Mechanistic Understanding of Tyrosinase Inhibition by Polymeric Proanthocyanidins from Acacia confusa Stem Bark and Their Effect on the Browning Resistance of Fresh-Cut Asparagus Lettuce
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
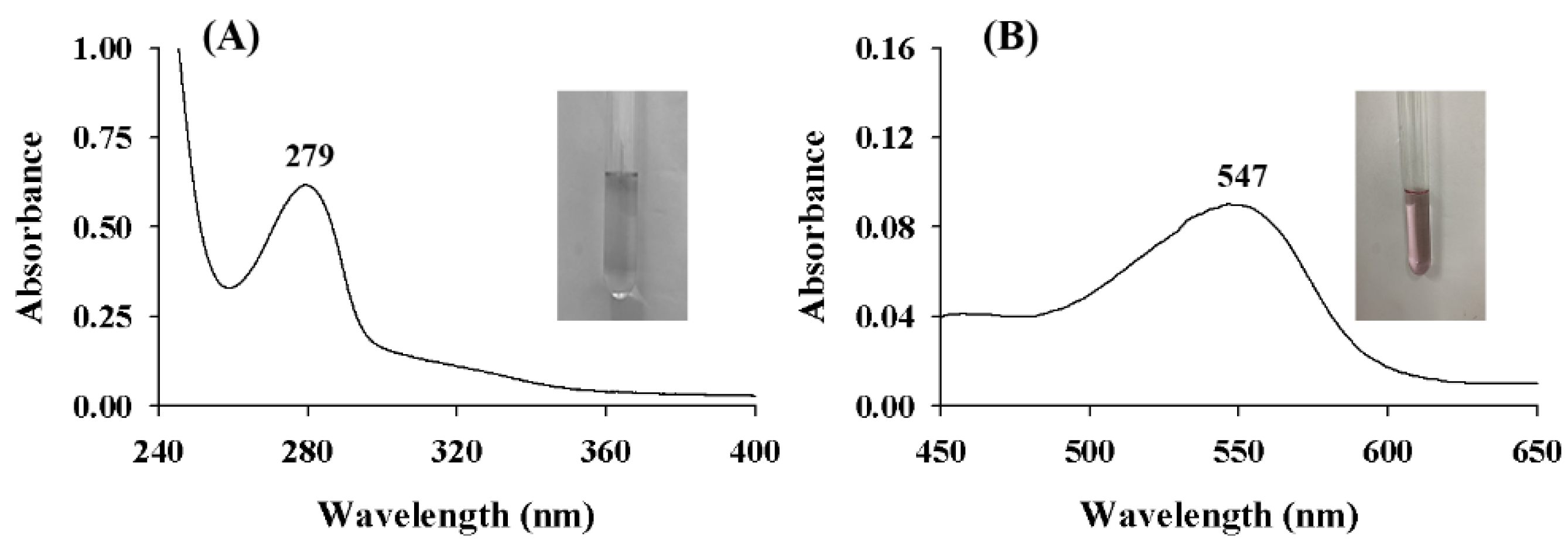
2.1. UV-vis Spectra of ASBPs
2.2. FT-IR Spectrum of ASBPs
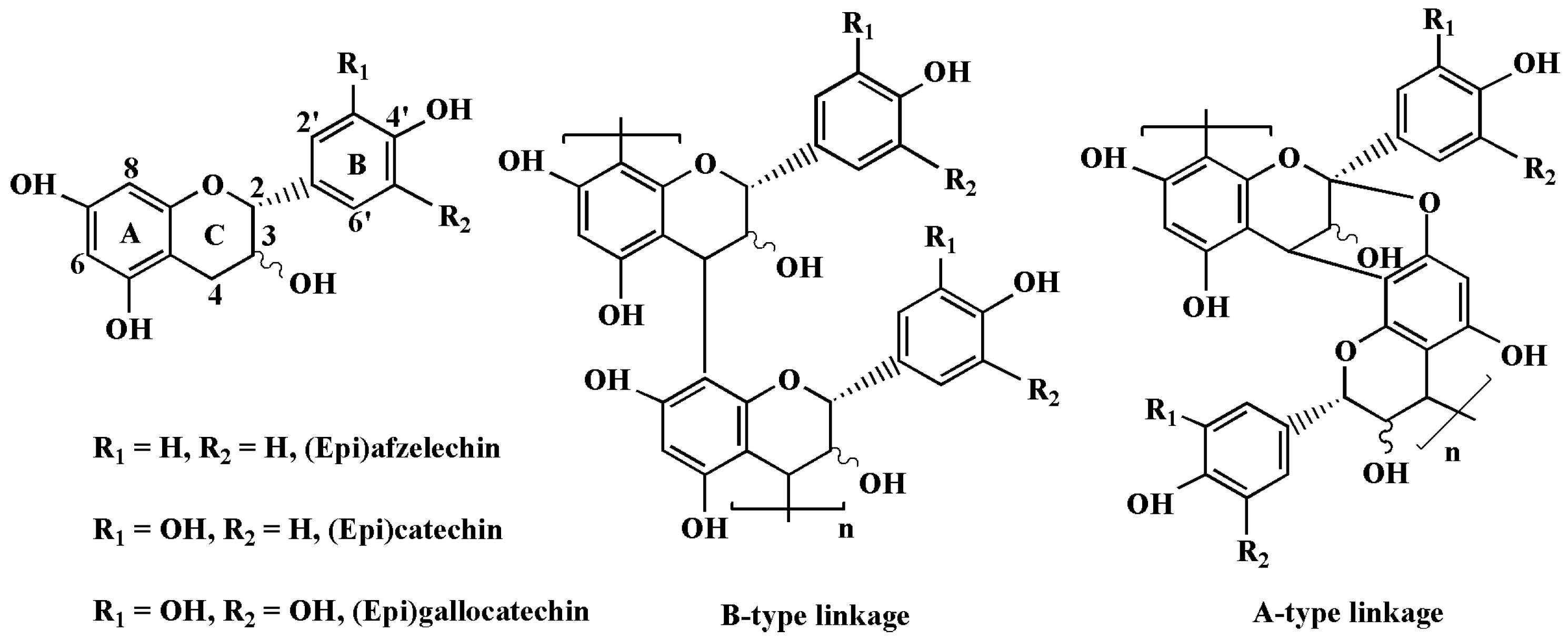
2.3. ESI Mass Spectrum of ASBPs
2.4. Thiolysis of ASBPs for HPLC-ESI-MS Analysis
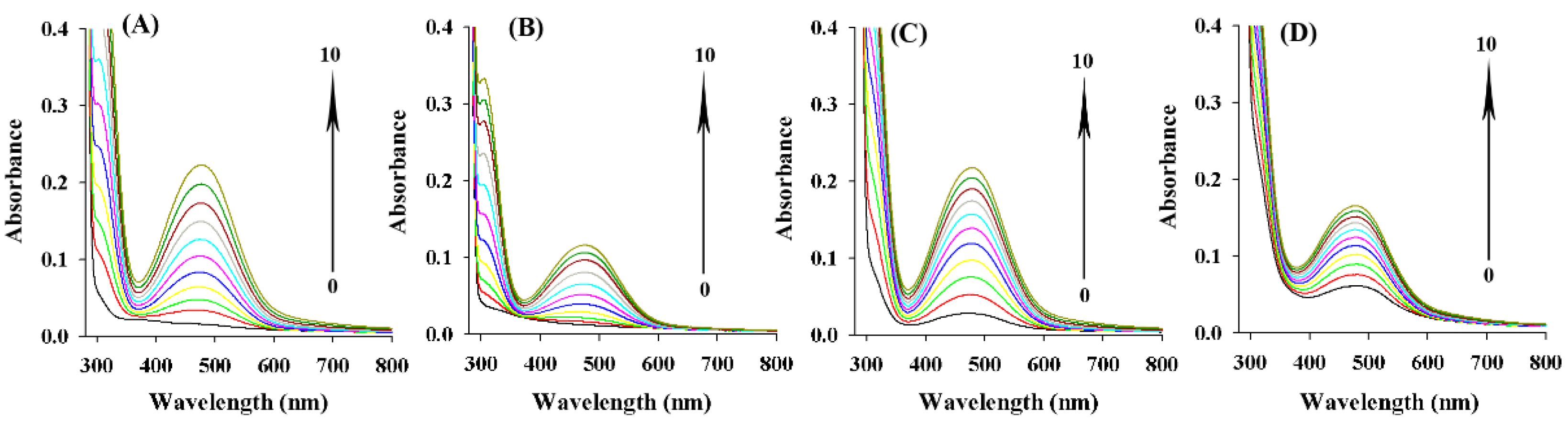
2.5. Inhibition of ASBPs on the Monophenolase Activity of Tyrosinase
2.6. Inhibition of ASBPs on the Diphenolase Activity of Tyrosinase
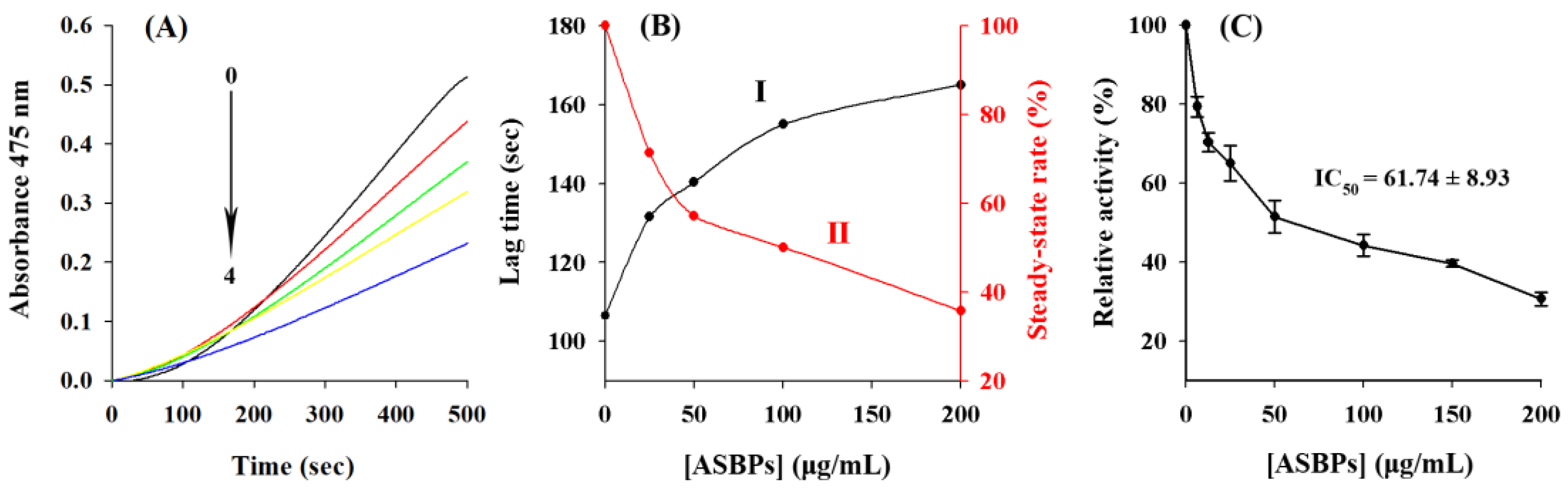
2.7. Inhibitory Effect of ASBPs on the Oxidation Process of L-Tyrosine and L-DOPA
2.8. Copper-Ion Chelating Ability
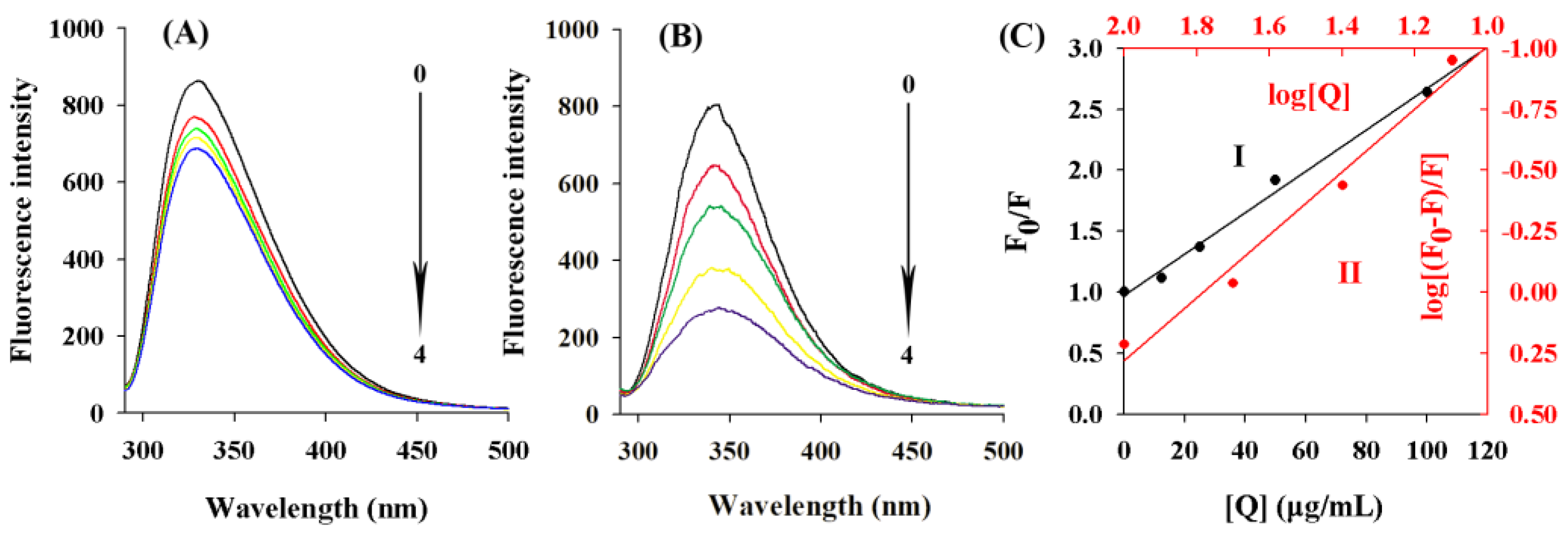
2.9. Fluorescence Quenching Analysis
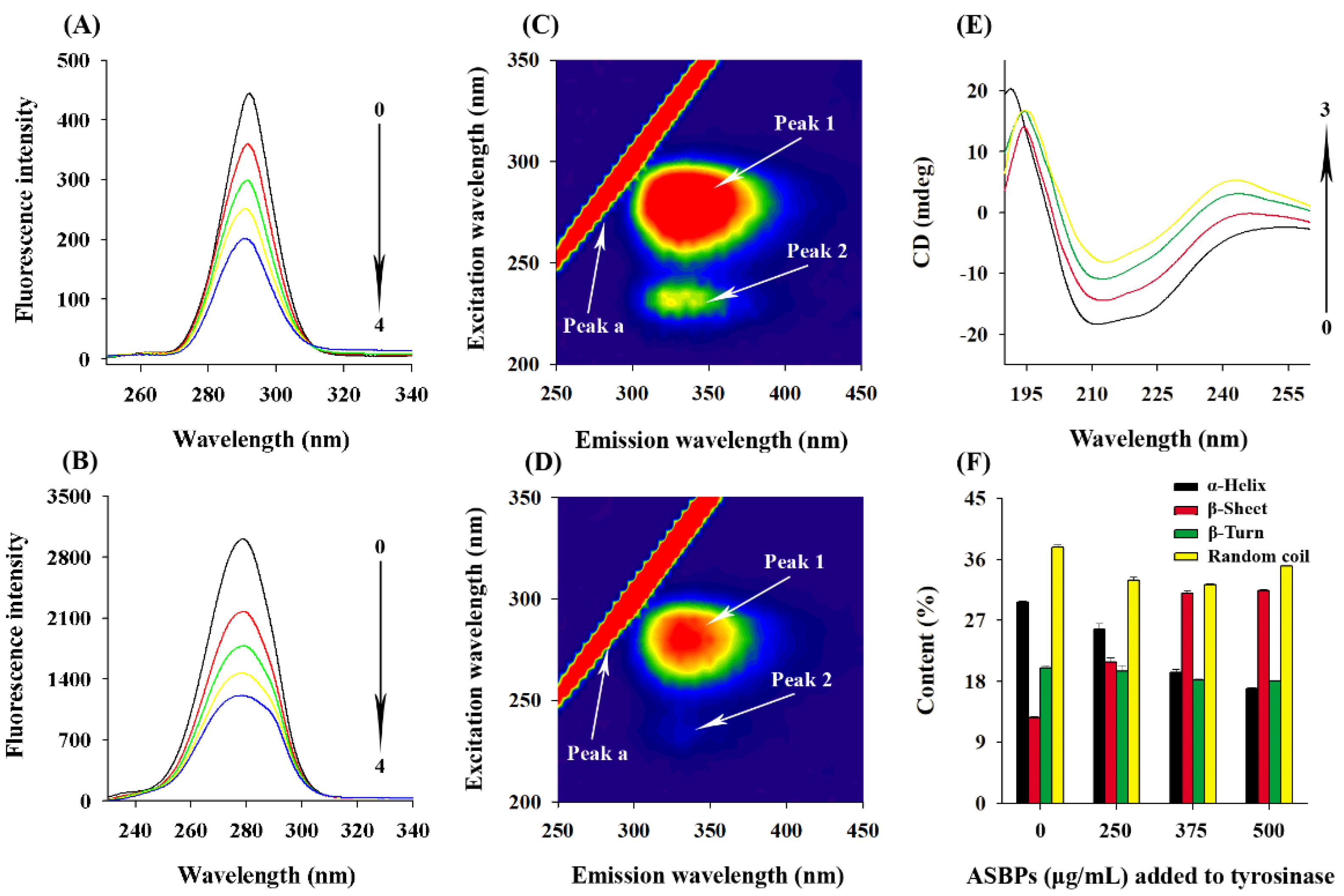
2.10. Synchronous Fluorescence Spectra
2.11. Three-Dimensional Fluorescence Spectra
2.12. CD Spectra
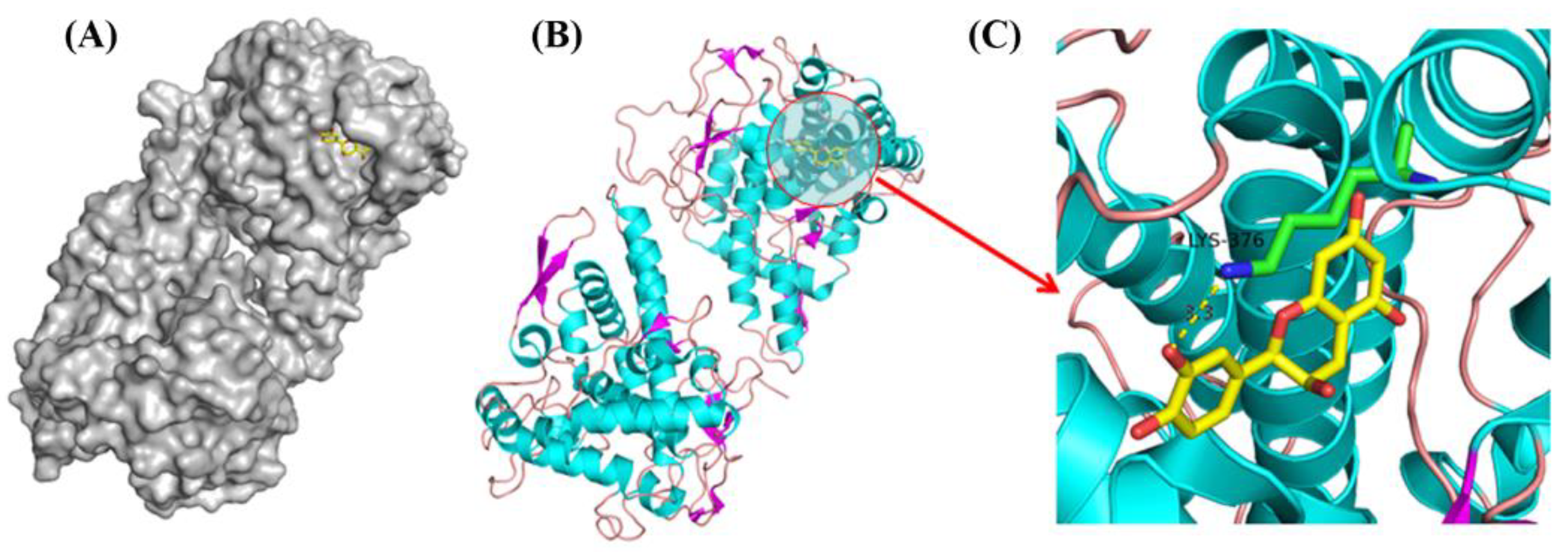
2.13. Molecular Docking
2.14. Antibrowning Effect of ASBPs
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Plant Materials
3.2. Extraction and Separation of ASBPs
3.3. Structural Elucidation of ASBPs
3.4. Effect of ASBPs on Tyrosinase Activity
3.5. Effect of ASBPs on the Oxidation of L-Tyrosine and L-DOPA
3.6. Copper-Ion Chelation
3.7. Fluorescence Spectroscopy
3.8. Far-UV CD Spectroscopy
3.9. Molecular Docking Study
3.10. Color and Weight Loss Measurements
3.11. PPO and POD Activity Measurements
3.12. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Lufu, R.; Ambaw, A.; Opara, U.L. Water loss of fresh fruit: Influencing pre-harvest, harvest and postharvest factors. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 272, 109519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, K.M.; Kwon, E.B.; Lee, B.; Kim, C.Y. Recent trends in controlling the enzymatic browning of fruit and vegetable products. Molecules 2020, 25, 2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, G.E.; Hassan, I.M.; Abd-Elrashid, A.M.; El-Massry, K.F.; Eh-Ghorab, A.H.; Manal, M.R.; Osman, F. Effect of clouding agents on the quality of apple juice during storage. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.C.; He, M.; Huang, Y.; Peng, Z.Y. Synthesis and biological evaluation of new kojic acid-1,3,4-oxadiazole hybrids as tyrosinase inhibitors and their application in the anti-browning of fresh-cut mushrooms. Food Chem. 2023, 409, 135275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, W.M.; Huang, Q.; Lin, M.Z.; Ou-Yang, C.; Huang, W.Y.; Wang, Y.X.; Xu, K.L.; Feng, H.L. Condensed tannins from longan bark as inhibitor of tyrosinase: Structure, activity, and mechanism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, W.M.; Lin, M.Z.; Wang, Y.X.; Xu, K.L.; Huang, W.Y.; Pan, D.D.; Zou, Z.R.; Peng, Y.Y. Inhibition of tyrosinase by cherimoya pericarp proanthocyanidins: Structural characterization, inhibitory activity and mechanism. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Ren, Y.J.; Liu, L.L.; Wei, S.D.; Yang, H.B. Proanthocyanidins isolated from the leaves of Photinia × fraseri block the cell cycle and induce apoptosis by inhibiting tyrosinase activity in melanoma cells. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 3978–3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monagas, M.; Quintanilla-Lopez, J.E.; Gomez-Cordoves, C.; Bartolome, B.; Lebron-Aguilar, R. MALDI-TOF MS analysis of plant proanthocyanidins. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 51, 358–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neto, C.C.; Krueger, C.G.; Lamoureaux, T.L.; Kondo, M.; Vaisberg, A.J.; Hurta, R.A.R.; Curtis, S.; Matchett, M.D.; Yeung, H.; Sweeney, M.I.; et al. MALDI-TOF MS characterization of proanthocyanidins from cranberry fruit (Vaccinium macrocarpon) that inhibit tumor cell growth and matrix metalloproteinase expression in vitro. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 86, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.D.; Chen, H.; Yan, T.; Lin, Y.M.; Zhou, H.C. Identification of antioxidant components and fatty acid profiles of the leaves and fruits from Averrhoa carambola. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 55, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliciano, R.P.; Krueger, C.G.; Reed, J.D. Methods to determine effects of cranberry proanthocyanidins on extraintestinal infections: Relevance for urinary tract health. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 1292–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Song, W.; Sun, K.K.; Du, H.W.; Wei, S.D. Structure elucidation and evaluation of antioxidant and tyrosinase inhibitory effect and mechanism of proanthocyanidins from leaf and fruit of Leucaena leucocephala. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2018, 38, 430–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.H.; Tung, Y.T.; Wang, S.Y.; Shyur, L.F.; Kuo, Y.H.; Chang, S.T. Phenolic antioxidants from the heartwood of Acacia confusa. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 5917–5921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, Y.T.; Chang, W.C.; Chen, P.S.; Chang, T.C.; Chang, S.T. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of phenolic antioxidants from Acacia confusa flowers and buds. J. Sep. Sci. 2011, 34, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.Y.; Chang, S.T. Antioxidant activities and xanthine oxidase inhibitory effects of phenolic phytochemicals from Acacia confusa twigs and branches. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 1578–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.Y.; Chang, S.T. Antioxidant potency of phenolic phytochemicals from the root extract of Acacia confusa. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 49, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.D.; Zhou, H.C.; Lin, Y.M.; Liao, M.M.; Chai, W.M. MALDI-TOF MS analysis of condensed tannins with potent antioxidant activity from the leaf, stem bark and root bark of Acacia confusa. Molecules 2010, 15, 4369–4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, W.M.; Wei, Q.M.; Deng, W.L.; Zheng, Y.L.; Chen, X.Y.; Huang, Q.; Ou-Yang, C.; Peng, Y.Y. Anti-melanogenesis properties of condensed tannins from Vigna angularis seeds with potent antioxidant and DNA damage protection activities. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellstrom, J.; Sinkkonen, J.; Karonen, M.; Mattila, P. Isolation and structure elucidation of procyanidin oligomers from saskatoon berries (Amelanchier alnifolia). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.Y.; Dixon, R.A. Proanthocyanidin biosynthesis-still more questions than answers? Phytochemistry 2005, 66, 2127–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.M.; Li, C.; Zhang, W.J.; Shi, Y.; Wen, Z.J.; Chen, Q.X.; Wang, Q. Kinetic and computational molecular docking simulation study of novel kojic acid derivatives as anti-tyrosinase and antioxidant agents. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2019, 34, 990–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, L.; Fattah, M.A.; Salem, E. Characterization of pure proanthocyanidins isolated from the hulls of faba beans. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1990, 38, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.L.; Yang, D.Y.; Peh, W.Y.E.; Lai, S.J.; Feng, X.; Yang, H.S. Structure and antioxidant activities of proanthocyanidins from elephant apple (Dillenia indica Linn.). J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, C2191–C2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oo, C.W.; Kassim, M.J.; Pizzi, A. Characterization and performance of Rhizophora apiculata mangrove polyflavonoid tannins in the adsorption of copper (II) and lead (II). Ind. Crops Prod. 2009, 30, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Hu, B.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Qian, H.F.; Qi, X.G. Inhibition study of red rice polyphenols on pancreatic α-amylase activity by kinetic analysis and molecular docking. J. Cereal Sci. 2017, 76, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, J.D.; Krueger, C.G.; Vestling, M.M. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry of oligomeric food polyphenols. Phytochemistry 2005, 66, 2248–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, Y.; Fujita, Y.; Ohnishi, S.; Tanaka, T.; Hirabaru, H.; Kai, T.; Sakaida, H.; Nishizono, S.; Kouno, I. Chemical constituents of the leaves of rabbiteye blueberry (Vaccinium ashei) and characterization of polymeric proanthocyanidins containing phenylpropanoid units and A-type linkages. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeRoux, E.; Doco, T.; Sarni-Manchado, P.; Lozano, Y.; Cheynier, V. A-type proanthocyanidins from pericarp of Litchi chinensis. Phytochemistry 1998, 48, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Lopez, J.N.; Ros, J.R.; Varon, R.; Garcia-Canovas, F. Oxygen Michaelis constant for tyrosinase. Biochem. J. 1993, 293, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Huang, H.H.; Zhao, M.M.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.X.; Lin, L.Z.; Xiao, C.Q. Mechanisms underlying the xanthine oxidase inhibitory effects of dietary flavonoids galangin and pinobanksin. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 24, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.X.; Tian, J.H.; Yang, W.H.; Chen, S.G.; Liu, D.H.; Fang, H.T.; Zhang, H.L.; Ye, X.Q. Inhibition mechanism of ferulic acid against α-amylase and α-glucosidase. Food Chem. 2020, 317, 126346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.L.; Li, J.D.; Zhang, L.L.; Wei, S.D.; Qin, Z.Y.; Liang, D.D.; Ding, B.M.; Chen, H.; Song, W. Conformational changes of tyrosinase caused by pentagalloylglucose binding: Implications for inhibitory effect and underlying mechanism. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Molina, F.; Munoz, J.L.; Varon, R.; Rodriguez-Lopez, J.N.; Garcia-Canovas, F.; Tudela, J. A review on spectrophotometric methods for measuring the monophenolase and diphenolase activities of tyrosinase. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 9739–9749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismaya, W.T.; Rozeboom, H.J.; Weijn, A.; Mes, J.J.; Fusetti, F.; Wichers, H.J.; Dijkstra, B.W. Crystal structure of Agaricus bisporus mushroom tyrosinase: Identity of the tetramer subunits and interaction with tropolone. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 5477–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, G.W.; Yan, J.K.; Gong, D.M. Inhibitory effect of morin on tyrosinase: Insights from spectroscopic and molecular docking studies. Food Chem. 2014, 163, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.T.; Jiang, J.; Tian, J.H.; Chen, S.G.; Ye, X.Q.; Hu, Y.Q.; Chen, J.C. Inhibitory mechanism of novel allosteric inhibitor, Chinese bayberry (Myrica rubra Sieb. et Zucc.) leaves proanthocyanidins against α-glucosidase. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 56, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.H.; Wang, C.L.; Shang, C.; You, X.; Zhang, L.Y.; Liu, W.B. Integrated study of the mechanism of tyrosinase inhibition by baicalein using kinetic, multispectroscopic and computational simulation analyses. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.F.; Hu, X.; Xu, X.M.; Zhang, G.W.; Gong, D.M. Inhibitory mechanism of two allosteric inhibitors, oleanolic acid and ursolic acid on α-glucosidase. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 107, 1844–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Zhang, G.W.; Lin, S.Y.; Gong, D.M. Inhibitory mechanism of apigenin on α-glucosidase and synergy analysis of flavonoids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 6939–6949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zhang, Y.; He, J.L.; Zhang, S.; Zeng, M.M.; Chen, J.; Zheng, Z.P. Preparation of tyrosinase inhibitors and antibrowning agents using green technology. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.Z.; Chai, W.M.; Ou-Yang, C.; Huang, Q.; Xu, X.H.; Peng, Y.Y. Antityrosinase mechanism of omeprazole and its application on the preservation of fresh-cut Fuji apple. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 117, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Yang, Q.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, T.; Zhou, B.; Qiao, L. Effect of purslane (Portulaca oleracea L.) extract on anti-browning of fresh-cut potato slices during storage. Food Chem. 2019, 283, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Chen, J.; Li, T.; Liu, C.M.; Zhai, Y.X.; McClements, D.J.; Liu, J.Y. Separation and characterization of polyphenolics from underutilized byproducts of fruit production (Choerospondias axillaris peels): Inhibitory activity of proanthocyanidins against glycolysis enzymes. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 3693–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.J.; Qin, Z.Y.; Wang, Z.C.; Wei, S.D.; Chen, H.; Zhu, T.; Liu, L.L.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Ding, B.M.; Song, W. Condensed tannins from Ulmus pumila L. leaves induce G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis via caspase-cascade activation in TFK-1 cholangiocarcinoma cells. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Liang, G.; Hu, Y.H.; Shi, Y.; Cai, Y.X.; Gao, H.J.; Chen, Q.X.; Wang, Q. Alpha-substituted derivatives of cinnamaldehyde as tyrosinase inhibitors: Inhibitory mechanism and molecular analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.L.; Wang, X.L.; Chen, K.; Dong, X.W.; Kong, L.M.; Zhao, D.Y.; Hider, R.C.; Zhou, T.T. Novel hydroxypyridinone derivatives containing an oxime ether moiety: Synthesis, inhibition on mushroom tyrosinase and application in anti-browning of fresh-cut apples. Food Chem. 2018, 242, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Kim, H.B.; Chung, H.S.; Moon, K.D. Browning control of fresh-cut lettuce by phytoncide treatment. Food Chem. 2014, 159, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, G.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, Z.; Wei, S.; Liang, D.; Liang, Y.; Song, W.; Ding, B. Mechanistic Understanding of Tyrosinase Inhibition by Polymeric Proanthocyanidins from Acacia confusa Stem Bark and Their Effect on the Browning Resistance of Fresh-Cut Asparagus Lettuce. Molecules 2023, 28, 3435. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083435
Li G, Zhao Y, Qin Z, Wei S, Liang D, Liang Y, Song W, Ding B. Mechanistic Understanding of Tyrosinase Inhibition by Polymeric Proanthocyanidins from Acacia confusa Stem Bark and Their Effect on the Browning Resistance of Fresh-Cut Asparagus Lettuce. Molecules. 2023; 28(8):3435. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083435
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Guanghui, Yaying Zhao, Zeya Qin, Shudong Wei, Dandan Liang, Yun Liang, Wei Song, and Baomiao Ding. 2023. "Mechanistic Understanding of Tyrosinase Inhibition by Polymeric Proanthocyanidins from Acacia confusa Stem Bark and Their Effect on the Browning Resistance of Fresh-Cut Asparagus Lettuce" Molecules 28, no. 8: 3435. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083435
APA StyleLi, G., Zhao, Y., Qin, Z., Wei, S., Liang, D., Liang, Y., Song, W., & Ding, B. (2023). Mechanistic Understanding of Tyrosinase Inhibition by Polymeric Proanthocyanidins from Acacia confusa Stem Bark and Their Effect on the Browning Resistance of Fresh-Cut Asparagus Lettuce. Molecules, 28(8), 3435. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083435




