Effects of Seawater Intrusion on the Groundwater Quality of Multi-Layered Aquifers in Eastern Saudi Arabia
Abstract
1. Introduction
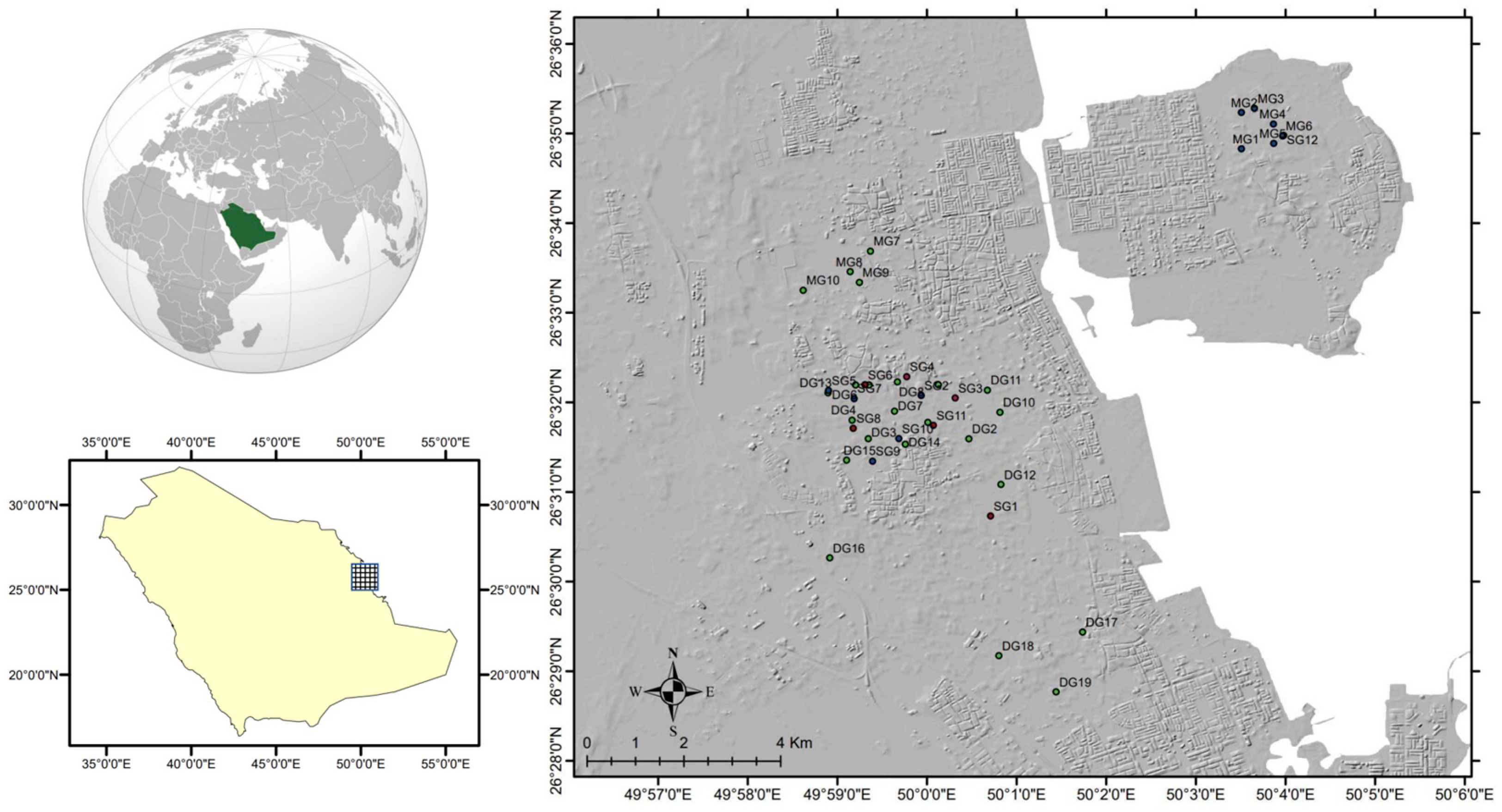
2. Study Area
3. Geological and Hydrogeological Setting
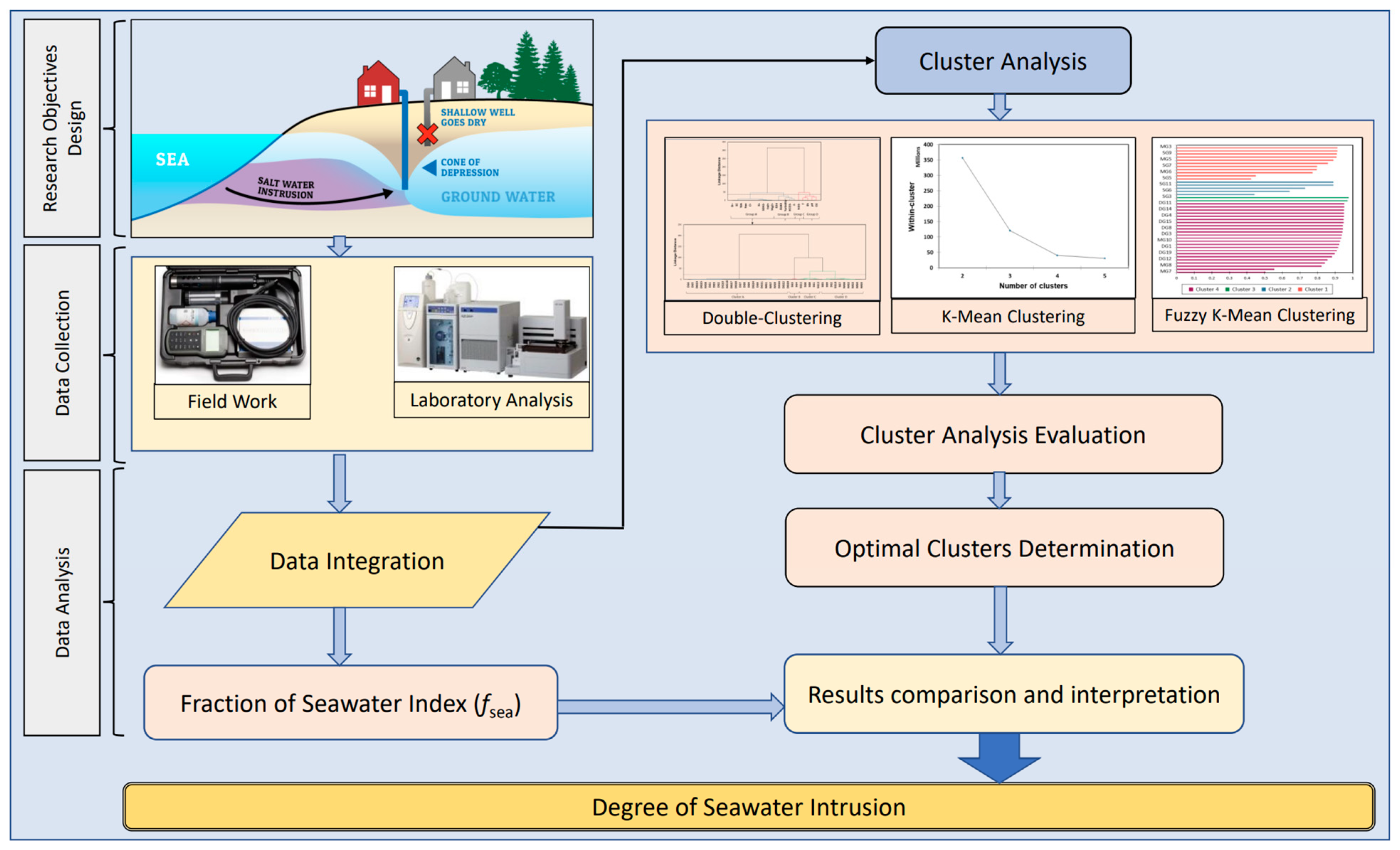
4. Proposed Methodology
4.1. Field Investigation and Water Sampling
4.2. Laboratory Analysis
4.3. K-Mean Cluster Analysis
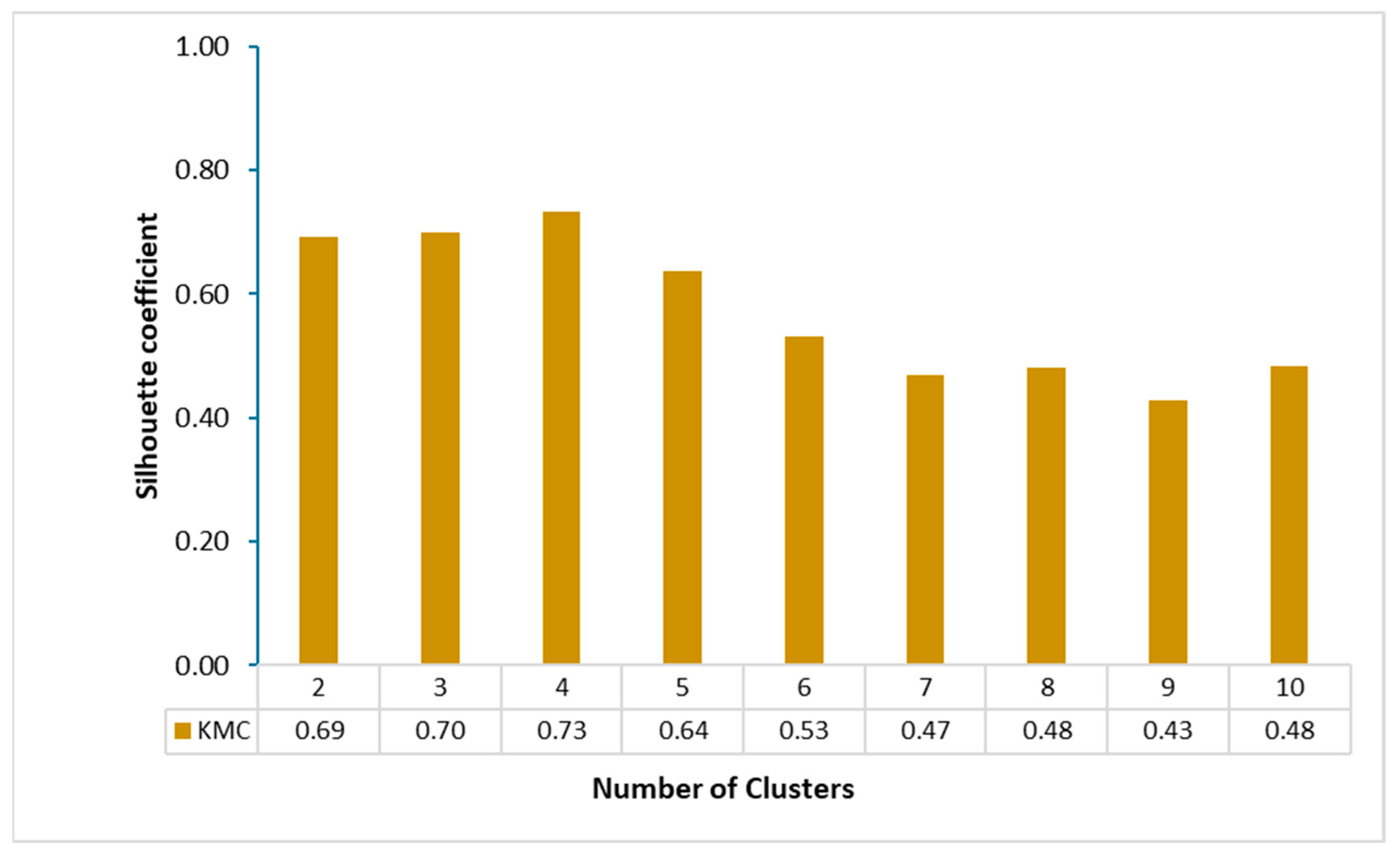
4.4. Silhouette Score
4.5. Fraction of Seawater Index (fsea)
4.6. Irrigation Water Quality Assessment
4.6.1. Sodium Adsorption Ratio (SAR)
4.6.2. Sodium Percentage (Na%)
4.6.3. Kelly’s Ratio (KR)
4.6.4. Potential Salinity (PS)
4.6.5. Electrical Conductivity (EC)
4.6.6. Magnesium Adsorption Ratio (MAR)
4.6.7. Permeability Index (PI)
5. Results and Discussion
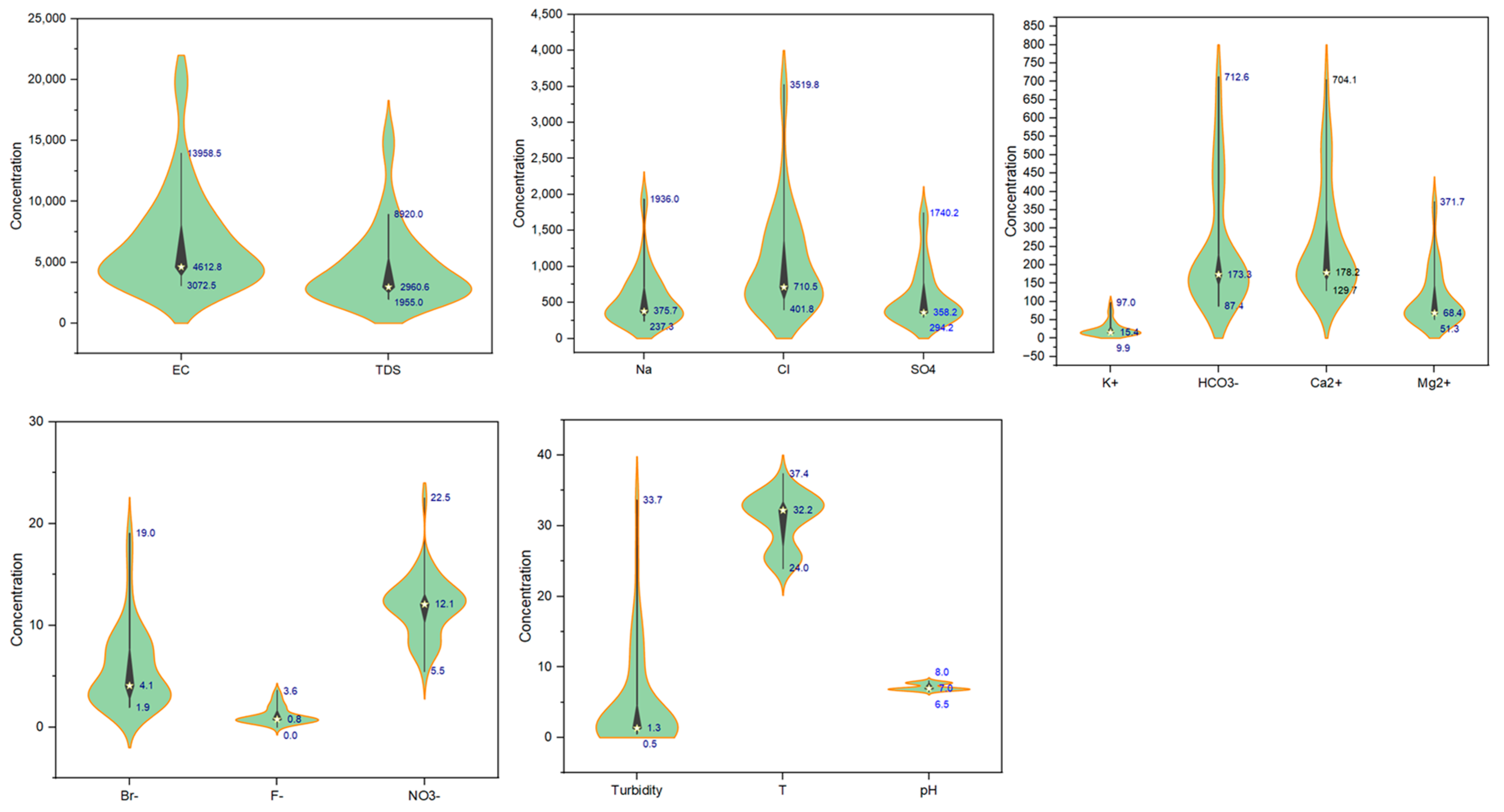
5.1. Groundwater Hydrochemistry and Water Type
5.2. K-Mean Cluster Analysis
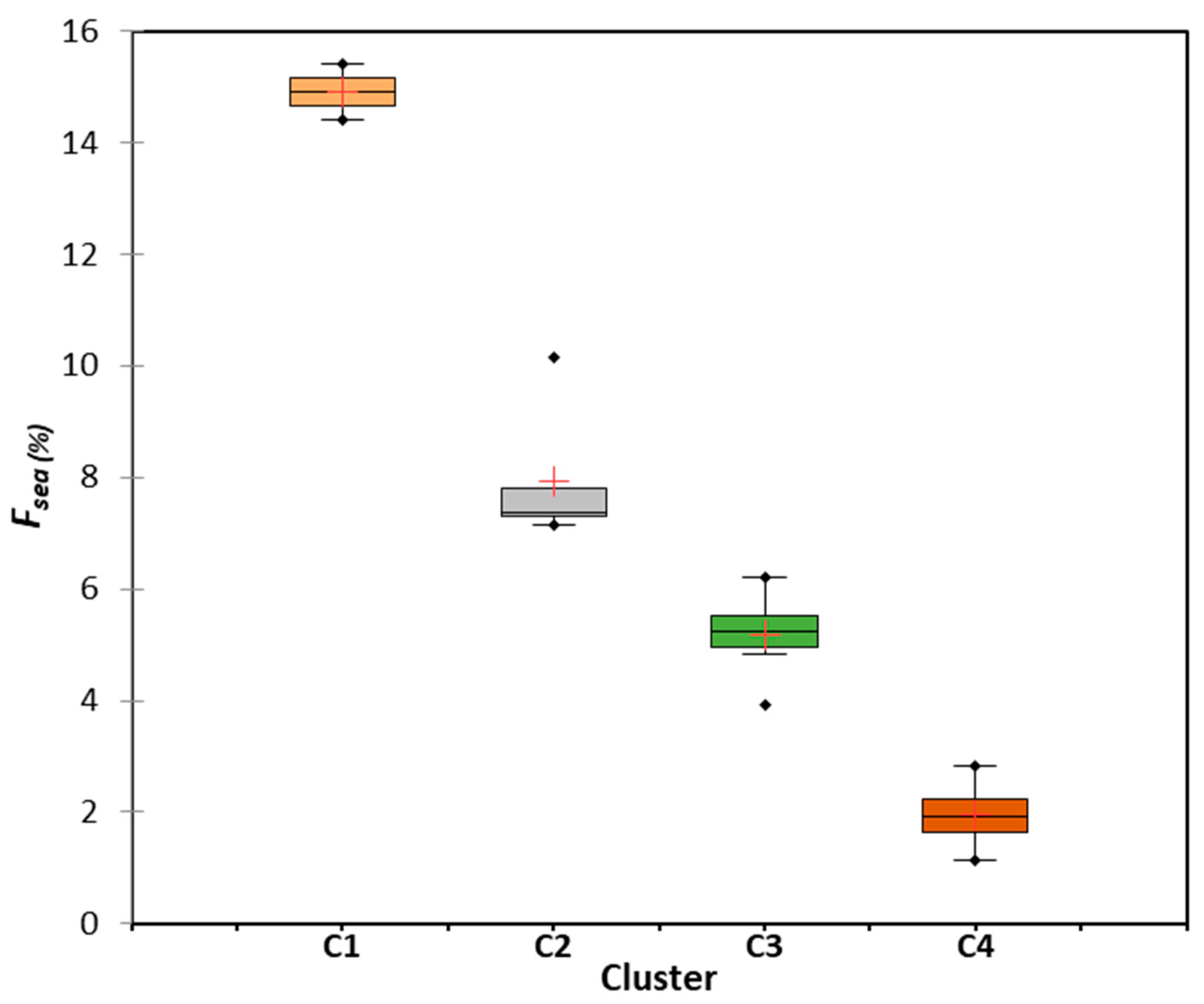
5.3. Seawater Intrusion Quantification
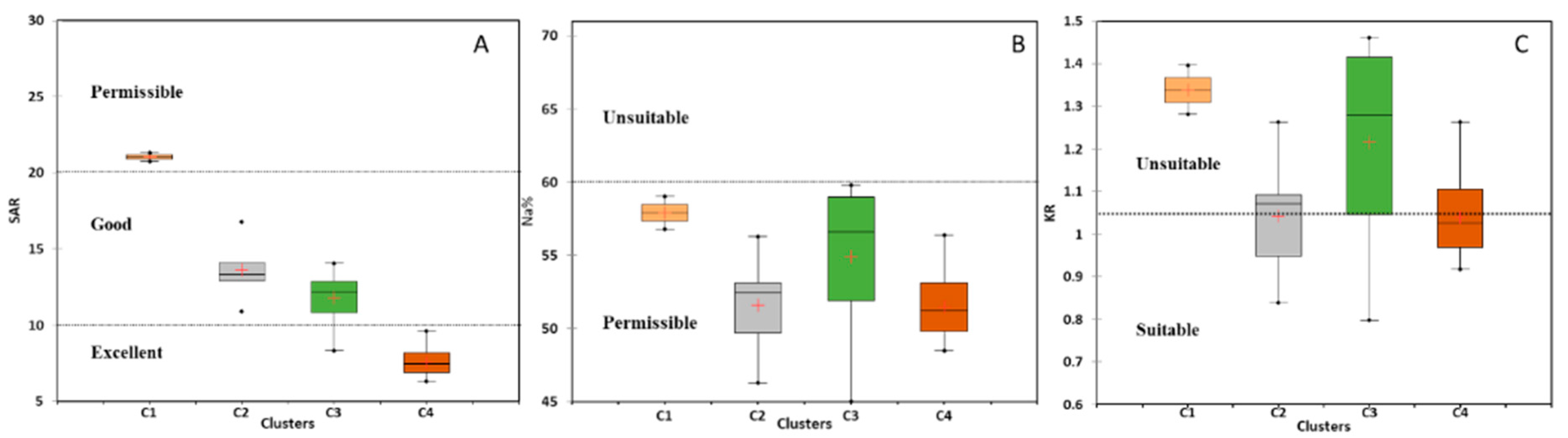
5.4. Water Suitability for Irrigation
5.4.1. Salinity Hazard
5.4.2. Sodium Hazard
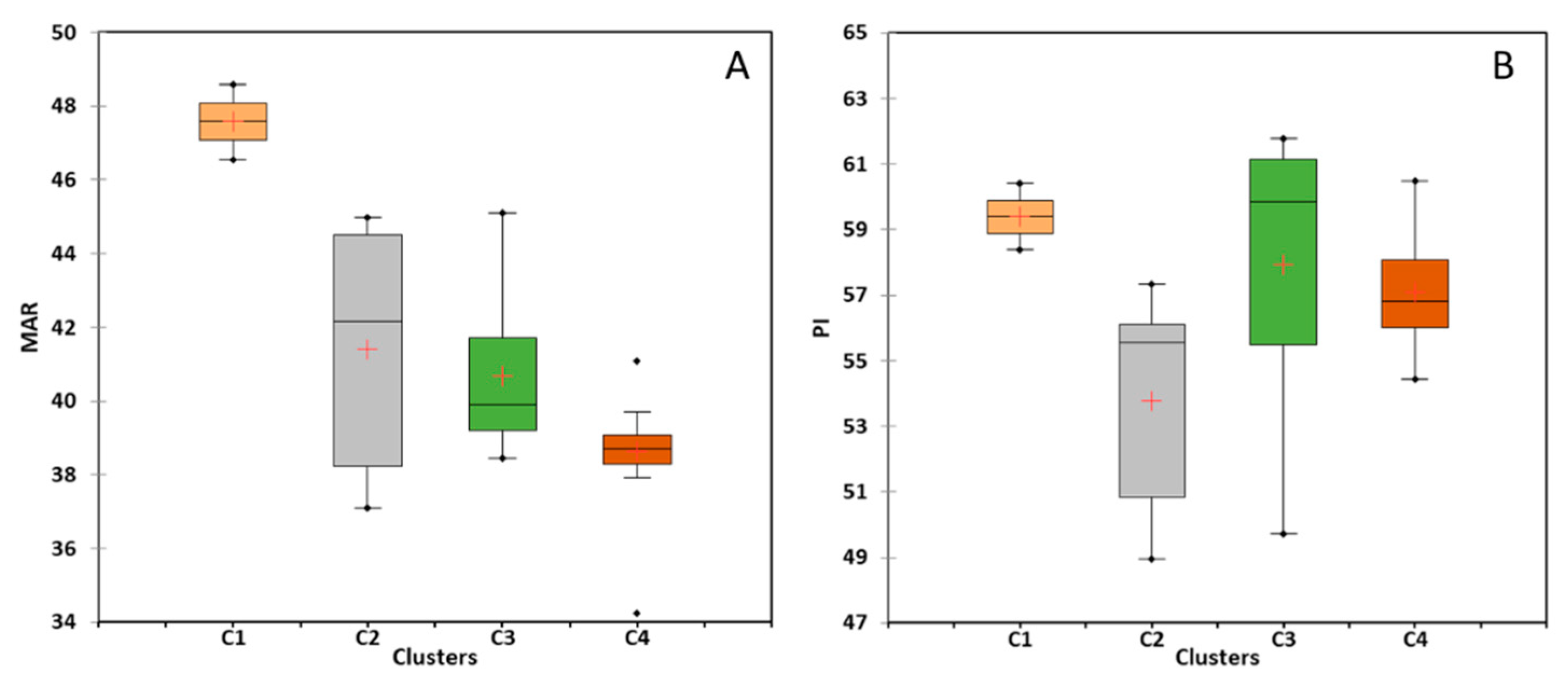
5.4.3. Magnesium Hazard
5.4.4. Carbonate Hazard
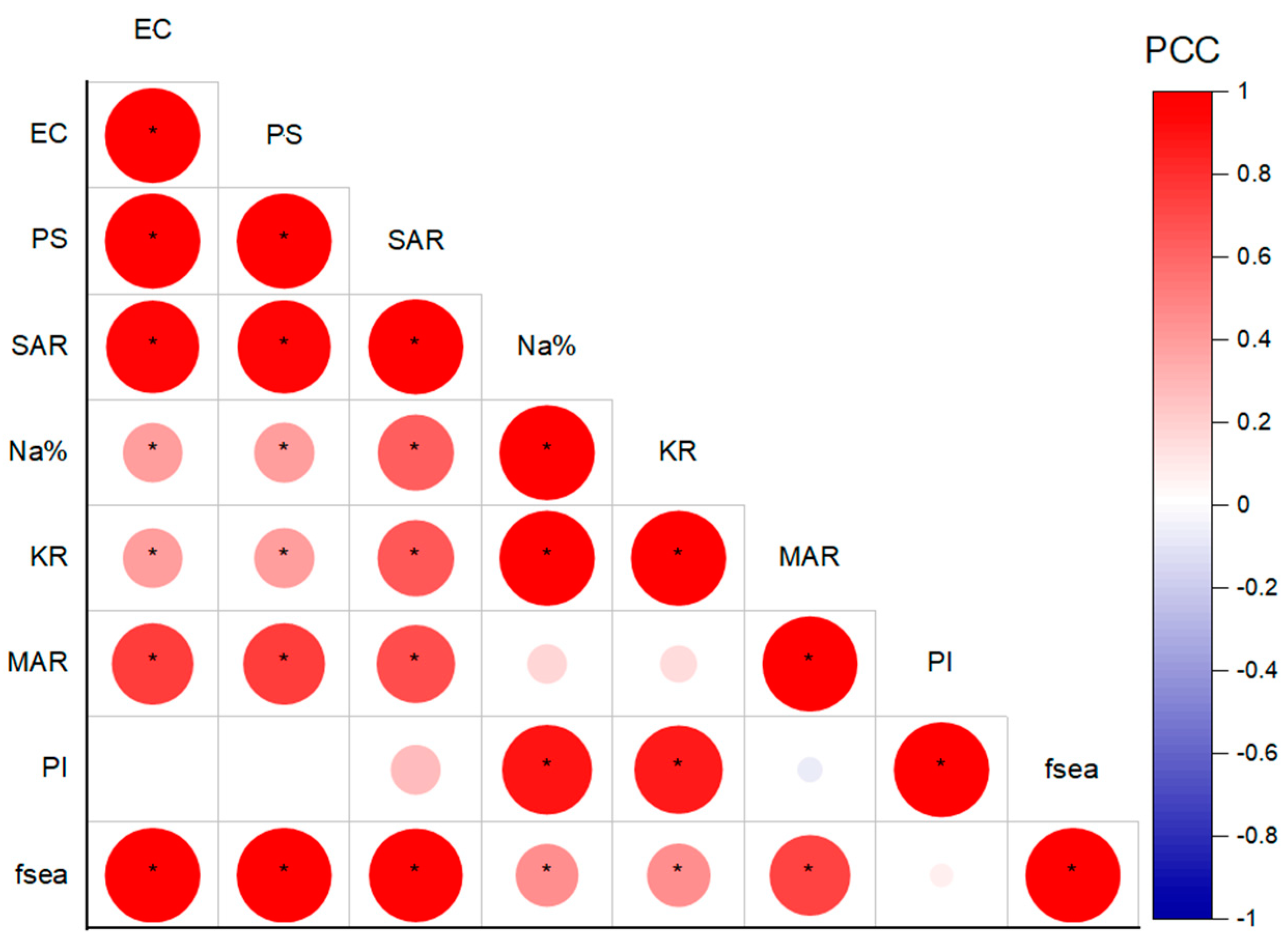
5.5. Relationship between Seawater Intrusion and Irrigation Hazards
6. Conclusions and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Li, Z.; Wang, G.; Wang, X.; Wan, L.; Shi, Z.; Wanke, H.; Uugulu, S.; Uahengo, C.-I. Groundwater quality and associated hydrogeochemical processes in Northwest Namibia. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 186, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, V.; Chau, K.W.; Fadaee, F.; Torkaman, J.; Ghaffari, A. Modeling of groundwater level fluctuations using dendrochronology in alluvial aquifers. J. Hydrol. 2015, 529, 1060–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benaafi, M.; Al-Shaibani, A. Hydrochemical and Isotopic Investigation of the Groundwater from Wajid Aquifer in Wadi Al-Dawasir, Southern Saudi Arabia. Water 2021, 13, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulipano, L.; Fidelibus, M.D.; Panagopoulos, A. Groundwater Management of Coastal Karstic Aquifers; COST Action 621, Report EUR 21366; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Werner, A.D.; Bakker, M.; Post, V.E.; Vandenbohede, A.; Lu, C.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Simmons, C.T.; Barry, D. Seawater intrusion processes, investigation and management: Recent advances and future challenges. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrocicco, M.; Colombani, N. The issue of groundwater salinization in coastal areas of the mediterranean region: A review. Water 2021, 13, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Xiong, G.; Chen, G.; Fu, T.; Yu, H.; Wu, J.; Liu, W.; Su, Q.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; et al. Characteristics of coastal aquifer contamination by seawater intrusion and anthropogenic activities in the coastal areas of the Bohai Sea, eastern China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2021, 217, 104830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Al Naeem, M.F.; Yusoff, I.; Ng, T.F.; Maity, J.P.; Alias, Y.; May, R.; Alborsh, H. A study on the impact of anthropogenic and geogenic factors on groundwater salinization and seawater intrusion in Gaza coastal aquifer, Palestine: An integrated multi-techniques approach. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2019, 156, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, P.; Kumari, R.; Mukherjee, S. Hydrochemistry in integration with stable isotopes (δ18O and δD) to assess seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers of Kachchh district, Gujarat, India. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 196, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Han, D.; Song, X. Past, present, and future of global seawater intrusion research: A bibliometric analysis. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batayneh, A.; Zaman, H.; Zumlot, T.; Ghrefat, H.; Mogren, S.; Nazzal, Y.; Elawadi, E.; Qaisy, S.; Bahkaly, I.; Altaani, A.A. Hydrochemical facies and ionic ratios of the coastal groundwater aquifer of saudi gulf of aqaba: Implication for seawater intrusion. J. Coast. Res. 2014, 30, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippis, G.; Foglia, L.; Giudici, M.; Mehl, S.; Margiotta, S.; Negri, S.L. Seawater intrusion in karstic, coastal aquifers: Current challenges and future scenarios in the Taranto area (southern Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 1340–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benaafi, M.; Tawabini, B.; Abba, S.I.; Humphrey, J.D.; Al-Areeq, A.M.; Alhulaibi, S.A.; Usman, A.G.; Aljundi, I.H. Integrated Hydrogeological, Hydrochemical, and Isotopic Assessment of Seawater Intrusion into Coastal Aquifers in Al-Qatif Area, Eastern Saudi Arabia. Molecules 2022, 27, 6841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, F. Impact of anthropogenic and natural processes on the evolution of groundwater chemistry in a rapidly urbanized coastal area, South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloppmann, W.; Bourhane, A.; Schomburgk, S. Groundwater salinization in France. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 2013, 7, 440–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziadi, A.; Hariga, N.T.; Tarhouni, J. Mineralization and pollution sources in the coastal aquifer of Lebna, Cap Bon, Tunisia. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2019, 151, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abba, S.I.; Benaafi, M.; Usman, A.G.; Ozsahin, D.U.; Tawabini, B.; Aljundi, I.H. Mapping of groundwater salinization and modelling using meta-heuristic algorithms for the coastal aquifer of eastern Saudi Arabia. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elhamid, H.; Javadi, A.; Abdelaty, I.; Sherif, M. Simulation of seawater intrusion in the Nile Delta aquifer under the conditions of climate change. Hydrol. Res. 2016, 47, 1198–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Currell, M.J. Delineating multiple salinization processes in a coastal plain aquifer, northern China: Hydrochemical and isotopic evidence. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 3473–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, D.T.; Yamada, T.; Ishidaira, H. Assessing the impact of sea level rise due to climate change on seawater intrusion in Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 77, 1632–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Koriem, M.A.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Antar, A.S.; Ewis, M.A.; He, Z.; Kheir, A.M.S. Seawater intrusion impacts on groundwater and soil quality in the northern part of the Nile Delta, Egypt. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, B.; Islam, A.; Majumder, A. Seawater intrusion into groundwater and its impact on irrigation and agriculture: Evidence from the coastal region of West Bengal, India. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 44, 101751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahnke, C.; Wannous, M.; Troeger, U.; Falk, M.; Struck, U. Impact of seawater intrusion and disposal of desalinization brines on groundwater quality in El Gouna, Egypt, Red Sea Area. Process analyses by means of chemical and isotopic signatures. Appl. Geochem. 2019, 100, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, S.H.; Ishida, K.; Oo, Z.M.; Sakai, H. Impacts of seawater intrusion on groundwater quality in Htantabin township of the deltaic region of southern Myanmar. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 14, 100645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheeduddin, M.; Yazicigil, H.; Al-Layla, R.I. Numerical modeling of a multi-aquifer system in eastern Saudi Arabia. J. Hydrol. 1989, 107, 193–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abderrahman, W.A.; Rasheeduddin, M. Management of groundwater resources in a coastal belt aquifer system of Saudi Arabia. Water Int. 2001, 26, 40–50. [Google Scholar]
- Ebert, C.H.V. Water resources and land use in the Qatif Oasis of Saudi Arabia. Geogr. Rev. 1965, 55, 496–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, R.W.; Ramire, L.F.; Redmond, C.D.; Elberg, E.L., Jr. Geology of the Arabian Peninsula Sedimentary Geology of Saudi Arabia; US Geological Survey Professional Paper 560-D; United States Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1966; 154p.
- Sharland, P.; Archer, R.; Casey, D.; Davies, R.; Hall, S.; Heward, A.; Horbury, A.; Simmons, M. Arabian Plate Sequence Stratigraphy. GeoArab. J. Middle East. Pet. Geosci. 2013, 18, 29–82. [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler, M.A. Late Permian to Holocene Paleofacies Evolution of the Arabian Plate and its Hydrocarbon Occurrences. GeoArabia 2001, 6, 445–504. [Google Scholar]
- Tleel, J.W. Surface geology of Dammam dome, eastern province, Saudi Arabia. Am. Assoc. Pet. Geol. Bull. 1973, 57, 558–576. [Google Scholar]
- Weijermars, R. Surface geology, lithostratigraphy and Tertiary growth of the Dammam Dome, Saudi Arabia: A new field guide. GeoArabia 1999, 4, 199–226. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Tamimi, M.H. Stratigraphical and Microfacies Analysis of the Early Paleogene Succession in the Dammam Dome, Eastern Saudi Arabia. M.Sc. Thesis, King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals, Dhahran, Saudi Arabia, 1985; 92p. [Google Scholar]
- Edgell, H.S. Aquifers of Saudi Arabia and their geological framework. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 1997, 22, 3–31. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Groundwater Sampling Guidelines; Environment Protection Authority: Southbank, Australia, 2000; 36p.
- Hartigan, J.A.; Wong, M.A. Algorithm AS 136: A k-means clustering algorithm. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C Appl. Stat. 1979, 28, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Pei, J.; Tong, H. Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques; Morgan Kaufmann: Burlington, MA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Rousseeuw, P.J. Silhouettes: A graphical aid to the interpretation and validation of cluster analysis. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 1987, 20, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardarsa, P.; Surinta, O. Water Quality Assessment in the Lam Pa Thao Dam, Chaiyaphum, Thailand with K-Means Clustering Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2021 Research, Invention, and Innovation Congress: Innovation Electricals and Electronics (RI2C), Bangkok, Thailand, 1–3 September 2021; pp. 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Arsene, D.; Predescu, A.; Pahonțu, B.; Chiru, C.G.; Apostol, E.S.; Truică, C.O. Advanced Strategies for Monitoring Water Consumption Patterns in Households Based on IoT and Machine Learning. Water 2022, 14, 2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelo, C.A.J.; Postma, D. Geochemistry, Groundwater and Pollution; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Tampo, L.; Mande, S.-L.A.-S.; Adekanmbi, A.O.; Boguido, G.; Akpataku, K.V.; Ayah, M.; Tchakala, I.; Gnazou, M.D.; Bawa, L.M.; Djaneye-Boundjou, G.; et al. Treated wastewater suitability for reuse in comparison to groundwater and surface water in a peri-urban area: Implications for water quality management. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 152780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USSL. Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline and Alkali Soils; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1954; Volume 78.
- Doneen, L.D. Notes on Water Quality in Agriculture; Department of Water Science and Engineering, University of California: Davis, CA, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Kelley, W.P. Alkali Soils; Reinhold Publishing Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1951; Volume 72. [Google Scholar]
- Kelley, W.P. Use of saline irrigation water. Soil. Sci. 1963, 95, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, D.K.; Mays, L.W. Groundwater Hydrology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ayers, R.S.; Westcot, D.W. Water Quality for Agriculture; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1985; Volume 29. [Google Scholar]
- Tiri, A.; Belkhiri, L.; Asma, M.; Mouni, L. Suitability and Assessment of Surface Water for Irrigation Purpose. In Water Chemistry; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Raghunath, H.M. Ground Water: Hydrogeology, Ground Water Survey and Pumping Tests, Rural Water Supply and Irrigation Systems; New Age International: New Delhi, India, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Domenico, P.A.; Schwartz, F.W. Physical and Chemical Hydrogeology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Hintze, J.L.; Nelson, R.D. Violin plots: A box plot-density trace synergism. Am. Stat. 1998, 52, 181–184. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: First Addendum to the Fourth Edition; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadrezapour, O.; Kisi, O.; Pourahmad, F. Fuzzy c-means and K-means clustering with genetic algorithm for identification of homogeneous regions of groundwater quality. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 3763–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandari, E.; Mohammadzadeh, H.; Nassery, H.; Vadiati, M.; Zadeh, A.M.; Kisi, O. Delineation of isotopic and hydrochemical evolution of karstic aquifers with different cluster-based (HCA, KM, FCM and GKM) methods. J. Hydrol. 2022, 609, 127706. [Google Scholar]
- Sangadi, P.; Kuppan, C.; Ravinathan, P. Effect of hydro-geochemical processes and saltwater intrusion on groundwater quality and irrigational suitability assessed by geo-statistical techniques in coastal region of eastern Andhra Pradesh, India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 175, 113390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, M. Salinization of groundwater in arid and semi-arid zones: An example from Tajarak, western Iran. Environ. Geol. 2007, 52, 1133–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Shahrivar, A.A.; Hagare, D.; Maheshwari, B. Impact of recycled water irrigation on soil salinity and its remediation. Soil. Syst. 2022, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunkari, E.D.; Abu, M.; Bayowobie, P.S.; Dokuz, U.E. Hydrogeochemical appraisal of groundwater quality in the Ga west municipality, Ghana: Implication for domestic and irrigation purposes. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 8, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimalla, N.; Dhakate, R.; Kasarla, A.; Taloor, A.K. Appraisal of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes in Central Telangana, India. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 10, 100334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, D. Groundwater Hydrology, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, H. Groundwater chemistry and groundwater quality index incorporating health risk weighting in Dingbian County, Ordos basin of northwest China. Geochemistry 2020, 80, 125607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, F.M. Significance of carbonates in irrigation waters. Soil Sci. 1950, 69, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Formation | Member | Lithology | Description | Thickness (m) | Hydrogeologic Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quaternary Deposits |  | Eolian Sands and Sabkha | 0–10 | ||
| Hofuf |  | Sandy Limestone | 0–95 | Neogene Aquifer | |
| Dam |  | Massive Limestone | 0–90 | ||
 | Dolomitic Limestone | ||||
| Hadrukh | 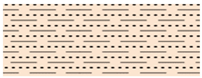 | Sand and Shale | 0–90 | ||
 | Shale | ||||
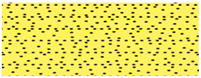 | Sandstone | ||||
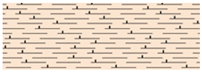 | Marl | Marl Aquitard | |||
| Dammam Dammam | Alat |  | Dolomitic Limestone | 0–80 | Alat Aquifer |
 | Dolomitic Shale | 0–30 | Alat Aquitard | ||
| Khobar | 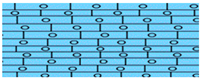 | Limestone | 0–70 | Khobar Aquifer | |
| Alevolina | 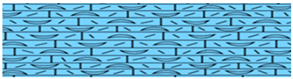 | Fossiliferous Limestone | 0–20 | Limestone Aquitard | |
| Saila | 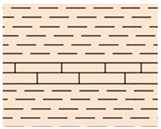 | Shale with limestone | 0–10 | Shale Aquitard | |
| Midra | |||||
| Rus | 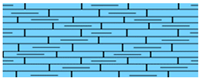 | Marl and chalky limestone | 60–100 | Shale Aquitard | |
| Umm Er Radhuma |  | Dolomitic Limestone | 200–400 | UER Aquifer |
| EC | PS | SAR | Na% | KR | MAR | PI | fsea | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
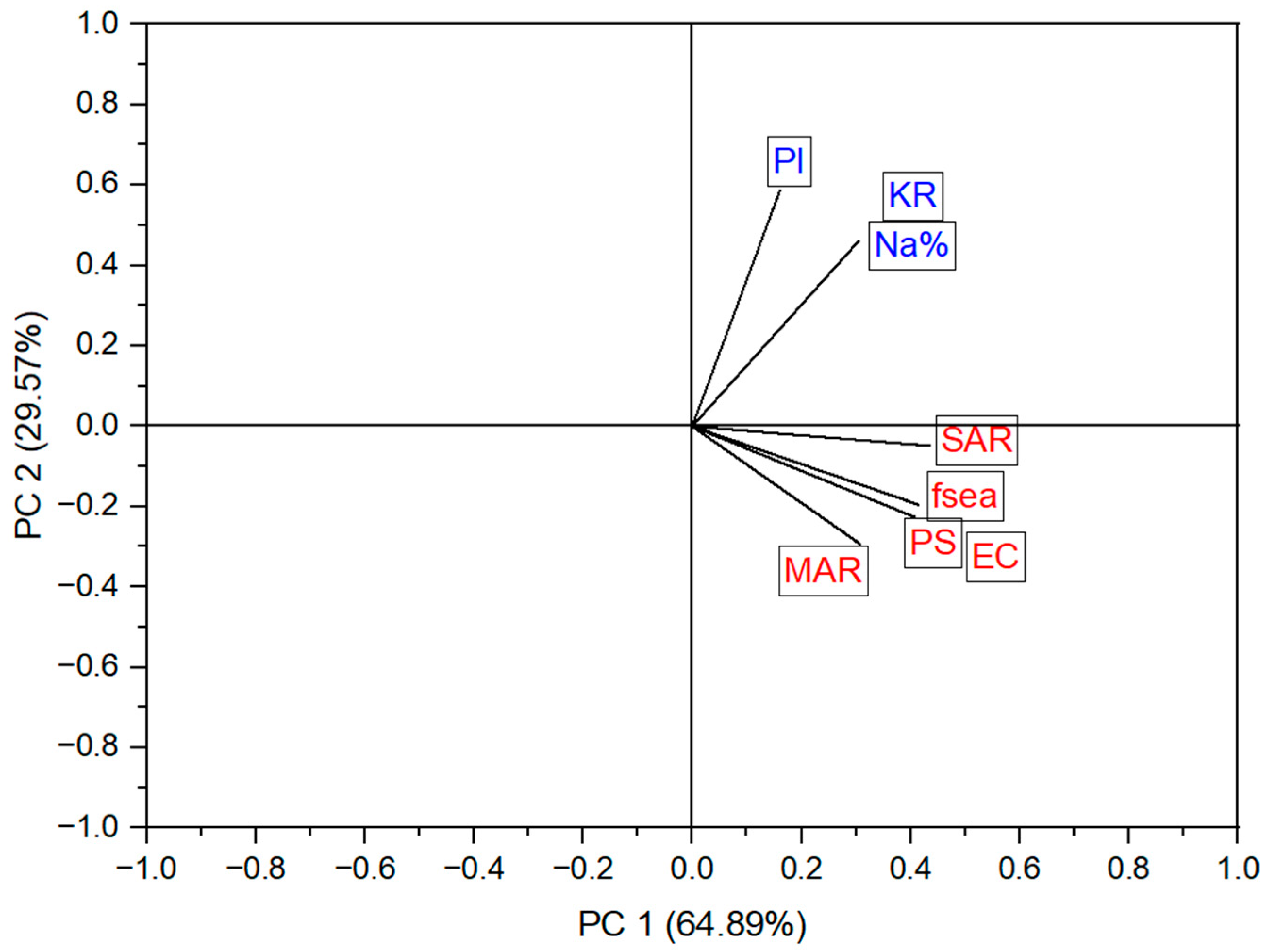
| F1 (64.89%) | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.99 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.37 | 0.94 |
| F2 (29.57%) | −0.35 | −0.35 | −0.08 | 0.71 | 0.71 | −0.45 | 0.90 | −0.30 |
| EC | PS | SAR | Na% | KR | MAR | PI | fsea | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 (64.89%) | 16.5 | 16.6 | 18.9 | 9.4 | 9.3 | 9.4 | 2.6 | 17.2 |
| F2 (29.57%) | 5.2 | 5.1 | 0.2 | 21.4 | 21.2 | 8.6 | 34.5 | 3.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Benaafi, M.; Abba, S.I.; Aljundi, I.H. Effects of Seawater Intrusion on the Groundwater Quality of Multi-Layered Aquifers in Eastern Saudi Arabia. Molecules 2023, 28, 3173. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073173
Benaafi M, Abba SI, Aljundi IH. Effects of Seawater Intrusion on the Groundwater Quality of Multi-Layered Aquifers in Eastern Saudi Arabia. Molecules. 2023; 28(7):3173. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073173
Chicago/Turabian StyleBenaafi, Mohammed, S. I. Abba, and Isam H. Aljundi. 2023. "Effects of Seawater Intrusion on the Groundwater Quality of Multi-Layered Aquifers in Eastern Saudi Arabia" Molecules 28, no. 7: 3173. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073173
APA StyleBenaafi, M., Abba, S. I., & Aljundi, I. H. (2023). Effects of Seawater Intrusion on the Groundwater Quality of Multi-Layered Aquifers in Eastern Saudi Arabia. Molecules, 28(7), 3173. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073173







