High-Entropy Spinel Ferrites with Broadband Wave Absorption Synthesized by Simple Solid-Phase Reaction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
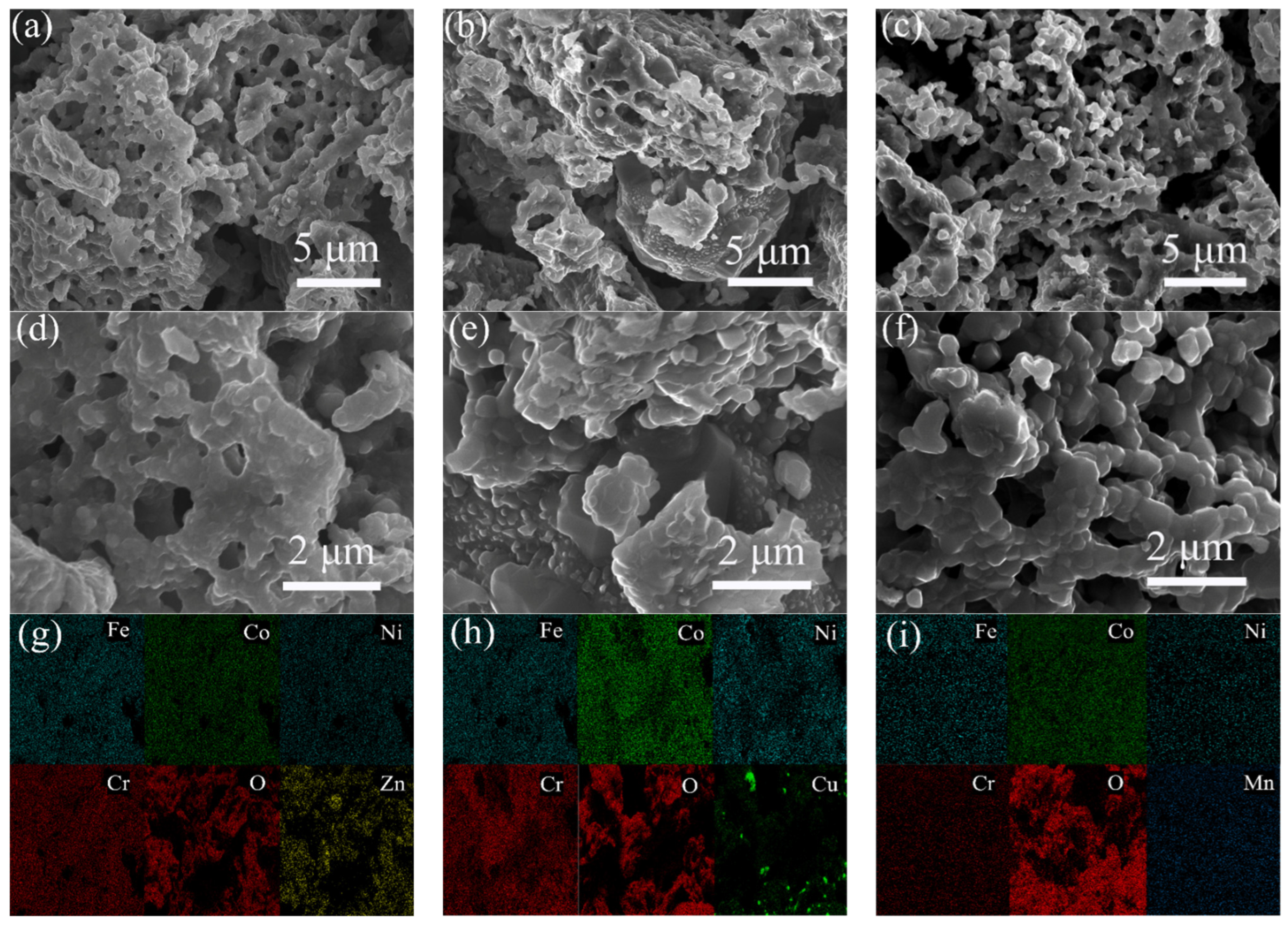
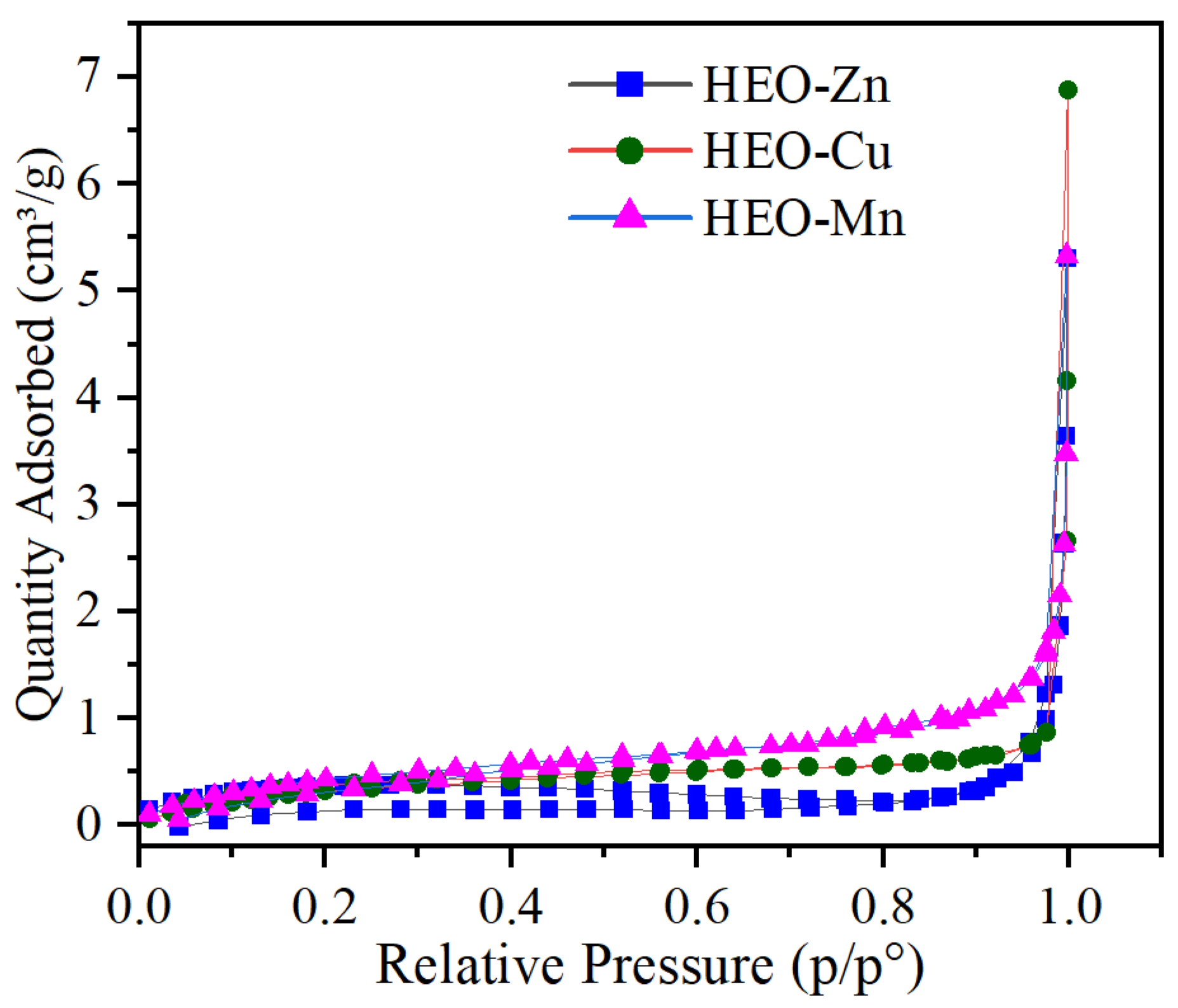
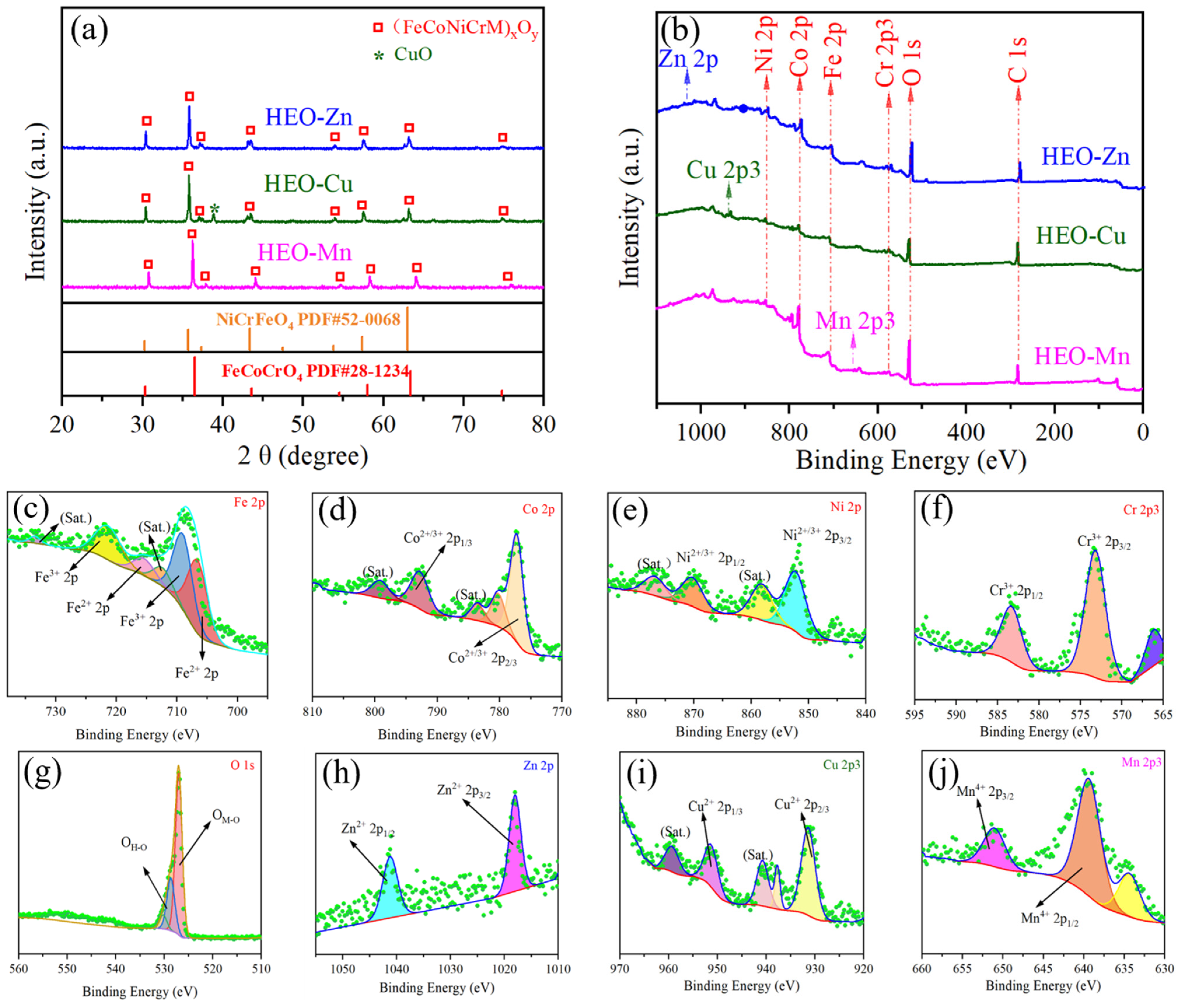
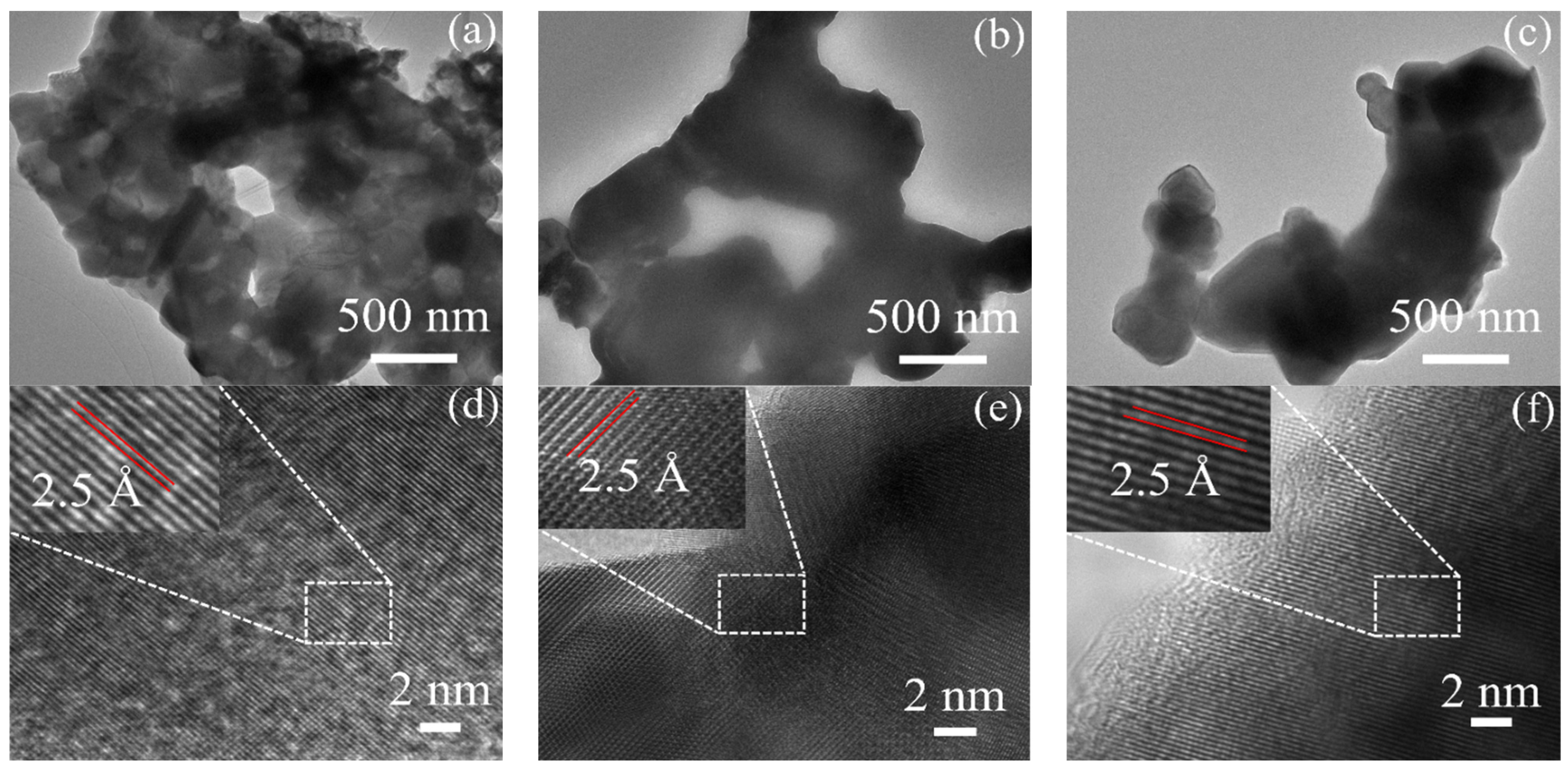
2.1. Structural Characterization
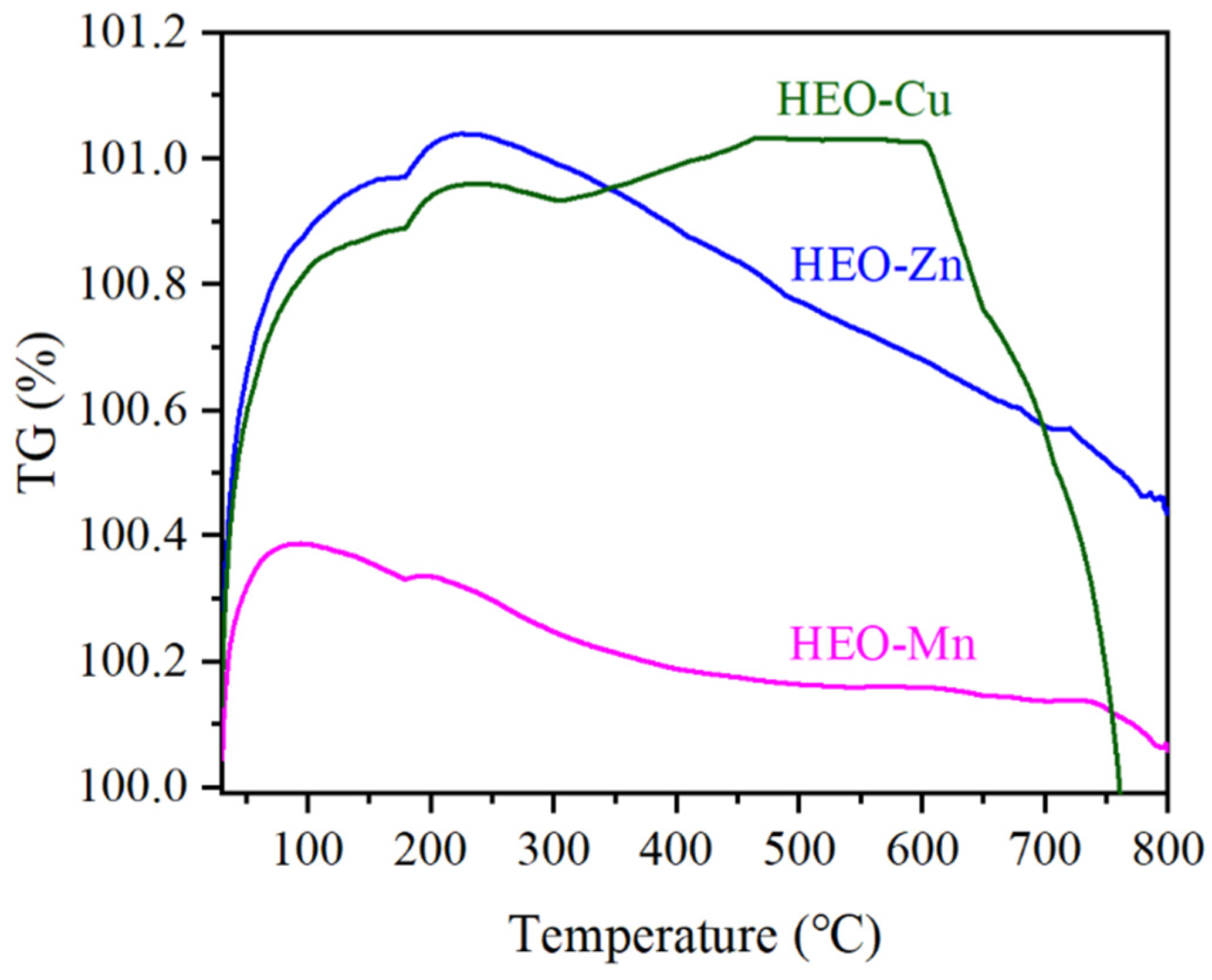
2.2. Physical Properties
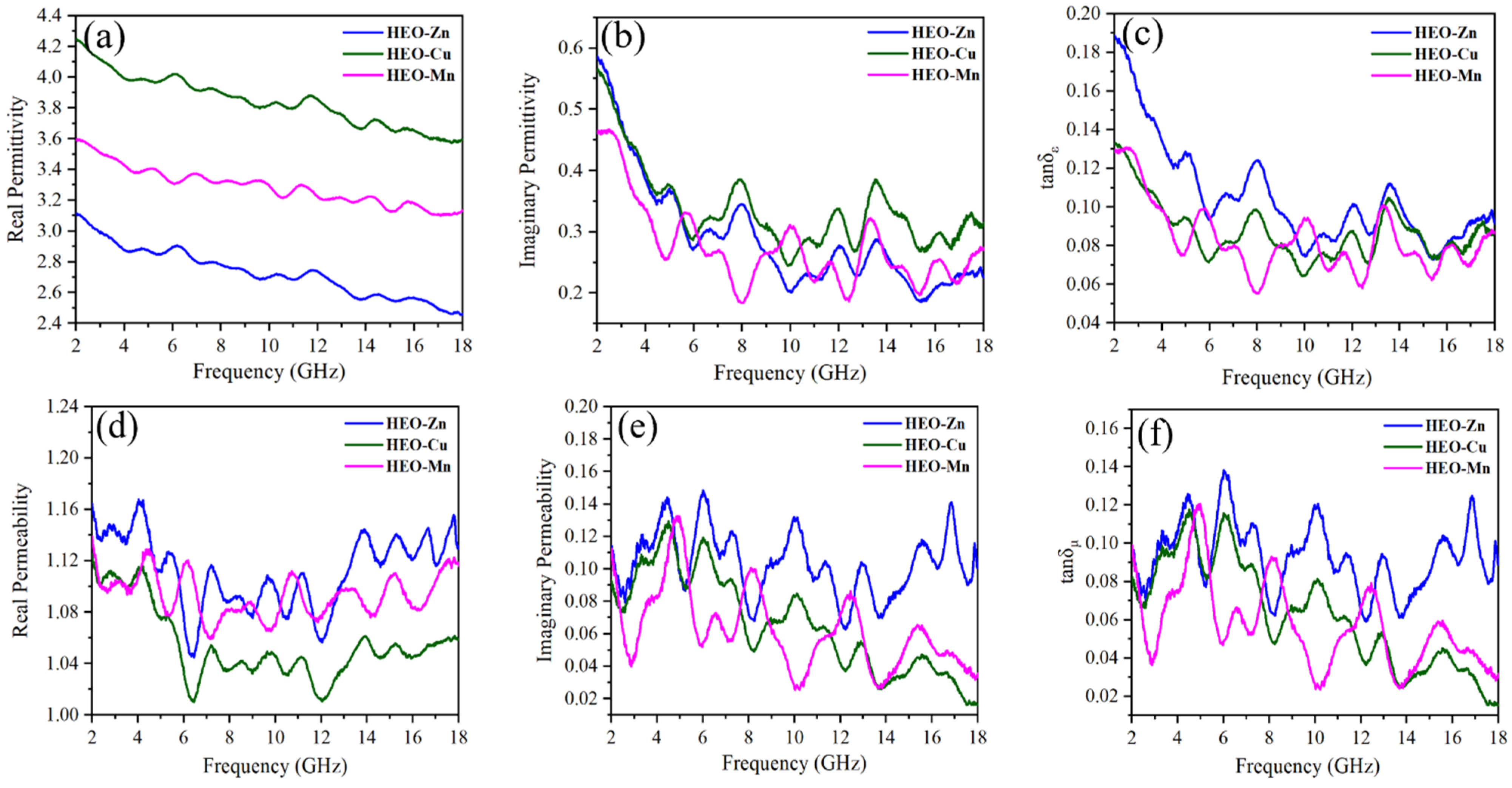
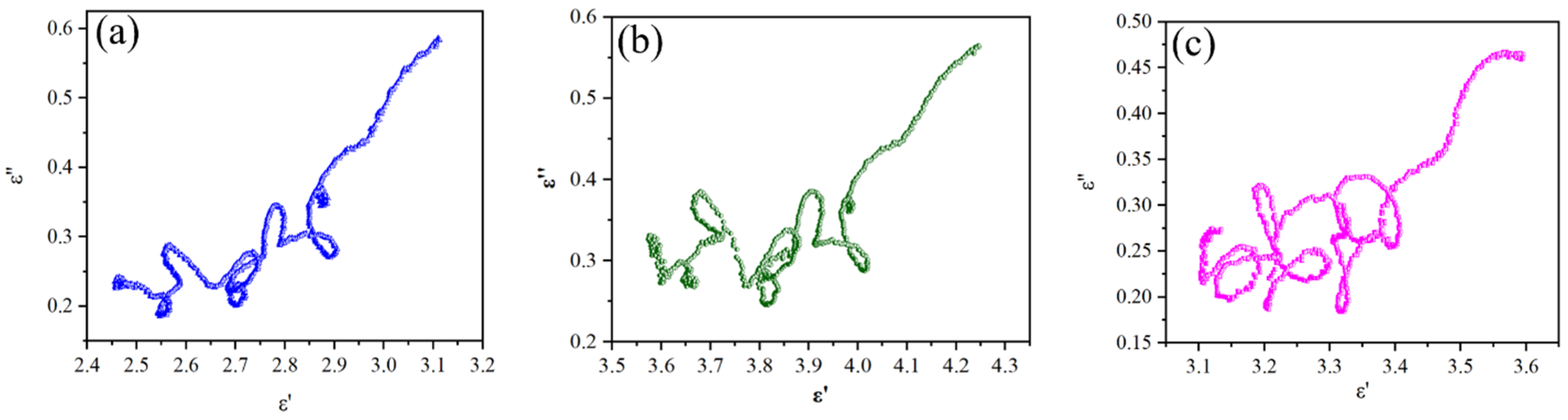
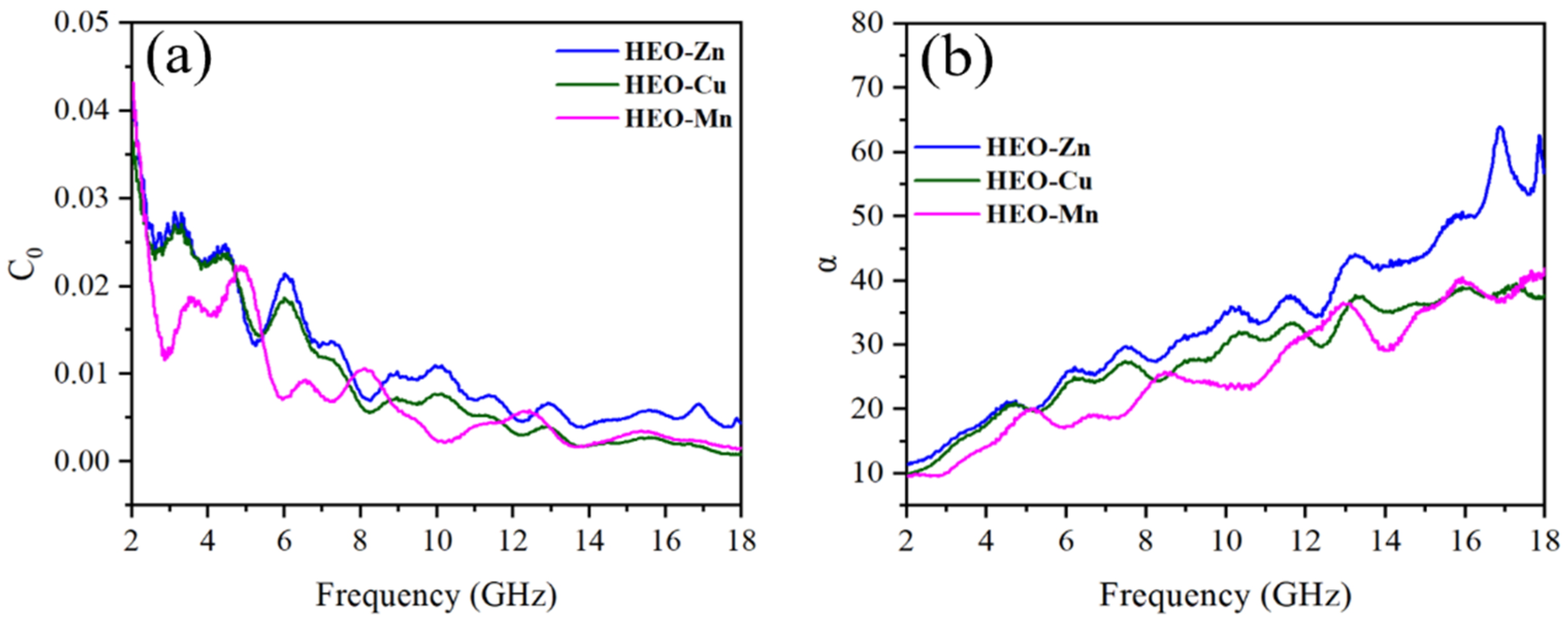
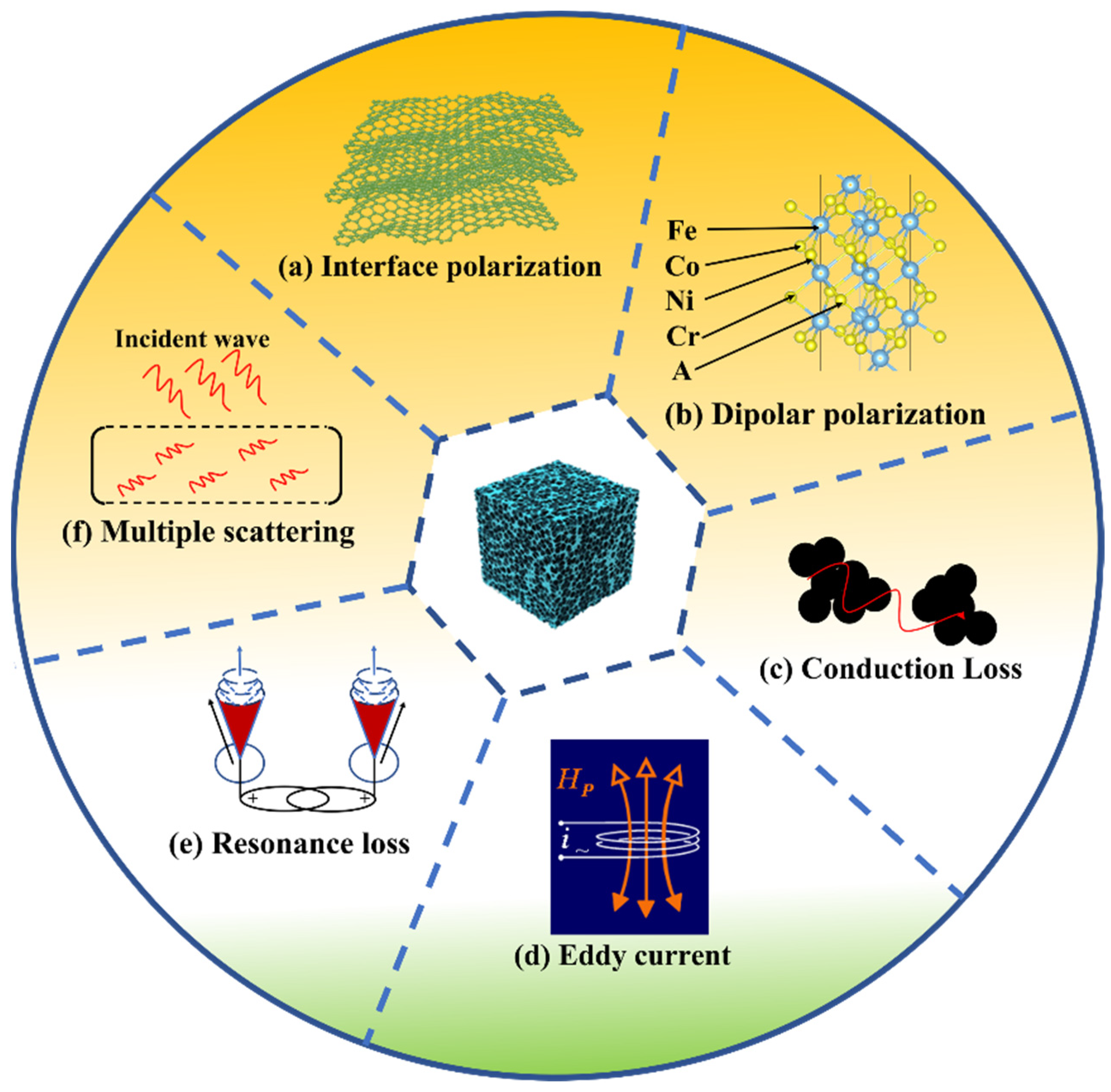
2.3. Wave Absorption Properties and Mechanism
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Raw Materials and Reagents
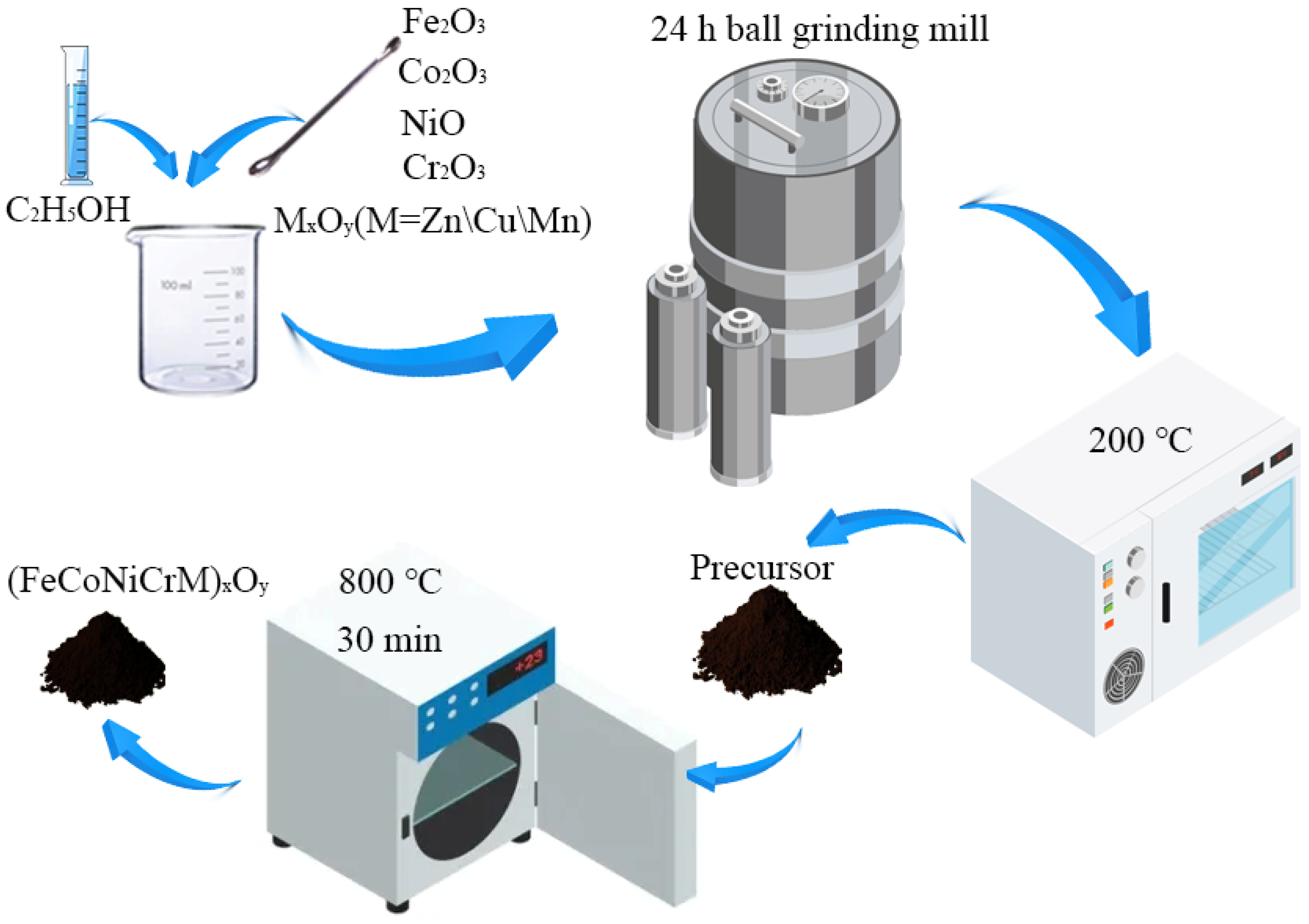
3.2. Preparation Process
3.3. Characterization
3.4. EM Parameter Measurement
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Kallumottakkal, M.; Hussein, M.I.; Iqbal, M.Z. Recent Progress of 2D Nanomaterials for Application on Microwave Absorption: A Comprehensive Study. Front. Mater. 2021, 8, 633079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudha, J.; Sivakala, S.; Patel, K.; Nair, P.R. Development of electromagnetic shielding materials from the conductive blends of polystyrene polyaniline-clay nanocomposite. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 1647–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Tan, G.; Gu, X.; Man, Q.; Li, F.; Chang, C.; Wang, X.; Li, R.-W. Microwave absorbing properties of FeCrMoNiPBCSi amorphous powders composite. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 705, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-S.; Mukhtar, A.; Wu, K.-M.; Gu, L.; Cao, X. Multi-Segmented Nanowires: A High Tech Bright Future. Materials 2019, 12, 3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhang, X.; Yi, Z.; Tang, J.; Yang, P.; Cai, R.; Yi, S.; Rao, J.; Zhang, Y. Core-Shell Structured SiO2@NiFe LDH Composite for Broadband Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhuo, Z.; Wei, L.; Ma, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, H. Altered Temporal Organization of Brief Spontaneous Brain Activities in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuroscience 2020, 425, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Gao, S.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; He, W.; Huang, W.; Luo, J. Carbon nanocages with N-doped carbon inner shell and Co/N-doped carbon outer shell as electromagnetic wave absorption materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 381, 122653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, M.; Yang, Q.; Li, H.; Xu, H.; Chai, Z.; Chen, K.; Liu, Z.; Tang, Z.; Ma, L.; et al. Phase Transition Induced Unusual Electrochemical Performance of V2CTX MXene for Aqueous Zinc Hybrid-Ion Battery. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Jian, X.; Zhang, L.; Mu, C.; Yin, L.; Xie, J.; Mahmood, N.; Dou, S.; Che, R.; Deng, L. Plasma-induced FeSiAl@Al2O3@SiO2 core–shell structure for exceptional microwave absorption and anti-oxidation at high temperature. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 384, 123371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Yao, Z.; Ng, V.M.H.; Zhou, J.; Kong, L.B.; Yue, K. Facile synthesis of ultrasmall Fe3O4 nanoparticles on MXenes for high microwave absorption performance. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 115, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.-J.; Wang, Z.-Q.; Jiang, J.-T.; Gong, Y.-X.; Yao, Y.-T.; Zhen, L. Flaky FeSi particles with tunable size, morphology and microstructure developing for high-efficiency and broadband absorbing materials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2021, 527, 167800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Gu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, J.; Pei, C.; Fan, F.; Ji, G. The enhanced microwave broadband absorbing ability of carbon microspheres via electromagnetic simulating honeycomb design. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 32, 25809–25819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, B.B.; Ni, Q. A broadband and tunable microwave absorption technology enabled by VGCFs/PDMS-EP shape memory composites. Compos. Struct. 2020, 238, 111954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Mukhtar, A.; Humayun, M.; Wu, K.; Du, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y. A Critical Review on Nanowire-Motors: Design, Mechanism and Applications. Chem. Rec. 2022, 22, e202200016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, D.; Dong, L.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, P.; Yi, S.; Dai, X.; Yin, C.; Du, Z.; et al. Microwave Absorption of α-Fe2O3@diatomite Composites. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Yang, H.-J.; Hou, Z.-L.; Song, W.-L.; Xu, H.; Kang, Y.-Q.; Jin, H.-B.; Fang, X.-Y.; Cao, M.-S. Ni-decorated SiC powders: Enhanced high-temperature dielectric properties and microwave absorption performance. Powder Technol. 2013, 237, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Song, W.-L.; Fang, X.-Y.; Shi, X.-L.; Hou, Z.-L.; Cao, M.-S. Tetra-needle zinc oxide/silica composites: High-temperature dielectric properties at X-band. Solid State Commun. 2013, 154, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Huyan, W.; Yang, F.; Yao, J.; Tan, R.; Chen, P.; Tao, X.; Yao, Z.; Zhou, J.; Liu, P. Achieving Ultra-Wideband and Elevated Temperature Electromagnetic Wave Absorption via Constructing Lightweight Porous Rigid Structure. Nano-Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunasfi; Mulyawan, A.; Mashadi; Suyanti; Adi, W.A. Synthesis of NiCexFe2-xO4 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.05) as Microwave Absorbing Materials via Solid-State Reaction Method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2021, 532, 167985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhao, B.; Xiang, H.; Dai, F.-Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, Y. High-entropy spinel ferrites MFe2O4 (M = Mg, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn)with tunable electromagnetic properties and strong microwave absorption. J. Adv. Ceram. 2022, 11, 754–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Ni, C.; Sun, X.; Du, W. Spinel structured MFe2O4 (M = Fe, Co, Ni, Mn, Zn) and their composites for microwave absorption: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 428, 131160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houbi, A.; Aldashevich, Z.A.; Atassi, Y.; Telmanovna, Z.B.; Saule, M.; Kubanych, K. Microwave absorbing properties of ferrites and their composites: A review. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2021, 529, 167839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.; Chen, C.; Tai, H.; Tang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, G.; Wan, X. Structural characterization and microwave absorbing performance of CuFe2O4/RGO composites. J. Solid State Chem. 2021, 297, 122051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.; Chen, C.; Tai, H.; Tang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, G.; Wan, X. The effect of Co2+, Cu2+ element ratio on the microwave absorption properties of Co2Cu1-xFe2O4/RGO composites. Mater. Lett. 2021, 289, 129423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Yao, Z.; Zhou, J.; Yang, Z.; Kong, L.B. Small magnetic Co-doped NiZn ferrite/graphene nanocomposites and their dual-region microwave absorption performance. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 9738–9749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Lv, Y.; Chen, X.; Wu, Z.; Wang, S.; Zou, Y. Synthesis and electromagnetic wave absorption performance of NiCo2O4 nanomaterials with different nanostructures. Crystengcomm 2019, 21, 4568–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Chen, G.L. Solid solution alloys of AlCoCrFeNiTix with excellent room-temperature mechanical properties. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 181904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, F.; Wu, L.; Zhao, H.; Sui, S.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, J.; He, W.; He, P.; Xu, B. Microstructure and high-temperature wear mechanism of laser cladded CoCrBFeNiSi high-entropy alloy amorphous coating. Mater. Lett. 2018, 211, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Zheng, H.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Fang, B. Ligand-free synthesis of noble metal nanocatalysts for electrocatalysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, W.; Zhou, H.; Fang, F.; Zhou, X.; Xie, Z.; Jiang, J. Microstructure and properties of novel CoCrFeNiTax eutectic high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 735, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Wang, H.; Chen, M.; Baker, I.; Yeh, J.; Liu, C.; Nieh, T. An assessment on the future development of high-entropy alloys: Summary from a recent workshop. Intermetallics 2015, 66, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shang, S.; Zhang, W. Synthesis and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of FeCoNi(Si0.6Al0.2B0.2) high-entropy nanocrystalline alloy powders. AIP Adv. 2019, 9, 125045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, A.; Xie, H.-X.; Xiang, H.-Z.; Zhang, Z.-G.; Zhang, H.; Ran, S. A novel six-component spinel-structure high-entropy oxide with ferrimagnetic property. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 503, 166594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Gopalan, S.; Pal, U.B.; Basu, S.N. Cu1.3Mn1.7O4 spinel coatings deposited by electrophoretic deposition on Crofer 22 APU substrates for solid oxide fuel cell applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 323, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talic, B.; Molin, S.; Wiik, K.; Hendriksen, P.V.; Lein, H.L. Comparison of iron and copper doped manganese cobalt spinel oxides as protective coatings for solid oxide fuel cell interconnects. J. Power Sources 2017, 372, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, X.; Bi, L. A high-entropy spinel ceramic oxide as the cathode for proton-conducting solid oxide fuel cells. J. Adv. Ceram. 2022, 11, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadabadi, F.H.; Masoudpanah, S.; Alamolhoda, S.; Koohdar, H. Electromagnetic microwave absorption properties of high entropy spinel ferrite ((MnNiCuZn)1-xCoxFe2O4)/graphene nanocomposites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, B.; Liu, X.; Xu, B.; Bi, L.; Wu, G. Electromagnetic wave absorption performance of NiCo2X4 (X = O, S, Se, Te) spinel structures. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 129907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Wang, M.; Yang, Z.; Qiu, H.; Padhiar, M.A.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Dang, J.; Gaponenko, N.V.; Bhatti, A.S. Trioctylphosphine-Assisted Pre-protection Low-Temperature Solvothermal Synthesis of Highly Stable CsPbBr3/TiO2 Nanocomposites. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 3786–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, S.; Yao, Y.; Han, X.; Chai, C.; Ma, H. Flower-like CoLa/Ti3C2Tx nanocomposites for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 929, 167326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Kan, A.; Ogawa, H. Microwave dielectric properties and crystal structures of spinel-structured MgAl2O4 ceramics synthesized by a molten-salt method. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 37, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yin, X.; Song, C.; Han, M.; Xu, H.; Duan, W.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, L. Self-Assembly Core-Shell Graphene-Bridged Hollow MXenes Spheres 3D Foam with Ultrahigh Specific EM Absorption Performance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1803938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-H.; Pan, S.-K.; Cheng, L.-C.; Yu, J.-J.; Huang, L. Effect of Misch-metal content on microwave absorption property of Ce2Co17 alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 11204–11210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Dong, J.; Fang, X.; Zheng, W.; Sun, Y.; Qian, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, Y. Ti3C2Tx MXene/polyaniline (PANI) sandwich intercalation structure composites constructed for microwave absorption. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 169, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Wei, H.; Dong, J.; Du, Y.; Fang, X.; Zheng, W.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, Z. Fabrication of urchin-like ZnO-MXene nanocomposites for high-performance electromagnetic absorption. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 10757–10762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, Y.; Zhou, W.; Luo, F.; Zhu, D. Titanium carbide (MXene) nanosheets as promising microwave absorbers. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 16412–16416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, K.M.; Sampath, S. Two-step oxygen reduction on spinel NiFe2O4 catalyst: Rechargeable, aqueous solution- and gel-based, Zn-air batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 292, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, A.; He, S.; Qin, N.; Chen, R.; Bao, D. Ce-doping induced enhancement of resistive switching performance of Pt/NiFe2O4/Pt memory devices. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, S481–S487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adi, W.A.; Yunasfi. Magnetic properties and microwave absorption characteristic of MWNT filled with magnetite coated iron nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2020, 262, 114760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, T. MOF–derived 1 D a-Fe2O3/NiFe2O4 heterojunction as efficient sensing materials of acetone vapors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 281, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupane, D.; Ghimire, M.; Adhikari, H.; Lisfi, A.; Mishra, S.R. Synthesis and magnetic study of magnetically hard-soft SrFe12-yAlyO19-x Wt.% Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 nanocomposites. AIP Adv. 2017, 7, 055602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenivasulu, N.; Kumar, U.N.; Madhav, K.M.V.V.; Thomas, T.; Bhattacharya, S.S. Structural and Electrochemical Investigations on Nanocrystalline High Entropy Spinel Oxides for Battery-Like Supercapacitor Applications. Chemistryselect 2022, 7, e202104015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alijani, H.Q.; Iravani, S.; Pourseyedi, S.; Torkzadeh-Mahani, M.; Barani, M.; Khatami, M. Biosynthesis of spinel nickel ferrite nanowhiskers and their biomedical applications. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Xiao, K.; Ouyang, T.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, N.; Liu, Z.-Q. Co-Cr mixed spinel oxide nanodots anchored on nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes as catalytic electrode for hydrogen peroxide sensing. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 585, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadabadi, F.H.; Masoudpanah, S.; Alamolhoda, S.; Koohdar, H. High-performance microwave absorbers based on (CoNiCuZn)1–xMnxFe2O4 spinel ferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 909, 164637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, G.; Gangwar, D.; Tripathi, H.; Aquilanti, G.; Rath, C. Crystal structure, local structure and magnetic properties of NiCr2-xFexO4 (x = 0.3–0.6) spinel. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 271, 124861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugesan, C.; Ugendar, K.; Okrasa, L.; Shen, J.; Chandrasekaran, G. Zinc substitution effect on the structural, spectroscopic and electrical properties of nanocrystalline MnFe2O4 spinel ferrite. Ceram. Int. 2020, 47, 1672–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.K.; Dhaliwal, A.; Kahlon, K. Effect of external magnetic field on attenuation coefficient for magnetic substances. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2015, 95, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Wang, B.; Ma, M.; Feng, A.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, Z.; Tan, G.; Cao, H.; Wu, G. Preparation of two-dimensional titanium carbide (Ti3C2Tx) and NiCo2O4 composites to achieve excellent microwave absorption properties. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 180, 107577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Wang, Z.; Yan, M.; Bi, H. Enhanced interfacial polarization relaxation effect on microwave absorption properties of submicron-sized hollow Fe3O4hemispheres. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2014, 47, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
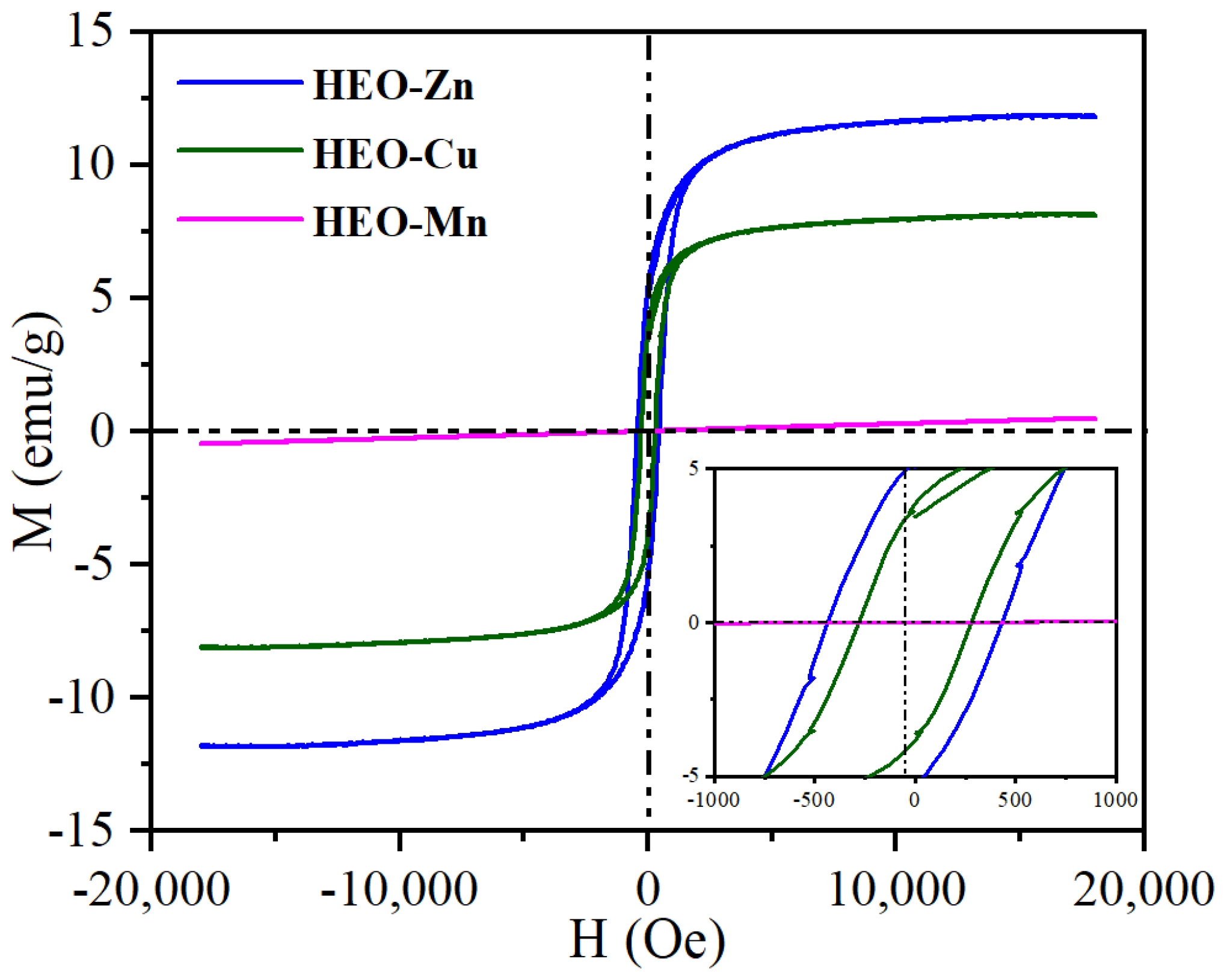

| Samples | Ms /emu/g | Hc /Oe | Br /emu/g |
|---|---|---|---|
| HEO-Zn | 12.0 | 433.4 | 5.5 |
| HEO-Cu | 8.2 | 278.6 | 3.9 |
| HEO-Mn | 0.48 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Samples | RLmin /dB | Thickness /mm | Frequency /GHz | Ratios /wt% | EAB /GHz | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RGO/Ti3C2Tx hybrids | −22.0 | 3.6 | - | - | 4.0 | [42] |
| CoFe@Ti3C2Tx | −36.3 | 2.2 | - | 60.0 | 2.6 | [43] |
| M-Ti3C2Tx/Ni | −24.3 | 2.2 | - | 60.0 | 2.6 | [44] |
| M-Ti3C2Tx/ZnO | −26.3 | 4.0 | - | 25.0 | 1.4 | [45] |
| FeCrMoNiPBCSi | −23.1 | 6.6 | 4.2 | 20.0 | 2.2 | [3] |
| Ti3C2 nanosheets filled composites | −11.0 | 1.4 | - | - | 5.6 | [46] |
| Ti3C2Tx | −17.0 | 1.4 | - | - | 5.6 | [46] |
| HEO-Zn | −27.9 | 8.6 | 15.7 | 50.0 | 6.8 | This work |
| HEO-Cu | −27.3 | 9.1 | 13.3 | 50.0 | 7.5 | This work |
| HEO-Mn | −25.5 | 9.8 | 12.9 | 50.0 | 6.9 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, X.; Duan, Z.; Wang, D.; Wang, S.; Lin, Z.; Ma, B.; Wu, K. High-Entropy Spinel Ferrites with Broadband Wave Absorption Synthesized by Simple Solid-Phase Reaction. Molecules 2023, 28, 3468. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083468
Chang X, Duan Z, Wang D, Wang S, Lin Z, Ma B, Wu K. High-Entropy Spinel Ferrites with Broadband Wave Absorption Synthesized by Simple Solid-Phase Reaction. Molecules. 2023; 28(8):3468. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083468
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Xiu, Zhiwei Duan, Dashuang Wang, Shushen Wang, Zhuang Lin, Ben Ma, and Kaiming Wu. 2023. "High-Entropy Spinel Ferrites with Broadband Wave Absorption Synthesized by Simple Solid-Phase Reaction" Molecules 28, no. 8: 3468. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083468
APA StyleChang, X., Duan, Z., Wang, D., Wang, S., Lin, Z., Ma, B., & Wu, K. (2023). High-Entropy Spinel Ferrites with Broadband Wave Absorption Synthesized by Simple Solid-Phase Reaction. Molecules, 28(8), 3468. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083468





