β-Carboline Alkaloids in Soy Sauce and Inhibition of Monoamine Oxidase (MAO)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Isolation of Tetrahydro-β-carboline-3-carboxylic Acid and β-Carboline Alkaloids from Soy Sauces
4.2. Formation of Harman from 1-Methyl-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydro-β-Carboline-3-Carboxylic Acid (MTCA)
4.3. Monoamine Oxidase (MAO-A and B) Assay and Inhibition by Soy Sauce and β-Carbolines Isolated from Soy Sauce
4.4. RP-HPLC chromatographic Analysis and Chemical Identification by MS
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Youdim, M.B.H.; Edmondson, D.; Tipton, K.F. The therapeutic potential of monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, J.C.; Chen, K.; Ridd, M.J. Monoamine oxidase: From genes to behavior. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1999, 22, 197–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Yasuhara, H. Clinical pharmacology of MAO inhibitors: Safety and future. Neurotoxicology 2004, 25, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, R.R.; Tipton, K.F. Assessment of enzyme inhibition: A review with examples from the development of monoamine oxidase and cholinesterase inhibitory drugs. Molecules 2017, 22, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolen, W.A.; Hoencamp, E.; Bouvy, P.F.; Haffmans, P.M.J. Reversible monoamine oxidase-A inhibitors in resistant major depression. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 1993, 16, S69–S76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carradori, S.; Fantacuzzi, M.; Ammazzalorso, A.; Angeli, A.; De Filippis, B.; Galati, S.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P.; Poli, G.; Tuccinardi, T.; et al. Resveratrol analogues as dual inhibitors of monoamine oxidase B and carbonic anhydrase VII: A new multi-target combination for neurodegenerative diseases? Molecules 2022, 27, 7816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behl, T.; Kaur, D.; Sehgal, A.; Singh, S.; Sharma, N.; Zengin, G.; Andronie-Cioara, F.L.; Toma, M.M.; Bungau, S.; Bumbu, A.G. Role of monoamine oxidase activity in Alzheimer’s Disease: An insight into the therapeutic potential of inhibitors. Molecules 2021, 26, 3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaurasiya, N.D.; Leon, F.; Muhammad, I.; Tekwani, B.L. Natural products inhibitors of monoamine oxidases: Potential new drug leads for neuroprotection, neurological disorders, and neuroblastoma. Molecules 2022, 27, 4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisani, L.; Catto, M.; Leonetti, F.; Nicolotti, O.; Stefanachi, A.; Campagna, F.; Carotti, A. Targeting monoamine oxidases with multipotent ligands: An emerging strategy in the search of new drugs against neurodegenerative diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 4568–4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaurasiya, N.D.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Muhammad, I.; Walker, L.A.; Tekwani, B.L. Monoamine oxidase inhibitory constituents of propolis: Kinetics and mechanism of inhibition of recombinant human MAO-A and MAO-B. Molecules 2014, 19, 18936–18952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, G.; Farooqui, R.; Kesler, N. Parkinson disease: A new link between monoamine oxidase and mitochondrial electron flow. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 4890–4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauptmann, N.; Grimsby, J.; Shih, J.C.; Cadenas, E. The metabolism of tyramine by monoamine oxidase A/B causes oxidative damage to mitochondrial DNA. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1996, 335, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langston, J.W.; Irwin, I.; Langston, E.B.; Forno, L.S. 1-Methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion (MPP+): Identification of a metabolite of MPTP, a toxin selective to the substantia nigra. Neurosci. Lett. 1984, 48, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herraiz, T.; Guillén, H.; Arán, V.J.; Idle, J.R.; Gonzalez, F.J. Comparative aromatic hydroxylation and N-demethylation of MPTP neurotoxin and its analogs, N-methylated β-carboline and isoquinoline alkaloids, by human cytochrome P450 2D6. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2006, 216, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herraiz, T.; Guillen, H.; Galisteo, J. N-methyltetrahydro-β-carboline analogs of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) neurotoxin are oxidized to neurotoxic β-carbolinium cations by heme peroxidases. Biochem. Biophys. Res Commun. 2007, 356, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herraiz, T.; Guillén, H. Monoamine oxidase-A inhibition and associated antioxidant activity in plant extracts with potential antidepressant actions. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 4810394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herraiz, T.; Flores, A.; Fernández, L. Analysis of monoamine oxidase (MAO) enzymatic activity by high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection combined with an assay of oxidation with a peroxidase and its application to MAO inhibitors from foods and plants. J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1073, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billett, E.E. Monoamine oxidase (MAO) in human peripheral tissues. Neurotoxicology 2004, 25, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, J.S.; Volkow, N.D.; Wang, G.J.; Pappas, N.; Logan, J.; MacGregor, R.; Alexoff, D.; Shea, C.; Schlyer, D.; Wolf, A.P.; et al. Inhibition of monoamine oxidase B in the brains of smokers. Nature 1996, 379, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, J.S.; Volkow, N.D.; Wang, G.J.; Pappas, N.; Logan, J.; Shea, C.; Alexoff, D.; MacGregor, R.R.; Schlyer, D.J.; Zezulkova, I.; et al. Brain monoamine oxidase A inhibition in cigarette smokers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 14065–14069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herraiz, T.; Chaparro, C. Human monoamine oxidase is inhibited by tobacco smoke: β-carboline alkaloids act as potent and reversible inhibitors. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 326, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herraiz, T. Relative exposure to β-carbolines norharman and harman from foods and tobacco smoke. Food Addit. Contam. 2004, 21, 1041–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herraiz, T.; Chaparro, C. Human monoamine oxidase enzyme inhibition by coffee and β-carbolines norharman and harman isolated from coffee. Life Sci. 2006, 78, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herraiz, T. Identification and occurrence of β-carboline alkaloids in raisins and inhibition of monoamine oxidase (MAO). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 8534–8540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlin, I.; SpreuxVaroquaux, O.; Said, S.; Launay, J.M. Effects of past history of major depression on smoking characteristics, monoamine oxidase-A and -B activities and withdrawal symptoms in dependent smokers. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1997, 45, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, A.C.; Muelken, P.; Alcheva, A.; Stepanov, I.; LeSage, M.G. Cigarette smoke extract, but not electronic cigarette aerosol extract, inhibits monoamine oxidase in vitro and produces greater acute aversive/anhedonic effects than nicotine alone on intracranial self-stimulation in rats. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 868088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernan, M.A.; Takkouche, B.; Caamano-Isorna, F.; Gestal-Otero, J.J. A meta-analysis of coffee drinking, cigarette smoking, and the risk of Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 2002, 52, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragonese, P.; Salemi, G.; Morgante, L.; Aridon, P.; Epifanio, A.; Buffa, D.; Scoppa, F.; Savettieri, G. A case-control study on cigarette, alcohol, and coffee consumption preceding Parkinson’s disease. Neuroepidemiology 2003, 22, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carneiro, S.M.; Oliveira, M.B.P.; Alves, R.C. Neuroprotective properties of coffee: An update. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 113, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzelczyk, J.; Budryn, G.; Peña-García, J.; Szwajgier, D.; Gałązka-Czarnecka, I.; Oracz, J.; Pérez-Sánchez, H. Evaluation of the inhibition of monoamine oxidase A by bioactive coffee compounds protecting serotonin degradation. Food Chem. 2021, 348, 129108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airaksinen, M.M.; Kari, I. Beta-Carbolines, psychoactive compounds in the mammalian body. Part II: Effects. Med. Biol. 1981, 59, 190–211. [Google Scholar]
- Baum, S.S.; Hill, R.; Rommelspacher, H. Harman-induced changes of extracellular concentrations of neurotransmitters in the nucleus accumbens of rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1996, 314, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husbands, S.M.; Glennon, R.A.; Gorgerat, S.; Gough, R.; Tyacke, R.; Crosby, J.; Nutt, D.J.; Lewis, J.W.; Hudson, A.L. β-Carboline binding to imidazoline receptors. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2001, 64, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, A.M.; Idle, J.R.; Herraiz, T.; Kupfer, A.; Gonzalez, F.J. Screening for endogenous substrates reveals that CYP2D6 is a 5-methoxyindolethylamine O-demethylase. Pharmacogenetics 2003, 13, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergene, E.; Schoener, E.P. Effects of harmane (1-methyl-β-carboline) on neurons in the nucleus accumbens of the rat. Pharm. Biochem. Behav. 1993, 44, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miralles, A.; Esteban, S.; Sastre-Coll, A.; Moranta, D.; Asensio, V.J.; Garcia-Sevilla, J.A. High-affinity binding of β-carbolines to imidazoline I-2B receptors and MAO-A in rat tissues: Norharman blocks the effect of morphine withdrawal on DOPA/noradrenaline synthesis in the brain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 518, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beato, A.; Gori, A.; Boucherle, B.; Peuchmaur, M.; Haudecoeur, R. β-Carboline as a privileged scaffold for multitarget strategies in Alzheimer’s disease therapy. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 1392–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarpley, M.; Oladapo, H.O.; Strepay, D.; Caligan, T.B.; Chdid, L.; Shehata, H.; Roques, J.R.; Thomas, R.; Laudeman, C.P.; Onyenwoke, R.U. Identification of harmine and β-carboline analogs from a high-throughput screen of an approved drug collection; profiling as differential inhibitors of DYRK1A and monoamine oxidase A and for in vitro and in vivo anti-cancer studies. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 162, 105821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prah, A.; Gavranić, T.; Perdih, A.; Sollner Dolenc, M.; Mavri, J. Computational insights into β-carboline inhibition of monoamine oxidase A. Molecules 2022, 27, 6711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostergren, A.; Annas, A.; Skog, K.; Lindquist, N.G.; Brittebo, E.B. Long-term retention of neurotoxic β-carbolines in brain neuromelanin. J. Neural Transm. 2004, 111, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, C.A.; Anderson, N.J.; Robinson, E.S.J.; Price, R.; Tyacke, R.J.; Husbands, S.M.; Dillon, M.P.; Eglen, R.M.; Hudson, A.L.; Nutt, D.J.; et al. Harmane and harmalan are bioactive components of classical clonidine-displacing substance. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 16385–16392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, N.J.; Tyacke, R.J.; Husbands, S.M.; Nutt, D.J.; Hudson, A.L.; Robinson, E.S.J. In vitro and ex vivo distribution of H-3 harmane, an endogenous β-carboline, in rat brain. Neuropharmacology 2006, 50, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herraiz, T. Analysis of the bioactive alkaloids tetrahydro-β-carboline and β-carboline in food. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 881, 483–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herraiz, T. Tetrahydro-β-carboline bioactive alkaloids in beverages and foods. In Nutraceutical Beverages: Chemistry, Nutrition, and Health Effects; ACS Symposium Series; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; Volume 871, pp. 405–426. [Google Scholar]
- Herraiz, T. Occurrence of tetrahydro-β-carboline-3-carboxylic acids in commercial foodstuffs. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 3057–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herraiz, T. Identification and occurrence of the bioactive β-carbolines norharman and harman in coffee brews. Food Addit. Contam. 2002, 19, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herraiz, T.; Peña, A.; Mateo, H.; Herraiz, M.; Salgado, A. Formation, characterization, and occurrence of β-carboline alkaloids derived from α-dicarbonyl compounds and L-tryptophan. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 9143–9153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herraiz, T.; Vera, F. Occurrence, formation from D-fructose and 3-deoxyglucosone, and activity of the carbohydrate-derived β-carbolines in foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 6650–6664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herraiz, T.; Ough, C.S. Chemical and technological factors determining tetrahydro-β-carboline-3-carboxylic acid content in fermented alcoholic beverages. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1993, 41, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herraiz, T.; Chaparro, C. Analysis of monoamine oxidase enzymatic activity by reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography and inhibition by β-carboline alkaloids occurring in foods and plants. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1120, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herraiz, T. Tetrahydro-β-carboline-3-carboxylic acid compounds in fish and meat: Possible precursors of co-mutagenic β-carbolines norharman and harman in cooked foods. Food Addit. Contam. 2000, 17, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herraiz, T.; Galisteo, J. Tetrahydro-β-carboline alkaloids occur in fruits and fruit juices. Activity as antioxidants and radical scavengers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 7156–7161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diem, S.; Gutsche, B.; Herderich, M. Degradation of tetrahydro-β-carbolines in the presence of nitrite: HPLC-MS analysis of the reaction products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 5993–5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herraiz, T. Occurrence of 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-β-carboline-3-carboxylic acid and 1-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-β-carboline-3-carboxylic acid in fruit juices, purees, and jams. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 3484–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herraiz, T. 1-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-β-carboline-3-carboxylic acid and 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-β-carboline-3-carboxylic acid in fruits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 4883–4887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herraiz, T.; Galisteo, J. Nitrosative deamination of 2’-deoxyguanosine and DNA by nitrite, and antinitrosating activity of β-carboline alkaloids and antioxidants. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 112, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakabayashi, K.; Ochiai, M.; Saito, H.; Tsuda, M.; Suwa, Y.; Nagao, M.; Sugimura, T. Presence of 1-methyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-β-carboline-3-carboxylic acid, a precursor of a mutagenic nitroso compound, in soy sauce. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 2912–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekkes, D.; Bode, W.T. Occurrence and partition of the β-carboline norharman in rat organs. Life Sci. 1993, 52, 2045–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, K.; Gonda, T.; Sawada, H.; Uezono, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Kawamura, T.; Ohtaki, K.; Kimura, K.; Akaike, A. Endogenously occurring β-carboline induces parkinsonism in nonprimate animals: A possible causative protoxin in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurochem. 1998, 70, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, T.; Greube, A.; Strauss, S.; Heineke, D.; Lehmann, J.; Rommelspacher, H. Comparison of the in-vitro binding characteristics of the β-carbolines harman and norharman in rat-brain and liver and in bovine adrenal-medulla. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharm. 1994, 349, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, E.S.J.; Anderson, N.J.; Crosby, J.; Nutt, D.J.; Hudson, A.L. Endogenous β-carbolines as clonidine-displacing substances. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 1009, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herraiz, T. N-methyltetrahydropyridines and pyridinium cations as toxins and comparison with naturally-occurring alkaloids. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 97, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aricioglu, F.; Altunbas, H. Harmane induces anxiolysis and antidepressant-like effects in rats. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 1009, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawanishi, K.; Eguchi, N.; Hayashi, T.; Hashimoto, Y. Relationship between occurrence of tremor/convulsion and level of β-carbolines in the brain after administration of β-carbolines into mice. Pharm. Biochem. Behav. 1994, 47, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herraiz, T.; Guillén, H.; Arán, V.J. Oxidative metabolism of the bioactive and naturally occurring β-carboline alkaloids, norharman and harman, by human cytochrome P450 enzymes. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2008, 21, 2172–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gearhart, D.A.; Toole, P.F.; Beach, J.W. Identification of brain proteins that interact with 2-methylnorharman: An analog of the parkinsonian-inducing toxin, MPP+. Neurosci. Res. 2002, 44, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, M.A.; Neafsey, E.J. β-Carboline analogs of N-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP): Endogenous factors underlying idiopathic Parkinsonism. Neurosci. Lett. 1985, 55, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Sablin, S.O.; Ramsay, R.R. Inhibition of monoamine oxidase A by β-carboline derivatives. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1997, 337, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youdim, M.B.H.; Weinstock, M. Therapeutic applications of selective and non-selective inhibitors of monoamine oxidase A and B that do not cause significant tyramine potentiation. Neurotoxicology 2004, 25, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, B.; Bannister, R.; Sever, P. Pressor amines and monoamine oxidase inhibitors for treatment of postural hypotension in autonomic failure: Llimitations and hazards. Lancet 1978, 1, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herraiz, T.; Guillen, H. Inhibition of the bioactivation of the neurotoxin MPTP by antioxidants, redox agents and monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 1773–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herraiz, T.; Aran, V.J.; Guillen, H. Nitroindazole compounds inhibit the oxidative activation of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) neurotoxin to neurotoxic pyridinium cations by human monoamine oxidase (MAO). Free Radic. Res. 2009, 43, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vindis, C.; Seguelas, M.H.; Bianchi, P.; Parini, A.; Cambon, C. Monoamine oxidase B induces ERK-dependent cell mitogenesis by hydrogen peroxide generation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 271, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkila, R.E.; Manzino, L.; Cabbat, F.S.; Duvoisin, R.C. Protection against the dopaminergic neurotoxicity of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine by monoamine-oxidase inhibitors. Nature 1984, 311, 467–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, C.H.; Oh, J.; Lim, J.S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.-S. Fermented soy products: Beneficial potential in neurodegenerative diseases. Foods 2021, 10, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-C.; Quang, T.H.; Yoon, C.-S.; Thanh Ngan, N.T.; Lim, S.I.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, Y.C.; Oh, H. Anti-neuroinflammatory activities of indole alkaloids from kanjang (Korean fermented soy source) in lipopolysaccharide-induced BV2 microglial cells. Food Chem. 2016, 213, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
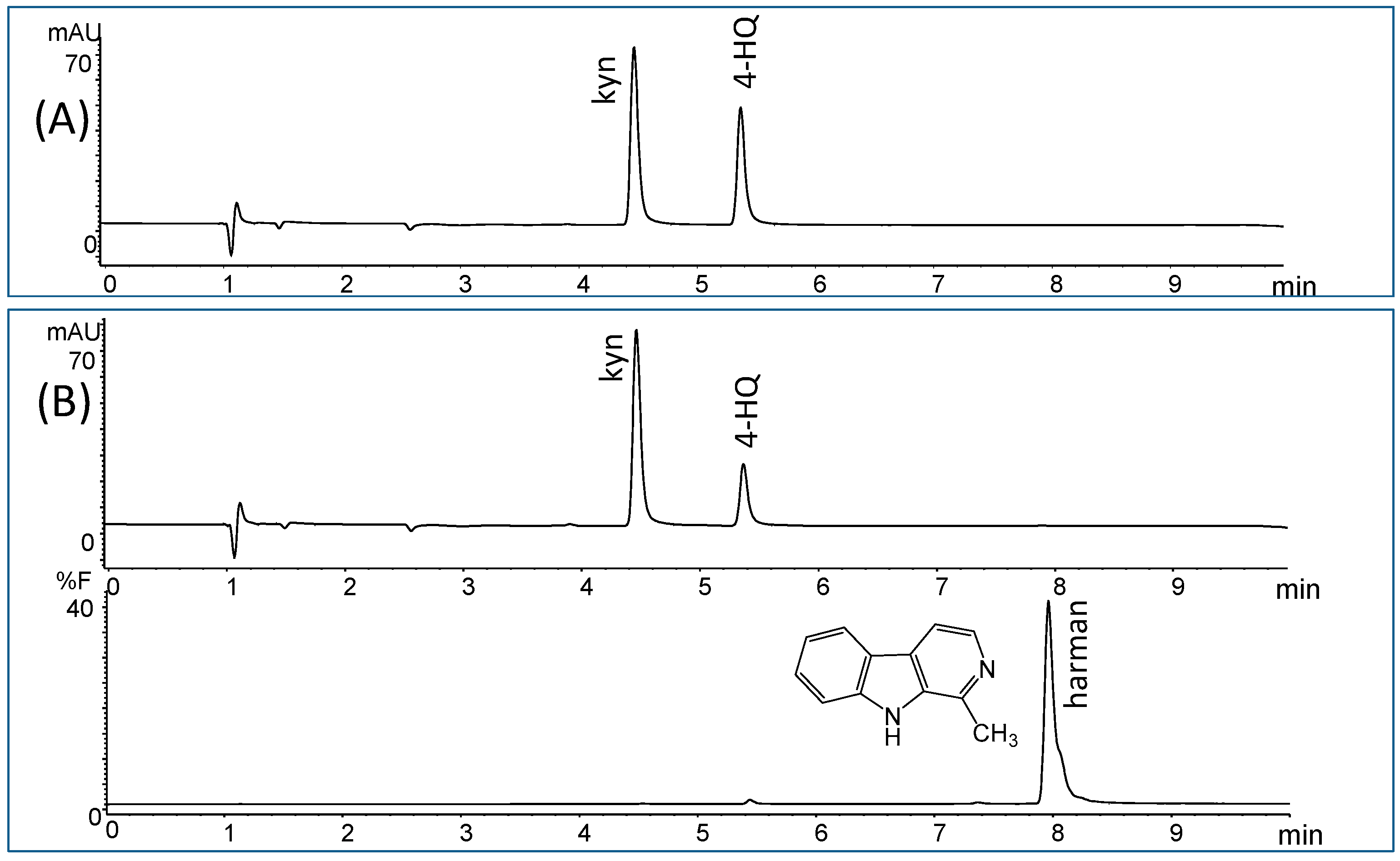


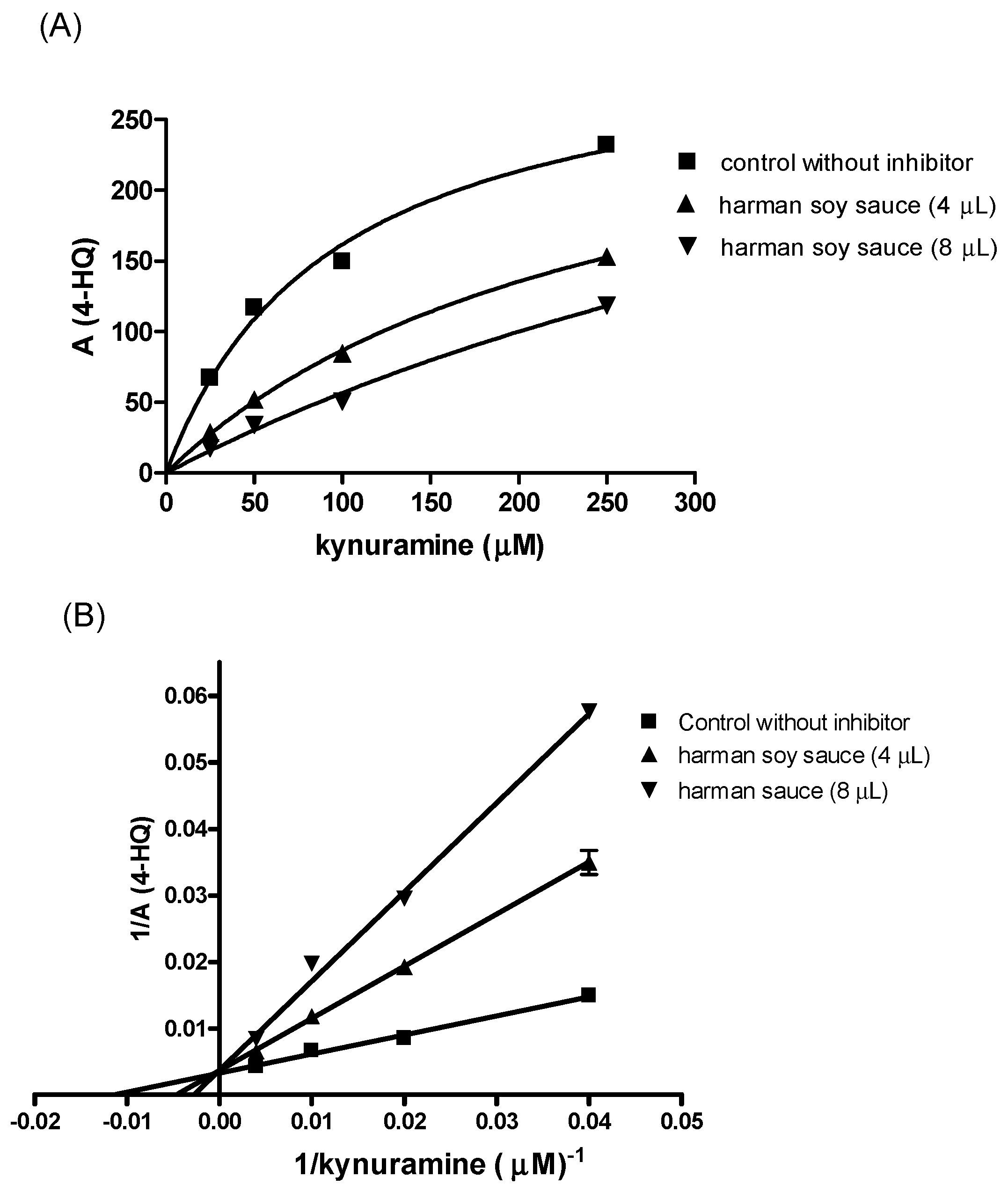
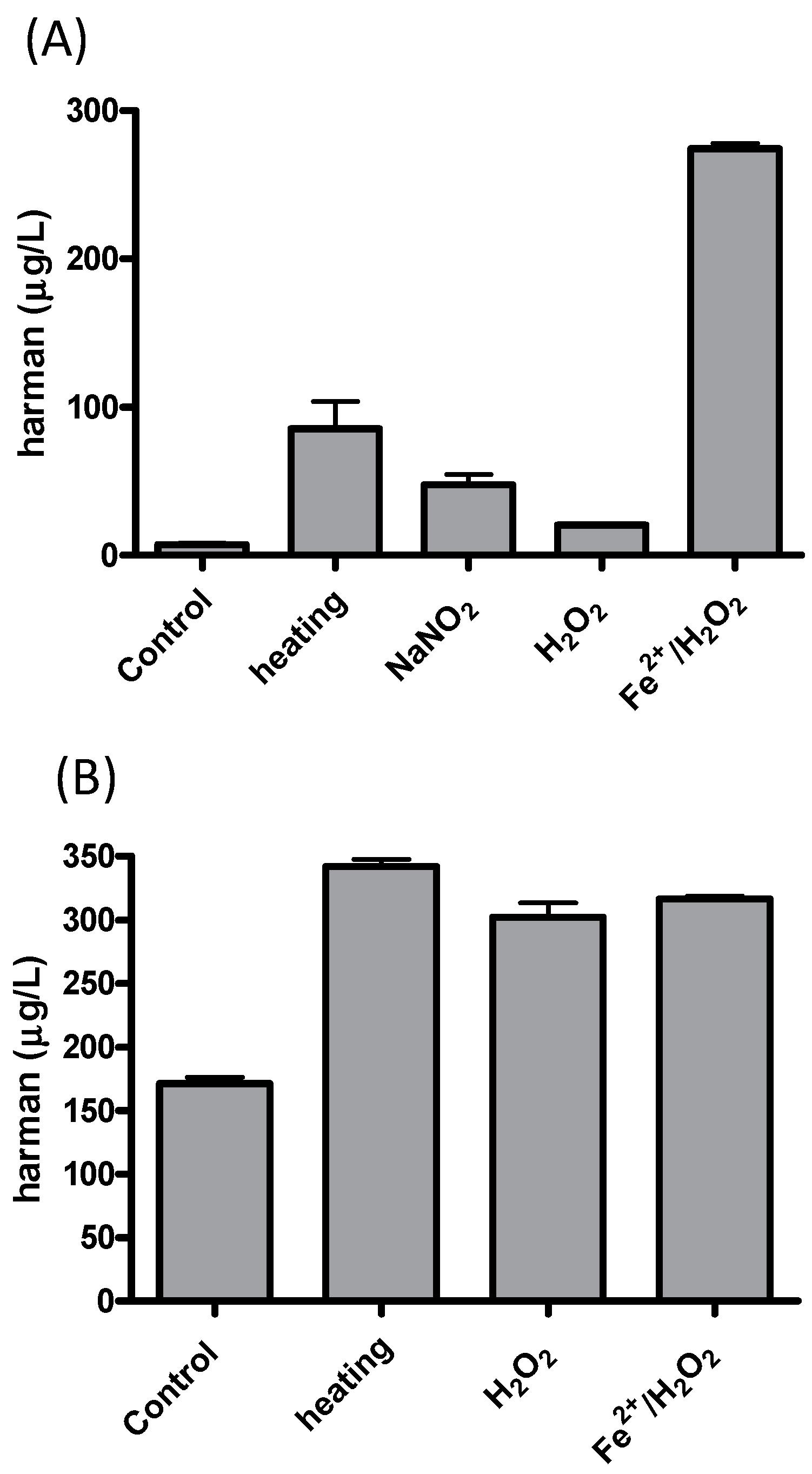

| β-Carbolines | X (μg/L) | Range |
|---|---|---|
| Norharman | 34.9 | 11.6–52 |
| Harman | 165.4 | 46.7–243 |
| THβC-3-COOH | X (mg/L) | Range |
| THCA | 18.8 | 2.2–69.6 |
| 1S,3S-MTCA | 161.6 | 43.6–360.5 |
| 1R,3S-MTCA | 42.8 | 8.9–88.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Herraiz, T. β-Carboline Alkaloids in Soy Sauce and Inhibition of Monoamine Oxidase (MAO). Molecules 2023, 28, 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062723
Herraiz T. β-Carboline Alkaloids in Soy Sauce and Inhibition of Monoamine Oxidase (MAO). Molecules. 2023; 28(6):2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062723
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerraiz, Tomás. 2023. "β-Carboline Alkaloids in Soy Sauce and Inhibition of Monoamine Oxidase (MAO)" Molecules 28, no. 6: 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062723
APA StyleHerraiz, T. (2023). β-Carboline Alkaloids in Soy Sauce and Inhibition of Monoamine Oxidase (MAO). Molecules, 28(6), 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062723








