A Porous π-Stacked Self-Assembly of Cup-Shaped Palladium Complex for Iodine Capture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
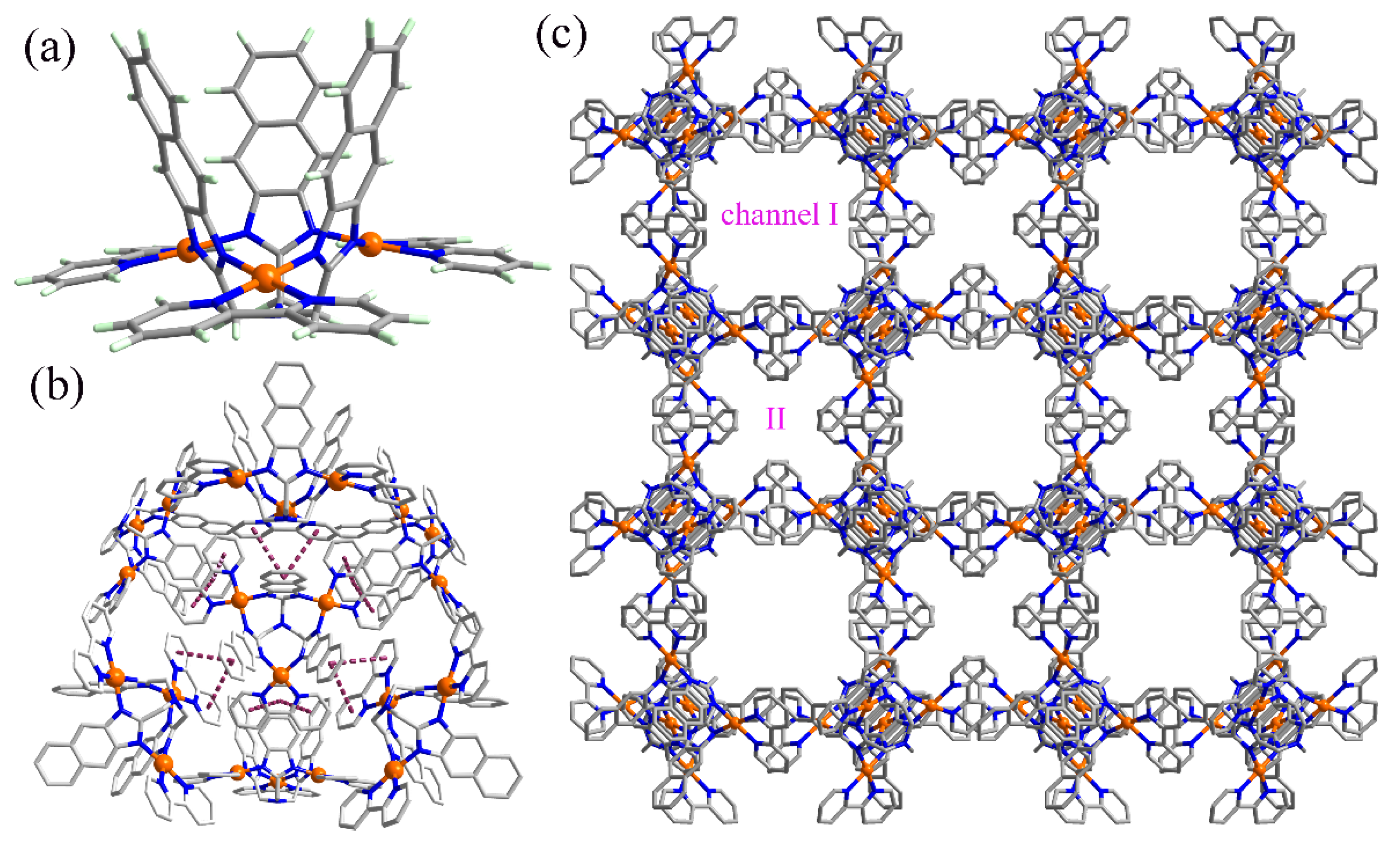
2.1. Structure Characterizations of the π-Stacked Self-Assembly
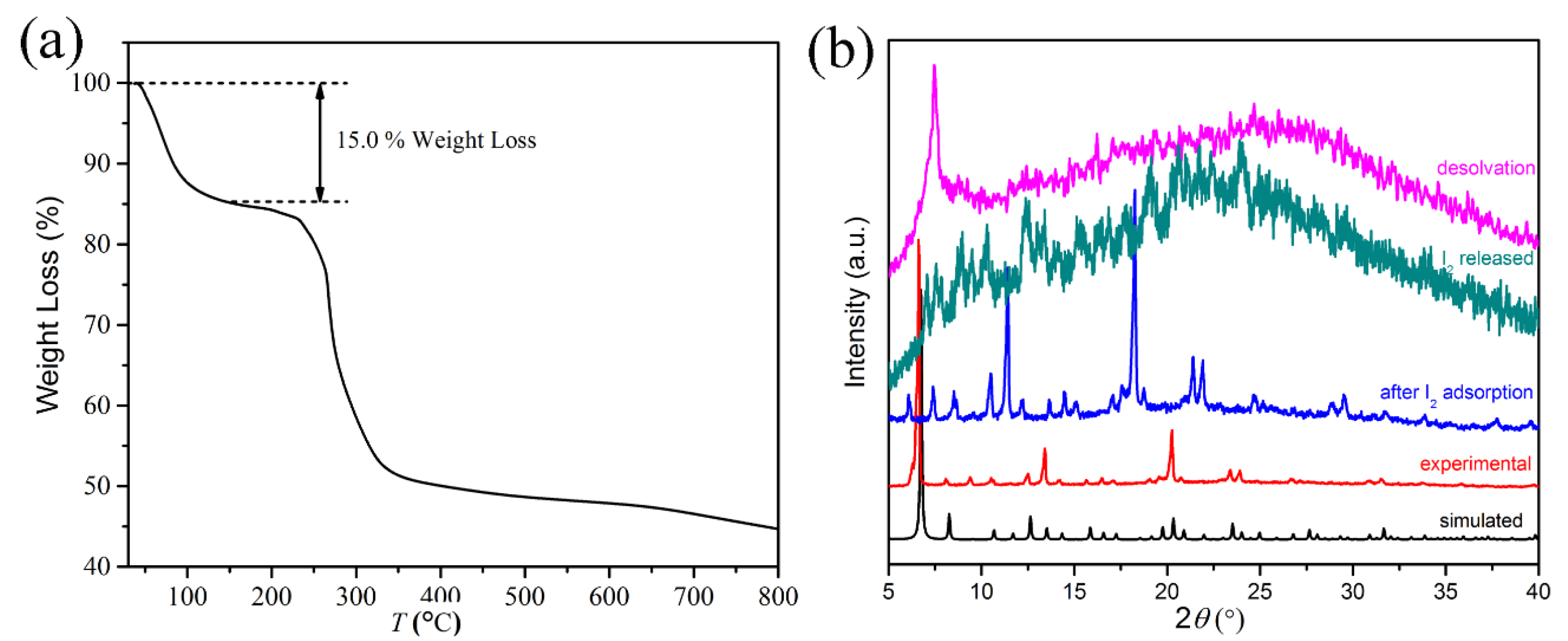
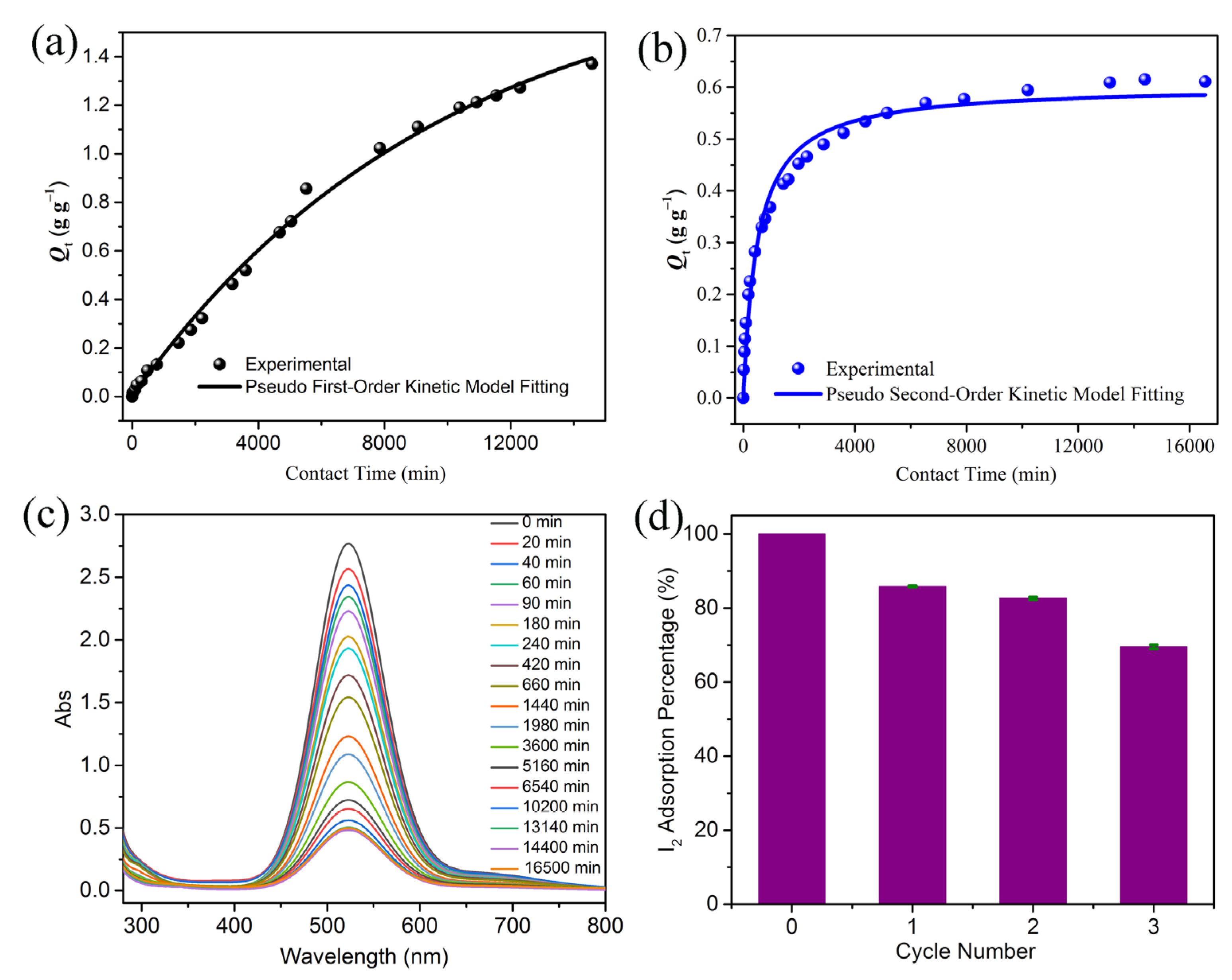
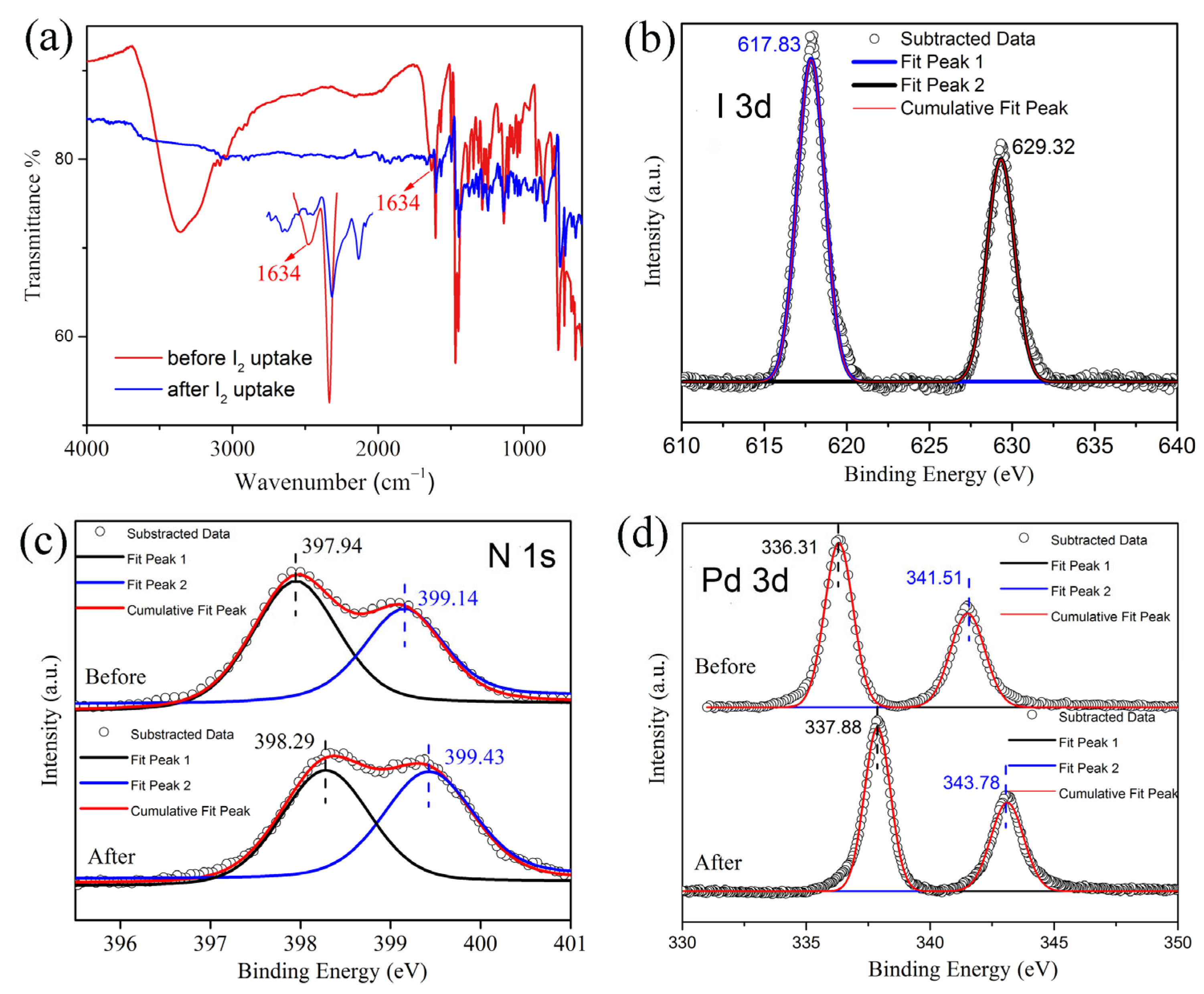
2.2. Iodine Adsorption Study
3. Experimental
3.1. Iodine Adsorption Study
3.2. Characterization
3.3. Crystallography
3.4. Synthesis of Compound 1
3.5. Iodine Adsorption Experiments
3.5.1. Iodine Vapor Adsorption
3.5.2. Iodine Adsorption in Solution
3.5.3. Iodine Release and Recyclability of Compound 1
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Xie, W.; Cui, D.; Zhang, S.-R.; Xu, Y.-H.; Jiang, D.-L. Iodine capture in porous organic polymers and metal∓organic frameworks materials. Mater. Horiz. 2019, 6, 1571–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, R.C.; Hippel, F.N.V. Nuclear waste management in the United States-starting over. Science 2009, 325, 151–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, A.; Sharma, S.; Dutta, S.; Shirolkar, M.M.; Dam, G.K.; Let, S.; Ghosh, S.K. Functionalized ionic porous organic polymers exhibiting high iodine uptake from both the vapor and aqueous medium. ACS. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 34188–34196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.J.; Qiao, Y.M.; Wang, J.L.; Xie, J.L.; Cui, B.; Fu, Y.; Lu, J.W.; Yang, Y.J.; Bu, N.S.; Yuan, Y.; et al. An azo-group-functionalized porous aromatic framework for achieving highly efficient capture of iodine. Molecules 2022, 27, 6297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintisch, E. Congress tells DOE to take fresh look at recycling spent reactor fuel. Science 2005, 310, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogilvy-Stuart, A.L.; Shalet, S.M. Effect of radiation on the human reproductive system. Environ. Health Perspect. 1993, 101, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.; He, X.H.; Pang, M.B.; Dong, X.T.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, W. Iodine capture using Zr-based metal–organic frameworks (Zr-MOFs): Adsorption performance and mechanism. ACS. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 20429–20439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; An, B.H.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, X. Synthesis of a triazaisotruxene-based porous organic polymer and its application in iodine capture. Molecules 2022, 27, 8722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimamoto, Y.S.; Takahashi, Y.; Terada, Y. Formation of organic iodine supplied as iodide in a soil-water system in Chiba, Japan. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 2086–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabri, M.A.; Al-Sayah, M.H.; Sen, S.; Ibrahim, T.H.; El-Kadri, O.M. Fluorescent aminal linked porous organic polymer for reversible iodine capture and sensing. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Hoeve, J.E.; Jacobson, M.Z. Worldwide health effects of the fukushima daiichi nuclear accident. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 8743–8757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.M. The radiotoxicology of iodine. J. Radioanal. Chem. 1981, 65, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, N.; Nakano, M.; Takamatsu, R.; Tanida, H. Inorganic iodine incorporation into soil organic matter: Evidence from iodine K-edge X-ray absorption near-edge structure. J. Environ. Radioact. 2010, 101, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.T.; Tu, C.Z.; Yin, H.J.; Liu, J.J.; Cheng, F.X.; Luo, F. Molecular iodine capture by covalent organic frameworks. Molecules 2022, 27, 9045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.-X.; Li, X.-J.; Zong, J.-S.; You, D.-J.; Liang, A.-P.; Zhou, Y.-L.; Li, X.-Q.; Liu, L.-L. Fabrication of protonated two-dimensional metal–organic framework nanosheets for highly efficient iodine capture from water. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 13883–13892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.R.; Maddock, J.; Nenoff, T.M.; Denecke, M.A.; Yang, S.; Schröder, M. Adsorption of iodine in metal–organic framework materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 3243–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.J.; Cui, B.; Zhao, T.; Luo, Y.F.; Zhang, H.C.; Xie, J.L.; Li, N.; Bu, N.S.; Yuan, Y.; Xia, L.X. A carbazole-functionalized porous aromatic framework for enhancing volatile iodine capture via lewis electron pairing. Molecules 2021, 26, 5263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Zou, D.L.; Yu, H.Y.; Liu, M.J.; Liu, Z.; Sun, W.T.; Xu, F.F.; Li, Y.X. Adsorption behavior of iodine by novel covalent organic polymers constructed through heterostructural mixed linkers. Front. Mater. 2019, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Ai, Z.T.; Hu, H.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.L.; Gao, X.P.; Qian, J.Y.; Su, X.F.; Xiao, S.T.; Xu, H.J.; et al. Synthesis of electron-rich porous organic polymers via schiff-base chemistry for efficient iodine capture. Molecules 2022, 27, 5161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.C.T.; Docao, S.; Hwang, I.C.; Song, M.K.; Choi, D.Y.; Moon, D.; Oleynikov, P.; Yoon, K.B. Capture of iodine and organic iodides using silica zeolites and the semiconductor behaviour of iodine in a silica zeolite. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 1050–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, K.W.; Chupas, P.J.; Nenoff, T.M. Radioactive iodine capture in silver-containing mordenites through nanoscale silver iodide formation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 8897–8899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reda, A.T.; Zhang, D.X.; Xu, X.Y.; Xu, S.Y. Highly stable iodine capture by pillared montmorillonite functionalized Bi2O3@g-C3N4 nanosheets. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 292, 120994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deuber, H. Investigations on the retention of elemental radioiodine by activated carbons at high temperatures. Nucl. Technol. 2017, 72, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.B.; Cui, X.L.; Xing, H.B. Recent advances in the capture and abatement of toxic gases and vapors by metal–organic frameworks. Mater. Chem. Front. 2021, 5, 5970–6013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Dastidar, P. Mixed ligand cordination polymers for metallogelation and iodine adsorption. Cryst. Growth Des. 2019, 19, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.N.; Shi, Y.; Liu, N.; Liu, F.Q. Theoretical screening and experimental synthesis of ultrahigh-iodine capture covalent organic frameworks. ACS. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 10513–10523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Ge, R.; Song, X.D.; Xing, X.Q.; Jiang, Q.K.; Lu, H.; Hao, C.; Guo, X.W.; Gao, Y.N.; et al. A 3D covalent organic framework with exceptionally high iodine capture capability. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.-J.; Xu, S.-Q.; Zhan, T.-G.; Qi, Q.-Y.; Wu, Z.-Q.; Zhao, X. Ultrahigh volatile iodine uptake by hollow microspheres formed from a heteropore covalent organic framework. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 7266–7269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Yang, Y.X.; Li, G.R.; Zhang, J.H.; He, Y.; Wang, R.; Lin, Z.; Cai, Z.W. Thiophene-based covalent organic frameworks for highly efficient iodine capture. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 107201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaguzin, A.S.; Sukhikh, T.S.; Kolesov, B.A.; Sokolov, M.N.; Fedin, V.P.; Adonin, S.A. Lodinated vs non-iodinated: Comparison of sorption selectivity by [Zn2(bdc)2dabco]n and superstructural 2-iodoterephtalate-based metal–organic framework. Polyhedron 2022, 212, 115587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaguzin, A.S.; Mahmoudi, G.; Sukhikh, T.S.; Sakhapov, I.F.; Zherebtsov, D.A.; Zubkov, F.I.; Valchuk, K.S.; Sokolov, M.N.; Fedin, V.P.; Adonin, S.A. 2D and 3D Zn (II) coordination polymers based on 4′-(Thiophen-2-yl)-4,2′:6′,4′’-terpyridine: Structures and features of sorption behavior. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1255, 132459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadollahi, M.; Hamadi, H.; Nobakht, V. Capture of iodine in solution and vapor phases by newly synthesized and characterized encapsulated Cu2O nanoparticles into the TMU-17-NH2 MOF. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 399, 122872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.L.; Cheng, D.S.; Cheng, Z.K.; Li, Z.Y.; Li, P.-Z. Effective iodine adsorption by nitrogen-rich nanoporous covalent organic frameworks. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasell, T.; Schmidtmann, M.; Cooper, A.I. Molecular doping of porous organic cages. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 14920–14923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, W.L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.L.; Yu, B.Q.; Bao, Z.B.; Jiang, J.Z. Porous organic cages for efficient gas selective separation and iodine capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Y.; Zhang, T.; Han, Y.N.; Chen, Q.; Li, C.P.; Xue, P.C. Multi-responsive fluorescent switches and iodine capture of porous hydrogen-bonded self-assemblies. J. Mater. Chem. C. 2021, 9, 9932–9940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, B.; Huang, X.Y.; Dai, L.; Cui, L.; Li, J.; Jia, X.S.; Li, C.J. Terphen[n]arenes and quaterphen[n]arenes (n = 3–6): One-pot synthesis, self-assembly into supramolecular gels, and iodine capture. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 131, 3925–3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Wang, F.; Liu, C.-H.; Wang, S.-T.; Sun, Y.-Y.; Fang, W.-H.; Zhang, J. Combination of aluminum molecular rings with chemical reduction centers for iodine capture and aggregation. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2022, 9, 4506–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zou, M.-Y.; Hu, H.-C.; Li, W.-H.; Cai, S.-L.; Zhang, W.-G.; Zheng, S.-R. Amorphous metal-organic frameworks obtained from a crystalline precursor for the capture of iodine with high capacities. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 5013–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; He, Y.L.; Tian, J.Y.; Sessler, J.L.; Chi, X.D. Reversible iodine capture by nonporous adaptive crystals of a bipyridine cage. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, K.C.; Zhou, Y.J.; Li, E.E.; Li, Z.T.; Zhao, R.; Huang, F.H. Reversible iodine capture by nonporous pillar[6]arene crystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 15320–15323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.Y.; Fang, W.-H.; Sun, Y.Y.; Wang, S.-T.; Zhang, J. Mesoporous assembly of aluminum molecular rings for iodine capture. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 2325–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.L.; Zhuo, Z.; Wang, B.; Cao, X.L.; Su, H.F.; Wang, W.; Huang, Y.G.; Hong, M.C. Constructing π-stacked supramolecular cage based hierarchical self-assemblies via π···π stacking and hydrogen bonding. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 10920–10929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, G.-L.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Z.-M.; Cao, X.-L.; Huang, Y.-G. A 2D metal-organic framework interpenetrated by a 2D supramolecular framework assembled by CH/π interactions. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2021, 130, 108705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhu, L.; Lin, G.H.; Chen, G.Y.; Liu, B.; Zhang, L.; Duan, T.; Lei, J.H. Controllable synthesis of porous Cu-BTC@polymer composite beads for iodine capture. ACS. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 42635–42645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Y.; Li, T.; Dong, X.T.; Pang, M.B.; Xiao, S.T.; Zhang, W. Hiophene-based MOFs for iodine capture: Effect of pore structures and interaction mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 425, 130578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.W.; Ding, C.H.; Zhang, Z.M.; Ke, H.Z.; Cheng, G. Functional porous organic polymer with high S and N for reversible iodine capture. Microporous. Mesoporous. Mater. 2020, 300, 110161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, E.M.; Chaudhuri, A.K.; Tan, J.C. Capture and immobilisation of iodine (I2) utilising polymer-based ZIF-8 nanocomposite membranes. Mol. Syst. Des. Eng. 2016, 1, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Doan, V.D.; Cho, W.J.; Madhav, M.V.; Kim, K.S. Anisotropic charge distribution and anisotropic van der waals radius leading to intriguing anisotropic noncovalent interactions. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodionov, V.O.; Presolski, S.I.; Gardinier, S.; Lim, Y.H.; Finn, M.G. Benzimidazole and related ligands for Cu-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 12696–12704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXTL-integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Spek, A.L. Single-crystal structure validation with the program PLATON. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2003, 36, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.-L.; Huang, M.; Chen, T.; Xu, X.-F.; Zhuo, Z.; Wang, W.; Huang, Y.-G. A Porous π-Stacked Self-Assembly of Cup-Shaped Palladium Complex for Iodine Capture. Molecules 2023, 28, 2881. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28072881
Li L-L, Huang M, Chen T, Xu X-F, Zhuo Z, Wang W, Huang Y-G. A Porous π-Stacked Self-Assembly of Cup-Shaped Palladium Complex for Iodine Capture. Molecules. 2023; 28(7):2881. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28072881
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Lin-Lin, Min Huang, Ting Chen, Xiao-Feng Xu, Zhu Zhuo, Wei Wang, and You-Gui Huang. 2023. "A Porous π-Stacked Self-Assembly of Cup-Shaped Palladium Complex for Iodine Capture" Molecules 28, no. 7: 2881. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28072881
APA StyleLi, L.-L., Huang, M., Chen, T., Xu, X.-F., Zhuo, Z., Wang, W., & Huang, Y.-G. (2023). A Porous π-Stacked Self-Assembly of Cup-Shaped Palladium Complex for Iodine Capture. Molecules, 28(7), 2881. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28072881





