolide I on Rats with Septic Encephalopathy Based on p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway. Tradit. Chin. Drug Res. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 30, 1083–1087. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.; Zhao, Z.-Z.; Li, P.; Zhu, C.-L.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J.; Deng, X.-M.; Wang, J.-F. Senkyunolide I Protects against Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy by Attenuating Sleep Deprivation in a Murine Model of Cecal Ligation and Puncture. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 6647258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Zhao, Z.Z.; Xie, J.; Wang, Y.P.; Yang, K.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J.F.; Deng, X.M. Senkyunolide I attenuates hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice via anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 97, 107717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.L.; Huang, J.; Chen, X.Y.; Xie, J.; Yang, Q.; Wang, J.F.; Deng, X.M. Senkyunolide I alleviates renal Ischemia-Reperfusion injury by inhibiting oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 102, 108393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zha, Y.-F.; Xie, J.; Ding, P.; Zhu, C.-L.; Li, P.; Zhao, Z.-Z.; Li, Y.-H.; Wang, J.-F. Senkyunolide I protect against lung injury via inhibiting formation of neutrophil extracellular trap in a murine model of cecal ligation and puncture. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 99, 107922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.-X.; Li, S.-Y.; Wang, Y.-L.; Yang, F.-Q.; Chen, H.; Xia, Z.-N. An ultrafiltration and high performance liquid chromatography coupled with diode array detector and mass spectrometry approach for screening and characterizing thrombin inhibitors from Rhizoma Chuanxiong. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1061–1062, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Tang, Y.; Duan, J.-A.; Guo, J.; Guo, S.; Su, S.; Shang, E.; Qian, D.; Ding, A. Roles of paeoniflorin and senkyunolide I in SiWu decoction on antiplatelet and anticoagulation activities. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 3335–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, H.; Yang, Z.; Yu, Q.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y. Synergistic Effects of Cryptotanshinone and Senkyunolide I in Guanxinning Tablet Against Endogenous Thrombus Formation in Zebrafish. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 622787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Dong, Z.; Zhu, Q. Effects of Ferulic Acid, Senkyunol ide H and Senkyunol ide I on Erythrocytes. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Med. Res. 2003, 14, 738–739. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, W.; Ni, J.; Xia, X.; Jiang, M.; Bai, G. Searching for synergistic calcium antagonists and novel therapeutic regimens for coronary heart disease therapy from a Traditional Chinese Medicine, Suxiao Jiuxin Pill. J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1092, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Y. Senkyunolide I Promotes Endothelial Cells Angiogenesis through PIGF Signaling Pathway. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2011, 18, 211–214. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.-H.; Liang, S.; Xu, D.-S.; Lin, X.; He, C.-Y.; Feng, Y.; Hong, Y.-L. Effect and mechanism of senkyunolide I as an anti-migraine compound from Ligusticum chuanxiong. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 63, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MuYin, D.; Chenchen, G.; Xianwen, D.; Yuan, W.; Shuang, L.; Yi, F. Pharmacodynamic Action of Senkyunolide I on Cortical Spreading Depression in Migraine Rats. Tradit. Chin. Drug Res. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 24, 217–221. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Liang, S.; Yu, X.-L.; Zhang, L.; Feng, L.-Y.; Feng, Y. Senkyunolide I attenuates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced inflammation in microglial cells. Brain Res. 2016, 1649, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Mimura, Y.; Naitoh, T.; Kimura, I.; Kimura, M. Chemical Structure-Activity of Cnidium Rhizome-Derived Phthalides for the Competence Inhibition of Proliferation in Primary Cultures of Mouse Aorta Smooth Muscle Cells. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 1993, 63, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Tang, Y.; Hu, P.-Y.; Liu, D.; Zhang, D.; Yue, P.; Guo, Y.; Yang, M. The influence and mechanism of ligustilide, senkyunolide I, and senkyunolide A on echinacoside transport through MDCK-MDR1 cells as blood-brain barrier in vitro model. Phytotherapy Res. 2018, 32, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.Y.; Liu, D.; Zheng, Q.; Wu, Q.; Tang, Y.; Yang, M. Elucidation of Transport Mechanism of Paeoniflorin and the Influence of Ligustilide, Senkyunolide I and Senkyunolide A on Paeoniflorin Transport through Mdck-Mdr1 Cells as Blood-Brain Barrier in Vitro Model. Molecules 2016, 21, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Q.; Wang, J.F.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.H.; He, D.; Tong, R.S.; She, S.Y. A validated LC-MS/MS method for the determination of senkyunolide I in dog plasma and its application to a pharmacokinetic and bioavailability studies. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2018, 32, e4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaokun, X.; Xiao, L.; Shuang, L.; Ze, Y.; Yan, D.; Yi, F. HPLC determination of senkyunolideⅠ in mice plasma and its pharmacokinetics. Chin. J. Pharm. Anal. 2013, 33, 371–375. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.-H.; Hong, Y.-L.; Feng, Y.; Xu, D.-S.; Liang, S.; Lin, X.; Shen, L. Comparative pharmacokinetics of senkyunolide I in a rat model of migraine versus normal controls. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2012, 37, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.-K.; Lin, X.; Liang, S.; Hong, Y.-L.; Shen, L.; Feng, Y. Identification of senkyunolide I metabolites in rats using ultra performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole-time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2013, 81–82, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, A.; Wang, L.; Xiao, H.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Yi, J. Identification of the absorbed components and metabolites in rat plasma after oral administration of Rhizoma Chuanxiong decoction by HPLC–ESI-MS/MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 56, 1046–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Luo, Z.Q.; Lv, B.R.; Zhao, H.Y.; Dong, L. Absorption and metabolism of Chuanxiong Rhizoma decoction with multi-component sequential metabolism method. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2016, 41, 1178–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.-F.; Zhang, N.; Lin, X.; Feng, Y. Release characteristics in vitro and pharmacokinetics of da chuanxiong fang multiunit drug delivery system in rats. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2011, 46, 1150–1155. [Google Scholar]
- Gai, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, W.; Feng, F.; Xie, N. The metabolism of YiGan San and subsequent pharmacokinetic evaluation of four metabolites in rat based on liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 972, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Zhao, L.; Rong, Y.; Zhu, G.; Liang, S.; Wang, S. The pharmacokinetic screening of multiple components of the Nao Mai Tong formula in rat plasma by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry combined with pattern recognition method and its application to comparative pharmacokinetics. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 131, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Cheng, C.; Olaleye, O.E.; Sun, Y.; Li, L.; Huang, Y.; Du, F.; Yang, J.; Wang, F.; Shi, Y.; et al. Pharmacokinetics-Based Identification of Potential Therapeutic Phthalides from XueBiJing, a Chinese Herbal Injection Used in Sepsis Management. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2018, 46, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Kang, J.; Zhao, W.; Qi, Y.; Liang, S. Validated LC-MS/MS method for simultaneous quantification of seven components of Naodesheng in rat serum after oral administration and its application to a pharmacokinetic study. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 174, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample | Detection Method | Mobile Phase | Column | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SI | HPLC | 0.05% phosphate–methanol | Apollo C18 (150 × 4.6 mm) | [39] |
| SI | LC-MS/MS | 0.1% formic acid–acetonitrile | Acquity BEH C18 column (2.1 × 50 mm, 1.7 μm) | [27] |
| SI | UPLC–MS/MS | 0.1% formic acid–acetonitrile | Acquity BEH C18 (2.1 × 100 mm, 1.7 μm) | [38] |
| SI | UPLC/Q-TOF-MS | 0.1% formic acid–acetonitrile | Grace C18 (4.6 × 150 mm,5 μm); Acquity HSS T3 (2.1 × 100 mm, 1.8 μm) | [40] |
| Root of A. sinensis | HPLC | 1% acetic acid–acetonitrile | Prevail 18 (4.6 × 250 mm, 4 μm) | [41] |
| Root of A. sinensis | UHPLC-QTOF-MS/MS | water–acetonitrile (both containing 0.1% formic acid) | CORTECS C18 (2.1 × 100 mm, 1.6 μm) | [42] |
| Rhizome of L. chuanxiong | LC-MS | water–methanol | Kromasil C18 (250 × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) | [43] |
| Rhizome of L. chuanxiong | HPLC-DAD-MS | 0.5% acetic acid–acetonitrile | Alltima C18 (4.6 × 250 mm, 5 μm) | [7] |
| Rhizome of L. chuanxiong | HPLC-ESI-MS/MS | 0.5% acetic acid–acetonitrile | Sapphire C18 (4.6 × 250 mm, 5 µm) | [35] |
| Rhizome of L. chuanxiong | UPLC-QTOF-MS | 0.1% formic acid–acetonitrile | X Select HSS T3 (2.1 × 100 mm, 2.5 μm) | [44] |
| Rhizome of L. chuanxiong | HPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS/MS | 0.1% formic acid–methanol | Kromasil-C18 (4.6 × 250 mm, 5 µm) | [45] |
| Rhizome of L. chuanxiong | HPLC-DAD; UPLC-QTOF-MS | 0.1% formic acid–methanol; 0.1% formic acid–methanol | ZORBAX SB-C18 (4.6 × 250 mm, 5 µm); Acquity BEH C18 (100 × 2.1 mm, 1.7 μm) | [46] |
| Rhizome of L. chuanxiong | GC-MS; TLC; HPLC-DAD; HPLC-MS | water–methanol | Zorbax SB-C18 (250 × 4.5 mm, 5 µm) | [47] |
| Xue-Fu-Zhu-Yu decoction | HPLC-ESI-MS | 0.08% acetic acid–methanol | Zorbax SB-C18 (4.6 × 250 mm, 5 µm) | [48] |
| Siwu decoction | UPLC-QTOF/MS/MS; HPLC-DAD | 0.1% formic acid–acetonitrile | Acquity BEH C18 (100 × 2.1 mm, 1.7 μm) | [49] |
| Danggui Buxue decoction | LC-MS; HPLC-DAD-ELSD | 0.1% formic acid–acetonitrile | Zorbax C18 (250 × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) | [50] |
| Danggui oral solution | LC-DAD-APCI-MS | water–methanol | Hypersil-Keystone C18 (150 × 2.1 mm, 5 μm) | [51] |
| Guanxinning injection | HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS | 0.08% formic acid–methanol | Ultimate XB-C18 (250 × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) | [52] |
| Xuebijing injection | UPLC-Q/TOF | (formic acid–acetonitrile–methanol, 0.5:60:40)–(formic acid–water, 0.5:100) | Acquity BEH C18 column (2.1 × 100 mm, 1.7 μm) | [53] |
| Danggui-Shaoyao powder | HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS/MS | 0.01% formic acid–acetonitrile | Alltima C18 (250 × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) | [54] |
| Xiaoyao powder | UPLC-MS/MS | (0.1% formic acid)–acetonitrile | Acquity BEH C18 (50 × 2.1 mm, 1.7 µm) | [55] |
| Xin-Sheng-Hua granule | UPLC-TQ-MS/MS | (0.1% formic acid)–acetonitrile | Hypersil GOLD (100 × 3 mm, 1.9 μm) | [56] |
| Xian-Xiong-Gu-Kang | LC-MS/MS | (0.05% formic acid)–acetonitrile | Acquity BEH C18 (2.1 × 100 mm, 1.7 μm) | [57] |
| Bu-Zhong-Yi-Qi Wan | SPE-HPLC-DAD-ELSD | water–acetonitrile | Spursil C18 (250 × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) | [58] |
| Medicinal Material | Content | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Angelica sinensis root | 0.137~0.505 mg/g | [59] |
| Angelica sinensis root | 0.149~1.006 mg/g | [60] |
| Angelica sinensis root | 0.276~0.296 mg/g | [42] |
| Ligusticum chuanxiong rhizome/Angelica sinensis root | 0.065~2.158 mg/g | [61] |
| Ligusticum chuanxiong rhizome | 10.9 mg/g | [7] |
| Chuanxiong Dispensing Granules | 2.08~6.07 mg/g | [23] |
| Preparation Name | Content | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Xiangfu-Siwu decoction | 0.02 mg/g | [49] |
| Taohong-Siwu decoction | 0.03 mg/g | [49] |
| Qinlian-Siwu decoction | 0.08 mg/g | [49] |
| Siwu decoction | 0.18 mg/g | [49] |
| Shaofu-Zhuyu decoction | 0.21 mg/g | [49] |
| Shaofu-Zhuyu decoction | 0.4 mg/g | [62] |
| Wuji Baifeng pills | 0.069 mg/g | [60] |
| Xiaoyao pills | 0.098 mg/g | [60] |
| Bazhen Yimu pills | 0.128 mg/g | [60] |
| Danggui Futongning pills | 0.142 mg/g | [60] |
| Bu-Zhong-Yi-Qi pills | 0.152 mg/g | [60] |
| Aifu Nuangong pills | 0.163 mg/g | [60] |
| Danggui Kushen pills | 0.169 mg/g | [60] |
| Concentrated Danggui pills | 0.423 mg/g | [60] |
| Bu-Zhong-Yi-Qi pills | 0.064~0.136 mg/g | [58] |
| Fuke Tiaojing tablets | 0.261 mg/g | [60] |
| Niuhuang Shangqing tablets | 0.292 mg/g | [60] |
| Tiaojing Zhitong tablets | 2.206 mg/g | [60] |
| Xin-Sheng-Hua granules | 0.003 mg/ml | [56] |
| Yangxue Qingnao granules | 0.323 mg/g | [60] |
| Danggui-Shaoyao powder | 0.9 mg/g | [54] |
| Xiaoyao powder | 1.45 mg/g | [55] |
| Guanxinning injection | 0~0.478 mg/ml | [52] |
| Xian-Xiong-Gu-Kang | 0.4 mg/ml | [57] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yin, H.; Du, L.; Chen, C. Senkyunolide I: A Review of Its Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics, and Drug-Likeness. Molecules 2023, 28, 3636. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083636
Huang Y, Wu Y, Yin H, Du L, Chen C. Senkyunolide I: A Review of Its Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics, and Drug-Likeness. Molecules. 2023; 28(8):3636. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083636
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Yan, Yan Wu, Hongxiang Yin, Leilei Du, and Chu Chen. 2023. "Senkyunolide I: A Review of Its Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics, and Drug-Likeness" Molecules 28, no. 8: 3636. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083636
APA StyleHuang, Y., Wu, Y., Yin, H., Du, L., & Chen, C. (2023). Senkyunolide I: A Review of Its Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics, and Drug-Likeness. Molecules, 28(8), 3636. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083636






