Aurora B Inhibitors as Cancer Therapeutics
Abstract
1. Aurora B and Cancer
2. Current Status of Aurora B Inhibitor Drug Development
3. Aurora B Inhibitors in Clinical Trials
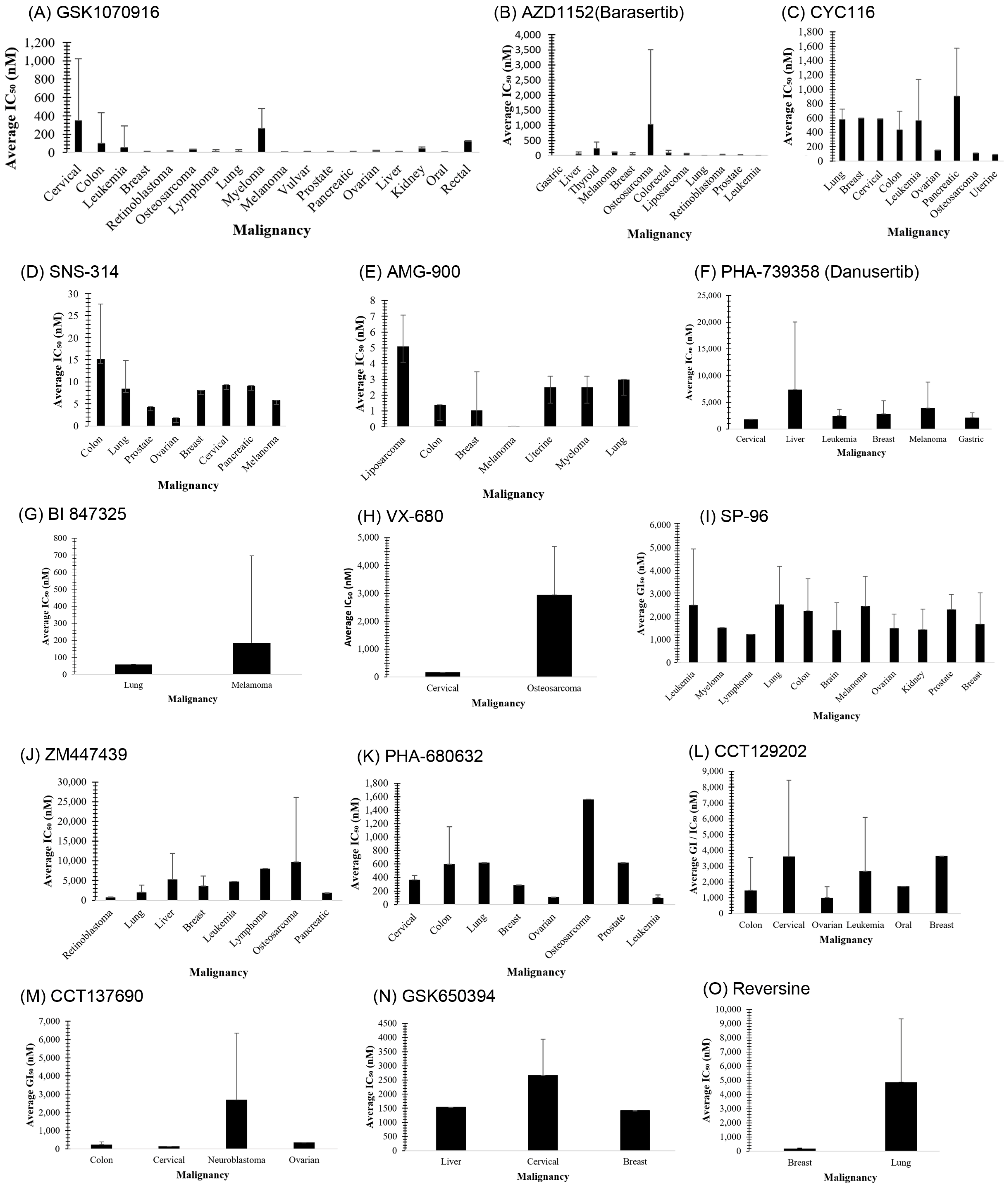
3.1. GSK1070916
3.2. AZD1152 (Barasertib)
3.3. CYC116
3.4. SNS-314
3.5. AMG 900
3.6. PHA-739358 (Danusertib)
3.7. BI 847325
3.8. VX-680 (MK-0457)
3.9. BI 811283
3.10. AT9283
3.11. MLN8237 (Alisertib)
3.12. ABT-348 (Ilorasertib)
3.13. TAK-901
3.14. CS2164
3.15. SP-96
4. Aurora B Inhibitors in Preclinical Development
4.1. ZM447439
4.2. PHA-680632
4.3. CCT129202
4.4. CCT137690
4.5. GSK650394
4.6. Reversine
4.7. Hesperadin
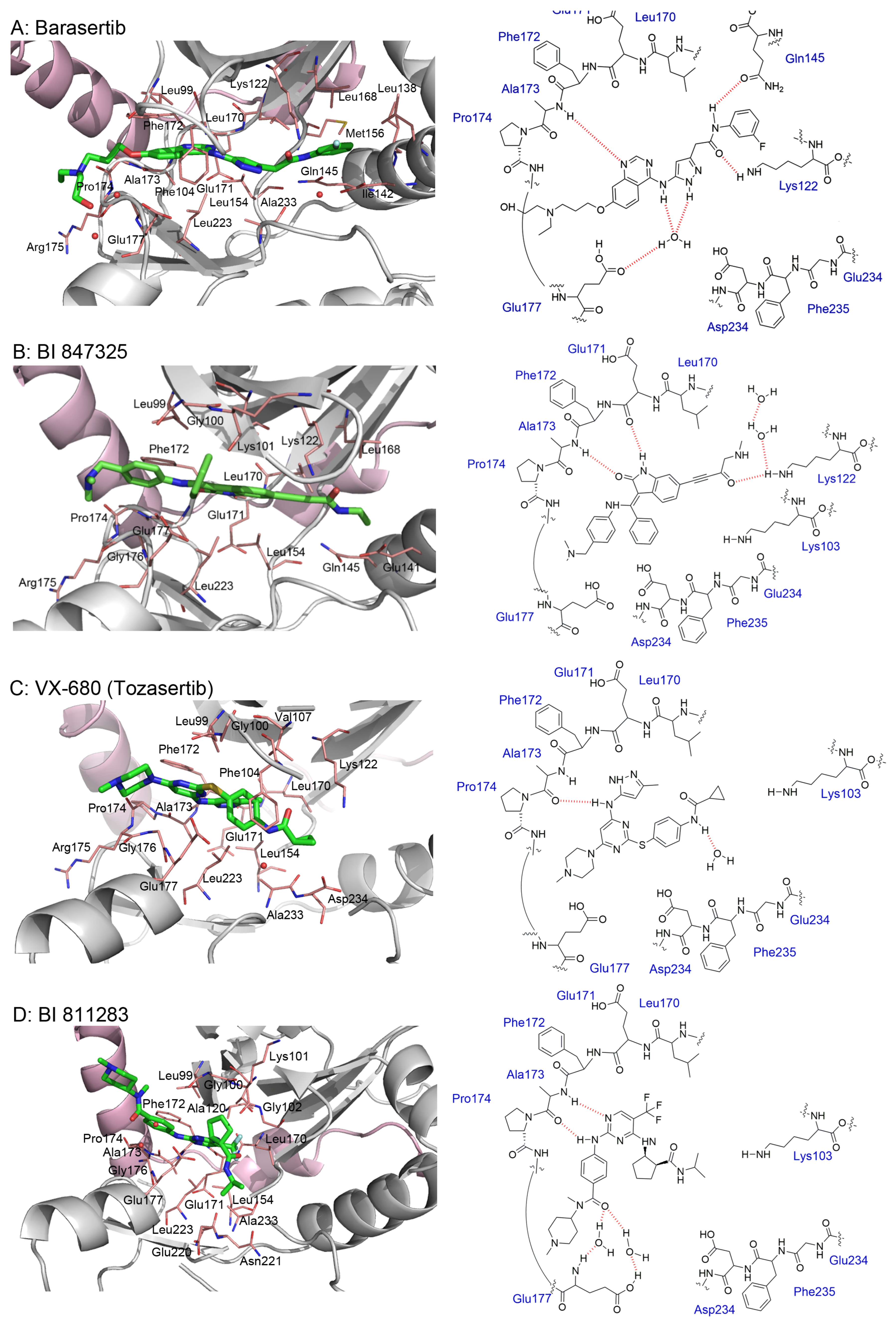
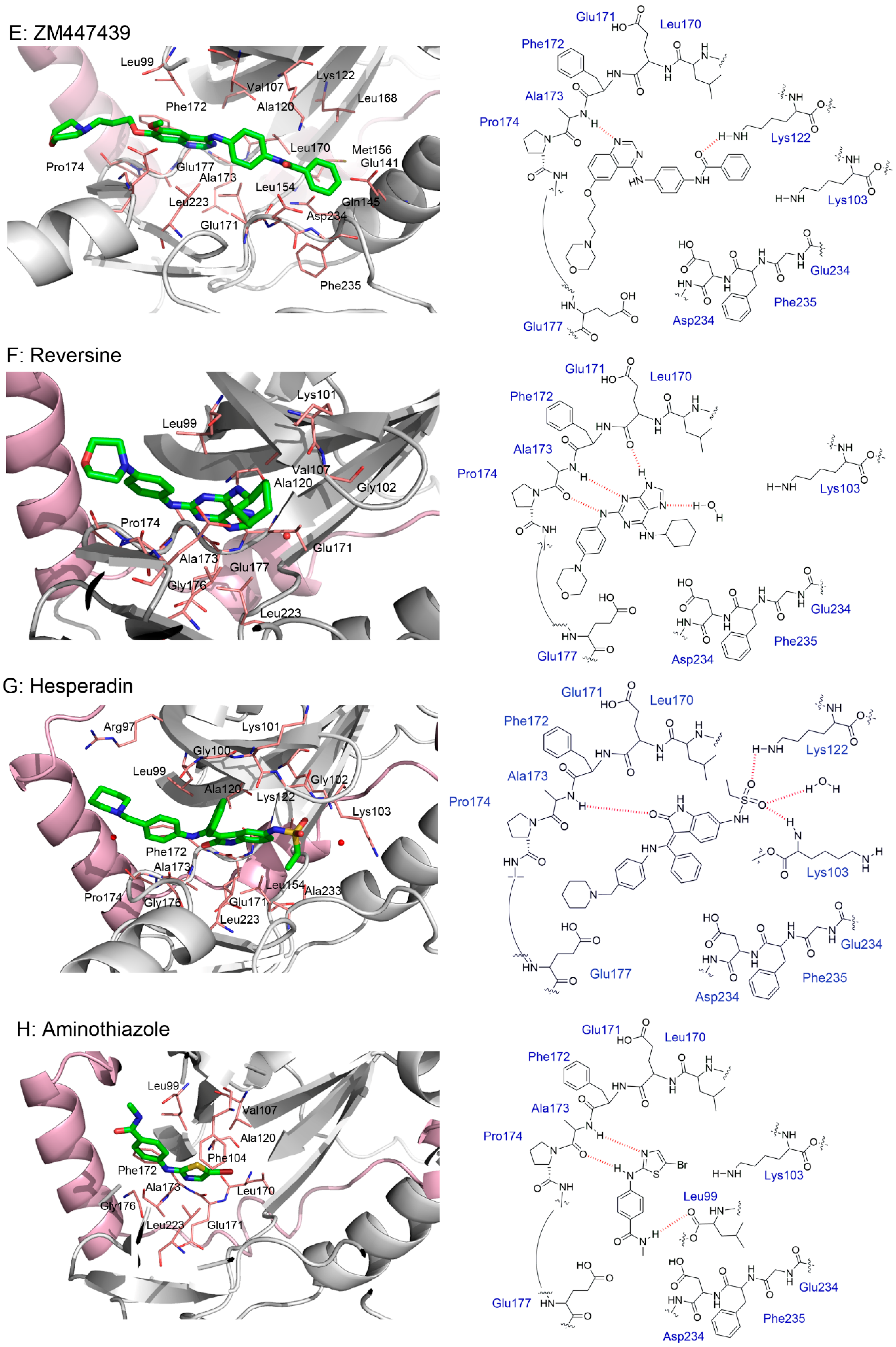
5. Crystal Structures and Ligand Protein Binding Interactions of Aurora B Inhibitors
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Hegyi, K.; Egervári, K.; Sándor, Z.; Méhes, G. Aurora Kinase B Expression in Breast Carcinoma: Cell Kinetic and Genetic Aspects. Pathobiology 2012, 79, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, R.; Körner, R.; Nigg, E.A. Exploring the Functional Interactions between Aurora B, INCENP, and Survivin in Mitosis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 3325–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McVey, S.L.; Cosby, J.K.; Nannas, N.J. Aurora B Tension Sensing Mechanisms in the Kinetochore Ensure Accurate Chromosome Segregation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, T.; Sykora, M.M.; Huis in ’t Veld, P.J.; Mechtler, K.; Peters, J.-M. Aurora B and Cdk1 Mediate Wapl Activation and Release of Acetylated Cohesin from Chromosomes by Phosphorylating Sororin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 13404–13409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasmyth, K.; Haering, C.H. Cohesin: Its Roles and Mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2009, 43, 525–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, F.L.; Vinod, B.; Novy, K.; Schittenhelm, R.B.; Huang, C.; Udugama, M.; Nunez-Iglesias, J.; Lin, J.I.; Hii, L.; Chan, J.; et al. Aurora Kinase B, a Novel Regulator of TERF1 Binding and Telomeric Integrity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 12340–12353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallm, J.-P.; Rippe, K. Aurora Kinase B Regulates Telomerase Activity via a Centromeric RNA in Stem Cells. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 1667–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.T.; Poon, R.Y.C. Aurora Kinases and DNA Damage Response. Mutat. Res. 2020, 821, 111716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amabile, G.; D’Alise, A.M.; Iovino, M.; Jones, P.; Santaguida, S.; Musacchio, A.; Taylor, S.; Cortese, R. The Aurora B Kinase Activity Is Required for the Maintenance of the Differentiated State of Murine Myoblasts. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmena, M.; Ruchaud, S.; Earnshaw, W.C. Making the Auroras Glow: Regulation of Aurora A and B Kinase Function by Interacting Proteins. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2009, 21, 796–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Sullivan, B.A.; Higgins, J.M.G. Regulation of Mitotic Chromosome Cohesion by Haspin and Aurora B. Dev. Cell 2006, 11, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramkumar, N.; Patel, J.V.; Anstatt, J.; Baum, B. Aurora B-Dependent Polarization of the Cortical Actomyosin Network during Mitotic Exit. EMBO Rep. 2021, 22, e52387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, B.; Han, S.J.Y.; Fontan, A.N.; Jema, S.; Joglekar, A.P. Aurora B Phosphorylates Bub1 to Promote Spindle Assembly Checkpoint Signaling. Curr. Biol. CB 2022, 32, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurden, M.D.; Anderhub, S.J.; Faisal, A.; Linardopoulos, S. Aurora B Prevents Premature Removal of Spindle Assembly Checkpoint Proteins from the Kinetochore: A Key Role for Aurora B in Mitosis. Oncotarget 2016, 9, 19525–19542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Gonzalez, P.; Westhorpe, F.G.; Taylor, S.S. The Spindle Assembly Checkpoint. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, R966–R980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelluma, N.; Brenkman, A.B.; van den Broek, N.J.F.; Cruijsen, C.W.A.; van Osch, M.H.J.; Lens, S.M.A.; Medema, R.H.; Kops, G.J.P.L. Mps1 Phosphorylates Borealin to Control Aurora B Activity and Chromosome Alignment. Cell 2008, 132, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Loyola, A.; Fernández-Miranda, G.; Trakala, M.; Partida, D.; Samejima, K.; Ogawa, H.; Cañamero, M.; de Martino, A.; Martínez-Ramírez, Á.; de Cárcer, G.; et al. Aurora B Overexpression Causes Aneuploidy and P21Cip1 Repression during Tumor Development. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2015, 35, 3566–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.-Z.; Jeng, Y.-M.; Hu, F.-C.; Pan, H.-W.; Tsao, H.-W.; Lai, P.-L.; Lee, P.-H.; Cheng, A.-L.; Hsu, H.-C. Significance of Aurora B Overexpression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Aurora B Overexpression in HCC. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portella, G.; Passaro, C.; Chieffi, P. Aurora B: A New Prognostic Marker and Therapeutic Target in Cancer. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 482–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.; Gao, K.; Chu, L.; Zhang, R.; Yang, J.; Zheng, J. Aurora Kinases: Novel Therapy Targets in Cancers. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 23937–23954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.G.; Chinnappan, D.; Urano, T.; Ravid, K. Mechanism of Aurora-B Degradation and Its Dependency on Intact KEN and A-Boxes: Identification of an Aneuploidy-Promoting Property. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 4977–4992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Barrera, M.; Monje-Casas, F. Increased Aurora B Activity Causes Continuous Disruption of Kinetochore–Microtubule Attachments and Spindle Instability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E3996–E4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldenson, B.; Crispino, J.D. The Aurora Kinases in Cell Cycle and Leukemia. Oncogene 2015, 34, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, B.; Limaye, A.; Kulkarni, A.B. Overview: Generation of Gene Knockout Mice. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. Editor. Board Juan Bonifacino. Al. 2009, 44, 19.12.1–19.12.17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Miranda, G.; Trakala, M.; Martín, J.; Escobar, B.; González, A.; Ghyselinck, N.B.; Ortega, S.; Cañamero, M.; Pérez de Castro, I.; Malumbres, M. Genetic Disruption of Aurora B Uncovers an Essential Role for Aurora C during Early Mammalian Development. Dev. Camb. Engl. 2011, 138, 2661–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.-Y.; Wood, J.L.; Ye, L.; Minter-Dykhouse, K.; Saunders, T.L.; Yu, X.; Chen, J. Aurora A Is Essential for Early Embryonic Development and Tumor Suppression. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 31785–31790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta-Simmons, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gorgun, G.; Gatt, M.; Mani, M.; Hideshima, T.; Takada, K.; Carlson, N.E.; Carrasco, D.E.; Tai, Y.-T.; et al. Aurora Kinase A Is a Target of Wnt/Beta-Catenin Involved in Multiple Myeloma Disease Progression. Blood 2009, 114, 2699–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, K.; Davydenko, O.; Fram, B.; Lampson, M.A.; Schultz, R.M. Maternally Recruited Aurora C Kinase Is More Stable than Aurora B to Support Mouse Oocyte Maturation and Early Development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E2215–E2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmins, S.; Crosio, C.; Kotaja, N.; Hirayama, J.; Monaco, L.; Höög, C.; van Duin, M.; Gossen, J.A.; Sassone-Corsi, P. Differential Functions of the Aurora-B and Aurora-C Kinases in Mammalian Spermatogenesis. Mol. Endocrinol. Baltim. Md. 2007, 21, 726–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavetsias, V.; Linardopoulos, S. Aurora Kinase Inhibitors: Current Status and Outlook. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, J.S.; Ho, A.L.; Tse, A.N.; Coward, J.; Cheema, H.; Ambrosini, G.; Keen, N.; Schwartz, G.K. Aurora B Kinase Regulates the Postmitotic Endoreduplication Checkpoint via Phosphorylation of the Retinoblastoma Protein at Serine 780. Mol. Biol. Cell 2009, 20, 2218–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakkaniga, N.R.; Zhang, L.; Belachew, B.; Gunaganti, N.; Frett, B.; Li, H. Discovery of SP-96, the First Non-ATP-Competitive Aurora Kinase B Inhibitor, for Reduced Myelosuppression. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 203, 112589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warkentin, A.A.; Lopez, M.S.; Lasater, E.A.; Lin, K.; He, B.-L.; Leung, A.Y.; Smith, C.C.; Shah, N.P.; Shokat, K.M. Overcoming Myelosuppression Due to Synthetic Lethal Toxicity for FLT3-Targeted Acute Myeloid Leukemia Therapy. eLife 2014, 3, e03445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.T.D.; Ha, P.T.; Tran, T.H.Y.; Nguyen, D.T.; Nguyen, H.N.; Bui, V.K.; Hoang, M.N. In Vitro Evaluation of Aurora Kinase Inhibitor—VX680—In Formulation of PLA-TPGS Nanoparticles. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 025010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanderPorten, E.C.; Taverna, P.; Hogan, J.N.; Ballinger, M.D.; Flanagan, W.M.; Fucini, R.V. The Aurora Kinase Inhibitor SNS-314 Shows Broad Therapeutic Potential with Chemotherapeutics and Synergy with Microtubule-Targeted Agents in a Colon Carcinoma Model. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, F.; Hurwitz, H.; Verschraegen, C.F.; Advani, R.; Berman, C.; Taverna, P.; Evanchik, M. Phase 1 Trial of SNS-314, a Novel Selective Inhibitor of Aurora Kinases A, B, and C, in Advanced Solid Tumor Patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 14642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, N.D.; Adams, J.L.; Burgess, J.L.; Chaudhari, A.M.; Copeland, R.A.; Donatelli, C.A.; Drewry, D.H.; Fisher, K.E.; Hamajima, T.; Hardwicke, M.A.; et al. Discovery of GSK1070916, a Potent and Selective Inhibitor of Aurora B/C Kinase. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 3973–4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeish, I.; Anthoney, A.; Loadman, P.; Berney, D.; Joel, S.; Halford, S.E.R.; Buxton, E.; Race, A.; Ikram, M.; Scarsbrook, A.; et al. A Phase I Pharmacokinetic (PK) and Pharmacodynamic (PD) Study of the Selective Aurora Kinase Inhibitor GSK1070916A. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ikezoe, T.; Nishioka, C.; Tasaka, T.; Taniguchi, A.; Kuwayama, Y.; Komatsu, N.; Bandobashi, K.; Togitani, K.; Koeffler, H.P.; et al. AZD1152, a Novel and Selective Aurora B Kinase Inhibitor, Induces Growth Arrest, Apoptosis, and Sensitization for Tubulin Depolymerizing Agent or Topoisomerase II Inhibitor in Human Acute Leukemia Cells in Vitro and in Vivo. Blood 2007, 110, 2034–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuboi, K.; Yokozawa, T.; Sakura, T.; Watanabe, T.; Fujisawa, S.; Yamauchi, T.; Uike, N.; Ando, K.; Kihara, R.; Tobinai, K.; et al. A Phase I Study to Assess the Safety, Pharmacokinetics and Efficacy of Barasertib (AZD1152), an Aurora B Kinase Inhibitor, in Japanese Patients with Advanced Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2011, 35, 1384–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, G.P.; Eyre, T.A.; Linton, K.M.; Radford, J.; Vallance, G.D.; Soilleux, E.; Hatton, C. A Phase II Trial of AZD1152 in Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 170, 886–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, G.K.; Carvajal, R.D.; Midgley, R.; Rodig, S.J.; Stockman, P.K.; Ataman, O.; Wilson, D.; Das, S.; Shapiro, G.I. Phase I Study of Barasertib (AZD1152), a Selective Inhibitor of Aurora B Kinase, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Investig. New Drugs 2013, 31, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, M.; Davies, M.; Oliver, S.; D’Souza, R.; Pike, L.; Stockman, P. Phase I Study of the Aurora B Kinase Inhibitor Barasertib (AZD1152) to Assess the Pharmacokinetics, Metabolism and Excretion in Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2012, 70, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löwenberg, B.; Muus, P.; Ossenkoppele, G.; Rousselot, P.; Cahn, J.-Y.; Ifrah, N.; Martinelli, G.; Amadori, S.; Berman, E.; Sonneveld, P.; et al. Phase ½ Study to Assess the Safety, Efficacy, and Pharmacokinetics of Barasertib (AZD1152) in Patients with Advanced Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood 2011, 118, 6030–6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantarjian, H.M.; Sekeres, M.A.; Ribrag, V.; Rousselot, P.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Jabbour, E.J.; Owen, K.; Stockman, P.K.; Oliver, S.D. Phase I Study Assessing the Safety and Tolerability of Barasertib (AZD1152) with Low-Dose Cytosine Arabinoside in Elderly Patients with AML. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2013, 13, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintás-Cardama, A.; Ravandi, F.; Liu-Dumlao, T.; Brandt, M.; Faderl, S.; Pierce, S.; Borthakur, G.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Cortes, J.; Kantarjian, H. Epigenetic Therapy Is Associated with Similar Survival Compared with Intensive Chemotherapy in Older Patients with Newly Diagnosed Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood 2012, 120, 4840–4845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, G.; Kantarjian, H.; Jabbour, E.; Quintas-Cardama, A.; Ando, K.; Bay, J.-O.; Wei, A.; Gröpper, S.; Owen, K.; Pike, L.; et al. Stage I Findings of a Two-Stage Phase II Study to Assess the Efficacy, Safety, and Tolerability of Barasertib (AZD1152) Compared with Low-Dose Cytosine Arabinoside (LDAC) in Elderly Patients (Pts) with Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML). J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boss, D.S.; Witteveen, P.O.; van der Sar, J.; Lolkema, M.P.; Voest, E.E.; Stockman, P.K.; Ataman, O.; Wilson, D.; Das, S.; Schellens, J.H. Clinical Evaluation of AZD1152, an i.v. Inhibitor of Aurora B Kinase, in Patients with Solid Malignant Tumors. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Corte, C.M.; Ajpacaja, L.; Cardnell, R.J.; Gay, C.M.; Wang, Q.; Shen, L.; Ramkumar, K.; Stewart, A.C.; Fan, Y.-H.; Adelman, C.A.; et al. 1749P—Activity of the Novel Aurora Kinase B Inhibitor AZD2811 in Biomarker-Defined Models of Small Cell Lung Cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, v716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, G.; Scaerou, F.; Midgley, C.; McClue, S.; Tosh, C.; Jackson, W.; MacCallum, D.; Wang, S.; Fischer, P.; Glover, D.; et al. Anti-Tumor Activity of CYC116, a Novel Small Molecule Inhibitor of Aurora Kinases and VEGFR2. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 5644. [Google Scholar]
- Payton, M.; Bush, T.L.; Chung, G.; Ziegler, B.; Eden, P.; McElroy, P.; Ross, S.; Cee, V.J.; Deak, H.L.; Hodous, B.L.; et al. Preclinical Evaluation of AMG 900, a Novel Potent and Highly Selective Pan-Aurora Kinase Inhibitor with Activity in Taxane-Resistant Tumor Cell Lines. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 9846–9854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, M.W.; Sekeres, M.A.; Gamelin, E.; Rasmussen, E.; Juan, G.; Anderson, A.; Chow, V.; Friberg, G.; Vogl, F.D.; Kantarjian, H. Phase 1 Study of AMG 900, an Orally Administered Pan-Aurora Kinase Inhibitor, in Adult Patients (Pts) with Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML). Blood 2015, 126, 4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carducci, M.; Shaheen, M.; Markman, B.; Hurvitz, S.; Mahadevan, D.; Kotasek, D.; Goodman, O.B.; Rasmussen, E.; Chow, V.; Juan, G.; et al. A Phase 1, First-in-Human Study of AMG 900, an Orally Administered Pan-Aurora Kinase Inhibitor, in Adult Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Investig. New Drugs 2018, 36, 1060–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meulenbeld, H.J.; Mathijssen, R.H.; Verweij, J.; de Wit, R.; de Jonge, M.J. Danusertib, an Aurora Kinase Inhibitor. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2012, 21, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meulenbeld, H.J.; Bleuse, J.P.; Vinci, E.M.; Raymond, E.; Vitali, G.; Santoro, A.; Dogliotti, L.; Berardi, R.; Cappuzzo, F.; Tagawa, S.T.; et al. Randomized Phase II Study of Danusertib in Patients with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer after Docetaxel Failure. BJU Int. 2013, 111, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, R.B.; Jones, S.F.; Aggarwal, C.; von Mehren, M.; Cheng, J.; Spigel, D.R.; Greco, F.A.; Mariani, M.; Rocchetti, M.; Ceruti, R.; et al. A Phase I Dose-Escalation Study of Danusertib (PHA-739358) Administered as a 24-Hour Infusion With and Without G-CSF in a 14-Day Cycle in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 6694–6701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borthakur, G.; Dombret, H.; Schafhausen, P.; Brummendorf, T.H.; Boissel, N.; Jabbour, E.; Mariani, M.; Capolongo, L.; Carpinelli, P.; Davite, C.; et al. A Phase I Study of Danusertib (PHA-739358) in Adult Patients with Accelerated or Blastic Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia and Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Resistant or Intolerant to Imatinib and/or Other Second Generation c-ABL Therapy. Haematologica 2015, 100, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steeghs, N.; Eskens, F.A.L.M.; Gelderblom, H.; Verweij, J.; Nortier, J.W.R.; Ouwerkerk, J.; van Noort, C.; Mariani, M.; Spinelli, R.; Carpinelli, P.; et al. Phase I Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Study of the Aurora Kinase Inhibitor Danusertib in Patients with Advanced or Metastatic Solid Tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5094–5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phadke, M.S.; Sini, P.; Smalley, K.S.M. The Novel ATP-Competitive MEK/Aurora Kinase Inhibitor BI-847325 Overcomes Acquired BRAF Inhibitor Resistance through Suppression of Mcl-1 and MEK Expression. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöffski, P.; Aftimos, P.; Dumez, H.; Deleporte, A.; De Block, K.; Costermans, J.; Billiet, M.; Meeus, M.-A.; Lee, C.; Schnell, D.; et al. A Phase I Study of Two Dosing Schedules of Oral BI 847325 in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2016, 77, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, E.A.; Bebbington, D.; Moore, J.; Rasmussen, R.K.; Ajose-Adeogun, A.O.; Nakayama, T.; Graham, J.A.; Demur, C.; Hercend, T.; Diu-Hercend, A.; et al. VX-680, a Potent and Selective Small-Molecule Inhibitor of the Aurora Kinases, Suppresses Tumor Growth in Vivo. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traynor, A.M.; Hewitt, M.; Liu, G.; Flaherty, K.T.; Clark, J.; Freedman, S.J.; Scott, B.B.; Leighton, A.M.; Watson, P.A.; Zhao, B.; et al. Phase I Dose Escalation Study of MK-0457, a Novel Aurora Kinase Inhibitor, in Adult Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2011, 67, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giles, F.J.; Swords, R.T.; Nagler, A.; Hochhaus, A.; Ottmann, O.G.; Rizzieri, D.A.; Talpaz, M.; Clark, J.; Watson, P.; Xiao, A.; et al. MK-0457, an Aurora Kinase and BCR–ABL Inhibitor, Is Active in Patients with BCR–ABL T315I Leukemia. Leukemia 2013, 27, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seymour, J.F.; Kim, D.W.; Rubin, E.; Haregewoin, A.; Clark, J.; Watson, P.; Hughes, T.; Dufva, I.; Jimenez, J.L.; Mahon, F.-X.; et al. A Phase 2 Study of MK-0457 in Patients with BCR-ABL T315I Mutant Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia and Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood Cancer J. 2014, 4, e238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürtler, U.; Tontsch-Grunt, U.; Jarvis, M.; Zahn, S.K.; Boehmelt, G.; Quant, J.; Adolf, G.R.; Solca, F. Effect of BI 811283, a Novel Inhibitor of Aurora B Kinase, on Tumor Senescence and Apoptosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, e13632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döhner, H.; Müller-Tidow, C.; Lübbert, M.; Fiedler, W.; Krämer, A.; Westermann, J.; Bug, G.; Schlenk, R.F.; Krug, U.; Goeldner, R.-G.; et al. A Phase I Trial Investigating the Aurora B Kinase Inhibitor BI 811283 in Combination with Cytarabine in Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 185, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mross, K.; Richly, H.; Frost, A.; Scharr, D.; Nokay, B.; Graeser, R.; Lee, C.; Hilbert, J.; Goeldner, R.-G.; Fietz, O.; et al. A Phase I Study of BI 811283, an Aurora B Kinase Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2016, 78, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, S.; Berdini, V.; Boulstridge, J.A.; Carr, M.G.; Cross, D.M.; Curry, J.; Devine, L.A.; Early, T.R.; Fazal, L.; Gill, A.L.; et al. Fragment-Based Discovery of the Pyrazol-4-Yl Urea (AT9283), a Multitargeted Kinase Inhibitor with Potent Aurora Kinase Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, A.E.; Murugesan, A.; DiPasquale, A.M.; Kouroukis, T.; Sandhu, I.; Kukreti, V.; Bahlis, N.J.; Lategan, J.; Reece, D.E.; Lyons, J.F.; et al. A Phase II Study of AT9283, an Aurora Kinase Inhibitor, in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma: NCIC Clinical Trials Group IND.191. Leuk. Lymphoma 2016, 57, 1463–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkenau, H.-T.; Plummer, R.; Molife, L.R.; Olmos, D.; Yap, T.A.; Squires, M.; Lewis, S.; Lock, V.; Yule, M.; Lyons, J.; et al. A Phase I Dose Escalation Study of AT9283, a Small Molecule Inhibitor of Aurora Kinases, in Patients with Advanced Solid Malignancies. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foran, J.; Ravandi, F.; Wierda, W.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Verstovsek, S.; Kadia, T.; Burger, J.; Yule, M.; Langford, G.; Lyons, J.; et al. A Phase I and Pharmacodynamic Study of AT9283, a Small-Molecule Inhibitor of Aurora Kinases in Patients With Relapsed/Refractory Leukemia or Myelofibrosis. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2014, 14, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vormoor, B.; Veal, G.; Griffin, M.; Boddy, A.; Irving, J.; Minto, L.; Case, M.; Banerji, U.; Swales, K.; Tall, J.; et al. A Phase I/II Trial of AT9283, a Selective Inhibitor of Aurora Kinase in Children with Relapsed or Refractory Acute Leukemia: Challenges to Run Early Phase Clinical Trials for Children with Leukemia: V Ormoor et al. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2016, 64, e26351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, L.; Marshall, L.V.; Pearson, A.D.J.; Morland, B.; Elliott, M.; Campbell-Hewson, Q.; Makin, G.; Halford, S.E.R.; Acton, G.; Ross, P.; et al. A Phase I Trial of AT9283 (a Selective Inhibitor of Aurora Kinases) in Children and Adolescents with Solid Tumors: A Cancer Research UK Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, M.G.; Ecsedy, J.A.; Meetze, K.A.; Balani, S.K.; Burenkova, O.; Chen, W.; Galvin, K.M.; Hoar, K.M.; Huck, J.J.; LeRoy, P.J.; et al. Antitumor Activity of MLN8054, an Orally Active Small-Molecule Inhibitor of Aurora A Kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 4106–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dees, E.C.; Infante, J.R.; Cohen, R.B.; O’Neil, B.H.; Jones, S.; von Mehren, M.; Danaee, H.; Lee, Y.; Ecsedy, J.; Manfredi, M.; et al. Phase 1 Study of MLN8054, a Selective Inhibitor of Aurora A Kinase in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2011, 67, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macarulla, T.; Cervantes, A.; Elez, E.; Rodríguez-Braun, E.; Baselga, J.; Roselló, S.; Sala, G.; Blasco, I.; Danaee, H.; Lee, Y.; et al. Phase I Study of the Selective Aurora A Kinase Inhibitor MLN8054 in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors: Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 2844–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtin, M.L.; Heyman, R.; Frey, R.R.; Soni, N.B.; Marcotte, P.A.; Pease, L.J.; Glaser, K.B.; Magoc, T.J.; Tapang, P.; Albert, D.H.; et al. Abstract C202: Discovery and Initial Characterization of the Clinical Compound ABT-348, a Potent Inhibitor of the VEGF, PDGF, and Aurora Kinase Families. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, C202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitland, M.L.; Sharma, M.; Zhao, B.; McKee, M.D.; Karovic, S.; Thomeas, V.; McIver, M.; Yang, H.; Piha-Paul, S.A.; Falchook, G.S.; et al. Pharmaco-Kinetics/Dynamics (PK/PD) Evaluation and Individual Patient Cross-over Studies with Growth Trajectory Assessment to Adaptively Develop Ilorasertib. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Manero, G.; Tibes, R.; Kadia, T.; Kantarjian, H.; Arellano, M.; Knight, E.A.; Xiong, H.; Qin, Q.; Munasinghe, W.; Roberts-Rapp, L.; et al. Phase 1 Dose Escalation Trial of Ilorasertib, a Dual Aurora/VEGF Receptor Kinase Inhibitor, in Patients with Hematologic Malignancies. Investig. New Drugs 2015, 33, 870–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitland, M.L.; Piha-Paul, S.; Falchook, G.; Kurzrock, R.; Nguyen, L.; Janisch, L.; Karovic, S.; McKee, M.; Hoening, E.; Wong, S.; et al. Clinical Pharmacodynamic/Exposure Characterisation of the Multikinase Inhibitor Ilorasertib (ABT-348) in a Phase 1 Dose-Escalation Trial. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 118, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, P.; Shi, L.; Matuszkiewicz, J.; Balakrishna, D.; Hoshino, T.; Zhang, L.; Elliott, S.; Fabrey, R.; Lee, B.; Halkowycz, P.; et al. Biological Characterization of TAK-901, an Investigational, Novel, Multitargeted Aurora B Kinase Inhibitor. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Shan, S.; Li, Z.-B.; Xin, L.-J.; Pan, D.-S.; Yang, Q.-J.; Liu, Y.-P.; Yue, X.-P.; Liu, X.-R.; Gao, J.-Z.; et al. CS2164, a Novel Multi-Target Inhibitor against Tumor Angiogenesis, Mitosis and Chronic Inflammation with Anti-Tumor Potency. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Yang, L.; Hao, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ning, Z.; Shi, Y. Phase I Dose-Escalation Study of Chiauranib, a Novel Angiogenic, Mitotic, and Chronic Inflammation Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardwicke, M.A.; Oleykowski, C.A.; Plant, R.; Wang, J.; Liao, Q.; Moss, K.; Newlander, K.; Adams, J.L.; Dhanak, D.; Yang, J.; et al. GSK1070916, a Potent Aurora B/C Kinase Inhibitor with Broad Antitumor Activity in Tissue Culture Cells and Human Tumor Xenograft Models. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 1808–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Gao, X.; Zhong, X.; Zhang, N.; Wang, R.; Zhang, H.; Pan, T.; Liu, X.; Yao, Y.; Wu, Q.; et al. Selective Inhibition of Aurora A and B Kinases Effectively Induces Cell Cycle Arrest in t(8;21) Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 117, 109113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortlock, A.A.; Foote, K.M.; Heron, N.M.; Jung, F.H.; Pasquet, G.; Lohmann, J.-J.M.; Warin, N.; Renaud, F.; De Savi, C.; Roberts, N.J.; et al. Discovery, Synthesis, and in Vivo Activity of a New Class of Pyrazoloquinazolines as Selective Inhibitors of Aurora B Kinase. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 2213–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollareddy, M.; Zheleva, D.; Džubák, P.; Srovnal, J.; Radová, L.; Doležal, D.; Koudelakova, V.; Brahmkshatriya, P.; Lepšík, M.; Hobza, P.; et al. Identification and Characterization of Drug Resistance Mechanisms in Cancer Cells against Aurora Kinase Inhibitors CYC116 and ZM447439. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.H.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, H.S.; Nam, S.T.; Lee, D.; Lee, M.B.; Min, K.Y.; Koo, J.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, Y.M.; et al. An Anti-Cancer Drug Candidate CYC116 Suppresses Type I Hypersensitive Immune Responses through the Inhibition of Fyn Kinase in Mast Cells. Biomol. Ther. 2019, 27, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Midgley, C.A.; Scaërou, F.; Grabarek, J.B.; Griffiths, G.; Jackson, W.; Kontopidis, G.; McClue, S.J.; McInnes, C.; Meades, C.; et al. Discovery of N-Phenyl-4-(Thiazol-5-Yl)Pyrimidin-2-Amine Aurora Kinase Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 4367–4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbitrario, J.P.; Belmont, B.J.; Evanchik, M.J.; Flanagan, W.M.; Fucini, R.V.; Hansen, S.K.; Harris, S.O.; Hashash, A.; Hoch, U.; Hogan, J.N.; et al. SNS-314, a Pan-Aurora Kinase Inhibitor, Shows Potent Anti-Tumor Activity and Dosing Flexibility in Vivo. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2010, 65, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oslob, J.D.; Romanowski, M.J.; Allen, D.A.; Baskaran, S.; Bui, M.; Elling, R.A.; Flanagan, W.M.; Fung, A.D.; Hanan, E.J.; Harris, S.; et al. Discovery of a Potent and Selective Aurora Kinase Inhibitor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 4880–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, K.S.; Andrade, A.F.; Silveira, V.S.; Marco Antonio, D.S.; Vasconcelos, E.J.R.; Antonini, S.R.R.; Tone, L.G.; Scrideli, C.A. The Aurora Kinase Inhibitor AMG 900 Increases Apoptosis and Induces Chemosensitivity to Anticancer Drugs in the NCI-H295 Adrenocortical Carcinoma Cell Line. Anticancer Drugs 2017, 28, 634–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bush, T.L.; Payton, M.; Heller, S.; Chung, G.; Hanestad, K.; Rottman, J.B.; Loberg, R.; Friberg, G.; Kendall, R.L.; Saffran, D.; et al. AMG 900, a Small-Molecule Inhibitor of Aurora Kinases, Potentiates the Activity of Microtubule-Targeting Agents in Human Metastatic Breast Cancer Models. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 2356–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpinelli, P.; Ceruti, R.; Giorgini, M.L.; Cappella, P.; Gianellini, L.; Croci, V.; Degrassi, A.; Texido, G.; Rocchetti, M.; Vianello, P.; et al. PHA-739358, a Potent Inhibitor of Aurora Kinases with a Selective Target Inhibition Profile Relevant to Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 3158–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sini, P.; Gürtler, U.; Zahn, S.K.; Baumann, C.; Rudolph, D.; Baumgartinger, R.; Strauss, E.; Haslinger, C.; Tontsch-Grunt, U.; Waizenegger, I.C.; et al. Pharmacological Profile of BI 847325, an Orally Bioavailable, ATP-Competitive Inhibitor of MEK and Aurora Kinases. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 2388–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.-F.; Luo, S.-K.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Xu, D.-R.; Wang, L.-H.; Yan, M.; Wang, X.-R.; Wan, X.-B.; Zheng, F.-M.; et al. Aurora Kinase Inhibitory VX-680 Increases Bax/Bcl-2 Ratio and Induces Apoptosis in Aurora-A-High Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood 2008, 111, 2854–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shionome, Y.; Yan, L.; Liu, S.; Saeki, T.; Ouchi, T. Integrity of P53 Associated Pathways Determines Induction of Apoptosis of Tumor Cells Resistant to Aurora-A Kinase Inhibitors. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tontsch-Grunt, U.; Gürtler, U.; Zahn, S.K.; Boehmelt, G.; Jarvis, M.; Adolf, G.R.; Solca, F. Abstract 1080: Molecular and Cellular Pharmacology of BI 811283, a Potent Inhibitor of Aurora B Kinase. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Liu, X.; Cooke, L.S.; Persky, D.O.; Miller, T.P.; Squires, M.; Mahadevan, D. AT9283, a Novel Aurora Kinase Inhibitor, Suppresses Tumor Growth in Aggressive B-Cell Lymphomas. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 130, 2997–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, M.G.; Ecsedy, J.A.; Chakravarty, A.; Silverman, L.; Zhang, M.; Hoar, K.M.; Stroud, S.G.; Chen, W.; Shinde, V.; Huck, J.J.; et al. Characterization of Alisertib (MLN8237), an Investigational Small-Molecule Inhibitor of Aurora A Kinase Using Novel In Vivo Pharmacodynamic Assays. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 7614–7624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Görgün, G.; Calabrese, E.; Hideshima, T.; Ecsedy, J.; Perrone, G.; Mani, M.; Ikeda, H.; Bianchi, G.; Hu, Y.; Cirstea, D.; et al. A Novel Aurora-A Kinase Inhibitor MLN8237 Induces Cytotoxicity and Cell-Cycle Arrest in Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2010, 115, 5202–5213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carol, H.; Boehm, I.; Reynolds, C.P.; Kang, M.H.; Maris, J.M.; Morton, C.L.; Gorlick, R.; Kolb, E.A.; Keir, S.T.; Wu, J.; et al. Efficacy and Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Evaluation of the Aurora Kinase A Inhibitor MLN8237 against Preclinical Models of Pediatric Cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2011, 68, 1291–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaser, K.B.; Li, J.; Marcotte, P.A.; Magoc, T.J.; Guo, J.; Reuter, D.R.; Tapang, P.; Wei, R.-Q.; Pease, L.J.; Bui, M.H.; et al. Preclinical Characterization of ABT-348, a Kinase Inhibitor Targeting the Aurora, Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor/Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Receptor, and Src Kinase Families. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 343, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-C.; Kaleta, L.; Rodriguez, L.E.; Ellis, P.A.; Bukofzer, G.; Clarin, J.; Schlessinger, S.; Li, J.; Glaser, K.; Michaelides, M.; et al. Abstract 858: Potent in Vivo Activity of the Aurora Kinase Inhibitor ABT-348 in Human Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Myelodysplastic Syndrome Xenograft Models. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, P.; Shi, L.; Matuszkiewicz, J.; Balakrishna, D.; Elliott, S.; Halkowycz, P.; Feher, V.; Paraselli, B.; Grimshaw, C.; Sang, B.; et al. Abstract B270: Profiling the Biochemical and Cellular Activities of TAK-901, a Potent Multi-targeted Aurora-B Kinase Inhibitor. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, B270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullinane, C.; Waldeck, K.L.; Binns, D.; Bogatyreva, E.; Bradley, D.P.; de Jong, R.; McArthur, G.A.; Hicks, R.J. Preclinical FLT-PET and FDG-PET Imaging of Tumor Response to the Multi-Targeted Aurora B Kinase Inhibitor, TAK-901. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2014, 41, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Shi, Y.; Chen, K.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Xie, S.; Zhao, J.; Luo, Y.; Fang, Z.; Fan, Y.; et al. CS2164 Exerts an Antitumor Effect against Human Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphomas in Vitro and in Vivo. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 369, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Zhao, H.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, J.; Shi, Y.; Yu, L.; Fang, Z.; Xu, B. CS2164 Suppresses Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cell Growth via Inhibiting VEGFR2 Signaling in Preclinical Models. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 853, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Fu, C.; Kong, Y.; Pan, D.; Wang, Y.; Huang, S.; Li, Z.; Ning, Z.; Lu, X.; Shan, S.; et al. Antitumor and Immunomodulatory Effects of a Novel Multitarget Inhibitor, CS2164, in Mouse Hepatocellular Carcinoma Models. Anticancer Drugs 2019, 30, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditchfield, C.; Johnson, V.L.; Tighe, A.; Ellston, R.; Haworth, C.; Johnson, T.; Mortlock, A.; Keen, N.; Taylor, S.S. Aurora B Couples Chromosome Alignment with Anaphase by Targeting BubR1, Mad2, and Cenp-E to Kinetochores. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 161, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soncini, C.; Carpinelli, P.; Gianellini, L.; Fancelli, D.; Vianello, P.; Rusconi, L.; Storici, P.; Zugnoni, P.; Pesenti, E.; Croci, V.; et al. PHA-680632, a Novel Aurora Kinase Inhibitor with Potent Antitumoral Activity. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 4080–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, F.; Sun, C.; Perumal, M.; Nguyen, Q.-D.; Bavetsias, V.; McDonald, E.; Martins, V.; Wilsher, N.; Raynaud, F.; Valenti, M.; et al. Characterization of CCT129202, a Novel Aurora Kinase Inhibitor and in Vivo Quantification of Biological Activity. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, A239. [Google Scholar]
- Faisal, A.; Vaughan, L.; Bavetsias, V.; Sun, C.; Atrash, B.; Avery, S.; Jamin, Y.; Robinson, S.P.; Workman, P.; Blagg, J.; et al. The Aurora Kinase Inhibitor CCT137690 Downregulates MYCN and Sensitizes MYCN-Amplified Neuroblastoma In Vivo. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 2115–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Fu, W.; Du, L.; Yao, H.; Hua, Z.; Li, J.; Lin, Z. Discovery of a Novel Aurora B Inhibitor GSK650394 with Potent Anticancer and Anti-Aspergillus Fumigatus Dual Efficacies in Vitro. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2022, 37, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Alise, A.M.; Amabile, G.; Iovino, M.; Di Giorgio, F.P.; Bartiromo, M.; Sessa, F.; Villa, F.; Musacchio, A.; Cortese, R. Reversine, a Novel Aurora Kinases Inhibitor, Inhibits Colony Formation of Human Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 1140–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauf, S.; Cole, R.W.; LaTerra, S.; Zimmer, C.; Schnapp, G.; Walter, R.; Heckel, A.; van Meel, J.; Rieder, C.L.; Peters, J.-M. The Small Molecule Hesperadin Reveals a Role for Aurora B in Correcting Kinetochore-Microtubule Attachment and in Maintaining the Spindle Assembly Checkpoint. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 161, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavanti, E.; Sero, V.; Vella, S.; Fanelli, M.; Michelacci, F.; Landuzzi, L.; Magagnoli, G.; Versteeg, R.; Picci, P.; Hattinger, C.M.; et al. Preclinical Validation of Aurora Kinases-Targeting Drugs in Osteosarcoma. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 2607–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieva, I.; Koychev, D.; Wang, Y.; Holstein, J.; Hopfenmüller, W.; Zeitz, M.; Grabowski, P. ZM447439, a Novel Promising Aurora Kinase Inhibitor, Provokes Antiproliferative and Proapoptotic Effects Alone and in Combination with Bio- and Chemotherapeutic Agents in Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor Cell Lines. Neuroendocrinology 2009, 91, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Zhang, P.; Frascogna, V.; Lecluse, Y.; Auperin, A.; Bourhis, J.; Deutsch, E. Enhancement of Radiation Response by Inhibition of Aurora-A Kinase Using SiRNA or a Selective Aurora Kinase Inhibitor PHA680632 in P53-Deficient Cancer Cells. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 97, 1664–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, F.; Sun, C.; Perumal, M.; Nguyen, Q.-D.; Bavetsias, V.; McDonald, E.; Martins, V.; Wilsher, N.E.; Raynaud, F.I.; Valenti, M.; et al. Mechanism of Action of the Aurora Kinase Inhibitor CCT129202 and in Vivo Quantification of Biological Activity. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 3147–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Liang, H.; Yang, H.; Zhou, K.; Xu, L.; Liu, J.; Lai, B.; Song, L.; Luo, H.; Peng, J.; et al. LincRNa-P21: Function and Mechanism in Cancer. Med. Oncol. 2017, 34, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bavetsias, V.; Large, J.M.; Sun, C.; Bouloc, N.; Kosmopoulou, M.; Matteucci, M.; Wilsher, N.E.; Martins, V.; Reynisson, J.; Atrash, B.; et al. Imidazo[4,5-b]Pyridine Derivatives As Inhibitors of Aurora Kinases: Lead Optimization Studies toward the Identification of an Orally Bioavailable Preclinical Development Candidate. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 5213–5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherk, A.B.; Frigo, D.E.; Schnackenberg, C.G.; Bray, J.D.; Laping, N.J.; Trizna, W.; Hammond, M.; Patterson, J.R.; Thompson, S.K.; Kazmin, D.; et al. Development of a Small Molecule Serum and Glucocorticoid-Regulated Kinase 1 Antagonist and Its Evaluation as a Prostate Cancer Therapeutic. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 7475–7483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Lan, C.; Zhou, J.; Fu, W.; Long, X.; An, Y.; Jiao, G.; Wang, K.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; et al. Development of a New Analog of SGK1 Inhibitor and Its Evaluation as a Therapeutic Molecule of Colorectal Cancer. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 2256–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Wang, H.; Guo, K.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, C.; Chen, L.; Lin, J. Reversine, a Substituted Purine, Exerts an Inhibitive Effect on Human Renal Carcinoma Cells via Induction of Cell Apoptosis and Polyploidy. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiruma, Y.; Koch, A.; Dharadhar, S.; Joosten, R.P.; Perrakis, A. Structural Basis of Reversine Selectivity in Inhibiting Mps1 More Potently than Aurora B Kinase. Proteins 2016, 84, 1761–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.-C.; Lee, Y.-R.; Liao, J.-D.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Chen, P.-T.; Tseng, Y.-S. Reversine Induced Multinucleated Cells, Cell Apoptosis and Autophagy in Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Huang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Weng, J.; Zhang, S.; Gu, W. Relation of AURKB Over-Expression to Low Survival Rate in BCRA and Reversine-Modulated Aurora B Kinase in Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessa, F.; Mapelli, M.; Ciferri, C.; Tarricone, C.; Areces, L.B.; Schneider, T.R.; Stukenberg, P.T.; Musacchio, A. Mechanism of Aurora B Activation by INCENP and Inhibition by Hesperadin. Mol. Cell 2005, 18, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladygina, N.G.; Latsis, R.V.; Yen, T. Effect of the pharmacological agent hesperadin on breast and prostate tumor cultured cells. Biomeditsinskaia Khimiia 2005, 51, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jetton, N.; Rothberg, K.G.; Hubbard, J.G.; Wise, J.; Li, Y.; Ball, H.L.; Ruben, L. The Cell Cycle as a Therapeutic Target against Trypanosoma Brucei: Hesperadin Inhibits Aurora Kinase-1 and Blocks Mitotic Progression in Bloodstream Forms. Mol. Microbiol. 2009, 72, 442–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xingyu, Z.; Peijie, M.; Dan, P.; Youg, W.; Daojun, W.; Xinzheng, C.; Xijun, Z.; Yangrong, S. Quercetin Suppresses Lung Cancer Growth by Targeting Aurora B Kinase. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 3156–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, J.S.; Ho, A.L.; Schwartz, G.K. The Induction of Polyploidy or Apoptosis by the Aurora A Kinase Inhibitor MK8745 Is P53-Dependent. Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girdler, F.; Gascoigne, K.E.; Eyers, P.A.; Hartmuth, S.; Crafter, C.; Foote, K.M.; Keen, N.J.; Taylor, S.S. Validating Aurora B as an Anti-Cancer Drug Target. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 3664–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willems, E.; Dedobbeleer, M.; Digregorio, M.; Lombard, A.; Lumapat, P.N.; Rogister, B. The Functional Diversity of Aurora Kinases: A Comprehensive Review. Cell Div. 2018, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tien, A.-C.; Lin, M.-H.; Su, L.-J.; Hong, Y.-R.; Cheng, T.-S.; Lee, Y.-C.G.; Lin, W.-J.; Still, I.H.; Huang, C.-Y.F. Identification of the Substrates and Interaction Proteins of Aurora Kinases from a Protein-Protein Interaction Model. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2004, 3, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyers, P.A.; Churchill, M.E.A.; Maller, J.L. The Aurora A and Aurora B Protein Kinases: A Single Amino Acid Difference Controls Intrinsic Activity and Activation by TPX2. Cell Cycle 2005, 4, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheetham, G.M.T.; Knegtel, R.M.A.; Coll, J.T.; Renwick, S.B.; Swenson, L.; Weber, P.; Lippke, J.A.; Austen, D.A. Crystal Structure of Aurora-2, an Oncogenic Serine/Threonine Kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 42419–42422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruff, E.F.; Muretta, J.M.; Thompson, A.R.; Lake, E.W.; Cyphers, S.; Albanese, S.K.; Hanson, S.M.; Behr, J.M.; Thomas, D.D.; Chodera, J.D.; et al. A Dynamic Mechanism for Allosteric Activation of Aurora Kinase A by Activation Loop Phosphorylation. eLife 2018, 7, e32766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorba, A.; Buosi, V.; Kutter, S.; Kern, N.; Pontiggia, F.; Cho, Y.-J.; Kern, D. Molecular Mechanism of Aurora A Kinase Autophosphorylation and Its Allosteric Activation by TPX2. eLife 2014, 3, e02667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kettenbach, A.N.; Schweppe, D.K.; Faherty, B.K.; Pechenick, D.; Pletnev, A.A.; Gerber, S.A. Quantitative Phosphoproteomics Identifies Substrates and Functional Modules of Aurora and Polo-Like Kinase Activities in Mitotic Cells. Sci. Signal. 2011, 4, rs5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, Y.W.; Dou, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yao, X.B. Function and Regulation of Aurora/Ipl1p Kinase Family in Cell Division. Cell Res. 2003, 13, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katayama, H.; Brinkley, W.R.; Sen, S. The Aurora Kinases: Role in Cell Transformation and Tumorigenesis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003, 22, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.R.; Koretke, K.K.; Birkeland, M.L.; Sanseau, P.; Patrick, D.R. Evolutionary Relationships of Aurora Kinases: Implications for Model Organism Studies and the Development of Anti-Cancer Drugs. BMC Evol. Biol. 2004, 4, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolanos-Garcia, V.M. Aurora Kinases. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2005, 37, 1572–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Bian, M.; Liu, J.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, C. A Single Amino Acid Change Converts Aurora-A into Aurora-B-like Kinase in Terms of Partner Specificity and Cellular Function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6939–6944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sessa, F.; Villa, F. Structure of Aurora B-INCENP in Complex with Barasertib Reveals a Potential Transinhibitory Mechanism. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Commun. 2014, 70, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bank, R.P.D. RCSB PDB—4C2V: Aurora B Kinase in Complex with the Specific Inhibitor Barasertib. Available online: https://www.rcsb.org/structure/4C2V (accessed on 17 February 2022).
- Bank, R.P.D. RCSB PDB—5EYK: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF AURORA B IN COMPLEX WITH BI 847325. Available online: https://www.rcsb.org/structure/5EYK (accessed on 28 July 2022).
- Bank, R.P.D. RCSB PDB—4B8M: Aurora B Kinase in Complex with VX-680. Available online: https://www.rcsb.org/structure/4b8m (accessed on 17 February 2022).
- Bank, R.P.D. RCSB PDB—5K3Y: Crystal Structure of AuroraB/INCENP in Complex with BI 811283. Available online: https://www.rcsb.org/structure/5K3Y (accessed on 28 July 2022).
- Bank, R.P.D. RCSB PDB—2VRX: Structure of Aurora B Kinase in Complex with ZM447439. Available online: https://www.rcsb.org/structure/2VRX (accessed on 28 July 2022).
- Bank, R.P.D. RCSB PDB—2VGO: Crystal Structure of Aurora B Kinase in Complex with Reversine Inhibitor. Available online: https://www.rcsb.org/structure/2VGO (accessed on 28 July 2022).
- Bank, R.P.D. RCSB PDB—2BFY: Complex of Aurora-B with INCENP and Hesperadin. Available online: https://www.rcsb.org/structure/2BFY (accessed on 17 February 2022).
- Bank, R.P.D. RCSB PDB—2VGP: Crystal Structure of Aurora B Kinase in Complex with a Aminothiazole Inhibitor. Available online: https://www.rcsb.org/structure/2VGP (accessed on 28 July 2022).
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Cancer Facts & Figures|American Cancer Society. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/global.html (accessed on 31 May 2022).
- Cheung, C.H.A.; Sarvagalla, S.; Lee, J.Y.-C.; Huang, Y.-C.; Coumar, M.S. Aurora Kinase Inhibitor Patents and Agents in Clinical Testing: An Update (2011–2013). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2014, 24, 1021–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falchook, G.S.; Bastida, C.C.; Kurzrock, R. Aurora Kinase Inhibitors in Oncology Clinical Trials: Current State of the Progress. Semin. Oncol. 2015, 42, 832–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Zhou, J.; Xu, F.; Bai, W.; Zhang, W. High Expression of Aurora-B Is Correlated with Poor Prognosis and Drug Resistance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2018, 33, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Cao, H.; Lou, S.; Shao, X.; Lv, W.; Qi, X.; Liu, Y.; Ying, M.; He, Q.; Yang, X. Sequential Treatment with Aurora B Inhibitors Enhances Cisplatin-Mediated Apoptosis via c-Myc. J. Mol. Med. Berl. Ger. 2015, 93, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaelis, M.; Selt, F.; Rothweiler, F.; Löschmann, N.; Nüsse, B.; Dirks, W.G.; Zehner, R.; Cinatl, J., Jr. Aurora Kinases as Targets in Drug-Resistant Neuroblastoma Cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Failes, T.W.; Mitic, G.; Abdel-Halim, H.; Po’uha, S.T.; Liu, M.; Hibbs, D.E.; Kavallaris, M. Evolution of Resistance to Aurora Kinase B Inhibitors in Leukaemia Cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girdler, F.; Sessa, F.; Patercoli, S.; Villa, F.; Musacchio, A.; Taylor, S. Molecular Basis of Drug Resistance in Aurora Kinases. Chem. Biol. 2008, 15, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Smallwood, A.; Yang, J.; Koretke, K.; Nurse, K.; Calamari, A.; Kirkpatrick, R.B.; Lai, Z. Modulation of Kinase-Inhibitor Interactions by Auxiliary Protein Binding: Crystallography Studies on Aurora A Interactions with VX-680 and with TPX2. Protein Sci. Publ. Protein Soc. 2008, 17, 1791–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liu, W.; Cao, Q.; Chen, C.; Chen, Z.; Xu, Z.; Li, W.; Liu, F.; Yao, X. Inhibition of Aurora B by CCT137690 Sensitizes Colorectal Cells to Radiotherapy. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 33, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Leteur, C.; Calderaro, J.; Girdler, F.; Zhang, P.; Frascogna, V.; Varna, M.; Opolon, P.; Castedo, M.; Bourhis, J.; et al. The Aurora B Kinase Inhibitor AZD1152 Sensitizes Cancer Cells to Fractionated Irradiation and Induces Mitotic Catastrophe. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 3172–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Anderson, M.G.; Tucker, L.A.; Shen, Y.; Glaser, K.B.; Shah, O.J. Inhibition of Aurora B Kinase Sensitizes a Subset of Human Glioma Cells to TRAIL Concomitant with Induction of TRAIL-R2. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 498–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sak, A.; Stuschke, M.; Groneberg, M.; Kuebler, D.; Poettgen, C.; Eberhardt, W.E.E. Inhibiting the Aurora B Kinase Potently Suppresses Repopulation During Fractionated Irradiation of Human Lung Cancer Cell Lines. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 84, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Wang, Y.A.; Sun, Y.; Ecsedy, J.; Sun, J.; Li, X.; Wang, P. Inhibition of Aurora A Enhances Radiosensitivity in Selected Lung Cancer Cell Lines. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Compound Name and Structure | In Vitro IC50 | Clinical Trial Remarks | Clinical Trials Identification Number(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
GSK1070916 [38] | A: 490 nM B: 0.38 nM C: 1.5 nM | Phase I—Advanced solid malignancies [39] | NCT01118611 |
AZD1152 (Barasertib) [40]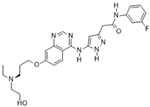 | A: 1359 nM B: 0.37 nM C: n/a | Phase I—Leukemia [41] | NCT00530699 |
| Phase II—Lymphoma [42] | NCT01354392 | ||
| Phase I—Advanced solid malignancies [43] | NCT00338182 | ||
| Phase I—Leukemia [44] | NCT01019161 | ||
| Phase I/II—Leukemia [45] | NCT00497991 | ||
| Phase I—Leukemia [46,47] | NCT00926731 | ||
| Phase II and III—Leukemia [47,48] | NCT00952588 | ||
| Phase I—Advanced solid malignancies [43] | NCT00497679 | ||
| Phase I—Advanced solid malignancies [49] | NCT00497731 | ||
| Phase I and II—Leukemia | NCT03217838 | ||
| Phase II—Small-cell lung cancer | NCT03366675 | ||
| Phase I—Advanced solid malignancies [50] | NCT02579226 | ||
| Phase II—Small-cell lung cancer | NCT04525391 | ||
| Phase II—Small-cell lung cancer | NCT04745689 | ||
| Phase I and II—Leukemia | NCT03217838 | ||
CYC116 [51]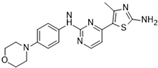 | A: 19 nM B: 69 nM C: 9.2 nM | Phase I—Advanced solid malignancies | NCT00560716 |
SNS-314 [37]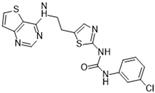 | A: 9 nM B: 31 nM C: 3 nM | Phase I—Advanced solid malignancies | NCT00519662 |
AMG 900 [52] | A: 5 nM B: 4 nM C: 1 nM | Phase I—Acute myeloid leukemia [53] | NCT01380756 |
| Phase I—Advanced solid malignancies [54] | NCT00858377 | ||
PHA-739358 (Danusertib) [55]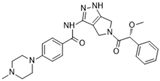 | A: 13 nM B: 79 nM C: 61 nM | Phase II—Multiple myeloma | NCT00872300 |
| Phase II—Hormone refractory prostate cancer [56] | NCT00766324 | ||
| Phase II—Leukemia | NCT00335868 | ||
| Phase I—Advanced solid malignancies [57] | n/a | ||
| Phase I—Leukemia [58] | n/a | ||
| Phase I—Advanced solid malignancies [59] | n/a | ||
BI 847325 [60]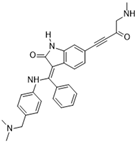 | A: 25 nM B: 3 nM C: 15 nM | Phase I—Advanced solid malignancies [61] | NCT01324830 |
VX-680 (MK-0457) [62]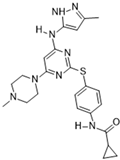 | A: 0.6 nM B: 18 nM C: 4.6 nM | Phase I—Advanced solid malignancies [63] | NCT02532868 |
| Phase I and II—Advanced colorectal and solid malignancies | NCT00099346 | ||
| Phase I and II—Leukemia [64] | NCT00111683 | ||
| Phase II—Leukemia [65] | NCT00405054 | ||
| Phase II—Advanced non-small cell lung cancer | NCT00290550 | ||
| Phase I—Leukemia | NCT00500006 | ||
BI 811283 [66]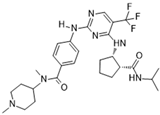 | A: n/a B: 9 nM C: n/a | Phase I and II—Leukemia [67] | NCT00632749 |
| Phase I—Advanced solid malignancies [68] | NCT00701324 | ||
AT9283 [69]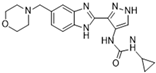 | A: 3 nM B: 3 nM C: <10 nM | Phase II—Multiple myeloma [70] | NCT01145989 |
| Phase I—Advanced solid malignancies and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma [71] | NCT00443976 | ||
| Phase I and II—Leukemia [72] | NCT00522990 | ||
| Phase I—Leukemia [73] | NCT01431664 | ||
| Phase I—Refractory solid malignancies [74] | NCT00985868 | ||
MLN8237 (Alisertib) [75]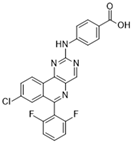 | A: 1.2 nM B: 396.5 nM C: n/a | Phase I—Advanced solid malignancies [76] | NCT00249301 |
| Phase I—Advanced solid malignancies [77] | NCT00652158 | ||
ABT-348 (Ilorasertib) [78]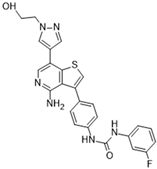 | A: 120 nM B: 7 nM C: 1 nM | Phase I—Advanced solid malignancies [79] | NCT02540876 |
| Phase II—Advanced solid malignancies | NCT02478320 | ||
| Phase I—Advanced hematologic malignancies [80] | NCT01110473 | ||
| Phase I—Advanced solid malignancies [81] | NCT01110486 | ||
TAK-901 [82] | A: 21 nM B: 15 nM C: n/a | Phase I—Advanced hematologic malignancies | NCT00807677 |
| Phase I—Advanced solid malignancies and lymphoma | NCT00935844 | ||
CS2164 (Chiauranib) [83]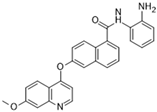 | A: n/a B: 9 nM C: n/a | Phase I—Advanced solid malignancies [84] | NCT02122809 |
| Phase I and II—Small-cell lung cancer | NCT05271292 | ||
| Phase I and II—Hepatocellular carcinoma | NCT03245190 | ||
| Phase I and II—Ovarian cancer | NCT03166891 | ||
| Phase I—Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma | NCT03074825 | ||
| Phase III—Ovarian cancer | NCT04921527 | ||
| Phase III—Small-cell lung cancer | NCT04830813 | ||
| Phase I and II—Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma | NCT03974243 | ||
| Phase II—Ovarian cancer | NCT03901118 | ||
| Phase I—Small-cell lung cancer | NCT03216343 |
| Compound Name and Structure | In Vitro IC50 | Preclinical In Vivo and In Vitro Activity |
|---|---|---|
SP-96 [32]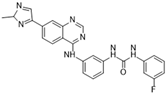 | A: n/a B: 0.316 nM C: n/a |
|
ZM447439 [111]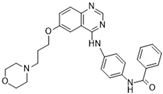 | A: 110 nM B: 130 nM C: n/a |
|
PHA-680632 [112]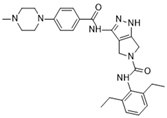 | A: 27 nM B: 135 nM C: 120 nM |
|
CCT129202 [113]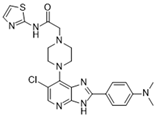 | A: 42 nM B: 198 nM C: 227 nM |
|
CCT137690 [114] | A: 15 nM B: 25 nM C: 19 nM |
|
GSK650394 [115]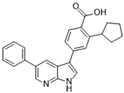 | A: n/a B: 5.28 nM C: n/a |
|
Reversine [116]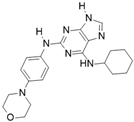 | A: 400 nM B: 500 nM C: 400 nM |
|
Hesperadin [117]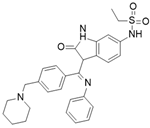 | A: n/a B: 250 nM C: n/a |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kovacs, A.H.; Zhao, D.; Hou, J. Aurora B Inhibitors as Cancer Therapeutics. Molecules 2023, 28, 3385. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083385
Kovacs AH, Zhao D, Hou J. Aurora B Inhibitors as Cancer Therapeutics. Molecules. 2023; 28(8):3385. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083385
Chicago/Turabian StyleKovacs, Antal H., Dong Zhao, and Jinqiang Hou. 2023. "Aurora B Inhibitors as Cancer Therapeutics" Molecules 28, no. 8: 3385. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083385
APA StyleKovacs, A. H., Zhao, D., & Hou, J. (2023). Aurora B Inhibitors as Cancer Therapeutics. Molecules, 28(8), 3385. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083385







