Ion-Imprinted Polymeric Materials for Selective Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions from Aqueous Solution
Abstract
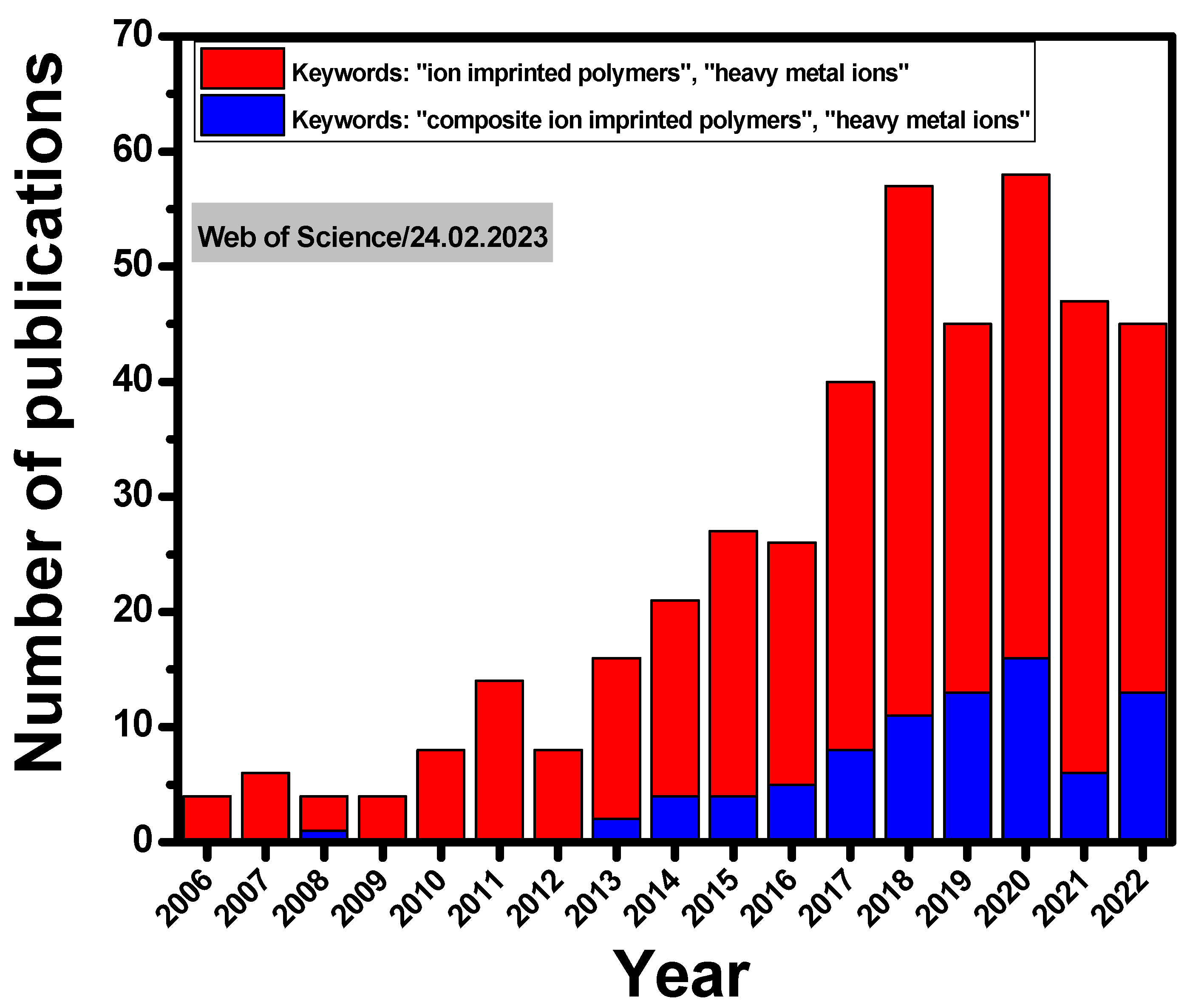
1. Introduction
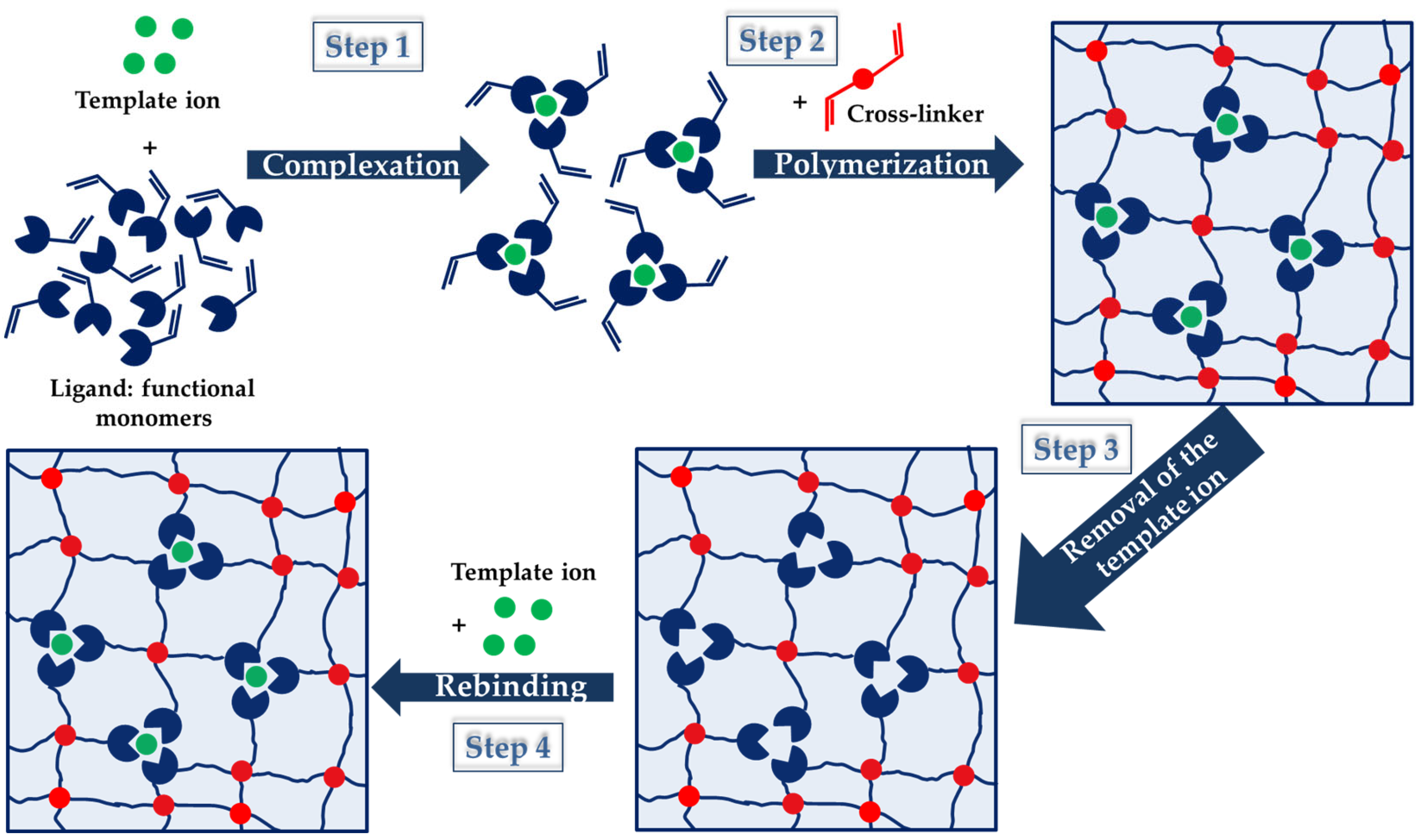
2. Important Features on IIPs’ Synthesis and Evaluation of Selective Binding Properties
2.1. Main Components of IIPs
2.1.1. Templates
2.1.2. Functional Monomers and Polymers
2.1.3. Cross-Linkers
2.1.4. Initiators
2.1.5. Porogens to Generate Porous 3D Structure within IIPs
2.1.6. Reagents to Leach out the Template Ion
2.2. Strategies to Prepare IIPs Materials
2.2.1. Bulk Polymerization
2.2.2. Precipitation Polymerization
2.2.3. Suspension Polymerization
2.2.4. Emulsion Polymerization
2.2.5. Sol–Gel Method
2.2.6. Surface-Imprinting
2.2.7. Other Imprinting Technologies
2.3. Evaluation of the Binding Performances of IIPs
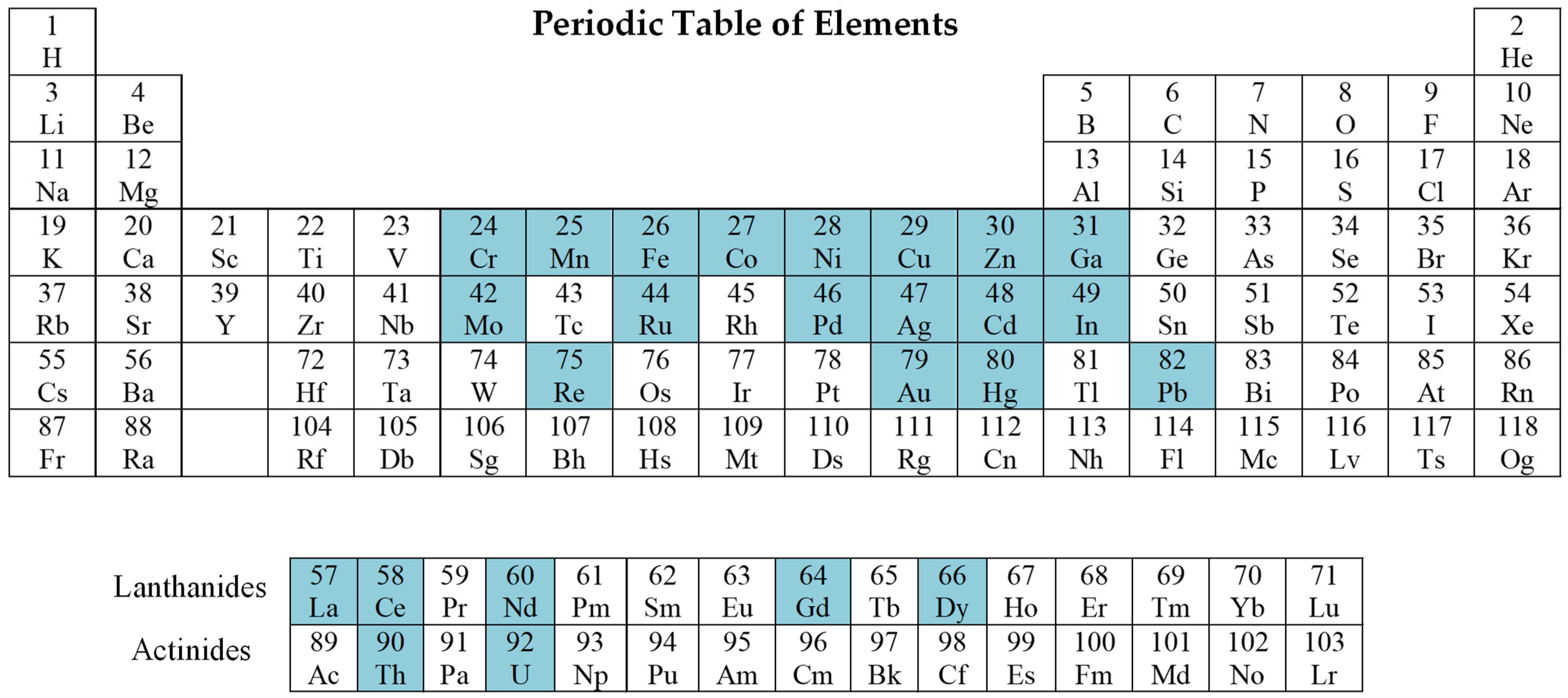
3. Ion-Imprinted Polymeric Materials for Selective Extraction of Transition Metal Ions
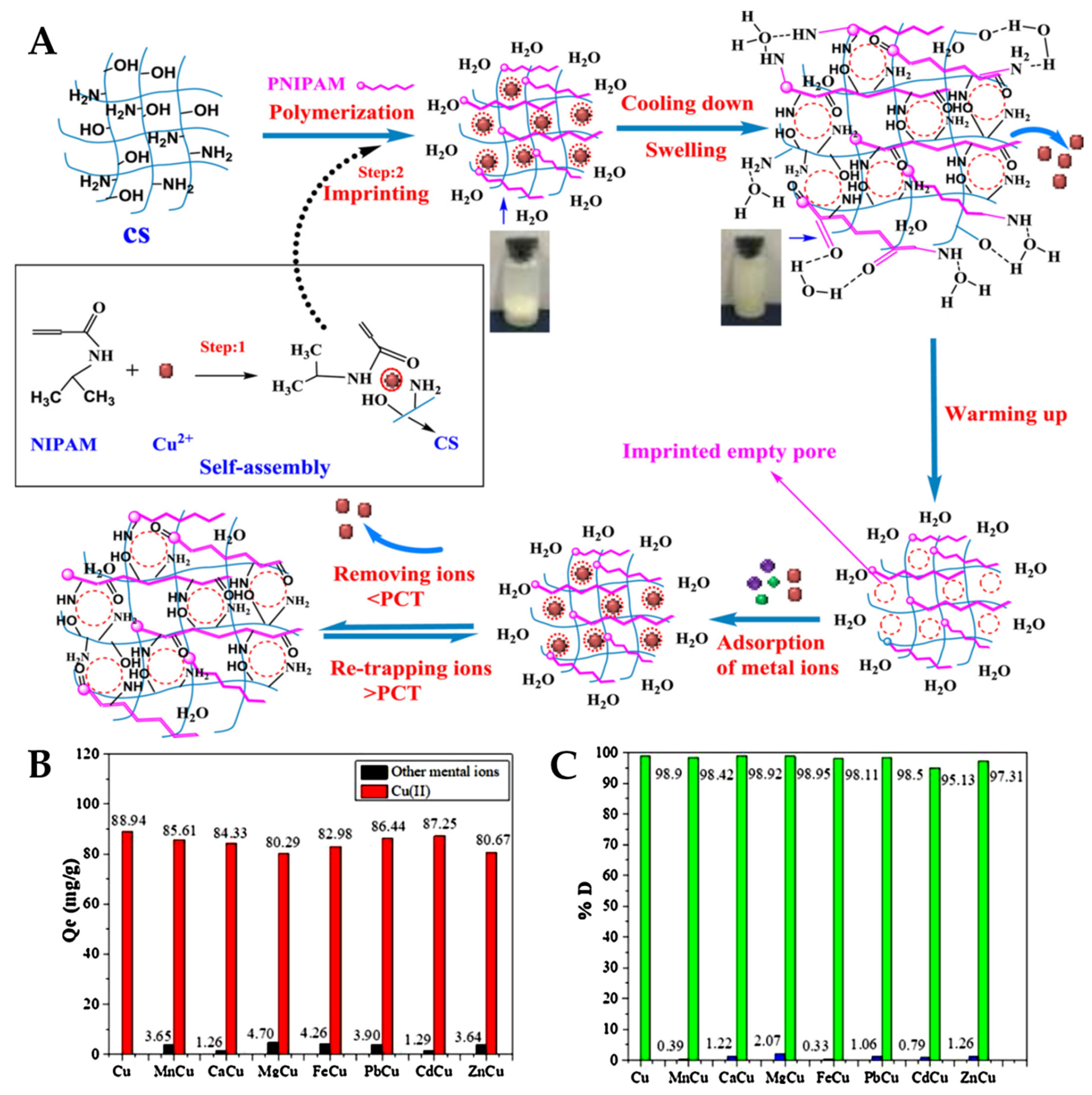
3.1. Copper-Imprinted Polymers
3.2. Cadmium-Imprinted Polymers
3.3. Zinc-Imprinted Polymers
3.4. Cobalt-Imprinted Polymers
3.5. Nickel-Imprinted Polymers
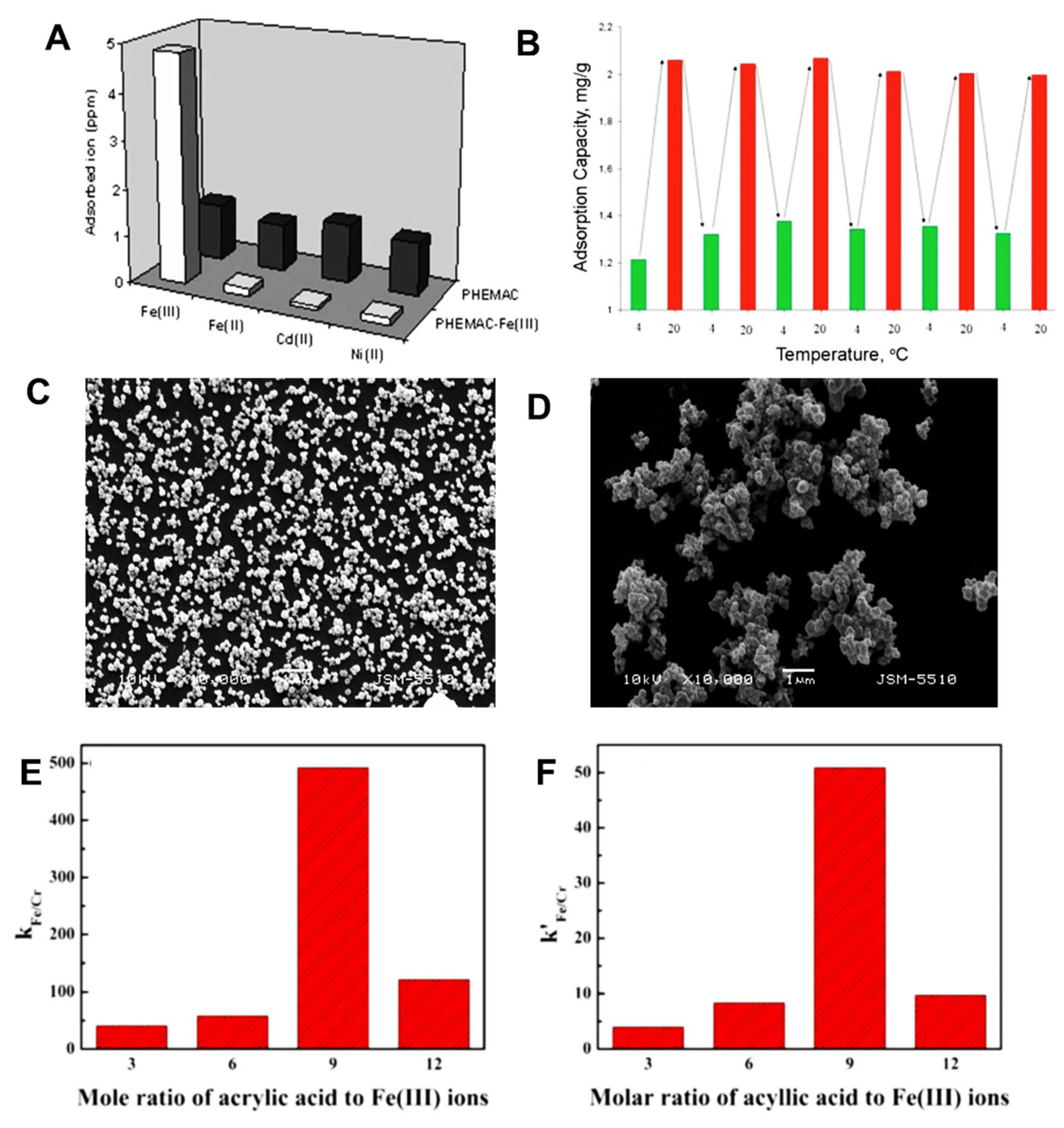
3.6. Iron-Imprinted Polymers
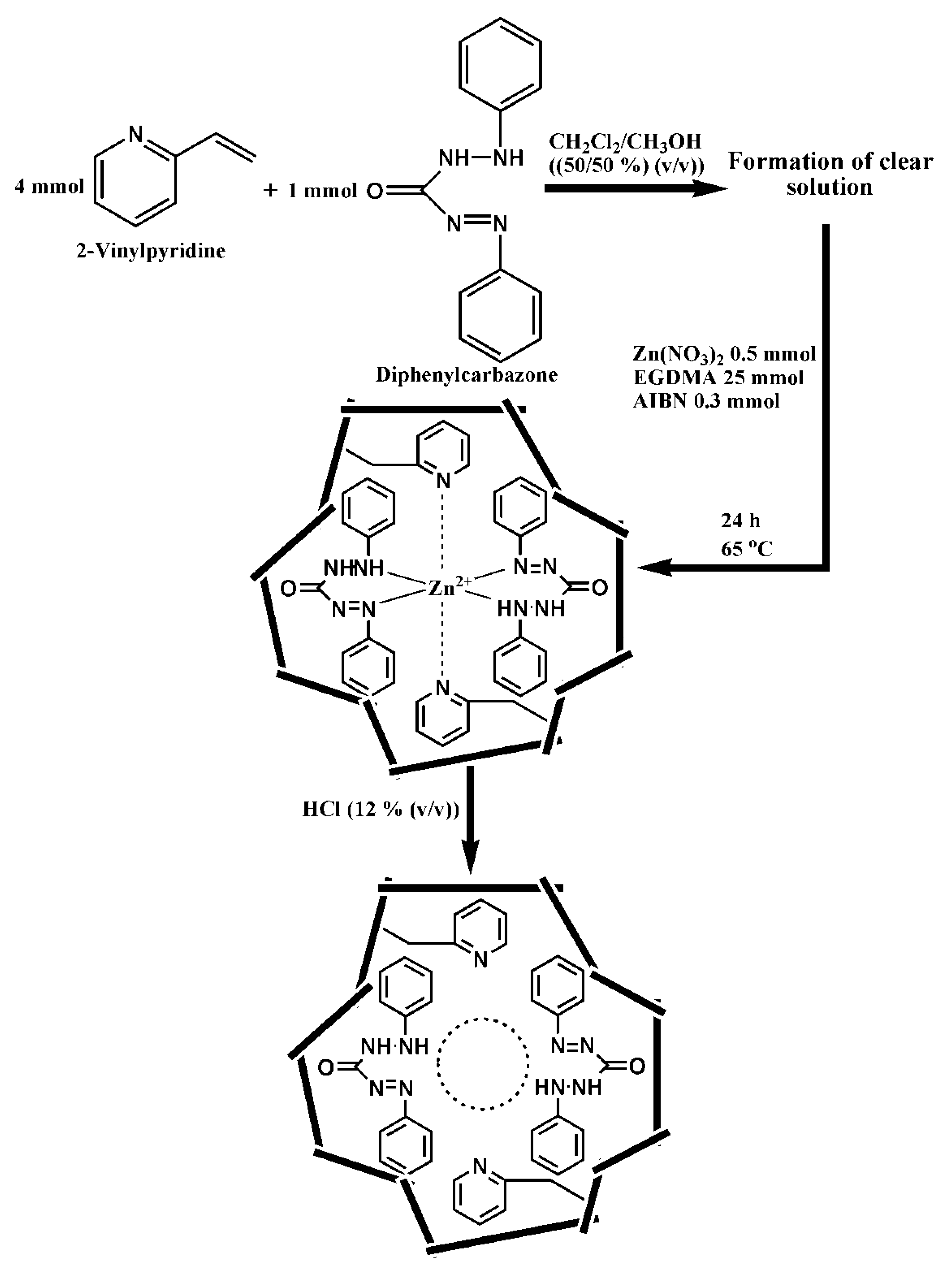
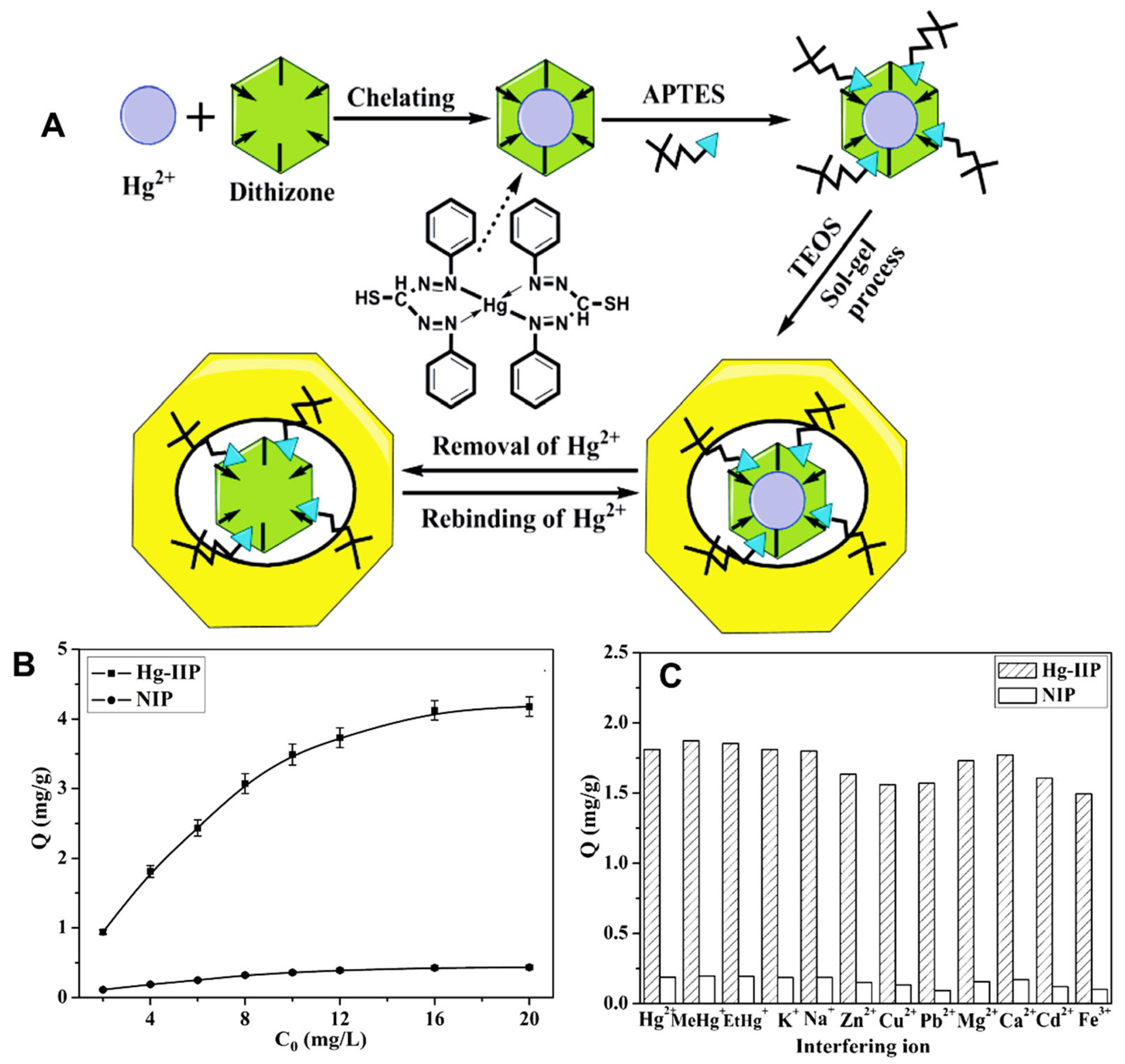
3.7. Mercury-Imprinted Polymers
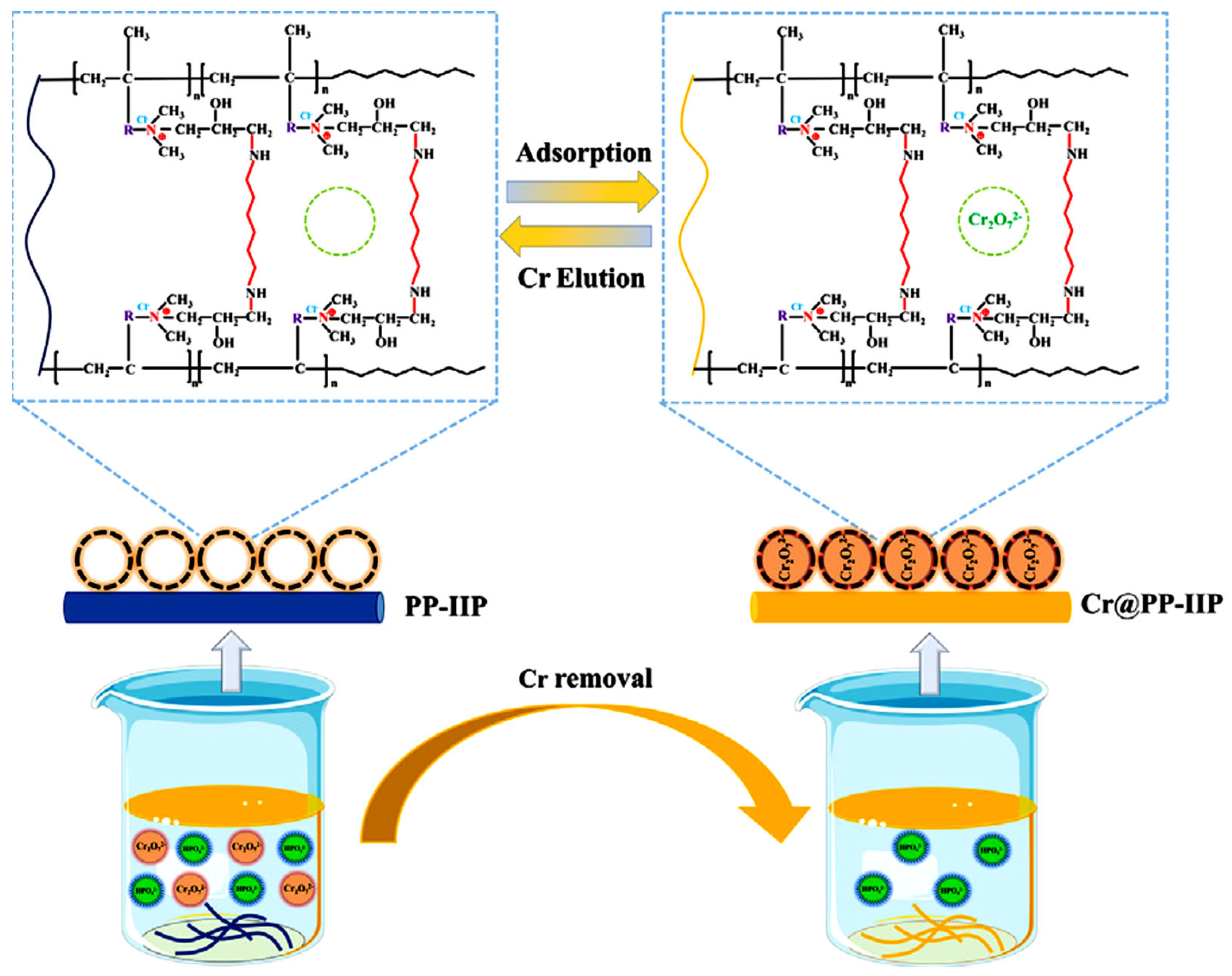
3.8. Chromium-Imprinted Polymers
3.9. Other Transition Metal Ions-Imprinted Polymers (Mn, Mo, Re, and Ru)
3.10. Ion-Imprinted Polymeric Materials for Selective Extraction of Precious Metals
3.10.1. Ruthenium-Imprinted Polymers
3.10.2. Silver-Imprinted Polymers
3.10.3. Gold-Imprinted Polymers
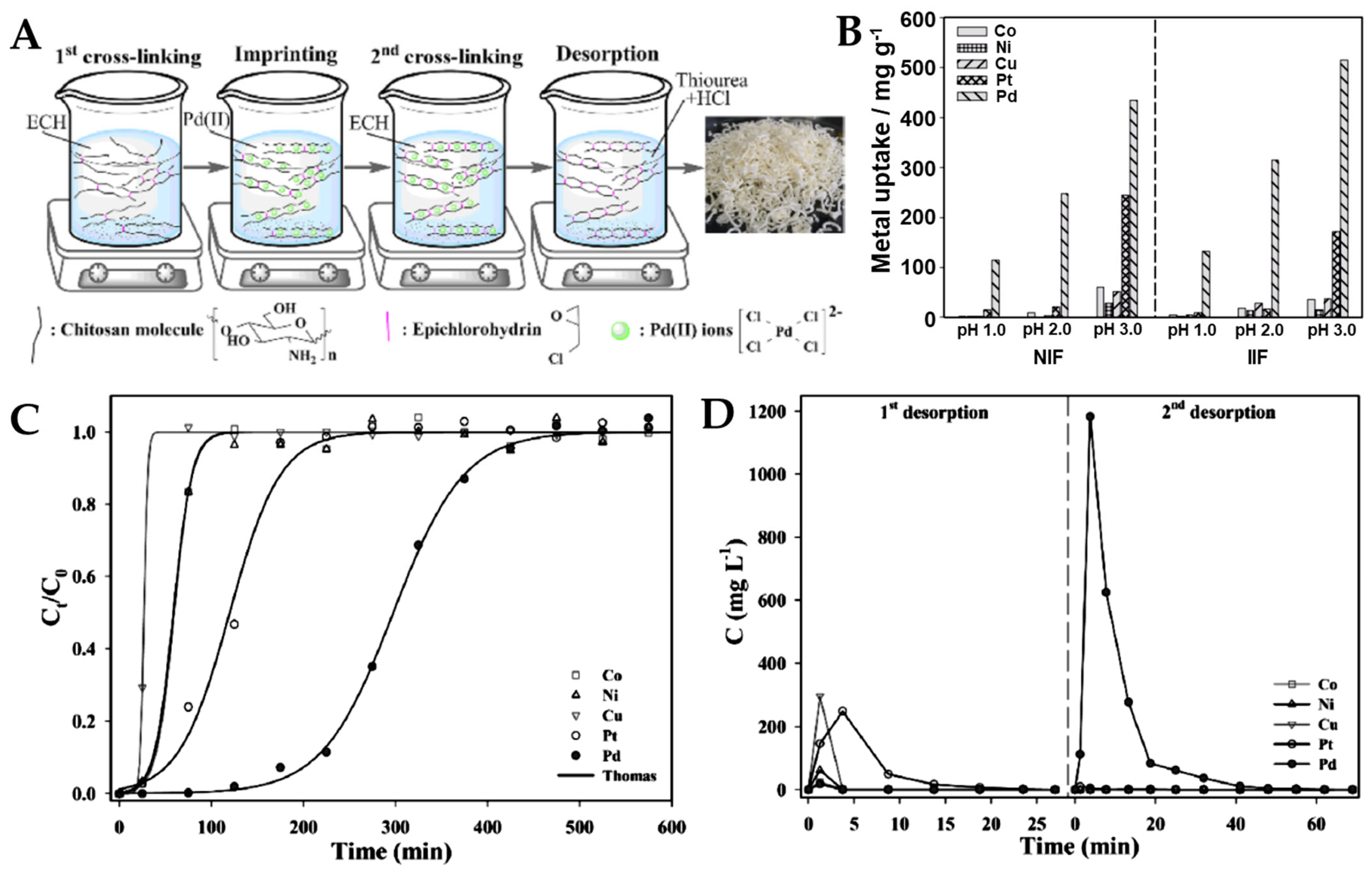
3.10.4. Palladium-Imprinted Polymers
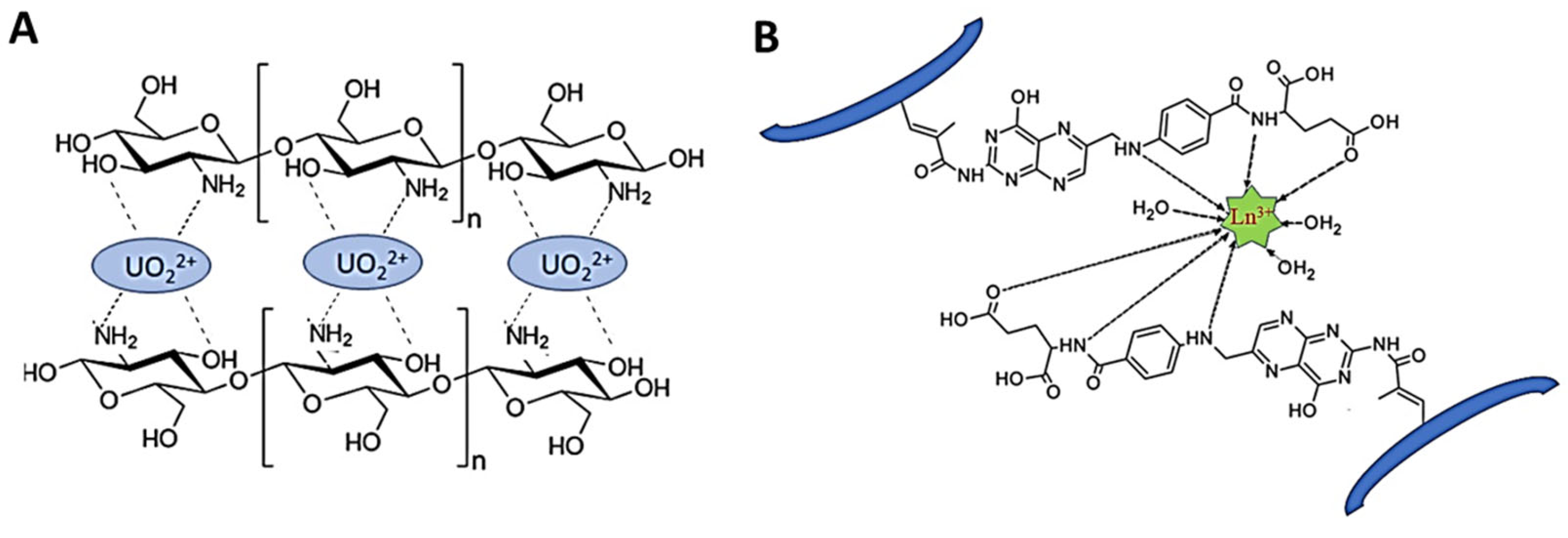
3.11. Ion-Imprinted Polymeric Materials for Selective Extraction of Radionuclides and Rare Earth Metal Ions (Ce, Dy, Gd, La, and Nd)
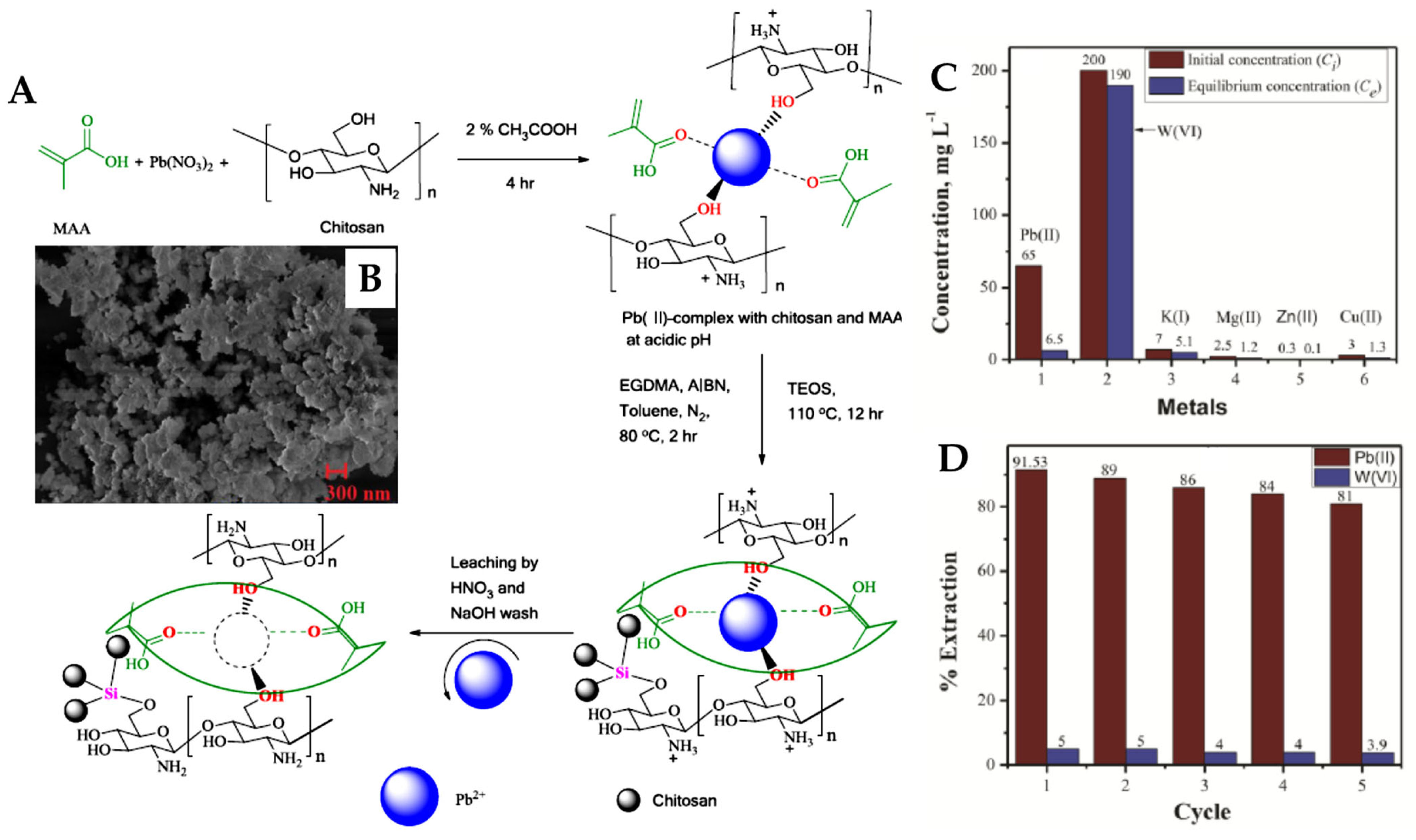
3.12. Other Group of Metal Ions-Imprinted Polymers (Ga, In, and Pb)
4. Conclusions and Perspectives
- The majority of analyzed papers reported investigations performed on ideal lab-based aqueous solutions in batch experiments, and only a few of them covered the IIPs performance in fixed-bed column setups and real water samples. Expanding the understanding of IIPs’ sorption behavior in such conditions is mandatory toward their successful implementation in large-scale industrial applications.
- The current scenario to increase the IIPs’ economic benefits is to use them in multiple sorption–desorption cycles. In this context, the identification of alternative eco-friendly regeneration approaches, reduction in generated waste, and minimization of operation costs, while maximizing IIPs’ lifespan, are priority research directions that should be extensively addressed in the future.
- In addition, the focus should also be directed to the development of stimuli-responsive imprinted polymers as a new generation of intelligent selective sorbents. Moreover, the application and development of combined approaches are expected to grow considerably in the following years.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, H. Human health and heavy metals exposure. In Life Support: The Environment and Human Health; McCally, M., Ed.; MIT Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Can Sener, S.E.; Thomas, V.M.; Hogan, D.E.; Maier, R.M.; Carbajales-Dale, M.; Barton, M.D.; Karanfil, T.; Crittenden, J.C.; Amy, G.L. Recovery of Critical Metals from Aqueous Sources. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 11616–11634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolisetty, S.; Peydayesh, M.; Mezzenga, R. Sustainable Technologies for Water Purification from Heavy Metals: Review and Analysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravan, A.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Jeevanantham, S.; Karishma, S.; Tajsabreen, B.; Yaashikaa, P.R.; Reshma, B. Effective water/wastewater treatment methodologies for toxic pollutants removal: Processes and applications towards sustainable development. Chemosphere 2021, 280, 130595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.F.; Mofijur, M.; Nuzhat, S.; Tasnim Chowdhury, A.; Rafa, N.; Uddin, A.; Inayat, A.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Ong, H.C.; Chia, W.Y.; et al. Recent developments in physical, biological, chemical, and hybrid treatment techniques for removing emerging contaminants from wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musarurwa, H.; Tawanda Tavengwa, N. Stimuli-responsive polymers and their applications in separation science. React. Funct. Polym. 2022, 175, 105282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiorghita, C.-A.; Mihai, M. Recent developments in layer-by-layer assembled systems application in water purification. Chemosphere 2021, 270, 129477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghiorghita, C.-A.; Dinu, M.V.; Lazar, M.M.; Dragan, E.S. Polysaccharide-Based Composite Hydrogels as Sustainable Materials for Removal of Pollutants from Wastewater. Molecules 2022, 27, 8574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, N.; Santos, C.; Teixeira, A.R.; Marchão, L.; Tavares, P.B.; Lucas, M.S.; Peres, J.A. Treatment of Agro-Industrial Wastewaters by Coagulation-Flocculation-Decantation and Advanced Oxidation Processes—A literature Review. Eng. Proc. 2022, 19, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Usama Saeed, M.; Hussain, N.; Sumrin, A.; Shahbaz, A.; Noor, S.; Bilal, M.; Aleya, L.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Microbial Bioremediation Strategies with Wastewater Treatment Potentialities—A Review. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 818, 151754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahbakhsh, J.; Vatanpour, V.; Khoshnam, M.; Zargar, M. Recent advancements in the application of new monomers and membrane modification techniques for the fabrication of thin film composite membranes: A review. React. Funct. Polym. 2021, 166, 105015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Liu, R.; Yang, J.; Shuai, Q.; Yuliarto, B.; Kaneti, Y.V.; Yamauchi, Y. Nanoarchitectured porous polymers and their environmental applications for removal of toxic metal ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 408, 127991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyganowski, P.; Leśniewicz, A.; Polowczyk, I.; Chęcmanowski, J.; Koźlecki, T.; Pohl, P.; Jermakowicz-Bartkowiak, D. Surface-activated anion exchange resins for synthesis and immobilization of gold and palladium nano- and microstructures. React. Funct. Polym. 2018, 124, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofińska-Chmiel, W.; Kołodyńska, D. Application of ion exchangers for the purification of galvanic wastewater from heavy metals. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 1097–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-G.; Sofinska-Chmiel, W.; Lv, G.-Y.; Kołodynska, D.; Chen, S.-H. Application of Modern Research Methods for the Physicochemical Characterization of Ion Exchangers. Materials 2021, 14, 7067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Shen, R.; Liu, R.; Shuai, Q. Thiol-functionalized magnetic covalent organic frameworks by a cutting strategy for efficient removal of Hg2+ from water. J. Hazard Mater. 2020, 392, 122320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragan, E.S.; Avram, E.; Dinu, M.V. Organic ion exchangers as beads. Synthesis, characterization and applications. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2006, 17, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragan, E.S.; Humelnicu, D.; Dinu, M.V. Design of porous strong base anion exchangers bearing N,N-dialkyl 2-hydroxyethyl ammonium groups with enhanced retention of Cr(VI) ions from aqueous solution. React. Funct. Polym. 2018, 124, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandratos, S.D. Trends in ion exchange: Analysis of the literature. React. Funct. Polym. 2021, 169, 105066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharia, M.-M.; Bucatariu, F.; Vasiliu, A.-L.; Mihai, M. Stable and reusable acrylic ion-exchangers. From HMIs highly polluted tailing pond to safe and clean water. Chemosphere 2022, 304, 135383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, J.; Branger, C.; Beurroies, I.; Denoyel, R.; Blanc, S.; Margaillan, A. Synthesis of a poly(vinylcatechol-co-divinylbenzene) resin and accessibility to catechol units. Polymer 2010, 51, 2472–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendy, E.A.; Ifthikar, J.; Ali, J.; Oyekunle, D.T.; Eikhlifia, Z.; Shahib, I.I.; Khodair, A.I.; Chen, Z. Removal of heavy metals by covalent organic frameworks (COFs): A review on its mechanism and adsorption properties. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinu, M.V.; Dinu, I.A.; Lazar, M.M.; Dragan, E.S. Insights into the Mechanism of Cu2+ Binding onto Chitosan Based Cryogel Composites: Equilibrium, Kinetics and Thermodynamics Studies. Cellulose Chem. Technol. 2018, 52, 181–192. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X. Molecular imprinting for anion recognition in aqueous media. Microchim. Acta 2012, 176, 23–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BelBruno, J.J. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 94–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhang, N.; Xu, Y.; Li, Z.; Yan, C.; Mei, K.; Ding, M.; Ding, S.; Guan, P.; Qian, L.; et al. Molecularly Imprinted Materials for Selective Biological Recognition. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2019, 40, 1900096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafa, A.M.; Barton, S.J.; Wren, S.P.; Barker, J. Review on molecularly imprinted polymers with a focus on their application to the analysis of protein biomarkers. Trends Analyt. Chem. 2021, 144, 116431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchekwagep, P.M.S.; Crapnell, R.D.; Banks, C.E.; Betlem, K.; Rinner, U.; Canfarotta, F.; Lowdon, J.W.; Eersels, K.; van Grinsven, B.; Peeters, M.; et al. A Critical Review on the Use of Molecular Imprinting for Trace Heavy Metal and Micropollutant Detection. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishide, H.; Deguchi, J.; Tsuchida, E. Selective adsorption of metal ions on crosslinked poly(vinylpyridine) resin prepared with a metal ion as a template. Chem. Lett. 1976, 5, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, T.P.; Kala, R.; Daniel, S. Metal ion-imprinted polymers—Novel materials for selective recognition of inorganics. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 578, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hande, P.E.; Samui, A.B.; Kulkarni, P.S. Highly selective monitoring of metals by using ion-imprinted polymers. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 7375–7404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdem, O.; Saylan, Y.; Andaç, M.; Denizli, A. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Removal of Metal Ions: An Alternative Treatment Method. Biomimetics 2018, 3, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Yang, H. Construction of natural polymeric imprinted materials and their applications in water treatment: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karrat, A.; Lamaoui, A.; Amine, A.; Palacios-Santander, J.M.; Cubillana-Aguilera, L. Applications of Chitosan in Molecularly and Ion Imprinted Polymers. Chem. Afr. 2020, 3, 513–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumkar, V.V.; Galamboš, M.; Viglašová, E.; Dano, M.; Šmelková, J. Ion-Imprinted Polymers: Synthesis, Characterization, and Adsorption of Radionuclides. Materials 2021, 14, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branger, C.; Meouche, W.; Margaillan, A. Recent advances on ion-imprinted polymers. React. Funct. Polym. 2013, 73, 859–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ouardi, Y.; Giove, A.; Laatikainen, M.; Branger, C.; Laatikainen, K. Benefit of ion imprinting technique in solid-phase extraction of heavy metals, special focus on the last decade. J. Env. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, B.; Wang, R. Insights into ion-imprinted materials for the recovery of metal ions: Preparation, evaluation and application. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 298, 121469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Dai, J.; Hu, B.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Dai, J.; Meng, M.; Li, C.; Yan, Y. Recent progresses on the adsorption and separation of ions by imprinting routes. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2019, 49, 265–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabanov, V.A.; Efendiev, A.A.; Orujev, D.D. Complex-forming polymeric sorbents with macromolecular arrangement favorable for ion sorption. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1979, 24, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohga, K.; Kurauchi, Y.; Yanase, H. Adsorption of Cu2+ or Hg2+ ion on resins prepared by crosslinking metal-complexed chitosans. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1987, 60, 444–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinu, M.V.; Dinu, I.A.; Lazar, M.M.; Dragan, E.S. Chitosan-Based Ion-Imprinted Cryo-Composites with Excellent Selectivity for Copper Ions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 186, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humelnicu, D.; Lazar, M.M.; Ignat, M.; Dinu, I.A.; Dragan, E.S.; Dinu, M.V. Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Multicomponent Aqueous Solutions by Eco-Friendly and Low-Cost Composite Sorbents with Anisotropic Pores. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 381, 120980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, S.; Burleigh, M.C.; Ju, Y.H.; Gao, H.J.; Lin, J.S.; Pennycook, S.J.; Barnes, C.E.; Xue, Z.L. Hierarchically Imprinted Sorbents for the Separation of Metal Ions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 992–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchen, W.; Schram, J. Metal-Ion-Selective Exchange Resins by Matrix Imprint with Methacrylates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Eng. 1988, 27, 1695–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.; Liu, L.; Wang, Q.; Saleem, M.H.; Bashir, S.; Ullah, S.; Peng, D. Copper Environmental Toxicology, Recent Advances, and Future Outlook: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 18003–18016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blades, B.; Ayton, S.; Hung, Y.H.; Bush, A.I.; La Fontaine, S. Copper and Lipid Metabolism: A reciprocal relationship. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2021, 1865, 129979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, J. Ion-Imprinted Composite Hydrogels with Excellent Mechanical Strength for Selective and Fast Removal of Cu2+. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, M.R.; Bajwa, S.Z.; Lieberzeit, P.A.; Khan, W.S.; Mujahid, A.; Ihsan, A.; Rehman, A. Molecularly Imprinted Porous Beads for the Selective Removal of Copper Ions. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germigiano, T.O.; Corazza, M.Z.; Segatelli, M.G.; Ribeiro, E.S.; Yabe, M.J.S.; Galunin, E.; Tarley, C.R.T. Synthesis of Novel Copper Ion-Selective Material Based on Hierarchically Imprinted Cross-Linked Poly(Acrylamide-co-Ethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate). React. Funct. Polym. 2014, 82, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Chen, J.P. Cu(II)-Imprinted Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/Poly(Acrylic Acid) Membrane for Greater Enhancement in Sequestration of Copper Ion in the Presence of Competitive Heavy Metal Ions: Material Development, Process Demonstration, and Study of Mechanisms. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 20223–20233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoai, N.T.; Yoo, D.-K.; Kim, D. Batch and Column Separation Characteristics of Copper-Imprinted Porous Polymer Micro-Beads Synthesized by a Direct Imprinting Method. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 173, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaipuang, A.; Phungpanya, C.; Thongponn, C.; Watla-iad, K.; Inkaew, P.; Machan, T.; Suwantong, O. Synthesis of Copper(II) Ion-Imprinted Polymers via Suspention Polymerization. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2018, 29, 3134–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Lu, H.; Liang, Y.; Zhu, F. Microwave-Assisted Magnetic Cu(II)-Imprinted-Polymer Based on Double Functional Monomers for Selective Removal of Cu(II) from Wastewater. J. Water Chem. Technol. 2022, 44, 431–439. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Tang, B.; Zhao, P.; Xi, M.; Li, Y. Synthesis of Copper and Lead Ion Imprinted Polymer Submicron Spheres to Removal Cu2+ and Pb2+. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2021, 31, 4628–4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Tripathi, A. Selective Solid Phase Extraction and Pre-Concentration of Cu(II) Ions from Aqueous Solution using Cu(II)-Ion Imprinted Polymeric Beads. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalilzadeh, M.; Ṣenel, S. Removal of Cu(II) Ions from Water by Ion-Imprinted Magnetic and Non-magnetic Cryogels: A comparison of Their Selective Cu(II) Removal Performances. J. Water Process Eng. 2016, 13, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuras, M.J.; Więckowska, E. Synthesis and Characterization of a New Copper(II) Ion-Imprinted Polymer. Polym. Bull. 2015, 72, 3227–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Zheng, L.; Fang, Z. Selective Adsorption of Cu(II) from Aqueous Solution by Ion Imprinted Magnetic Chitosan Microspheres Prepared from Steel Pickling Waste Liquor. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 97435–97445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, L.; Xiong, Q.; Chen, J. Preparation and Adsorption Characters of Cu(II)-Imprinted Chitosan/Attapulgite Polymer. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 31, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yun, M.; Yu, Z.; Chen, D.; Li, X. A Novel Cu(II) Ion-Imprinted Alginate–Chitosan Complex Adsorbent for Selective Separation of Cu(II) from Aqueous Solution. Polym. Bull. 2019, 76, 1861–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Wang, N.; Qiao, N.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Ren, Z. Facile Preparation of Ion-Imprinted Chitosan Microspheres Enwrapping Fe3O4 and Graphene Oxide by Inverse Suspension Crosslinking for Highly Selective Removal of Copper(II). ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 7401–7409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zheng, Q. Selective Adsorption Behavior of Ion-Imprinted Magnetic Chitosan Beads for Removal of Cu(II) Ions from Aqueous Solution. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 39, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Li, Z.; Wei, X.; Tang, L.; Li, M.; Liang, Z.; Yin, X.; Wei, S. Ion-Imprinted Thermosensitive Chitosan Derivative for Heavy Metal Remediation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 248, 116732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Kang, S.; Wang, W.; Zhang, T.; Song, S. Preparation of Ion-Imprinted Montmorillonite Nanosheets/Chitosan Gel Beads for Selective Recovery of Cu(II) from Wastewater. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Yang, F.; Zheng, Y.; Kang, J.; Qu, J.; Chen, J.P. Improvement of Metal Adsorption onto Chitosan/Sargassum sp. Composite Sorbent by an Innovative Ion-Imprint Technology. Water Res. 2011, 45, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tian, H.; Yuan, Y.; Yin, X.; Wei, X.; Tang, L.; Wei, S. Metal-ion-imprinted thermo-responsive materials obtained from bacterial cellulose: Synthesis, characterization, and adsorption evaluation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 11742–11755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, M.; Dickson, S.E.; Kim, Y.; Mekky, W. Preparation and characterization of ion selective membrane and its application for Cu2+ removal. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 60, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Kong, D.; Qiao, N.; Wang, N.; Wang, Q.; Liu, H.; Zhou, Z.; Ren, Z. Facile preparation of novel layer-by-layer surface ion-imprinted composite membrane for separation of Cu2+ from aqueous solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 457, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubier, A.; Wilkin, R.T.; Pichler, T. Cadmium in Soils and Groundwater: A Review. Appl. Geochem. 2019, 108, 104388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Li, K.; Dai, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, F.; Li, S. An Ultrasensitive Electrochemical Platform Based on Imprinted Chitosan/Gold Nanoparticles/Graphene Nanocomposite for Sensing Cadmium (II) Ions. Microchem. J. 2020, 155, 104710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Liang, Y. Application of Chitosan-N-Doped Graphene Oxide Ion-Imprinted Sensor in Cd(II) Ions Detection. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2021, 119, 108591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babakhani, A.; Sartaj, M. Synthesis, Characterization, and Performance Evaluation of Ion-Imprinted Crosslinked Chitosan (with Sodium Tripolyphosphate) for Cadmium Biosorption. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahangdale, D.; Kumar, A. Acrylamide Grafted Chitosan Based Ion Imprinted Polymer for the Recovery of Cadmium from Nickel-Cadmium Battery Waste. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 1828–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Gan, L.; Duan, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z. A Novel Cd2+-Imprinted Chitosan-Based Composite Membrane for Cd2+ Removal from Aqueous Solution. Mater. Lett. 2017, 198, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, H.; An, H.; Xie, Z. Ion-Imprinted Carboxymethyl Chitosan–Silica Hybrid Sorbent for Extraction of Cadmium from Water Samples. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 56, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Feng, C.; Li, M.; Zeng, Q.; Gan, Q.; Yang, H. Synthesis and Characterization of a Surface-Grafted Cd(II)Ion-Imprinted Polymer for Selective Separation of Cd(II) Ion from Aqueous Solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 332, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, F. Synthesis and Application of Ion-Imprinted Interpenetrating Polymer Network Gel for Selective Solid Phase Extraction of Cd2+. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 242, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murat, A.; Wang, L.; Abliz, S.; Yimit, A. Preparation, Characterization of Cd(II) Ion-Imprinted Microsphere and Its Selectivity for Template Ion. Coatings 2022, 12, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adauto, A.; Khan, S.; da Silva, M.A.; Neto, J.A.G.; Picasso, G.; Sotomayor, M.P.T. Synthesis, Characterization and Application of a Novel Ion Hybrid Imprinted Polymer to Adsorb Cd(II) in Different Samples. Environ. Res. 2020, 187, 109669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, P.T.; RanjanMisra, S.; Hussain, M. Nutritional aspects of essential trace elements in oral health and disease: An extensive review. Scientifica 2016, 2016, 5464373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannas, D.; Loi, E.; Serra, M.; Firinu, D.; Paolo Valera, P.; Zavattari, P. Relevance of essential trace elements in nutrition and drinking water for human health and autoimmune disease risk. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakerian, F.; Dadfarnia, S.; Shabani, A.M.H. Synthesis and application of nano-pore size ion imprinted polymer for solid phase extraction and determination of zinc in different matrices. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuras, M.J.; Perz, K.; Kolodzicjski, W.L. Synthesis, characterization and application of a novel zinc(II) ion-imprinted polymer. Polym. Bull. 2017, 74, 5029–5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsipur, M.; Rajabi, H.R.; Pourmortazavi, S.M.; Roushani, M. Ion imprinted polymeric nanoparticles for selective separation and sensitive determination of zinc ions in different matrices. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 117, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirawan, T.; Supriyanto, G.; Soegianto, A. Synthesis, characterization, and application of novel Zn(II)-ionic imprinted polymer for preconcentration of Zn(II) ions from aqueous solution. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 349, 012064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.; Gatabi, J.; Mohamadnia, Z. Preparation and characterization of Zn(II) ion-imprinted polymer based on salicylic acrylate for recovery of Zn(II) ions. Polimeros 2016, 26, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Ding, L. Modulated ion recognition by rhermosensitive ion-imprinted hydrogels with IPN structure. Mater. Lett. 2014, 131, 9–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behbahani, M.; Salarian, M.; Bagheri, A.; Tabani, H.; Omidi, O.; Fakhari, A. Synthesis, characterization and analytical application of Zn(II)-imprinted polymer as an efficient solid-phase extraction technique for trace determination of zinc in food samples. J. Food Comp. Anal. 2014, 34, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Jiang, Y.; Kim, D. Zn2+-imprinted porous polymer beads: Synthesis, structure, and selective adsorption behavior for template ion. React. Funct. Polym. 2013, 73, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, E.; Dadfarnia, S.; Shabani, A.M.H.; Ranjbar, M. Synthesis, characterization, and application of a Zn (II)-imprinted polymer grafted on graphene oxide/magnetic chitosan nanocomposite for selective extraction of zinc ions from different food samples. Food Chem. 2017, 237, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairnar, N.A.; Choudhary, B.C.; Karnakar, R.R.; Gite, V.V. Chitosan-based ion-imprinted polymer for selective extraction of Zn(II) in aqueous samples. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 102, 8234–8249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Qiao, X.; Lu, X.; Fan, X. Selective adsorption of Zn2+ on surface ion-imprinted polymer. Des. Water Treat. 2015, 57, 15455–15466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Hu, D.; Cheng, H. Preparation and Characterization of Co(II) Ion-Imprinted Composite Membrane Based on a Novel Functional Monomer. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2022, 334, 111707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, N.F.; Mehamod, F.S.; Suah, F.B.M. Fabrication and Binding Characterization of Ion Imprinted Polymers for Highly Selective Co2+ Ions in an Aqueous Medium. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, R.; Qiu, L.; Fang, L.; Yu, R.; Chen, Y.; Lu, X.; Luo, X. A Novel Magnetic and Hydrophilic Ion-Imprinted Polymer as a Selective Sorbent for the Removal of Cobalt Ions from Industrial Wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2268–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoddami, N.; Shemirani, F. A New Magnetic Ion-Imprinted Polymer as a Highly Selective Sorbent for Determination of Cobalt in Biological and Environmental Samples. Talanta 2016, 146, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Jiang, H.; Wu, L.; Yu, N.; Luo, Z.; Geng, W. Preparation of Magnetic Surface Ion-Imprinted Polymer Based on Functionalized Fe3O4 for Fast and Selective Adsorption of Cobalt Ions from Water. Water 2022, 14, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyki, M.H.; Shemirani, F.; Shirkhodaie, M. Aqueous Co(II) Adsorption Using 8-hydroxyquinoline Anchored γ-Fe2O3@Chitosan with Co(II) as Imprinted Ions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 87, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sáez, P.; Dinu, I.A.; Rodríguez, A.; Gómez, J.M.; Lazar, M.M.; Rossini, D.; Dinu, M.V. Composite Cryo-Beads of Chitosan Reinforced with Natural Zeolites with Remarkable Elasticity and Switching on/off Selectivity for Heavy Metal Ions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 2432–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, M.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Jiao, J.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, Z.; Ren, Z. Preparation of Surface Ion-Imprinted Materials Based on Modified Chitosan for Highly Selective Recognition and Adsorption of Nickel Ions in Aqueous Solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 6033–6042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Su, S.-J.; Liao, B.; Ding, S.-L.; Sun, W.-Y. Preparation and Properties of a Novel Macro Porous Ni2+-Imprinted Chitosan Foam Adsorbents for Adsorption of Nickel Ions from Aqueous Solution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 165, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhong, L.; Yang, S.; Liu, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Han, X.; Zhang, X. Adsorption of Ni(II) Ion on Ni(II) Ion-Imprinted Magnetic Chitosan/Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Composite. Colloid. Polym. Sci. 2015, 293, 2497–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Shang, H.; Zhang, X.; Sun, X. Synthesis and Application of Ion Imprinting Polymer Coated Magnetic Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Selective Adsorption of Nickel Ion. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 428, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi-Qeydari, S.R.; Samimi, A.; Mohebbi-Kalhori, D.; Ahmadi, E. A Mesoporous Melamine/Chitosan/Activated Carbon Biocomposite: Preparation, Characterization and Its Application for Ni(II) Uptake via Ion Imprinting. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 188, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Bai, Z.; Luo, W.; Zhai, L.; Wang, B.; Kang, X.; Zong, J. Ion Imprinted Adsorbent for the Removal of Ni(II) from Waste Water: Preparation, Characterization, and Adsorption. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2019, 40, 1751–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, X.; Peng, J. Highly Selective Removal and Recovery of Ni(II) from Aqueous Solution Using Magnetic Ion-Imprinted Chitosan Nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 271, 118435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamahkar, E.; Bakhshpour, M.; Andaç, M.; Denizli, A. Ion Imprinted Cryogels for Selective Removal of Ni(II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 179, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Yu, P.; Shen, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Yang, R.; Fu, X.; Chi, J.; Chen, X.; Feng, Y. Ion Imprinted Polymer Layer Modified Magnetic Nanocomposites for Selective Recycling of Aqueous Ni(II). J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 373, 133748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özkahraman, B.; Özbaş, Z.; Öztürk, A.B. Synthesis of Ion-Imprinted Alginate Based Beads: Selective adsorption behavior of nickel(II) ions. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 4303–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Luo, X.; Yin, X.; Wu, X. An Ion-Imprinted Polymer Based on the Novel Functional Monomer for Selective Removal of Ni(II) from Aqueous Solution. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 4776–4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Kong, D.; Zhu, H.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Liu, W.; Li, Q.; Zhang, W.; Ren, Z. Preparation and Adsorption Characteristics of an Ion-Imprinted Polymer for Fast Removal of Ni(II) Ions from Aqueous Solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 341, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozkütük, E.B.; Karabork, M. Fe3+- Imprinted polymeric systems. Hacettepe J. Biolog. Chem. 2007, 35, 195–202. [Google Scholar]
- Özkara, S.; Andaç, M.; Karakoç, V.; Say, R.; Denizli, A. Ion-Imprinted PHEMA based monolith for the removal of Fe3+ ions from aqueous solutions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 120, 1829–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabörk, M.; Ozkütük, E.B.; Ersöz, A.; Say, R. Selective preconcentration of Fe3+ using ion-imprinted thermosensitive particles. Hacettepe J. Biolog. Chem. 2010, 38, 27–39. [Google Scholar]
- Roushani, M.; Beygi, T.M.; Saedi, Z. Synthesis and application of ion-imprinted polymer for estractionand pre-concentration of iron ions in environmental water and food samples. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2016, 153, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darmawan, W.; Nurani, D.A.; Rahayu, D.U.C.; Abdullah, I. Synthesis of ion imprinted polymer for separation and preconcentration of Iron(III). AIP Conf. Proc. 2020, 2242, 040025. [Google Scholar]
- Khajeh, M.; Kaykhail, M.; Hashemi, H.; Mirmoghaddam, M. Imprinted polymer particles for iron uptake: Synthesis, characterization and analytical applications. Polym. Sci. B 2009, 51, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitreva, M.; Dakova, I.; Karadjova, I. Iron(II) ion imprinted polymer for Fe(II)/Fe(III) speciation in wine. Microchem. J. 2017, 132, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Tang, H.; Zhang, H.; Pei, L.; Zhou, P.; Shi, Y.; Cai, Z.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y. A novel ion-imprinted polymer for selective removal of trace Fe(III) from Cr(III)-containing solutions. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 186, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Tang, H.; Qing, P.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, X.; Cai, Z.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y. A monophosphonic group-functionalized ion-imprinted polymer for a removal of Fe3+ from highly concentrated basic chromium sulfate solution. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 37, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimen, D.; Göktürk, I.; Ylmaz, F. Removal of iron by chelation with molecularly imprinted supermacroporous cryogel. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2016, 44, 1158–1166. [Google Scholar]
- Karaboç, V. Designing of alternative polymeric nano-chelator for treatment in acute iron poisoning by molecular imprinting approach. Hacettepe J. Biolog. Chem. 2020, 48, 319–331. [Google Scholar]
- Sangu, H.D.; Akgönüllü, S.; Denizli, A. Ion-imprinted-based nanochelators for iron(III) removal from synthetic gastric fluid. Polym. Bull. 2022, 79, 8947–8965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakova, I.; Karadjova, I.; Georgieva, V.; Georgiev, G. Ion-imprinted polymethacrylic microbeads as new sorbent for preconcentration and speciation of mercury. Talanta 2009, 78, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Niu, D.; Bi, C.; Shen, B. Hg2+ Adsorption from a low-concentration aqueous solution on chitosan beads modified by combining polyamination with Hg2+-imprinted technology. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 13120–13127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yordanova, T.; Dakova, I.; Balashev, K.; Karadjova, I. Polymeric ion-imprinted nanoparticles for mercury speciation in surface waters. Microchem. J. 2014, 113, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Song, X.; Ma, J.; Chen, L. Hg2+ ion-imprinted polymers sorbents based on dithizone-Hg2+ chelation for mercury speciation analysis in environmental and biological samples. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 46444–46453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairi, N.A.S.; Yusof, N.A.; Abdullah, A.H.; Mohammad, F. Removal of toxic mercury from petroleum oil by newly synthesized molecularly-imprinted polymer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 10562–10577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakare, S.R.; Pal, M.R.; Jadhao, S.Z. Simple synthesis of highly selective and fast Hg(II) removal polymer from aqueous solution. Des. Mon. Polym. 2015, 18, 650–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mergola, L.; Scorrano, S.; Bloise, E.; Di Bello, M.P.; Massimo Catalano, M.; Vasapollo, G.; Del Sole, R. Novel polymeric sorbents based on imprinted Hg(II)-diphenylcarbazone complexes for mercury removal from drinking water. Polym. J. 2016, 48, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajri, A.K.; Jamussi, B.; Albalawi, A.E.; Alhawiti, O.H.N.; Alsharif, A.A. Designing of modified ion-imprinted chitosan particles for selective removal of mercury (II) ions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 286, 119207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasinzai, M.; Mustafa, G.; Asghar, N.; Ullah, H.; Zahid, M.; Lieberzeit, P.A.; Han, D.; Latif, U. Ion-imprinted polymer-based receptors for sensitive and selective detection of mercury ions in aqueous environment. J. Sens. 2018, 2018, 8972549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, E.; Aboufazeli, F.; Zhad, H.R.L.Z.; Sadeghi, O.; Amani, V. A novel magnetic ion imprinted nano-polymer for selective separation and determination of low levels of mercury(II) ions in fish samples. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 4040–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Fernández, R.; Peña-Vázquez, E.; Bermejo-Barrera, P. Determination of mercury in wastewater using a molecularly imprinted polymer as solid phase extraction sorbent and CV-ICP-OES. Atomic Spectr. 2016, 37, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesa, R.L.; Villa, J.E.L.; Khan, S.; Alves Peixoto, R.R.; Morgano, M.A.; Gonçalves, L.M.; Sotomayor, M.D.F.T.; Picasso, G. Rational design of an ion-imprinted polymer for aqueous methylmercury sorption. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Meng, X.; Han, J.; Liu, Z.; Meng, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, R.; Tian, S. Speciation, adsorption and determination of chromium(III) and chromium(VI) on a mesoporous surface imprinted polymer adsorbent by combining inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry and UV spectrophotometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 3949–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, M.; Ghaedi, M.; Dashtian, K.; Hajati, S. New ion-imprinted polymer-functionalized mesoporous SBA-15 for selective separation and preconcentration of Cr(III) ions: Modeling and optimization. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 105789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
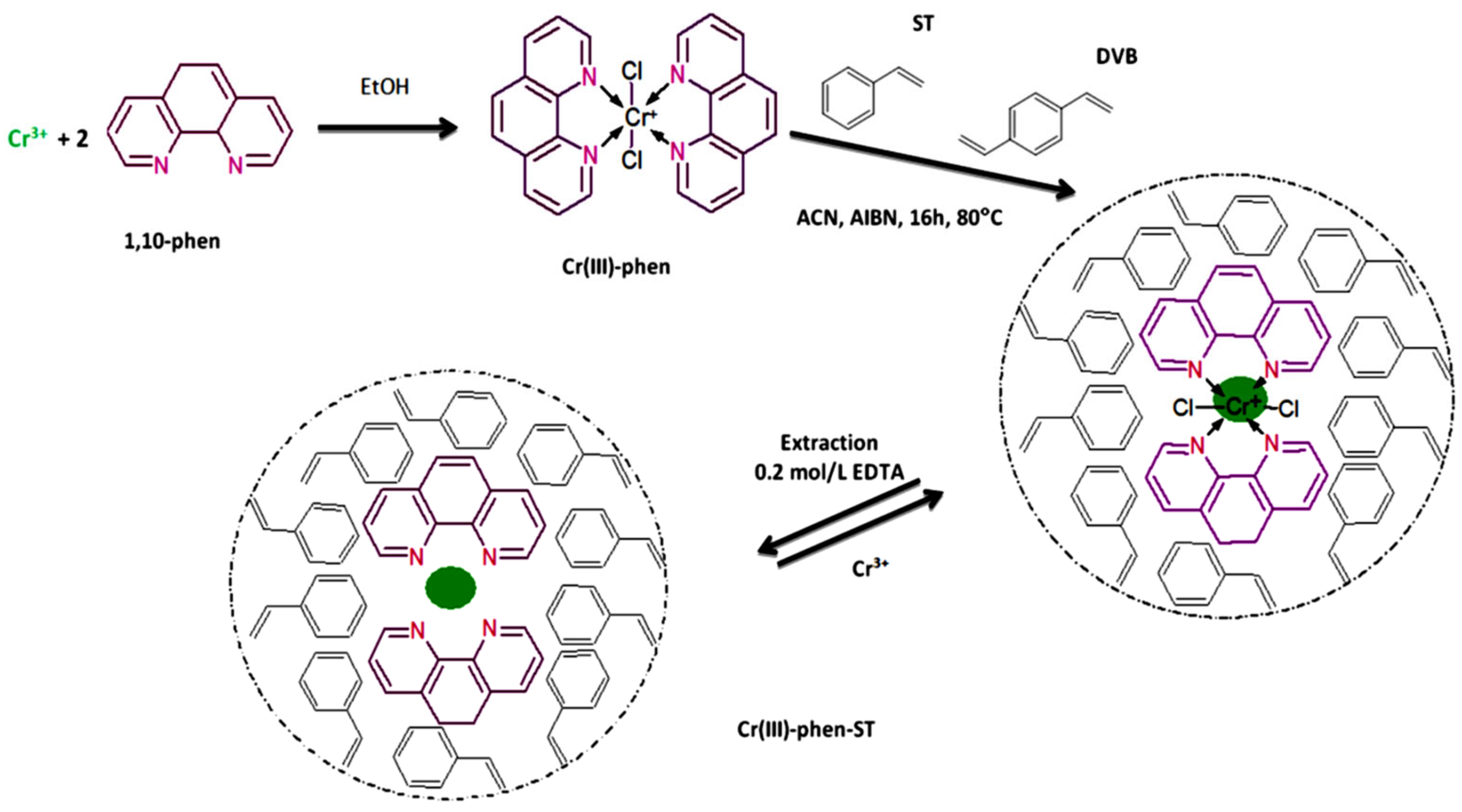
- Trzonkowska, L.; Leśniewska, B.; Godlewska-Żyłkiewicz, B. Studies on the effect of functional monomer and porogen on the properties of ion imprinted polymers based on Cr(III)-1,10-phenanthroline complex designed for selective removal of Cr(III) ions. React. Funct. Polym. 2017, 117, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzonkowska, L.; Leśniewska, B.; Godlewska-Żyłkiewicz, B. Development of solid phase extraction method based on ion imprinted polymer for determination of Cr(III) ions by ETAAS in waters. Water 2022, 14, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, N.H.; Monier, M.; Alatawi, R.A.S.; Alhawiti, A.S. Preparation of chromium (III) ion-imprinted polymer based on azo dye functionalized chitosan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 284, 119139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dakova, I.; Vasileva, P.; Karadjova, I. Cr(III) ion-imprinted hydrogel membrane for chromium speciation analysis in aater samples. Gels 2022, 8, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Zhang, F.; Wang, K.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, W. Fast removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution using Cr(VI)-imprinted polymer particles. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 4434–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Z.; Du, Y.; Wei, J.; Zhang, H.; Fan, L. Synthesis of a new ion-imprinted polymer for selective Cr(VI) adsorption from aqueous solutions effectively and rapidly. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 588, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etemadi, M.; Samadi, S.; Yazd, S.S.; Jafari, P.; Yousefi, N.; Aliabadi, M. Selective adsorption of Cr(VI) ions from aqueous solutions usingCr6+-imprinted Pebax/chitosan/GO/APTES nanofibrous adsorbent. Int. J. Biolog. Macromol. 2017, 95, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitreva, M.; Dakova, I.; Yordanova, T.; Karadjova, I. Chromate surface-imprinted silica gel sorbent for speciation of Cr in surface waters. Turk. J. Chem. 2016, 40, 921–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Dai, X.; Cheng, T.; Li, S. Highly sensitive and selective ion-imprinted polymers based on one-step electrodeposition of chitosan-graphene nanocomposites for the determination of Cr(VI). Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 195, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Xu, J.; Zhu, D.; Wang, D.; Xu, J.; Jiang, H.; Geng, W.; Wei, W.; Lian, Z. Ion-imprinted polypropylene fibers fabricated by the Ppasma-mediated grafting strategy for effcient and selective adsorption of Cr(VI). Polymers 2019, 11, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanpour, S.; Taghizadeh, M.; Yamini, Y. Magnetic Cr(VI) Ion Imprinted Polymer for the Fast Selective Adsorption of Cr(VI) from Aqueous Solution. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Fabrication of chromium imprinted polymer: A real magneto selective sorbent for chromium Cr (VI) removal in a real water sample. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 18668–18678. [CrossRef]
- Neolaka, Y.A.B.; Lawa, Y.; Naat, J.N.; Riwu, A.A.P.; Darmokoesoemo, H.; Supriyanto, G.; Holdsworth, C.I.; Amenaghawon, A.N.; Kusuma, H.S. A Cr(VI)-imprinted-poly(4-VP-co-EGDMA) sorbent prepared using precipitation polymerization and its application for selective adsorptive removal and solid phase extraction of Cr(VI) ions from electroplating industrial wastewater. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 147, 104451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Shen, Y.; Dang, W.; Yang, B.; Fu, W.; Wei Wang, W.; Bai, B. Fabrication of a photoelectric-sensitive imprinting polymer by PPy-cross-linked Gel/CS complex and its comprehensive treatment of Cr(VI). Polym. Bull. 2020, 77, 869–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Balouch, A.; Pathan, A.A.; Abdullah; Jagirani, M.S.; Mahar, A.M.; Rajput, M.U.H. Novel chromium imprinted polymer: Synthesis, characterization and analytical applicability for the selective remediation of Cr(VI) from an aqueous system. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2019, 99, 454–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velempini, T.; Pillay, K.; Mbianda, X.Y.; Arotiba, O.A. Epichlorohydrin crosslinked carboxymethylcellulose-ethylenediamine imprinted polymer for the selectiveuptake of Cr(VI). Int. J. Biolog. Macromol. 2017, 101, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Ren, Z.; Xi, Y.; Fang, L.; Fang, D.; Yang, L.; Penghui Shao, P.; Shi, H.; Yu, K.; Luo, X. Insights into the role of cross-linking agents on polymer template effect: A case study of anionic imprinted polymers. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 129611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajeh, M.; Sanchooli, E. Synthesis of ion-selective imprinted polymer for manganese removal from environmental water. Polym. Bull. 2011, 67, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Jia, M.; Men, J.; Wang, X. Mn2+ and Co2+ Removal from dilute solution using cysteine grafted cobalt/manganese imprinted crosslinked chitosan. Appl. Mechan. Mater. 2015, 751, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravind, A.; Mathew, B. Nano layered ion imprinted polymer based electrochemical sensor and sorbent for Mn (II) ions from real samples. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A Pure Appl. Chem. 2020, 57, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xue, J.; Zhou, X.; Fei, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhong, L.; Han, X. Adsorption of molybdate on molybdate-imprinted chitosan/triethanolamine gel beads. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 114, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanpour, S.; Taghizadeh, M. Rapid and selective separation of molybdenum ions using a novel magnetic Mo(VI) ion imprinted polymer: A study of the adsorption properties. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 100248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, K.; Wang, J.; Yu, H.; Cui, J.; Xiong, Y. Preparation of porous Mo(VI)-imprinted algae for recognizing molybdenum(VI). Solvent Extr. Ion Ex. 2021, 39, 622–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Song, Y.; Tong, Q.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Lou, Z.; Zhang, F.; Shan, W. Adsorption-controlled preparation of anionic imprinted amino-functionalization chitosan for recognizing rhenium(VII). Sep. Pur. Technol. 2017, 177, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Xie, L.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Shan, W.; Lou, Z.; Cui, J.; Yu, H. Superior adsorption of Re(VII) by anionic imprinted chitosan-silica composite: Adsorption performance, selectivity and mechanism study. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 108, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Jia, W.; Ou, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, X. Study on synthesis and adsorption properties of ReO4− ion-imprinted polymer. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 24356–24366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
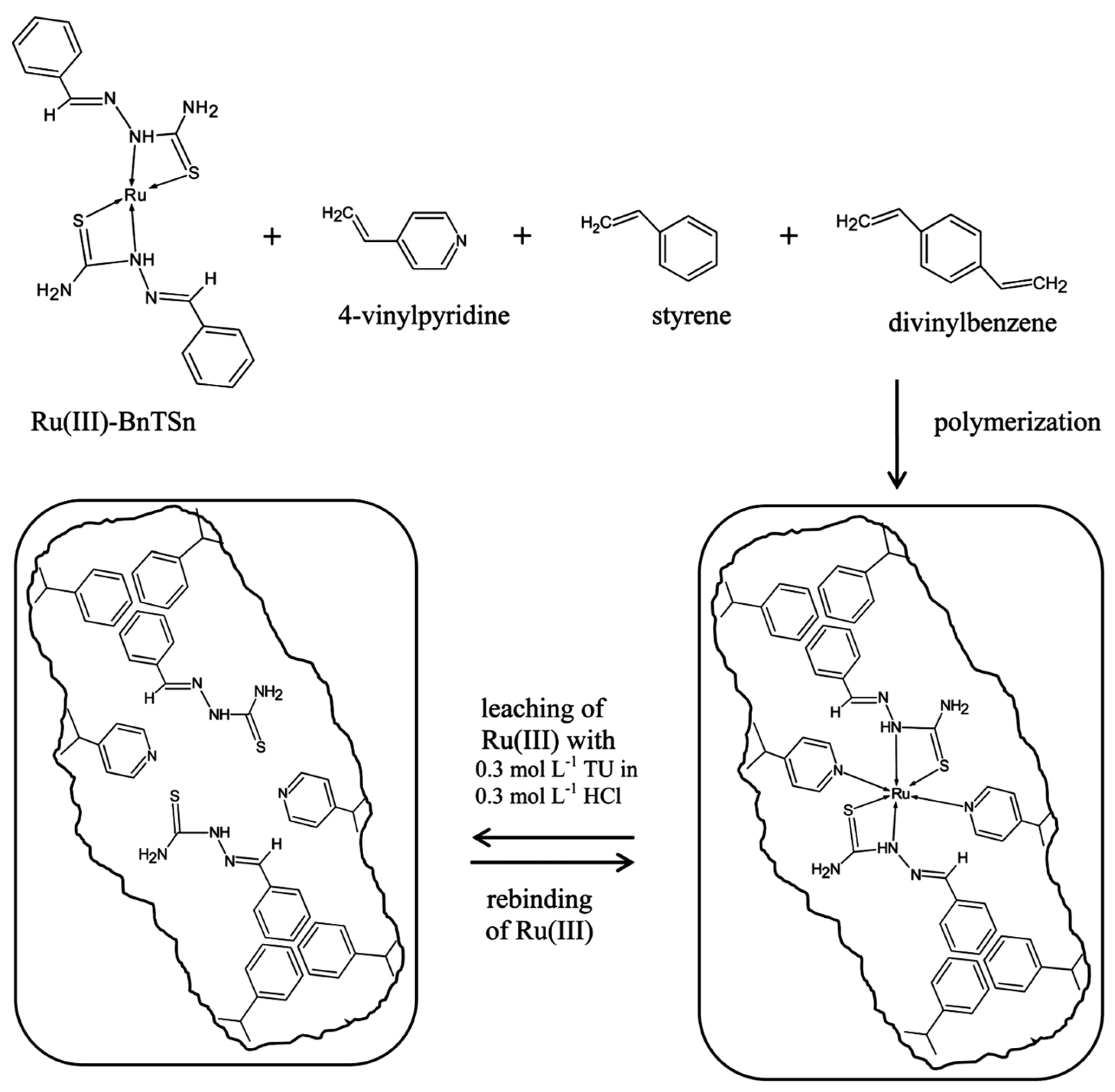
- Zambrzycka, E.; Kiedysz, U.; Wilczewska, A.Z.; Leśniewska, B.; Godlewska-Żyłkiewicz, B. A novel ion imprinted polymer as a highly selective sorbent for separation of ruthenium ions from environmental samples. Anal. Methods 2013, 6, 3096–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrzycka, E.; Godlewska-Żyłkiewicz, B. A new ion imprinted polymer based on Ru(III)-thiobarbituric acid complex for solid phase extraction of ruthenium(III) prior to its determination by ETAAS. Microchim. Acta 2014, 181, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianxian, Z.; Zhe, Z.; Zhihui, D.; Panfeng, R.; Yuan, L.; Xiao, L. Fabrication and characterization of an ion-imprinted membrane via blending poly(methyl methacrylate-co-2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) with polyvinylidene fluoride for selective adsorption of Ru(III). React. Funct. Polym. 2017, 115, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Monier, M.; Abdel-Latif, D.A.; Youssef, I. Preparation of ruthenium (III) ion-imprinted beads based on 2-pyridylthiourea modified chitosan. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 513, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ou, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Z.; Liu, C.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, J.; et al. Smart ion imprinted polymer for selective adsorption of Ru(III) and simultaneously waste sample being transformed as a catalyst. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 126072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
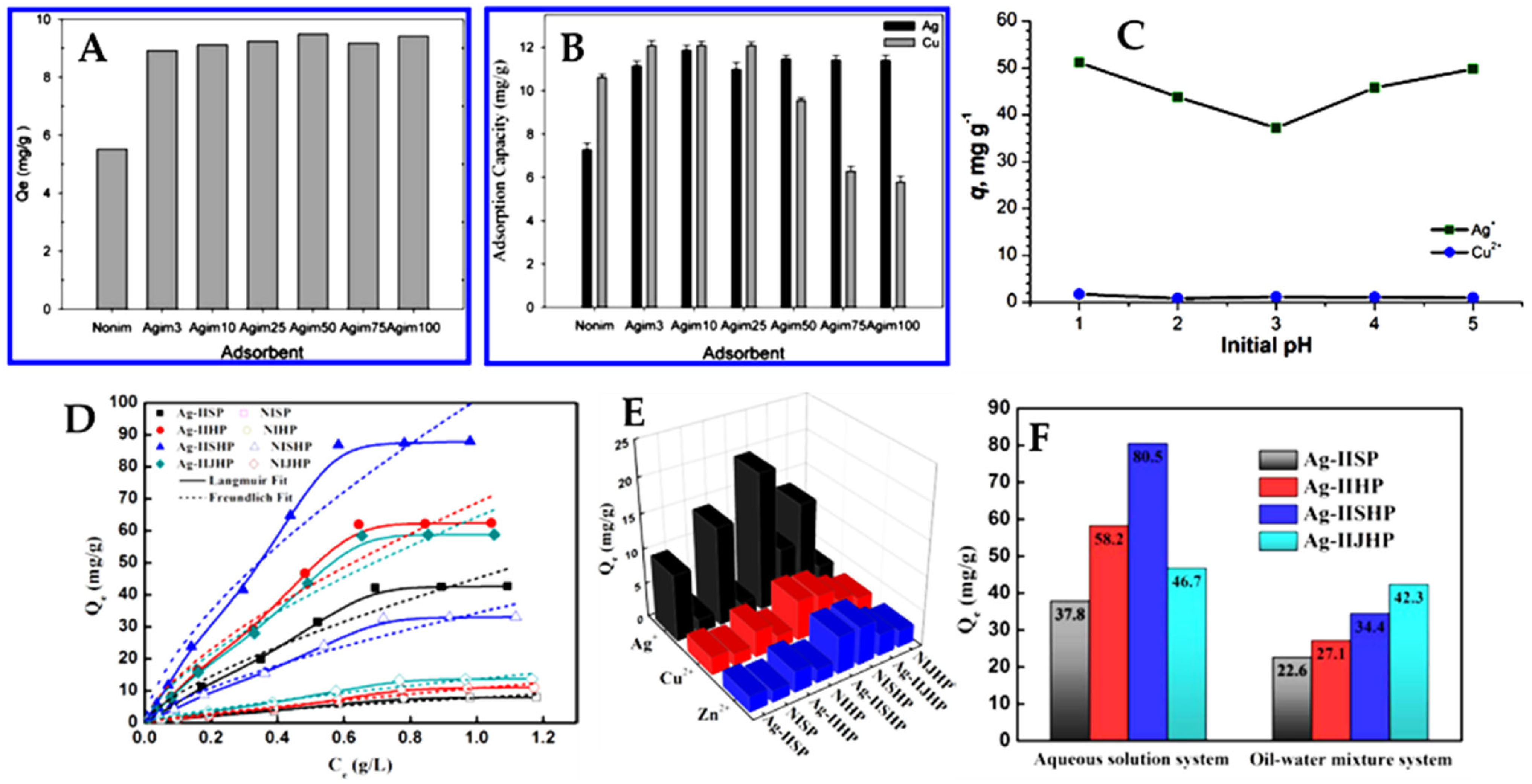
- Song, X.; Li, C.; Xu, R.; Wang, K. Molecular-Ion-Imprinted Chitosan Hydrogels for the Selective Adsorption of Silver(I) in Aqueous Solution. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 11261–11265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Helleur, R.; Zhang, Y. Ion-Imprinted Chitosan Gel Beads for Selective Adsorption of Ag+ from Aqueous Solutions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 130, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, H.; Yu, D.; Hu, G. Preparation and Properties of Ion-Imprinted Hollow Particles for the Selective Adsorption of Silver Ions. Langmuir 2015, 31, 1376–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, S.; Han, T.; Zhong, L.; Ma, C.; Zhou, Y.; Han, X. Improvement of Ag(I) Adsorption onto Chitosan/Triethanolamine Composite Sorbent by an Ion-Imprinted Technology. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 263, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamed, M.E.H.; Mbianda, X.Y.; Mulaba-Bafubiandi, A.F.; Marjanovic, L. Selective Extraction of Gold(III) from Metal Chloride Mixtures Using Ethylenediamine N-(2-(1-Imidazolyl)ethyl Chitosan Ion-Imprinted Chitosan. Hydrometallurgy 2013, 140, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Firlak, M.; Çubuk, S.; Yetimoğlu, E.K.; Kahraman, M.V. Recovery of Au(III) ions by Au(III)-Imprinted Hydrogel. Chem. Pap. 2016, 70, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Liu, J.; Li, M.; Guo, C.; Long, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xin, L. Mechanistic Study of Selective Adsorption and Reduction of Au(III) to Gold Nanoparticles by Ion-Imprinted Porous Alginate Microspheres. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monier, M.; Abdrel-Latif, D.A. Fabrication of Au(III) Ion-Imprinted Polymer Based on Thiol-Modified Chitosan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Wei, W.; Lin, X.; Bediako, J.K.; Reddy, D.H.K.; Song, M.-H.; Yun, Y.-S. Pd(II)-Imprinted Chitosan Adsorbent for Selective Adsorption of Pd(II): Optimizing the Imprinting Process through Box-Behnken Experimental Design. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 13057–13065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Wei, W.; Wu, X.; Zhou, T.; Mao, J.; Yun, Y.-S. Selective Recovery of Pd(II) from Extremely Acidic Solution Using Ion-Imprinted Chitosan Fiber: Adsorption Performance and Mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 299, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Lin, S.; Lu, X.J.; Wu, X.H.; Zhou, T.; Yun, Y.-S. Ion-Imprinted Chitosan Fiber for Recovery of Pd(II): Obtaining High Selectivity through Selective Adsorption and Two-Step Desorption. Environ. Res. 2020, 182, 108995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monier, M.; Abdel-Latif, D.A.; Abou El-Reash, Y.G. Ion-Imprinted Modified Chitosan Resin for Selective Removal of Pd(II) Ions. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2016, 469, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, T.P.; Metilda, P.; Gladis, J.M. Preconcentration Techniques for Uranium (VI) and Thorium (IV) Prior to Analytical Determination—An Overview. Talanta 2006, 68, 1047–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellah, A.; Chegrouche, S.; Barkat, M. The Removal of Uranium(VI) from Aqueous Solutions onto Activated Carbon: Kinetic and Thermodynamic Investigations. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 296, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellah, A.; Chegrouche, S.; Barkat, M. The Precipitation of Ammonium Uranyl Carbonate (AUC): Thermodynamic and Kinetic Investigations. Hydrometallurgy 2007, 85, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callura, J.C.; Perkins, K.M.; Noack, C.W.; Washburn, N.R.; Dzombak, D.A.; Karamalidis, A.K. SelectivecAdsorption of Rare Earth Elements onto Functionalized Silica Particles. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 1515–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, P.S.; Kelley, S.P.; Griggs, C.S.; Wallace, S.; Rogers, R.D. Surface Modification of Ionic Liquid-Spun Chitin Fibers for the Extraction of Uranium from Seawater: Seeking the Strength of Chitin and the Chemical Functionality of Chitosan. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 1828–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, X.; Hua, R.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Pang, C.; Wang, Y. Selective adsorption of uranyl ion on ion-imprinted chitosan/PVA cross-linked hydrogel. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 104, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Zhou, L.; Tang, X.; Xi, J.; Ouyang, J.; Liu, Z.; Huang, G.; Adesina, A. Macroporous ion-imprinted chitosan foams for the selective biosorption of U(VI) from aqueous solution. Int. J. Biol. Macrom. 2020, 164, 4155–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, N.; Alatawi, R.; Monier, M. Amidoxime modified chitosan based ion-imprinted polymer for selective removal of uranyl ions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 256, 117509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Dai, Y.; Zhou, L.; Ouyang, J.; Tang, X.; Liu, Z.; Adesina, A. Selective biosorption of U(VI) from aqueous solution by ion-imprinted honeycomb-like chitosan/kaolin clay composite foams. Int. J. Biol. Macrom. 2022, 206, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monier, M.; Abdel-Latif, D.A. Synthesis and characterization of ion-imprinted resin based on carboxymethyl cellulose for selective removal of UO22+. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 97, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.F.; Wang, H.Q.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, X.F.; Zhang, H.S.; Li, H.L.; Tang, J.H. Magnetic Th(IV)-ion imprinted polymers with salophen Schiff base for separation and recognition of Th(IV). J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2013, 295, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Chen, Z.; Wang, L.; Lv, T.; Shi, J. Removal of thorium (IV) from aqueous solution using magnetic ion-imprinted chitosan resin. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2016, 310, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, P.M.; Khurana, L.; Siddique, S.; Panicker, A.; Kandasubramanian, B. Ion-imprinted electrospun nanofibers of chitosan/1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate for the dynamic expulsion of thorium (IV) ions from mimicked effluents. Environ. Sci. Polut. Res. 2018, 25, 3320–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Bian, T.; Jiang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Li, Z. Bionic chitosan-carbon imprinted aerogel for high selective recovery of Gd(III) from end-of-life rare earth production. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, E.; Lin, X.; Zhang, D.; Xu, W.; Shi, J.; Hong, Y. Ionic imprinted CNTs-chitosan hybrid sponge with 3D network structure for selective and effective adsorption of Gd(III). Sep. Pur. Technol. 2021, 269, 118792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Zou, X.; Li, C.; Liu, Y.; Yan, Y.; Han, J. Synthesis and applications of Ce(III)-imprinted polymer based on attapulgite as the sacrificial support material for selective separation of cerium (III) ions. Microchim. Acta 2010, 171, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keçili, R.; Dolak, I.; Ziyadanoĝullari, B.; Ersöz, A.; Say, R. Ion imprinted cryogel-based supramacroporous traps for selective separation of cerium (III) in real samples. J. Rare Earths 2018, 36, 857–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.M.; Zakaria, E.S.; Khalil, M.; El-Tantawy, A.; El-Sayed, F.A. Synthesis of ion-imprinted polymers based on chitosan for high selectivity of La(III), Ce(III) and Sm(III) vis solid phase extraction. J. Molec. Liq. 2022, 356, 119058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, C.; Liu, Q.; Ren, Z.; Hu, H.; Sun, B.; Liu, C.; Shao, P.; Yang, L.; Pavlostathis, S.; Luo, X. Selective removal and recovery of La(III) using a phosphonic-based ion imprinted polymer: Adsorption performance, regeneration, and mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Xu, X.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, F.; Liu, E.; Li, C. An ion imprinted microporous chitosan membrane for efficiently selective adsorption of dysprosium. Sep. Pur. Technol. 2017, 189, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolak, I.; Keçili, R.; Hür, D.; Ersöz, A.; Say, R. In-imprinted polymers for selective recognition of Neodymium(III) in environmental sample. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 5328–5335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordberg, G.F.; Fowler, B.A.; Nordberg, M.; Friberg, L. Handbook on the Toxicology of Metals; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; p. 1024. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Song, Y.; Lou, Z.; Shan, W.; Xiong, Y. Novel Chitosan-Based Ions Imprinted Bio-Adsorbent for Enhanced Adsorption of Gallium(III) in Acidic Solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 320, 114413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Feng, C.; Li, M.; Zeng, Q.; Gan, Q. Synthesis and Application of a Surface-Grafted In (III) Ion-Imprinted Polymer for Selective Separation and Pre-Concentration of Indium (III) Ion from Aqueous Solution. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 154, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Meng, X.; Liang, X.; Yuan, J.; Hu, X.; Wu, Z.; Yuan, X. A Novel In(III) Ion-Imprinted Polymer (IIP) for Selective Extraction of In(III) Ions from Aqueous Solution. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 176, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hande, P.E.; Kamble, S.; Samui, A.B.; Kulkarni, P.S. Chitosan-Based Lead Ion-Imprinted Interpenetrating Polymer Network by Simultaneous Polymerization for Selective Extraction of Lead(II). Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 3668–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- René, W.; Lenoble, V.; Laatikainen, K.; Viguier, B.; Branger, C. Influence of the Synthesis Parameters on the Efficiency of Fluorescent Ion-Imprinted Polymers for Lead Detection. React. Funct. Polym. 2022, 170, 105134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, A.; Besharati-seidani, A.; Abbaspour, A.; Shamsipur, M. A Highly Selective Voltammetric Sensor for Sub-Nanomolar Detection of Lead Ions Using a Carbon Paste Electrode Impregnated with Novel Ion Imprinted Polymeric Nanobeads. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 118, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Lv, X.; Meng, X.; Yu, G.; Wang, D. Removal of Pb(II) from Aqueous Solution Using Dithiocarbamate Modified Chitosan Beads with Pb(II) as Imprinted Ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 220, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Chen, W.; Peng, X.; Cao, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wang, D.; Meng, X.; Yu, G. Biosorption of Lead from Aqueous Solutions by Ion-Imprinted Tetraethylenepentamine Modified Chitosan Beads. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 86, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Hua, T.; Chen, X. Selective Adsorption of Lead on Grafted and Crosslinked Chitosan Nanoparticles Prepared by using Pb2+ as Template. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 308, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Xiao, W.; Li, G.; Yang, F.; Wu, P.; Yang, T.; Chen, C.; Ding, P. A Novel Lead Ion-Imprinted Magnetic Biosorbent: Preparation, Optimization and Characterization. Environ. Technol. 2019, 40, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-X.; Dou, Q.; Jin, X.-H.; Sun, D.-X.; Wang, D.-D.; Yang, T.-R. Magnetic Pb(II) Ion-Imprinted Polymer Prepared by Surface Imprinting Technique and its Adsorption Properties. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Liu, A.; Chen, J.P. Introduction and Demonstration of a novel Pb(II)-Imprinted Polymeric Membrane with High Selectivity and Reusability for Treatment of Lead Contaminated Water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 439, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, M.; Zhu, K. Study on the Adsorption Behavior of Glutaric Acid Modified Pb(II) Imprinted Chitosan-Based Composite Membrane to Pb(II) in Aqueous Solution. Mater. Lett. 2019, 251, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
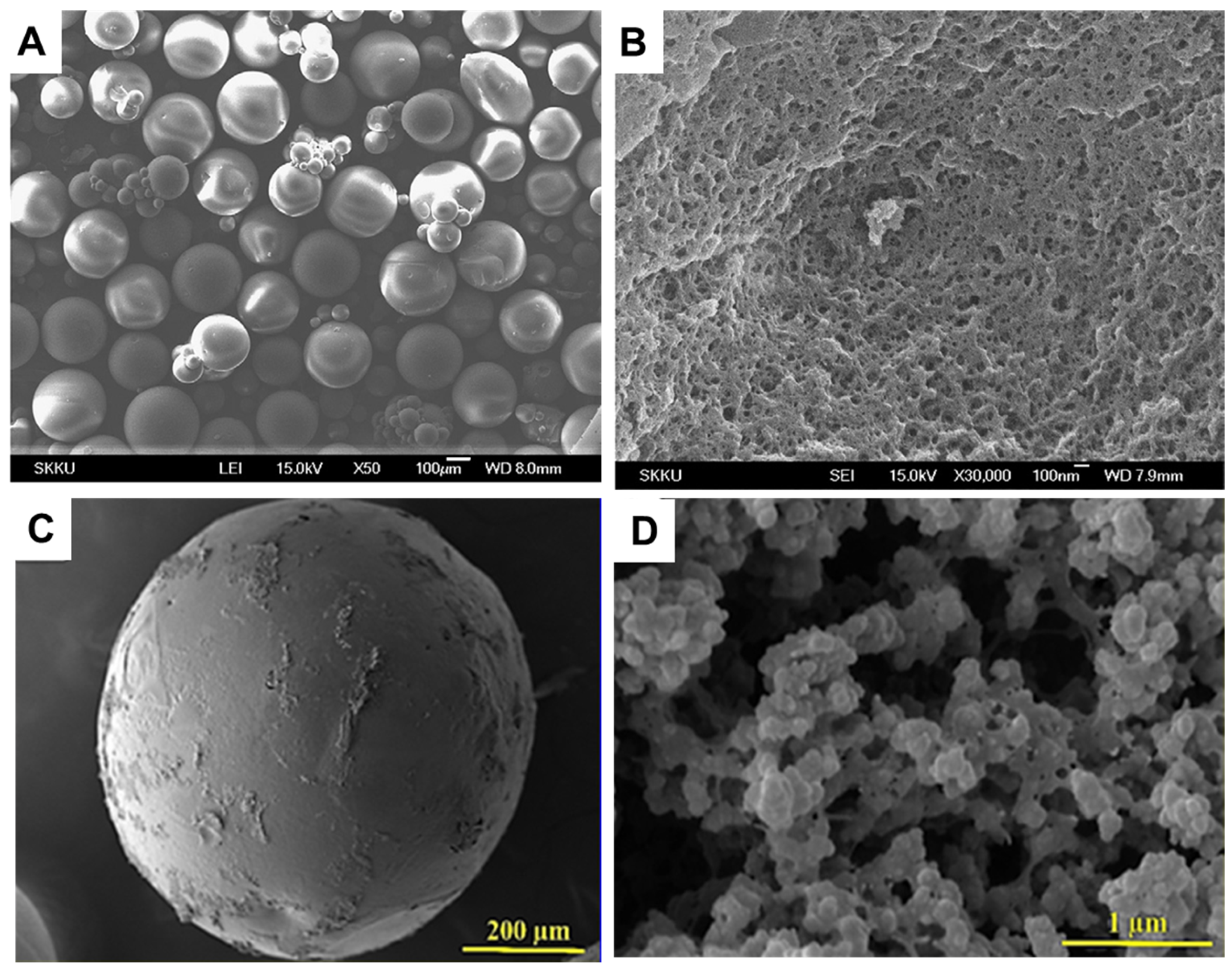



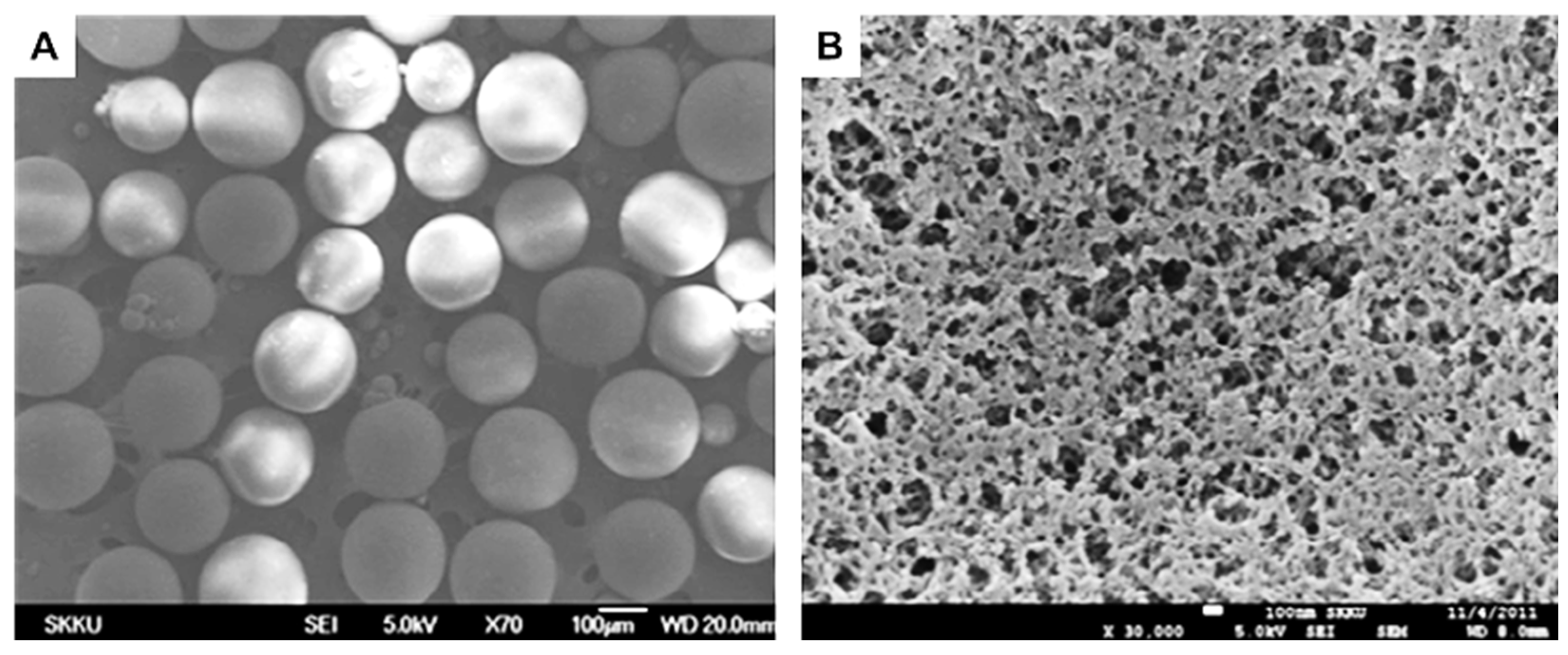


| Equation Number | Equation 1 | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Kinetic models | ||
| (3) | Pseudo-first order (PFO) model | |
| (4) | Pseudo-second order (PSO) model | |
| (5) | Intraparticle diffusion (IPD) model | |
| Isotherm models | ||
| (6) | Langmuir model | |
| (7) | Freundlich model | |
| (8) | Dubinin–Radushkevich (D–R) model | |
| (9) | Sips model | |
| (10) | Van’t Hoff equation | |
| (11) | Standard equilibrium constant | |
| (12) | Standard Gibbs free energy of sorption, kJ mol−1 | |
| Polymeric Material | Functional Groups | pH | Contact Time, min | qm, mg/g | Interfering Ions | k | Remarks on Adsorption Process | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH2-SiO2/PAAm hydrogels | –NH2 | 5 | 20 | 538 | Pb(II) Cd(II) Ni(II) | 5.58 6.05 5.89 | Batch adsorption; Fitting: Langmuir/PSO; Reusability: 6 cycles (96.8% recovery). | [48] |
| P(HEMA-co-MAH) cryogel membranes | –NH2; –COOH; –OH | 5.5 | 120 | 77.2 | Cd(II) Pb(II) Zn(II) | 3.7 11.1 2.08 | Batch adsorption; Fitting: Langmuir/PSO; Reusability: 3 cycles (97.8% recovery). | [57] |
| Fe3O4/P(HEMA-co-MAH) cryogel membranes | –NH2; –COOH; –OH | 5.5 | 120 | 179 | Cd(II) Pb(II) Zn(II) | 5.27 15.8 2.63 | Batch adsorption; Fitting: Langmuir/PSO; Reusability: 3 cycles (98.7% recovery). | [57] |
| P(MAA-co-4-VP) beads | –COOH | 6.2 | 180 | 14.92 | Ni(II) Zn(II) | 43.48 42.38 | Batch/column adsorption; Fitting: Langmuir; | [52] |
| P(MMA-co-PA) beads | –COOH | 5 | 60 | 19.2 | Zn(II) Ni(II) Co(II); | 57.7 26.8 34.0 | Batch adsorption; Reusability: 7 cycles (97% recovery). | [56] |
| Fe3O4-CS microspheres | –NH2; –OH | 5 | 480 | 109.89 | Zn(II) Ni(II) Cd(II) Cr(VI) | 38.866 7.103 31.679 2.297 | Batch adsorption; Fitting: Langmuir/PSO; Reusability: 5 cycles. | [59] |
| PAAm/CS/zeolite cryogels | –NH2; –OH | 4.5 | 20 | 260 | Co(II) Ni(II) Zn(II) Pb(II) | 7.28 24.42 47.02 34.85 | Batch adsorption, Fitting: Langmuir/PSO; Reusability: 5 cycles. | [23,42] |
| CS/zeolite cryogels | –NH2; –OH | 4.5 | 150 | 55.08 | Zn(II) Ni(II) Fe(III) Cr(III) | 4.1 4.61 1.84 11.33 | Batch adsorption; Fitting: Dubinin–Radushkevich and Sips/PSO; Reusability: 5 cycles | [43] |
| CS/ATT gels | –NH2; –OH | 5 | 60 | 35.20 | Pb(II) Cd(II) | 78.45 82.44 | Batch adsorption; Fitting: Freundlich/PSO; Reusability: 10 cycles (86% recovery) | [60] |
| ALG/CS beads | –NH2; –COOH; –OH | 5.7 | 480 | 83.33 | Zn(II) | 2.28 | Batch adsorption; Fitting: Langmuir/PFO; Reusability: 3 cycles | [61] |
| Fe3O4-CS/GO composites | –NH2; –OH | 6 | 120 | 132 | Zn(II) Ni(II) Co(II) Cd(II) | 45.44 85.04 86.9 29.83 | Batch adsorption; Fitting: Freundlich/PSO; Reusability: 5 cycles. | [62] |
| Polymeric Material | Functional Groups | pH | Contact Time, min | qm, mg/g | Interfering Ions | k | k’ | Remarks on Adsorption Process | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAm-g-CS gels | –NH2; –OH | 6 | 120 | 167 | Ag(I) Cu(II) Ni(II) Zn(II) | 4.56 4.13 4.11 4.20 | Batch adsorption; Fitting: Langmuir/PSO; Applied in selective recovery of Cd(II) ions from Ni/Cd battery waste; Reusability: 8 cycles | [74] | |
| CMCS-SiO2 composite | –NH-; –COOH; –OH | 5 | 30 | 20.7 | Pb(II) Co(II) | 5.3 1.5 | Batch/column adsorption; Fitting: PSO; | [76] | |
| ATU/N-propylmaleamic acid-functionalized SiO2 composite | –NH2; –C=S; –OH | 5 | 8 | 38.3 | Ni(II) Cu(II) Co(II) Pb(II) Zn(II) | 18.64 2.55 6.27 20.82 15.41 | Batch/column adsorption; Reusability: 6 cycles; Tested for determination and preconcentration of Cd(II) ions from synthetic, tap, lake, and mine water samples | [77] | |
| HMAM/DVE3 IPN hydrogel | –NH–; –OH | 6 | 16 | 179.86 | Cu(II) Ni(II) Pb(II) | 8.33 8.79 9.18 | Batch/column adsorption; Fitting: Freundlich/PSO; Reusability: 20 cycles (98.5% recovery) | [78] | |
| MA-co-AN/DVB microspheres | –COOH; –C≡N | 6 | 20.46 | Cu(II) Mn(II) Ni(II) Pb(II) | 15.2 4.10 9.20 3.01 | Column adsorption; Tested for Cd(II) preconcentration and determination from tap, spring, and river water samples; Reusability: 10 cycles. | [79] | ||
| 1-VI/MP/TRIM polymer resin | –N=; –SH; –OH | 7.2 | 120 | 16.99 | Pb(II) Zn(II) Hg(II) Cu(II) Ni(II) Ca(II) Mg(II) Na(I) | 67.4 13.9 1.2 9.7 6.4 168.9 69.1 42.6 | Batch adsorption; Fitting: Langmuir/PSO; Reusability: 4 cycles. | [80] | |
| 1-VI/AMP/TRIM polymer resin | –N=; –NH2; –OH | 7.2 | 120 | 10.40 | Pb(II) Zn(II) Hg(II) Cu(II) Ni(II) Ca(II) Mg(II) Na(I) | 24.4 5.2 1.1 1.1 1.1 194.3 624.6 10.0 | Batch adsorption; Fitting: Langmuir/PSO; Reusability: 4 cycles. | [80] |
| Polymeric Material | Functional Groups | pH | Contact Time, min | qm, mg/g | Interfering Ions | k | Remarks on Adsorption Process | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS films | –NH2; –OH | 4 | 240 | 20 | Zn(II) Cd(II) Co(II) Mg(II) Ca(II) Mn(II) | 20.352 7.138 56.980 8.888 55.150 49.249 | Batch adsorption; Fitting: Langmuir/PSO Selectivity coefficients: Reusability: 5 cycles | [101] |
| CS foam | –NH2; –OH | 6 | 120 | 69.93 | Co(II) Mn(II) | 3.63 3.88 | Batch adsorption; Fitting: Langmuir/PSO; Reusability: 5 cycles | [102] |
| Fe3O4-CS/PVA beads | –NH2; –OH | 5.5 | 360 | 500 | Cu(II) Ag(I) Zn(II) | 15.05 23.06 18.25 | Batch/Column adsorption; Fitting: Langmuir/PSO Reusability: 10 cycles | [103] |
| CS-AA/Fe3O4/MWCNTs | –NH2; –COOH; –OH | 6 | 40 | 19.86 | Pb(II) Cu(II) | 13.09 4.42 | Batch adsorption; Fitting: Freundlich/PSO; Reusability: 5 cycles | [104] |
| Melamine grafted CS/activated carbon biocomposite | –NH2; –N=; –OH | 5 | 120 | 109.86 | Zn(II) Cd(II) Cu(II) Pb(II) | 3.13 4.48 3.72 2.51 | Batch adsorption; Fitting: Langmuir/PFO; Reusability: 5 cycles | [105] |
| CMCS microspheres | –NH-; –COOH; –OH | 6 | 360 | 82.78 | Co(II) Mn(II) Cd(II) | 5.64 2.68 2.06 | Batch adsorption; Fitting: Langmuir/PFO; Reusability: 4 cycles | [106] |
| Fe3O4-CS nanoparticles | –NH2; –OH | 7 | 60 | 18.5 | Cu(II) Zn(II) | 3.02 14.35 | Batch adsorption; Fitting: Langmuir/PSO; Reusability: 15 cycles | [107] |
| PHEMA-MAH cryogels | –NH2; –COOH; –OH | 6.5 | 60 | 5.54 | Fe(III) Zn(II) Cu(II) | 4.3 3.6 4.2 | Batch adsorption; Fitting: Langmuir/Freundlich Reusability: 10 cycles | [108] |
| Fe3O4/bentonite/CoFe2O4/SiO2@ PVA nanocomposites | –OH | 5.5 | 120 | 33.76 | Cu(II) Zn(II) Cd(II) | 3.768 2.507 2.149 | Batch adsorption; Fitting: Langmuir/PSO; Reusability: 5 cycles | [109] |
| ALG beads | –COOH; –OH | 7 | 1440 | 352.14 | Cu(II) Co(II) Zn(II) | 6.38 6.62 7.10 | Batch adsorption; Fitting: Langmuir/Freundlich Reusability: 5 cycles | [110] |
| 2-(Allylmercapto) nicotinic acid (ANA) composites | –N=; –S–; –COOH | 6 | 20 | 38.85 | Cd(II) Co(II) Cu(II) Mg(II) Zn(II) | 16.89 4.23 32.74 219.59 33.63 | Batch adsorption; Fitting: Langmuir/PSO; Reusability: 5 cycles | [111] |
| PMAA/diphenylcarbazide composites | –COOH; –NH– | 7 | 30 | 86.3 | Na(I) K(I) Mg(II) Ca(II) Ba(II) Al(III) | 2.107 3.079 5.333 2.436 1.775 3.908 | Batch adsorption; Fitting: Freundlich/PSO; Reusability: 5 cycles | [112] |
| Template Ions | Polymeric Material | Functional Groups | pH | Contact Time, min | qm, mg/g | Interfering Ions | k | Remarks on Adsorption Process | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U(VI) | CS/PVA cross-linked hydrogel | –NH2; –OH | 5–6 | 120 | 156 | Th(IV) Cu(II) Zn(II) Fe(III) Co(II) Ni(II) Mn(II) | 6.11 5.05 9.52 7.07 11.51 7.50 9.71 | Batch adsorption; Fitting: Langmuir/PSO | [187] |
| U(VI) | Amidoxime modified CS | –NH2; –OH | 5 | 180 | 332 | Th(IV) Al(III) Eu(III) Fe(III) Co(II) Ni(II) Cu(II) Pb(II) | 9.47 16.78 12.91 11.14 17.73 17.24 10.55 21.97 | Batch adsorption; Fitting: Langmuir/PSO; Reusability: 5 cycles | [189] |
| U(VI) | Honeycomb-like CS/kaoline clay | –NH2; –OH | 5 | 120 | 286.85 | Fe(III) Al(III) Mn(II) Co(II) Ni(II) Ca(II) Mg(II) Cu(II) Na(I) K(I) | 7.2 10.66 12.87 14.04 18.10 25.41 45.34 4.91 84.73 64.17 | Batch adsorption; Fitting: Langmuir/PSO; Reusability: 5 cycles | [190] |
| U(VI) | CMC-SAL | –OH; –N= | 5 | 180 | 180 | Fe(III) Mn(II) Co(II) Cu(II) V(V) | 34.51 21.55 82.54 42.14 50.27 | Batch adsorption; Fitting: Langmuir/PSO; Reusability: 5 cycles | [191] |
| Th(IV) | Salophen Schiff base magnetic IIP | –OH; –N= | 4 | 30 | 42.54 | La(III) Ce(III) Nd(III) U(VI) | 649.2 595.8 96.6 71.1 | Batch adsorption; Fitting: Langmuir/PSO; Reusability: 9 cycles | [192] |
| Gd(III) | MWCNTs-PDA-CS-GO | –NH2; –OH | 7 | 150.86 | Dy(III) Nd(III) Pr(III) | 48.02 25.98 36.06 | Batch adsorption; Fitting: Langmuir/PSO; Reusability: 5 cycles | [195] | |
| Gd(III) | COOH-CNTs/CS-IIS sponge | –NH2; –COOH; –OH | 7 | 720 | 71.95 | Nd(III) Pr(III) Tb(III) Fe(III) | 9.95 9.69 4.48 28.35 | Batch adsorption; Fitting: Langmuir/PSO; Reusability: 5 cycles | [196] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lazar, M.M.; Ghiorghita, C.-A.; Dragan, E.S.; Humelnicu, D.; Dinu, M.V. Ion-Imprinted Polymeric Materials for Selective Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions from Aqueous Solution. Molecules 2023, 28, 2798. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062798
Lazar MM, Ghiorghita C-A, Dragan ES, Humelnicu D, Dinu MV. Ion-Imprinted Polymeric Materials for Selective Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions from Aqueous Solution. Molecules. 2023; 28(6):2798. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062798
Chicago/Turabian StyleLazar, Maria Marinela, Claudiu-Augustin Ghiorghita, Ecaterina Stela Dragan, Doina Humelnicu, and Maria Valentina Dinu. 2023. "Ion-Imprinted Polymeric Materials for Selective Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions from Aqueous Solution" Molecules 28, no. 6: 2798. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062798
APA StyleLazar, M. M., Ghiorghita, C.-A., Dragan, E. S., Humelnicu, D., & Dinu, M. V. (2023). Ion-Imprinted Polymeric Materials for Selective Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions from Aqueous Solution. Molecules, 28(6), 2798. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062798








