Dioscorea spp.: Bioactive Compounds and Potential for the Treatment of Inflammatory and Metabolic Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
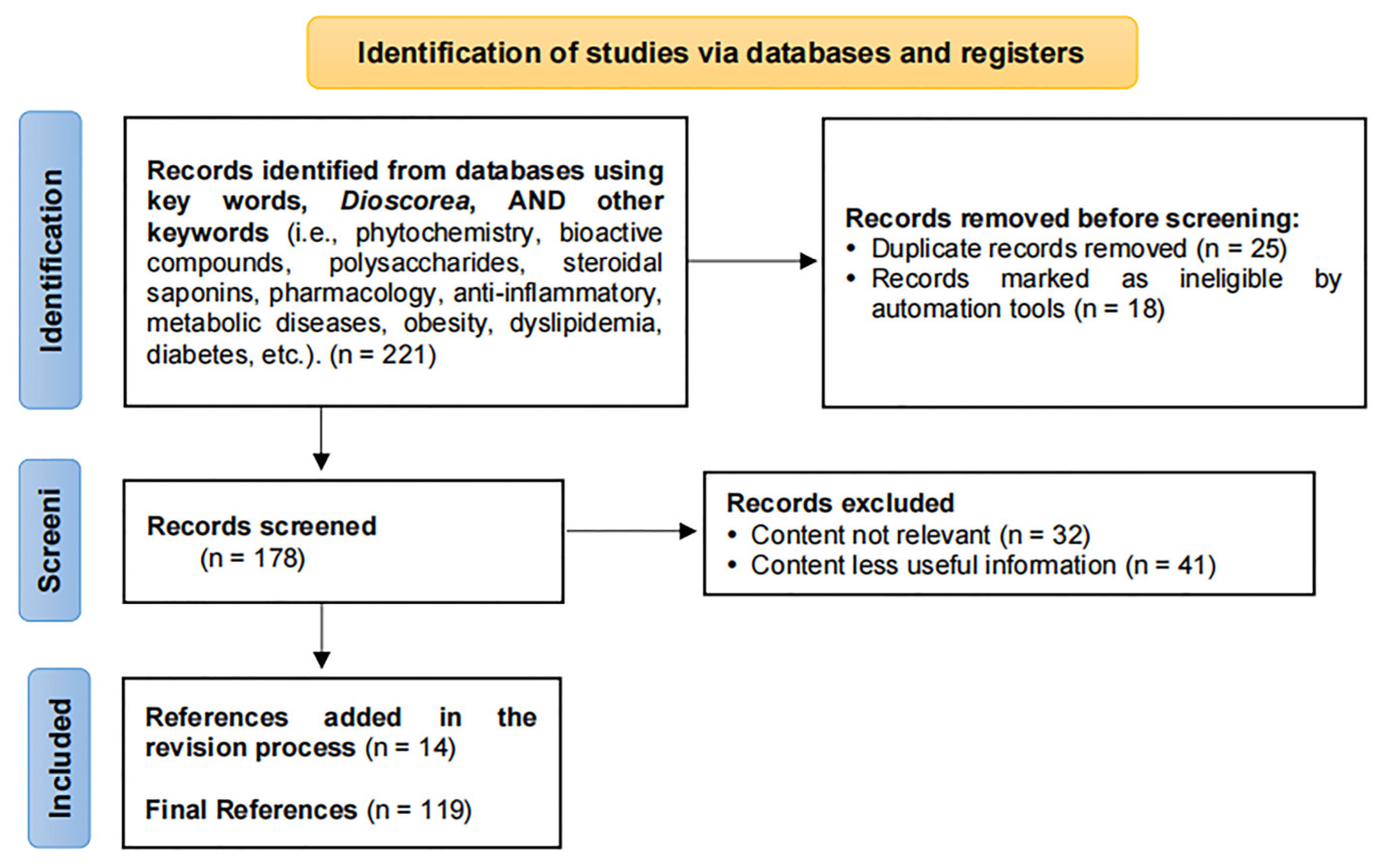
2. Methodology
3. Bioactive Compounds
3.1. Polysaccharides
3.2. Steroidal Saponins
3.3. Polyphenols
3.4. Allantoin
3.5. Alkaloids
3.6. Phenanthrene Derivatives
4. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
4.1. Enteritis
4.2. Arthritis
4.3. Dermatitis
4.4. Acute Pancreatitis
4.5. Neuroinflammation
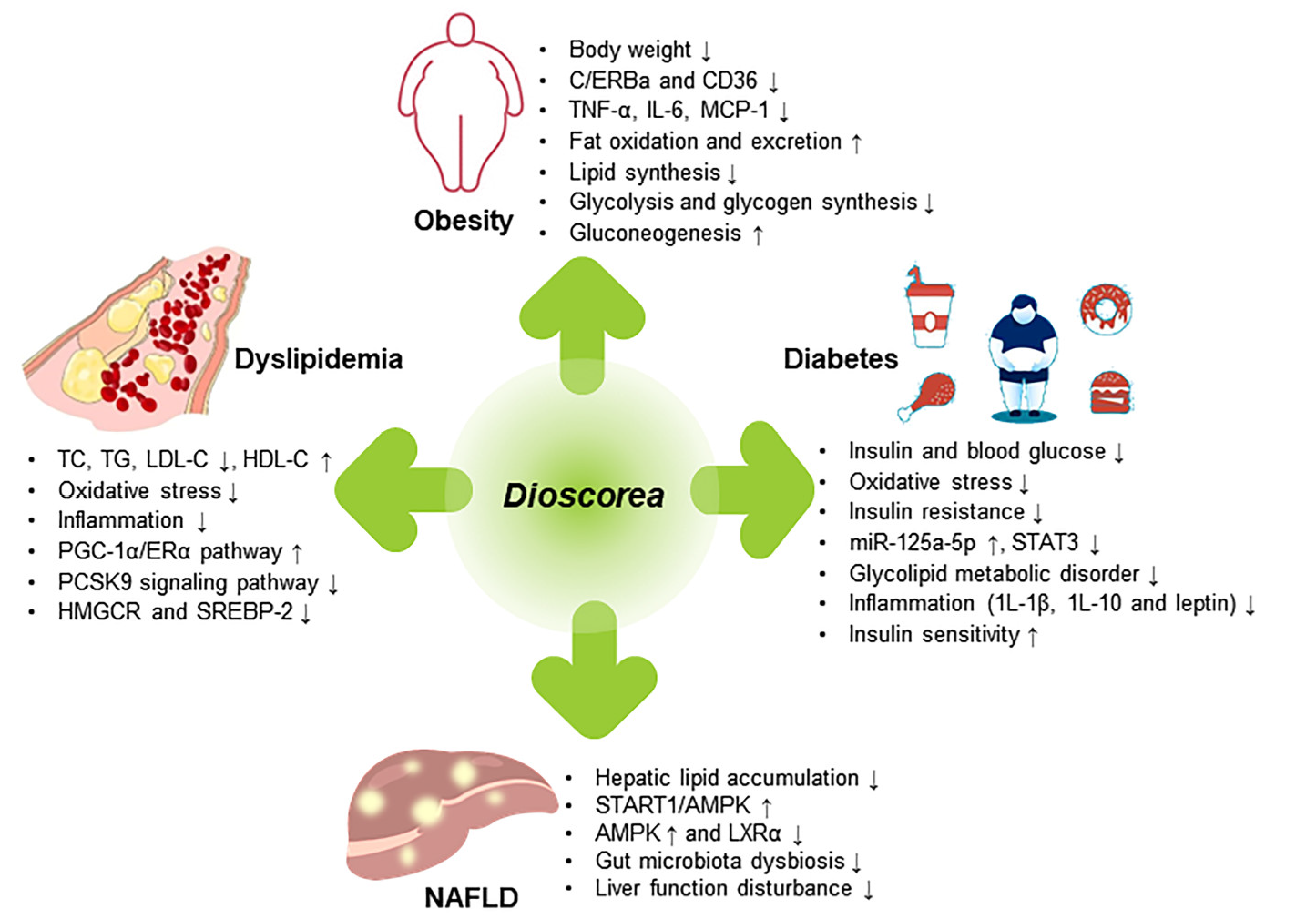
5. Prevention and Treatment of Metabolic Diseases
5.1. Obesity
5.2. Dyslipidemia
5.3. Diabetes
5.4. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saklayen, M.G. The Global Epidemic of the Metabolic Syndrome. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2018, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Z.; Guo, Y.; Huang, X.; Feng, B.; Tang, L.; Zheng, G.; Zhu, Y. Phytochemicals: Targeting Mitophagy to Treat Metabolic Disorders. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 686820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.G.; Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. NF-κB, Inflammation, and Metabolic Disease. Cell Metab. 2011, 13, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasmi, A.; Mujawdiya, P.K.; Noor, S.; Lysiuk, R.; Darmohray, R.; Piscopo, S.; Lenchyk, L.; Antonyak, H.; Dehtiarova, K.; Shanaida, M.; et al. Polyphenols in Metabolic Diseases. Molecules 2022, 27, 6280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Yi, H.; Wu, J.; Kuang, T.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Du, H.; Xu, T.; Jiang, G.; Fan, G. Therapeutic Effect of Berberine on Metabolic Diseases: Both Pharmacological Data and Clinical Evidence. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 110984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.; Gautam, D.N.S.; Radu, A.-F.; Behl, T.; Bungau, S.G.; Vesa, C.M. Reviewing the Traditional/Modern Uses, Phytochemistry, Essential Oils/Extracts and Pharmacology of Embelia ribes Burm. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuntia, A.; Martorell, M.; Ilango, K.; Bungau, S.G.; Radu, A.-F.; Behl, T.; Sharifi-Rad, J. Theoretical Evaluation of Cleome Species’ Bioactive Compounds and Therapeutic Potential: A Literature Review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 151, 113161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behl, T.; Upadhyay, T.; Singh, S.; Chigurupati, S.; Alsubayiel, A.M.; Mani, V.; Vargas-De-La-Cruz, C.; Uivarosan, D.; Bustea, C.; Sava, C.; et al. Polyphenols Targeting MAPK Mediated Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Molecules 2021, 26, 6570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behl, T.; Bungau, S.; Kumar, K.; Zengin, G.; Khan, F.; Kumar, A.; Kaur, R.; Venkatachalam, T.; Tit, D.M.; Vesa, C.M.; et al. Pleotropic Effects of Polyphenols in Cardiovascular System. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 130, 110714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J. Progress of Basic Research on Dioscorea spp. in China. Econ. For. Res. 1999, 17, 44–48. [Google Scholar]
- Asiedu, R.; Sartie, A. Crops That Feed the World 1. Yams: Yams for Income and Food Security. Food Secur. 2010, 2, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhan, B.; Panda, D. Potential of Neglected and Underutilized Yams (Dioscorea spp.) for Improving Nutritional Security and Health Benefits. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, N.; Wang, P.; Zhu, Q.; Sun, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Cao, T.; Chen, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, Q. Comprehensive Characterization of Yam Tuber Nutrition and Medicinal Quality of Dioscorea opposita and D. alata from Different Geographic Groups in China. J. Integr. Agric. 2020, 19, 2839–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epping, J.; Laibach, N. An Underutilized Orphan Tuber Crop—Chinese Yam: A Review. Planta 2020, 252, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obidiegwu, J.E.; Lyons, J.B.; Chilaka, C.A. The Dioscorea Genus (Yam)—An Appraisal of Nutritional and Therapeutic Potentials. Foods 2020, 9, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Das, G.; Shin, H.-S.; Patra, J.K. Dioscorea spp. (A Wild Edible Tuber): A Study on Its Ethnopharmacological Potential and Traditional Use by the Local People of Similipal Biosphere Reserve, India. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebot, V.; Lawac, F.; Legendre, L. The Greater Yam (Dioscorea alata L.): A Review of Its Phytochemical Content and Potential for Processed Products and Biofortification. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 115, 104987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adomėnienė, A.; Venskutonis, P.R. Dioscorea spp.: Comprehensive Review of Antioxidant Properties and Their Relation to Phytochemicals and Health Benefits. Molecules 2022, 27, 2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou-yang, S.; Jiang, T.; Zhu, L.; Yi, T. Dioscorea nipponica Makino: A Systematic Review on Its Ethnobotany, Phytochemical and Pharmacological Profiles. Chem. Cent. J. 2018, 12, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, B.B.; Vanni, K.; Farheen, A.; Jha, P.; Pandey, D.K.; Kumar, V. Dioscorea bulbifera L. (Dioscoreaceae): A Review of Its Ethnobotany, Pharmacology and Conservation Needs. South Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 140, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaniad, P.; Tewtrakul, S.; Sudsai, T.; Langyanai, S.; Kaewdana, K. Anti-Inflammatory, Wound Healing and Antioxidant Potential of Compounds from Dioscorea bulbifera L. Bulbils. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, X.; Yin, L.; Xu, L.; Peng, J. Dioscin: A Diverse Acting Natural Compound with Therapeutic Potential in Metabolic Diseases, Cancer, Inflammation and Infections. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 137, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semwal, P.; Painuli, S.; Cruz-Martins, N. Dioscorea deltoidea Wall. Ex Griseb: A Review of Traditional Uses, Bioactive Compounds and Biological Activities. Food Biosci. 2021, 41, 100969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhan, B.; Biswas, M.; Panda, D. Nutritional, Anti-Nutritional and Physico-Functional Properties of Wild Edible Yam (Dioscorea spp.) Tubers from Koraput, India. Food Biosci. 2020, 34, 100527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otegbayo, B.O.; Oguniyan, D.J.; Olunlade, B.A.; Oroniran, O.O.; Atobatele, O.E. Characterizing Genotypic Variation in Biochemical Composition, Anti-Nutritional and Mineral Bioavailability of Some Nigerian Yam (Dioscorea spp.) Land Races. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.-J.; Choi, S.-H.; Yoo, C.-S.; Choi, H.-Y.; Lee, S.-E.; Park, Y.-D. Development of an Analytical Method for Yam Saponins Using HPLC with Pulsed Amperometric Detection at Different Column Temperatures: Liquid Chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebot, V.; Malapa, R.; Molisalé, T. Development of HP-TLC Method for Rapid Quantification of Sugars, Catechins, Phenolic Acids and Saponins to Assess Yam (Dioscorea spp.) Tuber Flour Quality. Plant Genet. Resour. 2019, 17, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fel, B.; Baudouin, A.; Fache, F.; Czarnes, S.; Lebot, V.; Legendre, L. Caryatin and 3′-O-Methylcaryatin Contents in Edible Yams (Dioscorea spp.). J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 102, 104010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebot, V.; Faloye, B.; Okon, E.; Gueye, B. Simultaneous Quantification of Allantoin and Steroidal Saponins in Yam (Dioscorea spp.) Powders. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2019, 13, 100200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poornima, G.N.; Ravishankar, R.V. Evaluation of Phytonutrients and Vitamin Contents in a Wild Yam, Dioscorea belophylla (Prain) Haines. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 971–973. [Google Scholar]
- Senanayake, S.; Ranaweera, K.; Bamunuarachchi, A.; Gunaratne, A. Proximate Analysis And Phytochemical And Mineral Constituents In Four Cultivars Of Yams And Tuber Crops In Sri Lanka. Trop. Agric. Res. Ext. 2013, 15, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Cao, T.Q.; Yeo, C.; Shin, S.H.; Kim, H.; Hong, D.-H.; Hahn, D. Development and Validation of Quantitative Analysis Method for Phenanthrenes in Peels of the Dioscorea Genus. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 32, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-F.; Zhu, Q.; Wu, S. Preparation of Oligosaccharides from Chinese Yam and Their Antioxidant Activity. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 1107–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, L.; Ruan, Y.; Wen, C.; Ge, M.; Qian, Y.; Ma, B. Physicochemical Properties and Biological Activities of Polysaccharides from the Peel of Dioscorea opposita Thunb. Extracted by Four Different Methods. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 12, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, F.; Yang, T.-L.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, B.; Wang, Z.-P.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.-Z. Isolation, Structure and Activity of a Novel Water-Soluble Polysaccharide from Dioscorea opposita Thunb. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 133, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Xie, J.; Yu, Y.; Shen, M. Recent Progress in the Research of Yam Mucilage Polysaccharides: Isolation, Structure and Bioactivities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 1262–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Huang, G.; Chen, G. Extraction, Structural Analysis, Derivatization and Antioxidant Activity of Polysaccharide from Chinese Yam. Food Chem. 2021, 361, 130089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, C.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, F.; Li, X. Structural and Functional Analyses of Three Purified Polysaccharides Isolated from Chinese Huaishan-Yams. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estiasih, T.; Sunarharum, W.B.; Rahmawati, A. Hypoglycemic Activity of Water Soluble Polysaccharides of Yam (Dioscorea hispida Dents) Prepared by Aqueous, Papain, and Tempeh Inoculum Assisted Extractions. Int. J. Nutr. Food Eng. 2012, 6, 878–884. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, H.Y.; Li, J.R.; Liu, Y.G.; Gao, Q.; Wang, X.W.; Zhang, J.W.; Tanokura, M.; Xue, Y.L. Optimization of the Ultrafiltration-Assisted Extraction of Chinese Yam Polysaccharide Using Response Surface Methodology and Its Biological Activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 121, 1186–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, W.; Dai, W.; Liu, H.; Bu, H.; Ju, X.; Li, R.; Yuan, B. Structural Characterization of a Polysaccharide from Dioscorea opposita and Assessment of Its Hepatoprotective Activity. Process Biochem. 2022, 120, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Sener, B.; Kilic, M.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Naz, R.; Mudau, F.N.; Fokou, P.V.T.; Ezzat, S.M.; Bishbishy, M.H.E.; Taheri, Y.; et al. Dioscorea Plants: A Genus Rich in Vital Nutra- Pharmaceuticals—A Review. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2019, 18, 68–89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoon, K.D.; Kim, J. Preparative Separation of Dioscin Derivatives from Dioscorea villosa by Centrifugal Partition Chromatography Coupled with Evaporative Light Scattering Detection. J. Sep. Sci. 2008, 31, 2486–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sautour, M.; Mitaine-Offer, A.C.; Lacaille-Dubois, M.A. The Dioscorea Genus: A Review of Bioactive Steroid Saponins. J. Nat. Med. 2007, 61, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Xu, J.; Luo, L.; Hu, H.; Meng, X.; Li, X.; Chen, S. Predicting the Potential Global Distribution of Diosgenin-Contained Dioscorea Species. Chin. Med. 2018, 13, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.T.; Park, K.S.; Ryuk, J.A.; Kim, H.J.; Ko, B.S. Development of an Oriental Medicine Discrimination Method through Analysis of Steroidal Saponins in Dioscorea nipponica Makino and Their Anti-Osteosarcoma Effects. Molecules 2019, 24, 4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okubo, S.; Ohta, T.; Shoyama, Y.; Uto, T. Steroidal Saponins Isolated from the Rhizome of Dioscorea tokoro Inhibit Cell Growth and Autophagy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Life 2021, 11, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhuang, X.; Feng, X.; Zhong, L.; Ma, T. Antifungal Effects of Saponin Extract from Rhizomes of Dioscorea panthaica Prain et Burk against Candida albicans. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2018, 2018, 6095307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Z.; Cao, Z.; Jin, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Dou, J.; Zhu, Y.; Ito, Y.; Guo, Z. New Steroid Saponins from Dioscorea zingiberensis Yam and Their Medicinal Use against I/R via Anti-Inflammatory Effect. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 8314–8325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhou, B.; Miao, J.; Li, X.; Jing, S.; Zhang, D.; Yijia Wang, J.; Li, X.; Huang, L.; Gao, W. Multicomponent Analysis and Activities for Evaluation of Dioscorea oppositifolia and Dioscorea hamiltonii. Food Agric. Immunol. 2019, 30, 1148–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Choi, R.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Bi, C.; Zang, L.; Liu, Z.; Dong, T.; Bi, K.; Tsim, K. Antihyperlipidemic Effect of Protodioscin, an Active Ingredient Isolated from the Rhizomes of Dioscorea nipponica. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 1642–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.F.; Tang, Y.N.; Ji, H.; Xiao, Z.G.; Zhu, L.; Yi, T. Biotransformation of Dioscorea nipponica by Rat Intestinal Microflora and Cardioprotective Effects of Diosgenin. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 4176518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Watanabe, B.; Nakayasu, M.; Onjo, M.; Sugimoto, Y.; Mizutani, M. Novel Steroidal Saponins from Dioscorea esculenta (Togedokoro). Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2017, 81, 2253–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazir, R.; Kumar, V.; Dey, A.; Pandey, D.K. HPTLC Quantification of Diosgenin in Dioscorea deltoidea: Evaluation of Extraction Efficacy, Organ Selection, Drying Method and Seasonal Variation. South Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 138, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Li, S.; Tong, Z.; Yuan, X.; Xu, J.; Li, J. Geographical Variations in Fatty Acid and Steroid Saponin Biosynthesis in Dioscorea zingiberensis Rhizomes. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 170, 113779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, C.; Colombo, F.; Biella, S.; Stockley, C.; Restani, P. Polyphenols and Human Health: The Role of Bioavailability. Nutrients 2021, 13, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Tian, H.; Zhan, P.; Du, F.; Zong, A.; Xu, T. Isolation and Identification of Phenolic Compounds in Chinese Purple Yam and Evaluation of Antioxidant Activity. LWT 2018, 96, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, M.; Hossain, M.M.; Das, N.; Rahman, M.A.; Uddin, N.; Hasan, M.R.; Alam, M.J.; Islam, M.N.; Wahed, T.B.; Kundu, S.K. Investigation of Bioactivities of Methanolic and Ethyl Acetate Extracts of Dioscorea pentaphylla Leaf along with Its Phenolic Composition. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2019, 13, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, S.S.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.J.; Li, X.; Zhao, W.S.; Zhou, B.; Zhao, C.C.; Huang, L.Q.; Gao, W.Y. Phytochemical and Chemotaxonomic Studies on Dioscorea collettii. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2017, 71, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D.; Jin, T.; Zhang, R.; Hu, L.; Xing, Z.; Shi, N.; Shen, Y.; Gong, M. Phenolic Compounds Isolated from Dioscorea zingiberensis Protect against Pancreatic Acinar Cells Necrosis Induced by Sodium Taurocholate. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 1467–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Shi, X.; Ren, X.; Qin, Z. Chemical Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Phenolic Compounds from Dioscorea [Yam] Leaves. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 31, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Guo, X.; Li, X.; Dai, D.; Xu, X.; Ge, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, T. Organ- and Age-Specific Differences of Dioscorea polystachya Compounds Measured by UPLC-QTOF/MS. Chem. Biodivers. 2021, 18, e2000856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Meng, X.; Liu, Y.; Yin, C.; Zhang, T.; Wang, P.; Park, Y.-K.; Jung, H.W. Effects of a Rhizome Aqueous Extract of Dioscorea Batatas and Its Bioactive Compound, Allantoin in High Fat Diet and Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice and the Regulation of Liver, Pancreas and Skeletal Muscle Dysfunction. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 259, 112926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimenibo-Uadia, R.; Oriakhi, A. Proximate, Mineral and Phytochemical Composition of Dioscorea dumetorum Pax. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2017, 21, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corley, D.G.; Tempesta, S.; Iwu, M. Convulsant Alkaloids from Dioscorea dumetorum. Tetrahedron Lett. 1985, 26, 1615–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaruddin, Z.H.; Sapuan, S.M.; Yusoff, M.Z.M.; Jumaidin, R. Rapid Detection and Identification of Dioscorine Compounds in Dioscorea hispida Tuber Plants by LC-ESI-MS. BioResources 2020, 15, 5999–6011. Available online: https://jtatm.textiles.ncsu.edu/index.php/BioRes/article/view/BioRes_15_3_5999_Kamaruddin_Rapid_Detection_Identification_Discorine (accessed on 12 March 2023). [CrossRef]
- Haji, R.; Mohd, H.; Mohd, N.; Noordin, A.; Anuar, M.F. Development of Automatic Alkaloid Removal System for Dioscorea hispida. Front. Sci. 2011, 16–20. Available online: http://eprints.unisza.edu.my/id/eprint/3049 (accessed on 12 March 2023).
- Lim, J.S.; Hahn, D.; Gu, M.J.; Oh, J.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, J.-S. Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Effects of 2, 7-Dihydroxy-4, 6-Dimethoxy Phenanthrene Isolated from Dioscorea batatas Decne. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2019, 62, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, K.; Hu, T.; Liu, F.; Liao, S.; Zou, Y. 6,7-Dihydroxy-2,4-Dimethoxyphenanthrene from Chinese Yam Peels Alleviates DSS-Induced Intestinal Mucosal Injury in Mice via Modulation of the NF-κB/COX-2 Signaling Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 4720–4731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.S.; Oh, J.; Yun, H.S.; Lee, J.S.; Hahn, D.; Kim, J.-S. Anti-Neuroinflammatory Activity of 6,7-Dihydroxy-2,4-Dimethoxy Phenanthrene Isolated from Dioscorea batatas Decne Partly through Suppressing the P38 MAPK/NF-κB Pathway in BV2 Microglial Cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 282, 114633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudjada, A.; Touil, A.; Bensouici, C.; Bendif, H.; Rhouati, S. Phenanthrene and Dihydrophenanthrene Derivatives from Dioscorea communis with Anticholinesterase, and Antioxidant Activities. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 3278–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, D.; Campisi, J.; Verdin, E.; Carrera-Bastos, P.; Targ, S.; Franceschi, C.; Ferrucci, L.; Gilroy, D.W.; Fasano, A.; Miller, G.W.; et al. Chronic Inflammation in the Etiology of Disease across the Life Span. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1822–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xue, Z.; Zhu, S.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Dou, J.; Zhang, J.; Ito, Y.; Guo, Z. Diosgenin Revealed Potential Effect against Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion through HIKESHI/HSP70/NF-κB Anti-Inflammatory Axis. Phytomedicine 2022, 99, 153991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, R.; Chen, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, M. Gut Microbial Fermentation Promotes the Intestinal Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Chinese Yam Polysaccharides. Food Chem. 2023, 402, 134003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, P.A.; van Zelm, M.C.; Muir, J.G.; Gibson, P.R. Review Article: Short Chain Fatty Acids as Potential Therapeutic Agents in Human Gastrointestinal and Inflammatory Disorders. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 48, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Hu, S.; Zhang, H.; Guan, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Dioscorea alata L. Anthocyanins in a TNBS-Induced Colitis Model. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.S.; Oh, J.; Byeon, S.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, J.-S. Protective Effect of Dioscorea batatas Peel Extract Against Intestinal Inflammation. J. Med. Food 2018, 21, 1204–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; Tian, T.; Zhang, Q.; Wen, Y.; Zhu, J.; Xiao, D.; Cui, W.; Lin, Y. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Curcumin-Loaded Tetrahedral Framework Nucleic Acids on Acute Gouty Arthritis. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 8, 368–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biasizzo, M.; Kopitar-Jerala, N. Interplay Between NLRP3 Inflammasome and Autophagy. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 591803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Shi, G.; Li, W.; Xie, Y.; Li, F.; Jiang, D. Preventive Effect of Dioscin against Monosodium Urate-Mediated Gouty Arthritis through Inhibiting Inflammasome NLRP3 and TLR4/NF-kB Signaling Pathway Activation: An In Vivo and In Vitro Study. J. Nat. Med. 2021, 75, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Yu, D.; Zhang, N.; Liu, S. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Total Saponin Fraction from Dioscorea nipponica Makino on Gouty Arthritis and Its Influence on NALP3 Inflammasome. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2019, 25, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Yu, D.H.; Zhang, N.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, N.; Lin, F.F.; Liu, S.M. Therapeutic Effects of Total Saponins From Dioscorea nipponica Makino on Gouty Arthritis Based on the MAPK-PPARγ Signaling Pathway: An In Vitro Study. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2020, 15, 1934578X2090449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Song, H.; Guo, Y.; Xing, E.; Zhao, X.; Li, W.; Wang, J.; Yu, C. Effect of Diosgenin on T-Helper 17 Cells in Mice with Collagen-Induced Arthritis. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2020, 16, 486. [Google Scholar]
- Jegal, J.; Park, N.J.; Jo, B.G.; Bong, S.K.; Jegal, H.; Yang, M.; Kim, S.N. Anti-Atopic Properties of Gracillin Isolated from Dioscorea quinqueloba on 2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene-Induced Skin Lesions in Mice. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Li, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, H.; Mei, Z. Paeonol Ameliorates Chronic Itch and Spinal Astrocytic Activation via CXCR3 in an Experimental Dry Skin Model in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 805222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barlass, U.; Dutta, R.; Cheema, H.; George, J.; Sareen, A.; Dixit, A.; Yuan, Z.; Giri, B.; Meng, J.; Banerjee, S.; et al. Morphine Worsens the Severity and Prevents Pancreatic Regeneration in Mouse Models of Acute Pancreatitis. Gut 2017, 67, 600–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Niu, H.; Wan, C.; Yu, X.; Xin, G.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, Z.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; et al. Drug D, a Diosgenin Derive, Inhibits L-Arginine-Induced Acute Pancreatitis through Meditating GSDMD in the Endoplasmic Reticulum via the TXNIP/HIF-1α Pathway. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wen, L.; Zhang, R.; Wei, Z.; Shi, N.; Xiong, Q.; Xia, Q.; Xing, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Niu, H.; et al. Dihydrodiosgenin Protects against Experimental Acute Pancreatitis and Associated Lung Injury through Mitochondrial Protection and PI3Kγ/Akt Inhibition: Dydio Protects against Acute Pancreatitis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 1621–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, S.; Kim, Y.-S.; Jakaria, M.; Yu, Y.-J.; Ahn, J.-Y.; Kim, I.-S.; Choi, D.-K. Dioscorea nipponica Makino Rhizome Extract and Its Active Compound Dioscin Protect against Neuroinflammation and Scopolamine-Induced Memory Deficits. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giridharan, S.; Srinivasan, M. Mechanisms of NF-κB P65 and Strategies for Therapeutic Manipulation. J. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 11, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.Y. Dioscorea batatas Extract Attenuates High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice by Decreasing Expression of Inflammatory Cytokines. Med. Sci. Monit. 2015, 21, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinozaki, F.; Kamei, A.; Watanabe, Y.; Yasuoka, A.; Shimada, K.; Kondo, K.; Arai, S.; Kondo, T.; Abe, K. Propagule Powder of Japanese Yam (Dioscorea japonica) Reduces High-Fat Diet-Induced Metabolic Stress in Mice through the Regulation of Hepatic Gene Expression. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2020, 64, 2000284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, E.J.; Jegal, J.; Ahn, J.; Kim, J.; Yang, M.H. Anti-Obesity Effect of Dioscorea oppositifolia Extract in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice and Its Chemical Characterization. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 39, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D.; Gu, H.; Djukovic, D.; Bettcher, L.; Gong, M.; Zheng, W.; Hu, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, R.; Wang, D.; et al. Multiplatform Metabolomics Investigation of Antiadipogenic Effects on 3T3-L1 Adipocytes by a Potent Diarylheptanoid. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 2092–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Teng, H.; An, F.; Huang, Q.; Chen, L.; Song, H. The Beneficial Effects of Purple Yam (Dioscorea alata L.) Resistant Starch on Hyperlipidemia in High-Fat-Fed Hamsters. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 2642–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Hu, M.; Tao, J.; Yang, H.; Yan, P.; An, G.; Wang, H. The Protective Effects of Chinese Yam Polysaccharide against Obesity-Induced Insulin Resistance. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 55, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Yang, D.; Yin, Y.; Xiao, J. Estrogenic and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Pseudoprotodioscin in Atherosclerosis-Prone Mice: Insights into Endothelial Cells and Perivascular Adipose Tissues. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 869, 172887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Wang, C.; Jin, Y.; Ma, X.; Xie, T.; Wang, J.; Liu, K.; Sun, H. Disocin Prevents Postmenopausal Atherosclerosis in Ovariectomized LDLR-/- Mice through a PGC-1α/ERα Pathway Leading to Promotion of Autophagy and Inhibition of Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Apoptosis. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 148, 104414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Li, D.; Gao, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Zou, W. Di’ao Xinxuekang Capsule, a Chinese Medicinal Product, Decreases Serum Lipids Levels in High-Fat Diet-Fed ApoE–/– Mice by Downregulating PCSK9. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Li, R.; Liu, Y.; Lu, H.; Yu, L.; Zhang, F. Shuangyu Tiaozhi Granule Attenuates Hypercholesterolemia through the Reduction of Cholesterol Synthesis in Rat Fed a High Cholesterol Diet. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 4805926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Fujita, S.; Iemitsu, M. Dioscorea esculenta—Induced Increase in Muscle Sex Steroid Hormones Is Associated with Enhanced Insulin Sensitivity in a Type 2 Diabetes Rat Model. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Khan, M.Z.H.; Yuan, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Du, Z.; Zhao, Y. Preparation and Characterization of D. opposita Thunb Polysaccharide-Zinc Inclusion Complex and Evaluation of Anti-Diabetic Activities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 121, 1029–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.N.; Yin, L.H.; Jin, Y.; Qi, Y.; Han, X.; Xu, Y.W.; Liu, K.-X.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Peng, J.-Y. Effect and Possible Mechanisms of Dioscin on Ameliorating Metabolic Glycolipid Metabolic Disorder in Type-2-Diabetes. Phytomedicine 2020, 67, 153139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.; Tao, X.; Xu, L.; Qi, Y.; Yin, L.; Han, X.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, L.; Peng, J. Dioscin Alleviates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease through Adjusting Lipid Metabolism via SIRT1/AMPK Signaling Pathway. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 131, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.; Liang, S.; Liu, Q.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Du, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Cheng, B.; Ling, C. Diosgenin Prevents High-Fat Diet-Induced Rat Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease through the AMPK and LXR Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 41, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, R.; Zheng, Y.; Song, M.; Zhang, S.; Sun, Y.; Wei, M.; Fan, X. Diosgenin Ameliorates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Modulating the Gut Microbiota and Related Lipid/Amino Acid Metabolism in High Fat Diet-Fed Rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 854790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, S.; Sockalingam, S.; Dash, S. Obesity as a Multisystem Disease: Trends in Obesity Rates and Obesity-Related Complications. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blüher, M. Metabolically Healthy Obesity. Endocr. Rev. 2020, 41, bnaa004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappan, N.; Rehman, A. Dyslipidemia. StatPearls. 2022. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560891/ (accessed on 13 February 2023).
- Morais, I.C.P.d.S.; Moura, I.J.L.; Sabino, C.K.B.; Nicolau, L.A.D.; Souza, F.d.M.; Silva-Filho, J.C.d.; Oliveira, R.d.C.M.; Medeiros, J.V.R.; Lima, S.G.d.; Oliveira, A.P.d. Cardiovascular Effect of Diosgenin in Ovariectomized Rats. J. Med. Food 2019, 22, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, N.H.; Shaw, J.E.; Karuranga, S.; Huang, Y.; da Rocha Fernandes, J.D.; Ohlrogge, A.W.; Malanda, B. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global Estimates of Diabetes Prevalence for 2017 and Projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 138, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.N.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, Regional and Country-Level Diabetes Prevalence Estimates for 2021 and Projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Sathyapalan, T.; Atkin, S.L.; Sahebkar, A. Molecular Mechanisms Linking Oxidative Stress and Diabetes Mellitus. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 8609213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Ding, G.; Huang, W.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, W. Total Saponin of Dioscoreae hypoglaucae Rhizoma Ameliorates Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Nephropathy. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2016, 2016, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Xi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tang, J.; Zhou, X.; Chen, J.; Nie, C.; Zhu, Z.; Ma, B. Protective Effect of Dioscorea zingiberensis Ethanol Extract on the Disruption of Blood–Testes Barrier in High-fat Diet/Streptozotocin-induced Diabetic Mice by Upregulating ZO-1 and Nrf2. Andrologia 2020, 52, e13508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, Q.; Wang, J.; Hu, J.; Lou, G.; Xiong, H.; Peng, C.; Zheng, S.; Huang, Q. The Role of Diosgenin in Diabetes and Diabetic Complications. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 198, 105575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajiabolhassan, F.; Tavanai, E. Diabetes-Induced Auditory Complications: Are They Preventable? A Comprehensive Review of Interventions. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 278, 3653–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, E.E.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Rinella, M. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 2212–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, Q.; Chang, R.; Zhou, X.; Xu, C. Intestinal Barrier Function–Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Interactions and Possible Role of Gut Microbiota. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 2754–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compounds | Content | Specie | Plant Part | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protodioscin | 13.5–14.9 mg/g | D. nipponica | [26] | |
| Protogracillin | 7.7–8.4 mg/g | Tuber | ||
| Dioscin | 2.3–3.8 mg/g | |||
| Gracillin | 0.7–1.2 mg/g | |||
| Gallic acid | 1.34–2.35 mg/g DW | D. alata | Tubers and bulbils | [17] |
| Epicatechin | 0.45–10.71 mg/g DW | D. alata | Tubers and bulbils | [17] |
| Catechins | 25.18 mg/g | D. bulbifera | Bulbils | [27] |
| 6.96 mg/g | D. bulbifera | Tubers | ||
| 0.32 mg/g | D. esculenta | Tubers | ||
| Phenolic acids | 4.33 mg/g | D. bulbifera | Tubers | |
| 4.87 mg/g | D. alata | Tubers | ||
| 9.55 mg/g | D. nummularia | Tubers | ||
| Caryatin | 1030 µg/g DW | D. alata, D. bulbifera, D. cayenensis, D. dumetorumacc, D. esculentaacc, D. nummularia acc, D. pentaphylla | Tubers | [28] |
| 3′-O-Methyl caryatin | 457 µg/g DW | |||
| Allantoin | 4.23–20.8 mg/g | D. alata, D. bulbifera, D. cayenensis, D. dumetorum, D. esculenta, D. rotundata | Powders | [29] |
| 0.68 mg/100 g | D. belophylla | Tubers | [30] | |
| 1.64 mg/100 g | D. alata | Tubers | [31] | |
| 1.89 mg/100 g | D. esculenta | Tubers | [31] | |
| Alkaloid | 7.2–16 mg/100 g DW | D. oppositifolia, D. hamiltonii, D. pubera, D. wallichii, D. hispida, D. pentaphylla, D. bulbifera, D. glabra, D. alata | Tubers | [24] |
| 2,7-Dihydroxy-4,6-dimethoxyphenanthrene | 9.79–173.69 μg/g | D. batatas, D. polystachya, D. quinqueloba, D. bulbifera | Peels | [32] |
| 6,7-Dihydroxy-2,4-dimethoxyphenanthrene | 46.65–166.99 μg/g | D. batatas, D. polystachya | ||
| Batatasin | 97.19–419.73 μg/g | D. batatas, D. polystachya |
| Species | Metabolic Diseases | Study Type | Main Results | Bioactive Compounds | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D. batatas rhizome | Obesity | HFD-induced mice | Downregulated the adipogenic transcription factor and its target gene (CD36) Decreased the expression of proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, MCP-1, and IL-6) | - | [91] |
| D. Japonica propagules | Obesity | High-fat-loaded mice | Suppressed carbohydrate and fat metabolism disorders | - | [92] |
| D. oppositifolia rhizomes | Obesity | HFD-induced obese mice | Suppressed feeding efficiency and fat absorption | 3,5-dimethoxy-2,7-phenanthrenediol (3R,5R)-3,5-dihydroxy-1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3,5-heptanediol | [93] |
| D. zingiberensis rhizomes | Dyslipidemia | 3T3-L1 cells | Inhibited the differentiation and lipid accumulation of 3T3-L1 cells | Diarylheptanoid | [94] |
| D. alata tubers | Dyslipidemia | Hyperlipidemic hamsters | Ameliorated lipid metabolism in association with gut microbiota modulation | Resistant starch | [95] |
| Chinese yams rhizomes | Hyperlipidemia Insulin resistance | Obesity-induced insulin resistance and hyperlipidemia in mice | Lowered the levels of LDL, cholesterol, leptin and IL-1β in serum, and down-regulated the expression of MMP-3 in visceral fat tissues | Polysaccharides | [96] |
| Shanghai Winherb Medical S & T Development (Shanghai, China) | Atherosclerosis | Ovariectomized ApoE-/- mice Human umbilical vein endothelial cells and Macrophages | Increased the level of ERα and eNOS protein Suppress TNFα expression Antiadipogenic effects | Pseudoprotodioscin | [97] |
| Chenguang biotechnology Co. Ltd., (baoji, China | Atherosclerosis | HFD-OVX-treated LDLR-/- mice | Inhibited postmenopausal Atherosclerosis via inhibiting oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis and promoting autophagy partly through PGC-1α/ERα pathway | Disocin | [98] |
| D. nipponica Makino rhizomes | Lipid disorder Atherosclerosis | High-fat diet-fed ApoE-/- mice | Reduce the levels of three major modifiable lipid risk factors, LDL-C, HDL-C, and TG Inhibited PCSK9/LDLR signaling pathway | - | [99] |
| Dioscoreae rhizomes | Hypercholesterolemia | Hypercholesterolemic rat models | Decreased body weight gain, liver weight ratio, serum lipids levels and hepatic lipids accumulation | - | [100] |
| D. esculenta tubers | Diabetes | Type 2 diabetes rat model | Increased muscle sex steroid hormone levels and decreased insulin resistance | Diosgenin | [101] |
| D. opposita Thunb | Diabetes | STZ-induced diabetic rats | Decreased the glucose and insulin levels and MDA contents | Polysaccharides | [102] |
| D. nipponica rhizomes | T2DM | Insulin-induced HepG2 cells Palmitic acid-induced AML12 cells High-fat diet- and streptozotocin-induced T2DM rats | Inhibited miR-125a-5p/STAT3 signaling pathway and alleviate glycolipid metabolic disorder | Dioscin | [103] |
| Shanghai Tauto Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) | NAFLD | Mice models of NAFLD | Alleviated liver lipid accumulation symptoms and improved the levels of serum and hepatic biochemical parameters | Dioscin | [104] |
| - | NAFLD | HFD-induced NAFLD rat | Ameliorated the hepatic lipid accumulation and HFD-induced liver function disturbance | Diosgenin | [105] |
| Beijing gersion Bio-Technology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China) | NAFLD | High-fat diet-fed NAFLD rats | Suppressed excessive weight gain, reduced serum levels of total cholesterol and triglycerides, and decreased liver fat accumulation | Diosgenin | [106] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Tao, S.; Hou, G.; Zhao, F.; Tan, S.; Meng, Q. Dioscorea spp.: Bioactive Compounds and Potential for the Treatment of Inflammatory and Metabolic Diseases. Molecules 2023, 28, 2878. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062878
Wang Z, Zhao S, Tao S, Hou G, Zhao F, Tan S, Meng Q. Dioscorea spp.: Bioactive Compounds and Potential for the Treatment of Inflammatory and Metabolic Diseases. Molecules. 2023; 28(6):2878. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062878
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhen, Shengnan Zhao, Siyu Tao, Guige Hou, Fenglan Zhao, Shenpeng Tan, and Qingguo Meng. 2023. "Dioscorea spp.: Bioactive Compounds and Potential for the Treatment of Inflammatory and Metabolic Diseases" Molecules 28, no. 6: 2878. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062878
APA StyleWang, Z., Zhao, S., Tao, S., Hou, G., Zhao, F., Tan, S., & Meng, Q. (2023). Dioscorea spp.: Bioactive Compounds and Potential for the Treatment of Inflammatory and Metabolic Diseases. Molecules, 28(6), 2878. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062878






