Co-Doped CeO2/Activated C Nanocomposite Functionalized with Ionic Liquid for Colorimetric Biosensing of H2O2 via Peroxidase Mimicking
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of Cobalt-Doped Cerium Oxide/Activated Carbon Nanocomposite
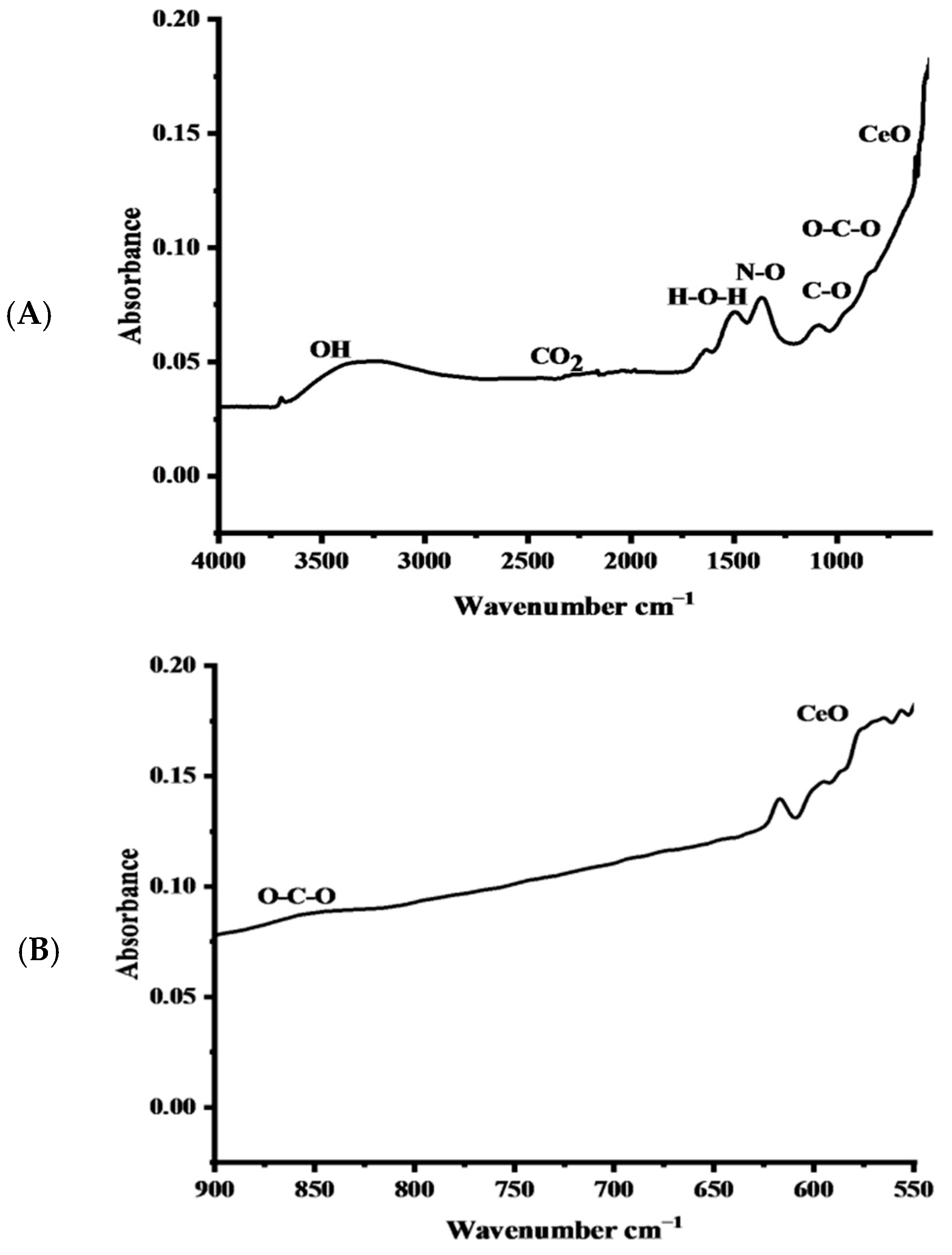
2.1.1. FTIR Spectra of the Nanocomposite
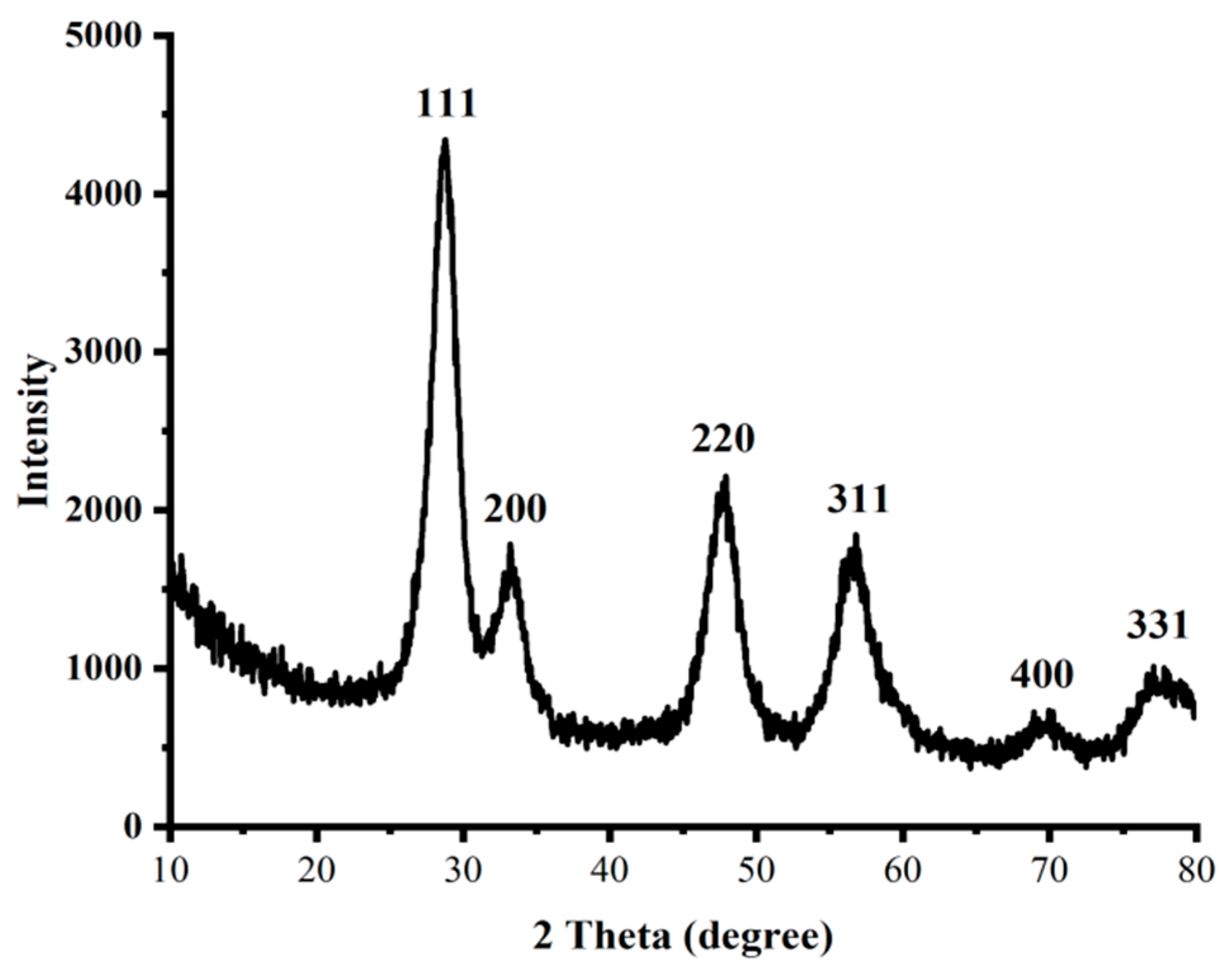
2.1.2. XRD Pattern of Synthesized Nanostructures
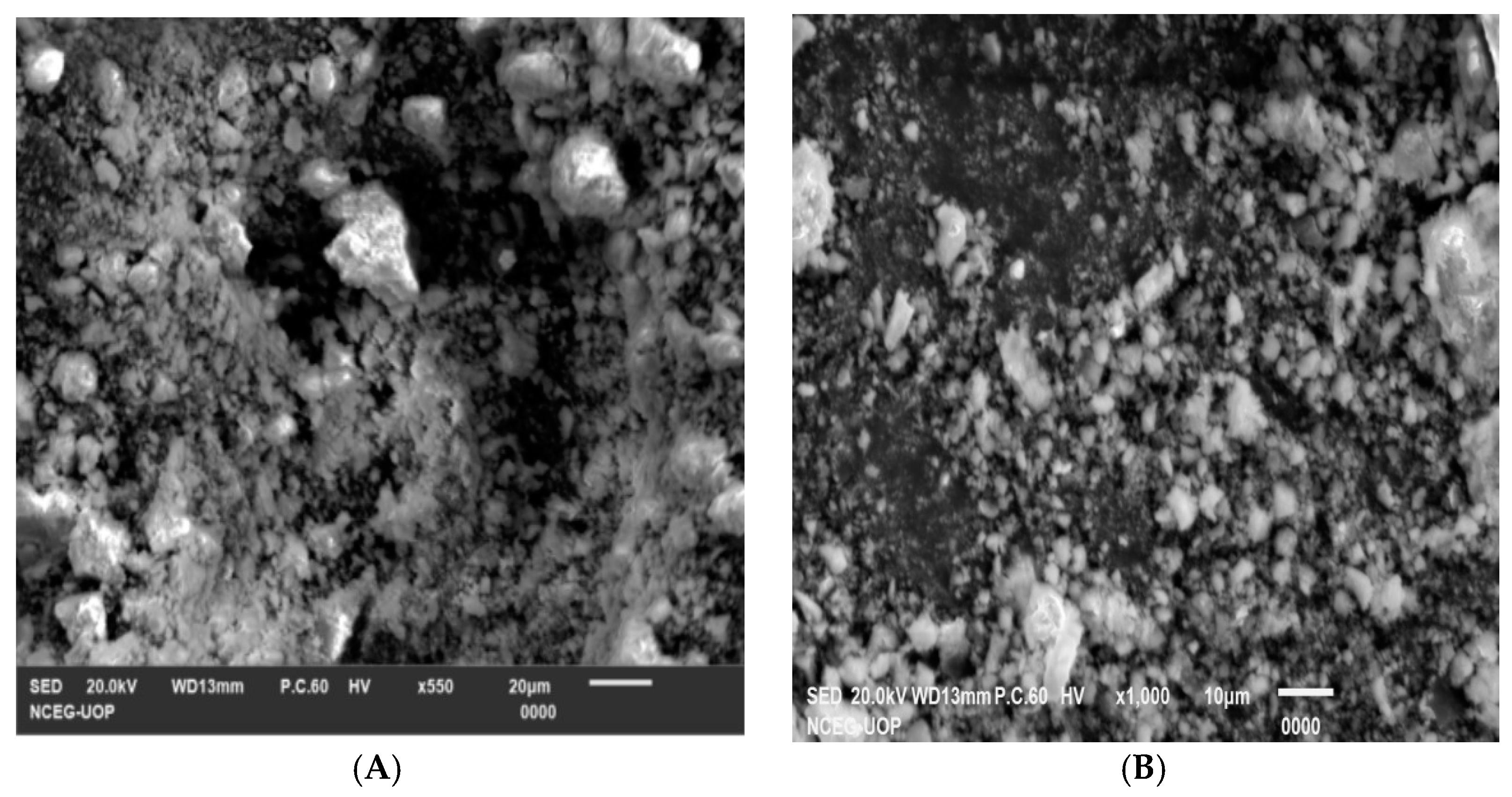
2.1.3. SEM Study of the Synthesized Nanostructures
2.1.4. EDX Analysis of the Synthesized Co/CeO2/C Nanocomposite
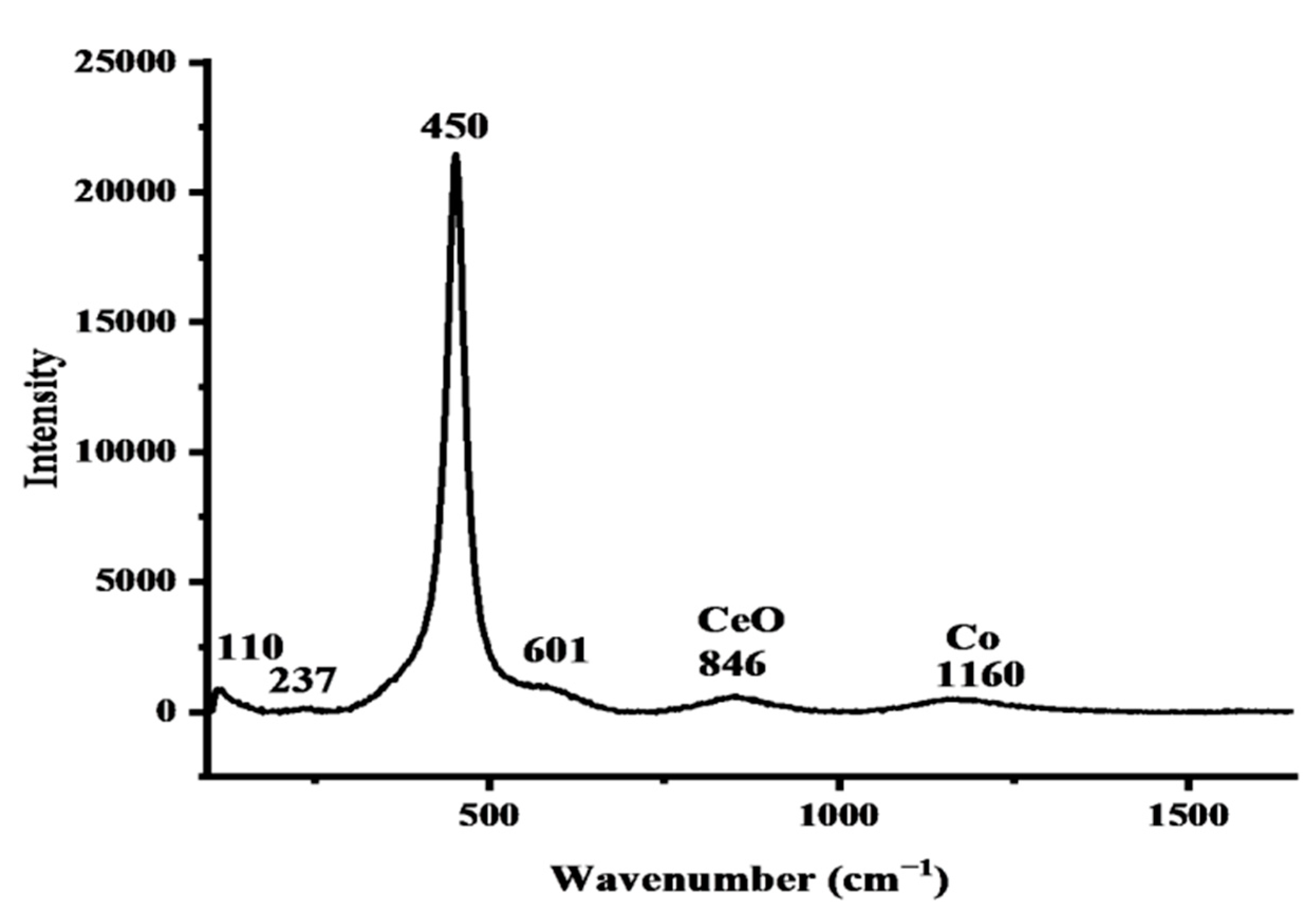
2.1.5. Raman Spectrum of the Synthesized Co/CeO2/C Nanocomposite
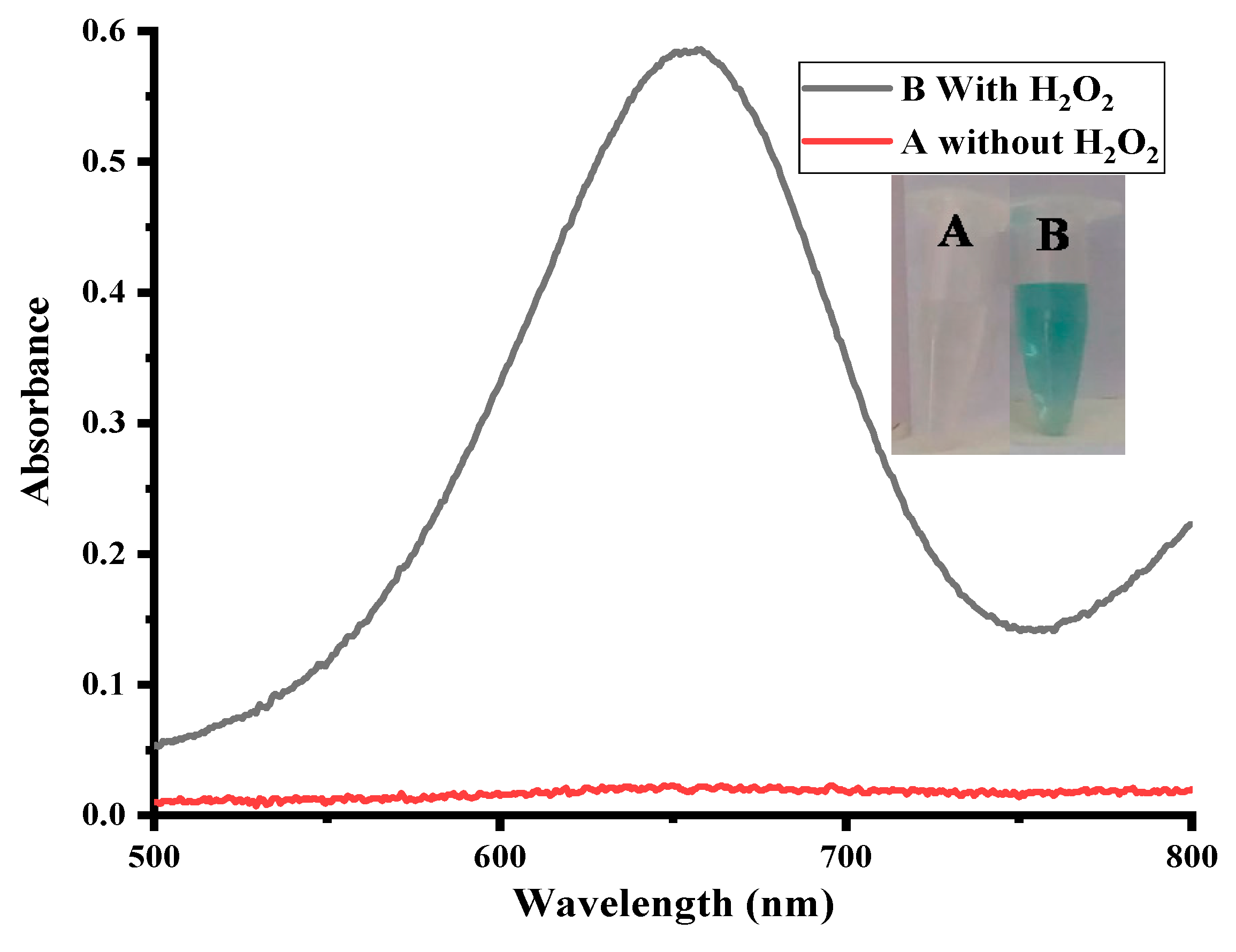
2.2. Colorimetric Sensing of H2O2
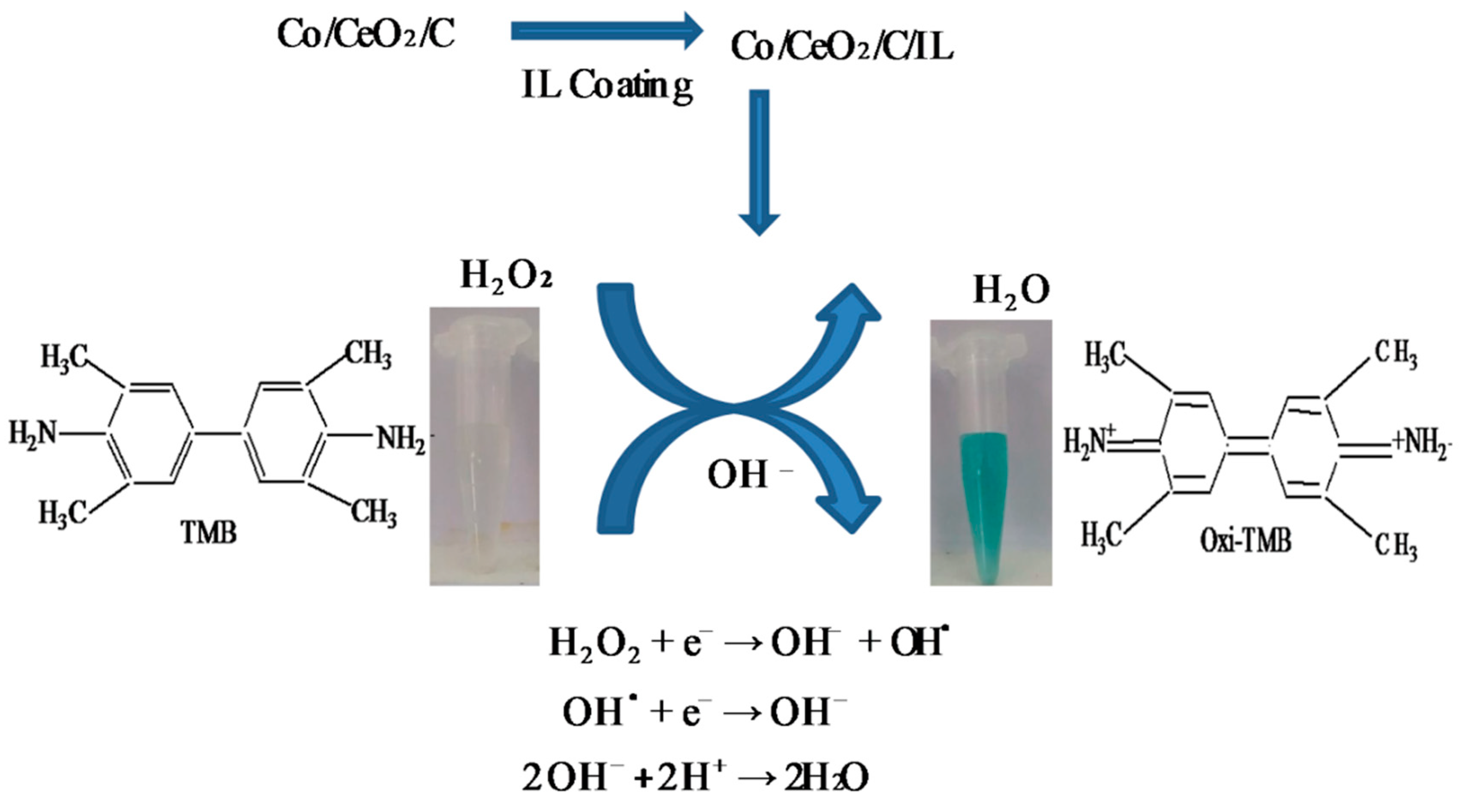
2.3. Mechanism for Sensing of H2O2
2.4. Optimization of Experimental Parameters
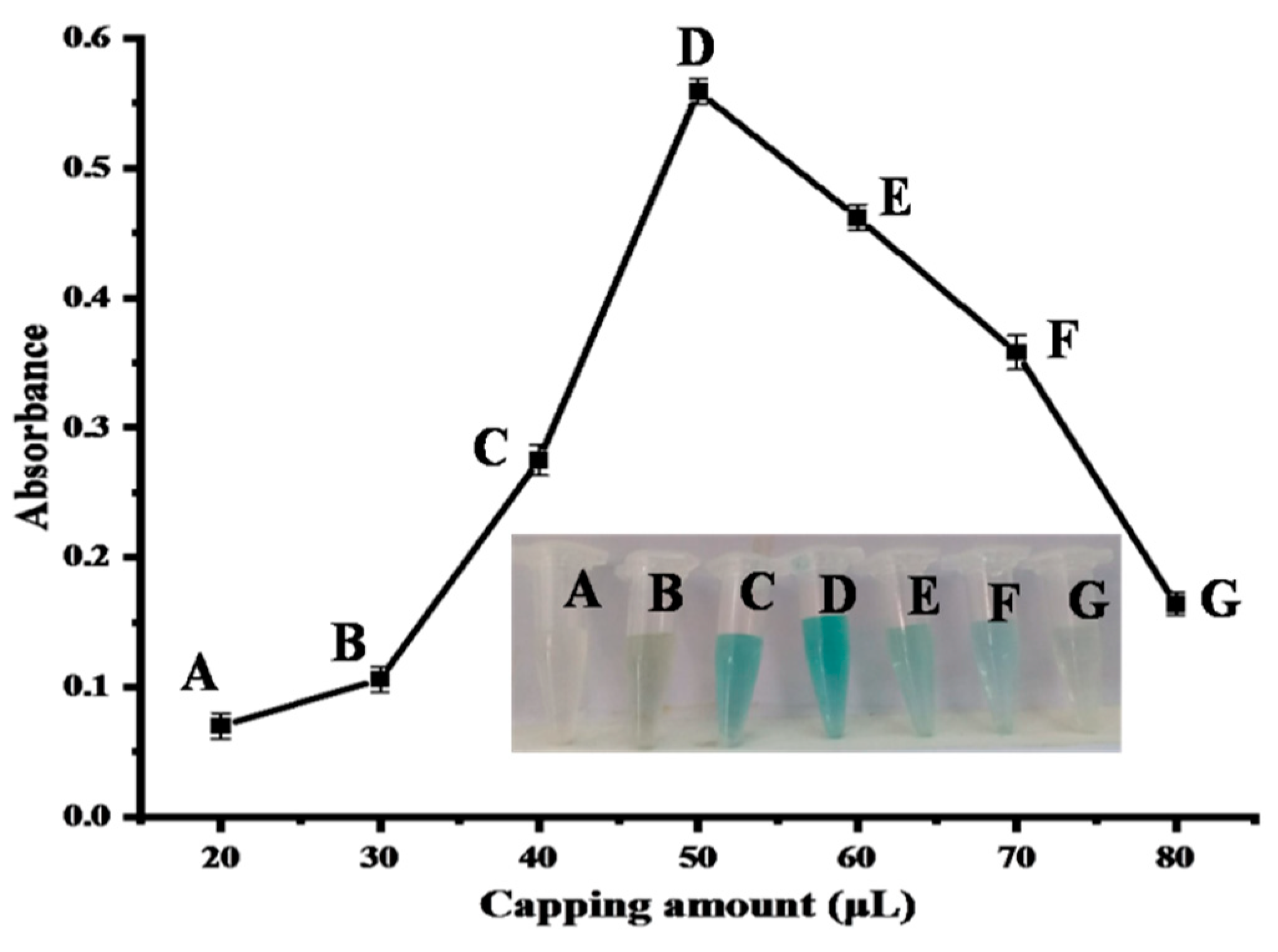
2.4.1. Effect of Capped Nanocomposite
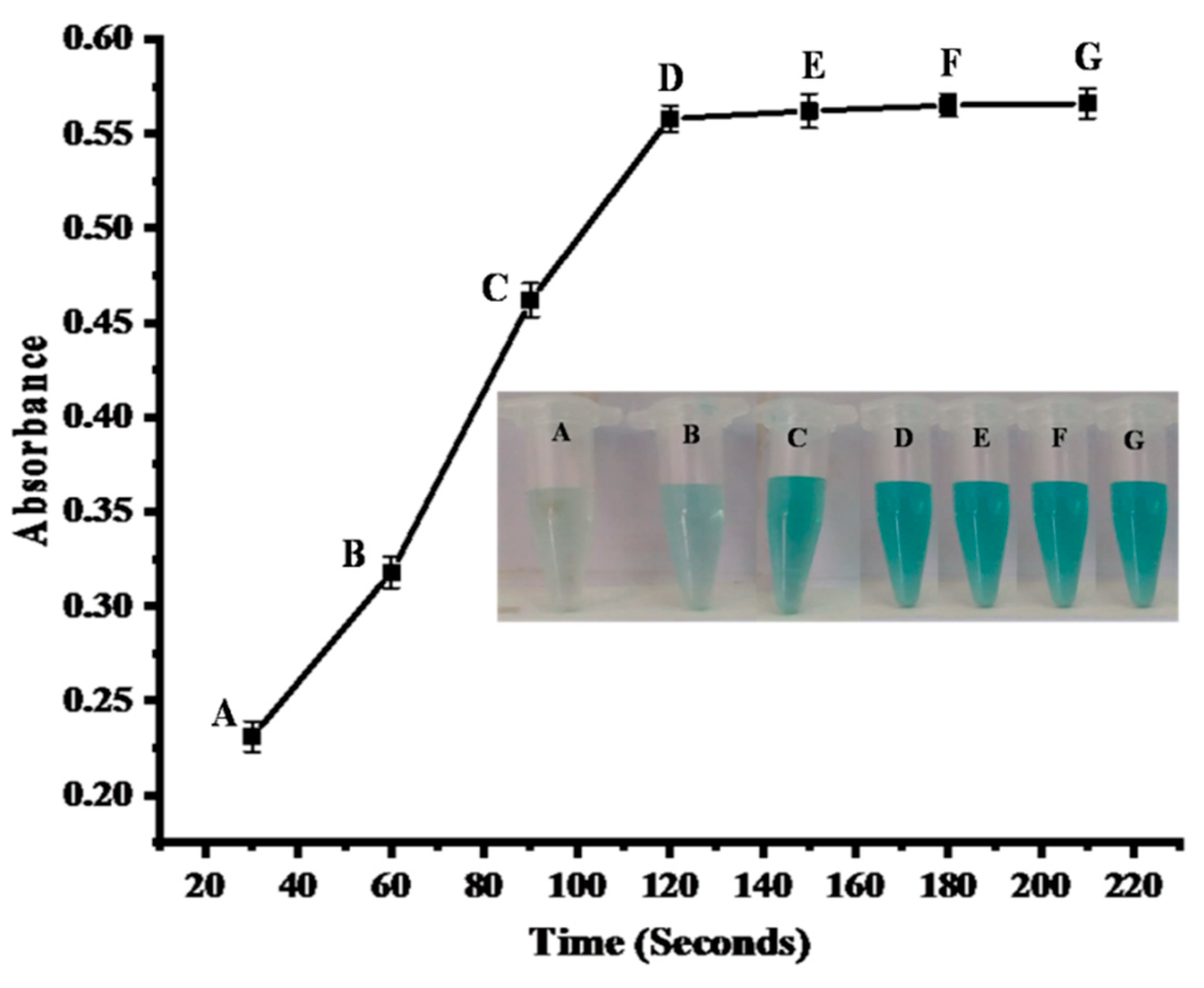
2.4.2. Time Optimization
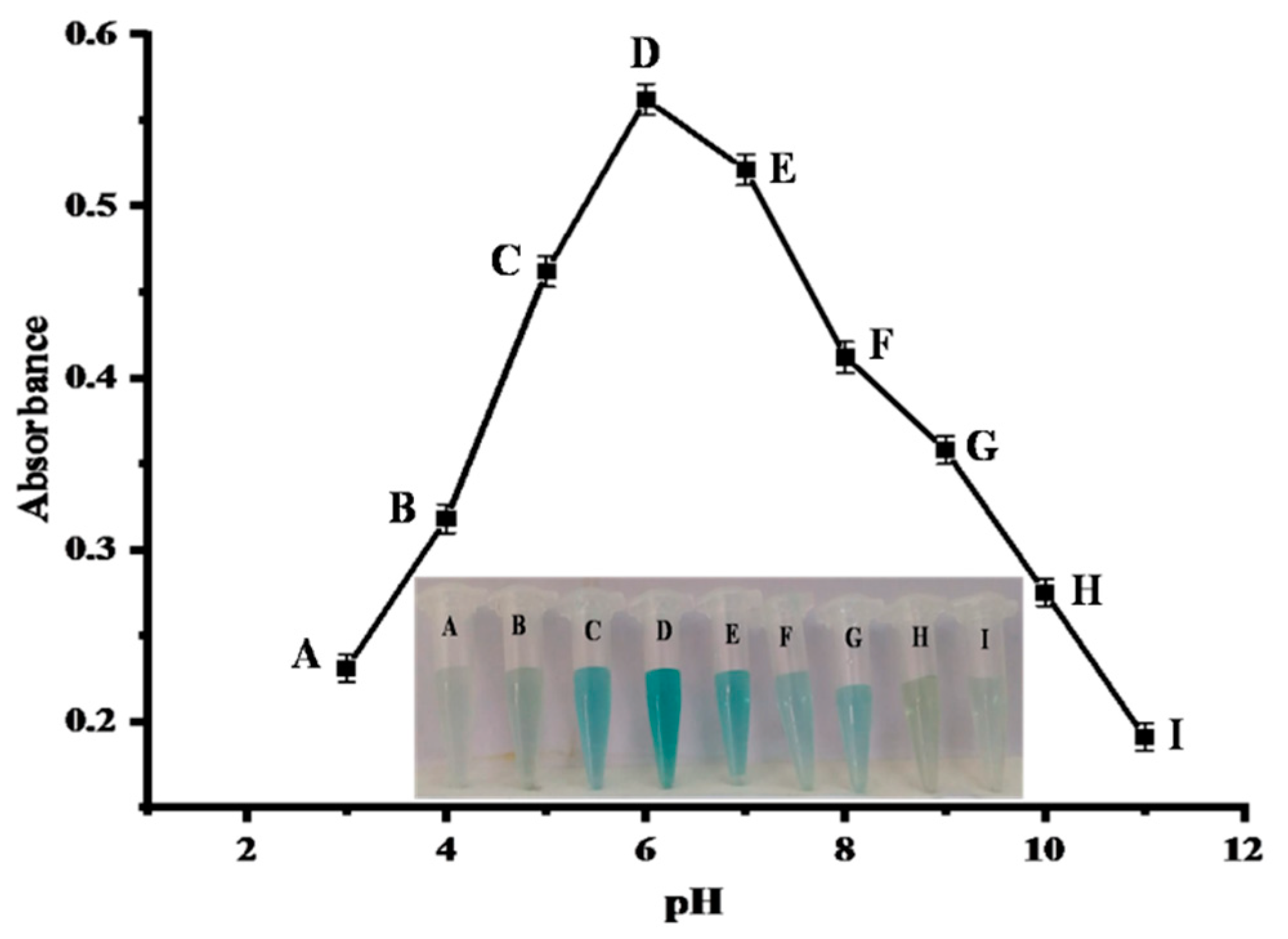
2.4.3. pH Optimization
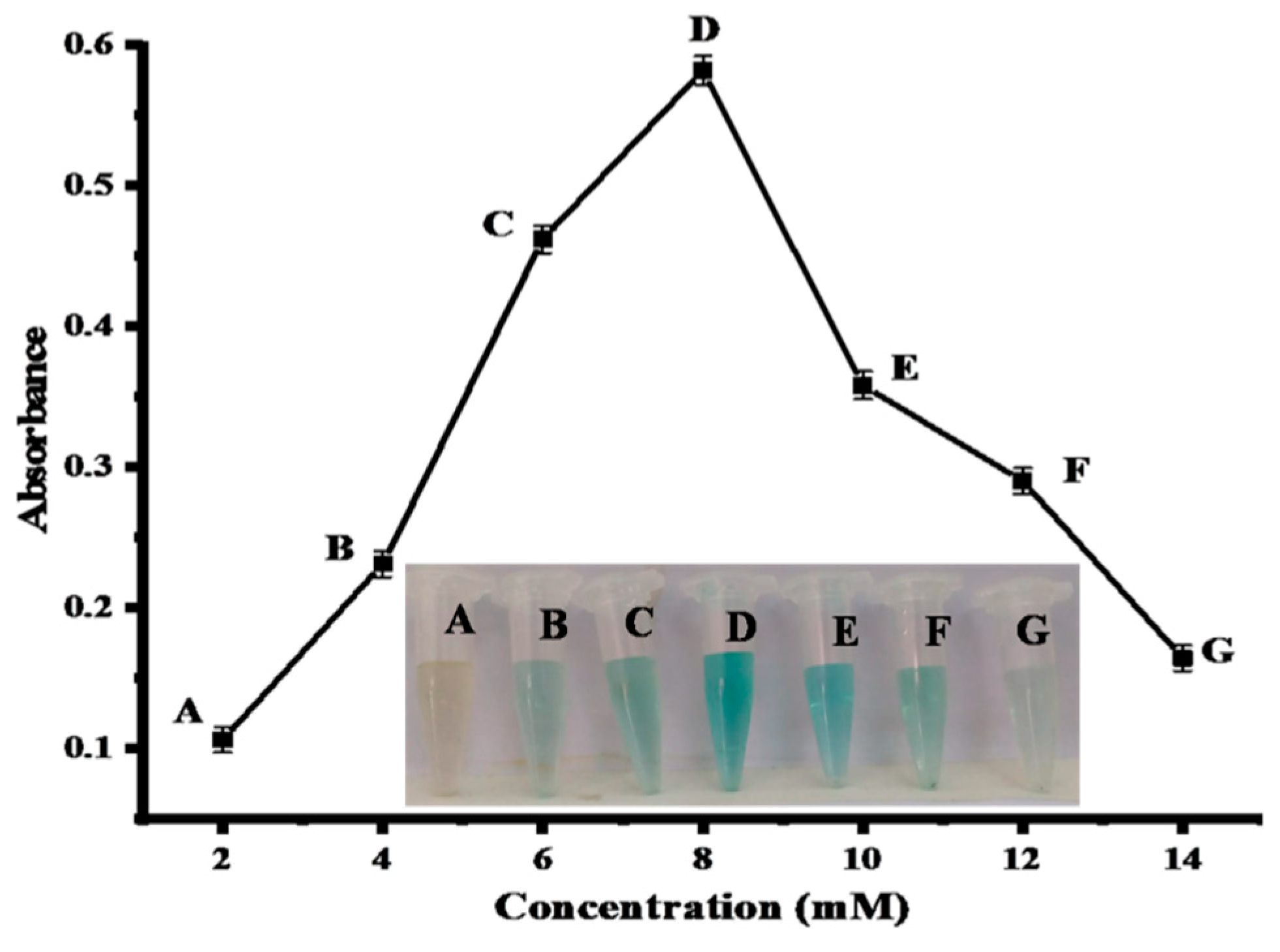
2.4.4. Effect of TMB Concentration
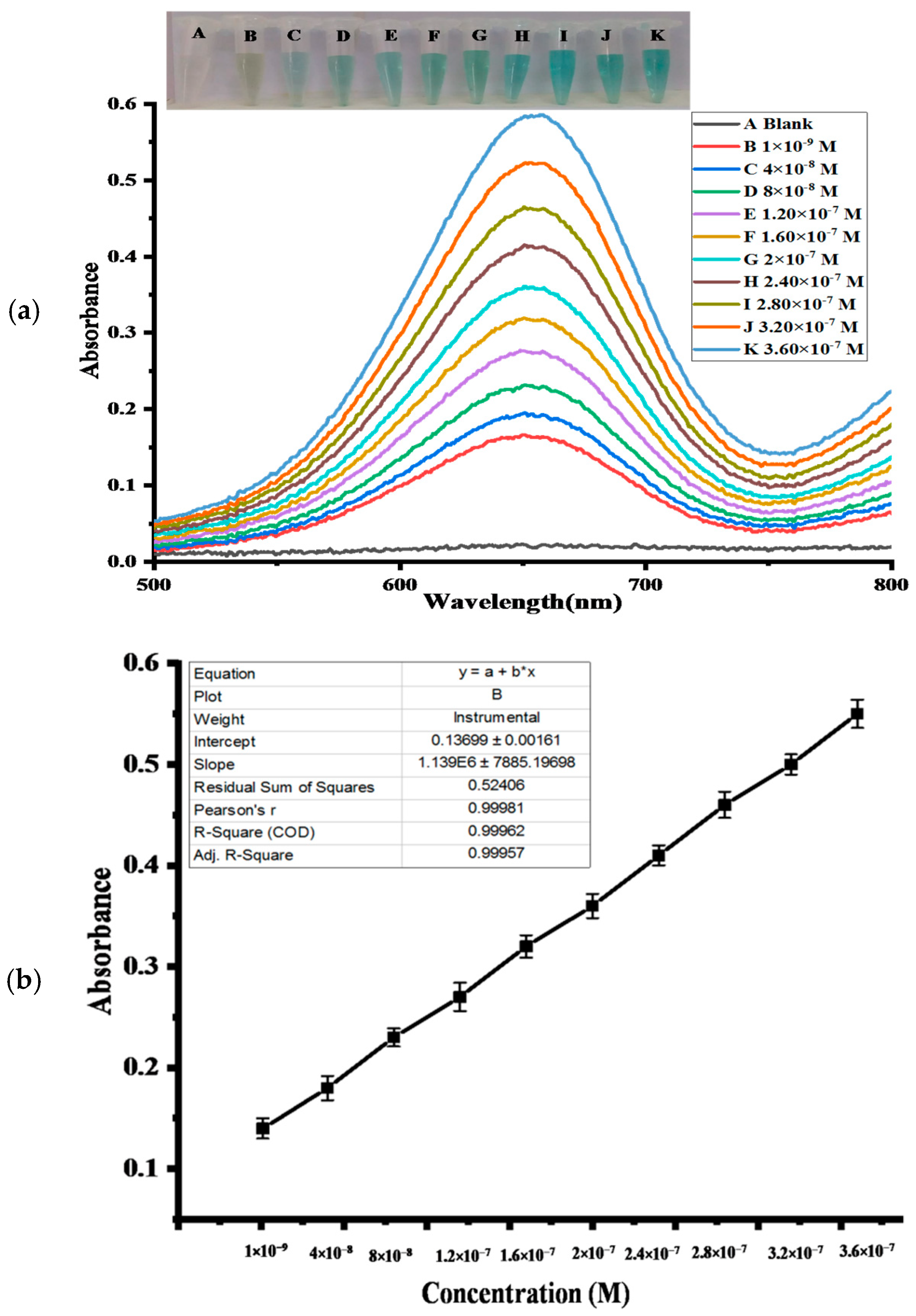
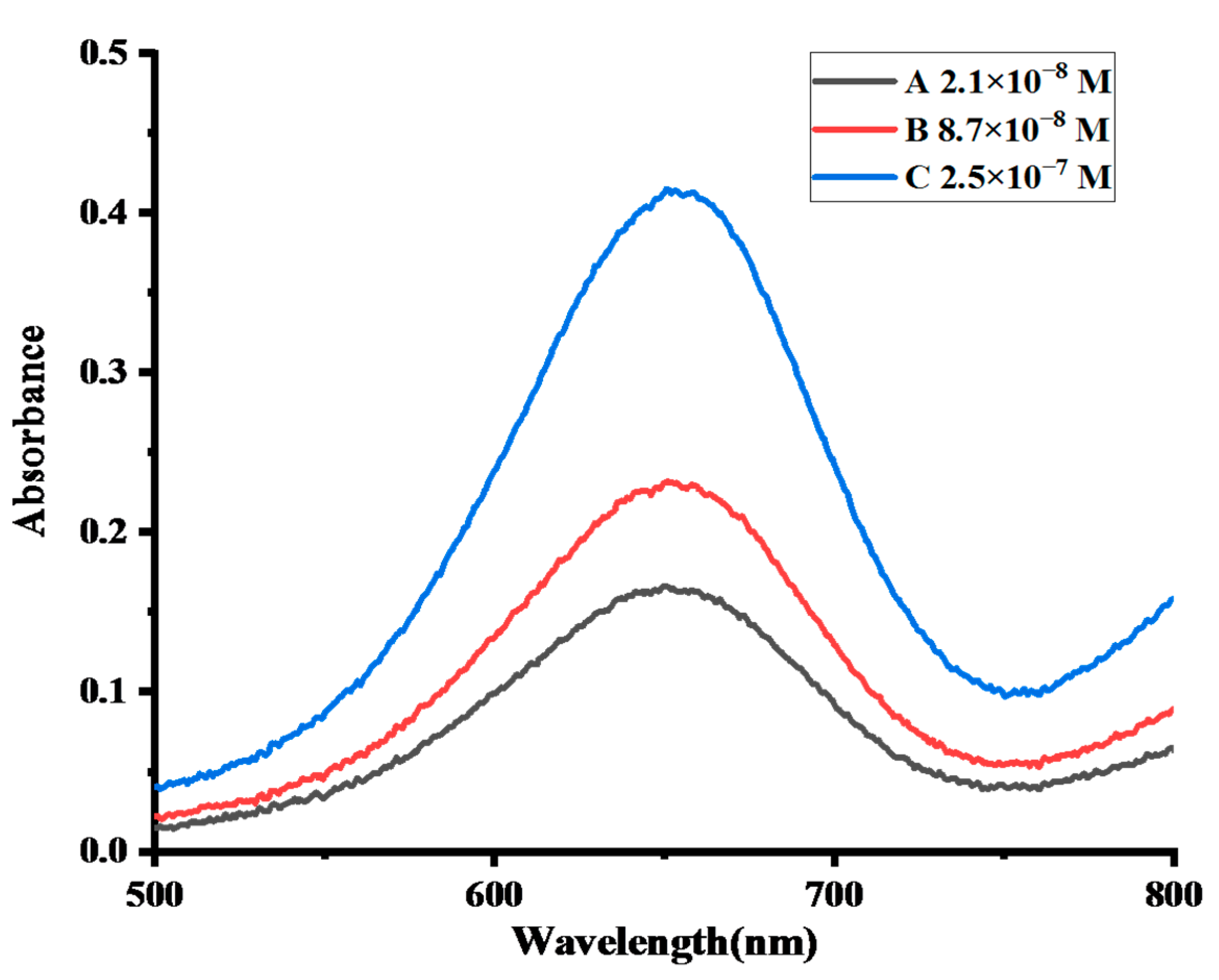
2.4.5. Colorimetric Determination of H2O2
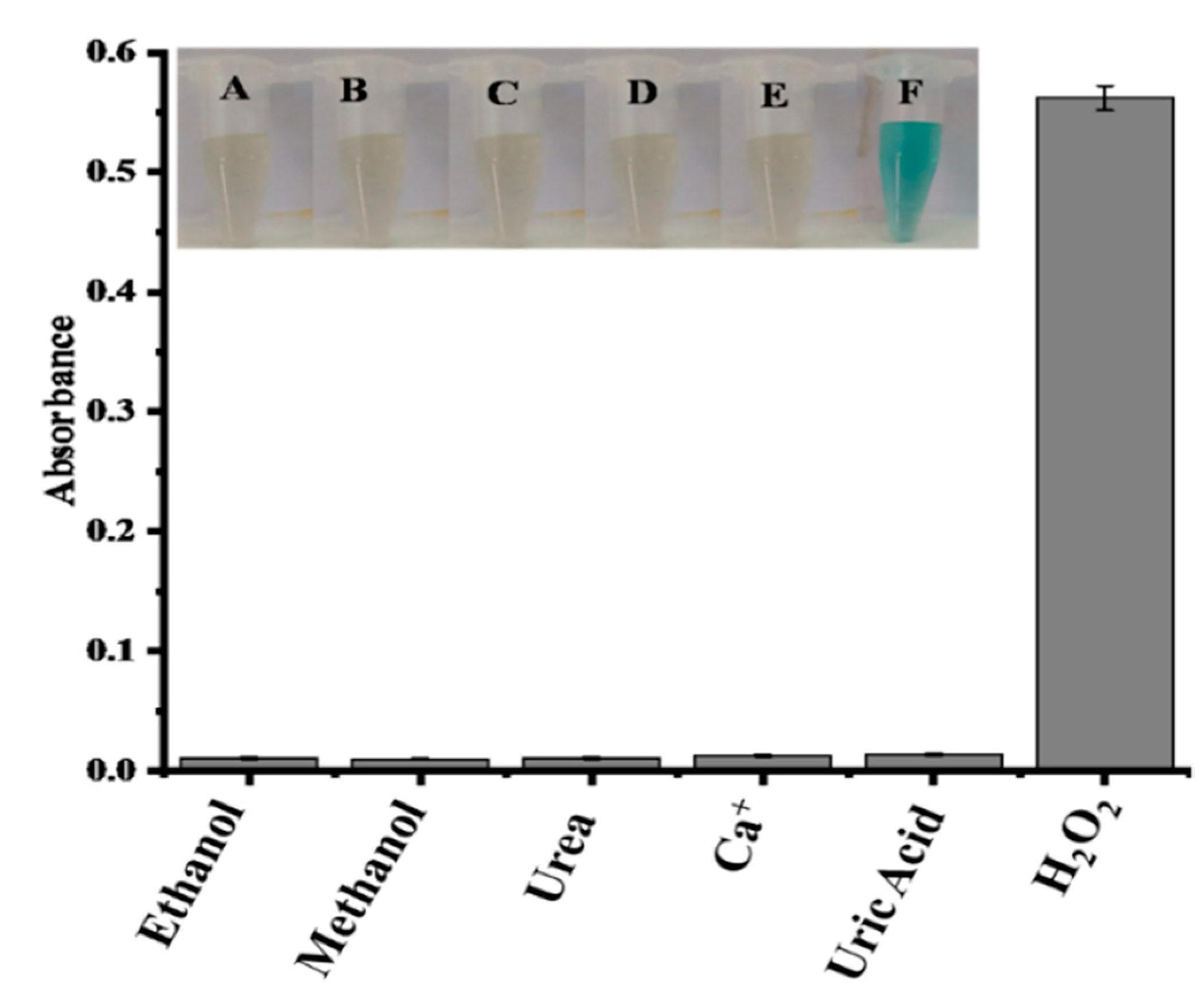
2.5. Interference Studies
2.6. Analysis of Real Samples
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Instrumentation
3.2. Synthesis of Cobalt-Doped Cerium Oxide/Activated Carbon Nanocomposite
3.3. Capping of Co/CeO2/C Nanocomposite with Ionic Liquid
3.4. Detection of Hydrogen Peroxide
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nishan, U.; Ullah, I.; Muhammad, N.; Afridi, S.; Asad, M.; Haq, S.U.; Khan, M.; Soylak, M.; Rahim, A. Investigation of Silver-Doped Iron Oxide Nanostructures Functionalized with Ionic Liquid for Colorimetric Sensing of Hydrogen Peroxide. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2023, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisham, M.B. Methods to detect hydrogen peroxide in living cells: Possibilities and pitfalls. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2013, 165, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisanti, M.P.; Martinez-Outschoorn, U.E.; Lin, Z.; Pavlides, S.; Whitaker-Menezes, D.; Pestell, R.G.; Howell, A.; Sotgia, F. Hydrogen peroxide fuels aging, inflammation, cancer metabolism and metastasis: The seed and soil also needs “fertilizer”. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 2440–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nossol, E.; Zarbin, A.J. A Simple and Innovative Route to Prepare a Novel Carbon Nanotube/Prussian Blue Electrode and its Utilization as a Highly Sensitive H2O2Amperometric Sensor. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 3980–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishan, U.; Haq, S.U.; Rahim, A.; Asad, M.; Badshah, A.; Shah, A.-U.A.; Iqbal, A.; Muhammad, N. Ionic-Liquid-Stabilized TiO2 Nanostructures: A Platform for Detection of Hydrogen Peroxide. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 32754–32762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, K.; Wada, M.; Kuroda, N.; Akiyama, S.; Imai, K. High-Performance Liquid Chromatographic Determination of Hydrogen Peroxide with Peroxyoxalate Chemiluminescence Detection. J. Liq. Chromatogr. 1994, 17, 2111–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yu, J.; Ye, W.; Yao, X.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, S.; Jia, L. Spectrophotometric determination of mercury(II) ions based on their stimulation effect on the peroxidase-like activity of molybdenum disulfide nanosheets. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 2481–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad Irani-nezhad, M.; Khataee, A.; Hassanzadeh, J.; Orooji, Y. A Chemiluminescent Method for the Detection of H2O2 and Glucose Based on Intrinsic Peroxidase-Like Activity of WS2 Quantum Dots. Molecules 2019, 24, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wu, G.; Cai, Z.; Oyama, M.; Chen, X. Advances in enzyme-free electrochemical sensors for hydrogen peroxide, glucose, and uric acid. Microchim. Acta 2014, 181, 689–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-Y.; Cai, Y.-J.; Yang, C.-H.; Wu, C.-H.; Wei, Y.; Wen, T.-C.; Wang, T.-L.; Shieh, Y.-T.; Lin, W.-C.; Chen, W.-J. Highly sensitive and selective electrochemical determination of dopamine and ascorbic acid at Ag/Ag2S modified electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 1955–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Liu, Q.; Ge, C.; Xing, Z.; Asiri, A.M.; Al-Youbi, A.O.; Sun, X. Ultrathin graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets: A low-cost, green, and highly efficient electrocatalyst toward the reduction of hydrogen peroxide and its glucose biosensing application. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 8921–8924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ju, P.; Zhang, D.; Han, X.; Zheng, L.; Yin, X.; Sun, C. Colorimetric detection of H2O2 using flower-like Fe2(MoO4)3 microparticles as a peroxidase mimic. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choleva, T.G.; Gatselou, V.A.; Tsogas, G.Z.; Giokas, D.L. Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of rhodium nanoparticles, and their application to the colorimetric determination of hydrogen peroxide and glucose. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Huang, L.; Yang, X.; Elzatahry, A.A.; Alghamdi, A.; Deng, Y. Rational design of a stable peroxidase mimic for colorimetric detection of H2O2 and glucose: A synergistic CeO2/Zeolite Y nanocomposite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 535, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remani, K.; Binitha, N. Cobalt doped ceria catalysts for the oxidative abatement of gaseous pollutants and colorimetric detection of H2O2. Mater. Res. Bull. 2021, 139, 111253. [Google Scholar]
- Rauf, S.; Nawaz, M.A.H.; Muhammad, N.; Raza, R.; Shahid, S.A.; Marty, J.L.; Hayat, A. Protic ionic liquids as a versatile modulator and stabilizer in regulating artificial peroxidase activity of carbon materials for glucose colorimetric sensing. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 243, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zha, J.; Zhang, P.; Xiong, Y.; Su, L.; Ye, F. Sphere-like CoS with nanostructures as peroxidase mimics for colorimetric determination of H2O2 and mercury ions. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 66963–66970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, R.D.; Seddon, K.R. Ionic Liquids--Solvents of the Future? Science 2003, 302, 792–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, C.; Shen, Z.; Wu, A. A colorimetric nitrite detection system with excellent selectivity and high sensitivity based on Ag@Au nanoparticles. Analyst 2015, 140, 1076–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishan, U.; Niaz, A.; Muhammad, N.; Asad, M.; Shah, A.-U.A.; Khan, N.; Khan, M.; Shujah, S.; Rahim, A. Non-enzymatic colorimetric biosensor for hydrogen peroxide using lignin-based silver nanoparticles tuned with ionic liquid as a peroxidase mimic. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, M.; Lima, R.; Riccardi, C.; Tranquilin, R.; Bueno, P.; Varela, J.; Longo, E. Preparation and characterization of ceria nanospheres by microwave-hydrothermal method. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 4509–4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, O.L.; Diaconeasa, Z.; Mesaroş, A.; Vodnar, D.C.; Cuibus, L.; Ciontea, L.; Socaciu, C. FT-IR Studies of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles and Natural Zeolite Materials. Bull. Univ. Agric. Sci. Veter-Med. Cluj-Napoca. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 72, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketzial, J.J.; Nesaraj, A.S. Synthesis of CeO2 nanoparticles by chemical precipitation and the effect of a surfactant on the distribution of particle sizes. J. Ceram. Process. Res. 2011, 12, 74–79. [Google Scholar]
- Varga, E.; Pusztai, P.; Óvári, L.; Oszkó, A.; Erdőhelyi, A.; Papp, C.; Steinrück, H.-P.; Kónya, Z.; Kiss, J. Probing the interaction of Rh, Co and bimetallic Rh–Co nanoparticles with the CeO2 support: Catalytic materials for alternative energy generation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 27154–27166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojoudi, N.; Mirghaffari, N.; Soleimani, M.; Shariatmadari, H.; Belver, C.; Bedia, J. Phenol adsorption on high microporous activated carbons prepared from oily sludge: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridharan, M.; Maiyalagan, T.; Panomsuwan, G.; Techapiesancharoenkij, R. Enhanced Electrocatalytic Activity of Cobalt-Doped Ceria Embedded on Nitrogen, Sulfur-Doped Reduced Graphene Oxide as an Electrocatalyst for Oxygen Reduction Reaction. Catalysts 2021, 12, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadar, Y.S.; Balamurugan, A.; Devarajan, V.; Subramanian, R.; Kumar, S.D. Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of cobalt doped cerium oxide (CeO2:Co) nanoparticles by using hydrothermal method. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarif, F.; Khurshid, S.; Muhammad, N.; Zahid Qureshi, M.; Shah, N.S. Colorimetric Sensing of Hydrogen Peroxide Using Ionic-Liquid-Sensitized Zero-Valent Copper Nanoparticle (nZVCu). ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 6066–6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, A.A.; Labis, J.; Alam, M.; Ramay, S.M.; Ahmad, N.; Mahmood, A. Effect of cobalt doping on structural, optical and redox properties cerium oxide nanoparticles. Phase Transit. 2016, 89, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezfuli, A.S.; Ganjali, M.R.; Naderi, H.R.; Norouzi, P. A high performance supercapacitor based on a ceria/graphene nanocomposite synthesized by a facile sonochemical method. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 46050–46058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Hope, G.A. Raman and Fluorescence Spectroscopy of CeO2, Er2O3, Nd2O3, Tm2O3, Yb2O3, La2O3, and Tb4O7. J. Spectrosc. 2015, 2015, 940172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streletskiy, O.A.; Zavidovskiy, I.A.; Balabanyan, V.Y.; Tsiskarashvili, A.V. Tsiskarashvili Antibacterial properties of modified aC and ta-C coatings: The effects of the sp2/sp3 ratio, oxidation, nitridation, and silver incorporation. Appl. Phys. A 2022, 128, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushkarev, V.V.; Kovalchuk, V.I.; D’Itri, J.L. Probing Defect Sites on the CeO2 Surface with Dioxygen. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 5341–5348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shafie, A.S.; Ahsan, I.; Radhwani, M.; Al-Khangi, M.A.; El-Azazy, M. Synthesis and Application of Cobalt Oxide (Co3O4)-Impregnated Olive Stones Biochar for the Removal of Rifampicin and Tigecycline: Multivariate Controlled Performance. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Mehta, B. Nanostructured TiO2 thin films sensitized by CeO2 as an inexpensive photoanode for enhanced photoactivity of water oxidation. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 749, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, I.Y.; Burhan, J.; Jaladi, F.; Lim, C.M.; Usman, A.; Kumara, N.; Tsang, S.C.E.; Mahadi, A.H. Effect of Cr doping in CeO2 nanostructures on photocatalysis and H2O2 assisted methylene blue dye degradation. Catal. Today 2021, 375, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velegraki, T.; Poulios, I.; Charalabaki, M.; Kalogerakis, N.; Samaras, P.; Mantzavinos, D. Photocatalytic and sonolytic oxidation of acid orange 7 in aqueous solution. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2006, 62, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achilleos, A.; Hapeshi, E.; Xekoukoulotakis, N.P.; Mantzavinos, D.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Factors affecting diclofenac decomposition in water by UV-A/TiO2 photocatalysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 161, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Yadav, P.K.; Chandra, S.; Bano, D.; Talat, M.; Hasan, S.H. Peroxidase mimetic activity of fluorescent NS-carbon quantum dots and their application in colorimetric detection of H2O2 and glutathione in human blood serum. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 5256–5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaidan, A.; Addad, A.; Tahon, J.-F.; Barras, A.; Toufaily, J.; Hamieh, T.; Szunerits, S.; Boukherroub, R. Ultrasmall CuS-BSA-Cu3(PO4)2 nanozyme for highly efficient colorimetric sensing of H2O2 and glucose in contact lens care solutions and human serum. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1109, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Q.; Li, S.; Cao, H.; Huang, Y. Co3O4/CuO hollow nanocage hybrids with high oxidase-like activity for biosensing of dopamine. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 94, 858–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarif, F.; Rauf, S.; Qureshi, M.Z.; Shah, N.S.; Hayat, A.; Muhammad, N.; Rahim, A.; Nawaz, M.H.; Nasir, M. Ionic liquid coated iron nanoparticles are promising peroxidase mimics for optical determination of H2O2. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarif, F.; Rauf, S.; Khurshid, S.; Muhammad, N.; Hayat, A.; Rahim, A.; Shah, N.S.; Yang, C.P. Effect of pyridinium based ionic liquid on the sensing property of Ni0 nanoparticle for the colorimetric detection of hydrogen peroxide. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1219, 128620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Song, X.; Chen, Y.; Rong, M.; Zhao, T.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, X. Intrinsic peroxidase-like catalytic activity of nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots and their application in the colorimetric detection of H2O2 and glucose. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 869, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ma, H.; Xu, H.; Wen, J.; Huang, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Fan, K.; Li, D.; Gu, C. Hollow and porous nickel sulfide nanocubes prepared from a metal-organic framework as an efficient enzyme mimic for colorimetric detection of hydrogen peroxide. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishan, U.; Bashir, F.; Muhammad, N.; Khan, N.; Rahim, A.; Shah, M.; Nazir, R.; Sayed, M. Ionic liquid as a moderator for improved sensing properties of TiO2 nanostructures for the detection of acetone biomarker in diabetes mellitus. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 294, 111681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishan, U.; Gul, R.; Muhammad, N.; Asad, M.; Rahim, A.; Shah, M.; Iqbal, J.; Uddin, J.; Shah, A.-U.A.; Shujah, S. Colorimetric based sensing of dopamine using ionic liquid functionalized drug mediated silver nanostructures. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asad, M.; Muhammad, N.; Khan, N.; Shah, M.; Khan, M.; Khan, M.; Badshah, A.; Latif, Z.; Nishan, U. Colorimetric acetone sensor based on ionic liquid functionalized drug-mediated silver nanostructures. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 221, 115043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
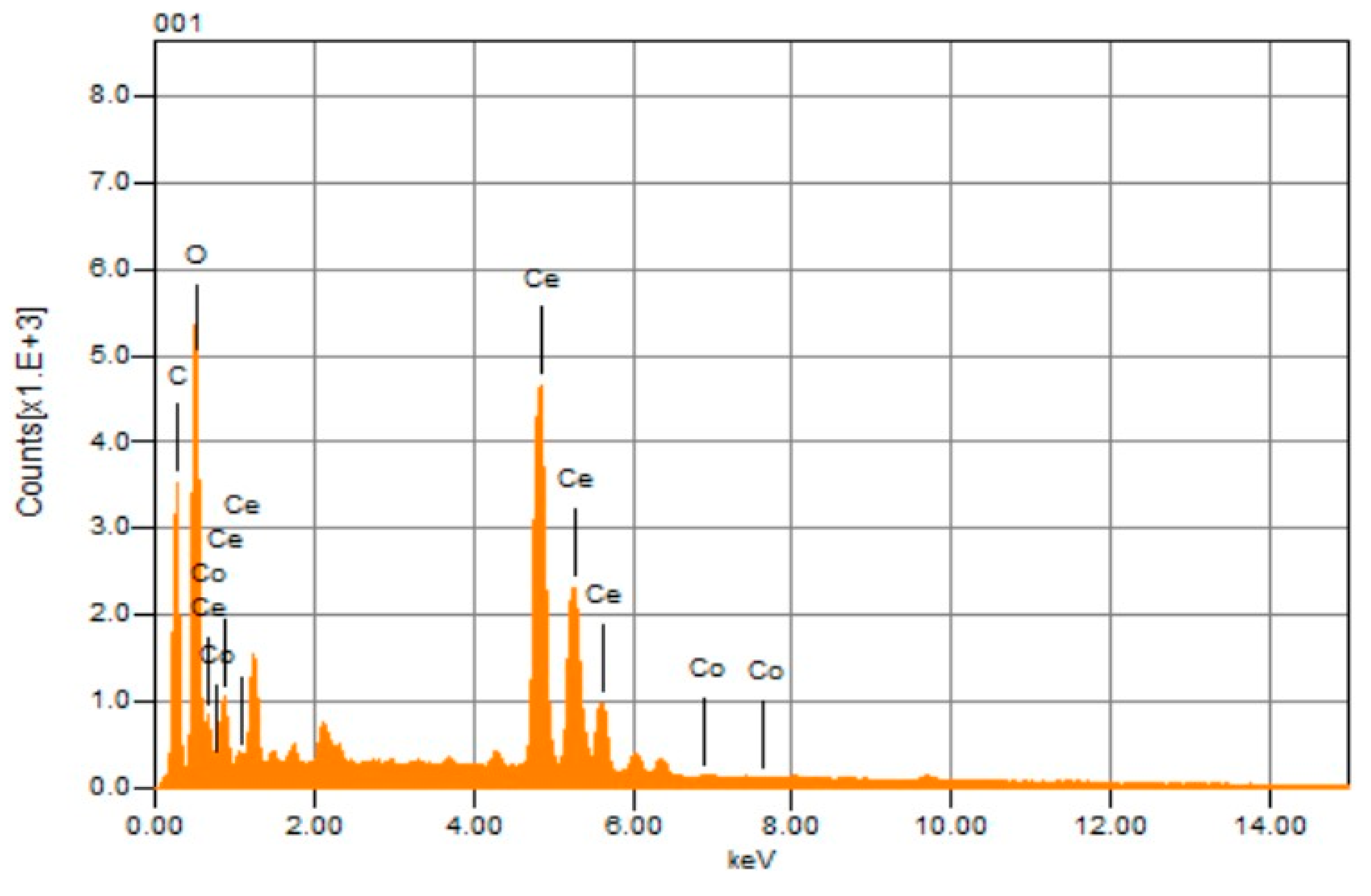
| Element | Line Type | Weight % | Sigma | Atomic % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | K | 13.90 | 0.01 | 37.33 |
| O | K | 23.95 | 0.05 | 48.30 |
| Co | K | 0.20 | 0.03 | 0.11 |
| Ce | L | 61.94 | 0.14 | 14.26 |
| Total | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Samples | Detected (nM) | H2O2 Added (nM) | H2O2 Found (nM) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4 | 17 | 21 | 123 | 0.728 |
| 2 | 5 | 82 | 87 | 106 | 0.639 |
| 3 | 6 | 244 | 250 | 102 | 0.459 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khaliq, A.; Nazir, R.; Khan, M.; Rahim, A.; Asad, M.; Shah, M.; Khan, M.; Ullah, R.; Ali, E.A.; Khan, A.; et al. Co-Doped CeO2/Activated C Nanocomposite Functionalized with Ionic Liquid for Colorimetric Biosensing of H2O2 via Peroxidase Mimicking. Molecules 2023, 28, 3325. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083325
Khaliq A, Nazir R, Khan M, Rahim A, Asad M, Shah M, Khan M, Ullah R, Ali EA, Khan A, et al. Co-Doped CeO2/Activated C Nanocomposite Functionalized with Ionic Liquid for Colorimetric Biosensing of H2O2 via Peroxidase Mimicking. Molecules. 2023; 28(8):3325. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083325
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhaliq, Abdul, Ruqia Nazir, Muslim Khan, Abdur Rahim, Muhammad Asad, Mohibullah Shah, Mansoor Khan, Riaz Ullah, Essam A. Ali, Ajmir Khan, and et al. 2023. "Co-Doped CeO2/Activated C Nanocomposite Functionalized with Ionic Liquid for Colorimetric Biosensing of H2O2 via Peroxidase Mimicking" Molecules 28, no. 8: 3325. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083325
APA StyleKhaliq, A., Nazir, R., Khan, M., Rahim, A., Asad, M., Shah, M., Khan, M., Ullah, R., Ali, E. A., Khan, A., & Nishan, U. (2023). Co-Doped CeO2/Activated C Nanocomposite Functionalized with Ionic Liquid for Colorimetric Biosensing of H2O2 via Peroxidase Mimicking. Molecules, 28(8), 3325. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083325








