Electrospun Nanofiber Membrane: An Efficient and Environmentally Friendly Material for the Removal of Metals and Dyes
Abstract
1. Introduction
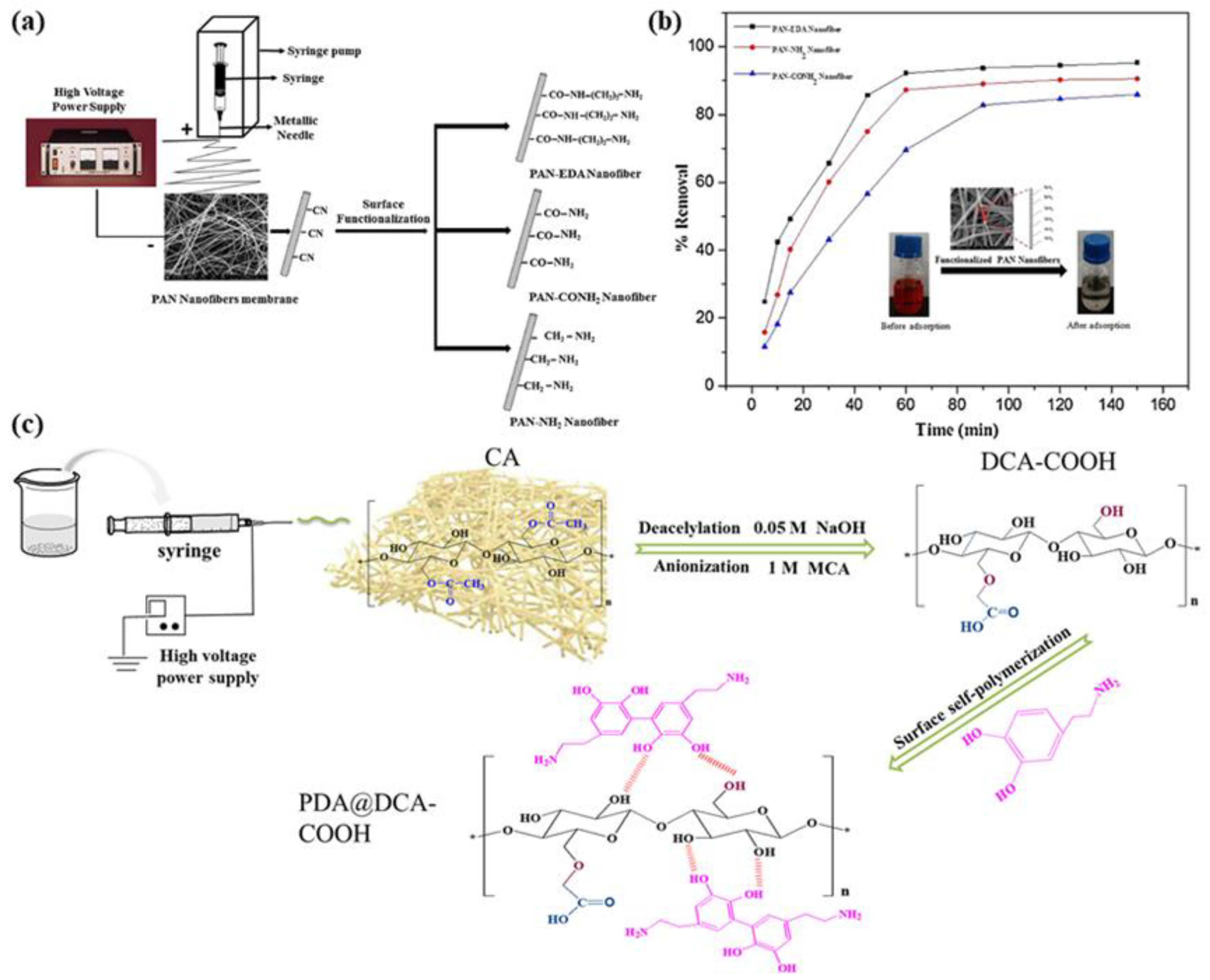
2. Preparation and Structure of Nanofiber Membrane
2.1. Electrospinning Technology
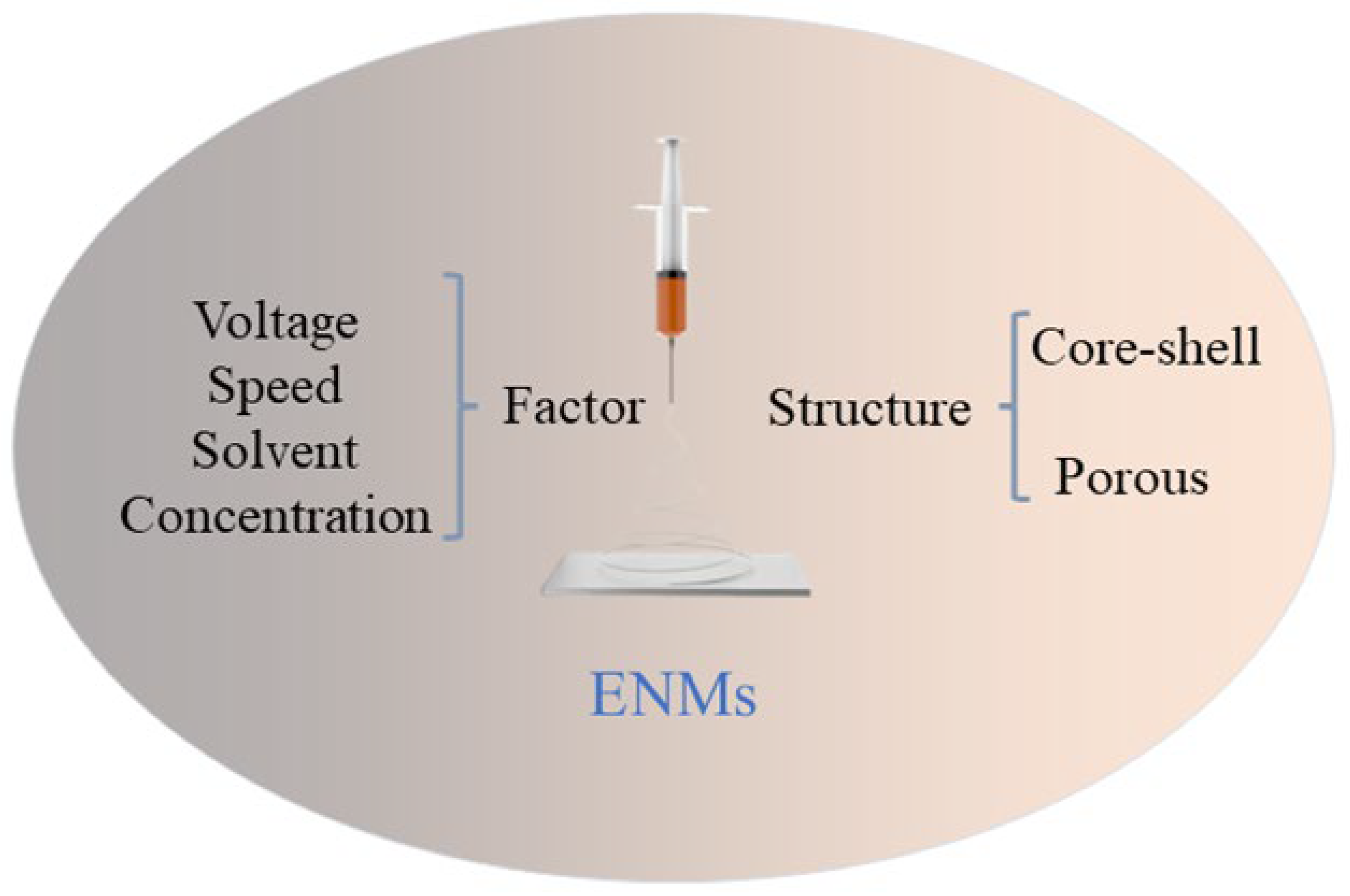
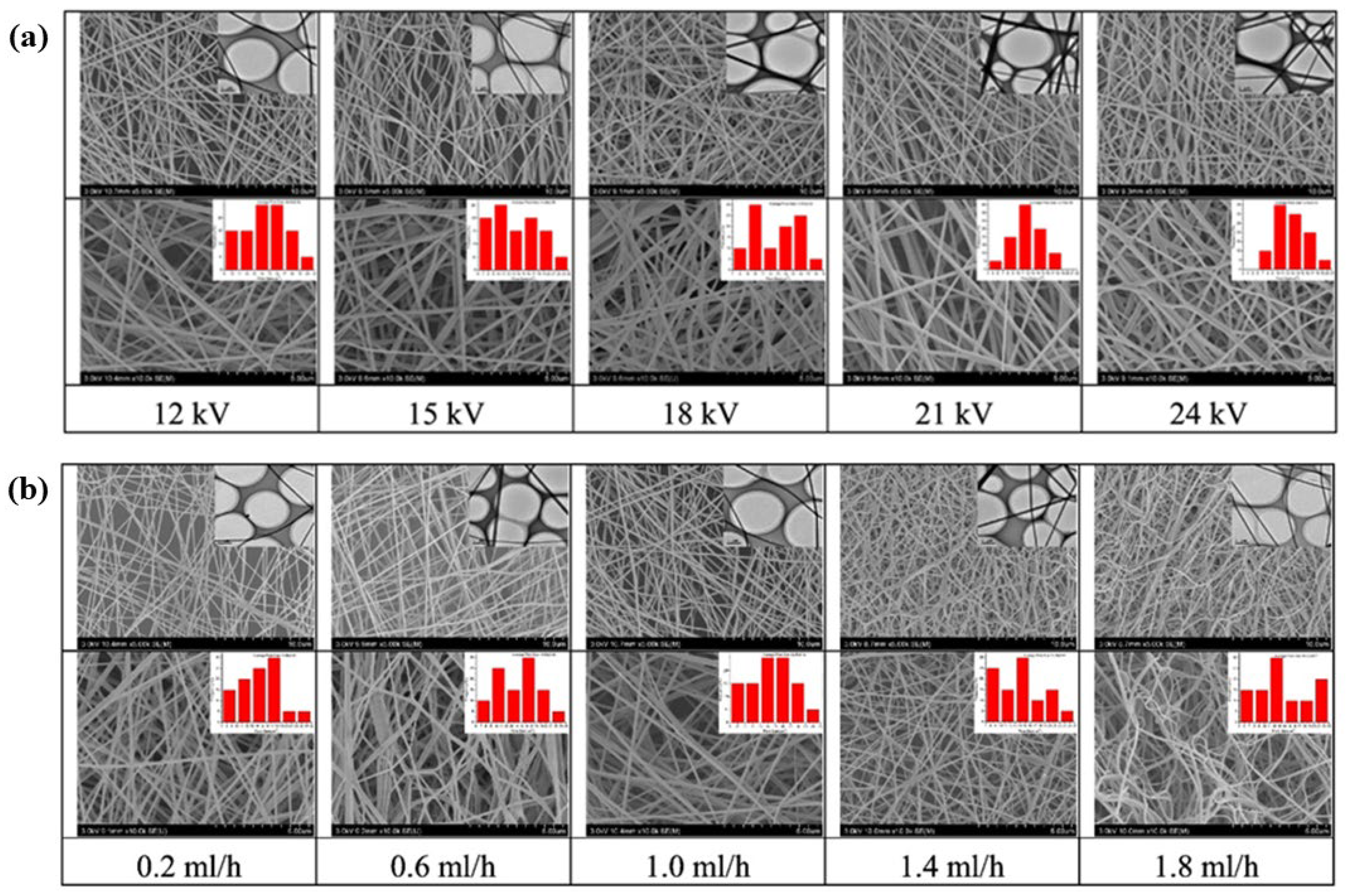
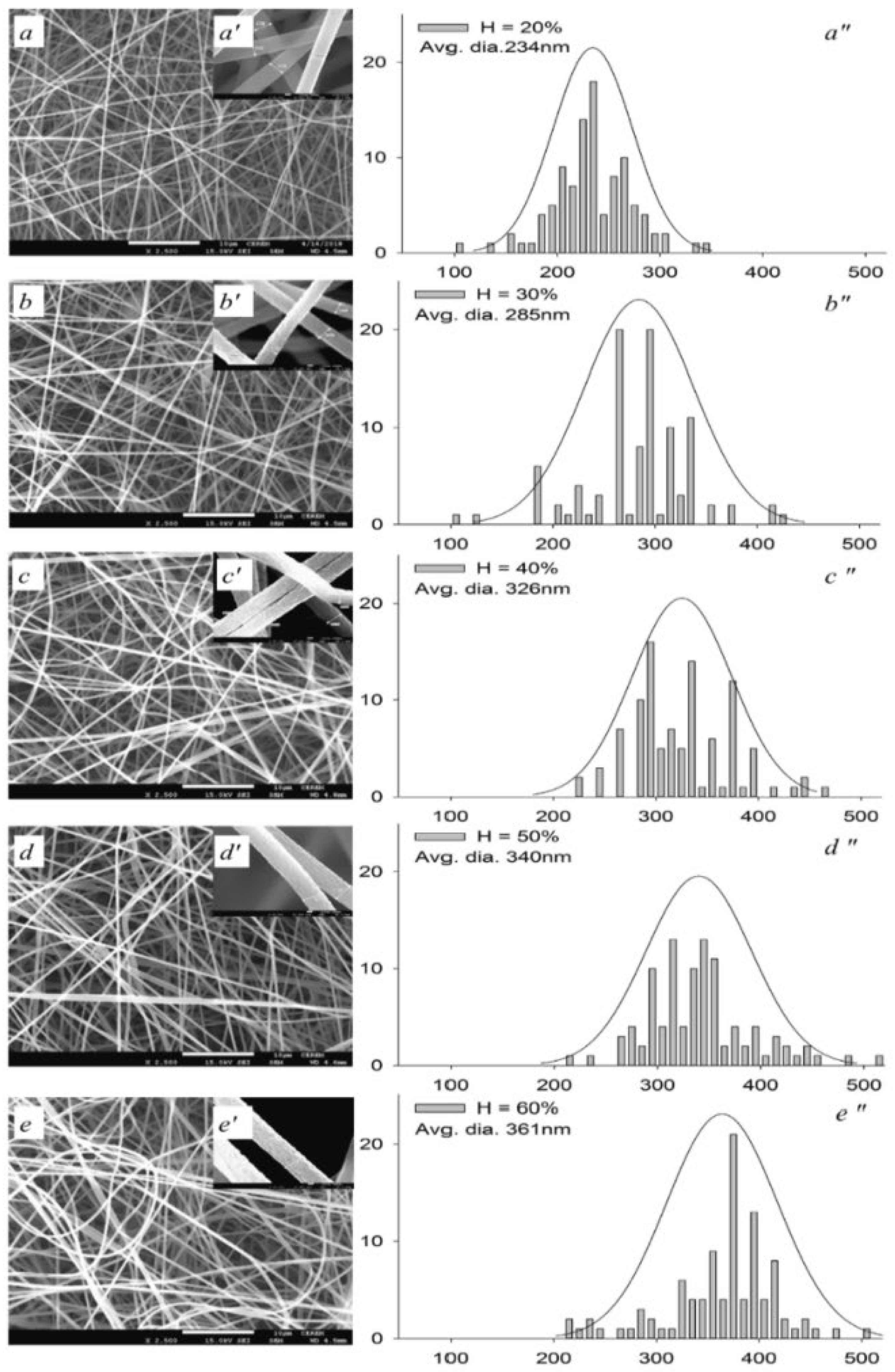
2.2. Factors Affecting Electrospinning
2.3. Nanofiber Membrane Structure
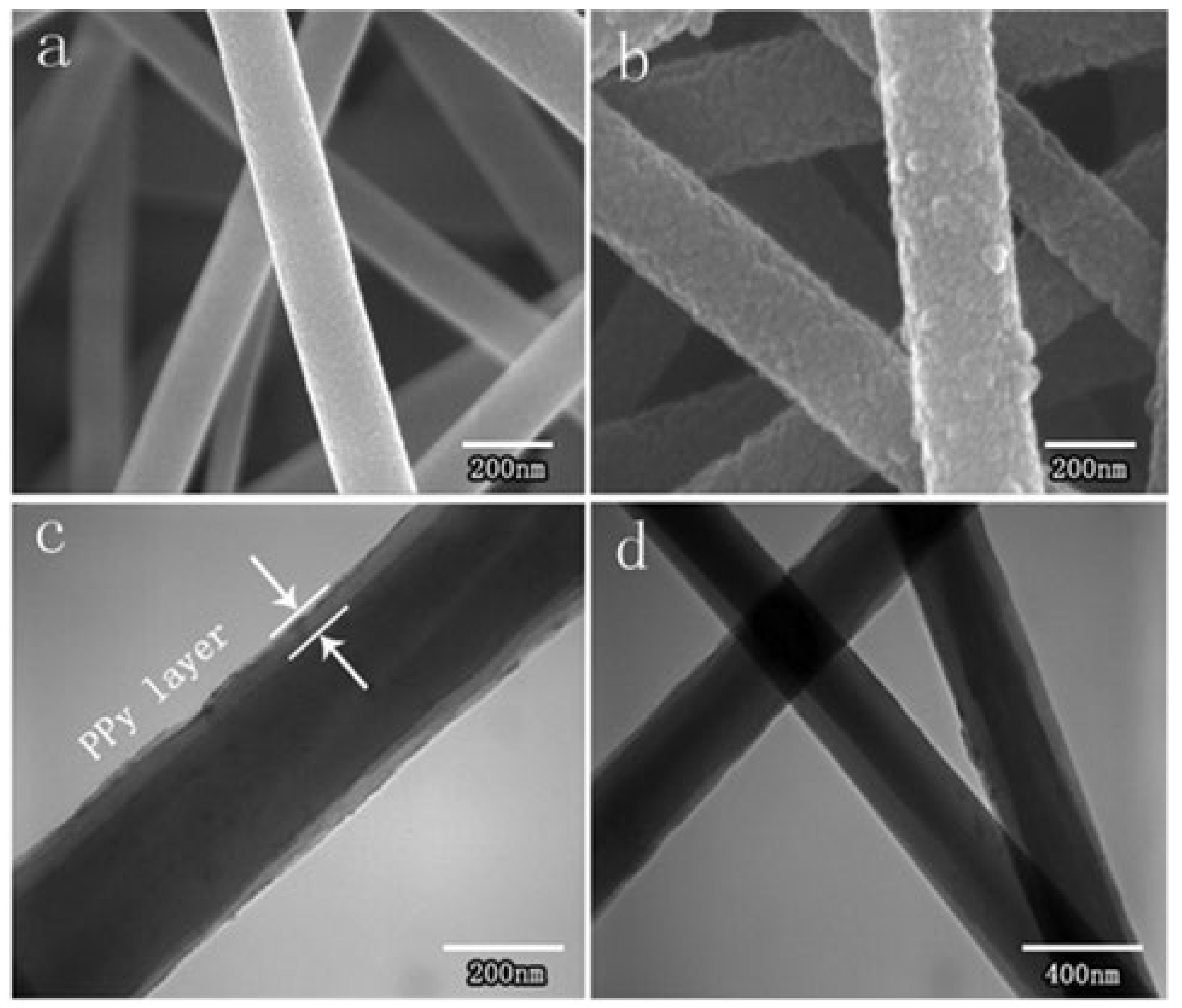
2.3.1. Core–Shell Structure Electrospray Nanofiber Membrane
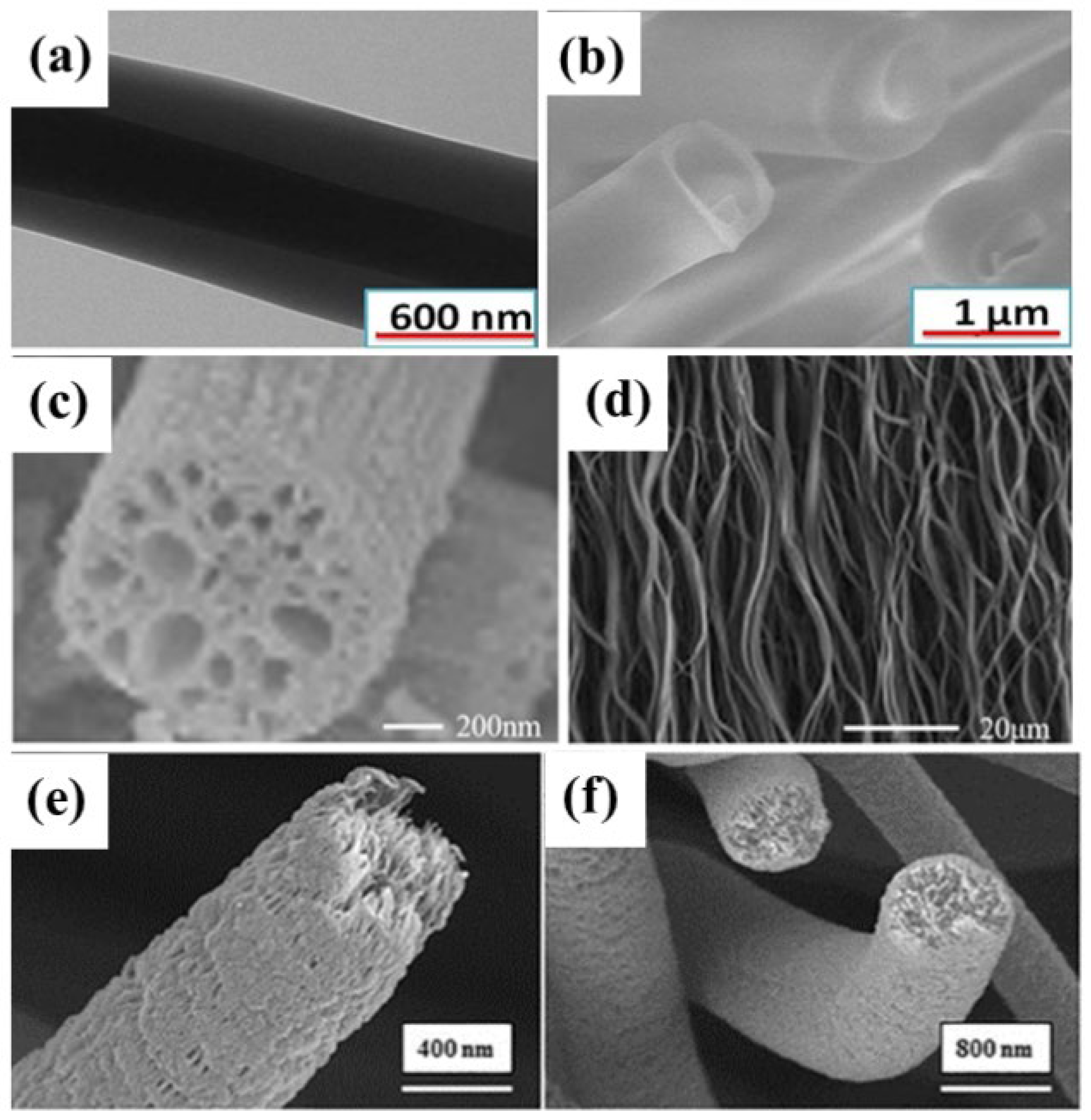
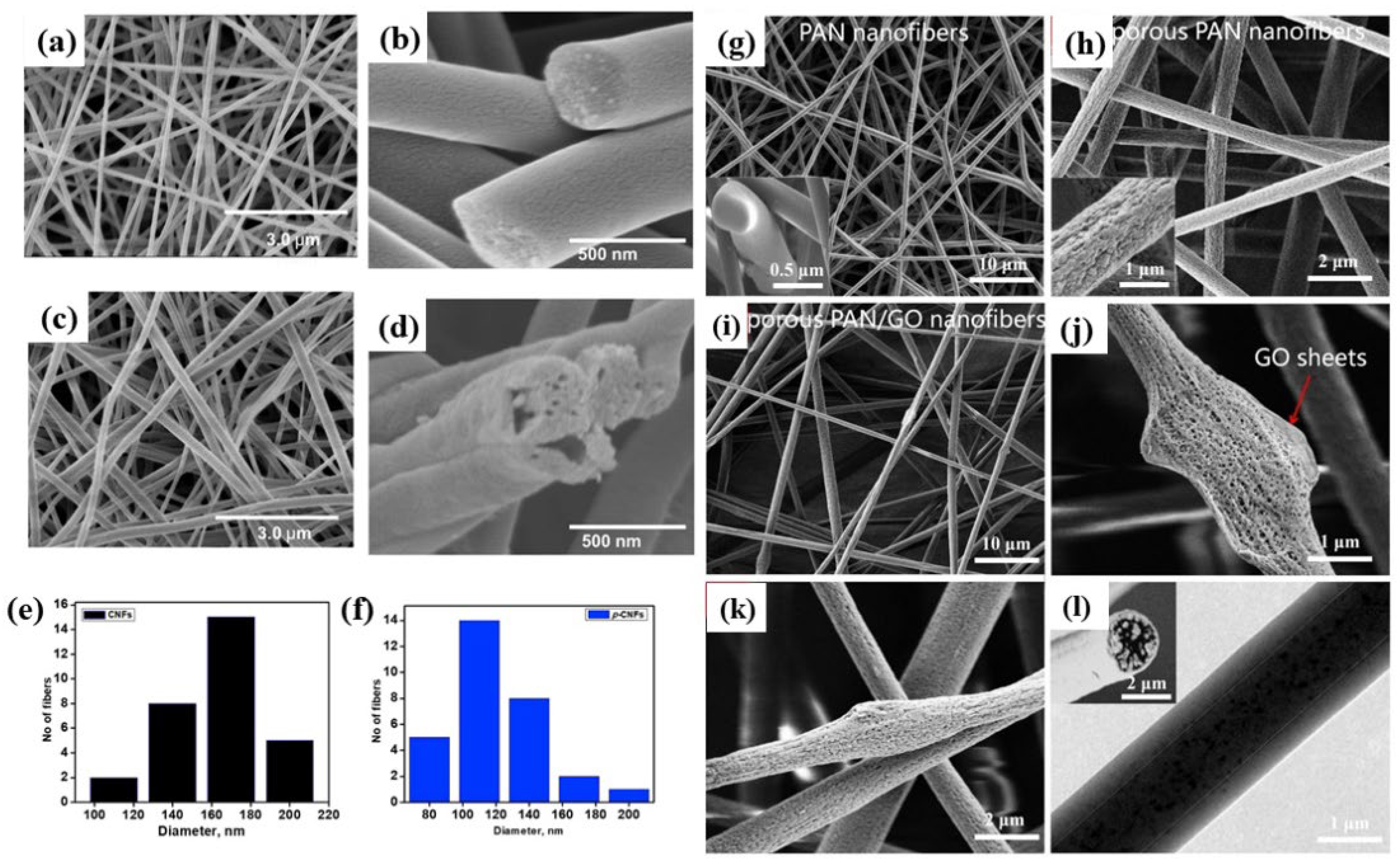
2.3.2. Porous Nanofiber Membrane
3. Applications of ENM Wastewater Treatment
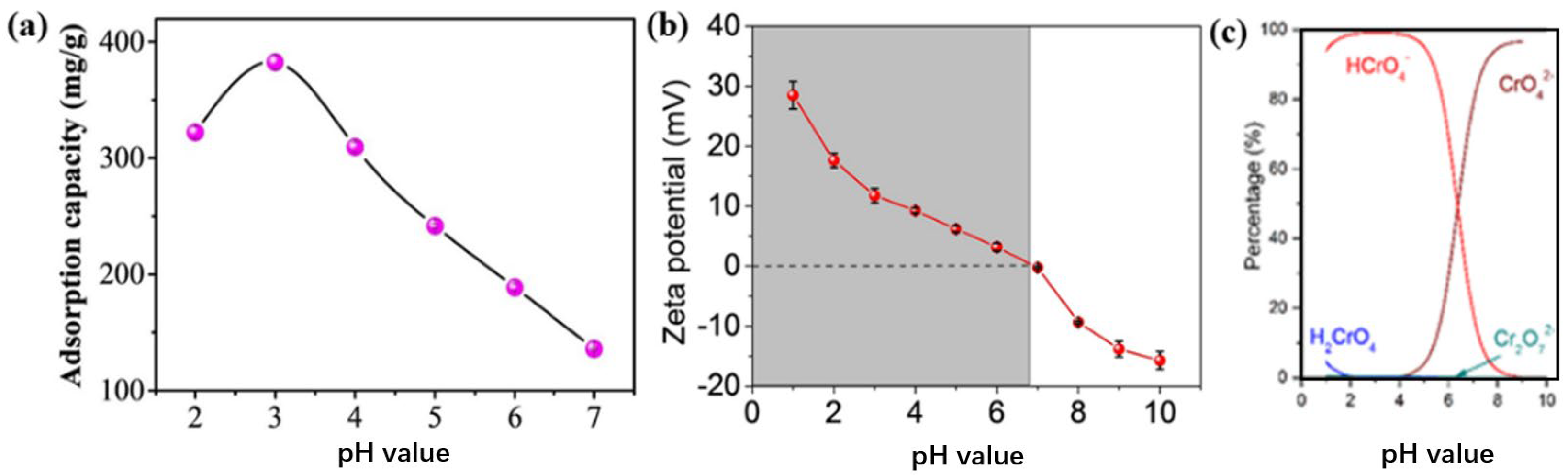
3.1. Heavy Metal Ion Removal
3.1.1. Heavy Metal Ion Adsorption
| Nanofiber Adsorbent | Polymer | Surface Area (m2·g−1) | Heavy Metal Ions | Maximum Adsorption Capacity (mg·g−1) | pH | T (°C) | Sample Volume (mL) | Kinetics Model | Isotherms Model | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDA/MnO2/PAN | PAN | 66 | Pb2+ | 185.19 | 6 | 25 | / | Pseudo-second-order model | Langmuir isotherm model | [76] |
| PVA/PEI | PVA PEI | / | Cr6+ | 150 | 4 | 25 | 10 | Pseudo-first-order model | Langmuir isotherm model | [77] |
| PAN/Fe2O3@Fe2O3 | PAN | / | Pb2+ | 57 | / | 25 | 50 | Pseudo-first-order model | Langmuir isotherm model | [78] |
| PAN-CNT/TiO2-NH2 | PAN | / | Cr6+ | 714 | 2 | 20 | 100 | Pseudo-first-order model | Freundlich isotherm model | [79] |
| PA6@Mg (OH)2 | PA6 | / | Cr6+ | 294.6 | 3 | 25 | 40 | Pseudo-second-order model | Freundlich isotherm model | [80] |
| PVA@SiO2 | PVA | 370 | Cu2+ | 489.12 | 6 | 25 | 100 | / | Redlich-Peterson isotherm model | [81] |
| CS-PGMA-PEI | CS | / | Cr6+ | 138.96 | 2 | 25 | 10 | Pseudo-second-order model | Langmuir isotherm model | [82] |
| EDTA-EDA-PAN | PAN | / | Cr6+ | 66 | 3 | 25 | 25 | Pseudo-second-order | Freundlich isotherm model | [83] |
| m-PEI/PVDF | CCN | / | Cr6+ | 109 | 3 | 25 | / | Pseudo-second-order | Freundlich isotherm model | [84] |
| HMO-PAN | PAN | / | Pb2+ | 194 | 7 | 25 | 20 | Pseudo- second- order model | Freundlich isotherm model | [85] |
| CA/Fe3O4 | CA | / | Pb2+ | 44 | 6 | 27 | 50 | Pseudo- second- order model | Freundlich isotherm model | [86] |
| PA6/Fe3O4/o-MWCNTs | PA6 | / | Pb2+ | 49 | 6 | 25 | 50 | / | / | [87] |
| Lys-CNFs | CNFs | 220 | Pb2+ | 270 | 6 | 25 | 50 | Pseudo-second-order model | Langmuir isotherm model | [88] |
| Thiol-functionalized cellulose | CS | / | Pb2+ | 22 | 4 | 25 | 50 | Pseudo-second-order model | Langmuir isotherm model | [89] |
| CS-DTPA/PEO | CS | / | Pb2+ | 142 | 5 | 25 | / | Pseudo-second-order model | Langmuir isotherm model | [90] |
| Hal/Fe3O4/PEO/CS | CS | 38 | Pb2+ | 67 | 7 | 25 | / | Pseudo-second-order model | Langmuir isotherm model | [91] |
| Palygorskite/chitin | ChNFs | / | Pb2+ | 53.7 | 7 | 25 | 50 | Pseudo-second-order model | Freundlich isotherm model | [92] |
| MgAl-EDTA-LDH@PAN | PAN | / | Cu2+ | 120.7 | 5 | 25 | / | Pseudo-second-order model | Langmuir isotherm model | [93] |
| Adsorbent | Surface Area | Adsorption of Metal Ions | Maximum Adsorption Capacity (mg·g−1) | pH | T (°C) | Sample Volume | Kinetics Model | Isotherms Model | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rGO/PEI-KOH | / | Cr6+ | 398 | 2 | 25 | 2 | Pseudo-second-order model | Langmuir isotherm model | [76] |
| Fe3O4@Arg-PPy NC | 22 | Cr6+ | 322 | 2 | 25 | / | Pseudo-second-order model | / | [77] |
| PPy-rGO/Fe3O4 | 80 | Cr6+ | 226 | 3 | 30 | 40 | Pseudo-second-order model | Langmuir isotherm model | [79] |
| Hierarchical MnO2 microspheres | 252 | Pb2+ | 139 | 3 | 30 | 100 | / | Freundlich isotherm model | [82] |
| NTA-β-CD-CS | / | Hg2+ | 178.3 | 6 | 25 | / | Pseudo-second-order | Langmuir isotherm model | [83] |
| C-phenylcalix pyrogallolarene | / | Cu2+ | 8 | 5 | 25 | / | / | / | [94] |
| Sepiolite@polyethyleneimine/SA | / | Pb2+ | 1094 | 5.5 | 25 | 10 | Pseudo-second-order model | Langmuir model | [95] |
| SA@PEI-CDs | / | Pb2+ | 380 | 4 | 25 | 10 | Pseudo-second-order model | Freundlich isotherm model | [96] |
| PAAO cryogels | / | Pb2+ | 450 | 5 | 25 | 75 | Pseudo-second-order model | Freundlich isotherm model | [97] |
| CS/PVP/PVA | 2.12 | Pb2+ | 16 | / | 25 | / | Pseudo-second-order model | Langmuir isotherm model | [68] |
| Cellulose/chitosan/alginic acid hydrogels | / | Cu2+ | 760 | / | 25 | / | Pseudo-first-order model | Freundlich isotherm mode | [98] |
| Nanocellulose/sodium alginate/carboxymethyl-chitosan | 284 | Pb2+ | 472 | 5 | 25 | 50 | Pseudo-second-order model | Langmuir model | [99] |
3.1.2. Heavy Metal Ion Filtration
3.1.3. Summary of Heavy Metal Removal
3.2. Dye Removal
3.2.1. Adsorption of Dyes
| Nanofiber Adsorbent | Polymer | Surface Area (m2·g−1) | Dyes | Maximum Adsorption Capacity (mg·g−1) | pH | T (°C) | Sample Volume | Kinetics Model | Isotherms Model | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPy/PANi | PANi | / | CR | 250 | 6 | 25 | 150 | Pseudo-second-order model | Langmuir isotherm model | [110] |
| Gelatin/calcium Alginate | SA | / | MB | 2046 | 4 | 25 | 25 | Pseudo-second-order mode | Langmuir isotherm model | [16] |
| GO/CS | CS | / | MB | 584 | 5 | 25 | 50 | Pseudo-second-order model | Freundlich isotherm mode | [111] |
| Carboxylated Mn2O3 | Carboxylated | 148 | MB | 1175 | 9 | 25 | 400 | Pseudo-second-order model | Langmuir isotherm model | [112] |
| Functionalized PAN | PAN | / | MG | 200 | 8 | 25 | / | Pseudo-second-order kinetic model. | Langmuir isotherm model | [113] |
| PVP/alumina | PVP | 417 | MO | 351 | 5.5 | 25 | 30 | Pseudo-second-order model | Langmuir isotherm model | [114] |
| PAN-CNT | PAN | / | MG | 88 | 10 | 25 | / | Pseudo-second-order model. | / | [115] |
| Sodium alginate/polyvinyl alcohol | PVA | / | MB | 9 | / | 25 | / | / | / | [116] |
| Vinyl-modified mesoporous poly(acrylic acid)/SiO2 | PAA | 523 | MG | 220 | 30 | 50 | Pseudo-second-order model | Freundlich isotherm model | [117] | |
| NiFe LDH/PAN/GO | PAN | / | RB | 6.19 | 6 | 25 | 40 | Pseudo-first-order model | Langmuir isotherm model | [42] |
| Mesoporous carbon | PVP | 1642 | MC | 567 | 3 | / | 10 | Pseudo-second-order kinetic model | Langmuir adsorption isotherm model | [118] |
| ZnO-HT-PAN_H | PAN | / | RB | 267 | / | 25 | 15 | Pseudo-first-order model | Langmuir isotherm model | [119] |
| PVDF/PDA | PVDF | / | MB | 173 | / | 25 | 50 | Pseudo-second-order model | Langmuir isotherm model | [120] |
| Adsorbent | Surface Area (m2·g−1) | Dyes | Maximum Adsorption Capacity (m2·g−1) | pH | T (°C) | Sample Volume | Kinetics Model | Isotherms Model | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NTA-β-CD-CS | / | MB | 162 | 6 | 25 | 25 | Pseudo-second-order mode | Langmuir isotherm model | [89] |
| T-QT/CS | 68.4 | MB | 917 | 9 | 25 | / | Pseudo-second-order model | Langmuir isotherm model | [121] |
| CS2/CMC2-PEG | / | CR | 1053 | / | 25 | 20 | Pseudo-second-order model | Freundlich isotherm model | [122] |
| Pectin/graphene oxide aerogel | / | RhB | 419 | / | 25 | 100 | Pseudo-first-order model | Freundlich isotherm model | [123] |
| Benzenesulfonyl hydrazone modified guar gum | 19 | CR | 1065 | 10 | 25 | 10 | Pseudo-second-order model | Langmuir isotherm model | [124] |
| Barberry stem powder | / | RR 195 | 27 | / | / | / | Pseudo-first-order model | Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms model | [125] |
| α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles | 165 | RR 195 | 20 | / | / | / | Pseudo-second-order model | Langmuir isotherm model | [126] |
| Ca-alginate/citric acid (CA)-sawdust/UiO-66-NH2 hydrogel beads | 15 | MB | 25 | 6 | 25 | 10 | Pseudo-second-order model | Freundlich isotherm model | [127] |
3.2.2. Summary of Dye Removal
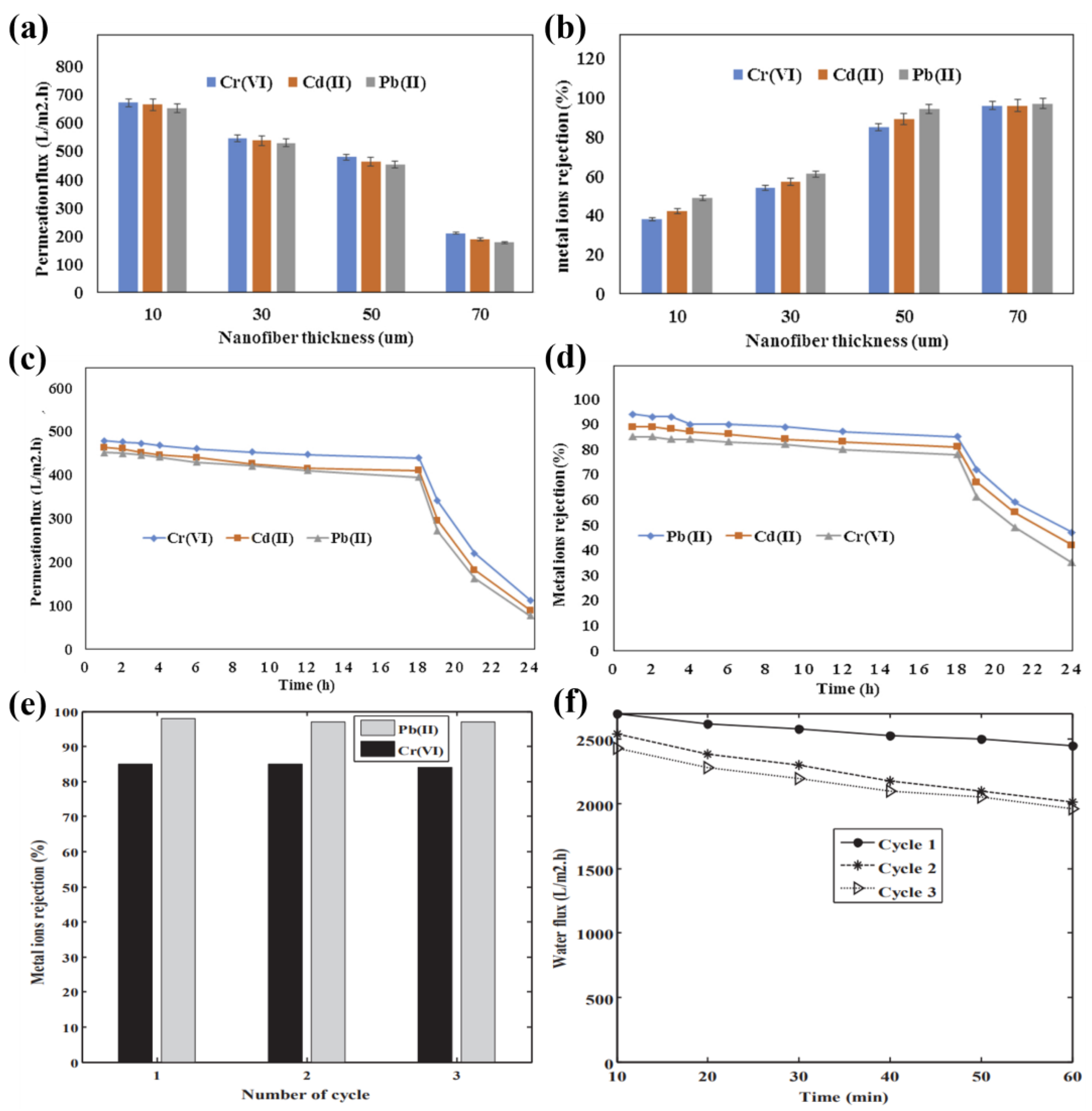
3.3. Factors Affecting Performance
3.4. The More Advantageous ENMs
4. Summary and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, R.; Liang, R.; Dai, T.; Chen, J.; Shuai, X.; Liu, C. Pectin-based adsorbents for heavy metal ions: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 91, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu Poudel, M.; Shin, M.; Joo Kim, H. Interface engineering of MIL-88 derived MnFe-LDH and MnFe2O3 on three-dimensional carbon nanofibers for the efficient adsorption of Cr(VI), Pb(II), and As(III) ions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 287, 120463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hmtshirazi, R.; Mohammadi, T.; Asadi, A.A.; Tofighy, M.A. Electrospun nanofiber affinity membranes for water treatment applications: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 47, 102795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.; Le, T.-H.; Lee, H.; Lee, J.; Kim, M.; Lee, S.; Chang, M.; Yoon, H. Macrocyclic ligand-embedded graphene-in-polymer nanofiber membranes for lithium ion recovery. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, T.N.; Ma, C.Y.; Hsiao, P.H.; Ko, W.C.; Huang, Y.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Jain, J.; Huang, E.W. Tunable Mechanical and Electrical Properties of Coaxial Electrospun Composite Nanofibers of P(VDF-TrFE) and P(VDF-TrFE-CTFE). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clementino, M.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Z. Oxidative Stress and Metabolic Reprogramming in Cr(VI) Carcinogenesis. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2018, 8, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.Y.; Murphy, A.; Sun, H.; Costa, M. Molecular and epigenetic mechanisms of Cr(VI)-induced carcinogenesis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 377, 114636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; He, J.; Wang, L.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, G.; Liu, W.; Shu, Y.; Gong, W.; Ma, X.L.; et al. Epigenetic alterations of CXCL5 in Cr(VI)-induced carcinogenesis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838 Pt 1, 155713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Shetty, M.; Karthik, K.V.; Patil, J.H.; Murthy Shekhar, S.; Desai, S.M.; Hiremath, P.G.; Ravishankar, R. Sorption studies of Cr (VI) ions from synthetic waste water using chitosan embedded in calcium alginate beads. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 76, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, L.M.; Espinosa, E.; Mendoza Zelis, P.; Morcillo Martin, R.; De Haro Niza, J.; Rodriguez, A. Cellulose nanofibers/PVA blend polymeric beads containing in-situ prepared magnetic nanorods as dye pollutants adsorbents. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 209 Pt A, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Fu, R.; Huang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, B.; Lin, S.; Yan, B.; Yang, Q.; Chen, S. Efficient and recyclable ultra-thin diameter polyacrylonitrile nanofiber membrane: Selective adsorption of cationic dyes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 302, 122109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ma, H.; Xing, B. Electrospinning of multifunctional cellulose acetate membrane and its adsorption properties for ionic dyes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 158, 1342–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgouvelas, D.; Abdelhamid, H.N.; Li, J.; Edlund, U.; Mathew, A.P. All-cellulose functional membranes for water treatment: Adsorption of metal ions and catalytic decolorization of dyes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 264, 118044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadirvelu, K.; Fathima, N.N. Keratin functionalized electrospun PEI/PAN microfiltration system as a simple and sustainable approach for anionic dye removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.S.; Venkatesh, K.; Gui, E.L.; Jayaraman, S.; Singh, G.; Arthanareeswaran, G. Electrospun carbon nanofibers/TiO2-PAN hybrid membranes for effective removal of metal ions and cationic dye. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2018, 10, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Qi, P.; Ju, J.; Wang, Q.; Hao, L.; Wang, R.; Sui, K.; Tan, Y. Gelatin/alginate composite nanofiber membranes for effective and even adsorption of cationic dyes. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 162, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauke, V.P.; Maity, A.; Chetty, A. High-performance towards removal of toxic hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution using graphene oxide-alpha cyclodextrin-polypyrrole nanocomposites. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 211, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, D.W.; Birkinshaw, C.; O’Dwyer, T.F. Heavy metal adsorbents prepared from the modification of cellulose: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 6709–6724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradinaru, L.M.; Bercea, M.; Vlad, S.; Barbalata Mandru, M.; Drobota, M.; Aflori, M.; Ciobanu, R.C. Preparation and characterization of electrospun magnetic poly(ether urethane) nanocomposite mats: Relationships between the viscosity of the polymer solutions and the electrospinning ability. Polymer 2022, 256, 125186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Lou, T. Simultaneous adsorption for cationic and anionic dyes using chitosan/electrospun sodium alginate nanofiber composite sponges. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 276, 118728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimbalkar, M.N.; Bhat, B.R. Simultaneous adsorption of methylene blue and heavy metals from water using Zr-MOF having free carboxylic group. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.-F.; Zhang, D.; Huang, T.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Y. Ultrasonication-assisted deposition of graphene oxide on electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride) membrane and the adsorption behavior. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayati, B.; Maleki, A.; Najafi, F.; Gharibi, F.; McKay, G.; Gupta, V.K.; Harikaranahalli Puttaiah, S.; Marzban, N. Heavy metal adsorption using PAMAM/CNT nanocomposite from aqueous solution in batch and continuous fixed bed systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 346, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Li, M.; Song, Y. Theoretical study of M2CO2 MXenes stability and adsorption properties for heavy metals ions removal from water. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2023, 220, 112042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, R.; Jiao, T.; Zou, G.; Zhan, F.; Yin, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, J.; Peng, Q. Facile Preparation of Hierarchical AgNP-Loaded MXene/Fe(3)O(4)/Polymer Nanocomposites by Electrospinning with Enhanced Catalytic Performance for Wastewater Treatment. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 1897–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning and Electrospun Nanofibers: Methods, Materials, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5298–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, V.V.; Wang, L.; Padhye, R. Electrospun nanofiber materials to filter air pollutants—A review. J. Ind. Text. 2016, 47, 2253–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wei, T.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, C.; Jiang, H.; Chang, J.; Sheng, L.; Zhou, Q.; Yuan, L.; Fan, Z. Electrostatic interaction in electrospun nanofibers: Double-layer carbon protection of CoFe2O4 nanosheets enabling ultralong-life and ultrahigh-rate lithium ion storage. Nano Energy 2018, 48, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, D.N.; Khan, M.Q.; Nguyen, N.T.; Phan, T.T.; Ullah, A.; Khatri, M.; Kien, N.N.; Kim, I.S. A review on the fabrication of several carbohydrate polymers into nanofibrous structures using electrospinning for removal of metal ions and dyes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 252, 117175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akampumuza, O.; Gao, H.; Zhang, H.; Wu, D.; Qin, X.-H. Raising Nanofiber Output: The Progress, Mechanisms, Challenges, and Reasons for the Pursuit. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2018, 303, 1700269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Wen, Z.; Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Philippe François-Xavier, C.; Wintgens, T. Bipolar jet electrospinning bi-functional nanofibrous membrane for simultaneous and sequential filtration of Cd2+ and BPA from water: Competition and synergistic effect. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 332, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, K.; Kim, K.; Wang, X.; Fang, D.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. High flux ultrafiltration membranes based on electrospun nanofibrous PAN scaffolds and chitosan coating. Polymer 2006, 47, 2434–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilad, M.R.; Westbroek, P.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Assessment and optimization of electrospun nanofiber-membranes in a membrane bioreactor (MBR). J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 380, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, W.; Huang, C. Electrospun nanofiber membranes for wastewater treatment applications. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 250, 117116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.K.; Mishra, P.; Verma, K.; Mondal, A.; Chaudhary, R.G.; Abolhasani, M.M.; Loganathan, S. Electrospinning production of nanofibrous membranes. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 17, 767–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, R.T.; Jones, J.J.; Harris, M.T.; Basaran, O.A. Electrohydrodynamic tip streaming and emission of charged drops from liquid cones. Nat. Phys. 2007, 4, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Chang, F.C. Cu(II) and Au(III) recovery with electrospun lignosulfonate CO(2)-activated carbon fiber. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 203, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Aboagye, A.; Kelkar, A.; Lai, C.; Fong, H. A review: Carbon nanofibers from electrospun polyacrylonitrile and their applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 49, 463–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Li, S.; Xu, L.; Ahmed, A. Controllable preparation and formation mechanism of nanofiber membranes with large pore sizes using a modified electrospinning. Mater. Des. 2019, 178, 107867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aijaz, M.O.; Karim, M.R.; Alharbi, H.F.; Alharthi, N.H. Novel optimised highly aligned electrospun PEI-PAN nanofiber mats with excellent wettability. Polymer 2019, 180, 121665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, G.; Matsuda, R.; Sato, H.; Hori, A.; Takata, M.; Kitagawa, S. Effect of functional groups in MIL-101 on water sorption behavior. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 157, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, R.; Sabzehmeidani, M.M.; Parvinnia, M.; Ghaedi, M. Removal of hexavalent chromium ions and mixture dyes by electrospun PAN/graphene oxide nanofiber decorated with bimetallic nickel–iron LDH. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2022, 18, 100750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabetzadeh, N.; Gharehaghaji, A.A.; Javanbakht, M. Porous PAN micro/nanofiber separators for enhanced lithium-ion battery performance. Solid State Ion. 2018, 325, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Jiang, H.; Wang, R.; Xie, Y.; Zhao, C. Fabrication of metronidazole loaded poly (epsilon-caprolactone)/zein core/shell nanofiber membranes via coaxial electrospinning for guided tissue regeneration. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 490, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Ma, W.; Wu, S.; Tang, G.; Cui, J.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, F.; Xiong, R.; Huang, C. Electrospun frogspawn structured membrane for gravity-driven oil-water separation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 547, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cao, J.; Xu, Q.; Wang, S.; Wang, B.; Liu, Z. Effects of various factors on the modification of carbon nanotubes with polyvinyl alcohol in supercritical CO2 and their application in electrospun fibers. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2014, 30, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Hu, Q.-H.; Wang, Q.-Y.; Xiang, Y.-L.; Huang, S.-H.; Liu, Y.-Z.; Li, S.-Y.; Chen, Q.-L.; Zhou, Q.-H. Efficiently selective removal of Pb(II) by magnetic ion-imprinted membrane based on polyacrylonitrile electro-spun nanofibers. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 284, 120280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.G.; Jiang, X.; Chen, P.C.; Yu, A.G.; Huang, X.J. Preparation of coaxial-electrospun poly[bis(p-methylphenoxy)]phosphazene nanofiber membrane for enzyme immobilization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 14136–14148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.J.; Chen, Y.F.; Hsiao, P.H.; Lam, T.N.; Ko, W.C.; Luo, M.Y.; Chuang, W.T.; Su, C.J.; Chang, J.H.; Chung, C.F.; et al. In-Situ Synchrotron SAXS and WAXS Investigation on the Deformation of Single and Coaxial Electrospun P(VDF-TrFE)-Based Nanofibers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Pan, K.; He, Q.; Cao, B. Polyacrylonitrile/polypyrrole core/shell nanofiber mat for the removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 244–245, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, S.; Xiao, W.; Luo, J.; Li, B.; Wang, L.; Xue, H.; Gao, J. Flexible PDA@ACNTs decorated polymer nanofiber composite with superhydrophilicity and underwater superoleophobicity for efficient separation of oil-in-water emulsion. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 614, 118500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.-f.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, N.; Huang, T.; Wang, Y. Polydopamine-assisted deposition of polypyrrole on electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanofibers for bidirectional removal of cation and anion dyes. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 354, 432–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahar, F.K.; He, L.; Wei, K.; Mehdi, M.; Zhu, M.; Gu, J.; Zhang, K.; Khatri, Z.; Kim, I. Rapid adsorption of lead ions using porous carbon nanofibers. Chemosphere 2019, 225, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.-Q.; Yuan, X.; Wang, T. Porous polyacrylonitrile/graphene oxide nanofibers designed for high efficient adsorption of chromium ions (VI) in aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 392, 123730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.-M.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 2223–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, M.B.; Awasthi, G.P.; Kim, H.J. Novel insight into the adsorption of Cr(VI) and Pb(II) ions by MOF derived Co-Al layered double hydroxide @hematite nanorods on 3D porous carbon nanofiber network. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 129312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, T.; Ye, Z.; Rahaman, M.S. High performance nanocomposite nanofiltration membranes with polydopamine-modified cellulose nanocrystals for efficient dye/salt separation. Desalination 2022, 521, 115385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sahadevan, R.; Crandall, C.; Menkhaus, T.J.; Fong, H. Hot-pressed PAN/PVDF hybrid electrospun nanofiber membranes for ultrafiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 611, 118327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arribas, P.; García-Payo, M.C.; Khayet, M.; Gil, L. Heat-treated optimized polysulfone electrospun nanofibrous membranes for high performance wastewater microfiltration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 226, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Xu, C.; Yu, D.; Qi, Z.; Wang, Y.; Peng, Y. Enhanced phosphate remediation of contaminated natural water by magnetic zeolitic imidazolate framework-8@engineering nanomaterials (ZIF8@ENMs). J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 613, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liao, Q.; Hou, B.; He, C.; Liu, J.; Li, B.; Yu, M.; Liu, Y.; Lai, B.; Yang, B. Synchronous reduction and removal of hexavalent chromium from wastewater by modified magnetic chitosan beads. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 304, 122363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.K.; Panigrahi, G.K.; Sahoo, J.K.; Pradhan, A.K.; Purohit, A.K.; Dhal, J.P. Electrospun magnetic polyacrylonitrile-GO hybrid nanofibers for removing Cr(VI) from water. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 326, 115364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Zhang, C.; Luo, S.; Jiang, L.; Li, Q.; Kong, Y.; Cao, J. HMGA2 mediates Cr (VI)-induced metabolic reprogramming through binding to mitochondrial D-Loop region. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 244, 114085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamshidifard, S.; Koushkbaghi, S.; Hosseini, S.; Rezaei, S.; Karamipour, A.; Jafari Rad, A.; Irani, M. Incorporation of UiO-66-NH2 MOF into the PAN/chitosan nanofibers for adsorption and membrane filtration of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Cr(VI) ions from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 368, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, E.; Madaeni, S.S.; Rajabi, L.; Derakhshan, A.A.; Daraei, S.; Vatanpour, V. Static and dynamic adsorption of copper ions on chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol thin adsorptive membranes: Combined effect of polyethylene glycol and aminated multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 215–216, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Liu, X.; Liao, J.; Lin, H.; Liu, F. PEI modified multiwalled carbon nanotube as a novel additive in PAN nanofiber membrane for enhanced removal of heavy metal ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 375, 122086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Pan, B.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Lv, L.; Wu, J. Selective Removal of Cu(II) Ions by Using Cation-exchange Resin-Supported Polyethyleneimine (PEI) Nanoclusters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3508–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Li, K.; Shi, W.; Cai, J. Preparation and performance evaluation of chitosan/polyvinylpyrrolidone/polyvinyl alcohol electrospun nanofiber membrane for heavy metal ions and organic pollutants removal. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 210, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, B.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, C. Water-insoluble sericin/beta-cyclodextrin/PVA composite electrospun nanofibers as effective adsorbents towards methylene blue. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 136, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sağ, Y.s.; Aktay, Y. Kinetic studies on sorption of Cr(VI) and Cu(II) ions by chitin, chitosan and Rhizopus arrhizus. Biochem. Eng. J. 2002, 12, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habiba, U.; Afifi, A.M.; Salleh, A.; Ang, B.C. Chitosan/(polyvinyl alcohol)/zeolite electrospun composite nanofibrous membrane for adsorption of Cr(6+), Fe(3+) and Ni(2). J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 322 Pt A, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Hu, Z.; Lei, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X. Fluorescent magnetic chitosan-based hydrogel incorporating Amino-Functionalized Fe3O4 and cellulose nanofibers modified with carbon dots for adsorption and detection of Cr (VI). Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 658, 130673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, Y.; Cao, L.; Yang, C. Enhanced chromium (VI) adsorption using nanosized chitosan fibers tailored by electrospinning. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 125, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, C. Removal of Cr (VI) with a spiral wound chitosan nanofiber membrane module via dead-end filtration. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 544, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamayo Marin, J.A.; Londono, S.R.; Delgado, J.; Navia Porras, D.P.; Valencia Zapata, M.E.; Mina Hernandez, J.H.; Valencia, C.H.; Grande Tovar, C.D. Biocompatible and Antimicrobial Electrospun Membranes Based on Nanocomposites of Chitosan/Poly (Vinyl Alcohol)/Graphene Oxide. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, R.; Chao, S.; Sun, B.; Wang, C.; Li, X. Polydopamine coating assisted synthesis of MnO2 loaded inorganic/organic composite electrospun fiber adsorbent for efficient removal of Pb2+ from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 344, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Shi, Q.; Korfiatis, G.; Christodoulatos, C.; Wang, H.; Meng, X. Chromate removal by electrospun PVA/PEI nanofibers: Adsorption, reduction, and effects of co-existing ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 387, 124179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenstein, K.E.; Myung, N.V.; Parkin, G.F.; Cwiertny, D.M. Performance comparison of hematite (alpha-Fe(2)O(3))-polymer composite and core-shell nanofibers as point-of-use filtration platforms for metal sequestration. Water Res. 2019, 148, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.; Nasser, W.S.; Osman, T.A.; Toprak, M.S.; Muhammed, M.; Uheida, A. Removal of chromium (VI) from aqueous solutions using surface modified composite nanofibers. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2017, 505, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.-B.; Wang, J.-N.; Wu, J.; Li, C.-J. “Flower-Like” PA6@Mg(OH)2 electrospun nanofibers with Cr (VI)-removal capacity. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 254, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Li, F.; Wang, H.; Fu, L.; Zhang, B.; Li, G. Effects of poly (vinyl alcohol) (PVA) content on preparation of novel thiol-functionalized mesoporous PVA/SiO2 composite nanofiber membranes and their application for adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution. Polymer 2010, 51, 6203–6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Li, L.; Chen, B.; Shi, S.; Nie, J.; Ma, G. Functionalized chitosan electrospun nanofiber membranes for heavy-metal removal. Polymer 2019, 163, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Lei, X.; Cai, N.; Xie, X.; Xue, Y.; Yu, F. Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Water by Magnetic Cellulose-Based Beads with Embedded Chemically Modified Magnetite Nanoparticles and Activated Carbon. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 3960–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, B.; Ma, H.; Yu, M.; Li, L.; Li, J. Electrospun nanofibrous polyethylenimine mat: A potential adsorbent for the removal of chromate and arsenate from drinking water. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 30739–30746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.; Farnood, R.; Kumar, V. HMO-incorporated electrospun nanofiber recyclable membranes: Characterization and adsorptive performance for Pb(II) and As(V). J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, T.I.; El-Kady, M.F.; Zaki, A.E.H.M.; El-Kholy, S.M. Preparation and application of magnetite nanoparticles immobilized on cellulose acetate nanofibers for lead removal from polluted water. Water Supply 2016, 17, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassyouni, D.; Mohamed, M.; El-Ashtoukhy, E.-S.; El-Latif, M.A.; Zaatout, A.; Hamad, H. Fabrication and characterization of electrospun Fe3O4/o-MWCNTs/polyamide 6 hybrid nanofibrous membrane composite as an efficient and recoverable adsorbent for removal of Pb (II). Microchem. J. 2019, 149, 103998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Zhao, L.; Qiao, L.; Du, K. Proteinaceous porous nanofiber membrane-type adsorbent derived from amyloid lysozyme protofilaments for highly efficient lead(II) biologic scavenging. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.Y.; Bae, J.H.; Hasegawa, Y.; An, S.; Kim, I.S.; Lee, H.; Kim, M. Thiol-functionalized cellulose nanofiber membranes for the effective adsorption of heavy metal ions in water. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 234, 115881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surgutskaia, N.S.; Martino, A.D.; Zednik, J.; Ozaltin, K.; Lovecka, L.; Bergerova, E.D.; Kimmer, D.; Svoboda, J.; Sedlarik, V. Efficient Cu2+, Pb2+ and Ni2+ ion removal from wastewater using electrospun DTPA-modified chitosan/polyethylene oxide nanofibers. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 247, 116914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, F.; Lv, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, D.; Shao, Z. Halloysite nanotubes and Fe3O4 nanoparticles enhanced adsorption removal of heavy metal using electrospun membranes. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 161, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamah, S.C.; Goh, P.S.; Ismail, A.F.; Amin, M.A.M.; Ahmad, N.A.; Suzaimi, N.D.; Raji, Y.O. Facile preparation of palygorskite/chitin nanofibers hybrids nanomaterial with remarkable adsorption capacity. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2020, 262, 114725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Lin, J.; Zhang, N.; Chen, L.; Zhong, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ling, Q. Preparation of MgAl-EDTA-LDH based electrospun nanofiber membrane and its adsorption properties of copper(II) from wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 345, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumina; Priastomo, Y.; Setiawan, H.R.; Mutmainah; Kurniawan, Y.S.; Ohto, K. Simultaneous removal of lead(II), chromium(III), and copper(II) heavy metal ions through an adsorption process using C-phenylcalix[4]pyrogallolarene material. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Song, Y.; Yin, P.; Xu, Q.; Yang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, W.; Cai, H. Fabrication of the composite sepiolite@polyethyleneimine/sodium alginate and its excellent adsorption performance for heavy metal ions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2022, 228, 106647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Arkin, K.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, J.; Bei, Y.; Liu, D.; Shang, Q. Preparation of a composite material based on self-assembly of biomass carbon dots and sodium alginate hydrogel and its green, efficient and visual adsorption performance for Pb2+. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 106921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liao, C.; Guo, X.-X.; Hou, S.-C.; He, W.-D. PAAO cryogels from amidoximated P(acrylic acid-co-acrylonitrile) for the adsorption of lead ion. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 171, 111192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, B.; Ma, J.; Zhu, R. Preparation and characterization of carboxymethyl cellulose/chitosan/alginic acid hydrogels with adjustable pore structure for adsorption of heavy metal ions. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 179, 111577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, L.; Hu, D.; Yang, R.; Zhang, J.; Guan, Y.; Lv, F.; Gao, H. A mesoporous nanocellulose/sodium alginate/carboxymethyl-chitosan gel beads for efficient adsorption of Cu2+ and Pb2+. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 187, 922–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koushkbaghi, S.; Zakialamdari, A.; Pishnamazi, M.; Ramandi, H.F.; Aliabadi, M.; Irani, M. Aminated-Fe3O4 nanoparticles filled chitosan/PVA/PES dual layers nanofibrous membrane for the removal of Cr(VI) and Pb(II) ions from aqueous solutions in adsorption and membrane processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 337, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Mokhtari-Shourijeh, Z.; Ghane-Karade, A. Dye removal from wastewater by the cross-linked blend nanofiber and homogenous surface diffusion modeling. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2017, 36, 1634–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.; Guo, J.; Deng, Z.; Yu, J.; Dai, Y. Adsorption and reduction of Cr(VI) in water by iron-based metal-organic frameworks (Fe-MOFs) composite electrospun nanofibrous membranes. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 370, 133566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ru, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Ge, M.; Liu, H.; Wu, S.; Cao, C.; Ren, X.; et al. Recent advances in applications for air pollutants purification and perspectives of electrospun nanofibers. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 378, 134567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, A.; Mishra, B.G.; Hota, G. Adsorptive removal of Congo red dye from wastewater by mixed iron oxide–alumina nanocomposites. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 5443–5451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Hota, G. Synthesis of novel surface functionalized electrospun PAN nanofibers matrix for efficient adsorption of anionic CR dye from water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5301–5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Ansari, M.O.; Parveen, N.; Barakat, M.A.; Cho, M.H. Simple route for the generation of differently functionalized PVC@graphene–polyaniline fiber bundles for the removal of Congo red from wastewater. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 61486–61494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari-Shourijeh, Z.; Langari, S.; Montazerghaem, L.; Mahmoodi, N.M. Synthesis of porous aminated PAN/PVDF composite nanofibers by electrospinning: Characterization and Direct Red 23 removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Mokhtari-Shourijeh, Z. Preparation of PVA-chitosan blend nanofiber and its dye removal ability from colored wastewater. Fibers Polym. 2015, 16, 1861–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Mokhtari-Shourijeh, Z. Modified poly(vinyl alcohol)-triethylenetetramine nanofiber by glutaraldehyde: Preparation and dye removal ability from wastewater. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 57, 20076–20083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chafai, H.; Laabd, M.; Elbariji, S.; Bazzaoui, M.; Albourine, A. Study of congo red adsorption on the polyaniline and polypyrrole. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2016, 38, 832–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Shi, Y.; Yang, D.; Liu, Y.; Qu, J.; Yu, Z.-Z. Graphene oxide/chitosan aerogel microspheres with honeycomb cobweb and radially oriented microchannel structures for broad-spectrum and rapid adsorption of water contaminants. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 21809–21819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenjian, A.; Maleknia, L.; Chizari Fard, G.; Almasian, A. Mesoporous carboxylated Mn2O3 nanofibers: Synthesis, characterization and dye removal property. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 86, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Hota, G. Adsorptive removal of malachite green dye by functionalized electrospun PAN nanofibers membrane. Fibers Polym. 2014, 15, 2272–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Li, Z.; Wu, Y.-n.; Zhang, B.; Li, F. Dendrimer-based preparation of mesoporous alumina nanofibers by electrospinning and their application in dye adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 264, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yar, A.; Parlayici, e. Carbon nanotubes/polyacrylonitrile composite nanofiber mats for highly efficient dye adsorption. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 651, 129703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Sang, C.; Wang, J.; Guo, J. Preparation of sodium alginate/polyvinyl alcohol composite nanofiber membranes for adsorption of dyes. Text. Res. J. 2021, 92, 3154–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Jia, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F. Sorption of malachite green on vinyl-modified mesoporous poly(acrylic acid)/SiO2 composite nanofiber membranes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 149, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, M.; Qiao, J.; Li, F.; Bera, P.K. Electrospun mesoporous carbon nanofibers produced from phenolic resin and their use in the adsorption of large dye molecules. Carbon 2012, 50, 2877–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, D.-N.; Rebia, R.A.; Saito, Y.; Kharaghani, D.; Khatri, M.; Tanaka, T.; Lee, H.; Kim, I.-S. Zinc oxide nanoparticles attached to polyacrylonitrile nanofibers with hinokitiol as gluing agent for synergistic antibacterial activities and effective dye removal. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 85, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.-f.; Zhang, N.; Wei, X.; Yang, J.-h.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.-w. Blend-electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride)/polydopamine membranes: Self-polymerization of dopamine and the excellent adsorption/separation abilities. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 14430–14443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.-R.; Jiang, H.-L.; Shi, N.; Lv, H.-W.; Liu, Z.-J.; He, F.-A. A novel tetrafluoroterephthalonitrile-crosslinked quercetin/chitosan adsorbent and its adsorption properties for dyes. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1282, 135150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Chen, S.; Duan, H.; He, J.; Luo, Y. Removal of anionic and cationic dyes using porous chitosan/carboxymethyl cellulose-PEG hydrogels: Optimization, adsorption kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamics studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 231, 123213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Qin, M.; Han, C.; Bai, X.; Wu, Y.; Yao, D.; Zheng, Y. Pectin/graphene oxide aerogel with bamboo-like structure for enhanced dyes adsorption. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 652, 129837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Xie, Z.; Xue, S.; Long, J.; Shi, W.; Liu, Y. Preparation of benzenesulfonyl hydrazone modified guar gum and its adsorption properties for dyes and phytotoxicity assays. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 234, 123700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamranifar, M.; Khodadadi, M.; Samiei, V.; Dehdashti, B.; Noori Sepehr, M.; Rafati, L.; Nasseh, N. Comparison the removal of reactive red 195 dye using powder and ash of barberry stem as a low cost adsorbent from aqueous solutions: Isotherm and kinetic study. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 255, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, M.Y.; Ahmed, I.S.; Mohamed, T.Y.; Khatab, M. A controlled, template-free, and hydrothermal synthesis route to sphere-like 伪-Fe2O3 nanostructures for textile dye removal. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 20001–20013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallakpour, S.; Sirous, F.; Dinari, M. Comparative study for removal of cationic and anionic dyes using alginate-based hydrogels filled with citric acid-sawdust/UiO-66-NH2 hybrid. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 238, 124034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, O.; Polat, T.G.; Tunç, S. Development of poly(vinyl alcohol)/β-cyclodextrin/P(MVE-MA) composite nanofibers as effective and selective adsorbent and filtration material for the removal and separation of cationic dyes from water. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 322, 116130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Dong, J.; Gong, C.; Zhang, S.; Yang, J.; Zhang, A.; Feng, Z. Bendable poly(vinylidene fluoride)/polydopamine/β-cyclodextrin composite electrospun membranes for highly efficient and bidirectional adsorption of cation and anion dyes from aqueous media. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 219, 109256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hsiao, B.S. Electrospun nanofiber membranes. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2016, 12, 62–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijing, L.D.; Woo, Y.C.; Shim, W.-G.; He, T.; Choi, J.-S.; Kim, S.-H.; Shon, H.K. Superhydrophobic nanofiber membrane containing carbon nanotubes for high-performance direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 502, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Yang, M.; Xu, W.; He, S.; Men, Y. Natural polysaccharides-modified graphene oxide for adsorption of organic dyes from aqueous solutions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 486, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Bi, G.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Q.; Xu, H.; Li, X. Mussel-inspired polydopamine biopolymer decorated with magnetic nanoparticles for multiple pollutants removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 270, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Xue, W.; Cui, L.; Xing, W.; Cao, X.; Li, H. Use of hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin/polyethylene glycol 400, modified Fe3O4 nanoparticles for congo red removal. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 64, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Li, Y.; Sun, B.; Chao, S.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Zhu, G. Highly flexible magnesium silicate nanofibrous membranes for effective removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 1603–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anusiya, G.; Jaiganesh, R. A review on fabrication methods of nanofibers and a special focus on application of cellulose nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2022, 4, 100262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Lotfikatouli, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, T.; Ma, H.; Mao, X.; Hsiao, B.S. Nanostructured all-cellulose membranes for efficient ultrafiltration of wastewater. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 650, 120422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, A.; Salehi, M.; Jansone-Popova, S. Production of polyacrylonitrile/ionic covalent organic framework hybrid nanofibers for effective removal of chromium(VI) from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 427, 128167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Jeong, Y.J.; Park, W.H. Poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibrous membranes via green electrospinning and tannin coating for selective removal of Pb(II) ion. Chemosphere 2022, 307 Pt 1, 135719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Guo, J.; Gong, Y.; Yu, Y. Amidoxime functionalized low-cost cellulose-based adsorbent derived from waste cigarette filters for efficient heavy metal removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandel, D.R.; Kim, H.-J.; Lim, J.-M.; Poudel, M.B.; Cho, M.; Kim, H.-W.; Oh, B.-T.; Nah, C.; Lee, S.H.; Dahal, B.; et al. Cold plasma-assisted regeneration of biochar for dye adsorption. Chemosphere 2022, 309, 136638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himmler, M.; Schubert, D.W.; Dahne, L.; Egri, G.; Fuchsluger, T.A. Electrospun PCL Scaffolds as Drug Carrier for Corneal Wound Dressing Using Layer-by-Layer Coating of Hyaluronic Acid and Heparin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Guo, W.; Zhang, S.; Guo, R.; Zhang, L. Electrospun Nanofiber Membrane: An Efficient and Environmentally Friendly Material for the Removal of Metals and Dyes. Molecules 2023, 28, 3288. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083288
Li L, Guo W, Zhang S, Guo R, Zhang L. Electrospun Nanofiber Membrane: An Efficient and Environmentally Friendly Material for the Removal of Metals and Dyes. Molecules. 2023; 28(8):3288. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083288
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Li, Wei Guo, Shenggui Zhang, Ruibin Guo, and Li Zhang. 2023. "Electrospun Nanofiber Membrane: An Efficient and Environmentally Friendly Material for the Removal of Metals and Dyes" Molecules 28, no. 8: 3288. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083288
APA StyleLi, L., Guo, W., Zhang, S., Guo, R., & Zhang, L. (2023). Electrospun Nanofiber Membrane: An Efficient and Environmentally Friendly Material for the Removal of Metals and Dyes. Molecules, 28(8), 3288. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28083288