Systematic Studies on Anti-Cancer Evaluation of Stilbene and Dibenzo[b,f]oxepine Derivatives
Abstract
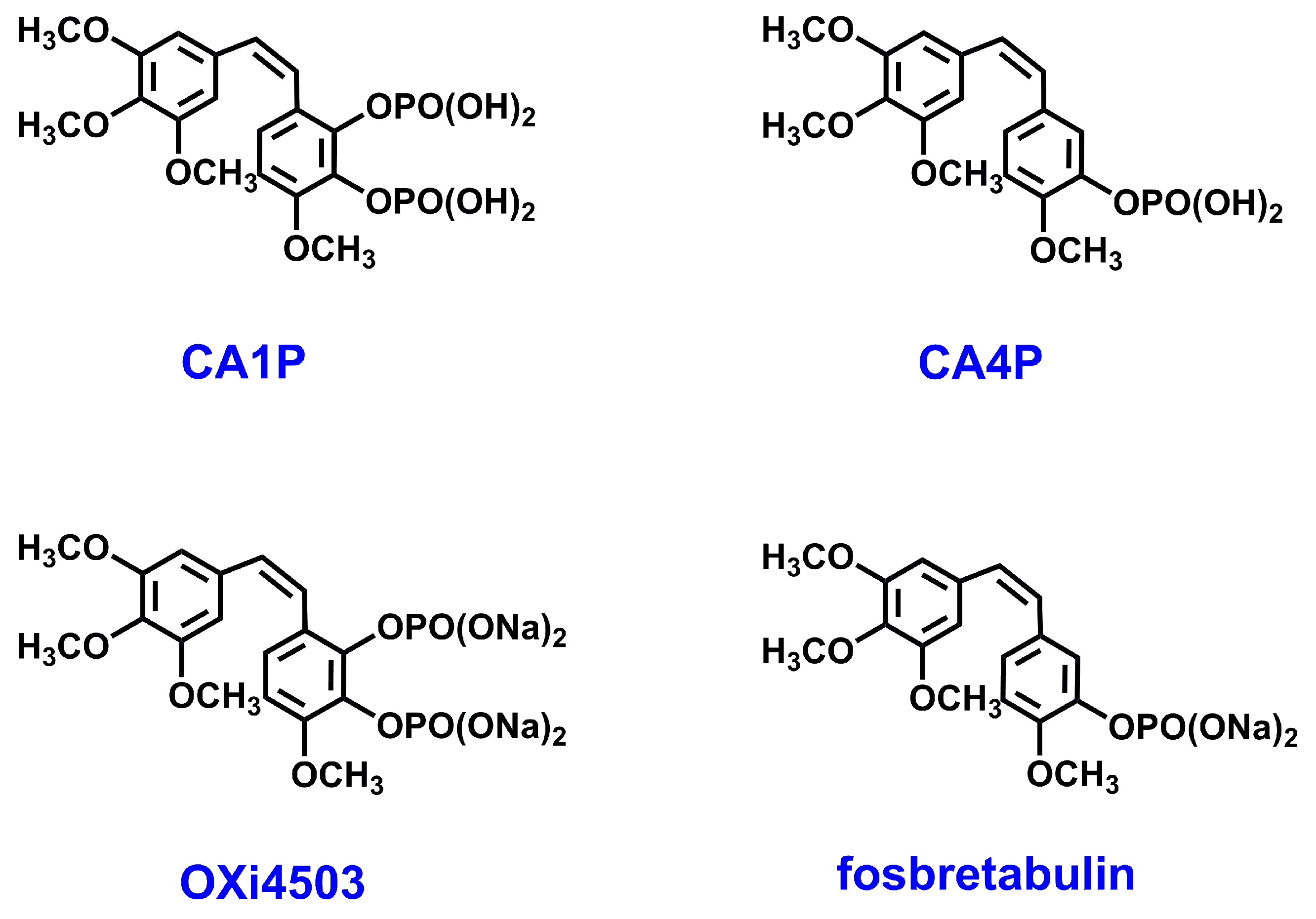
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry and NMR Spectra
2.2. Anti-Cancer Potential of Stilbenes and Oxepines
2.3. The Structure of Microtubular Cytoskeleton in HT116 Cells Treated with Compound (1d)
2.4. Computational Analysis and Molecular Docking Simulations
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemistry
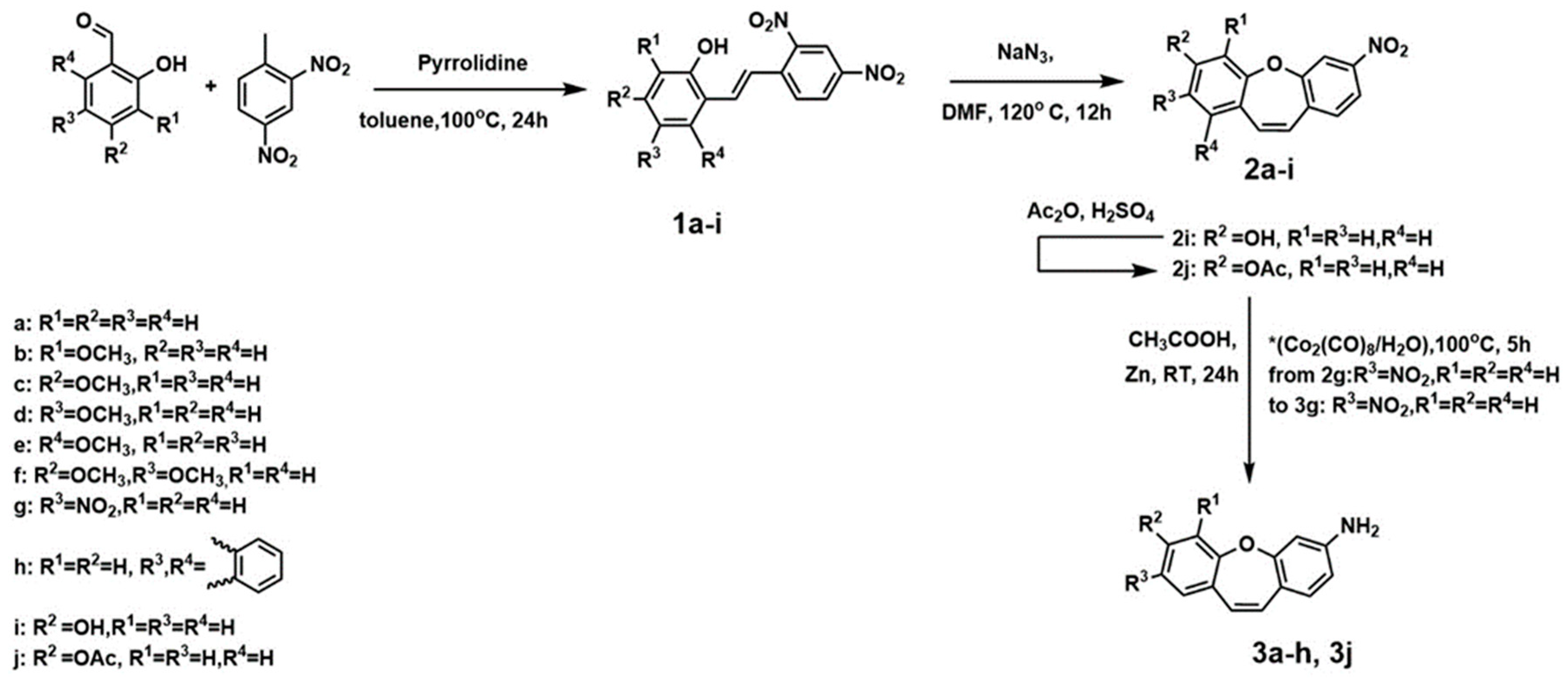
4.1.1. PROCEDURE A—Obtained Compounds 1a–1i (Figure 6)

4.1.2. PROCEDURE B—Obtained Compounds 2a–2i (Figure 7)

4.1.3. PROCEDURE C—Obtained Compound 2j (Figure 7)
4.1.4. PROCEDURE D—Obtained Compound 3a–3f and 3j (Figure 8)

4.1.5. PROCEDURE E—Obtained Compound 3g (Figure 8)
4.2. NMR Measurements
4.3. Biological Evaluation
4.3.1. Cell Culturing
4.3.2. MTT Cytotoxicity Assay
4.3.3. Immunofluorescence
4.4. Computational Aspects
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Quesada, S.; Bini, M.; Lebreton, C.; Ray-Coquard, I. Update on New Treatments for Rare Ovarian Tumours. Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2023, 35, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, X.; Zhou, D.; Lu, J.; Qin, D.; Zhou, J.; Liu, H.J. Cancer Nanomedicine in Preoperative Therapeutics: Nanotechnology-Enabled Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy, Radiotherapy, Immunotherapy, and Phototherapy. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 24, 136–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tymon-Rosario, J.; Gorman, M.; Richardson, D.L.; Washington, C.; Santin, A.D. Advances in Antibody-Drug Conjugates for Gynecologic Malignancies. Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2023, 35, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.H.; Chen, R.J.; Chiu, H.W.; Yang, L.X.; Wang, Y.L.; Chen, Y.Y.; Yeh, Y.L.; Liao, M.Y.; Wang, Y.J. Nanoparticles Augment the Therapeutic Window of RT and Immunotherapy for Treating Cancers: Pivotal Role of Autophagy. Theranostics 2023, 13, 40–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Li, M.; Wu, L.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Gao, J.; Lu, Z. Progress in the Application of Hydrogels in Immunotherapy of Gastrointestinal Tumors. Drug Deliv. 2023, 30, 2161670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhai, B.Z.; Wu, Y.J.; Wang, Y. Recent Progress in the Development of Nanomaterials Targeting Multiple Cancer Metabolic Pathways: A Review of Mechanistic Approaches for Cancer Treatment. Drug Deliv. 2023, 30, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawash, M. Highlights on Specific Biological Targets; Cyclin-Dependent Kinases, Epidermal Growth Factor Receptors, Ras Protein, and Cancer Stem Cells in Anticancer Drug Development. Drug Res. 2019, 69, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, D.; Duijf, P.H.G.; Khanna, K.K. Mitotic Slippage: An Old Tale with a New Twist. Cell Cycle 2019, 18, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borys, F.; Joachimiak, E.; Krawczyk, H.; Fabczak, H. Intrinsic and Extrinsic Factors Affecting Microtubule Dynamics in Normal and Cancer Cells. Molecules 2020, 25, 3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, M.O.; Prota, A.E. Microtubule-Targeting Agents: Strategies to Hijack the Cytoskeleton. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 776–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreca, M.; Spanò, V.; Rocca, R.; Bivacqua, R.; Abel, A.C.; Maruca, A.; Montalbano, A.; Raimondi, M.V.; Tarantelli, C.; Gaudio, E.; et al. Development of [1,2]Oxazoloisoindoles Tubulin Polymerization Inhibitors: Further Chemical Modifications and Potential Therapeutic Effects against Lymphomas. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 243, 114744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Ren, Y.; Deng, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Luo, M.; Liu, S.; Chen, J. Design, Synthesis, and Bioevaluation of Pyrazolo [1,5-a]Pyrimidine Derivatives as Tubulin Polymerization Inhibitors Targeting the Colchicine Binding Site with Potent Anticancer Activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 202, 112519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.N.; Wang, J.J.; Ji, Y.T.; Zhao, G.D.; Tang, L.Q.; Zhang, C.M.; Guo, X.L.; Liu, Z.P. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of 1-Methyl-1,4-Dihydroindeno[1,2-c]Pyrazole Analogues as Potential Anticancer Agents Targeting Tubulin Colchicine Binding Site. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 5341–5355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreca, M.; Spanò, V.; Raimondi, M.V.; Tarantelli, C.; Spriano, F.; Bertoni, F.; Barraja, P.; Montalbano, A. Recurrence of the Oxazole Motif in Tubulin Colchicine Site Inhibitors with Anti-Tumor Activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. Rep. 2021, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadizadeh, F.; Ghodsi, R.; Mirzaei, S.; Sahebkar, A. In Silico Exploration of Novel Tubulin Inhibitors: A Combination of Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulations, Pharmacophore Modeling, and Virtual Screening. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2022, 2022, 4004068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labbozzetta, M.; Barreca, M.; Spanò, V.; Raimondi, M.V.; Poma, P.; Notarbartolo, M.; Barraja, P.; Montalbano, A. Novel Insights on [1,2]Oxazolo[5,4-e]Isoindoles on Multidrug Resistant Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cell Line. Drug Dev. Res. 2022, 83, 1331–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhyani, P.; Quispe, C.; Sharma, E.; Bahukhandi, A.; Sati, P.; Attri, D.C.; Szopa, A.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Docea, A.O.; Mardare, I.; et al. Anticancer Potential of Alkaloids: A Key Emphasis to Colchicine, Vinblastine, Vincristine, Vindesine, Vinorelbine and Vincamine. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawash, M. Recent Advances of Tubulin Inhibitors Targeting the Colchicine Binding Site for Cancer Therapy. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnst, K.E.; Banerjee, S.; Chen, H.; Deng, S.; Hwang, D.J.; Li, W.; Miller, D.D. Current Advances of Tubulin Inhibitors as Dual Acting Small Molecules for Cancer Therapy. Med. Res. Rev. 2019, 39, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemann, D.W.; Chaplin, D.J.; Horsman, M.R. Realizing the Potential of Vascular Targeted Therapy: The Rationale for Combining Vascular Disrupting Agents and Anti-Angiogenic Agents to Treat Cancer. Cancer Investig. 2017, 35, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatoprak, G.Ş.; Akkol, E.K.; Genç, Y.; Bardakci, H.; Yücel, Ç.; Sobarzo-Sánchez, E. Combretastatins: An Overview of Structure, Probable Mechanisms of Action and Potential Applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varsha, K.; Sharma, A.; Kaur, A.; Madan, J.; Pandey, R.S.; Jain, U.K.; Chandra, R. Nanostructures Cancer Therapy; Elsevier Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 775–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czop, M.; Bogucka-Kocka, A.; Kubrak, T.; Knap-Czop, K.; Makuch-Kocka, A.; Galkowski, D.; Wawer, J.; Kocki, T.; Kocki, J. Imaging Flow Cytometric Analysis of Stilbene-Dependent Apoptosis in Drug Resistant Human Leukemic Cell Lines. Molecules 2019, 24, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.Y.; Im, E.; Kim, N.D.; Baldi, A.; Jang, J.Y.; Kim, N.D. Mechanism of Resveratrol-Induced Programmed Cell Death and New Drug Discovery against Cancer: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grisham, R.; Ky, B.; Tewari, K.S.; Chaplin, D.J.; Walker, J. Clinical Trial Experience with CA4P Anticancer Therapy: Focus on Efficacy, Cardiovascular Adverse Events, and Hypertension Management. Gynecol. Oncol. Res. Pract. 2018, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chillemi, R.; Cardullo, N.; Greco, V.; Malfa, G.; Tomasello, B.; Sciuto, S. Synthesis of Amphiphilic Resveratrol Lipoconjugates and Evaluation of Their Anticancer Activity towards Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cell Line. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 96, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau, L.; Soucek, R.; Pujol, M.D. Resveratrol Derivatives: Synthesis and Their Biological Activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 246, 114962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondratyuk, T.P.; Park, E.J.; Marler, L.E.; Ahn, S.; Yuan, Y.; Choi, Y.; Yu, R.; van Breemen, R.B.; Sun, B.; Hoshino, J.; et al. Resveratrol Derivatives as Promising Chemopreventive Agents with Improved Potency and Selectivity. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 1249–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, V.L.; Toseef, T.; Nazumudeen, F.B.; Rivoira, C.; Spatafora, C.; Tringali, C.; Rotenberg, S.A. Anti-Tumor Properties of Cis-Resveratrol Methylated Analogues in Metastatic Mouse Melanoma Cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 402, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockdale, D.P.; Beutler, J.A.; Wiemer, D.F. Substitution of a Triazole for the Central Olefin in Biologically Active Stilbenes. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 75, 128980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torijano-Gutiérrez, S.; Díaz-Oltra, S.; Falomir, E.; Murga, J.; Carda, M.; Marco, J.A. Synthesis of Combretastatin A-4 O-Alkyl Derivatives and Evaluation of Their Cytotoxic, Antiangiogenic and Antitelomerase Activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 7267–7274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobylka, P.; Kucinska, M.; Kujawski, J.; Lazewski, D.; Wierzchowski, M.; Murias, M. Resveratrol Analogues as Selective Estrogen Signaling Pathway Modulators: Structure-Activity Relationship. Molecules 2022, 27, 6973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koolaji, N.; Abu-Mellal, A.; Tran, V.H.; Duke, R.K.; Duke, C.C. Synthesis of C- and O-Prenylated Tetrahydroxystilbenes and O-Prenylated Cinnamates and Their Action towards Cancer Cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 63, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí-Centelles, R.; Cejudo-Marín, R.; Falomir, E.; Murga, J.; Carda, M.; Alberto Marco, J. Inhibition of VEGF Expression in Cancer Cells and Endothelial Cell Differentiation by Synthetic Stilbene Derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 3010–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plyutinskaya, A.D.; Nemtsova, E.R.; Pankratov, A.A.; Shegai, P.V.; Krylov, S.S.; Iskandarova, V.N.; Maksimenko, A.S.; Demchuk, D.V.; Kuptsova, T.S.; Semenova, M.N.; et al. Cytostatic Activity of Combretastatin A-4 Derivatives in an In Vitro System. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2023, 174, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoni, D.; Romagnoli, R.; Baruchello, R.; Rondanin, R.; Rizzi, M.; Pavani, M.G.; Alloatti, D.; Giannini, G.; Marcellini, M.; Riccioni, T.; et al. Novel Combretastatin Analogues Endowed with Antitumor Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 3143–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousuf, M.; Jinka, S.; Adhikari, S.S.; Banerjee, R. Methoxy-Enriched Cationic Stilbenes as Anticancer Therapeutics. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 98, 103719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska-Przyjemska, M.; Kaczmarek, M.; Krajka-Kuźniak, V.; Wierzchowski, M.; Baer-Dubowska, W. Effect of Methoxy Stilbenes-Analogs of Resveratrol-on the Viability and Induction of Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Human Myeloid Leukemia Cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 474, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbicz, D.; Tobiasz, P.; Borys, F.; Pilżys, T.; Marcinkowski, M.; Poterała, M.; Grzesiuk, E.; Krawczyk, H. The Stilbene and Dibenzo[b,f]Oxepine Derivatives as Anticancer Compounds. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 123, 109781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbicz, D.; Mielecki, D.; Wrzesinski, M.; Pilzys, T.; Marcinkowski, M.; Piwowarski, J.; Debski, J.; Palak, E.; Szczecinski, P.; Krawczyk, H.; et al. Evaluation of Anti-Cancer Activity of Stilbene and Methoxydibenzo[b,f] Oxepin Derivatives. Curr. Cancer. Drug Targets 2018, 18, 706–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanthou, C.; Greco, O.; Stratford, A.; Cook, I.; Knight, R.; Benzakour, O.; Tozer, G. The Tubulin-Binding Agent Combretastatin A-4-Phosphate Arrests Endothelial Cells in Mitosis and Induces Mitotic Cell Death. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 165, 1401–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cenciarelli, C.; Tanzarella, C.; Vitale, I.; Pisano, C.; Crateri, P.; Meschini, S.; Arancia, G.; Antoccia, A. The Tubulin-Depolymerising Agent Combretastatin-4 Induces Ectopic Aster Assembly and Mitotic Catastrophe in Lung Cancer Cells H460. Apoptosis 2008, 13, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.Y.; He, Q.R.; Wang, Y.L.; Wang, H.R.; Jiang, T.C.; Tang, J.J.; Gao, J.M. Exploring Diverse-Ring Analogues on Combretastatin A4 (CA-4) Olefin as Microtubule-Targeting Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghizadeh, M.S.; Niazi, A.; Moghadam, A.; Afsharifar, A. Experimental, Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamic Studies of Natural Products Targeting Overexpressed Receptors in Breast Cancer. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0267961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, R.; Chacko, S.; Bose, P.; Lapenna, A.; Pattanayak, S.P. Structure Based Multitargeted Molecular Docking Analysis of Selected Furanocoumarins against Breast Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoddard, B.L.; Koshland, D.E. Molecular Recognition Analyzed by Docking Simulations: The Aspartate Receptor and Isocitrate Dehydrogenase from Escherichia Coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 1146–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooijmans, N.; Kuntz, I.D. Molecular Recognition and Docking Algorithms. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2003, 32, 335–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, G.R.; Singh, S.B.; Niven, M.L.; Hamel, E.; Schmidt, J.M. Isolation, structure, and synthesis of combretastatins A-1 and B-1, potent new inhibitors of microtubule assembly, derived from Combretum caffrum. J. Nat. Prod. 1987, 50, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubowska, J.; Mikuła-Pietrasik, J.; Ksiązek, K.; Krawczyk, H. Cytotoxicity Studies of Novel Combretastatin and Pterostilbene Derivatives. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 320895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Tamura, T.; Nakamura, R.; Hosoe, S.; Matsubara, M.; Nagata, K.; Kodaira, H.; Uemori, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Suzuki, M.; et al. Development of a Novel Class of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor (PPAR) Gamma Ligands as an Anticancer Agent with a Unique Binding Mode Based on a Non-Thiazolidinedione Scaffold. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 115122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taweesak, P.; Thongaram, P.; Kraikruan, P.; Thanetchaiyakup, A.; Chuanopparat, N.; Hsieh, H.P.; Uang, B.J.; Ngernmeesri, P. One-Pot Synthesis of Dibenzo[b,f]Oxepines and Total Synthesis of Bauhinoxepin C. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 1955–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidachary, G.; Veera Prasad, K.; Divya, D.; Singh, A.; Ramesh, U.; Sridhar, B.; China Raju, B. Convenient One-Pot Synthesis, Anti-Mycobacterial and Anticancer Activities of Novel Benzoxepinoisoxazolones and Pyrazolones. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 76, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Montgomery, J.A., Jr.; Vreven, T.; Kudin, K.N.; Burant, J.C.; et al. Gaussian 03, Revision E.01. Available online: https://gaussian.com/g03citation/ (accessed on 14 April 2023).
- Tomasi, J.; Mennucci, B.; Cammi, R. Quantum Mechanical Continuum Solvation Models. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 2999–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorléans, A.; Gigant, B.; Ravelli, R.B.; Mailliet, P.; Mikol, V.; Knossow, M. Variations in the colchicine-binding domain provide insight into the structural switch of tubulin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13775–13779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martino, G.; Edler, M.C.; La Regina, G.; Coluccia, A.; Barbera, M.C.; Barrow, D.; Nicholson, R.I.; Chiosis, G.; Brancale, A.; Hamel, E.; et al. New arylthioindoles: Potent Inhibitors of tubulin polymerization. 2. Structure—Activity relationships and molecular modeling studies. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massarotti, A.; Coluccia, A.; Silvestri, R.; Sorba, G.; Brancale, A. The tubulin colchicine domain: A molecular modeling perspective. ChemMedChem 2012, 7, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravelli, R.B.G.; Gigant, B.; Curmi, P.A.; Jourdain, I.; Lachkar, S.; Sobel, A.; Knossow, M. Insight into tubulin regulation from a complex with colchicine and a stathmin-like domain. Nature 2004, 428, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handoko, S.D.; Ouyang, X.; Su, C.T.T.; Kwoh, C.K.; Ong, Y.S. QuickVina: Accelerating AutoDock Vina Using Gradient-Based Heuristics for Global Optimization. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2012, 9, 1266–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hachem, N.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Khalil, A.; Kobeissy, F.H.; Nemer, G. AutoDock and AutoDockTools for Protein-Ligand Docking: Beta-Site Amyloid Precursor Protein Cleaving Enzyme 1(BACE1) as a Case Study. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1598, 391–403. [Google Scholar]
- The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System; Version 1.3; Schrödinger LLC.: Bengaluru, India, 2010.
- Salentin, S.; Schreiber, S.; Haupt, V.J.; Adasme, M.F.; Schroeder, M. PLIP: Fully Automated Protein-Ligand Interaction Profiler. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W443–W447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Compound | HEK293 | HDF-A | HCT116 | SI1 | SI2 | MCF-7 | SI3 | SI4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 (μM) | IC50 (μM) | IC50 (μM) | IC50 (μM) | |||||
| 1a | 18 ± 1 | 38 ± 1 | 23 ± 1 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 36 ± 2 | 0.5 | 1.1 |
| 1c | 34 ± 4 | 40 ± 4 | 38 ± 5 | 0.9 | 1.1 | 43 ± 2 | 0.7 | 1.0 |
| 1d | 33 ± 2 | 40 ± 2 | 18 ± 3 | 1.8 | 2.2 | 47 ± 1 | 0.7 | 0.9 |
| 1i | 54 ± 2 | 41 ± 2 | 52 ± 2 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 69 ± 3 | 0.8 | 0.6 |
| 2i | 88 ± 5 | 93 ± 7 | 55 ± 4 | 1.6 | 1.7 | 67 ± 6 | 1.2 | 1.4 |
| 2j | 85 ± 4 | ND | 53 ± 3 | 1.6 | ND | 36 ± 3 | 2.4 | ND |
| 3h | 48 ± 3 | 127 * | 66 ± 2 | 0.7 | 1.9 * | ND | ND | ND |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borys, F.; Tobiasz, P.; Poterała, M.; Fabczak, H.; Krawczyk, H.; Joachimiak, E. Systematic Studies on Anti-Cancer Evaluation of Stilbene and Dibenzo[b,f]oxepine Derivatives. Molecules 2023, 28, 3558. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083558
Borys F, Tobiasz P, Poterała M, Fabczak H, Krawczyk H, Joachimiak E. Systematic Studies on Anti-Cancer Evaluation of Stilbene and Dibenzo[b,f]oxepine Derivatives. Molecules. 2023; 28(8):3558. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083558
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorys, Filip, Piotr Tobiasz, Marcin Poterała, Hanna Fabczak, Hanna Krawczyk, and Ewa Joachimiak. 2023. "Systematic Studies on Anti-Cancer Evaluation of Stilbene and Dibenzo[b,f]oxepine Derivatives" Molecules 28, no. 8: 3558. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083558
APA StyleBorys, F., Tobiasz, P., Poterała, M., Fabczak, H., Krawczyk, H., & Joachimiak, E. (2023). Systematic Studies on Anti-Cancer Evaluation of Stilbene and Dibenzo[b,f]oxepine Derivatives. Molecules, 28(8), 3558. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083558







