Mechanical Properties of 3-Hydroxybutyric Acid-Induced Vesicles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
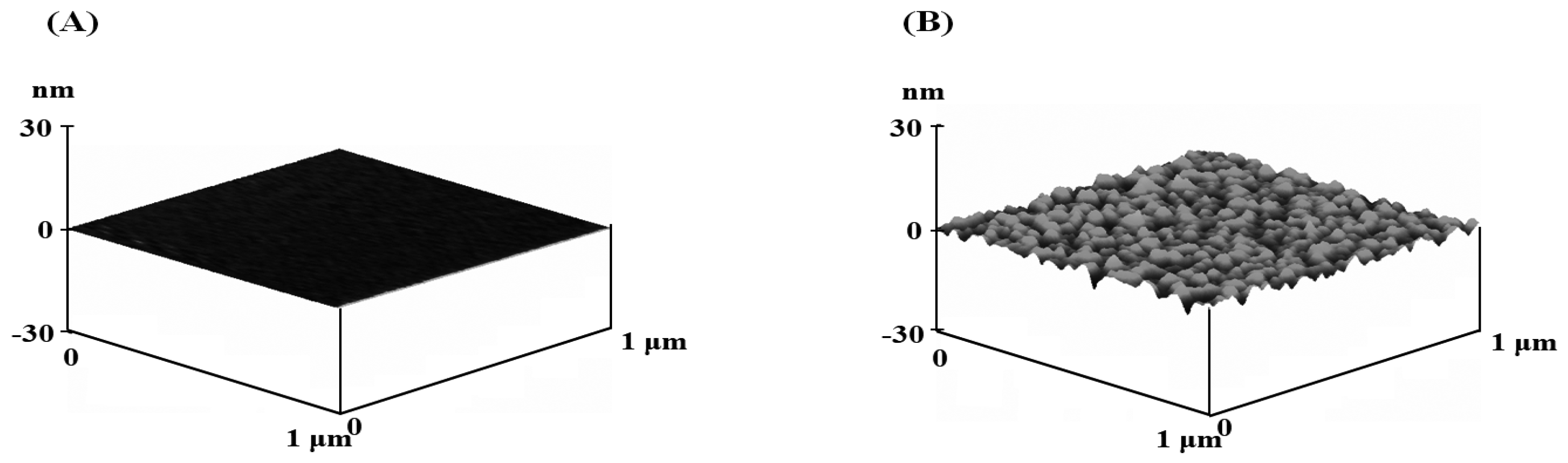
2.1. Suface Morphology
2.2. Force Measurements
2.3. Theoretical Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nowak, K.; Jurek, T.; Zawadzki, M. Postmortem Determination of Short-Term Markers of Hyperglycemia for the Purposes of Medicolegal Opinions. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleiman, S.F.; Henry, J.; Alhaddad, R.; El Hayek, L.; Abou Haidar, E.; Stringer, T.; Ulja, D.; Karuppagounder, S.S.; Holson, E.B.; Ratan, R.R.; et al. Exercise promotes the expression of brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) through the action of the ketone body beta-hydroxybutyrate. Elife 2016, 5, 5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, J.-T.; Lin, P.-H.; Tolstikov, V.; Oyekunle, T.; Chen, E.Y.; Bussberg, V.; Greenwood, B.; Sarangarajan, R.; Narain, N.R.; Kiebish, M.A.; et al. Metabolomic effects of androgen deprivation therapy treatment for prostate cancer. Cancer Med. 2019, 9, 3691–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhao, J.; Milutinovic, P.S.; Brosnan, R.J.; Eger, E.I.; Sonner, J.M. Anesthetic properties of the ketone bodies beta-hydroxybutyric acid and acetone. Anesth. Analg. 2007, 105, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, T.T.; Leiske, D.L.; Rosenfeld, L.; Sonner, J.M.; Fuller, G.G. 3-Hydroxybutyric Acid Interacts with Lipid Mono layers at Concentrations That Impair Consciousness. Langmuir 2013, 29, 1948–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohner, K.; Latal, A.; Degovics, G.; Garidel, P. Packing characteristics of a model system mimicking cytoplasmic bacterial membranes. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2001, 111, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Stevens, C.F. Probing synaptic vesicle fusion by altering mechanical properties of the neuronal surface membrane. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 18018–18022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Hernandez, I.C.; López-Ortega, O.; Acevedo-Ochoa, E.; Cervantes-Díaz, R.; Romero-Ramírez, S.; Sosa-Hernández, V.A.; Meza-Sánchez, D.E.; Juárez-Vega, G.; Pérez-Martínez, C.A.; Chávez-Munguía, B.; et al. Tetraspanin 33 (TSPAN33) regulates endocytosis and migration of human B lymphocytes by affecting the tension of the plasma membrane. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 3449–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadka, N.K.; Teng, P.; Cai, J.; Pan, J. Modulation of lipid membrane structural and mechanical properties by a peptidomimetic derived from reduced amide scaffold. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2017, 1859, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engler, A.J.; Richert, L.; Wong, J.Y.; Picart, C.; Discher, D.E. Surface probe measurements of the elasticity of sectioned tissue, thin gels and polyelectrolyte multilayer films: Correlations between substrate stiffness and cell adhesion. Surf. Sci. 2004, 570, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, C.J.; Shah, M.K.; Powell, L.C.; Armstrong, I. Application of AFM from microbial cell to biofilm. Scanning 2010, 32, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, F.; Kumar, S.; Varadarajan, K.M. Quantification of Adhesion Force of Bacteria on the Surface of Biomaterials: Techniques and Assays. ACS Biomater Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 2093–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-W. Probe chemistry effect on surface properties of asymmetric-phase lipid bilayers. Colloids Surf. B 2010, 75, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Cabello, F.J.M.; Trefalt, G.; Maroni, P.; Borkovec, M. Electric double-layer potentials and surface regulation properties measured by colloidal-probe atomic force microscopy. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 90, 012301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, J.M.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, P.; Unocic, R.R.; Guo, D.; Okatan, M.B.; Dai, S.; Cummings, P.T.; Kalinin, S.V.; Feng, G.; et al. Fundamental aspects of electric double layer force-distance measurements at liquid-solid interfaces using atomic force microscopy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iturri, J.; Toca-Herrera, J.L. Characterization of Cell Scaffolds by Atomic Force Microscopy. Polymers 2017, 9, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Qian, X.; Guan, L.; Zhang, M.; Li, Q.; Wu, A.; Dong, M. Studying the Adhesion Force and Glass Transition of Thin Polystyrene Films by Atomic Force Microscopy. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regan, D.; Williams, J.; Borri, P.; Langbein, W. Lipid Bilayer Thickness Measured by Quantitative DIC Reveals Phase Transitions and Effects of Substrate Hydrophilicity. Langmuir 2019, 35, 13805–13814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisenhorn, A.L.; Khorsandi, M.; Kasas, S.; Gotzos, V.; Butt, H.-J. Deformation and height anomaly of soft surfaces studied with an AFM. Nanotechnology 1993, 4, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laney, D.E.; Garcia, R.A.; Parsons, S.M.; Hansma, H.G. Changes in the elastic properties of cholinergic synaptic vesicles as measured by atomic force microscopy. Biophys. J. 1997, 72, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, J.; Park, J.-W. Trehalose-Induced Variation in Mechanical Properties of Vesicles in Aqueous Solution. J. Membr. Biol. 2015, 248, 1121–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-W.; Lee, G.U. Properties of mixed lipid monolayers assembled on hydrophobic surfaces through vesicle adsorption. Langmuir 2006, 22, 5057–5063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radmacher, M.; Fritz, M.; Kacher, C.M.; Walters, D.A.; Hansma, P.K. Imaging adhesion forces and elasticity of lysozyme adsorbed on mica with the atomic-force microscope. Langmuir 1994, 10, 3809–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ratio of 3-Hydroxybutyric-Acid to Lipid | 0 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slope of 1st steric force (N/m) | 0.7 ± 0.01 | 0.69 ± 0.01 | 0.67 ± 0.01 | 0.65 ± 0.01 | 0. 65 ± 0.01 | 0.65 ± 0.01 |
| Slope of 2nd steric force (N/m) | 3.6 ± 0.01 | 3.5 ± 0.01 | 3.4 ± 0.01 | 3.3 ± 0.01 | 3.3 ± 0.01 | 3.3 ± 0.01 |
| Ratio of 3-Hydroxybutyric Acid/Lipid | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.0 | |
| Eves × 106 (Pa) | 81 ± 2 | 80 ± 2 | 78 ± 2 | 76 ± 2 | 76 ± 2 | 76 ± 2 |
| kc × 10−19 (J) | 11.3 ± 0.3 | 11.1 ± 0.3 | 10.7 ± 0.3 | 10.5 ± 0.3 | 10.5 ± 0.3 | 10.5 ± 0.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, S.J.; Hadinoto, K.; Park, J.-W. Mechanical Properties of 3-Hydroxybutyric Acid-Induced Vesicles. Molecules 2023, 28, 2742. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062742
Jung SJ, Hadinoto K, Park J-W. Mechanical Properties of 3-Hydroxybutyric Acid-Induced Vesicles. Molecules. 2023; 28(6):2742. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062742
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Seung Jun, Kunn Hadinoto, and Jin-Won Park. 2023. "Mechanical Properties of 3-Hydroxybutyric Acid-Induced Vesicles" Molecules 28, no. 6: 2742. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062742
APA StyleJung, S. J., Hadinoto, K., & Park, J.-W. (2023). Mechanical Properties of 3-Hydroxybutyric Acid-Induced Vesicles. Molecules, 28(6), 2742. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062742








