Molecular Characterization of Some Bacillus Species from Vegetables and Evaluation of Their Antimicrobial and Antibiotic Potency
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation and Identification
2.2. Morphological Characterization
2.3. Antimicrobial Activity Assessment
2.4. Antibiotic Susceptibility Profile of the Isolates
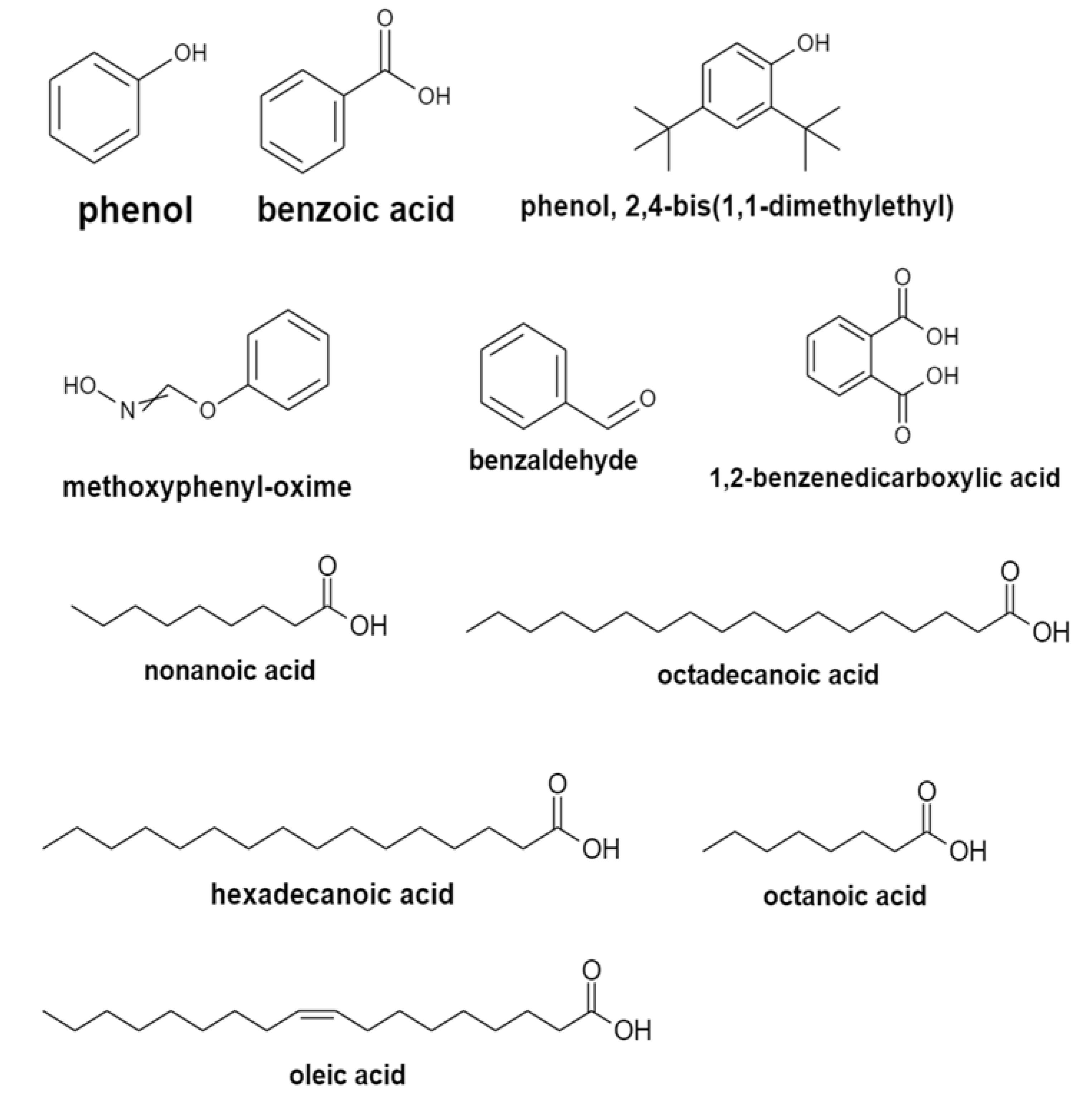
2.5. Analysis of the Isolates Using GC–MS
2.6. Molecular Characterization
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Isolation of Potential Strains of the Genus Bacillus spp.
4.2. Screening for Antagonistic Activity of Isolated Bacteria against Potent Bacterial Pathogens
4.3. Antibiotic Susceptibility of the Bacillus Strains
4.4. Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrum Analysis of the Metabolites
4.5. Molecular Characterization of the Bacterial Isolates
4.6. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Serwecińska, L. Antimicrobials and Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria: A Risk to the Environment and to Public Health. Water 2020, 12, 3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenbichler, J.; Dietrich, J.; Peipp, H. Secondary fungal metabolites and their biological activities, V. Investigations concerning the induction of the biosynthesis of toxic secondary metabolites in basidiomycetes. Biol. Chem. Hoppe-Seyler 1994, 375, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaning Danquah, C.; Minkah, P.A.B.; Osei Duah Junior, I.; Amankwah, K.B.; Somuah, S.O. Antimicrobial Compounds from Microorganisms. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaou, N.; Stavropoulou, E.; Voidarou, C.; Tsigalou, C.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Towards Advances in Medicinal Plant Antimicrobial Activity: A Review Study on Challenges and Future Perspectives. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakal, S.N.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. Finding Novel Antibiotic Substances from Medicinal Plants—Antimicrobial Properties of Nigella Sativa Directed against Multidrug-resistant Bacteria. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017, 7, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, T.; Wang, Y. The role of bacterial signaling networks in antibiotics response and resistance regulation. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2022, 4, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, D.; Traxler, M.F.; López, D.; Kolter, R. Antibiotics as signal molecules. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 5492–5505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demain, A.; Sanchez, S. Microbial drug discovery: 80 years of progress. J. Antibiot. 2009, 62, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spears, J.L.; Kramer, R.; Nikiforov, A.I.; Rihner, M.O.; Lambert, E.A. Safety Assessment of Bacillus subtilis MB40 for Use in Foods and Dietary Supplements. Nutrients 2021, 13, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liang, S.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ren, X. The Effect of Chlorogenic Acid on Bacillus subtilis Based on Metabolomics. Molecules 2020, 25, 4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, N.; Czaplewski, L.; Piddock, L.J. Discovery and development of new antibacterial drugs: Learning from experience? J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 1452–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventola, C.L. The antibiotic resistance crisis: Part 1: Causes and threats. P T A Peer-Rev. J. Formul. Manag. 2015, 40, 277–283. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25859123/ (accessed on 19 May 2022).
- Terreni, M.; Taccani, M.; Pregnolato, M. New Antibiotics for Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial Strains: Latest Research Developments and Future Perspectives. Molecules 2021, 26, 2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hölzel, C.S.; Tetens, J.L.; Schwaiger, K. Unraveling the Role of Vegetables in Spreading Antimicrobial-Resistant Bacteria: A Need for Quantitative Risk Assessment. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2018, 15, 671–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allydice-Francis, K.; Brown, P.D. Diversity of Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Determinants in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Associated with Fresh Vegetables. Int. J. Microbiol. 2012, 2012, 426241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Niaz, Z.; Shah, P.T.; Shakeela, Q.; Uzma, B.; Ahmed, S. Antibiogram of ESBL and MBL producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa among the population of Hazara division. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2020, 70, 1979–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, F.; Van Duin, D. Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae: A menace to our most vulnerable patients. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2013, 80, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Kamal, S.; Shakeela, Q.; Ahmed, S. Extended-spectrum and Metallo-beta lactamase enzymes mediated resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa in clinically isolated specimens. Kuwait J. Sci. 2021, 48, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saqib, S.; Munis, M.F.H.; Zaman, W.; Ullah, F.; Shah, S.N.; Ayaz, A.; Farooq, M.; Bahadur, S. Synthesis, characterization and use of iron oxide nano particles for antibacterial activity. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2019, 82, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, K.; Beppu, T. Antibiotics in microbial coculture. J. Antibiot. 2017, 70, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Gui, Y.; Li, Z.; Jiang, C.; Guo, J.; Niu, D. Induced Systemic Resistance for Improving Plant Immunity by Beneficial Microbes. Plants 2022, 11, 386. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8839143/ (accessed on 7 January 2023).
- Jagannath, S.; Matthew, W.; Alan, M.; Batter, H.; Spears, I.R. Gait Retraining and Incidence of Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome in Army Recruits. Off. J. Am. Coll. Sport. Med. 2014, 46, 1684–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Kumar, S.; Goswami, P.; Sangwan, V.; Singh, R. Antibiotic resistance among commercially available probiotics. Food Res. Int. J. 2014, 57, 176–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citron, D.M.; Appleman, M.D. In vitro activities of daptomycin, ciprofloxacin, and other antimicrobial agents against the cells and spores of clinical isolates of Bacillus species. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 3814–3818. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17021118/ (accessed on 15 September 2022).
- Jensen, L.B.; Baloda, S.; Boye, M.; Aarestrup, F.M. Antimicrobial resistance among Pseudomonas spp. and the Bacillus cereus group isolated from Danish agricultural soil. Environ. Int. 2001, 26, 581–587. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11485227/ (accessed on 27 June 2022).
- Fiedler, G.; Schneider, C.; Igbinosa, E.O.; Kabisch, J.; Brinks, E.; Becker, B.; Stoll, D.A.; Cho, G.-S.; Huch, M.; Franz, C.M.A.P. Antibiotics resistance and toxin profiles of Bacillus cereus-group isolates from fresh vegetables from German retail markets. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimpong, D.B.; Sørensen, K.I.; Thorsen, L.; Stuer-Lauridsen, B.; Abdelgadir, W.S.; Nielsen, D.S.; Derkx, P.M.; Jespersen, L. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Bacillus strains isolated from primary starters for African traditional bread production and characterization of the bacitracin operon and bacitracin biosynthesis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 7903–7914. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22941078/ (accessed on 28 December 2022).
- Compaore, C.S.; Jensen, L.B.; Diawara, B.; Ouedraogo, G.A.; Jakobsen, M.; Ouoba, L.I. Resistance to antimicrobials and acid and bile tolerance of Bacillus spp isolated from Bikalga, fermented seeds of Hibiscus sabdariffa. Afr. J. Food Sci. 2013, 7, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, V.; Ferrão, J.; Pimentel, L.; Pintado, M.; Fernandes, T. One Health, Fermented Foods, and Gut Microbiota. Foods 2018, 7, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, L.; Eijsink, V.G.; Meadow, R.; Gåseidnes, S. A novel strain of Brevibacillus laterosporus produces chitinases that contribute to its biocontrol potential. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 1601–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, M.; Habib, S.; Zaman, W.; Hussain, S.; Ali, H.; Saqib, S. Synthesis and characterization of microbial mediated cadmium oxide nanoparticles. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2020, 83, 1574–1584. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32757348/ (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Balcázar, J.L.; Rojas-Luna, T. Inhibitory activity of probiotic Bacillus subtilis UTM 126 against Vibrio species confers protection against vibriosis in juvenile shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Curr. Microbiol. 2007, 55, 409–412. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17680306/ (accessed on 18 December 2022).
- Barghouthi, S.A.; Ayyad, I.; Ayesh, M.; Abu-Lafi, S. Isolation, identification, and characterization of the novel antibacterial agent methoxyphenyl-oxime from Streptomyces pratensis QUBC97 isolate. J. Antibiot. Res. 2017, 1, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ullah, I.; Khan, A.L.; Ali, L.; Khan, A.R.; Waqas, M.; Hussain, J.; Lee, I.-J.; Shin, J.-H. Benzaldehyde as an insecticidal, antimicrobial, and antioxidant compound produced by Photorhabdus temperata M1021. J. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, A.; Venâncio, A. The Potential of Fatty Acids and Their Derivatives as Antifungal Agents: A Review. Toxins 2022, 14, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desbois, A.P.; Smith, V.J. Antibacterial free fatty acids: Activities, mechanisms of action and biotechnological potential. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 1629–1642. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19956944/ (accessed on 11 January 2023).
- Ghazala, I.; Chiab, N.; Najib, S.M.; Gargouri-Bouzid, R. Volatile organic compounds from Bacillus mojavensis I4 promote plant growth and inhibit phytopathogens. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2022, 121, 101887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massawe, V.C.; Hanif, A.; Farzand, A.; Mburu, D.K.; Ochola, S.O.; Wu, L.; Tahir, H.A.S.; Gu, Q.; Wu, H.; Gao, X. Volatile Compounds of Endophytic Bacillus spp. have Biocontrol Activity Against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Phytopathology 2018, 108, 1373–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongkun, W.; Yichi, L.; Yuan, Y.; Depeng, C.h.; Jianmin, C.; Guangjun, S.; Yongfeng, A.; Zhiyan, C.; Yongfeng, Z.h.; Fenglong, W.; et al. Identification of non-volatile and volatile organic compounds produced by Bacillus siamensis LZ88 and their antifungal activity against Alternaria alternata. Biol. Control 2022, 169, 104901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, A.; Krishna Reddy, M.M.; Chandra, R. Identification of low molecular weight aromatic compounds by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) from kraft lignin degradation by three Bacillus sp. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2007, 59, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surya, M.; Thiruvudainambi, S.; Ebenezar, E.G.; Vanniarajan, C.; Kumutha, K.; Vellaikumar, S. GC-MS Analysis of antimicrobial compounds produced by Bacillus spp. against rice sheath rot pathogen Sarocladium oryzae. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2020, 8, 1417–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nas, F.; Aissaoui, N.; Mahjoubi, M.; Mosbah, A.; Arab, M.; Abdelwahed, S.; Klouche-Khelil, N. A comparative GC–MS analysis of bioactive secondary metabolites produced by halotolerant Bacillus spp. isolated from the Great Sebkha of Oran. Int. Microbiol. 2021, 24, 455–470. Available online: https://sci-hub.ru/10.1007/s10123-021-00185-x (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Sabu, R.; Radhakrishnan, E.K. Bioprospecting of endophytic bacteria from zingiber officinale with antibacterial activities. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2016, 5, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beiranvand, M.; Amin, M.; Hashemi-Shahraki, A.; Romani, B.; Yaghoubi, S.; Sadeghi, P. Antimicrobial activity of endophytic bacterial populations isolated from medical plants of Iran. Iran J. Microbiol. 2017, 9, 11–18. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5533999/ (accessed on 22 June 2022).
- Khan, Z.A.; Siddiqui, M.F.; Park, S. Current and Emerging Methods of Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 49. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31058811/ (accessed on 15 May 2021).
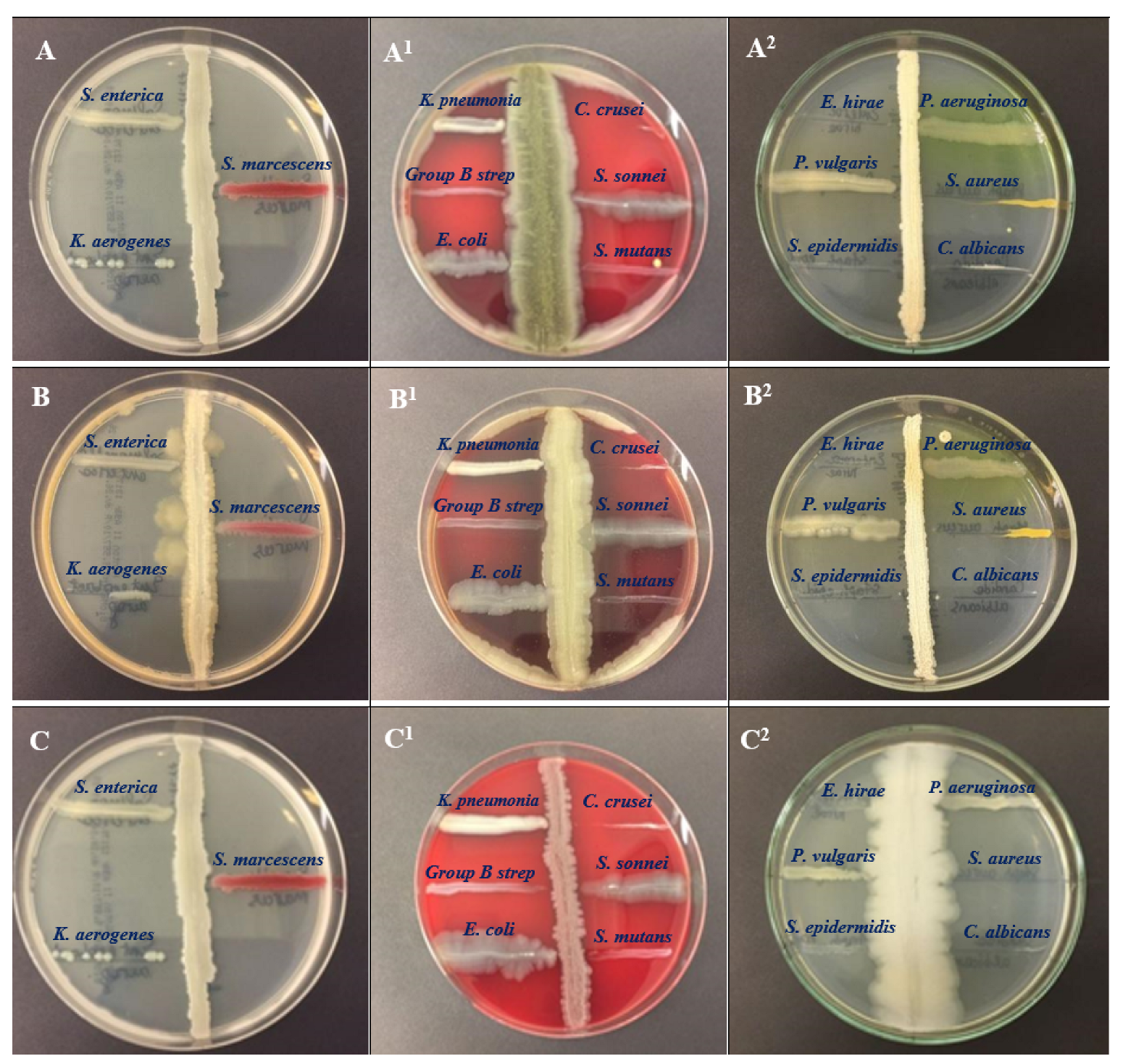

| Bacterial Species | Media | Colony Color and Texture | Microscopic Presentation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bacillus subtilis O-3 (BSS11) | bacillus medium | white, irregular, flat | gram positive, spore-forming, rod. |
| Bacillus subtilis Md1-42 (BSS17) | bacillus medium | white, irregular, flat | gram positive, spore-forming, rod. |
| Bacillus subtilis Khozestan2 (BSS19) | bacillus medium | white, irregular, flat | gram positive, spore-forming, rod. |
| Species of Microorganism | BSS11 (C), mm | BSS11 (BC), mm | BSS11 (SC), mm | BSS17 (C), mm | BSS17 (BC), mm | BSS17 (SC), mm | BSS19 (C), mm | BSS19 (BC), mm | BSS19 (SC), mm | Control (Streptomycin) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213 | 19 ± 1.33 * | 21 ± 1.33 * | 25 ± 1.53 * | 22 ± 0.50 * | 26 ± 0.44 * | 30 ± 2.50 * | 22 ± 1.55 | 26 ± 1.24 | 29 ± 1.54 | 29 ± 0.33 *** |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis ATCC 12228 | 18 ± 1.20 * | 20 ± 1.33 * | 25 ± 1.20 * | 19 ± 1.00 | 20 ± 1.26 | 22 ± 1.50 | 18 ± 1.42 * | 18 ± 1.44 * | 19 ± 1.54 * | 22 ± 0.33 *** |
| Streptococcus group B | 16 ± 1.20 | 15 ± 1.00 | 19 ± 1.20 | 13 ± 1.16 * | 15 ± 1.14 * | 17 ± 1.15 * | 15 ± 1.33 * | 14 ± 1.17 * | 16 ± 1.33 * | 22 ± 0.33 *** |
| Streptococcus mutans ATCC 25175 | 16 ± 1.22 * | 17 ± 1.22 * | 17 ± 1.82 * | 14 ± 1.33 | 16 ± 1.33 | 19 ± 1.33 | 18 ± 0.31 * | 19 ± 1.00 * | 20 ± 1.32 * | 16 ± 0.33 *** |
| Candida albicans ATCC 2091 | 27 ± 2.00 * | 25 ± 1.50 * | 30 ± 2.50 * | 29 ± 1.00 | 31 ± 1.22 | 35 ± 1.26 | 38 ± 1.49 | 35 ± 1.62 | 40 ± 1.22 | 39 ± 0.33 *** |
| Candida krusei ATCC 14243 | 25 ± 2.33 * | 27 ± 2.33 * | 29 ± 2.35 * | 23 ± 1.38 | 25 ± 0.33 | 25 ± 1.34 | 23 ± 2.00 * | 26 ± 1.66 * | 27 ± 2.00 * | 35 ± 0.33 *** |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027 | 14 ± 1.22 | 17 ± 0.33 | 17 ± 1.51 | 13 ± 0.44 | 12 ± 1.44 | 13 ± 1.10 | 20 ± 1.27 * | 20 ± 1.53 * | 22 ± 1.81 * | 23 *** |
| Shigella sonnei ATCC 25931 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 19 ± 0.33 *** |
| Klebsiella pneumonia ATCC 13883 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 ± 0.33 *** |
| Salmonella enterica ATCC 35664 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 19 ± 0.33 *** |
| Klebsiella aerogenes ATCC 13048 | 14 ± 1.82 * | 17 ± 1.57 * | 17 ± 1.82 * | 9 ± 1.33 * | 12 ± 1.22 * | 13 ± 1.63 * | 16 ± 0.53 * | 13 ± 1.53 * | 16 ± 1.53 * | 17 ± 0.33 *** |
| Enterococcus hirae ATCC 10541 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 ± 0.33 *** |
| Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 | 18 ± 1.22 * | 19 ± 1.57 * | 20 ± 1.24 * | 22 ± 1.44 * | 20 ± 1.31 * | 22 ± 1.54 * | 19 ± 0.49 | 22 ± 0.46 | 22 ± 1.17 | 23 ± 0.33 *** |
| Serratia marcescens ATCC 13880 | 13 ± 1.22 * | 15 ± 0.33 * | 15 ± 1.56 * | 17 ± 1.22 | 18 ± 1.55 | 18 ± 1.64 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 24 ± 0.33 *** |
| Proteus Vulgaris ATCC 6380 | 17 ± 1.33 * | 16 ± 0.33 * | 18 ± 1.34 * | 11 ± 1.33 * | 11 ± 1.54 * | 13 ± 1.53 * | 0 | 0 | 0 | 22 ± 0.33 *** |
| Antibiotic (AB, Charge in μg) Used | Bacillus Strains | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BSS11 | BSS17 | BSS19 | |||||
| Diameter (mm) | S/R | Diameter (mm) | S/R | Diameter (mm) | S/R | ||
| Penicillins | Penicillin G (PEN, 10) | 30 ± 0.98 bc | S | 24 ± 0.56 ab | S | 23 ± 0.29 a | S |
| Ampicillin (AMP, 10) | 30 ± 1.43 ab | S | 27 ± 1.34 ab | S | 27± 0.38 a | S | |
| Amoxycillin (AMOX, 30) | 32 ± 0.98 abc | S | 30 ± 1.30 abc | S | 12 ± 0.29 ab | S | |
| Amoxycillin-clavulanic acid (AMC, 30) | 28 ± 1.05 bcd | S | 23 ± 0.33 abc | S | 0 ± 0.00 b | S | |
| Carbenicillin (CAR, 100) | 38 ± 0.28 abc | S | 28 ± 0.35 ab | S | 10 ± 0.28 abc | S | |
| Cloxacillin (CX, 5) | 0 ± 0.00 b | R | 0 ± 0.00 b | R | 0 ± 0.00 b | R | |
| Macrolides | Erythromycin (ERO, 15) | 35 ± 0.31 ab | S | 32 ± 1.41 abc | S | 30 ± 0.23 a | S |
| Azithromycin (AZM, 15) | 36 ± 0.28 a | S | 35 ± 1.43 ab | S | 27 ± 1.33 ab | S | |
| Cephalosporins | Cefepime (FEP, 30) | 35 ± 0.51 ab | S | 25 ± 0.57 a | S | 38 ± 0.86 ab | S |
| Cefepime/clavulanic acid FEC-40 | 36 ± 0.98 a | S | 30 ± 0.36 a | S | 39 ± 0.67 a | S | |
| Cephalatin (KF, 30) | 32 ± 0.33 ab | S | 40 ± 0.37 ab | S | 26 ± 1.32 abc | S | |
| Cefotaxime (CTX, 30) | 26 ± 0.98 a | S | 40 ± 0.52 a | S | 24 ± 0.98 ab | S | |
| Aminoglycosides | Gentamicin (CN, 120) | 40 ± 0.28 ab | S | 40 ± 0.27 ab | S | 38 ± 0.28 ab | S |
| Streptomycin (STR, 10) | 26 ± 0.19 ab | S | 25 ± 0.48 ab | S | 22 ± 0.20 ab | S | |
| Tobramycin (TOB, 10) | 33 ± 0.98 a | S | 39± 1.18 a | S | 22 ± 0.23 abc | S | |
| Tetracyclines | Tetracycline (TET, 30) | 35 ± 0.28 a | S | 30 ± 0.33 a | S | 20 ± 1.18 ab | S |
| Polypeptides | Polymyxin (PB, 300) | 0 ± 0.00 b | R | 0 ± 0.00 b | R | 0 ± 0.00 b | R |
| Bacitromycin (B, 10) | 0 ± 0.00 b | R | 0 ± 0.00 b | R | 0 ± 0.00 b | R | |
| Bacillus subtilis O-3 (BSS11) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Name | Molecular Formula | Molecular Mass, g/mol | Retention Time (min) | Pubchem Compound CID | Similarities | Area, % |
| 1 | 2-Butanone | C4H8O | 72.11 | 2.111 | 6569 | 75 | 9.68622 |
| 2 | Acetic acid ethenyl ester | C4H6O2 | 86.09 | 2.63 | 7904 | 63 | 3.553507 |
| 3 | 2-Pentanone, 3-methyl- | C6H12O | 100.16 | 2.993 | 11262 | 80 | 3.452664 |
| 4 | Disulfide, dimethyl | C2H6S2 | 94.2 | 3.578 | 12232 | 81 | 2.579829 |
| 5 | 2-Heptanone, 6-methyl- | C8H16O | 128.21 | 5.602 | 13572 | 85 | 2.012434 |
| 6 | Pyrazine, methyl- | C5H6N2 | 94.11 | 5.95 | 7976 | 93 | 4.364266 |
| 7 | Pyrazine, 2,5-dimethyl- | C6H8N2 | 108.14 | 6.722 | 31252 | 92 | 4.600645 |
| 8 | 1-Hexanol | C6H14O | 102.17 | 7.055 | 8103 | 74 | 1.171664 |
| 9 | Pyrazine, trimethyl- | C7H10N2 | 122.17 | 7.824 | 26808 | 75 | 1.113828 |
| 10 | Pyrazine, 3-ethyl-2,5-dimethyl- | C8H12N2 | 136.19 | 8.355 | 25916 | 80 | 2.579326 |
| 11 | 1-Hexanol, 2-ethyl- | C8H18O | 130.229 | 8.864 | 7720 | 84 | 0.5058 |
| 12 | Pyrrole | C4H5N | 67.09 | 9.166 | 8027 | 90 | 0.639997 |
| 13 | Benzaldehyde | C7H6O | 106.12 | 9.374 | 240 | 82 | 7.155098 |
| 14 | Acetic acid, trifluoro-, nonyl ester | C11H19F3O2 | 240.26 | 10.344 | 6428483 | 73 | 0.416699 |
| 15 | (S)-(+)-6-Methyl-1-octanol | C9H20O | 144.25 | 10.605 | 13548104 | 79 | 0.560066 |
| 16 | Oxime-, methoxy-phenyl-_ | C8H9NO2 | 151.16 | 12.025 | 9602988 | 70 | 2.008104 |
| 17 | Acetamide | C2H5NO | 59.07 | 12.1 | 178 | 96 | 11.58042 |
| 18 | Propanamide | C3H7NO | 73.09 | 12.612 | 6578 | 71 | 0.730287 |
| 19 | 2,4-Decadienal, (E,E)- | C10H16O | 152.23 | 12.825 | 5283349 | 68 | 0.893933 |
| 20 | Hexanoic acid | C6H12O2 | 116.16 | 13.043 | 8892 | 60 | 0.301542 |
| 21 | 2-Tetradecanone | C14H28O | 212.37 | 13.441 | 75364 | 86 | 1.671165 |
| 22 | (R)-(−)-4-Methylhexanoic acid | C7H14O2 | 130.18 | 13.913 | 12600623 | 70 | 0.496031 |
| 23 | Hexanoic acid, 2-ethyl- | C8H16O2 | 144.21 | 14.172 | 8697 | 66 | 0.587733 |
| 24 | Phenol | C6H6O | 94.11 | 14.738 | 996 | 96 | 4.246424 |
| 25 | Octanoic acid | C8H16O2 | 144.21 | 15.283 | 379 | 67 | 0.803864 |
| 26 | 2,4,7,9-Tetramethyl-5-decyn-4,7-diol | C14H26O2 | 226.35 | 15.658 | 31362 | 69 | 0.481144 |
| 27 | Nonanoic acid | C9H18O2 | 158.24 | 16.331 | 8158 | 82 | 1.003712 |
| 28 | 2-Octyl benzoate | C15H22O2 | 234.33 | 17.33 | 243800 | 66 | 0.967435 |
| 29 | Phenol, 2,4-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)- | C14H22O | 206.32 | 17.784 | 7311 | 87 | 1.242429 |
| 30 | Benzoic acid, pentyl ester | C12H16O2 | 192.25 | 18.345 | 16296 | 68 | 0.712256 |
| 31 | Benzoic acid | C7H6O2 | 122.12 | 18.705 | 243 | 85 | 0.94121 |
| 32 | 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, bis(2-methylpropyl) ester | C16H22O4 | 278.34 | 19.822 | 6782 | 93 | 2.287847 |
| 33 | Dibutyl phthalate | C16H22O4 | 278.34 | 21.072 | 3026 | 74 | 2.75918 |
| 34 | Hexadecanoic acid | C16H32O2 | 256.42 | 22.573 | 985 | 71 | 6.166636 |
| 35 | Oleic Acid | C18H34O2 | 282.5 | 24.497 | 445639 | 82 | 8.522779 |
| 36 | 9,12-Octadecadienoic acid (Z,Z)- | C18H32O2 | 280.4 | 25.011 | 5280450 | 71 | 3.023523 |
| Bacillus subtilis Md1-42 (BSS17) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Name | Molecular Formula | Molecular Mass, g/mol | Retention Time (min) | Pubchem Compound CID | Similarities | Area, % |
| 1 | (2-Aziridinylethyl)amine | C4H10N2 | 86.14 | 1.157 | 97697 | 78 | 0.440368 |
| 2 | 1-Propen-2-ol, acetate | C5H8O2 | 100.12 | 1.664 | 7916 | 76 | 0.91485 |
| 3 | 2,3-Butanedione | C4H6O2 | 86.09 | 2.649 | 650 | 93 | 17.04656 |
| 4 | 3-Penten-1-ol | C5H10O | 86.13 | 5.699 | 510370 | 83 | 0.269452 |
| 5 | Acetoin | C4H8O2 | 88.11 | 6.247 | 179 | 76 | 37.17943 |
| 6 | 3-Pentanol, 2-methyl- | C6H14O | 102.17 | 7.009 | 11264 | 80 | 1.154491 |
| 7 | 2-Nonen-1-ol | C9H18O | 142.24 | 7.108 | 61896 | 68 | 0.420964 |
| 8 | 2-Hydroxy-3-pentanone | C5H10O2 | 102.13 | 7.215 | 521790 | 81 | 1.137636 |
| 9 | Ethane-1,1-diol dibutanoate | C10H18O4 | 202.25 | 8.244 | 551339 | 77 | 0.624527 |
| 10 | Acetic acid | C2H4O2 | 60.05 | 8.355 | 176 | 93 | 0.854423 |
| 11 | 1-Hexanol, 2-ethyl- | C8H18O | 130.229 | 8.889 | 7720 | 84 | 0.206645 |
| 12 | Benzaldehyde | C7H6O | 106.12 | 9.399 | 240 | 92 | 2.022607 |
| 13 | 2,3-Butanediol | C4H10O2 | 90.12 | 9.483 | 262 | 78 | 3.407863 |
| 14 | 1,6-Octadien-3-ol, 3,7-dimethyl- | C10H18O | 154.25 | 9.632 | 6549 | 83 | 0.530564 |
| 15 | Propanoic acid, 2-methyl- | C4H8O2 | 88.11 | 9.833 | 6590 | 82 | 3.007214 |
| 16 | 2,3-Butanediol, [R-(R*,R*)]- | C4H10O2 | 90.12 | 9.927 | 225936 | 75 | 0.516676 |
| 17 | 1-Nonanol | C9H20O | 144.25 | 10.367 | 8914 | 79 | 0.235951 |
| 18 | (S)-(+)-6-Methyl-1-octanol | C9H20O | 144.25 | 10.63 | 13548104 | 86 | 0.668355 |
| 19 | Butanoic acid, 2-methyl- | C5H10O2 | 102.13 | 11.076 | 8314 | 81 | 2.487502 |
| 20 | Oxime-, methoxy-phenyl-_ | C8H9NO2 | 151.16 | 12.051 | 151.16 | 70 | 0.59943 |
| 21 | 2,4-Decadienal | C10H16O | 152.23 | 12.855 | 5283349 | 70 | 0.310428 |
| 22 | 2,2,4-Trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol diisobutyrate | C16H30O4 | 286.41 | 13.615 | 23284 | 73 | 0.259067 |
| 23 | (R)-(−)-4-Methylhexanoic acid | C7H14O2 | 130.18 | 13.942 | 12600623 | 74 | 0.173808 |
| 24 | Phenol | C6H6O | 94.11 | 14.772 | 996 | 94 | 0.427543 |
| 25 | Octanoic acid | C8H16O2 | 144.21 | 15.313 | 379 | 68 | 0.235055 |
| 26 | Nonanoic acid | C9H18O2 | 158.24 | 16.358 | 8158 | 87 | 0.268447 |
| 27 | Hexadecanoic acid, methyl ester | C17H34O2 | 270.5 | 17.011 | 8181 | 89 | 0.296456 |
| 28 | 2-Octyl benzoate | C15H22O2 | 234.33 | 17.353 | 243800 | 67 | 0.301277 |
| 29 | Benzoic acid, heptyl ester | C14H20O2 | 220.31 | 18.076 | 81591 | 75 | 0.189386 |
| 30 | Benzoic acid, undecyl ester | C18H28O2 | 276.4 | 18.368 | 229159 | 70 | 0.218367 |
| 31 | Benzoic acid | C7H6O2 | 122.12 | 18.538 | 243 | 84 | 0.270263 |
| 32 | 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, bis(2-methylpropyl) ester | C16H22O4 | C16H22O4 | 19.238 | 6782 | 91 | 0.666223 |
| 33 | Phenol, 2,4-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)- | C14H22O | 206.32 | 19.849 | 7311 | 86 | 0.746427 |
| 34 | Oleic Acid | C18H34O2 | 282.5 | 20.98 | 445639 | 68 | 0.295063 |
| 35 | Dibutyl phthalate | C16H22O4 | 278.34 | 21.113 | 3026 | 82 | 1.029155 |
| 36 | Hexadecanoic acid | C16H32O2 | 256.42 | 22.592 | 985 | 85 | 3.51103 |
| 37 | Octadecanoic acid | C18H36O2 | 284.5 | 24.242 | 5281 | 68 | 3.107501 |
| 38 | Oleic Acid | C18H34O2 | 282.5 | 24.525 | 445639 | 84 | 5.557709 |
| 39 | 9,12-Octadecadienoic acid (Z,Z)- | C18H32O2 | 280.4 | 25.047 | 5280450 | 84 | 9.157715 |
| Bacillus subtilis Khozestan2 (BSS19) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Name | Molecular Formula | Molecular Mass, g/mol | Retention Time (min) | Pubchem Compound CID | Similarities | Area, % |
| 1 | Carbamic acid, monoammonium salt | CH6N2O2 | 78.071 | 1.134 | 517232 | 88 | 1.700997 |
| 2 | Ethanol | C2H6O | 46.07 | 2.234 | 702 | 81 | 0.46569 |
| 3 | 1-Butanol | C4H10O | 74.12 | 4.321 | 263 | 91 | 6.044015 |
| 4 | 2-Heptanone, 6-methyl- | C8H16O | 128.21 | 5.599 | 13572 | 85 | 1.508914 |
| 5 | 2-Heptanone, 5-methyl- | C8H16O | 128.21 | 5.839 | 28965 | 87 | 0.899369 |
| 6 | Pyrazine, 2,5-dimethyl- | C6H8N2 | 108.14 | 6.717 | 31252 | 94 | 6.575729 |
| 7 | Acetic acid | C2H4O2 | 60.05 | 8.318 | 176 | 93 | 4.27265 |
| 8 | 2-Decanone | C10H20O | 156.26 | 8.399 | 12741 | 76 | 3.555438 |
| 9 | 1-Hexanol, 2-ethyl- | C8H18O | 130.229 | 8.859 | 7720 | 85 | 1.019178 |
| 10 | Benzaldehyde | C7H6O | 106.12 | 9.361 | 240 | 91 | 3.066211 |
| 11 | 1-Octene, 6-methyl- | C9H18 | 126.24 | 9.587 | 518716 | 77 | 0.767838 |
| 12 | Propanoic acid, 2-methyl- | C4H8O2 | 88.11 | 9.796 | 6590 | 85 | 8.705907 |
| 13 | 1-Octanol, 2-methyl- | C9H20O | 144.25 | 9.896 | 102495 | 82 | 0.837655 |
| 14 | 1-Nonanol | C9H20O | 144.25 | 10.342 | 8914 | 81 | 1.748035 |
| 15 | (S)-(+)-6-Methyl-1-octanol | C9H20O | 144.25 | 10.604 | 13548104 | 90 | 3.260679 |
| 16 | Benzeneacetaldehyde | C8H8O | 120.15 | 10.821 | 998 | 69 | 2.227017 |
| 17 | 2-Furanmethanol | C5H6O2 | 98.1 | 10.918 | 7361 | 87 | 1.948174 |
| 18 | Hexanoic acid, 2-methyl- | C7H14O2 | 130.18 | 11.036 | 20653 | 80 | 25.50356 |
| 19 | 2-Dodecanone | C12H24O | 184.32 | 11.198 | 22556 | 77 | 1.361537 |
| 20 | Oxime-, methoxy-phenyl-_ | C8H9NO2 | 151.16 | 12.018 | 9602988 | 65 | 1.54511 |
| 21 | 2(5H)-Furanone | C4H4O2 | 84.07 | 12.114 | 10341 | 77 | 2.40381 |
| 22 | Formamide | CH3NO | 45.041 | 12.32 | 713 | 77 | 0.972164 |
| 23 | 2-Tetradecanone | C14H28O | 212.37 | 13.44 | 75364 | 80 | 1.097307 |
| 24 | Maltol | C6H6O3 | 126.11 | 14.375 | 8369 | 93 | 4.442068 |
| 25 | Ethanone, 1-(1H-pyrrol-2-yl)- | C6H7NO | 109.13 | 14.429 | 14079 | 67 | 1.456046 |
| 26 | Phenol | C6H6O | 94.11 | 14.739 | 996 | 96 | 6.642077 |
| 27 | 4H-Pyran-4-one, 2,3-dihydro-3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyl- | C6H8O4 | 144.12 | 17.293 | 119838 | 88 | 1.650456 |
| 28 | Benzoic acid, hept-2-yl ester | C14H20O2 | 220.31 | 18.053 | 243678 | 75 | 0.421796 |
| 29 | Benzoic acid | C7H6O2 | 122.12 | 18.698 | 243 | 91 | 1.317335 |
| 30 | 5-Hydroxymethyldihydrofuran-2-one | C5H8O3 | 116.11 | 19.196 | 98431 | 73 | 0.384416 |
| 31 | 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, bis(2-methylpropyl) ester | C16H22O4 | C16H22O4 | 19.356 | 6782 | 91 | 0.986222 |
| 32 | Phenol, 2,4-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)- | C14H22O | 206.32 | 19.786 | 7311 | 85 | 1.085735 |
| No | Isolates | 16S rRNA Amplified Region Length | % Similarity | NCBI Accession No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BSS11 | 1443 bp | 99% with Bacillus subtilis O-3 | GQ870259 |
| 2 | BSS17 | 1454 bp | 99% with Bacillus subtilis Md1-42 | MF581448 |
| 3 | BSS19 | 1450 bp | 99% with Bacillus subtilis Khozestan2 | MH036316 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koilybayeva, M.; Shynykul, Z.; Ustenova, G.; Abzaliyeva, S.; Alimzhanova, M.; Amirkhanova, A.; Turgumbayeva, A.; Mustafina, K.; Yeleken, G.; Raganina, K.; et al. Molecular Characterization of Some Bacillus Species from Vegetables and Evaluation of Their Antimicrobial and Antibiotic Potency. Molecules 2023, 28, 3210. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073210
Koilybayeva M, Shynykul Z, Ustenova G, Abzaliyeva S, Alimzhanova M, Amirkhanova A, Turgumbayeva A, Mustafina K, Yeleken G, Raganina K, et al. Molecular Characterization of Some Bacillus Species from Vegetables and Evaluation of Their Antimicrobial and Antibiotic Potency. Molecules. 2023; 28(7):3210. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073210
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoilybayeva, Moldir, Zhanserik Shynykul, Gulbaram Ustenova, Symbat Abzaliyeva, Mereke Alimzhanova, Akerke Amirkhanova, Aknur Turgumbayeva, Kamilya Mustafina, Gulnur Yeleken, Karlygash Raganina, and et al. 2023. "Molecular Characterization of Some Bacillus Species from Vegetables and Evaluation of Their Antimicrobial and Antibiotic Potency" Molecules 28, no. 7: 3210. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073210
APA StyleKoilybayeva, M., Shynykul, Z., Ustenova, G., Abzaliyeva, S., Alimzhanova, M., Amirkhanova, A., Turgumbayeva, A., Mustafina, K., Yeleken, G., Raganina, K., & Kapsalyamova, E. (2023). Molecular Characterization of Some Bacillus Species from Vegetables and Evaluation of Their Antimicrobial and Antibiotic Potency. Molecules, 28(7), 3210. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073210







