Removal Performance and Mechanism of Emerging Pollutant Chloroquine Phosphate from Water by Iron and Magnesium Co-Modified Rape Straw Biochar
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
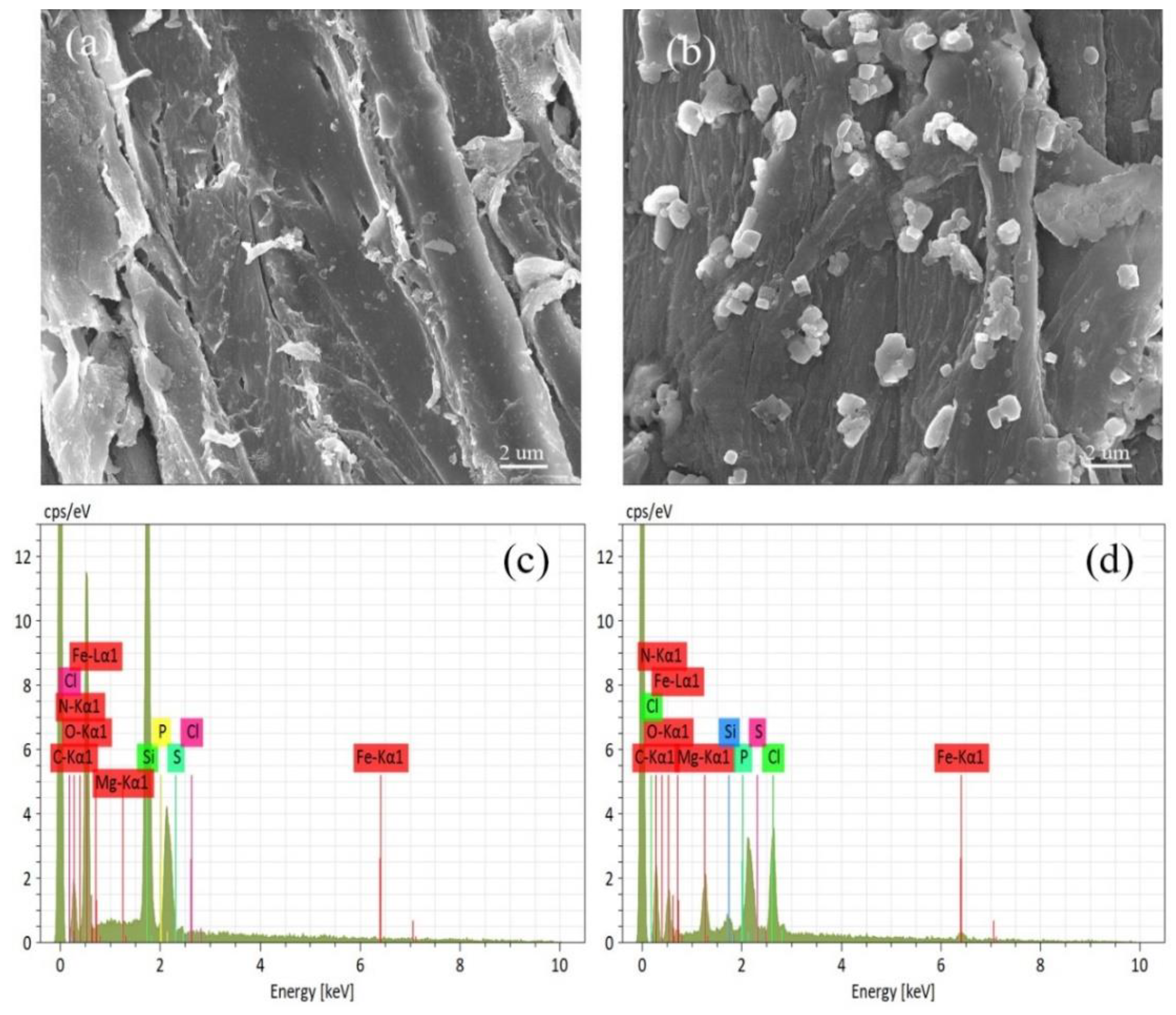
2.1. Characterization of Prepared Biochars
2.2. Batch Adsorption Experiments
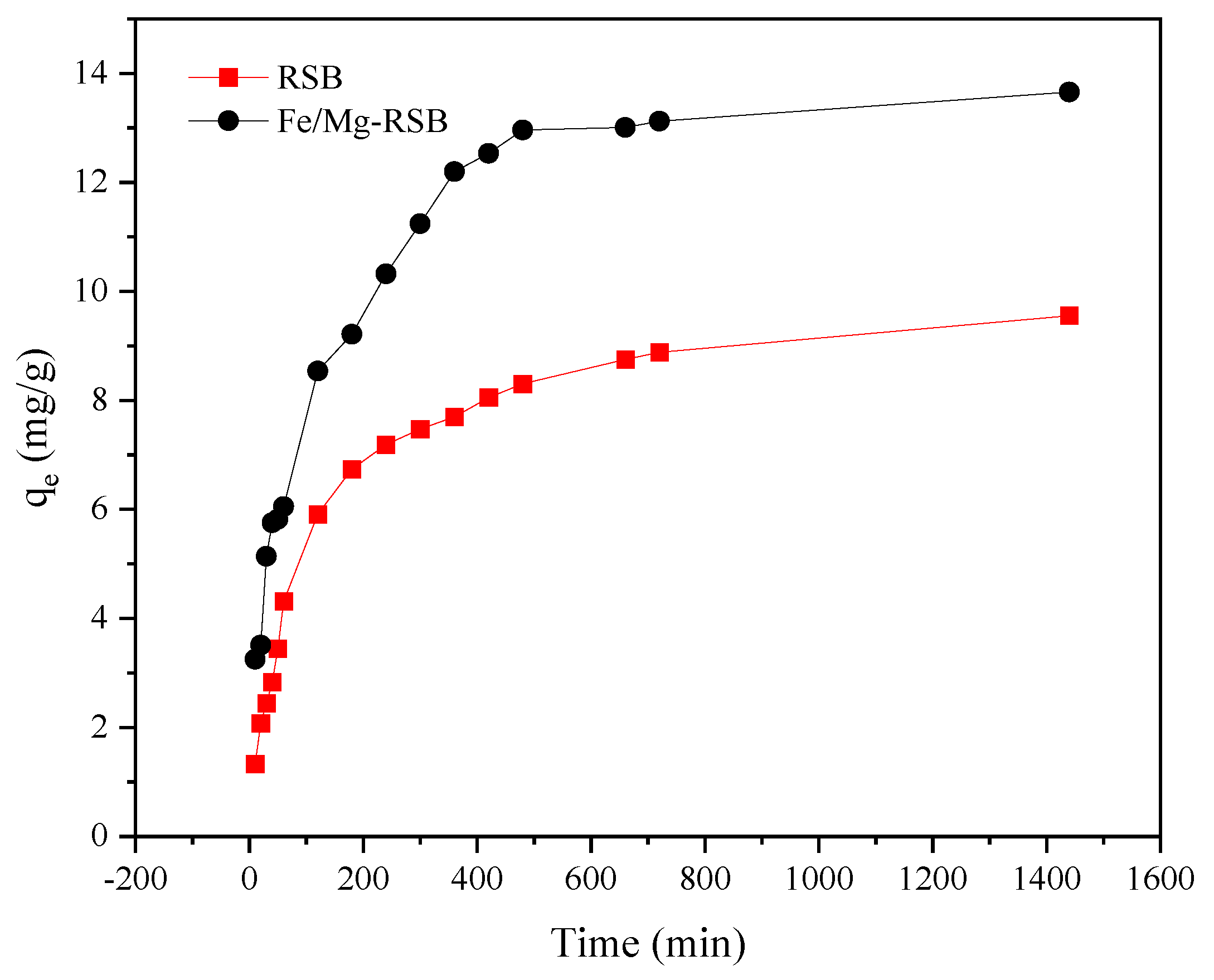
2.2.1. Adsorption Kinetics
2.2.2. Adsorption Isotherms
2.3. Effects of Reaction Conditions
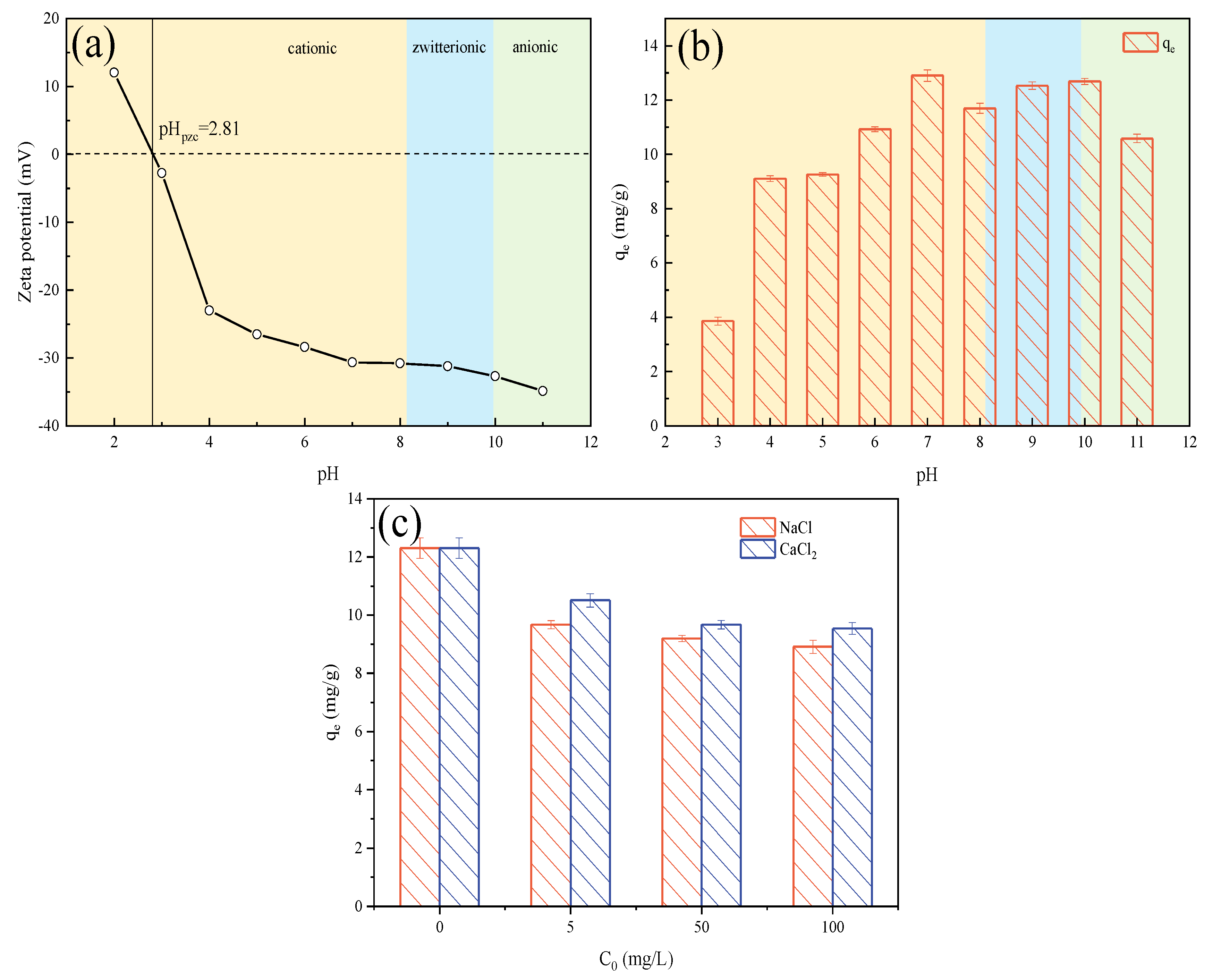
2.3.1. Effect of Solution pH
2.3.2. Effect of Ionic Strength
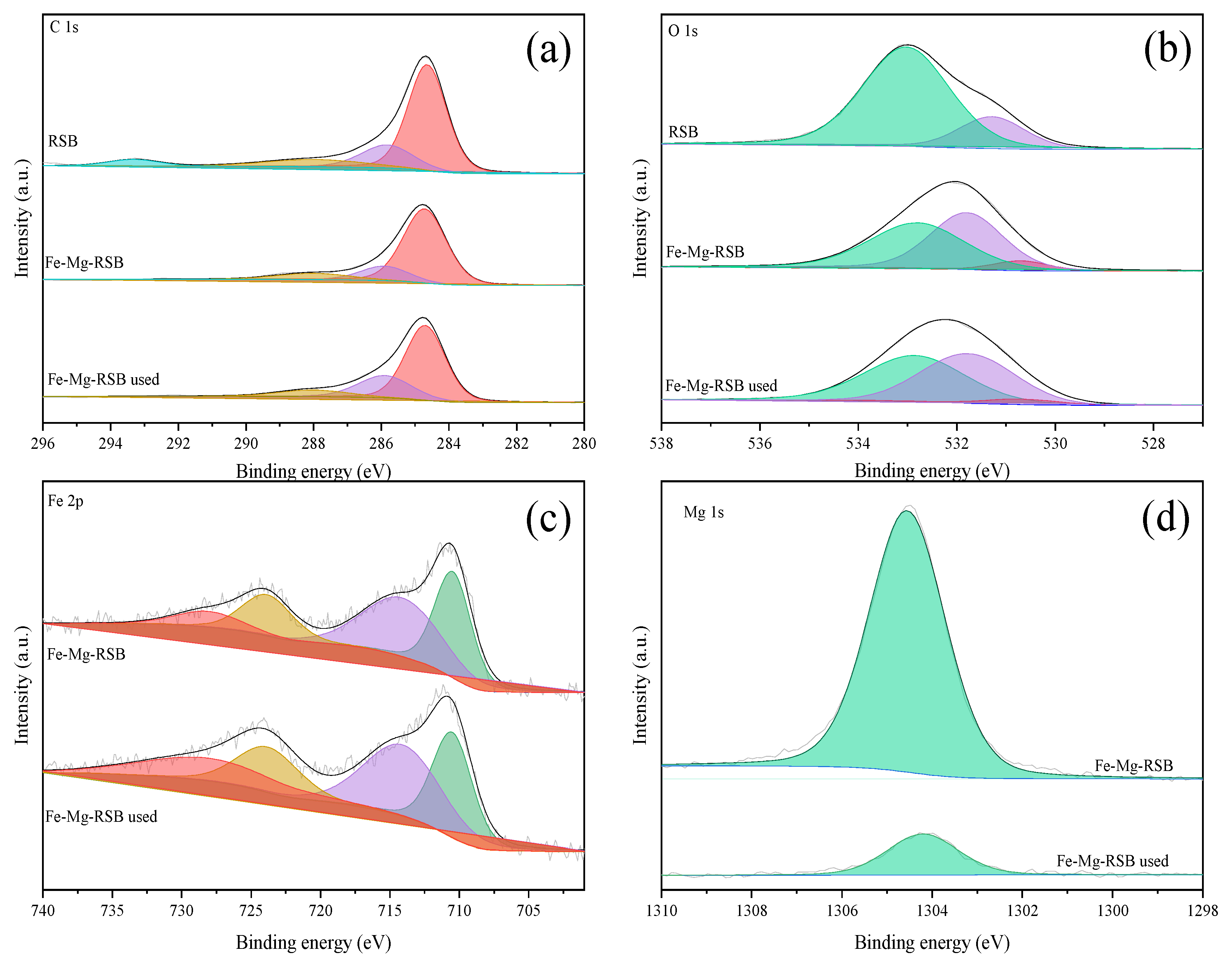
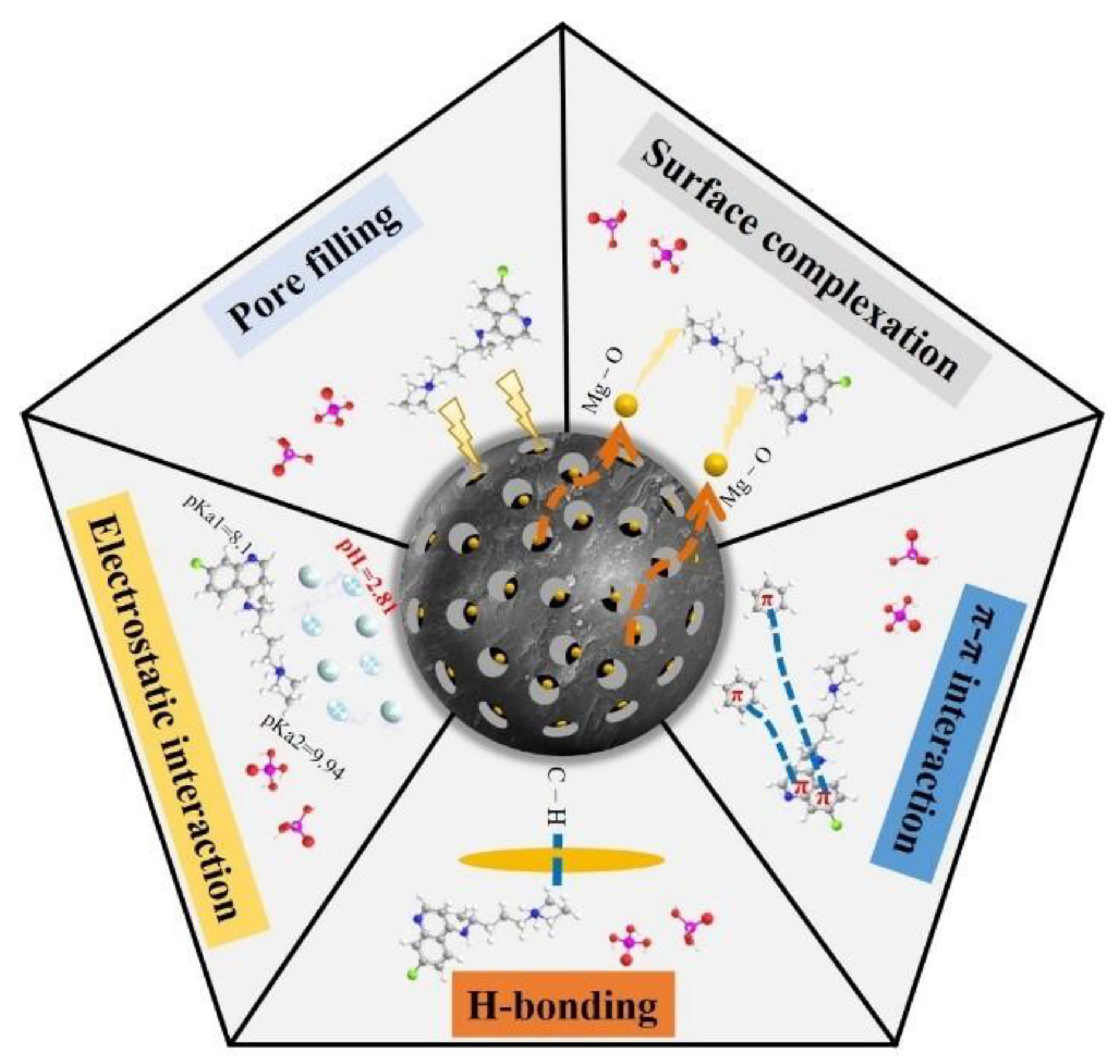
2.4. Adsorption Mechanism
2.5. Fixed Bed Adsorption of CQP
2.6. Reusability
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Synthesis and Characterization of Biochars
3.3. Batch Adsorption Experiments and Data Analysis
3.4. Fixed Bed Column Experiments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 2023.
- Sanders, J.M.; Monogue, M.L.; Jodlowski, T.Z.; Cutrell, J.B. Pharmacologic treatments for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A review. JAMA 2020, 323, 1824–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- China Economic Industrial Research Institute. Report on In-Depth Market Analysis and Investment strategy Planning of China’s Chloroquine Industry (2022–2027). 2022. Available online: https://www.huaon.com/channel/medicines/787248.html (accessed on 4 April 2023). (In Chinese).
- Wong, Y.K.; Yang, J.; He, Y. Caution and clarity required in the use of chloroquine for COVID-19. Lancet Rheumatol. 2020, 2, e255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, S.; Vogt, B.; Pieters, R.; Bouwman, H.; Bezuidenhout, C. Impact of Potential COVID-19 Treatment on South African Water Sources Already Threatened by Pharmaceutical Pollution. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2020, 39, 1305–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dan, J.; Rao, P.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, M.; He, Z.; Zhang, W.; Gao, N.; Deng, J.; Chen, J. Catalytic performance of wrapped CoO by MgO in oxidative degradation of chloroquine phosphate with peroxymonosulfate. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 573, 151430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, A.; Hwa, K.-Y. Construction of zinc selenide microspheres decorated with octadecylamine-functionalized reduced graphene oxide as an effective catalyst for the dual-mode detection of chloroquine phosphate. Mater. Today Chem. 2022, 24, 100862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.-H.; Ji, H.; Wang, C.-C.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.-H.; Zhao, C.; Wang, A.; Fu, H.; Wang, P.; Zhao, X. Photocatalysis-activated SR-AOP over PDINH/MIL-88A (Fe) composites for boosted chloroquine phosphate degradation: Performance, mechanism, pathway and DFT calculations. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 293, 120229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Wu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, X.; Dai, H.; Wei, Y.; Xu, G.; Hu, F. Activation of peroxymonosulfate by single atom Co-NC catalysts for high-efficient removal of chloroquine phosphate via non-radical pathways: Electron-transfer mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midassi, S.; Bedoui, A.; Bensalah, N. Efficient degradation of chloroquine drug by electro-Fenton oxidation: Effects of operating conditions and degradation mechanism. Chemosphere 2020, 260, 127558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-González, R.B.; Flores-Contreras, E.A.; Parra-Saldívar, R.; Iqbal, H.M. Bio-removal of emerging pollutants by advanced bioremediation techniques. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliano, E.; Sgroi, M.; Falciglia, P.P.; Vagliasindi, F.G.; Roccaro, P. Removal of poly-and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from water by adsorption: Role of PFAS chain length, effect of organic matter and challenges in adsorbent regeneration. Water Res. 2020, 171, 115381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchelkia, N.; Mouni, L.; Belkhiri, L.; Bouzaza, A.; Bollinger, J.-C.; Madani, K.; Dahmoune, F. Removal of lead (II) from water using activated carbon developed from jujube stones, a low-cost sorbent. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 1645–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammar, A.C.; Mouni, L.; Bollinger, J.-C.; Belkhiri, L.; Bouzaza, A.; Assadi, A.A.; Belkacemi, H. Modeling and optimization of process parameters in elucidating the adsorption mechanism of Gallic acid on activated carbon prepared from date stones. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 3113–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamouche, M.; Mouni, L.; Ayachi, A.; Merniz, I. Use of commercial activated carbon for the purification of synthetic water polluted by a pharmaceutical product. Desalin. Water Treat. 2019, 172, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araujo, C.M.B.; Wernke, G.; Ghislandi, M.G.; Diório, A.; Vieira, M.F.; Bergamasco, R.; Sobrinho, M.A.D.M.; Rodrigues, A.E. Continuous removal of pharmaceutical drug chloroquine and Safranin-O dye from water using agar-graphene oxide hydrogel: Selective adsorption in batch and fixed-bed experiments. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-X.; Liu, L.; Li, Q.-F.; Xiao, H.; Wang, M.-L.; Tu, H.-C.; Lin, J.-M.; Zhao, R.-S. Nitrogen-rich based conjugated microporous polymers for highly efficient adsorption and removal of COVID-19 antiviral drug chloroquine phosphate from environmental waters. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 305, 122517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barquilha, C.E.; Braga, M.C. Adsorption of organic and inorganic pollutants onto biochars: Challenges, operating conditions, and mechanisms. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2021, 15, 100728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Meng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y. Effects of modification and magnetization of rice straw derived biochar on adsorption of tetracycline from water. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 311, 123455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wu, C.; Chai, C.; Cao, S.; Bai, X.; Ma, K.; Jin, X.; Shi, X.; Jin, P. Adsorption of micropollutants from wastewater using iron and nitrogen co-doped biochar: Performance, kinetics and mechanism studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zuo, X.; Yang, S.; Chen, R.; Cai, T.; Ding, D. Evaluation of potassium ferrate activated biochar for the simultaneous adsorption of copper and sulfadiazine: Competitive versus synergistic. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Chen, N.; Liu, T.; Feng, C. KHCO3 activated biochar supporting MgO for Pb(II) and Cd(II) adsorption from water: Experimental study and DFT calculation analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 426, 128059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Song, C.; Wang, P.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhan, S. Generating dual-active species by triple-atom sites through peroxymonosulfate activation for treating micropollutants in complex water. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2300085120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, T.; Han, C.; Lv, X.; Bai, L.; Sun, X.; Zhang, P. Facile synthesis of Fe-modified lignin-based biochar for ultra-fast adsorption of methylene blue: Selective adsorption and mechanism studies. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 344, 126186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Tan, X.; Almatrafi, E.; Ye, S.; Song, B.; Chen, Q.; Yang, H.; Fu, Q.; Deng, Y.; Zeng, Z.; et al. Alfalfa biochar supported Mg-Fe layered double hydroxide as filter media to remove trace metal(loid)s from stormwater. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 844, 156835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, M.; Pang, Y.; Hao, Z.; Hu, M.; Qiu, R.; Chen, Z. Enhanced adsorption of tetracycline by an iron and manganese oxides loaded biochar: Kinetics, mechanism and column adsorption. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 320, 124264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Yan, X.; Mi, X.; Wu, Y.; Qian, J.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, G.-H. Enhanced catalytic degradation of aqueous doxycycline (DOX) in Mg-Fe-LDH@ biochar composite-activated peroxymonosulfate system: Performances, degradation pathways, mechanisms and environmental implications. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 425, 131457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Okoye, P.; Hummadi, E.; Hameed, B. High-performance porous biochar from the pyrolysis of natural and renewable seaweed (Gelidiella acerosa) and its application for the adsorption of methylene blue. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 278, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, D.; Huang, Y.; Gu, S.; Chen, W. Understanding reactions and pore-forming mechanisms between waste cotton woven and FeCl3 during the synthesis of magnetic activated carbon. Chemosphere 2020, 241, 125120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.-L.; Liu, W.-J.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, H. Magnesium Oxide Embedded Nitrogen Self-Doped Biochar Composites: Fast and High-Efficiency Adsorption of Heavy Metals in an Aqueous Solution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 10081–10089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Fan, S.; Xu, H. Effect of Fe–N modification on the properties of biochars and their adsorption behavior on tetracycline removal from aqueous solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 325, 124732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premarathna, K.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Sarkar, B.; Kwon, E.E.; Bhatnagar, A.; Ok, Y.S.; Vithanage, M. Biochar-based engineered composites for sorptive decontamination of water: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 372, 536–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, M.-H.; Liu, H.; Liu, H.; Zheng, Z.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, C.; Wen, D. Pyrolyzing pharmaceutical sludge to biochar as an efficient adsorbent for deep removal of fluoroquinolone antibiotics from pharmaceutical wastewater: Performance and mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 426, 127798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.-T.; Vo, T.-D.; Nguyen, T.-B.; Dat, N.D.; Huu, B.T.; Nguyen, X.-C.; Tran, T.; Le, T.-N.; Duong, T.-G.; Bui, M.-H.; et al. Adsorption of norfloxacin from aqueous solution on biochar derived from spent coffee ground: Master variables and response surface method optimized adsorption process. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Huang, J.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Chen, H.; Hu, X.; Gao, B. Mechanisms and adsorption capacities of hydrogen peroxide modified ball milled biochar for the removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 337, 125432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gang, D.D.; Zhang, J.; Lei, X.; Lian, Q.; Holmes, W.E.; Zappi, M.E.; Yao, H. Insight into the activation mechanisms of biochar by boric acid and its application for the removal of sulfamethoxazole. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhou, C.; Yang, R.; Xing, Y.; Xu, S.; Jiang, D.; Tian, D.; Shi, W. Interfacial Engineering of the CoxP–Fe2P Heterostructure for Efficient and Robust Electrochemical Overall Water Splitting. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 7737–7748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Huang, L.; Wu, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, S.; Xiao, X.; Li, M.; Zou, X. Adsorption of sulfonamides on biochars derived from waste residues and its mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shi, J.; Luo, X. Enhanced adsorption of rhodamine B from water by Fe-N co-modified biochar: Preparation, performance, mechanism and reusability. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 343, 126103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Wu, X.; Syed-Hassan, S.S.A.; Zhang, S.; Mood, S.H.; Milan, Y.J.; Garcia-Perez, M. Characteristics and mechanisms of phosphorous adsorption by rape straw-derived biochar functionalized with calcium from eggshell. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 318, 124063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Yang, J.; Gao, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Xu, Z. Removal of chromium (VI) from water by porous carbon derived from corn straw: Influencing factors, regeneration and mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 369, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-Y.; Lin, P.-Y.; Hsieh, S.-L.; Kirankumar, R.; Patel, A.K.; Singhania, R.-R.; Dong, C.-D.; Chen, C.-W.; Hsieh, S. Engineered mesoporous biochar derived from rice husk for efficient removal of malachite green from wastewaters. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 347, 126749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.D. Chloroquine phosphate. In Analytical Profiles of Drug Substances; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1976; Volume 5, pp. 61–85. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.-B.; Truong, Q.-M.; Chen, C.-W.; Doong, R.-A.; Chen, W.-H.; Dong, C.-D. Mesoporous and adsorption behavior of algal biochar prepared via sequential hydrothermal carbonization and ZnCl2 activation. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 346, 126351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Chen, S.; Qi, Y.; Yang, L.; Wu, L.; He, L.; Li, P.; Qi, X.; Gao, F.; Ding, Y.; et al. An efficient, green and sustainable potassium hydroxide activated magnetic corn cob biochar for imidacloprid removal. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Luo, Z.; Du, S.; Yang, J.; Zhi, D.; Zhou, Y. Sustainable biochar/MgFe2O4 adsorbent for levofloxacin removal: Adsorption performances and mechanisms. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 340, 125698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, S.; Ke, X.-X.; Shao, Z.-D.; Zhong, L.-B.; Zhao, Q.-B.; Zheng, Y.-M. Fish scale-based biochar with defined pore size and ultrahigh specific surface area for highly efficient adsorption of ciprofloxacin. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 131962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, X.; Lv, S.; Yang, J.; Cui, S.; Zhao, Z. Carboxyl-functionalized biochar derived from walnut shells with enhanced aqueous adsorption of sulfonamide antibiotics. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 280, 111749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Wang, Z.; Guo, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, J.; Xie, X. Enhanced adsorption of ciprofloxacin by KOH modified biochar derived from potato stems and leaves. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 77, 1127–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, Z.; Shen, J.; Kang, J.; Zhao, S.; Wang, B.; Chen, Q.; Li, X. Dynamic adsorption models and artificial neural network prediction of mercury adsorption by a dendrimer-grafted polyacrylonitrile fiber in fixed-bed column. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 310, 127511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, M.; Gong, Y.; Zeng, E.Y. Efficient removal of mercury from simulated groundwater using thiol-modified graphene oxide/Fe–Mn composite in fixed-bed columns: Experimental performance and mathematical modeling. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 714, 136636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizito, S.; Wu, S.; Wandera, S.M.; Guo, L.; Dong, R. Evaluation of ammonium adsorption in biochar-fixed beds for treatment of anaerobically digested swine slurry: Experimental optimization and modeling. Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 563–564, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Kinetic Equation | Parameters | RSB | Fe/Mg-RSB |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order | qm (mg/g) | 8.47 | 12.46 |
| K1 (min−1) | 0.01 | 0.01 | |
| R2 | 0.97 | 0.919 | |
| Pseudo-second-order | qm (mg/g) | 9.86 | 14.17 |
| K2 (g/(mg·min)) | 11.06 | 41.74 | |
| R2 | 0.995 | 0.971 | |
| Intra-particle diffusion | K1 (mg/(g·min0.5)) | 0.601 | 0.691 |
| R2 | 0.952 | 0.907 | |
| K2 (mg/(g·min0.5)) | 0.261 | 0.479 | |
| R2 | 0.941 | 0.982 | |
| K3 (mg/(g·min0.5)) | 0.073 | 0.045 | |
| R2 | 0.964 | 0.971 |
| Operation Parameters | m0 (g) | Yoon-Nelson Model | Yan Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C0 (mg/L) | Q0 (mL/min) | KYN (min−1) | τ (min) | R2 | qy (mg/g) | a | R2 | |
| 10 | 4 | 0.6 | 0.0134 | 109.465 | 0.985 | 8.364 | 0.533 | 0.978 |
| 30 | 4 | 0.6 | 0.0225 | 67.166 | 0.979 | 17.381 | 0.547 | 0.954 |
| 50 | 4 | 0.6 | 0.0466 | 26.166 | 0.918 | 29.419 | 0.278 | 0.820 |
| 30 | 2 | 0.6 | 0.0073 | 174.907 | 0.985 | 21.409 | 0.536 | 0.964 |
| 30 | 6 | 0.6 | 0.0524 | 23.277 | 0.839 | 21.057 | 0.314 | 0.780 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, H.; He, J.; Liu, Y.; Ji, X.; Wang, G.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y. Removal Performance and Mechanism of Emerging Pollutant Chloroquine Phosphate from Water by Iron and Magnesium Co-Modified Rape Straw Biochar. Molecules 2023, 28, 3290. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083290
Sun H, He J, Liu Y, Ji X, Wang G, Yang X, Zhang Y. Removal Performance and Mechanism of Emerging Pollutant Chloroquine Phosphate from Water by Iron and Magnesium Co-Modified Rape Straw Biochar. Molecules. 2023; 28(8):3290. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083290
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Hongwei, Jinjin He, Yucan Liu, Xianguo Ji, Gang Wang, Xiaoyong Yang, and Yanxiang Zhang. 2023. "Removal Performance and Mechanism of Emerging Pollutant Chloroquine Phosphate from Water by Iron and Magnesium Co-Modified Rape Straw Biochar" Molecules 28, no. 8: 3290. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083290
APA StyleSun, H., He, J., Liu, Y., Ji, X., Wang, G., Yang, X., & Zhang, Y. (2023). Removal Performance and Mechanism of Emerging Pollutant Chloroquine Phosphate from Water by Iron and Magnesium Co-Modified Rape Straw Biochar. Molecules, 28(8), 3290. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083290






