Nobiletin Intake Attenuates Hepatic Lipid Profiling and Oxidative Stress in HFD-Induced Nonalcoholic-Fatty-Liver-Disease Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
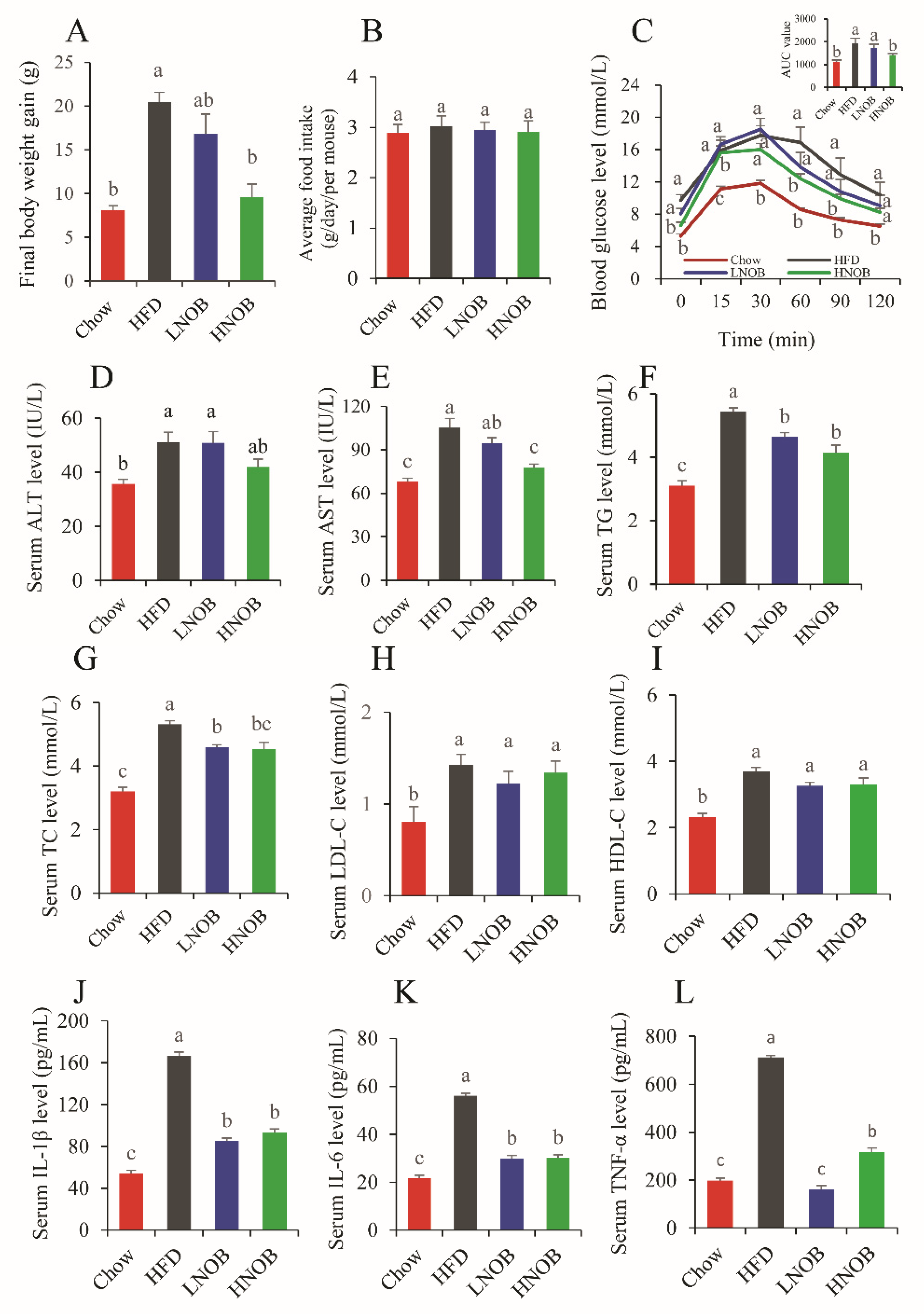
2.1. Effects of NOB on Body Weight Gain, Food Intake, and GTT in HFD-Induced NAFLD Mice
2.2. Effect of Dietary NOB on Serum Biochemistry in HFD-Induced NAFLD Mice
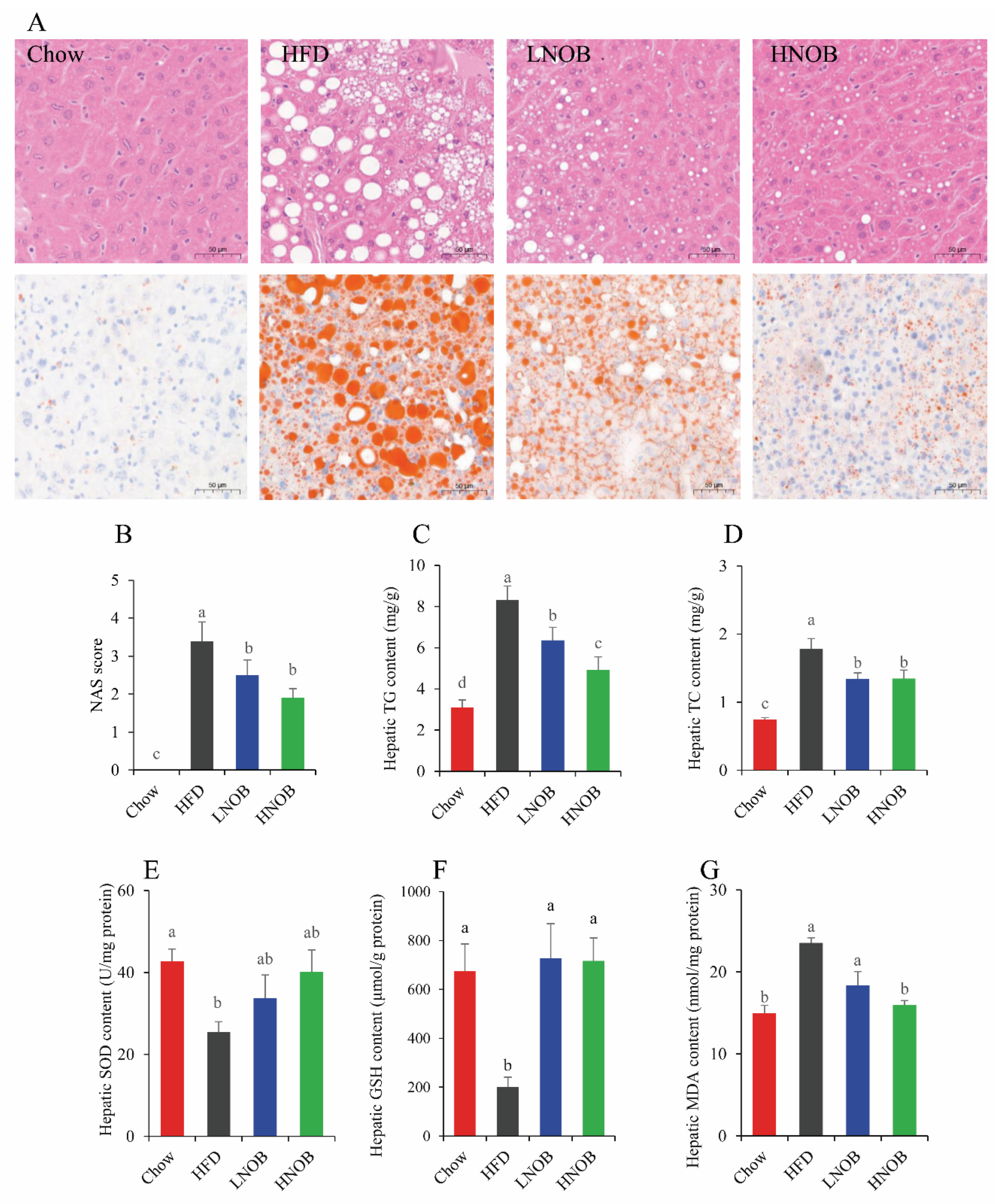
2.3. Effect of NOB Supplementation on Hepatic Lipid Accumulation in HFD-Induced NAFLD Mice
2.4. Effect of NOB Supplementation on Hepatic Oxidative Damage in HFD-Induced NAFLD Mice
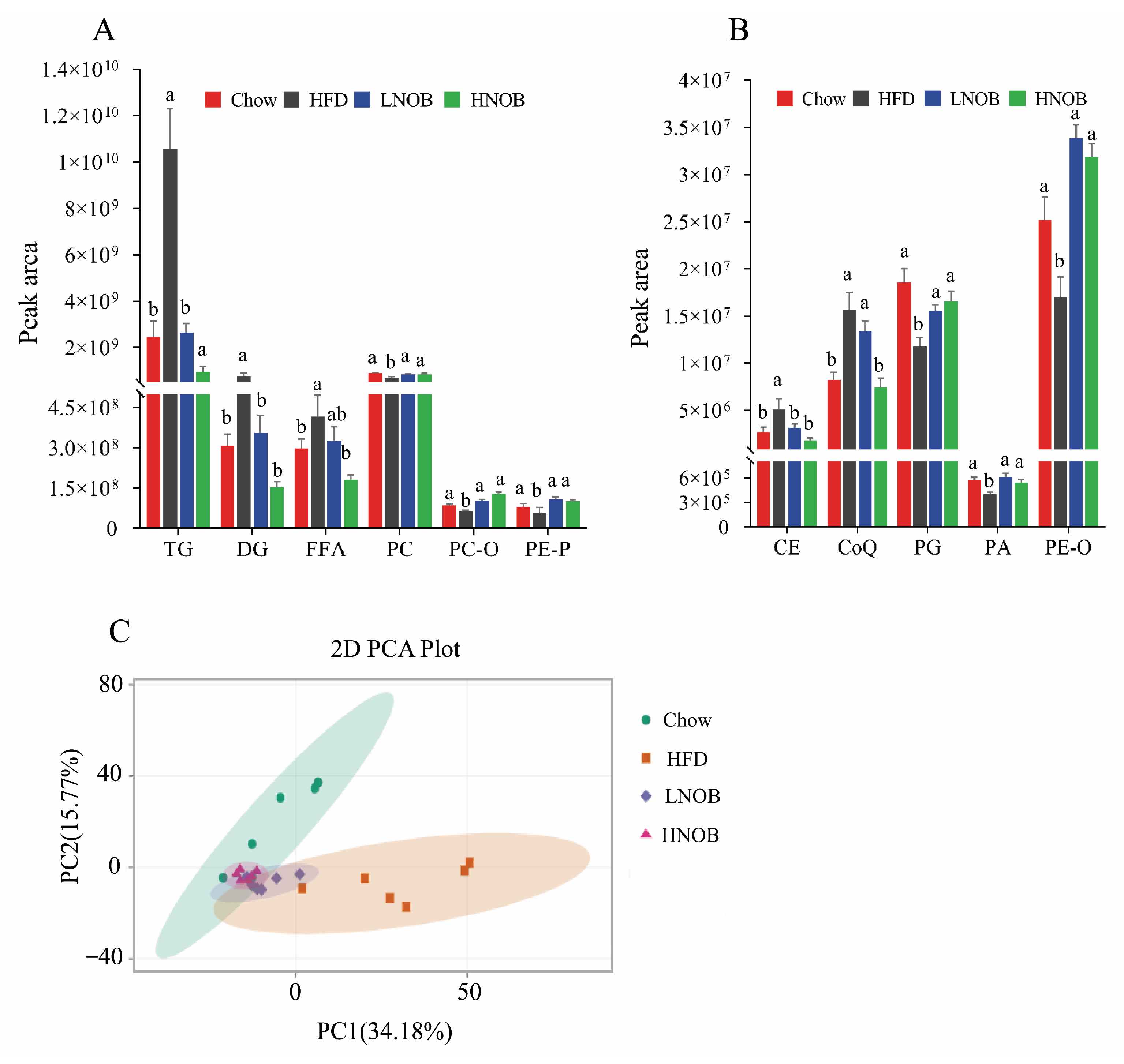
2.5. Lipidomic Analysis after NOB Supplementation
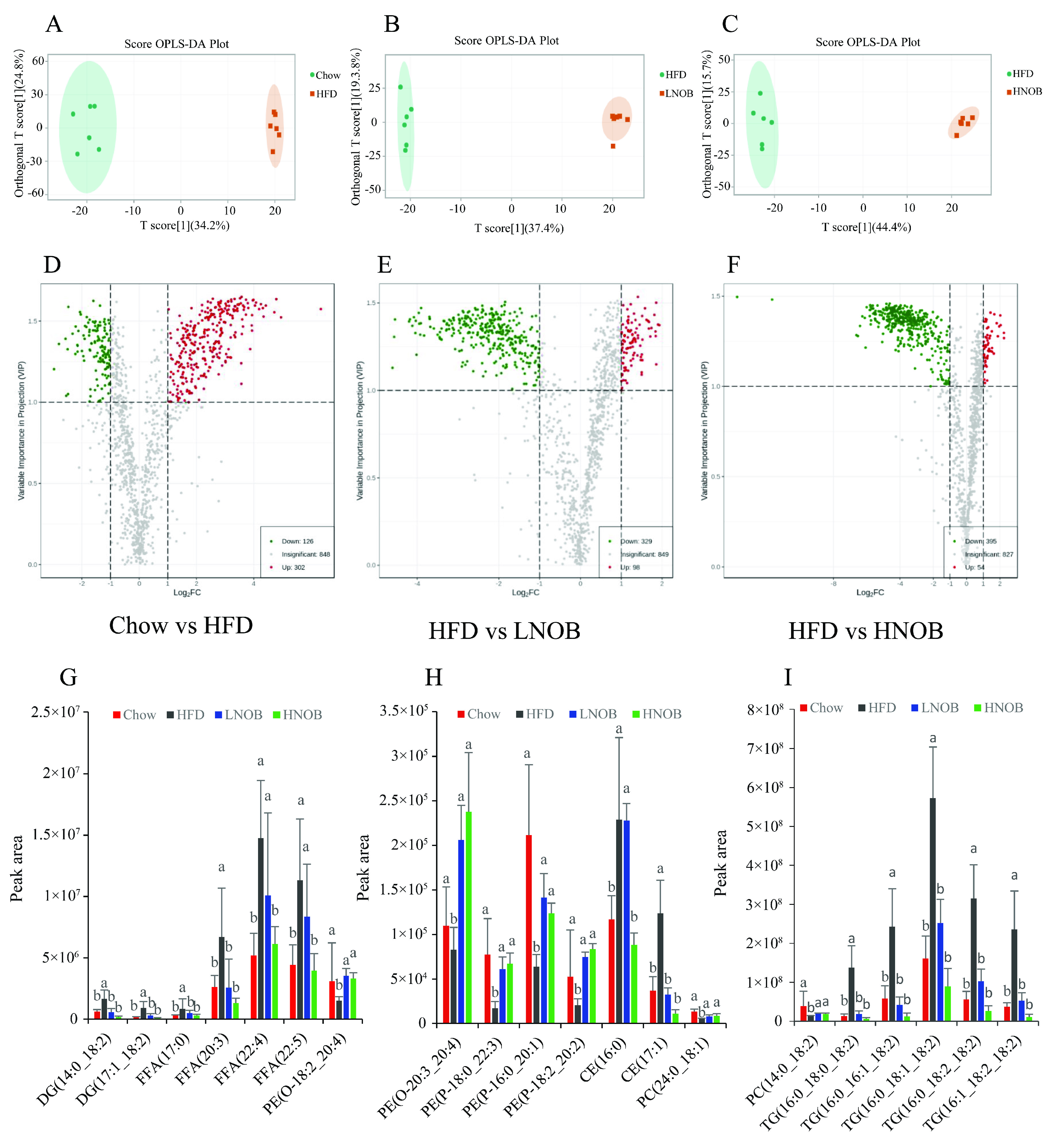
2.6. NOB Supplementation Changed the Important Differential Lipid Species in The Liver
2.7. Pathway Analysis
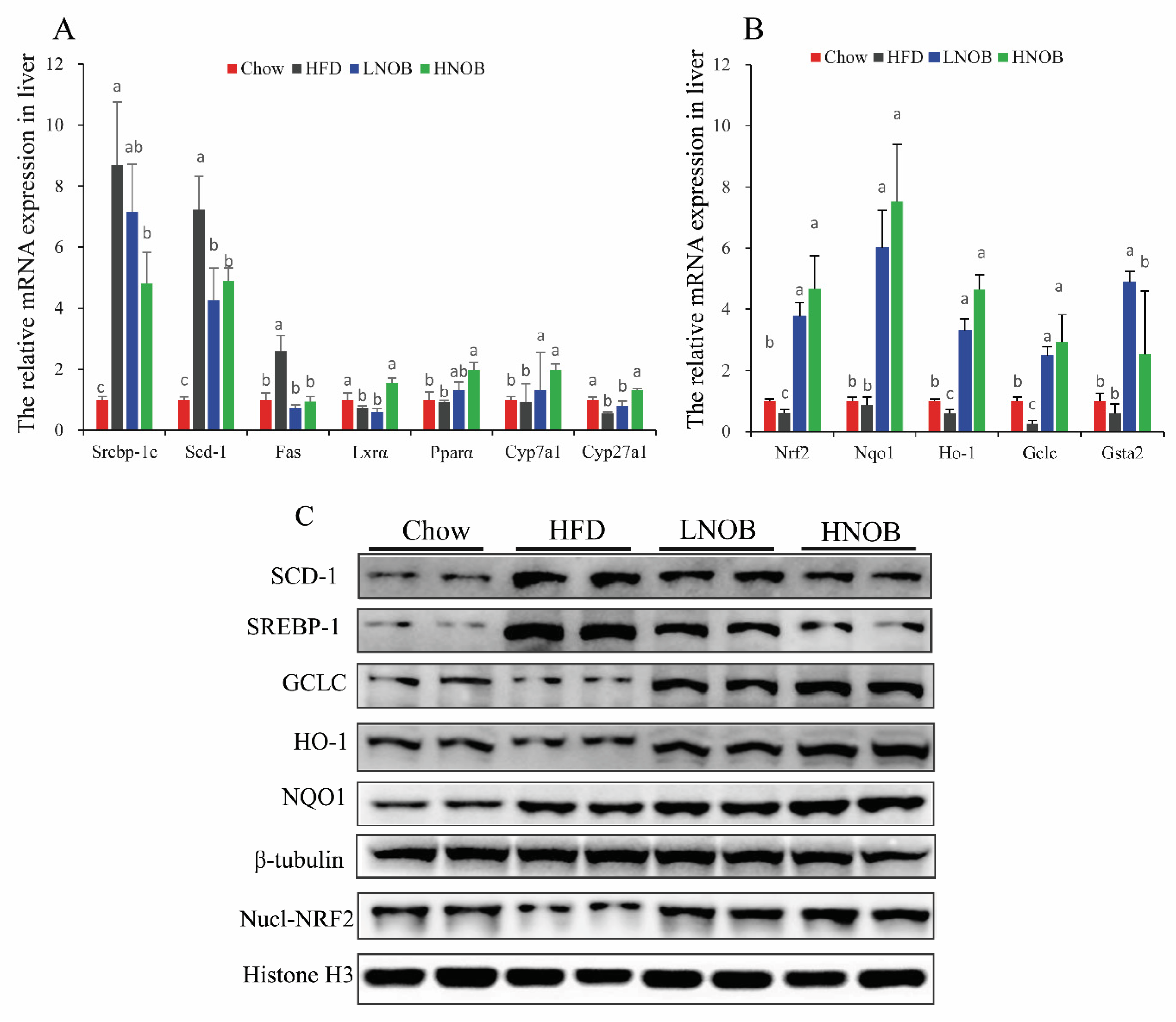
2.8. Effect of NOB Supplementation on the Expression of Genes and Proteins Involved in Hepatic Lipid Metabolism and Oxidative Stress
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Animal Experiments
4.3. Glucose Tolerance Test (GTT)
4.4. Biochemical Analysis and Hepatic Histological Analysis
4.5. Liver Lipidomic Analysis
4.6. RNA Extraction and mRNA Expression Levels using Quantitative Real-Time PCR (RT-qPCR)
4.7. Western Blots (WBs)
4.8. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, Z.; Gao, W.; Zeng, S.L.; Li, P.; Liu, E.H. Chemical structures, bioactivities and molecular mechanisms of citrus polymethoxyflavones. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 40, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, N.M.; Telford, D.E.; Sutherland, B.G.; Edwards, J.Y.; Huff, M.W. Nobiletin Corrects Intestinal Lipid Metabolism in Ldlr-/-Mice Fed a High-fat Diet. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39 (Suppl. 1), A684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-Y.; Liang, J.-J.; Wang, D.-L.; Chen, J.-B.; Cao, J.-P.; Wang, Y.; Sun, C.-D. Nobiletin as a chemopreventive natural product against cancer, a comprehensive review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvihill, E.E.; Assini, J.M.; Lee, J.K.; Allister, E.M.; Sutherland, B.G.; Koppes, J.B.; Sawyez, C.G.; Edwards, J.Y.; Telford, D.E.; Charbonneau, A. Nobiletin attenuates VLDL overproduction, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerosis in mice with diet-induced insulin resistance. Diabetes 2011, 60, 1446–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, N.M.; Burke, A.C.; Samsoondar, J.P.; Seigel, K.E.; Wang, A.; Telford, D.E.; Sutherland, B.G.; O’Dwyer, C.; Steinberg, G.R.; Fullerton, M.D. The citrus flavonoid nobiletin confers protection from metabolic dysregulation in high-fat-fed mice independent of AMPK [S]. J. Lipid Res. 2020, 61, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuk, T.; Kim, Y.; Yang, J.; Sung, J.; Jeong, H.S.; Lee, J. Nobiletin inhibits hepatic lipogenesis via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 7420265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundi, M.S.; Velapati, S.; Patel, J.; Kellogg, T.A.; Abu Dayyeh, B.K.; Hurt, R.T. Evolution of NAFLD and its management. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2020, 35, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makri, E.; Goulas, A.; Polyzos, S.A. Epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis and emerging treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Arch. Med. Res. 2021, 52, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.-G.; Kim, S.-U.; Wong, V.W.-S. New trends on obesity and NAFLD in Asia. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Golabi, P.; de Avila, L.; Paik, J.M.; Srishord, M.; Fukui, N.; Qiu, Y.; Burns, L.; Afendy, A.; Nader, F. The global epidemiology of NAFLD and NASH in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Stepanova, M.; Ong, J.; Trimble, G.; AlQahtani, S.; Younossi, I.; Ahmed, A.; Racila, A.; Henry, L. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is the most rapidly increasing indication for liver transplantation in the United States. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 19, 580–589.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusi, K. Role of insulin resistance and lipotoxicity in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Clin. Liver Dis. 2009, 13, 545–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delli Bovi, A.P.; Marciano, F.; Mandato, C.; Siano, M.A.; Savoia, M.; Vajro, P. Oxidative stress in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. An updated mini review. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 595371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabbia, D.; Cannella, L.; De Martin, S. The role of oxidative stress in NAFLD–NASH–HCC transition—Focus on NADPH oxidases. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Han, X. Lipidomics: Techniques, applications, and outcomes related to biomedical sciences. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 954–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Gross, R.W. Global analyses of cellular lipidomes directly from crude extracts of biological samples by ESI mass spectrometry: A bridge to lipidomics. J. Lipid Res. 2003, 44, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibanez, C.; Mouhid, L.; Reglero, G.; Ramirez de Molina, A. Lipidomics insights in health and nutritional intervention studies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 7827–7842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Lan, Y.; Zhu, X.; Li, J.; Chen, T.; Huang, Q.; Ho, C.-T.; Chen, Y.; Cao, Y. Hepatic lipidomics analysis reveals the antiobesity and cholesterol-lowering effects of tangeretin in high-fat diet-fed rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 6142–6153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Chen, T.; Xie, X.; Wang, X.; Luo, Y.; Xu, N.; Sa, Z.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Z.; Hu, X. Hepatic Lipidomics Analysis Reveals the Ameliorative Effects of Highland Barley β-Glucan on Western Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 9287–9298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskrey, B.H.; Megson, I.L.; Rossi, A.G.; Whitfield, P.D. Emerging importance of omega-3 fatty acids in the innate immune response: Molecular mechanisms and lipidomic strategies for their analysis. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 1390–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Videla, L.A.; Rodrigo, R.; Orellana, M.; Fernandez, V.; Tapia, G.; Quiñones, L.; Varela, N.; Contreras, J.; Lazarte, R.; Csendes, A. Oxidative stress-related parameters in the liver of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients. Clin. Sci. 2004, 106, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Tan, S.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, C. Citrus reticulata Blanco peel extract ameliorates hepatic steatosis, oxidative stress and inflammation in HF and MCD diet-induced NASH C57BL/6 J mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 83, 108426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, Z.; Tan, S.; Li, H.; Jiang, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, R.; Li, M. Tangeretin improves hepatic steatosis and oxidative stress through the Nrf2 pathway in high fat diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease mice. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 2782–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Choi, M.S.; Woo, J.T.; Jeong, M.J.; Kim, S.R.; Jung, U.J. Long-term dietary supplementation with low-dose nobiletin ameliorates hepatic steatosis, insulin resistance, and inflammation without altering fat mass in diet-induced obesity. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesharwani, S.S.; Mallya, P.; Kumar, V.A.; Jain, V.; Sharma, S.; Dey, S. Nobiletin as a molecule for formulation development: An overview of advanced formulation and nanotechnology-based strategies of nobiletin. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunbupha, S.; Pakdeechote, P.; Maneesai, P.; Prasarttong, P. Nobiletin alleviates high-fat diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by modulating AdipoR1 and gp91phox expression in rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2021, 87, 108526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Xu, M.; Jeong, S.; Qian, Y.; Wu, H.; Xia, Q.; Kong, X. The role of Nrf2 in liver disease: Novel molecular mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 9, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A. Hepatic lipotoxicity and the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: The central role of nontriglyceride fatty acid metabolites. Hepatology 2010, 52, 774–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferré, P.; Phan, F.; Foufelle, F. SREBP-1c and lipogenesis in the liver: An update1. Biochem. J. 2021, 478, 3723–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paton, C.M.; Ntambi, J.M. Biochemical and physiological function of stearoyl-CoA desaturase. Am. J. Physiol. -Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 297, E28–E37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, M.; Kim, Y.C.; Gray-Keller, M.P.; Attie, A.D.; Ntambi, J.M. The Biosynthesis of Hepatic Cholesterol Esters and Triglycerides Is Impaired in Mice with a Disruption of the Gene for Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase 1. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 30132–30138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peet, D.J.; Turley, S.D.; Ma, W.; Janowski, B.A.; Lobaccaro, J.-M.A.; Hammer, R.E.; Mangelsdorf, D.J. Cholesterol and bile acid metabolism are impaired in mice lacking the nuclear oxysterol receptor LXRα. Cell 1998, 93, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Gan, L.; Yang, C.S.; Liu, A.B.; Lu, W.; Shao, P.; Dai, Z.; Sun, P.; Luo, Z. Effects of stigmasterol and β-sitosterol on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in a mouse model: A lipidomic analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 3417–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puri, P.; Baillie, R.A.; Wiest, M.M.; Mirshahi, F.; Choudhury, J.; Cheung, O.; Sargeant, C.; Contos, M.J.; Sanyal, A.J. A lipidomic analysis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2007, 46, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.M.; Van Natta, M.; Behling, C.; Contos, M.J.; Cummings, O.W.; Ferrell, L.D.; Liu, Y.C.; Torbenson, M.S.; Unalp-Arida, A. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Chen, L.; Chen, H.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y. Analysis of flavonoid metabolites in citrus peels (Citrus reticulata “Dahongpao”) using UPLC-ESI-MS/MS. Molecules 2019, 24, 2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.-J.; Gao, H.; Hu, J.-L.; Nie, Q.-X.; Chen, H.-H.; Xiong, T.; Nie, S.-P.; Xie, M.-Y. Polysaccharides from fermented Momordica charantia ameliorate obesity in high-fat induced obese rats. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Class Description | Ingredients | Chow (g) | HFD (g) | LNOB (g) | HNOB (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein | Casein, Lactic, 30 Mesh | 200.00 | 200.00 | 200.00 | 200.00 |
| Protein | Cystine, L | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 |
| Carbohydrate | Lodex 10 | 35.00 | 125.00 | 125.00 | 125.00 |
| Carbohydrate | Sucrose, Fine Granulated | 354.00 | 72.80 | 72.80 | 72.80 |
| Fiber | Solka Floc, FCC200 | 50.00 | 50.00 | 50.00 | 50.00 |
| Fat | Lard | 20.00 | 245.00 | 245.00 | 245.00 |
| Fat | Soybean Oil, USP | 25.00 | 25.00 | 25.00 | 25.00 |
| Mineral | S10026B | 50.00 | 50.00 | 50.00 | 50.00 |
| Vitamin | Choline Bitartrate | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 |
| Vitamin | V10001C | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Dye | Dye, Blue FD&C #1, Alum. Lake 35–42% | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| compound | NOB | 0 | 0 | 0.77 | 1.54 |
| Total | 1055.05 g | 773.85 g | 774.62 g | 776.16 g | |
| Gene | Forward Primer (5’->3’) | Reverse Primer (5’->3’) |
|---|---|---|
| Nrf2 | GCCTCCAAAGGATGTCAATCA | GCCTCACCTCTGCTGCAAGTA |
| NQO1 | TGGCGTAGTTGAATGATGTCTT | TTCGGTATTACGATCCTCCCT |
| HO-1 | CCACATTGGACAGAGTTCACAG | CCTCACAGATGGCGTCACTTC |
| GCLC | GCACATCTACCACGCAGTCAAG | CATCGCCTCCATTCAGTAACAAC |
| GSTA2 | TGTCCTTCCCATAGAGGTCAT | TGCTTCACTACTTCAATGCCC |
| SREBP-1c | ATCCAAGGGCATCTGAGAACTC | ATCCAAGGGCAGTTCTTGTG |
| SCD-1 | TCCTCCTTGGATTGTGTAGAAACTT | AATGTCAGAAGAAATCAGGTGGGTA |
| FAS | CTGAGATCCCAGCACTTCTTGA | GCCTCCGAAGCCAAATGAG |
| LXRα | TCAGAAGAACAGATCCGCTTG | CGCCTGTTACACTGTTGCT |
| PPARα | AGGCTGTAAGGGCTTCTTTCG | GGCATTTGTTCCGGTTCTTC |
| CYP7A1 | AACAACCTGCCAGTACTAGATAGC | GTGTAGAGTGAAGTCCTCCTTAGC |
| CYP27A1 | GCCTCACCTATGGGATCTTCA | TCAAAGCCTGACGCAGATG |
| β-actin | TGT CCA CCT TCC AGC AGA TGT | AGCTCAGTAACAGTCCGCCTAGA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ke, Z.; Fan, C.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Tian, W.; Yu, Q. Nobiletin Intake Attenuates Hepatic Lipid Profiling and Oxidative Stress in HFD-Induced Nonalcoholic-Fatty-Liver-Disease Mice. Molecules 2023, 28, 2570. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062570
Ke Z, Fan C, Li J, Wang L, Li H, Tian W, Yu Q. Nobiletin Intake Attenuates Hepatic Lipid Profiling and Oxidative Stress in HFD-Induced Nonalcoholic-Fatty-Liver-Disease Mice. Molecules. 2023; 28(6):2570. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062570
Chicago/Turabian StyleKe, Zunli, Chaowen Fan, Jun Li, La Wang, Haiyang Li, Weiyi Tian, and Qi Yu. 2023. "Nobiletin Intake Attenuates Hepatic Lipid Profiling and Oxidative Stress in HFD-Induced Nonalcoholic-Fatty-Liver-Disease Mice" Molecules 28, no. 6: 2570. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062570
APA StyleKe, Z., Fan, C., Li, J., Wang, L., Li, H., Tian, W., & Yu, Q. (2023). Nobiletin Intake Attenuates Hepatic Lipid Profiling and Oxidative Stress in HFD-Induced Nonalcoholic-Fatty-Liver-Disease Mice. Molecules, 28(6), 2570. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062570






