Chemical and Thermal Characteristics of Ion-Exchanged Lignosulfonate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
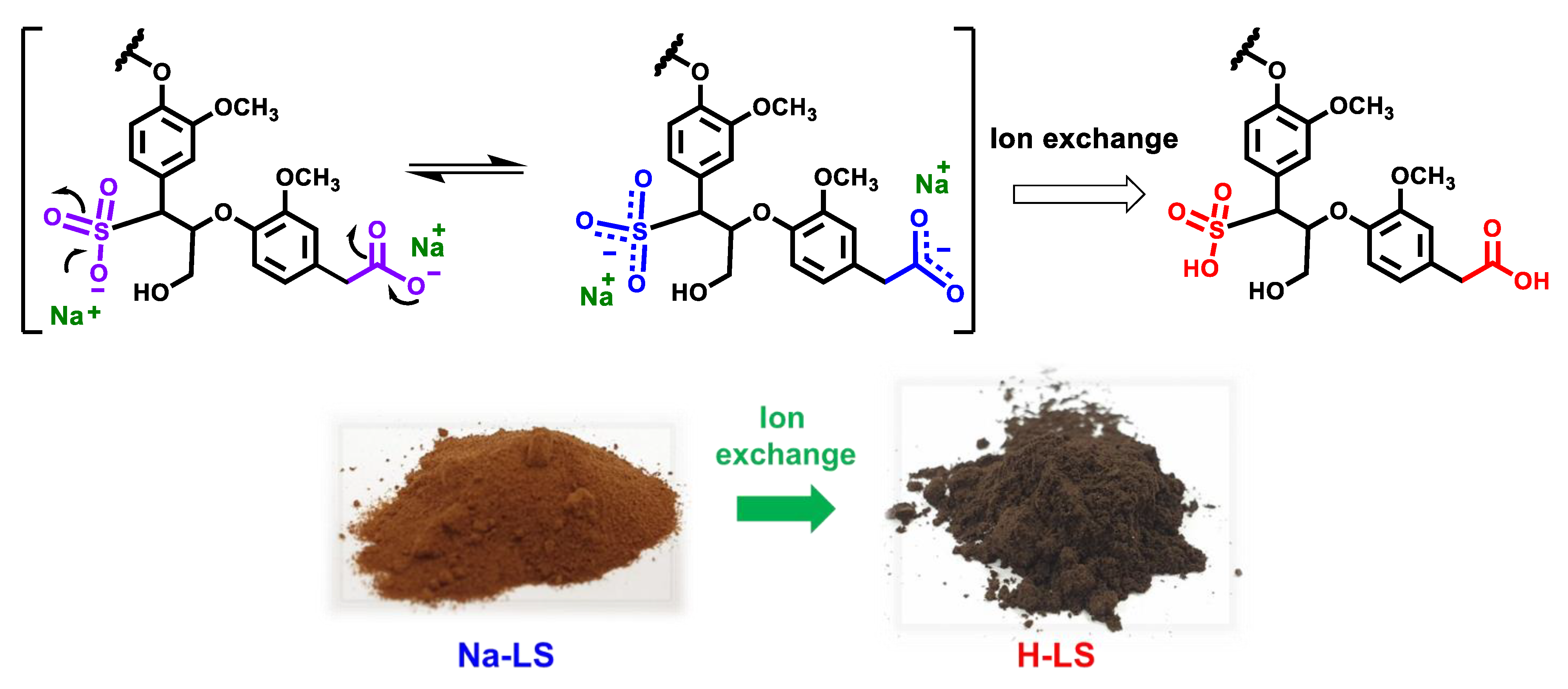
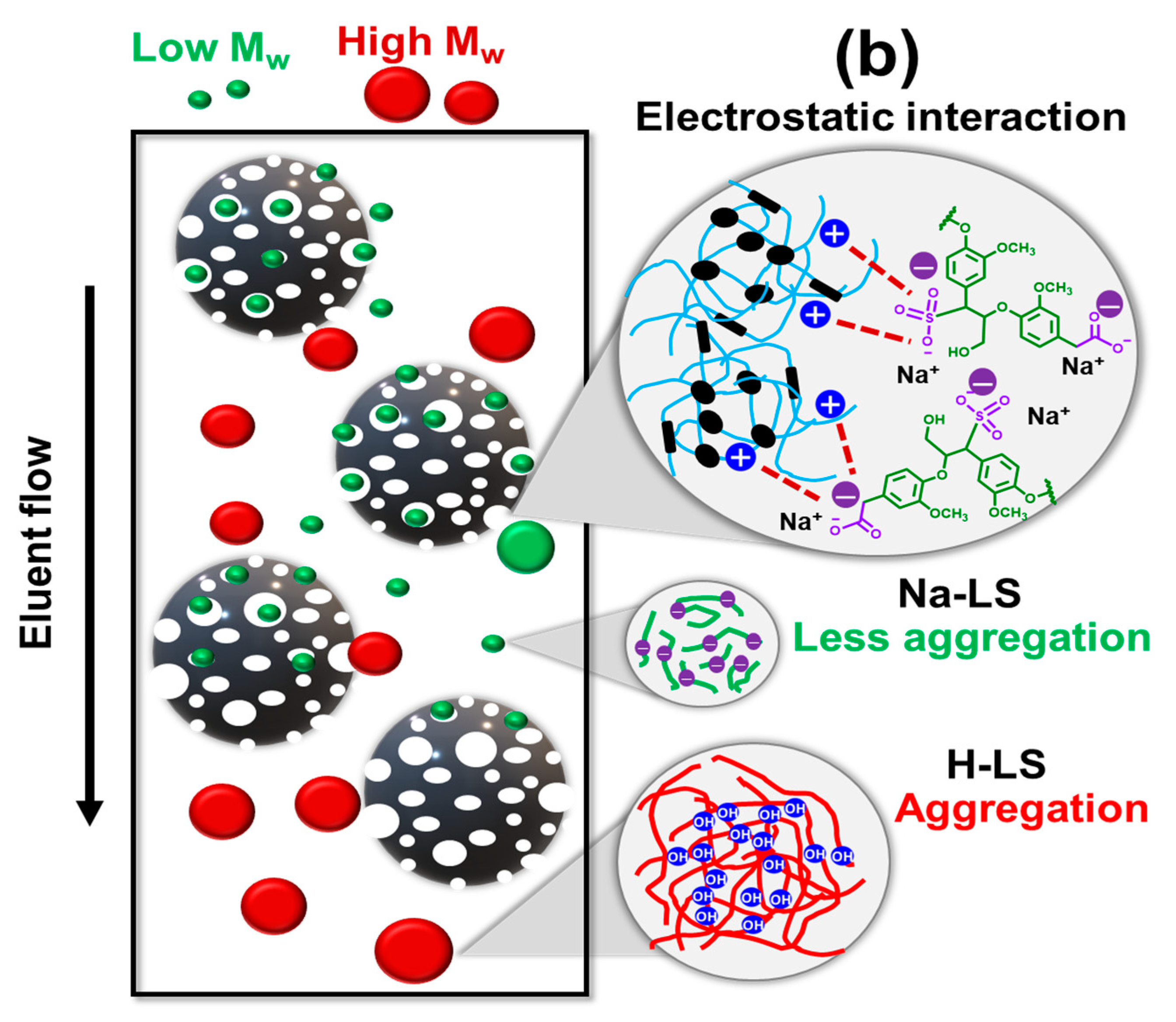
2.1. Ion-Exchanged Lignosulfonate
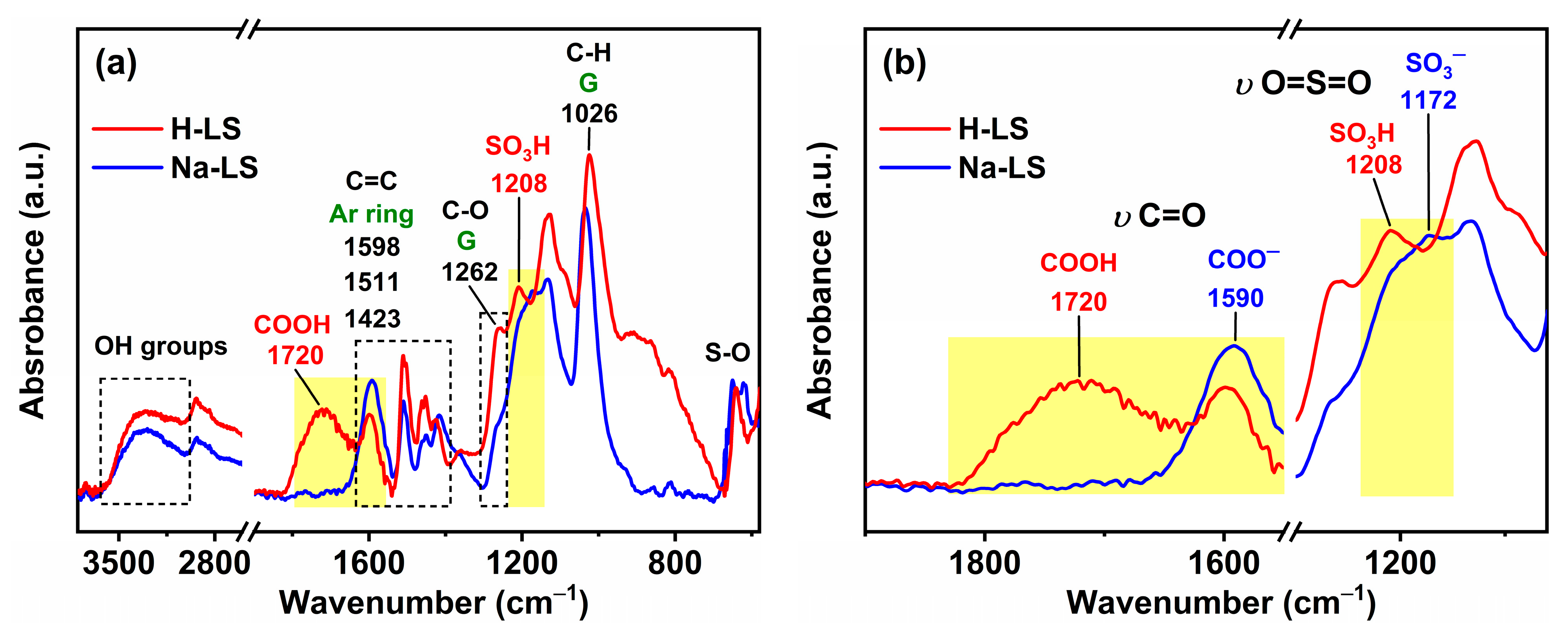
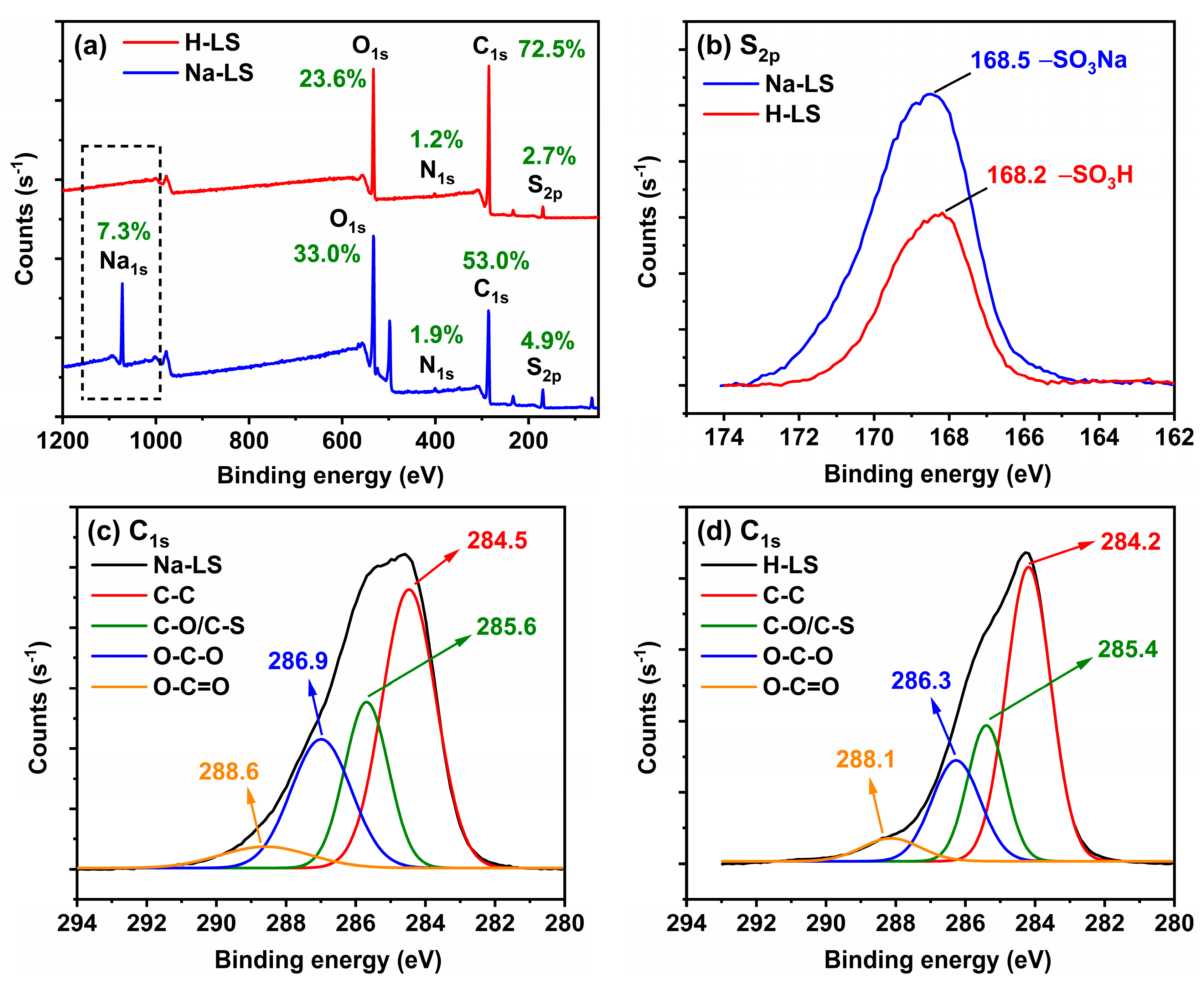
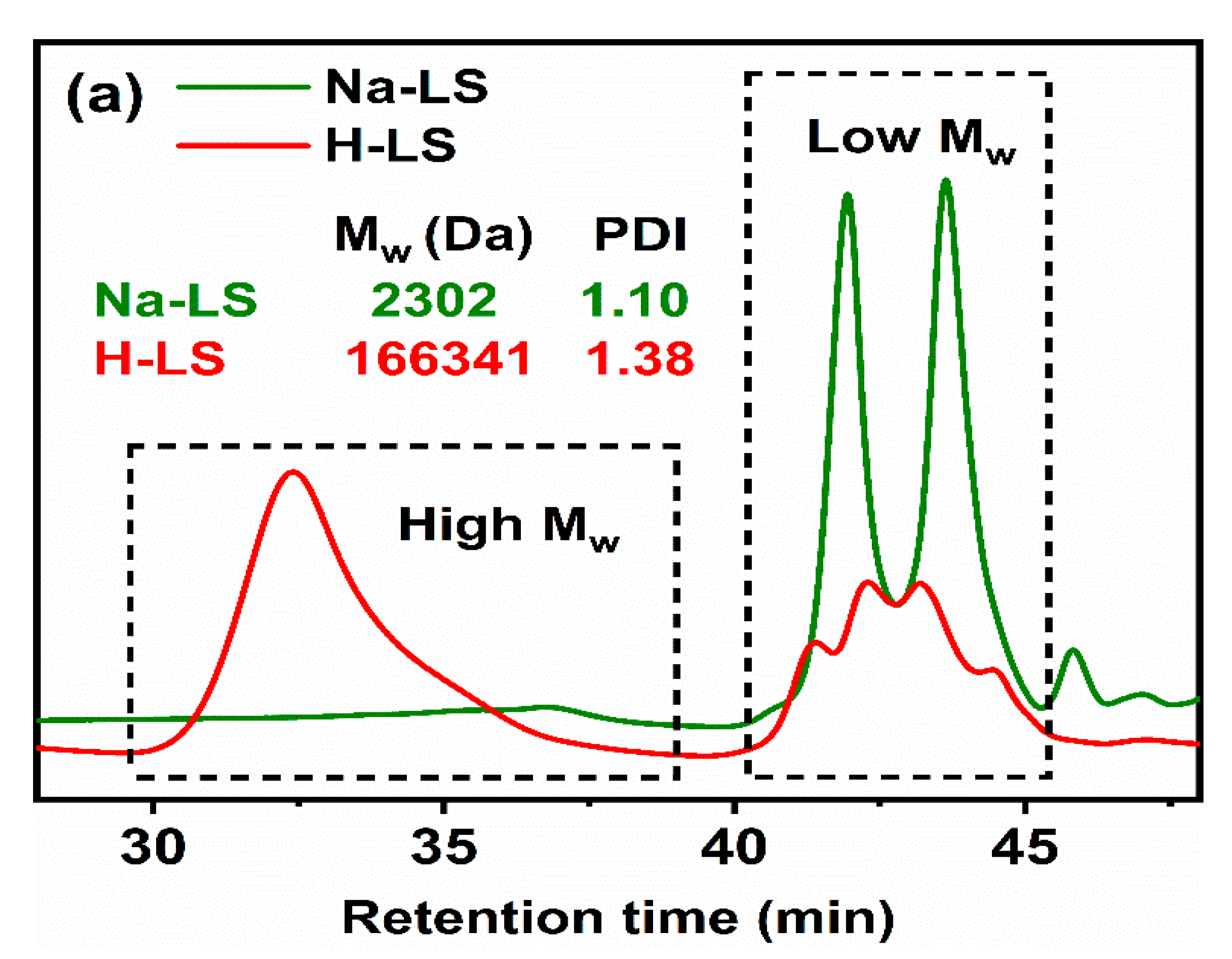
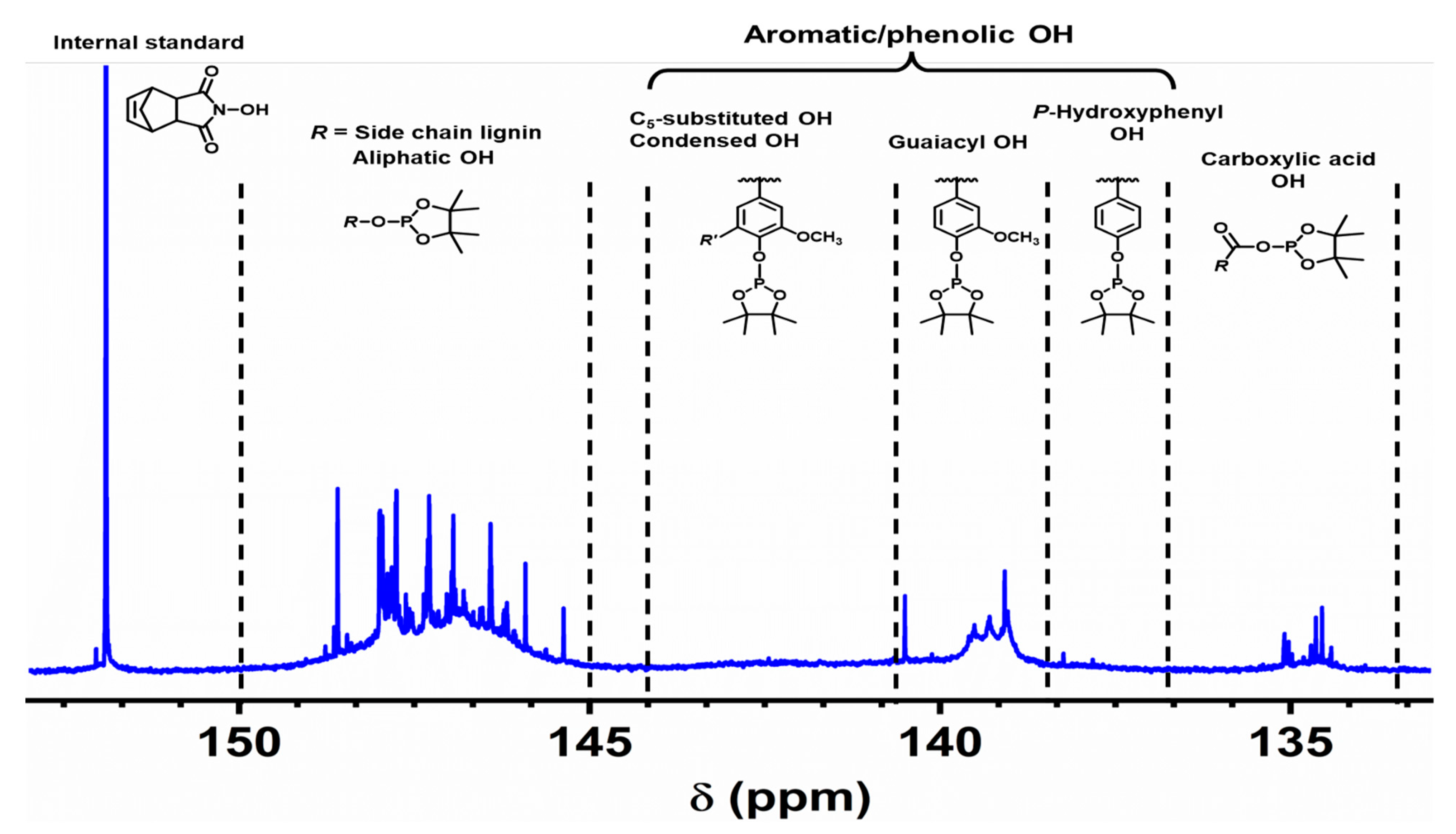
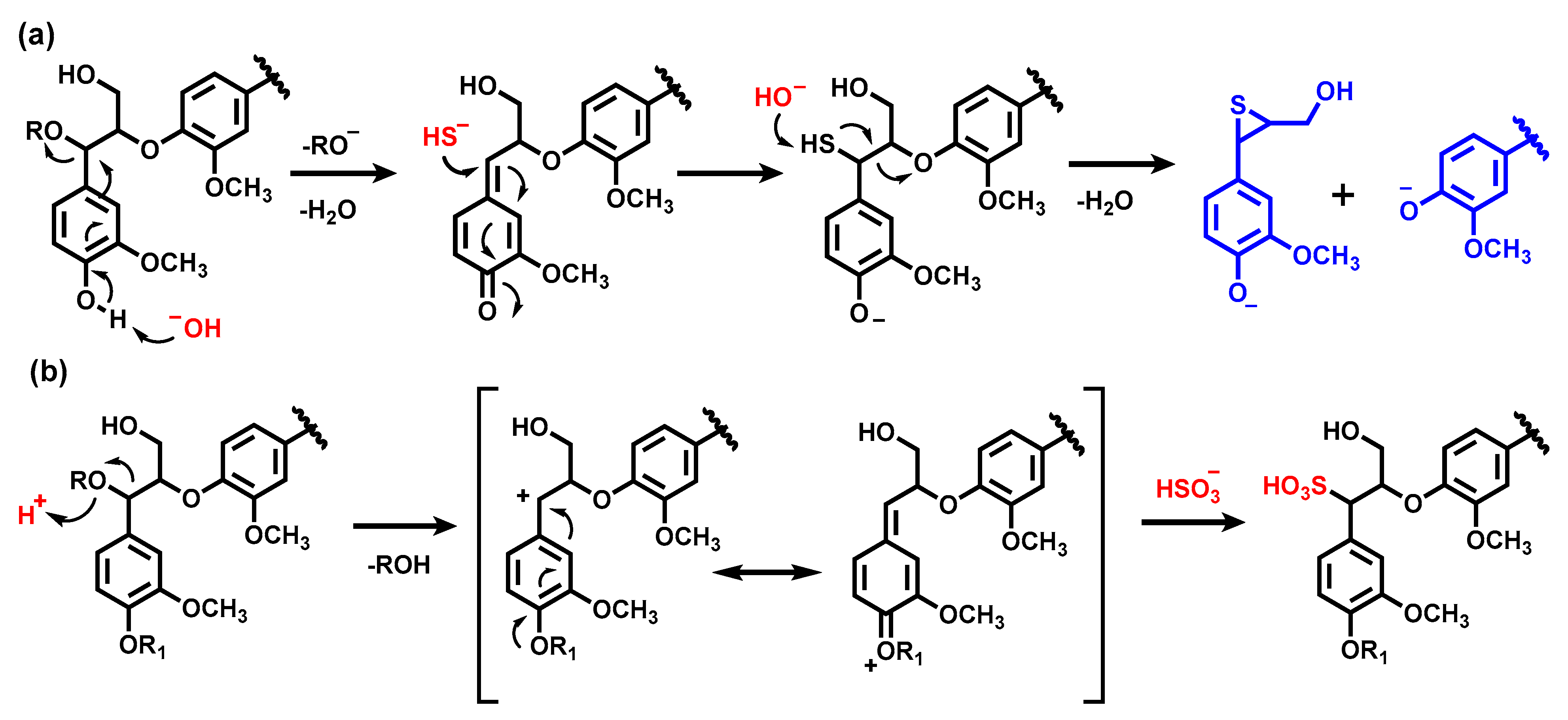
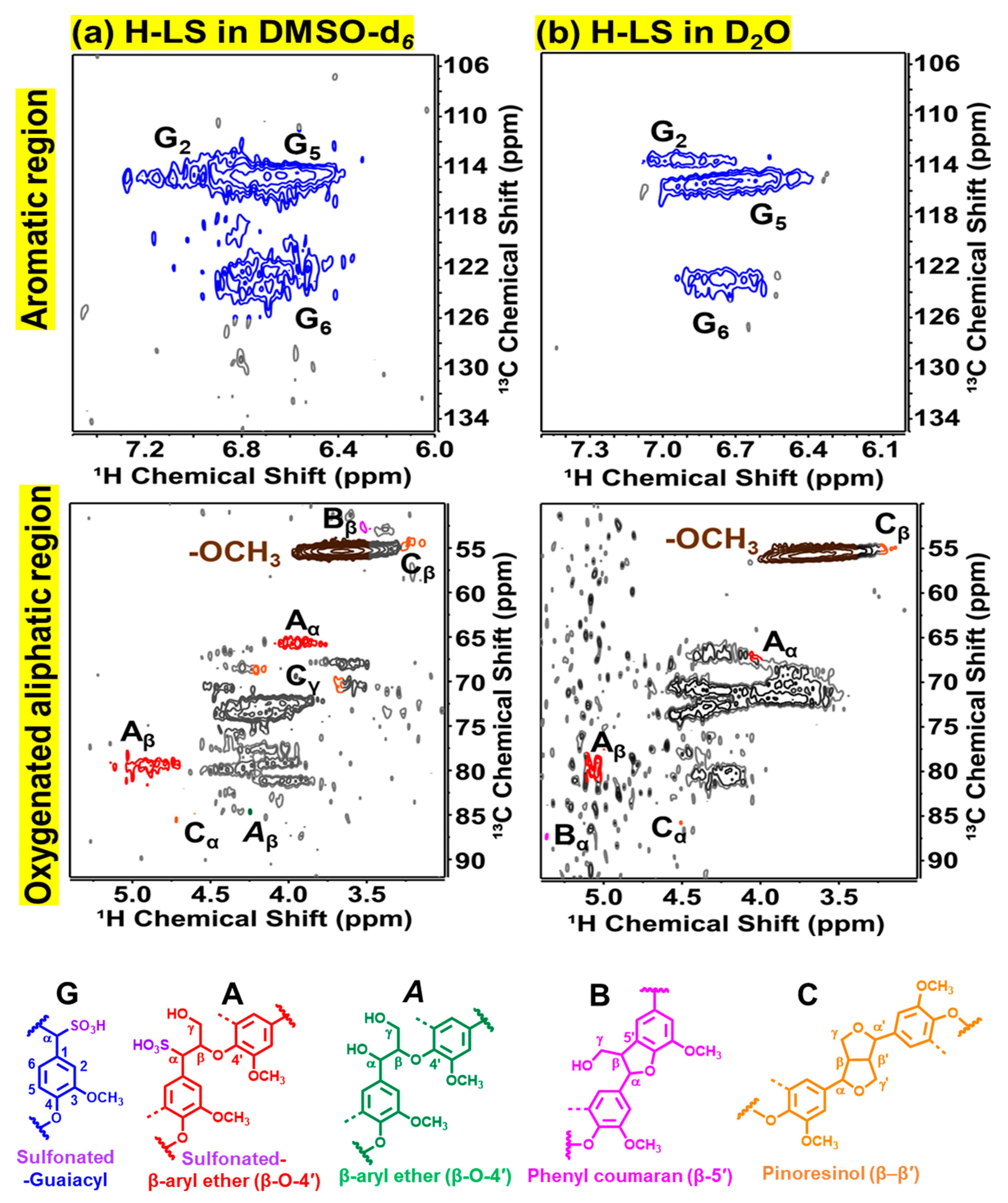
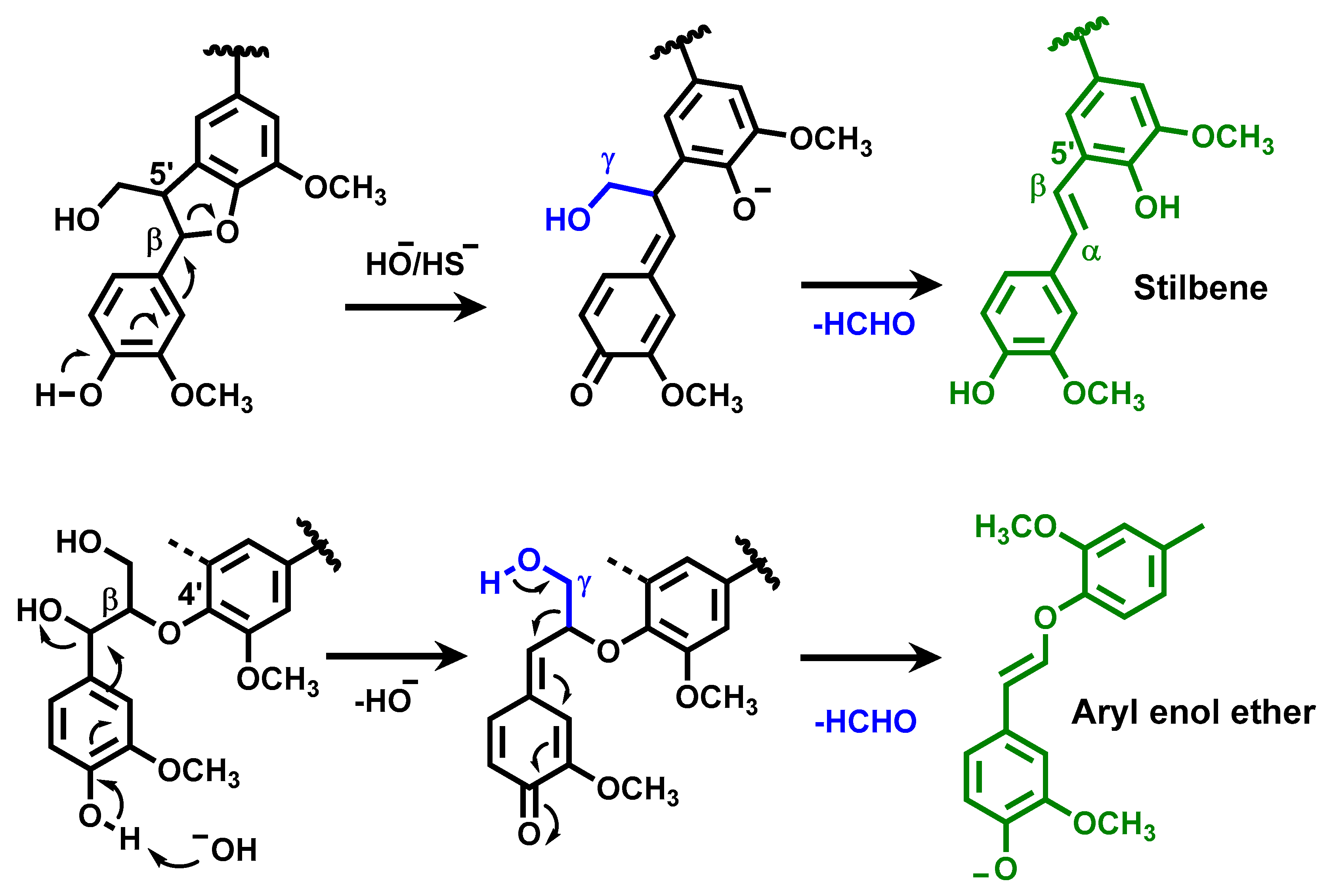
2.2. Chemical Structure of Ion-Exchanged Lignosulfonate
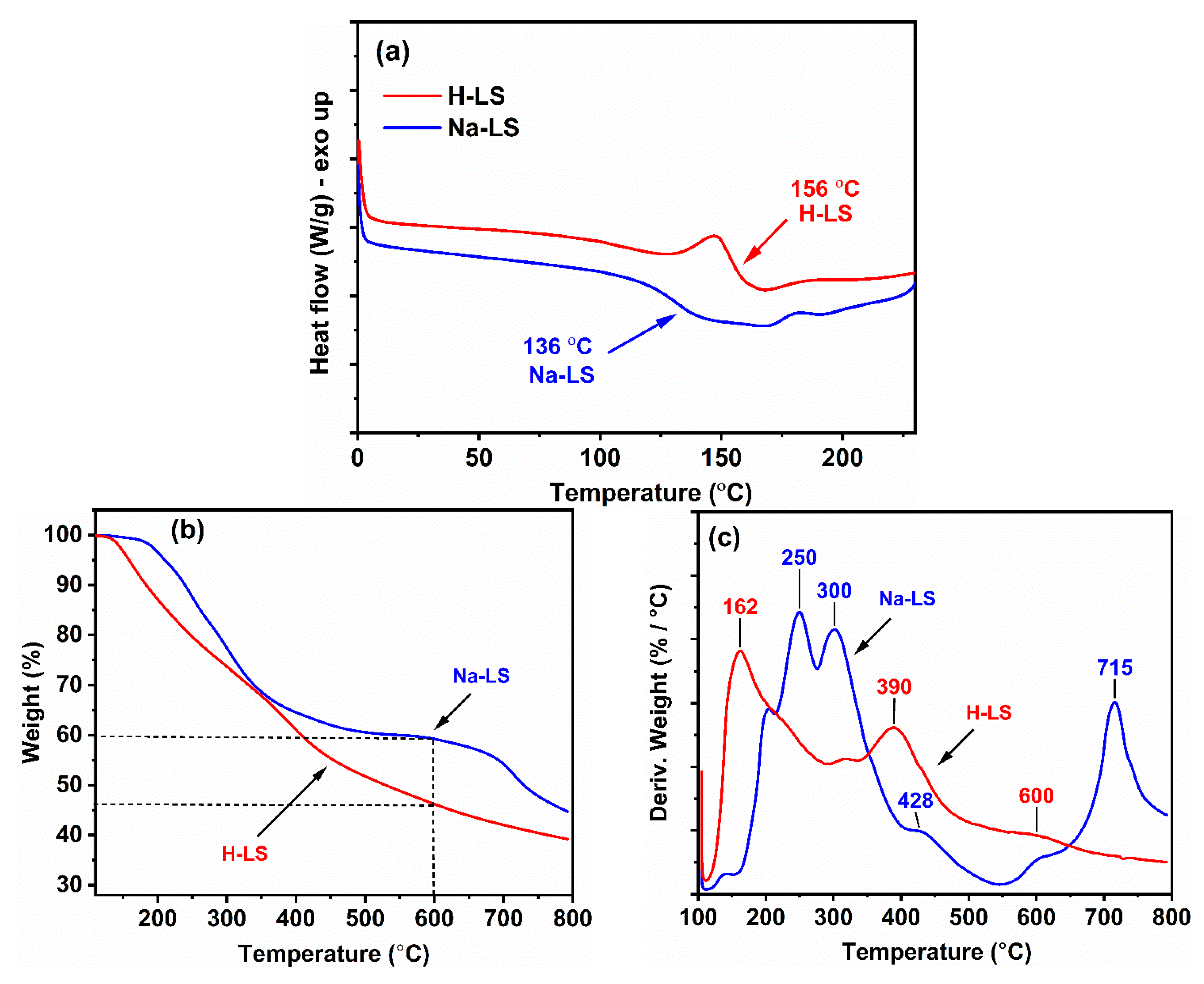
2.3. Thermal Behavior of Ion-Exchanged Lignosulfonate
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials
3.2. Ion Exchange Procedure
3.3. Attenuated Total Reflection-FTIR (ATR-FTIR) Spectroscopy
3.4. Elemental Analysis and Ash Content
3.5. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Analysis
3.6. Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC) Analysis
3.7. Quantitative 31P Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
3.8. 1H–13C Heteronuclear Single Quantum Coherence (HSQC) NMR Spectroscopy
3.9. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Analysis
3.10. Thermogravimetric Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Sadeghifar, H.; Ragauskas, A. Perspective on Technical Lignin Fractionation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 8086–8101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhao, X.; Wang, A.; Huber, G.W.; Zhang, T. Catalytic Transformation of Lignin for the Production of Chemicals and Fuels. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 11559–11624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourençon, T.V.; Hansel, F.A.; Da Silva, T.A.; Ramos, L.P.; De Muniz, G.I.B.; Magalhães, W.L.E. Hardwood and Softwood Kraft Lignins Fractionation by Simple Sequential Acid Precipitation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 154, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthäuser, J.; Biziks, V.; Mai, C.; Militz, H. Lignin and Lignin-Derived Compounds for Wood Applications—A Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishtal, A.; Kraslawski, A. Challenges in Industrial Applications of Technical Lignins. BioResources 2011, 6, 3547–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Eraghi Kazzaz, A.; AlipoorMazandarani, N.; Hosseinpour Feizi, Z.; Fatehi, P. Production of Flocculants, Adsorbents, and Dispersants from Lignin. Molecules 2018, 23, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winestrand, S.; Järnström, L.; Jönsson, L.J. Fractionated Lignosulfonates for Laccase-Catalyzed Oxygen-Scavenging Films and Coatings. Molecules 2021, 26, 6322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, Y. Conversion of Technical Lignins to Functional Materials with Retained Polymeric Properties. J. Wood Sci. 2015, 61, 230–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chen, W.; Zhong, L.; Peng, X.; Sun, R.; Fang, J.; Zheng, S. Conversion of Xylose into Furfural Using Lignosulfonic Acid as Catalyst in Ionic Liquid. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 7430–7435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D. Preparation of a Sulfonated Carbonaceous Material from Lignosulfonate and Its Usefulness as an Esterification Catalyst. Molecules 2013, 18, 8168–8180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Peng, X.W.; Zhong, L.X.; Li, Y.; Sun, R.C. Lignosulfonic Acid: A Renewable and Effective Biomass-Based Catalyst for Multicomponent Reactions. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 1366–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesari, L.; Mutelet, F.; Canabady-Rochelle, L. Antioxidant Properties of Phenolic Surrogates of Lignin Depolymerisation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 129, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, B.; Yang, S.; Fang, W.; Yuan, T.Q.; Argyropoulos, D.S.; Sun, R.C. Structure-Property Relationships for Technical Lignins for the Production of Lignin-Phenol-Formaldehyde Resins. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 108, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Crestini, C.; Ben, H.; Hao, N.; Pu, Y.; Ragauskas, A.J.; Argyropoulos, D.S. Determination of Hydroxyl Groups in Biorefinery Resources via Quantitative 31P NMR Spectroscopy. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 2627–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korntner, P.; Sumerskii, I.; Bacher, M.; Rosenau, T.; Potthast, A. Characterization of Technical Lignins by NMR Spectroscopy: Optimization of Functional Group Analysis by 31P NMR Spectroscopy. Holzforschung 2015, 69, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uraki, Y.; Chen, C.L.; Gratzl, J.S. Sonolysis of Chloro-Organics in Bleach Plant E-1 Effluents. Holzforschung 1997, 51, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stücker, A.; Podschun, J.; Saake, B.; Lehnen, R. A Novel Quantitative 31P NMR Spectroscopic Analysis of Hydroxyl Groups in Lignosulfonic Acids. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 3481–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; McDonald, A.G. Fractionation and Characterization of Industrial Lignins. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2014, 62, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodil Cherif, M.; Trache, D.; Brosse, N.; Benaliouche, F.; Tarchoun, A.F. Comparison of the Physicochemical Properties and Thermal Stability of Organosolv and Kraft Lignins from Hardwood and Softwood Biomass for Their Potential Valorization. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 6541–6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komisarz, K.; Majka, T.M.; Pielichowski, K. Chemical Transformation of Lignosulfonates to Lignosulfonamides with Improved Thermal Characteristics. Fibers 2022, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmilä, V.; Hosseinpourpia, R.; Adamopoulos, S.; Eceiza, A. Characterization of Wood-Based Industrial Biorefinery Lignosulfonates and Supercritical Water Hydrolysis Lignin. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 5835–5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Max, J.-J.; Chapados, C. Infrared Spectroscopy of Aqueous Carboxylic Acids: Comparison between Different Acids and Their Salts. J. Phys. Chem. A 2004, 108, 3324–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Fu, S.; Chen, Y. Basic Understanding of the Color Distinction of Lignin and the Proper Selection of Lignin in Color-Depended Utilizations. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 147, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazachenko, A.S.; Vasilieva, N.Y.; Malyar, Y.N.; Karacharov, A.A.; Kondrasenko, A.A.; Levdanskiy, A.V.; Borovkova, V.S.; Miroshnikova, A.V.; Issaoui, N.; Kazachenko, A.S.; et al. Sulfation of Arabinogalactan with Ammonium Sulfamate. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, L.; Uribe, L.; Hernandez, V.; Vidal, C.; Texeira Mendonça, R. Assessment of the Use of Lignosulfonates to Separate Chalcopyrite and Molybdenite by Flotation. Powder Technol. 2020, 359, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahvazi, B.; Cloutier, É.; Wojciechowicz, O.; Ngo, T.D. Lignin Profiling: A Guide for Selecting Appropriate Lignins as Precursors in Biomaterials Development. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 5090–5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, O.Y.; Meier, S.; Prothmann, J.; Turner, C.; Riisager, A.; Hulteberg, C.P. Oxidative Depolymerisation of Lignosulphonate Lignin into Low-Molecular-Weight Products with Cu–Mn/δ-Al2O3. Top. Catal. 2019, 62, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, C.; Hu, C.; Hu, Q.; Sun, C.; Li, L.; Liang, X.; Dong, Y.; Gu, X. Effective Depolymerization of Sodium Lignosulfonate over SO42−/TiO2 Catalyst. Catalysts 2020, 10, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibowo, E.S.; Park, B. The Role of Acetone-Fractionated Kraft Lignin Molecular Structure on Surface Adhesion to Formaldehyde-Based Resins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 225, 1449–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mun, J.S.; Pe, J.A.; Mun, S.P. Chemical Characterization of Kraft Lignin Prepared from Mixed Hardwoods. Molecules 2021, 26, 4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.; Seydibeyoĝlu, M.Ö.; Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M. Characterization of Industrial Lignins for Their Utilization in Future Value Added Applications. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 4230–4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, X.; Ke, L.; Qiu, X.; Guo, Y.; Pang, Y. Sulfonation of Alkali Lignin and Its Potential Use in Dispersant for Cement. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2009, 30, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melilli, G.; Adolfsson, K.H.; Impagnatiello, A.; Rizza, G.; Hakkarainen, M. Intriguing Carbon Flake Formation during Microwave-Assisted Hydrothermal Carbonization of Sodium Lignosulfonate. Glob. Challenges 2020, 4, 1900111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Xing, C.; Li, B.; Shen, W. Spherical Carbon with SO3H Groups as an Efficient Solid Acid Catalyst for 2,4,5-Triphenyl–Imidazole Synthesis. ChemistrySelect 2016, 1, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myrvold, B.O. A New Model for the Structure of Lignosulphonates. Part 1. Behaviour in Dilute Solutions. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2008, 27, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Li, J. Aqueous Gel Permeation Chromatographic Methods for Technical Lignins. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2000, 20, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, M.V.; Oliet, M.; Rodríguez, F.; García, J.; Gilarranz, M.A.; Rodríguez, J.J. Modification of Ammonium Lignosulfonate by Phenolation for Use in Phenolic Resins. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 1013–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredheim, G.E.; Braaten, S.M.; Christensen, B.E. Molecular Weight Determination of Lignosulfonates by Size-Exclusion Chromatography and Multi-Angle Laser Light Scattering. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 942, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, L.; Liu, L.Y.; Cho, M.; Karaaslan, M.A.; Renneckar, S. Revisiting the Molar Mass and Conformation of Derivatized Fractionated Softwood Kraft Lignin. Biomacromolecules 2022, 23, 708–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demuner, I.F.; Colodette, J.L.; Demuner, A.J.; Jardim, C.M. Biorefinery Review: Wide-Reaching Products through Kraft Lignin. BioResources 2019, 14, 7543–7581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yoo, C.G.; Pu, Y.; Ragauskas, A.J. 31P NMR Chemical Shifts of Solvents and Products Impurities in Biomass Pretreatments. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 1265–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giummarella, N.; Lindén, P.A.; Areskogh, D.; Lawoko, M. Fractional Profiling of Kraft Lignin Structure: Unravelling Insights on Lignin Reaction Mechanisms. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 1112–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáez-Jiménez, V.; Baratto, M.C.; Pogni, R.; Rencoret, J.; Gutiérrez, A.; Santos, J.I.; Martínez, A.T.; Ruiz-Dueñas, F.J. Demonstration of Lignin-to-Peroxidase Direct Electron Transfer: A Transient-State Kinetics, Directed Mutagenesis, EPR, and NMR Study. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 23201–23213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khokarale, S.G.; Le-That, T.; Mikkola, J.P. Carbohydrate Free Lignin: A Dissolution-Recovery Cycle of Sodium Lignosulfonate in a Switchable Ionic Liquid System. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 7032–7040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magina, S.; Marques, A.P.; Evtuguin, D.V. Study on the Residual Lignin in Eucalyptus Globulus Sulphite Pulp. Holzforschung 2015, 69, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitschke, N.; Vemulapalli, S.P.B.; Dittmar, T. NMR Spectroscopy of Dissolved Organic Matter: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.P.; Evtuguin, D.V.; Magina, S.; Amado, F.M.L.; Prates, A. Structure of Lignosulphonates from Acidic Magnesium-Based Sulphite Pulping of Eucalyptus Globulus. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2009, 29, 337–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Li, F.; Cao, X.; Sun, R. Production of Vanillin from Lignin: The Relationship between β-O-4 Linkages and Vanillin Yield. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 116, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crestini, C.; Lange, H.; Sette, M.; Argyropoulos, D.S. On the Structure of Softwood Kraft Lignin. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 4104–4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uraki, Y.; Sugiyama, Y.; Koda, K.; Kubo, S.; Kishimoto, T.; Kadla, J.F. Thermal Mobility of β-O-4-Type Artificial Lignin. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, M.; Liu, C.; Zhang, A.; Sun, R. Ring-Opening Graft Polymerization of Propylene Carbonate onto Xylan in an Ionic Liquid. Molecules 2015, 20, 6033–6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Shu, F.; He, C.; Liu, S.; Leksawasdi, N.; Wang, Q.; Qi, W.; Alam, M.A.; Yuan, Z.; Gao, Y. Preparation and Investigation of Highly Selective Solid Acid Catalysts with Sodium Lignosulfonate for Hydrolysis of Hemicellulose in Corncob. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 10922–10929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Hu, J.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, R. Thermal Conversion of Lignin to Phenols: Relevance between Chemical Structure and Pyrolysis Behaviors. Fuel 2016, 182, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.L.; Xue, B.L.; Sun, S.L.; Sun, R.C. Quantitative Structural Characterization and Thermal Properties of Birch Lignins after Auto-Catalyzed Organosolv Pretreatment and Enzymatic Hydrolysis. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 88, 1663–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaranto, J.; Mavrikakis, M. Density Functional Theory Studies of HCOOH Decomposition on Pd(111). Surf. Sci. 2016, 650, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sameni, J.; Krigstin, S.; dos Santos Rosa, D.; Leao, A.; Sain, M. Thermal Characteristics of Lignin Residue from Industrial Processes. BioResources 2013, 9, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, X.; Deng, Y.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, P.; Qiu, X. Adsorption Characteristics of Lignosulfonates in Salt-Free and Salt-Added Aqueous Solutions. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 3313–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xue, Y.; Wu, J.; Wu, H.; Qin, G.; Li, C.; Ding, J.; Liu, J.; Gan, L.; Long, M. Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Hemicelluloses from Miscanthus to Monosaccharides or Xylo-Oligosaccharides by Recombinant Hemicellulases. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2016, 79, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample | C (%) | H (%) | N (%) | S (%) | O (%) | O/C Ratio | Ash Content (%) | SO3Na/SO3H Density * (mmol/g) | Empirical Formula |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na-LS | 42.26 | 4.55 | 1.04 | 6.85 | 26.83 | 0.63 | 18.46 ± 2.1 | 2.14 | C3.52H4.55N0.07S0.21O1.68 |
| H-LS | 48.98 | 5.46 | 1.07 | 7.59 | 35.46 | 0.72 | 1.44 ± 0.1 | 2.37 | C4.08H5.46N0.08S0.24O2.22 |
| OH Content | H-LS (mmol/g) | SKL (mmol/g) * | HKL (mmol/g) * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aliphatic OH | 2.44 | 2.27 | 1.14 |
| Aromatic/Phenolic OH | 1.03 | 3.52 | 3.75 |
| Syringyl OH | 0.00 | 0.17 | 1.52 |
| Condensed OH/ other C5-substituted | 0.39 | 1.26 | 1.00 |
| Guaiacyl OH | 0.56 | 1.86 | 0.98 |
| p-Hydroxyphenyl OH | 0.08 | 0.23 | 0.25 |
| Carboxylic OH | 0.20 | 0.32 | 0.48 |
| Lignin Units | Abundance (per 100 Aromatic Units) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H-LS (DMSO-d6) | H-LS (D2O) | SKL * | HKL * | |
| (A) Sulfonated β-O-4′ | 41.4 | 38.9 | - | - |
| (A) β-aryl ether (β-O-4′) | 1.2 | - | 7.2 | 3.4 |
| (B) Phenyl coumaran (β-5′) | 4.3 | 3.2 | 2.3 | 0 |
| (C) Pinoresinols (β–β′) | 7.4 | 6.6 | 3.7 | 4.5 |
| S/G | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wibowo, E.S.; Park, B.-D. Chemical and Thermal Characteristics of Ion-Exchanged Lignosulfonate. Molecules 2023, 28, 2755. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062755
Wibowo ES, Park B-D. Chemical and Thermal Characteristics of Ion-Exchanged Lignosulfonate. Molecules. 2023; 28(6):2755. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062755
Chicago/Turabian StyleWibowo, Eko Setio, and Byung-Dae Park. 2023. "Chemical and Thermal Characteristics of Ion-Exchanged Lignosulfonate" Molecules 28, no. 6: 2755. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062755
APA StyleWibowo, E. S., & Park, B.-D. (2023). Chemical and Thermal Characteristics of Ion-Exchanged Lignosulfonate. Molecules, 28(6), 2755. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062755






