Taipan Natriuretic Peptides Are Potent and Selective Agonists for the Natriuretic Peptide Receptor A
Abstract
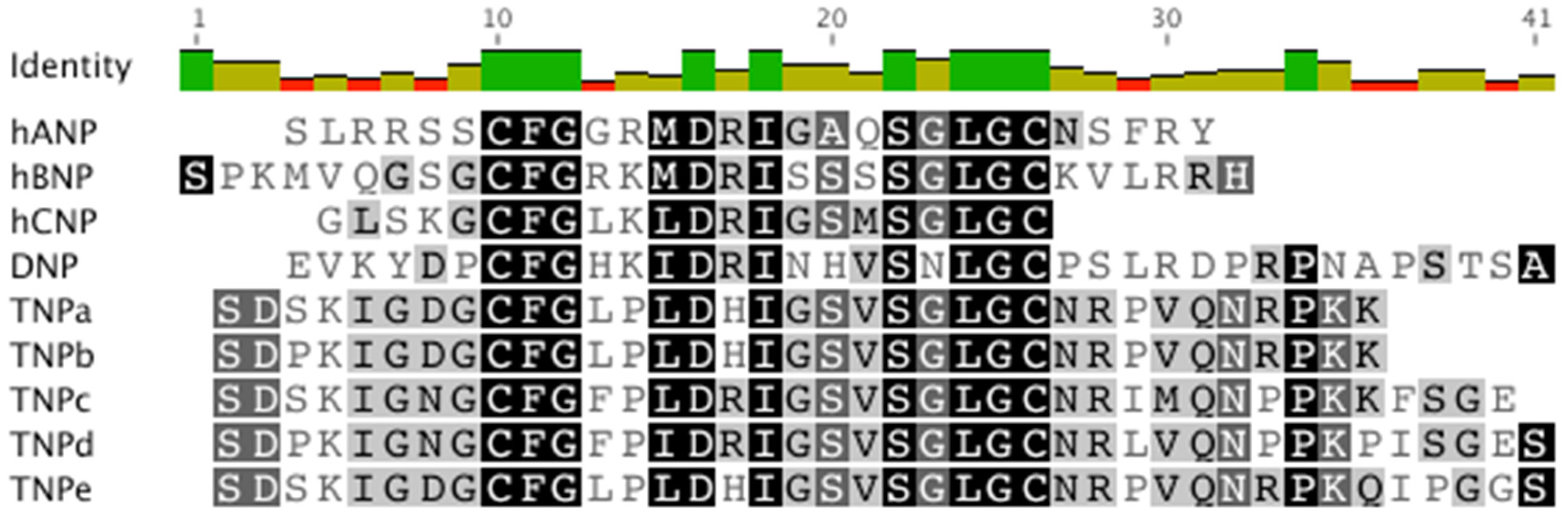
1. Introduction
2. Results
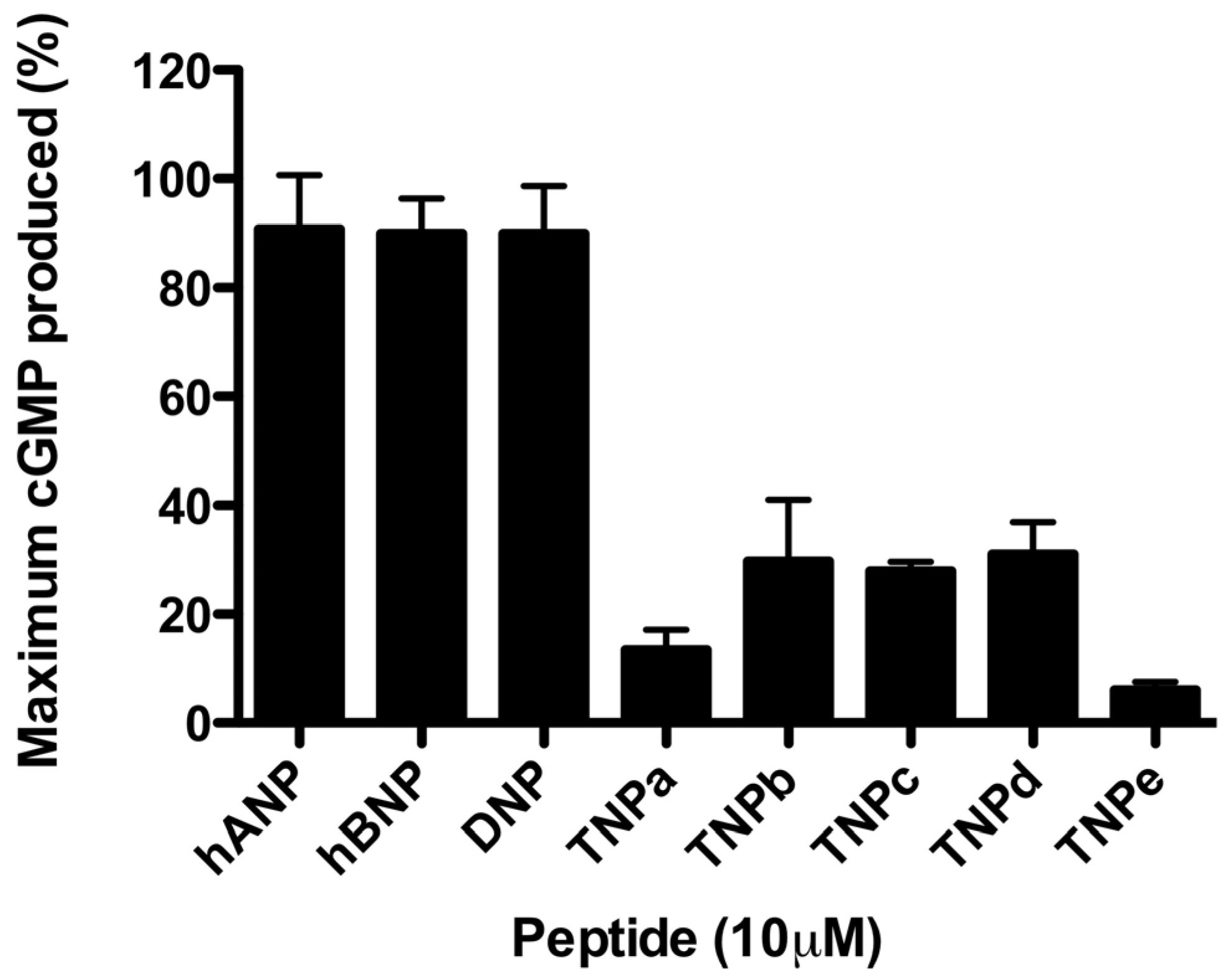
2.1. rNPR-A Activation
2.2. hNPR-A Activation
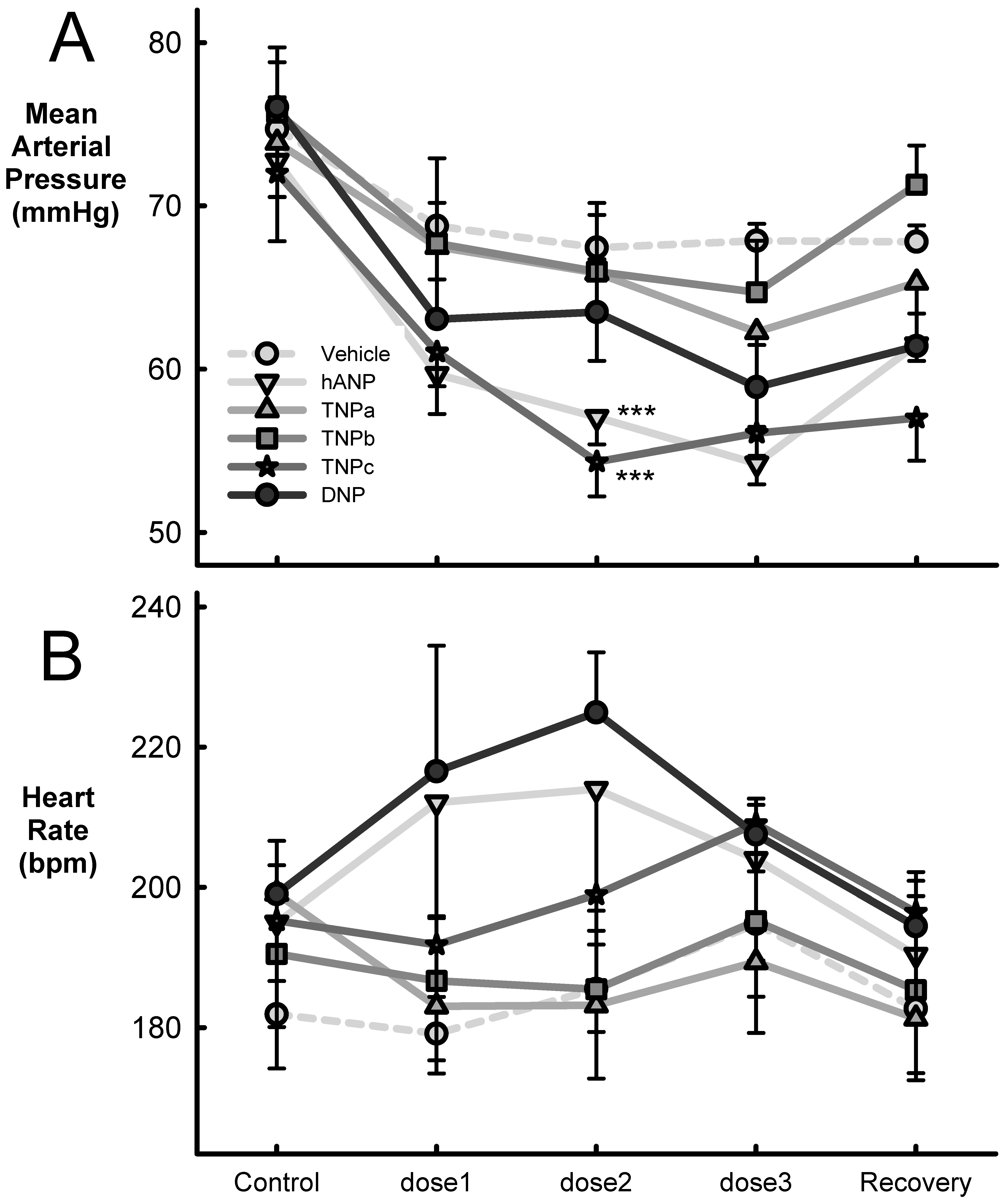
2.3. Effect on Blood Pressure and Heart Rate
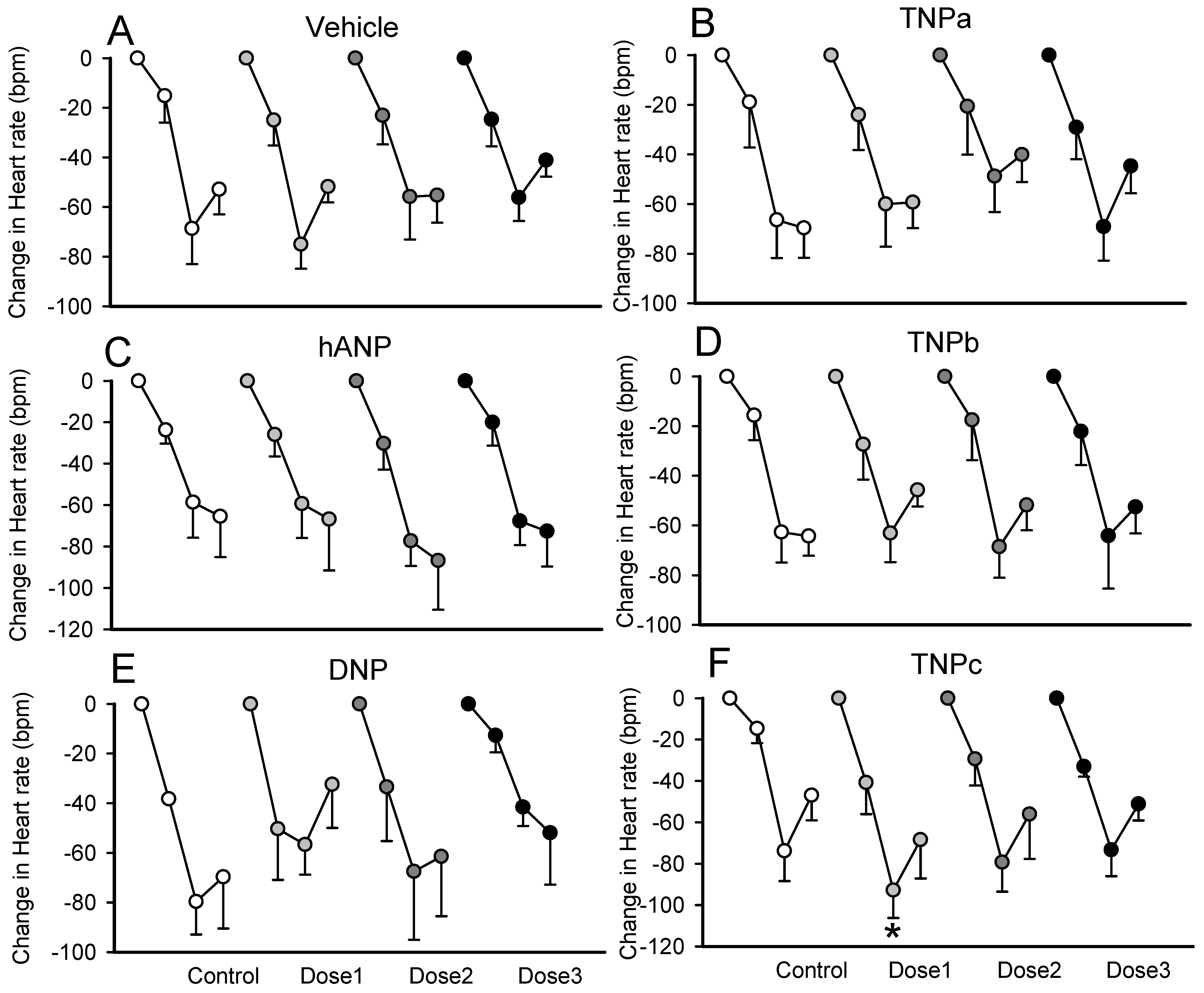
2.4. Effect on the Bezold–Jarisch Reflex Bradycardia
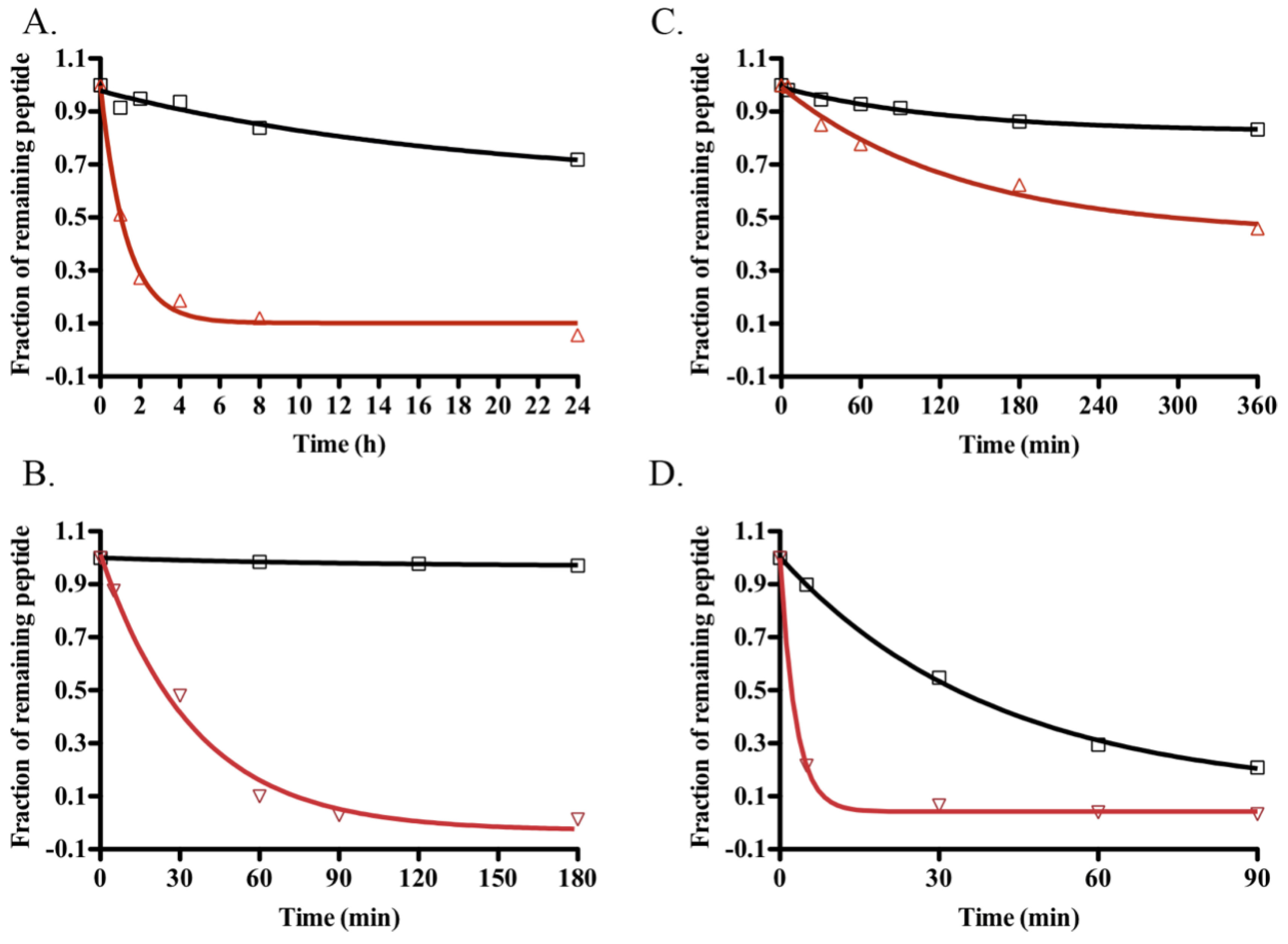
2.5. Stability Assays
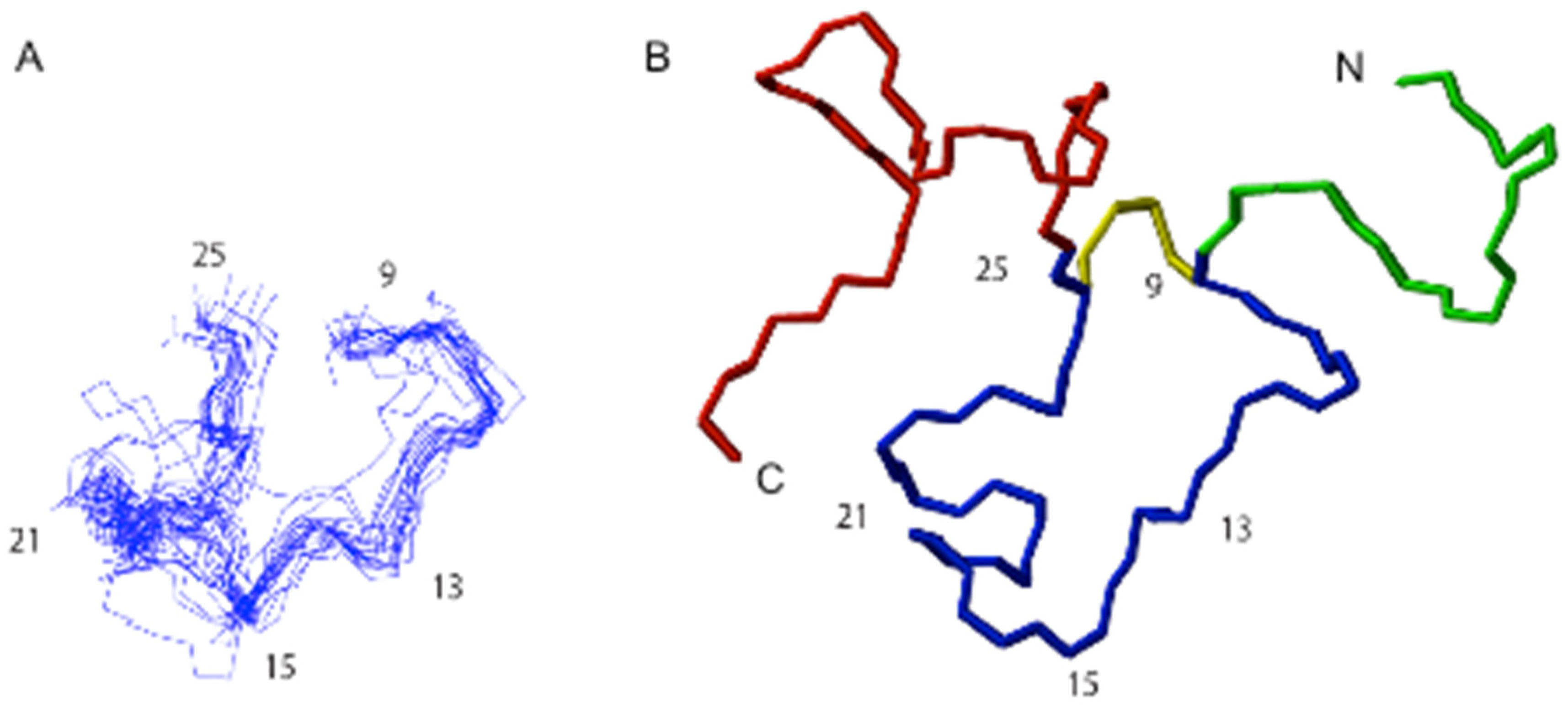
2.6. Structural Analysis of TNPc
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Peptide Synthesis
4.3. Peptide Quantification
4.4. Mass Spectrometry
4.5. HPLC Analysis
4.6. Cell Culture
4.7. Transfection
4.8. cGMP ALPHAscreen
4.9. Animals
4.10. Heart Rate and Blood Pressure Measurements
4.11. Drugs
4.12. Data Analysis
4.13. Statistical Analysis
4.14. Stability
4.15. NMR Structural Characterisation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- de Bold, A.J.; Borenstein, H.; Veress, A.; Sonnenberg, H. A rapid and potent natriuretic response to intravenous injection of atrial myocardial extract in rats. Life Sci. 1981, 28, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, Y.; Nakao, K.; Itoh, H.; Suga, S.; Ogawa, Y.; Imura, H. Vascular natriuretic peptide. Lancet 1992, 340, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpe, M. Natriuretic peptides and cardio-renal disease. Int. J. Cardiol. 2014, 176, 630–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpe, M.; Carnovali, M.; Mastromarino, V. The natriuretic peptides system in the pathophysiology of heart failure: From molecular basis to treatment. Clin. Sci. 2016, 130, 57–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maisel, A.S.; Krishnaswamy, P.; Nowak, R.M.; McCord, J.; Hollander, J.E.; Duc, P.; Omland, T.; Storrow, A.B.; Abraham, W.T.; Wu, A.H.; et al. Rapid measurement of B-type natriuretic peptide in the emergency diagnosis of heart failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, N.; Zelnick, L.; Go, A.; Anderson, A.; Christenson, R.; Deo, R.; Defilippi, C.; Lash, J.; He, J.; Ky, B.; et al. Cardiac Biomarkers and Risk of Incident Heart Failure in Chronic Kidney Disease: The CRIC (Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort) Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e012336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colucci, W.S.; Elkayam, U.; Horton, D.P.; Abraham, W.T.; Bourge, R.C.; Johnson, A.D.; Wagoner, L.E.; Givertz, M.M.; Liang, C.S.; Neibaur, M.; et al. Intravenous nesiritide, a natriuretic peptide, in the treatment of decompensated congestive heart failure. Nesiritide Study Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlueter, N.; Elkayam, U.; Horton, D.P.; Abraham, W.T.; Bourge, R.C.; Johnson, A.D.; Wagoner, L.E.; Givertz, M.M.; Liang, C.S.; Neibaur, M. Metabolic actions of natriuretic peptides and therapeutic potential in the metabolic syndrome. Pharm. Ther. 2014, 144, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, J.E.; Don-Wauchope, A.C. Evaluation of natriuretic peptide recommendations in heart failure clinical practice guidelines. Clin Biochem. 2016, 49, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridharan, S.; Kini, R.M. Decoding the molecular switches of natriuretic peptides which differentiate its vascular and renal functions. Biochem. J. 2018, 475, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yandle, T.G.; Richards, A.M.; Nicholls, M.G.; Cuneo, R.; Espiner, E.A.; Livesey, J.H. Metabolic clearance rate and plasma half life of alpha-human atrial natriuretic peptide in man. Life Sci. 1986, 38, 1827–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.S.; Lowe, D.G.; Lewis, M.; Hellmiss, R.; Chen, E.; Goeddel, D.V. Differential activation by atrial and brain natriuretic peptides of two different receptor guanylate cyclases. Nature 1989, 341, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, D.G.; Chang, M.S.; Hellmiss, R.; Chen, E.; Singh, S.; Garbers, D.L.; Goeddel, D.V. Human atrial natriuretic peptide receptor defines a new paradigm for second messenger signal transduction. EMBO J. 1989, 8, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, G.Y.; Nussenzveig, D.R.; Okolicany, J.; Price, D.A.; Maack, T. Dynamics of atrial natriuretic factor-guanylate cyclase receptors and receptor-ligand complexes in cultured glomerular mesangial and renomedullary interstitial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 11987–11994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.L.; Dukkipati, A.; Garcia, K. Structural determinants of natriuretic peptide receptor specificity and degeneracy. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 361, 698–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, K.S.; Makhlouf, G.M. Identification of the G protein-activating domain of the natriuretic peptide clearance receptor (NPR-C). J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 17587–17592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, S.J.; Espiner, E.A.; Richards, A.M.; Yandle, T.G.; Frampton, C. Renal, endocrine, and hemodynamic effects of human brain natriuretic peptide in normal man. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1993, 76, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Kenny, A.J.; Bourne, A.; Ingram, J. Hydrolysis of human and pig brain natriuretic peptides, urodilatin, C-type natriuretic peptide and some C-receptor ligands by endopeptidase-24.11. Biochem. J. 1993, 291, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargnoux, A.S.; Klouche, K.; Fareh, J.; Barazer, I.; Villard-Saussine, S.; Dupuy, A.M.; Leray-Moragues, H.; Giuliani, I.; Canaud, B.; Cristol, J.P. Prohormone brain natriuretic peptide (proBNP), BNP and N-terminal-proBNP circulating levels in chronic hemodialysis patients. Correlation with ventricular function, fluid removal and effect of hemodiafiltration. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2008, 46, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Nakao, K.; Nishimura, K.; Sugawara, A.; Okumura, K.; Obata, K.; Sonoda, R.; Ban, T.; Yasue, H.; Imura, H. Clinical application of atrial natriuretic polypeptide in patients with congestive heart failure: Beneficial effects on left ventricular function. Circulation 1987, 76, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, M.; Yasue, H.; Morita, E.; Sakaino, N.; Jougasaki, M.; Kurose, M.; Mukoyama, M.; Saito, Y.; Nakao, K.; Imura, H. Hemodynamic, renal, and hormonal responses to brain natriuretic peptide infusion in patients with congestive heart failure. Circulation 1991, 84, 1581–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suwa, M.; Seino, Y.; Nomachi, Y.; Matsuki, S.; Funahashi, K. Multicenter prospective investigation on efficacy and safety of carperitide for acute heart failure in the ‘real world’ of therapy. Circ. J. 2005, 69, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisy, O.; Huntley, B.K.; McCormick, D.J.; Kurlansky, P.A.; Burnett, J.C., Jr. Design, synthesis, and actions of a novel chimeric natriuretic peptide: CD-NP. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 52, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meems, L.M.G.; Burnett, J.C., Jr. Innovative Therapeutics: Designer Natriuretic Peptides. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2016, 1, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawakami, R.; Lee, C.Y.W.; Scott, C.; Bailey, K.R.; Schirger, J.A.; Chen, H.H.; Benike, S.L.; Cannone, V.; Martin, F.L.; Sangaralingham, S.J.; et al. A Human Study to Evaluate Safety, Tolerability, and Cyclic GMP Activating Properties of Cenderitide in Subjects with Stable Chronic Heart Failure. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2018, 104, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichiki, T.; Dzhoyashvili, N.; Burnett, J.C., Jr. Natriuretic peptide based therapeutics for heart failure: Cenderitide: A novel first-in-class designer natriuretic peptide. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 281, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeks, T.A.; Fry, B.G.; Alewood, P.F. Privileged frameworks from snake venom. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 1939–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Vink, S.; Jin, A.H.; Poth, K.J.; Head, G.A.; Alewood, P.F. Natriuretic peptide drug leads from snake venom. Toxicon 2012, 59, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.N.; Sunagar, K.; Undheim, E.A.; Koludarov, I.; Chan, A.H.; Sanders, K.; Ali, S.A.; Hendrikx, I.; Dunstan, N.; Fry, B.G. Venom down under: Dynamic evolution of Australian elapid snake toxins. Toxins 2013, 5, 2621–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasoulis, T.; Isbister, G.K. A Review and Database of Snake Venom Proteomes. Toxins 2017, 9, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondetti, M.A.; Williams, N.J.; Sabo, E.F.; Pluscec, J.; Weaver, E.R.; Kocy, O. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors from the venom of Bothrops jararaca. Isolation, elucidation of structure, and synthesis. Biochemistry 1971, 10, 4033–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweitz, H.; Vigne, P.; Moinier, D.; Frelin, C.; Lazdunski, M. A new member of the natriuretic peptide family is present in the venom of the green mamba (Dendroaspis angusticeps). J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 13928–13932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waheed, H.; Moin, S.G.; Choudhary, M.I. Snake Venom: From Deadly Toxins to Life-saving Therapeutics. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 1874–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeks, T.; Lavergne, V.; Sunagar, K.; Jones, A.; Undheim, E.; Dunstan, N.; Fry, B.; Alewood, P.F. Deep venomics of the Pseudonaja genus reveals inter- and intra-specific variation. J. Proteomics 2016, 133, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, B.G.; Wickramaratana, J.C.; Lemme, S.; Beuve, A.; Garbers, D.; Hodgson, W.C.; Alewood, P. Novel natriuretic peptides from the venom of the inland taipan (Oxyuranus microlepidotus): Isolation, chemical and biological characterisation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 327, 1011–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St. Pierre, L.; Flight, S.; Masci, P.P.; Hanchard, K.J.; Lewis, R.J.; Alewood, P.F.; de Jersey, J.; Lavin, M.F. Cloning and characterisation of natriuretic peptides from the venom glands of Australian elapids. Biochimie 2006, 88, 1923–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suga, S.; Nakao, K.; Mukoyama, M.; Arai, H.; Hosoda, K.; Ogawa, Y.; Imura, H. Characterization of natriuretic peptide receptors in cultured cells. Hypertension 1992, 19, 762–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.H.; Lainchbury, J.G.; Burnett, J.C., Jr. Natriuretic peptide receptors and neutral endopeptidase in mediating the renal actions of a new therapeutic synthetic natriuretic peptide dendroaspis natriuretic peptide. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2002, 40, 1186–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drinane, M.C.; Sherman, J.A.; Hall, A.E.; Simons, M.; Mulligan-Kehoe, M.J. Plasminogen and plasmin activity in patients with coronary artery disease. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craik, D.; Munro, S.; Nielsen, K.; Shehan, P.; Tregear, G.; Wade, J. The conformation of porcine-brain natriuretic peptide by two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy. Eur. J. Biochem. 1991, 201, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inooka, H.; Kikuchi, T.; Endo, S.; Ishibashi, Y.; Wakimasu, M.; Mizuta, E. Conformation in solution of porcine brain natriuretic peptide determined by combined use of nuclear magnetic resonance and distance geometry. Eur. J. Biochem. 1990, 193, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Ohkubo, T.; Kyogoku, Y.; Koyama, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Go, N. The conformation of alpha-human atrial natriuretic polypeptide in solution. J. Biochem. 1988, 104, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theriault, Y.; Boulanger, Y.; Weber, P.L.; Reid, B.R. Two-dimensional 1H-NMR investigation of the water conformation of the atrial natriuretic factor (ANF 101-126). Biopolymers 1987, 26, 1075–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, A.M.; Alewood, D.; Alewood, P.F.; Gallagher, C.H.; Kuchel, P.W. Conformations of platypus venom C-type natriuretic peptide in aqueous solution and sodium dodecyl sulfate micelles. Toxicon 2002, 40, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.; Rösch, P.; Adermann, K.; Forssmann, W.G.; Wokaun, A. 1H-NMR studies of the natriuretic peptide urodilatin: Sequence-specific resonance assignment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1994, 1207, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenfeld, J.R.; Sehl, P.; Quan, C.; Burnier, J.P.; Lowe, D.G. Agonist selectivity for three species of natriuretic peptide receptor-A. Mol. Pharmacol. 1995, 47, 172–180. [Google Scholar]
- Reeks, T.; Jones, A.; Brust, A.; Sridharan, S.; Corcilius, L.; Wilkinson, B.L.; Thaysen-Andersen, M.; Payne, R.J.; Kini, R.M.; Daly, N.L.; et al. A defined alpha-helix in the bifunctional O-glycosylated natriuretic peptide TcNPa from the venom of Tropidechis carinatus. Angew Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2015, 54, 4828–4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Chow, D.C.; Martick, M.M.; Garcia, K.C. Allosteric activation of a spring-loaded natriuretic peptide receptor dimer by hormone. Science 2001, 293, 1657–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, H.; Qiu, Y.; Ogata, C.M.; Misono, K.S. Crystal structure of hormone-bound atrial natriuretic peptide receptor extracellular domain: Rotation mechanism for transmembrane signal transduction. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 28625–28631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Tom, J.Y.; Oare, D.; Yen, R.; Fairbrother, W.J.; Wells, J.A.; Cunningham, B.C. Minimization of a Polypeptide Hormone. Science 1995, 270, 1657–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olins, G.M.; Patton, D.R.; Bovy, P.R.; Mehta, P.P. A linear analog of atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) discriminates guanylate cyclase-coupled ANP receptors from non-coupled receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 10989–10993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johns, D.G.; Ao, Z.; Heidrich, B.J.; Hunsberger, G.E.; Graham, T.; Payne, L.; Elshourbagy, N.; Lu, Q.; Aiyar, N.; Douglas, S.A. Dendroaspis natriuretic peptide binds to the natriuretic peptide clearance receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 358, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, D.M.; Potter, L.R. Dendroaspis natriuretic peptide and the designer natriuretic peptide, CD-NP, are resistant to proteolytic inactivation. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2011, 51, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickey, D.M.; Yoder, A.R.; Potter, L.R. A familial mutation renders atrial natriuretic Peptide resistant to proteolytic degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 19196–19202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Yu, G.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, S.; Li, R.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Q. A novel natriuretic peptide from the cobra venom. Toxicon 2011, 57, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridharan, S.; Kini, R.M. Tail wags the dog: Activity of krait natriuretic peptide is determined by its C-terminal tail in a natriuretic peptide receptor-independent manner. Biochem. J. 2015, 469, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bovy, P.R. Structure activity in the atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) family. Med. Res. Rev. 1990, 10, 115–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickey, D.M.; Barbieri, K.A.; McGuirk, C.M.; Potter, L.R. Arg13 of B-type natriuretic Peptide reciprocally modulates binding to guanylyl cyclase but not clearance receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2010, 78, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, J. Different inhibitory potencies of various ANF-analogues in the isolated aorta from four rodent species. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1991, 68, 282–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, L.H.; Madsen, T.D.; Goth, C.K.; Clausen, H.; Chen, Y.; Dzhoyashvili, N.; Iyer, S.R.; Sangaralingham, S.J.; Burnett, J.C., Jr.; Rehfeld, J.F.; et al. Discovery of O-glycans on atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) that affect both its proteolytic degradation and potency at its cognate receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 12567–12578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, B.C.; Lowe, D.G.; Li, B.; Bennett, B.D.; Wells, J.A. Production of an atrial natriuretic peptide variant that is specific for type A receptor. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 2508–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suga, S.; Nakao, K.; Hosoda, K.; Mukoyama, M.; Ogawa, Y.; Shirakami, G.; Arai, H.; Saito, Y.; Kambayashi, Y. Receptor selectivity of natriuretic peptide family, atrial natriuretic peptide, brain natriuretic peptide, and C-type natriuretic peptide. Endocrinology 1992, 130, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.X.; Noda, Y.; Chino, N.; Nishiuchi, Y.; Kimura, T.; Sakakibara, S.; Imai, M. Structure-activity relationships of alpha-human atrial natriuretic peptide. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1988, 147, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, A.J.; Stephenson, S.L. Role of endopeptidase-24.11 in the inactivation of atrial natriuretic peptide. FEBS Lett. 1988, 232, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnolzer, M.; Alewood, P.; Jones, A.; Alewood, D.; Kent, S.B. In situ neutralization in Boc-chemistry solid phase peptide synthesis. Rapid, high yield assembly of difficult sequences. Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 1992, 40, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moffatt, F.; Senkans, P.; Ricketts, D. Approaches towards the quantitative analysis of peptides and proteins by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography in the absence of a pure reference sample. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 891, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tallarida, G.; Iellamo, F.; Raimondi, G.; Legramante, J.M.; Cassarino, S.; Marazza, D.; Di Nardo, P.; Peruzzi, G. On the role of neural mechanisms in the cardiocirculatory inhibitory action of alpha-human atrial natriuretic peptide in the anesthetized rabbit. J. Hypertens. 1991, 9, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takata, M.; Denton, K.M.; Woods, R.L. Anderson WP. Renal effects of atrial natriuretic peptide in conscious rabbits with renal wrap hypertension. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 1989, 11, 59–74. [Google Scholar]
- Christy, I.J.; Denton, K.M.; Anderson, W.P. Renal denervation potentiates the natriuretic and diuretic effects of atrial natriuretic peptide in anaesthetized rabbits. Clin. Exp. Pharm. Physiol. 1994, 21, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bax, A.; Davis, D.G. Mlev-17-based two-dimensional homonuclear magnetization transfer spectroscopy. J. Magn. Reson. 1985, 65, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derome, A.E.; Williamson, M.P. Rapid-Pulsing Artifacts in Double-Quantum-Filtered Cosy. J. Magn. Reson. 1990, 88, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Ernst, R.R.; Wuthrich, K. A two-dimensional nuclear Overhauser enhancement (2D NOE) experiment for the elucidation of complete proton-proton cross-relaxation networks in biological macromolecules. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1980, 95, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piotto, M.; Saudek, V.; Sklenar, V. Gradient-tailored excitation for single-quantum NMR spectroscopy of aqueous solutions. J. Biomol. NMR 1992, 2, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guntert, P.; Mumenthaler, C.; Wuthrich, K. Torsion angle dynamics for NMR structure calculation with the new program DYANA. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 273, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunger, A.T.; Adams, P.D.; Clore, G.M.; De Lano, W.L.; Gros, P.; Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W.; Jiang, J.S.; Kuszewski, J.; Nilges, M.; Pannu, N.S.; et al. Crystallography & NMR system: A new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 1998, 54, 905–921. [Google Scholar]
- Drummond, A.J.; Ashton, B.S.B.; Buxton, S.; Cheung, M.; Cooper, A.; Duran, C.; Field, M.; Heled, J.; Kearse, M.; Markowitz, S.; et al. Geneious v5.4. 2011. Available online: http://www.geneious.com/ (accessed on 20 February 2023).
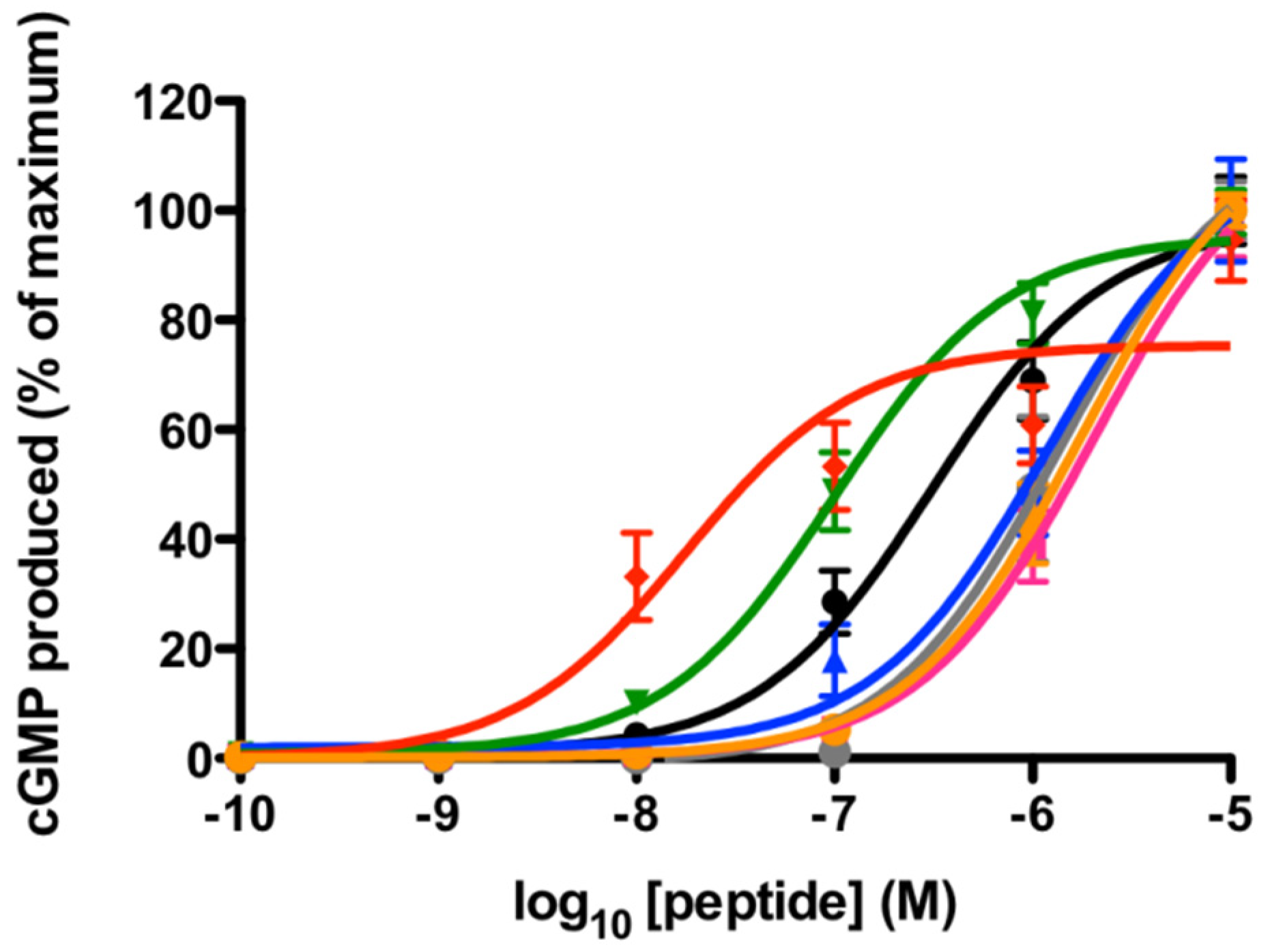
| Peptide | rNPR-A EC50 (95% CI) | hNPR-A EC50 (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
| hANP | 310 (205.1–480.2) | 2.5 (1.65–3.69) |
| hBNP | 1400 (794.6–2366) | 120 (68.9–209.4) |
| TNPa | 2020 (1453–2796) | >10,000 |
| TNPb | 1200 (729.6–1913) | >10,000 |
| TNPc | 100 (72.98–141) | >10,000 |
| TNPd | 18 (9.44–33.67) | >10,000 |
| TNPe | 1800 (1288–2439) | >10,000 |
| n | Veh1 | Veh2 | Veh3 | SED | Between Doses | Average Response | Veh vs. Treat | hANP vs. Treat | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Veh | 10 | ||||||||
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | −3.0 | −5.9 | −7.5 | 1.6 | * | −5.5 ± 0.9 | |||
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | −5.8 | −6.7 | −5.4 | 1.1 | NS | −5.9 ± 0.6 | |||
| Mean BP (mmHg) | −5.9 | −7.3 | −6.8 | 1.1 | NS | −6.7 ± 0.7 | |||
| HR (bpm) | −2.8 | 3.6 | 12.9 | 7.3 | NS | 4.6 ± 4.2 | |||
| Dose (mg/kg/min) | |||||||||
| hANP | 8 | 1 | 2 | 4 | |||||
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | −10.6 | −13.0 | −14.5 | 1.6 | NS | −12.7 ± 0.9 | *** | ||
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | −9.7 | −12.3 | −14.4 | 1.4 | * | −12.1 ± 0.8 | *** | ||
| Mean BP (mmHg) | −13.1 | −15.7 | −18.5 | 1.3 | ** | −15.8 ± 0.7 | *** | ||
| HR (bpm) | 17.1 | 19.0 | 9.0 | 5.5 | NS | 15.1 ± 3.2 | NS | ||
| TNPa | 5 | ||||||||
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | −2.8 | −4.9 | −9.4 | 2.3 | * | −5.7 ± 1.3 | NS | *** | |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | −6.0 | −7.7 | −9.9 | 1.6 | NS | −7.9 ± 0.9 | NS | * | |
| Mean BP (mmHg) | −6.4 | −8.0 | −11.6 | 1.8 | NS | −8.7 ± 1.1 | NS | *** | |
| HR (bpm) | −16.1 | −15.9 | −9.8 | 6.6 | NS | −13.9 ± 3.8 | * | *** | |
| TNPb | 5 | ||||||||
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | −7.9 | −8.8 | −10.0 | 2.4 | NS | −8.9 ± 1.4 | NS | NS | |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | −7.0 | −7.9 | −8.6 | 1.6 | NS | −7.8 ± 0.9 | NS | * | |
| Mean BP (mmHg) | −8.0 | −9.8 | −11.0 | 1.8 | NS | −9.6 ± 1.1 | NS | *** | |
| HR (bpm) | −3.9 | −5.1 | 4.7 | 6.0 | NS | −1.4 ± 3.5 | NS | NS | |
| TNPc | 5 | ||||||||
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | −9.1 | −15.6 | −14.9 | 1.3 | NS | −13.2 ± 0.8 | *** | NS | |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | −10.0 | −14.7 | −12.8 | 1.1 | NS | −12.5 ± 0.6 | *** | NS | |
| Mean BP (mmHg) | −11.0 | −17.7 | −15.9 | 1.2 | NS | −14.9 ± 0.7 | *** | NS | |
| HR (bpm) | −3.5 | 3.7 | 13.8 | 6.6 | NS | 4.7 ± 3.8 | NS | NS | |
| DNP | 5 | ||||||||
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | −11.7 | −11.9 | −16.4 | 1.4 | NS | −13.3 ± 0.8 | *** | NS | |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | −8.5 | −6.9 | −11.7 | 1.6 | NS | −9.0 ± 0.9 | NS | NS | |
| Mean BP (mmHg) | −13.0 | −12.6 | −17.2 | 1.4 | NS | −14.2 ± 0.8 | *** | NS | |
| HR (BPM) | 17.5 | 25.9 | 8.5 | 11.1 | NS | 17.3 ± 6.4 | NS | NS | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vink, S.; Akondi, K.B.; Jin, J.; Poth, K.; Torres, A.M.; Kuchel, P.W.; Burke, S.L.; Head, G.A.; Alewood, P.F. Taipan Natriuretic Peptides Are Potent and Selective Agonists for the Natriuretic Peptide Receptor A. Molecules 2023, 28, 3063. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073063
Vink S, Akondi KB, Jin J, Poth K, Torres AM, Kuchel PW, Burke SL, Head GA, Alewood PF. Taipan Natriuretic Peptides Are Potent and Selective Agonists for the Natriuretic Peptide Receptor A. Molecules. 2023; 28(7):3063. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073063
Chicago/Turabian StyleVink, Simone, Kalyana Bharati Akondi, Jean Jin, Kim Poth, Allan M. Torres, Philip W. Kuchel, Sandra L. Burke, Geoffrey A. Head, and Paul F. Alewood. 2023. "Taipan Natriuretic Peptides Are Potent and Selective Agonists for the Natriuretic Peptide Receptor A" Molecules 28, no. 7: 3063. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073063
APA StyleVink, S., Akondi, K. B., Jin, J., Poth, K., Torres, A. M., Kuchel, P. W., Burke, S. L., Head, G. A., & Alewood, P. F. (2023). Taipan Natriuretic Peptides Are Potent and Selective Agonists for the Natriuretic Peptide Receptor A. Molecules, 28(7), 3063. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073063






