Abstract
LsrK is a bacterial kinase that triggers the quorum sensing, and it represents a druggable target for the identification of new agents for fighting antimicrobial resistance. Herein, we exploited tryptophan fluorescence spectroscopy (TFS) as a suitable technique for the identification of potential LsrK ligands from an in-house library of chemicals comprising synthetic compounds as well as secondary metabolites. Three secondary metabolites (Hib-ester, Hib-carbaldehyde and (R)-ASME) showed effective binding to LsrK, with KD values in the sub-micromolar range. The conformational changes were confirmed via circular dichroism and molecular docking results further validated the findings and displayed the specific mode of interaction. The activity of the identified compounds on the biofilm formation by some Staphylococcus spp. was investigated. Hib-carbaldehyde and (R)-ASME were able to reduce the production of biofilm, with (R)-ASME resulting in the most effective compound with an EC50 of 14 mg/well. The successful application of TFS highlights its usefulness in searching for promising LsrK inhibitor candidates with inhibitor efficacy against biofilm formation.
1. Introduction
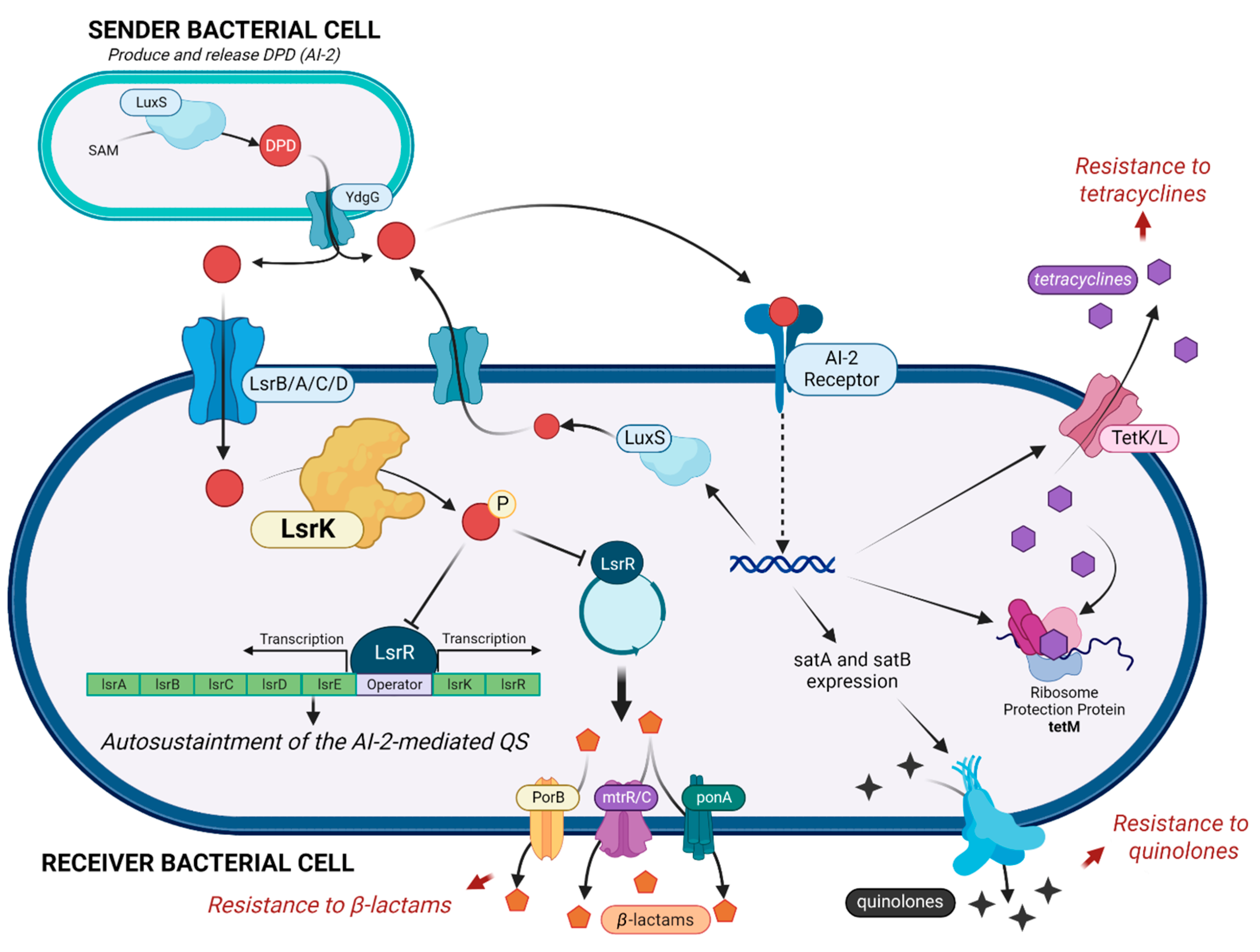
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and the worldwide increase in superbug infections are recognized by the World Health Organization (WHO) as global concerns for public health and the sustainability of healthcare systems [1]. Superbug bacteria are responsible for about 25% of infections and almost 30% of AMR-related deaths, and they are expected to become the primary cause of death by the year 2050 [1]. To challenge this inauspicious perspective, one of the strategic objectives of the WHO is the research of new pharmaceutical tools and medicines [2]. Overuse, inappropriate prescription, and extensive agricultural use of antibiotics have clearly been exposing bacteria to strong, selective evolutive pressure, leading to the development of protective mechanisms to inactivate, remove, and in general circumvent the toxicity of antibiotics [3]. Conventional antibacterial drugs usually interfere with bacterial cell wall biosynthesis, protein synthesis, or DNA replication, and the search for new antimicrobials is still mainly focused on these strategies, thus exposing these new drugs to the same resistance mechanism [4,5,6]. The search for new targets and innovative antibacterial strategies and weapons has become mandatory. An innovative strategy to deal with AMR is to interfere with biofilm formation and with bacterial quorum sensing (QS). About 80% of all human bacterial infections are complicated by biofilms, within which bacteria have a 1000-fold higher tolerance to antibiotics [6,7]. The QS signaling is the most effective mechanism that bacteria use to communicate and organize in biofilms. QS is mediated by diverse autoinducers. [5] Particularly, AI-2 is produced and sensed by both Gram- and Gram+ bacteria and plays a crucial role in maintaining QS. LsrK is a pivotal key kinase in triggering the QS cascade [8,9,10]. LsrK is responsible for the phosphorylation of Autoinducer-2 (AI-2, the QS messenger most exploited by both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria) to phospho-4,5-Dihydroxy-2,3-pentanedione (P-DPD) [8,11]. This represents the key triggering step in the AI-2-mediated QS cascade (Figure 1). P-DPD binds to the transcriptional repressor LsrR. LsrR dissociates from the promoter region of the lsrRK and lsrACDBFG operons, inducing the transcription of genes involved in bacterial virulence and in the auto-sustainment of QS [12]. Several studies proved the role of LsrK in bacterial QS [13,14]. LsrK mutants do not activate lsr transcription because of the lack of P-DPD with reduced expression of the Lsr transporter and extracellular AI-2 accumulation [13]. Furthermore, when LsrK and ATP were added in the extracellular medium, the phosphorylation of AI-2 outside the cell avoids the internalization of P-DPD due to its negative charge. As a result, a reduction in lsr gene expression and attenuation of QS were observed [13].
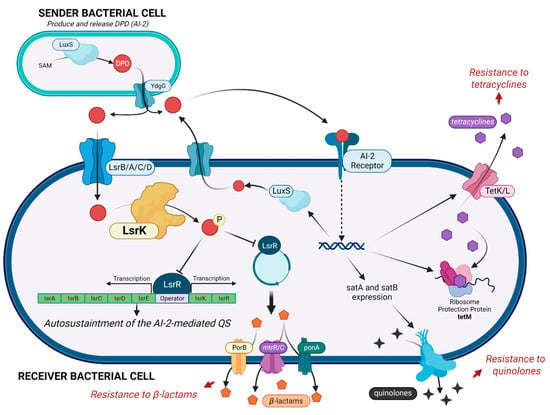
Figure 1.
AI-2 mediated cascade, with a focus on the key role of LsrK kinase in controlling the auto-sustaintment of QS and the diverse mechanisms involved in antimicrobial resistance. (Created with BioRender).
The multifunctional capabilities of LsrK in the bacterial virulence and AMR make this kinase an attractive candidate for drug development. To date, this target is almost unexplored, and few compounds have been proposed as LsrK inhibitors. However, these pilot studies pave the way for a more complete understanding of the role of the bacterial LsrK kinase inhibition in the autoinducer-2-mediated QS cascade and will allow for the discovery of novel innovative non-antibiotic therapies [8,11]. To date, LsrK inhibitors have been identified by exploiting different indirect strategies (Figure S1) [12]. Briefly, meclofenamic acid (1) and its halogenated derivatives 3–8 (Figure S1A) were identified via a structure-based virtual screening approach performed on a LsrK homology model developed before the X-ray structures of the kinase were resolved [15]. Compounds 9–12 (Figure S1B) were designed by a member of our group by exploiting the structure–activity relationship deciphered around the main backbone of DPD; a spyrocyclohexyl-dioxolane moiety replaced the diol portion essential for LsrK-mediated phosphorylation, whereas the diketo group was embedded in diverse heteroaromatic rings [16]. Lastly, several structural unrelated LsrK inhibitors (Figure S1C) were identified through an automatized target-based HTS, with hapargoside and rosolic acid being active in a cell-based AI-2 QS interference assay [17]. Although the LsrK inhibitory activity for these compounds is reported, no experimental evidence of their binding to the protein was still investigated. Moreover, to complicate the canvas, we still lack experimental evidence of the binding mode of DPD or LsrK inhibitors with the protein, and the putative catalytic binding site has just been postulated thanks to the three LsrK crystallographic structures (PDB ID: 5YA0, 5YA1, and 5YA2) [18] together with the homology comparison with other bacterial kinases, such as glycerol kinase (GK) or xylulose kinase (XK) [18]. As part of our ongoing research on the bacterial Lsrk, in this paper we present the first application of the tryptophan fluorescence spectroscopy (TFS) for studying the ligand–LsrK binding, and we applied this biophysical assay to cherry-pick compounds that potentially target the bacterial kinase from an in-house library of small molecules and secondary metabolites. In addition, the conformational changes of LsrK upon binding with the identified ligands were discussed on the basis of circular dichroism (CD) and the binding of the ligands to the protein was lastly rationalized via molecular docking. These facile methods can provide binding mechanisms between LsrK kinase and potential inhibitors and may facilitate the discovery of novel drugs for fighting AMR through an innovative mechanism of action.
2. Results and Discussion
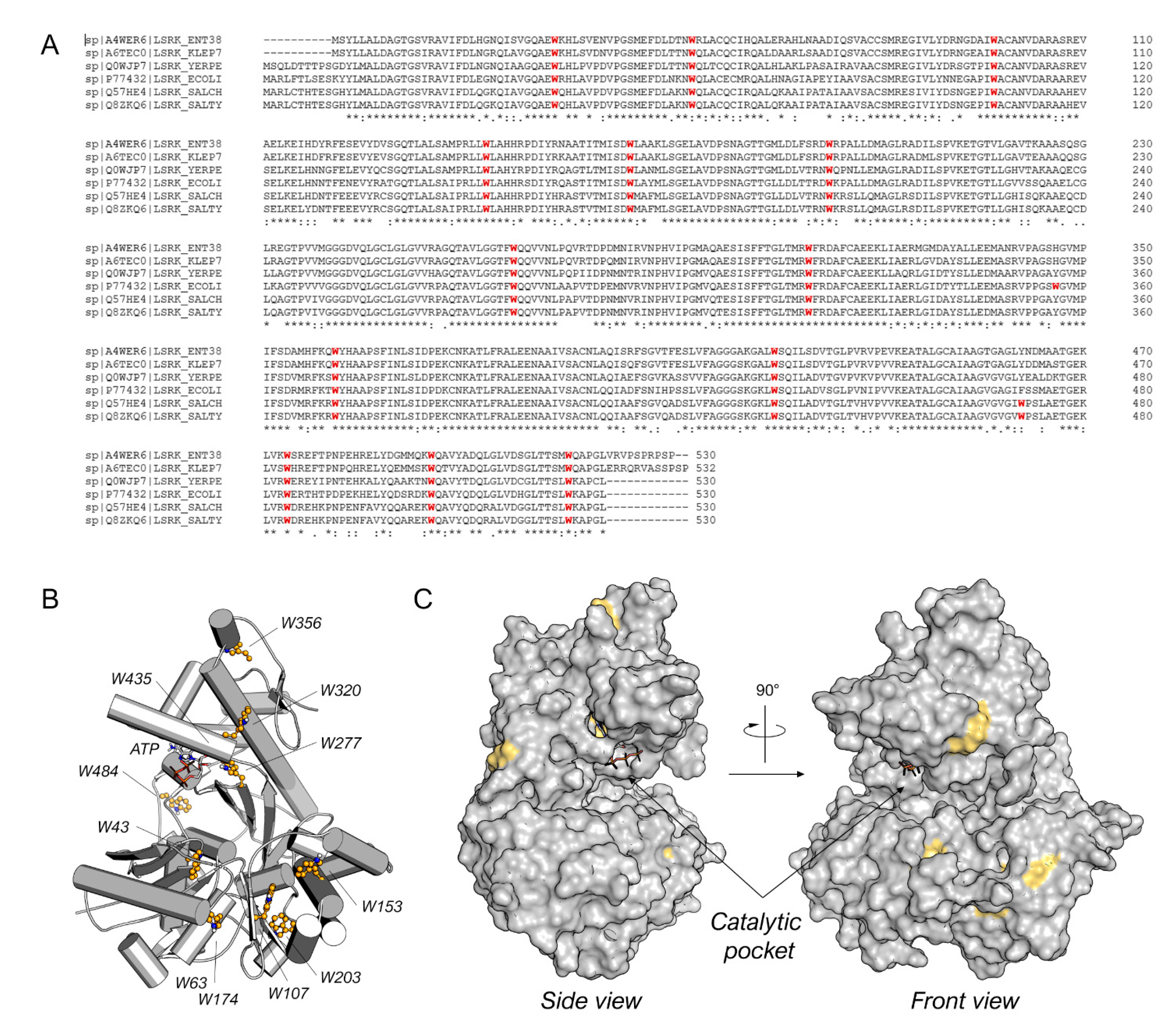
Among the diverse techniques useful for studying the protein–ligand binding, we selected the TFS. Indeed, tryptophan is known to emit intrinsic fluorescence that can be measured via fluorescence spectroscopy [19]. Interactions with binding ligands can change the tryptophan microenvironment, resulting in shifts of the maximum fluorescence peak and variations in intensity [20]. Bacterial LsrK is rich in tryptophan (Figure 2A), with thirteen highly conserved tryptophan residues among diverse bacteria species (e.g., Enterobacter sp., Klebsiella pneumonia, Yersinia pestis, Escherichia coli, Salmonella choleraesuis, and Salmonella typhimurium). Only E. coli and both Salmonella spp. LsrKs possess an additional tryptophan residue in positions 356 and 471, respectively. The location of tryptophan residues on the protein was highlighted on the crystallographic structures of Escherichia coli LsrK (ecLsrK). As illustrated in Figure 2B,C, four of the thirteen conserved tryptophan residues (Trp43, Trp277, Trp320, and Trp435) are situated close to the catalytic binding pocket, while the remaining are distributed across the protein’s surface. In particular, Trp435 and Trp277 are in close contact with ATP, whereas Trp43 and Trp320 are part of the catalytic cleft, where DPD is supposed to bind.
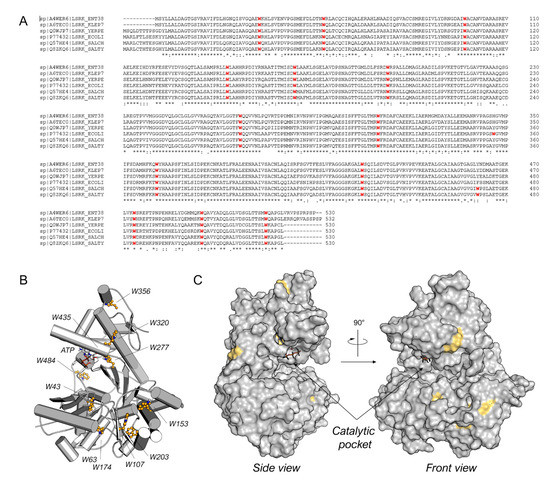
Figure 2.
(A) Sequence alignment for Enterobacter sp. (ENT38), K. pneumonia (KLEP7), Y. pestis (YERPE), E. coli (ECOLI), S. choleraesuis (SALCH), and S. typhimurium LsrK. All tryptophan residues are colored in red. Below the sequence alignment is a key denoting conserved amino acid residues (*), conservative substitutions (:), and semi-conservative substitutions (.). The non-conserved tryptophan residues between E. coli and S. typhimurium LsrK are highlighted in the red square. (B) Tryptophan residue position on the structure of ecLsrK (PDB ID: 5YA1). Lsrk is visualized as cartoons in grey. ATP is represented in stick mode. The tryptophan residues are highlighted in ball-and-stick with carbon atom in yellow. (C) Visualization of the tryptophan residues exposed on the surface of the protein. The putative catalytic pocket is indicated.
The ubiquitous presence of tryptophan residues in the LsrK led us to hypothesize that changes in the intrinsic tryptophan fluorescence, upon ligand binding, might effectively reflect the strength of the LsrK–ligand interactions and the protein conformational change [20]. Based on these premises, we firstly investigated via TFS the secondary metabolite produced by some species of lichen, namely fumarprotocetraric acid (FP), which has been isolated by our group within a nature-aided drug discovery (NADD) program. FP was used as pilot molecule to investigate its binding with LsrK, since it has been demonstrated as a promising LsrK inhibitor (IC50 of 7 μM) [17] and strong antimicrobial agent [21]. Recombinant LsrK was expressed as previously reported [9]. LsrK was titrated by the successive addition of FP (from 0.01 nM up to 4 μM). An amount of 1 μL of the appropriate concentration of ligands was progressively added so as to contain the overall dilution of the protein solution below 1%. The fluorescence quenching at 330 nm (the maximum in fluorescence emission) was analyzed. Figure 3A shows the quenching of the fluorescence emission of the Trp residue of ecLsrK by the addition of aliquots of FP solution. The LsrK fluorescence decreased with the increasing compound concentrations, which suggests that this decrease reflected the interaction of the bacterial kinase with FP. The absence of considerable changes in the wavelength of the emission maximum of LsrK is evidence that the presence of FP does not exert a great influence on the polarity of the microenvironment of the cavity around the Trp residue. The variation of F0/F with the concentration of FP (Stern–Volmer plot) was not linear and showed a negative deviation. The negative deviation in the plot may arise by the presence of two populations of fluorophores with different accessibility to the quencher. Indeed, LsrK is a structured protein, thus the tryptophan residues involved in the binding site of the ligand are readily available for quenching, whereas the others not involved in binding will not be quenched (Figure 2). Moreover, some tryptophan residues are buried within the protein, and this contributes overall to a heterogeneous quenching. This condition is reflected in a negative deviation from the linearity of the Stern–Volmer plot [22,23,24,25]. Therefore, the data have been treated using a modified Stern–Volmer equation.
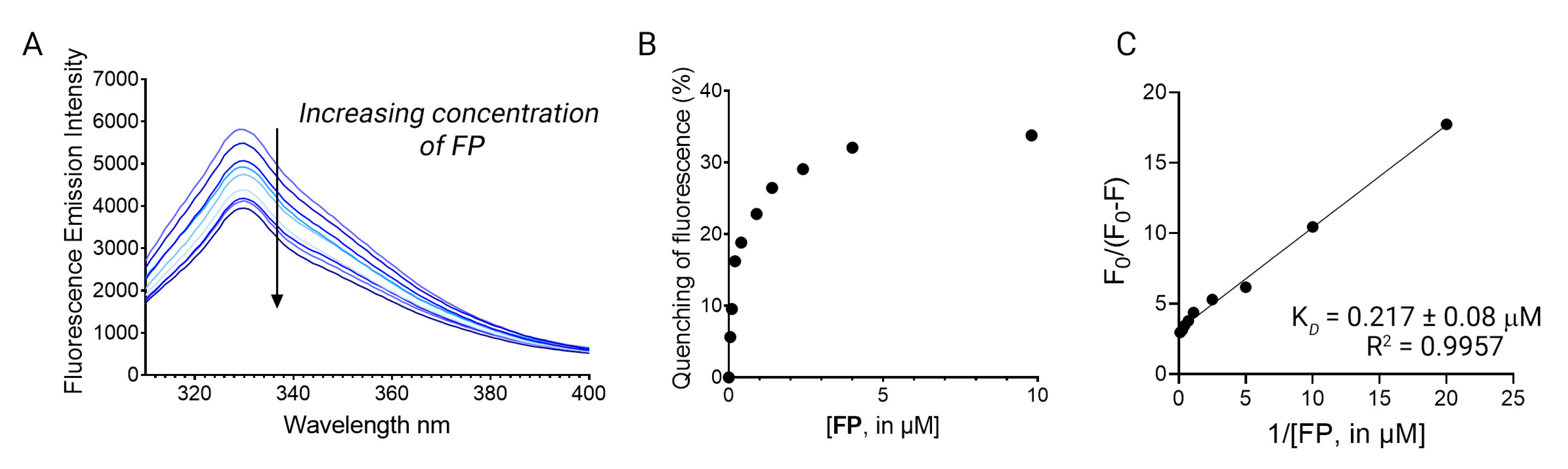
where F0 is the emission fluorescence of LsrK in the absence of ligands, F is the emission fluorescence of the protein in the presence of the ligand at the concentration [Q], fa is the fraction of accessible fluorophore to the ligands, and KSV is the Stern–Volmer constant. The analysis of the data using the modified Stern–Volmer equation is the classical model used in the interpretation of some results of fluorescence quenching in protein solution when the Stern–Volmer plot negatively deviates from linearity, [26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33] since it allows for investigating in detail the quenching mechanism that is occurring between ligands and proteins. Indeed, the linearity of the modified Stern–Volmer plots indicates static quenching (i.e., binding) in the presence of an inaccessible population of fluorophores and the plot allows for the calculation of the dissociation constant (KD) and the percentage of fluorophores accessible to the quenchers. fa is calculated as the reciprocal of the intercept, whereas KD is given by the product of fa and the slope of the line interpolating the points in the graph [34]. Accordingly, FP binds LsrK with static quenching to 26% of accessible Trp residues, and results in a KD of 217 ± 8 nM (Figure 3B).
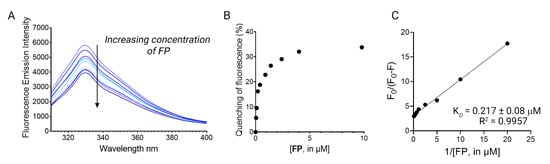
Figure 3.
(A) The fluorescence quenching spectra of LsrK in the presence of FP, [LsrK] = 0.1 μM, [ligand] ranging from 0 to 10 μM, T = 298 K, pH = 7.4, λex = 280 nm; the experiments were performed in triplicate; (B) % of fluorescence quenching vs. ligand concentration. (C) Modified Stern–Volmer plot for the binding of FP to LsrK. The points are interpolated using linear regression for the quantification of the KD; the values (±SD) are the results of three independent measurements.
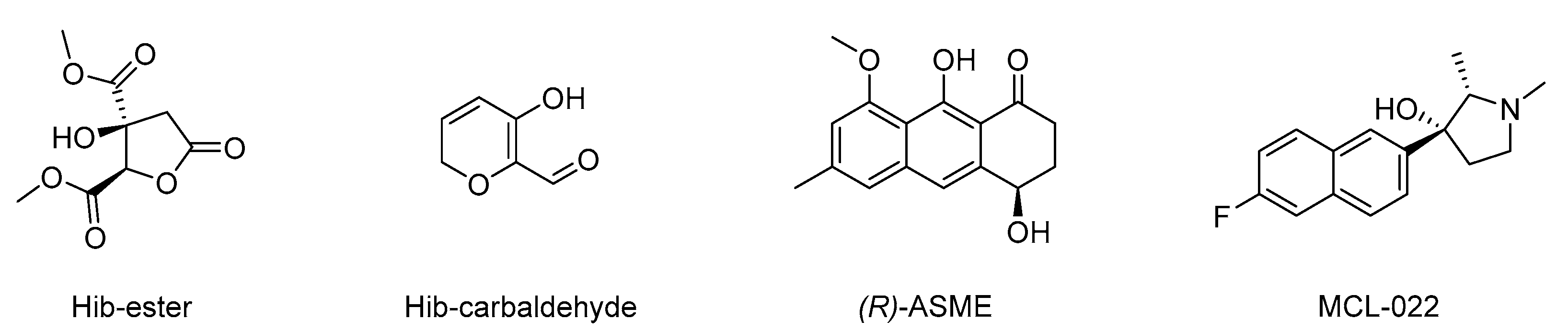
Once the suitability of TFS in studying the ligand–LsrK interaction was proven, following the encouraging results obtained with FP we screened our in-house compound library for potential ligands that could bind to LsrK. Such chemical libraries are usually assembled from compounds and intermediates produced during other medicinal chemistry investigations performed by research groups in academia and industry. The test’s small molecules were primarily obtained from an in-house collection of compounds (MedChemLab, MCL, Department of Drug Sciences, University of Pavia, Pavia, Italy). The MCL compound library consists of non-commercial small molecules synthesized and assessed during several drug discovery projects performed in the past years by our research group, including several secondary metabolites extracted from the proper plant drugs during nature-aided drug discovery programs [35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44]. Representative compounds of the MCL library were initially assessed in a low-throughput primary screening against recombinant LsrK via TFS. All the compounds were screened in duplicate at a 100 μM concentration against a 0.1 μM solution of LsrK. The intrinsic fluorescence spectra were then collected in the range of 300–400 nm by keeping the excitation wavelength at 295 nm and the fluorescence emission reduction at 330 nm (the maximum of the emission spectra) was measured. To establish a cutoff point for quenching, we chose FP as a reference compound (e.g., reduction in the fluorescence emission > 30% at the tested concentration). Only four compounds (Figure 4) significantly decreased the LsrK fluorescence by more than 30%, namely dimethyl (2R,3S)-3-hydroxy-5-oxotetrahydrofuran-2,3-dicarboxylate (Hib-ester), 5-hydroxy-2H-pyran-6-carbaldehyde (Hib-carbaldehyde), (R)-(−)-aloesaponol III 8-methyl ether [(R)-ASME], and (2S,3R)-3-(6-fluoronaphthalen-2-yl)-1,2-dimethylpyrrolidin-3-ol (MCL-022), and they were selected for further characterization. Interestingly, Hib-ester and Hib-carbaldehyde are two secondary metabolites isolated from the calyces of Hibiscus sabdariffa, [35,36,37] whereas (R)-ASME was isolated from Eremurus persicus [38]. Conversely, MCL-022 is a synthetic compound initially designed as an antinociceptive agent [39,40].
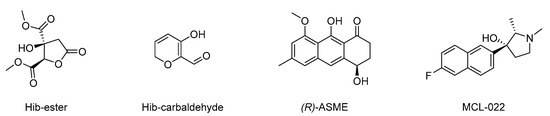
Figure 4.
Chemical structure of dimethyl (2R,3S)-3-hydroxy-5-oxotetrahydrofuran-2,3-dicarboxylate (Hib-ester), 5-hydroxy-2H-pyran-6-carbaldehyde (Hib-carbaldeyde), (R)-(−)-aloesaponol III 8-methyl ether [(R)-ASME], and (2S,3R)-3-(6-fluoronaphthalen-2-yl)-1,2-dimethylpyrrolidin-3-ol (MCL-022).
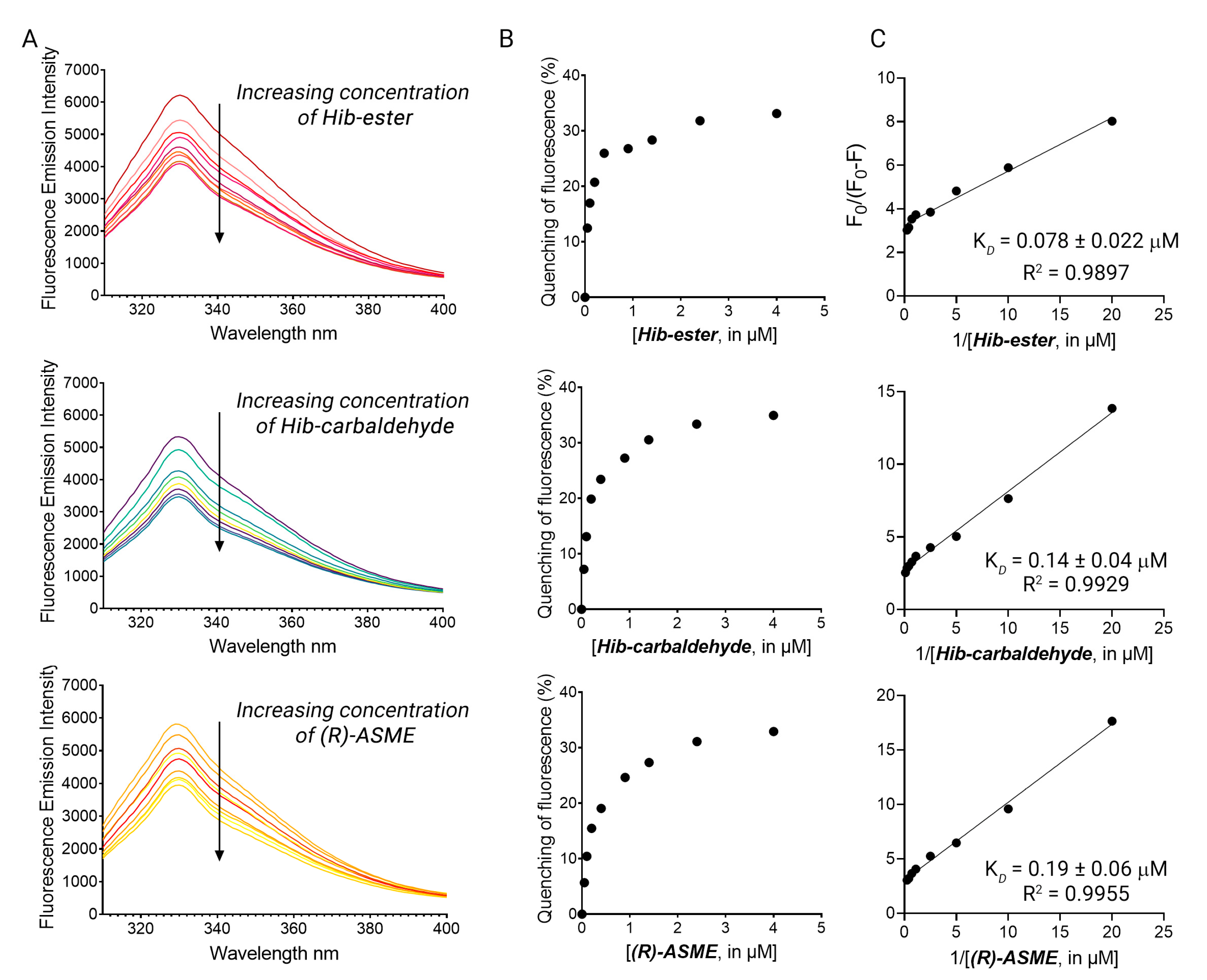
The four primary hits were validated using dose-response studies to avoid false-positive results, and the KD was determined. The intrinsic fluorescence of the four primary hits alone was recorded first, to confirm the absence of interference between the fluorescence of the compounds with that of the protein. Hib-ester, Hib-carbaldehyde, and (R)-ASME did not emit fluorescence at 330 nm when excited at 295 nm. Conversely, MCL-022 possessed intrinsic fluorescence in the experimental conditions and it was therefore marked as false-positive and discarded. LsrK was titrated by the successive addition of selected compounds as described for FP. Figure 5A shows the fluorescence emission spectra in the range 300–400 nm of LsrK in the presence of increasing concentrations of the ligand. Hib-ester, Hib-carbaldehyde, and (R)-ASME quenched the intrinsic fluorescence of LsrK in a dose-dependent manner, whereas no quenching of fluorescence emission was detected when only PBS was added to the mixtures of the recombinant protein. Analysis of the tryptophan quenching data using the modified Stern–Volmer equation showed the dependence of F0/ΔF on the reciprocal values of the quencher concentration [Q]−1 exhibited a good linear relationship, thus confirming that the quenching mechanism between the ligands and LsrK occurred though a static quenching, resulting in KD values of 78, 140, and 190 nM for Hib-ester, Hib-carbaldehyde, and (R)-ASME, respectively (Figure 5B,C). To assess whether these compounds might compete with ATP for the binding to LsrK, the binding of ATP for LsrK was studied via TFS, resulting in a KD of 5.07 ± 0.23 µM (Figure S2). The identified secondary metabolites possess a binding affinity 26–63-fold higher that ATP, and therefore they might considerably compete with and displace ATP from its binding site. This suggests a possible ATP-competitive inhibition of the LsrK kinase.
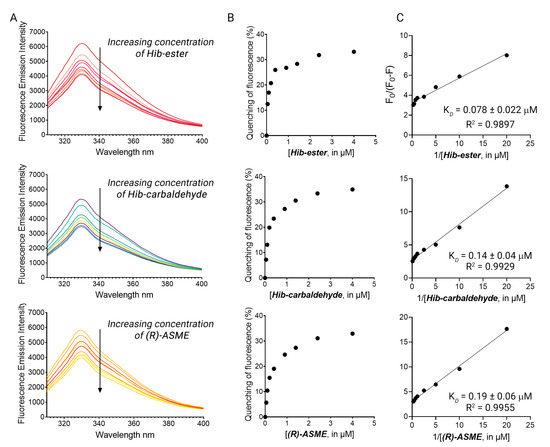
Figure 5.
(A) The fluorescence quenching spectra of LsrK in the presence of Hib-ester, Hib-carbaldehyde, and (R)-ASME, [LsrK] = 0.1 μM, [ligand] ranging from 0 to 4 μM, T = 298 K, pH = 7.4, λex = 280 nm; the experiments were performed in triplicate; (B) % of fluorescence quenching vs. ligand concentration. (C) Modified Stern–Volmer plot for the binding of Hib-ester, Hib-carbaldehyde, and (R)-ASME to LsrK. The points are interpolated using linear regression for the quantification of the KD; the values (±SD) are the results of three independent measurements.
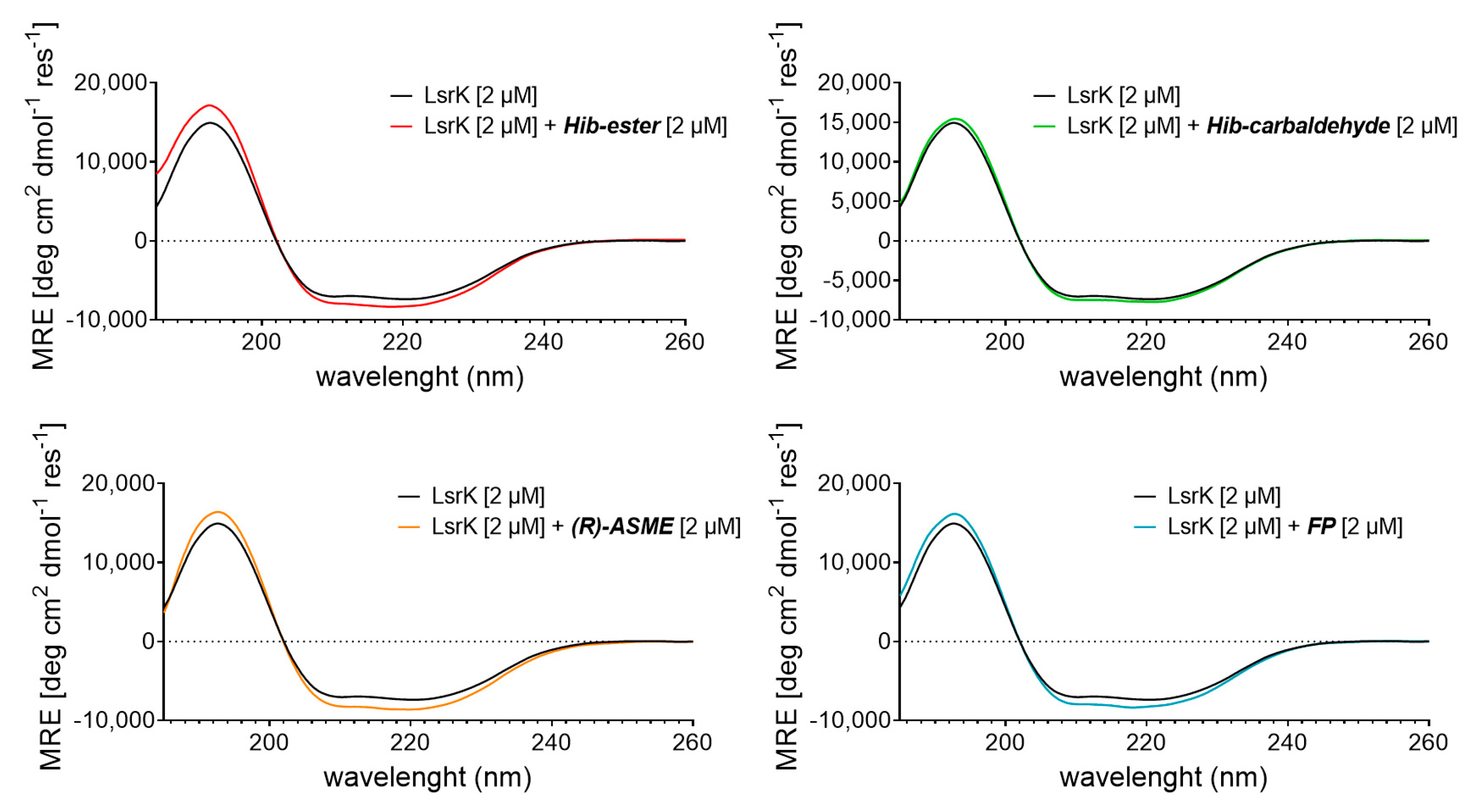
To characterize in more detail the interaction between the selected natural products and LsrK, we referred to circular dichroism (CD) [45,46]. More specifically, we measured the Far-UV CD spectrum of the bacterial protein in the presence or absence of a saturating concentration of each compound. The results were expressed as the mean residue ellipticity (MRE in deg cm2 dmol−1 res−1, Equation (S1). Far UV-CD spectra of apo-LsrK at 2 μM revealed a positive band at 195 nm and a negative band with two minimum at 208 nm (n → π*) and 223 nm (π → π*), characteristic of an alpha–helix structure. Deconvolution of the CD spectrum by using BestSel [47] confirmed that the protein is a helix-strand protein and allowed us to estimate the relative content of the secondary structure elements of the protein (Table S1). This result agrees with the crystallographic structure of the protein and the secondary structure content calculated from the available crystallographic structure of the apo-LsrK (PDB ID: 5YA0) [18]. Figure 6 shows the CD spectra of LsrK in the complex with the ligands, in comparison with the spectra of LsrK alone. The presence of each compound modifies the spectrum of the protein, in terms of both an increase in the maximum and a decrease in the minimum, suggesting a change in its conformation as a result of an interaction with the ligands. Briefly, the CD spectra of LsrK upon binding with the four ligands at a molar ratio ligand:LsrK of 1:1 showed an increased ellipticity value at 195 nm and decreased ellipticity at 208 and 223 nm, thereby illustrating that an increase in the α-helical content occurred. Conversely, a slight reduction in the β-sheets and, more importantly, in the turns and the random portions of the protein, was observed. No further variations were observed at a ligand concentration ten times higher than the protein, thus revealing the reaching of saturation binding at 2 μM, as already observed during the TFS studies. This variation was much more marked for FP, Hib-carbaldehyde, and (R)-ASME than for Hib-ester. This suggests a shift of LsrK towards a more ordered conformation, upon complex formation with the ligands. The variation in the secondary structural components of LsrK upon binding with the four ligands was calculated. When FP was present, the contents of the α-helix, β-sheet, β-turn, and random coil structures were changed to 49.5%, 17.6%, 2.6%, and 30.3%, respectively. In the presence of (R)-ASME, the contents of the α-helix, β-sheet, β-turn, and random coil structures were changed to 47.0%, 16.8%, 0%, and 36.2%, respectively. Similarly, in the presence of Hib-ester, the contents of the α-helix, β-sheet, β-turn, and random coil structures were changed to 47.2%, 15.6%, 6.4%, and 30.8%, respectively. Only Hib-carbaldehyde induced little variation in the LsrK conformation. Therefore, the CD experimental analysis showed that the interaction of the identified hit compounds with LsrK clearly lead to conformational changes in the protein, thus confirming their binding.
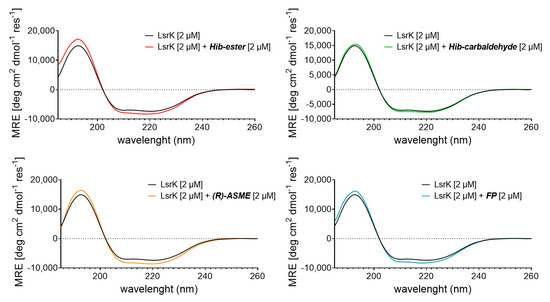
Figure 6.
Far-UV CD spectra of LsrK in presence or absence of the indicated compounds. The reported spectra are the average of six scans and corrected for buffer blank.
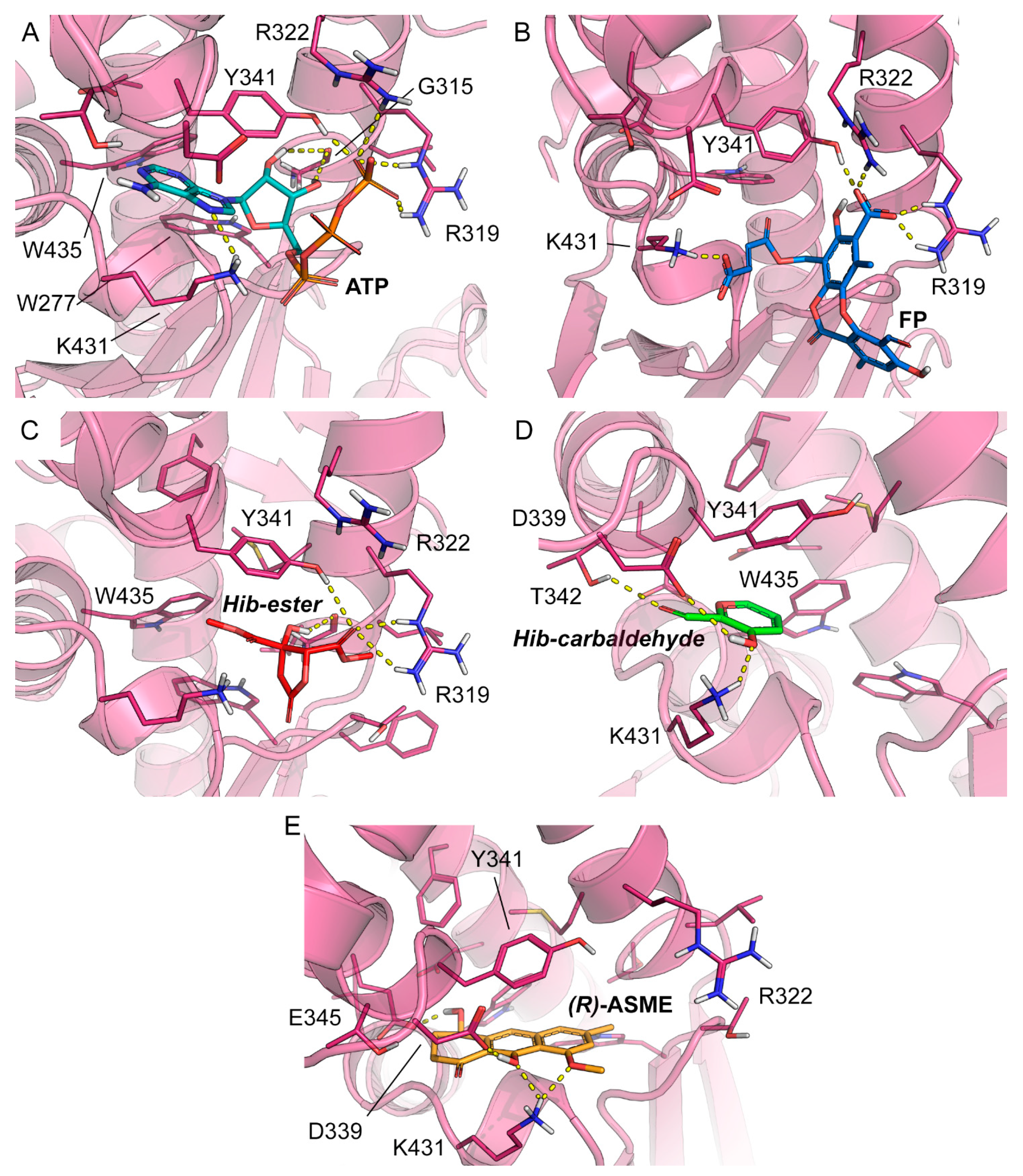
To rationalize the spectroscopic results at the molecular level and to identify the likely binding mode of FP, Hib-ester, Hib-carbaldehyde, and (R)-ASME to LsrK, molecular docking was performed with Glide, which is part of the Schrödinger Platform: Maestro [48,49,50]. More specifically, an X-ray structure of LsrK (in a complex with ATP; PDB ID: 5YA1) was used as receptor for docking [18]. The receptor grid was centered onto the co-crystallized ligand, and ATP and the docking of the four identified secondary metabolites was performed in standard precision mode (“Glide SP”). The docking results indicate that the four investigated small molecules are likely to bind to LsrK in an ATP-competitive manner (Table 1 and Figure 7). With the exception of Hib-ester, all of the generated docking poses extend to the deepest part of the ATP binding pocket and are characterized by good protein-ligand surface complementarity. The most convincing and, at the same time, top-ranked docking pose obtained for any of the investigated ligands was obtained for (R)-ASME (GlideScore—8.184 kcal mol−1). It is noted that the docking scores (Table 1) do not correlate with the measured KD values. Considering the facts that (i) the highest and lowest measured KD values measured for these compounds differ only by a factor of 2, (ii) the capacity of scoring functions to predict binding free energies is inherently limited, and (iii) the number of data points to test for any correlation is extremely low, this result is well within expectations. Focusing on the binding mode, ATP and all investigated ligands are predicted to form aromatic (or hydrophobic) interactions with Y341. Ligand binding is expected to be sustained by a network of hydrogen bonds (Table 1). Indeed, all investigated ligands are predicted to form at least two hydrogen bonds, primarily with R319, K431, T342, Y342, and/or D339, of which at least one hydrogen bond is known to be formed between ATP and the protein (namely, R319). Overall, the results obtained from docking indicate an ATP-competitive binding of the four compounds of interest.

Table 1.
Docking scores and (predicted) interactions of ATP, FP, Hib-ester, Hib-carbaldehyde, and (R)-ASME with LsrK.
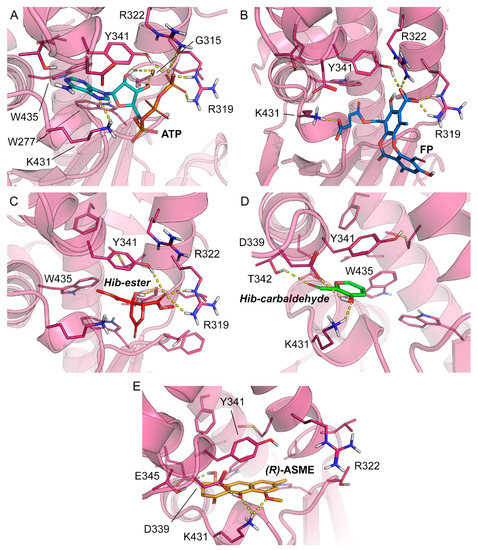
Figure 7.
Co-crystallized pose of (A) ATP (teal carbon atoms) and the binding poses predicted for (B) FP (blue carbon atoms), (C) Hib-ester (red carbon atoms), (D) Hib-carbaldehyde (green carbon atoms), and (E) (R)-ASME (orange carbon atoms). The reference crystal structure used for the docking calculation (PDB ID: 5YA1) of LsrK is shown in the magenta cartoon; important interacting residues are visualized in sticks representation with magenta carbon atoms. Model atoms except for carbons are color-coded: oxygen (red) and nitrogen (blue). Hydrogen bonds are represented as yellow dotted lines.
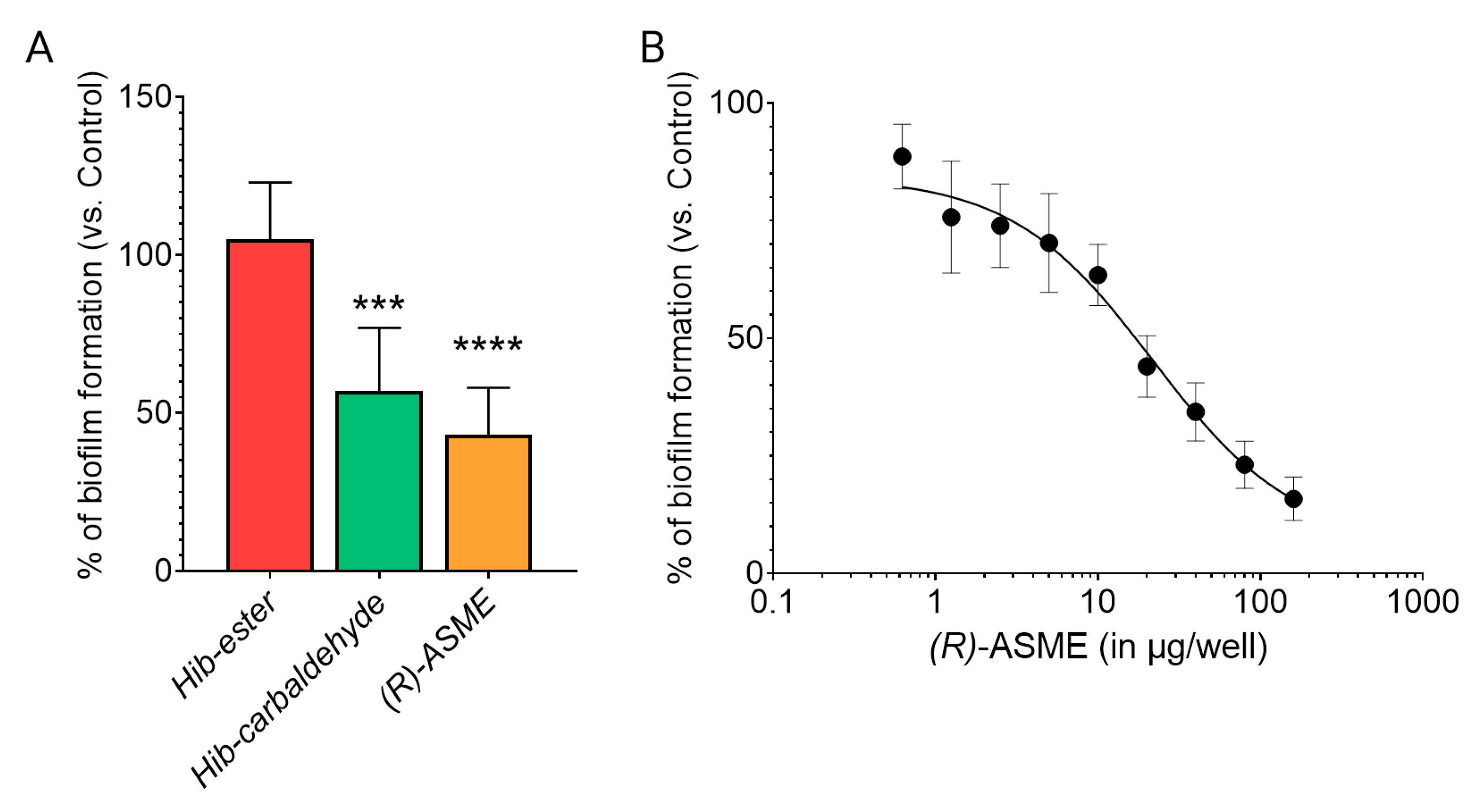
Once the capability in binding LsrK was demonstrated, the efficacy of the three identified compounds in inhibiting the biofilm formation was evaluated on the culture of Staphylococcus spp. [7]. Hib-ester, Hib-carbaldehyde, and (R)-ASME were initially assessed at 40 μg/well and the biofilm inhibitory activity was reported as percentages of the biofilm produced by the positive control (Figure 8A). Despite the sub-micromolar affinity toward LsrK, Hib-ester did not exert any effect on biofilm formation at the tested concentration. Conversely, Hib-carbaldehyde and (R)-ASME caused more than 40% biofilm inhibition at the tested concentration. Clearly, the most active compound was (R)-ASME, with a biofilm inhibition rate of 60% ± 15 at 40 μg/well, followed by Hib-carbaldehyde that exerted a biofilm inhibition rate of 47% ± 22 at the same concentration. Statistical analysis confirmed the significance of the results. (R)-ASME, which resulted as the most effective compound, was further assessed in a dose-response study resulting in an EC50 of 14 ± 4 μg/well, thus indicating its high potential as an effective inhibitor of biofilm formation (Figure 8B). Interestingly, both Hib-carbaldehyde and (R)-ASME did not negatively affected the bacterial viability (measured as planktonic bacterial growth), thus demonstrating that the antibiofilm activity is not correlated with any intrinsic antibacterial activity of the compounds.
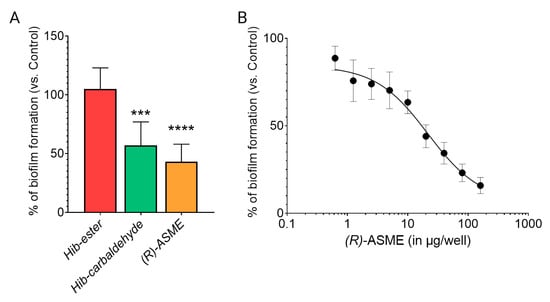
Figure 8.
Effect of inhibitors on biofilm formation by staphylococci. (A) Staphylococcal cells were incubated with 40 μg/well of each inhibitor at 37 °C for 24 h. Biofilm was stained with crystal violet, and the absorbance was measured at 595 nm. (B) Staphylococcal cells were incubated with increasing concentration of ASME at 37 °C for 24 h. Biofilm formation was detected as indicated above. Values are expressed as percentage of the control (no inhibitor added). Data indicate the average of two independent experiments, each performed in quadruplicate. p values were determined using a two-tailed, two-sample unequal variance Student’s t-test in Prism 4.0 (GraphPad, Prism 4.0, San Diego, CA 92121, USA) with *** p < 0.001 and **** p < 0.0001 vs. control.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Isolation and Purification of Hib-Ester and Hib-Carbaldehyde
The chalices of Hibiscus sabdariffa were finely ground using a knife mill, suspended in 80% ethanol, and subjected to microwave radiation. The mixture was cooled to room temperature, filtered, and concentrated under a reduced pressure to obtain the crude extract as a thick reddish oil. The crude was purified via a liquid–liquid extraction and the organic phase was divided into two aliquots and concentrated. The two aliquots were treated in different ways for the isolation of the two metabolites. For the purification of Hib-ester, the crude was dissolved in methanol and treated with the PS carbonate anionic resin (Polymer-supported carbonate) to catch all the acidic species contained in the extract. The resin was then treated with 0.1% HCl in methanol, for the recovery of the retained metabolites, thus obtaining a simplified fraction which was further purified via silica gel chromatography to give Hib-ester in a 0.22% yield. The yield was calculated on the weight of the vegetable drug used. The second aliquot of crude was subjected to a liquid–liquid extraction using dichloromethane and water. The organic phase was fractionated via chromatography on a silica gel, to isolate Hib-carbaldehyde in a 1.1% yield over the weight of the plant drug used.
3.2. Isolation and Purification of (R)-ASME
The dried roots of E. persicus were extracted with ethanol under microwave irradiation. The suspension was filtered, and the collected solution was concentrated. The ethanolic extract was partitioned between water and dichloromethane. The organic layer was collected, dried, and concentrated. The title compound was purified from the crude via crystallization from acetone.
3.3. Isolation and Purification of Fumarprotocetraric Acid
Thalli of C. foliacea were finely grinded and extracted with ethyl acetate under mw irradiation. The crude extract was initially treated with methanol to promote the crystallization of usnic acid. The filtrate was concentrated and the fumarprotocetraric acid was recovered via precipitation from the secondary extract via treatment with a mixture of chloroform:ethanol 1:2.
3.4. Expression and Purification of LsrK
Culture was grown at 37 °C to an OD600 of 0.3, transferred to 22 °C, and grown to an OD600 of 0.9. Expression was subsequently induced with 0.1 mM isopropyl 1-thio-β-D-galactopyranoside (IPTG) (Inalco, Milan, Italy) for 9 h. Cells were harvested and resuspended in 25 mM potassium phosphate, pH 7.0, 50 mM NaCl, 10 mM β-mercaptoethanol, 1 mM MgCl2, 2.5 µg mL−1 DNase, and protease inhibitors and lysed via sonication (70% amplitude, 12 × 30″ on/off, 1′30″ interval between sonication steps). The cell debris was removed via centrifugation and proteins purified from the supernatants via Ni+2-affinity chromatography on a HiTrap chelating column (GE Healthcare, Buckinghamshire, UK). Protein purity was assessed via 12.5 % SDS-PAGE and Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining. A bicinchoninic acid protein assay (Pierce, Rockford, IL, USA) was used to measure the concentration of purified proteins.
3.5. Fluorescence Binding Studies
Fluorescence quenching experiments were carried out on Jasco spectrofluorometer (FP-6200) using a 10-mm quartz cuvette. The temperature was maintained at 25 ± 0.1 °C using an external thermostatic Peltier device. The stock solution of the ligands was prepared in DMSO and the working solution at the appropriate concentration was prepared in PBS. Protein solution (0.1 μM) was titrated with increasing concentrations of ligand and the fluorescence emission spectrum was recorded in the range of 310–400 nm by keeping the excitation wavelength constant at 295 nm. The excitation and emission slit widths were kept at 5 nm. The final spectra were obtained by subtracting with the corresponding blank. For data analysis, the fluorescence intensity at λmax was plotted against [ligand, μM] and then the modified Stern–Volmer equation (Equation (1)) was used to derive binding parameters viz. binding dissociation constant (KD).
3.6. Circular Dichroism
Far-UV (195–250 nm) CD measurements were performed at 20 °C in a 0.1-cm pathlength quartz cuvette. CD spectra were recorded on a Jasco J-720 spectropolarimeter. Appropriate blanks corresponding to the buffer were subtracted to correct the absorbance or fluorescence background. The results are expressed as the mean residue ellipticity (MRE in deg cm2 dmol−1 res−1), which is defined using the following equation:
where n is the number of amino acid residues (530 for LsrK), l is the path length of the cell (0.1 cm), and Cp is the molar (M) concentration of the protein. All the spectroscopic measurements were performed in 20 mM phosphate buffer pH 7.4. Six scans were averaged for each spectrum, and the contribution from the buffer was subtracted in each case.
3.7. Docking
Docking with Glide in standard precision mode (“SP mode”) was performed on the X-ray structure of LsrK in the complex with ATP (PDB 5YA1). The structure was imported into the Schrödinger Platform for small molecule drug discovery. Next, the X-ray structure was interpreted and processed with the Protein Preparation Wizard (part of the platform) with default settings. As part of this process, the structure was checked for completeness, hydrogens were added, hydrogen bonds optimized, solvent molecules removed, and a restrained minimization of the structure was performed with the OPLS4 force field and the default convergence RMSD tolerance of 0.3 Å. In preparation for docking with Glide, a receptor grid was generated. The enclosing box was centered onto the co-crystallized ligand, ATP. Its size was defined based on the amount of ATP (i.e., the option “dock ligands similar in size to the workspace ligand” was used). The docking algorithm was run with default settings, i.e., the enabled sampling of nitrogen inversions, enabled sampling of ring conformations, and enabled biasing of the sampling of torsions for all predefined functional groups. The hydroxy groups of Y341 and T342 were defined as flexible.
3.8. Biofilm Formation
Overnight cultures of staphylococci were diluted 1:200 in Brain Heart Infusion broth (BHI) containing 0.5% glucose. Aliquots (200 μL) of the diluted bacterial suspensions were added to 96-well flat-bottom sterile polystyrene microplates (Costar; Corning, New York, NY, USA) and incubated statically for 24 h at 37 °C in the presence or absence of inhibitors. Biofilms formed on the plates were gently washed twice with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 4.3 mM Na2HPO4 [pH 7.4]) to remove planktonic and loosely adhering bacteria. Adherent cells were fixed with 25% formaldehyde for 10 min, stained with 0.1% crystal violet for 15 min, and after several washings, the wells were air-dried. For a quantitative estimation of the biofilm density, bound crystal violet was solubilized with 10% glacial acetic acid, and the absorbance of the solubilized dye was read at 595 nm in a microplate reader (model 680; Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Hercules, CA, USA).
4. Conclusions
To sum up, in this study we apply for the first time TFS as a simple and reliable analytical method for uncovering highly promising LsrK inhibitor candidates. Accordingly, we exploited TFS to identify within an in-house library of synthetic compounds and plant secondary metabolites potential LsrK-binding hit compounds that could provide for new anti-AMR therapeutic drugs. The fluorescence results indicated that the native fluorescence of LsrK is effectively quenched in the presence of the already published LsrK inhibitor FP and of the secondary metabolites Hib-ester, Hib-carbaldehyde, and (R)-ASME, herein identified via the static quenching mechanism, resulting in a binding affinity for the four compounds to LsrK in the sub-micromolar range. The changes in LsrK conformation observed via CD spectroscopy upon treatment of the protein with the identified hits confirmed the ligand–protein binding and supported the TFS results. Moreover, molecular docking indicated that the binding of the secondary metabolites likely occurs at the ATP binding site, with hydrogen bonds playing a key role in the anchoring of the ligand. Interestingly, Hib-carbaldehyde and (R)-ASME displayed activity against Staphylococcus spp. biofilm formation without negatively affecting bacterial viability. (R)-ASME resulted in the most potent compounds with an EC50 of 14 mg/well, indicating its potential as an effective inhibitor of biofilm formation. Thus, this secondary metabolite hold promise as a potential candidate to serve as an effective anti-biofilm drug that can mitigate the risk of bacterial resistance.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/molecules28062542/s1, Figure S1: Chemical structure, LsrK inhibitory activity and approach exploited for the identification of the LsrK inhibitors reported in literature. Figure S2: % of fluorescence quenching vs. ATP for the binding of ATP to LsrK. Table S1: Percentage of secondary structural components in LsrK.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.L. and G.P.; methodology, R.L, G.M., C.M., F.M, A.P., V.C. and J.K.; software, J.K.; validation, P.L., D.R., E.M., G.P., J.K. and S.C.; writing—original draft preparation, R.L.; writing—review and editing, P.L., D.R., E.M., G.P., J.K. and S.C.; supervision, S.C.; funding acquisition, S.C. and G.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by EU funding within the NextGeneration EU-MUR PNRR Extended Partnership initiative on Emerging Infectious Diseases (Project no. PE00000007, INF-ACT) granted by S.C. and G.P.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- World Bank. Drug-Resistant Infections: A Threat to Our Economic Future (Final Report); The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; pp. 1–132. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Global Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System (GLASS) Report; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 978-92-4-151344-9. [Google Scholar]
- Irfan, M.; Almotiri, A.; AlZeyadi, Z.A. Antimicrobial Resistance and Its Drivers—A Review. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwen, S.A.; Collignon, P.J. Antimicrobial Resistance: A One Health Perspective. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6, 521–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munita, J.M.; Arias, C.A. Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 481–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, J.; Rafiq, Q.A.; Ratcliffe, E. Antimicrobial resistance mechanisms and potential synthetic treatments. Futur. Sci. OA 2018, 4, FSO290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idrees, M.; Sawant, S.; Karodia, N.; Rahman, A. Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm: Morphology, Genetics, Pathogenesis and Treatment Strategies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.T.; Xavier, K.B.; Campagna, S.R.; Taga, M.E.; Semmelhack, M.F.; Bassler, B.L.; Hughson, F.M. Salmonella typhimurium Recognizes a Chemically Distinct Form of the Bacterial Quorum-Sensing Signal AI-2. Mol. Cell 2004, 15, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, K.B.; Bassler, B.L. Interference with AI-2-mediated bacterial cell-cell communication. Nature 2005, 437, 750–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Attila, C.; Wang, L.; Wood, T.K.; Valdes, J.J.; Bentley, W.E. Quorum Sensing in Escherichia coli Is Signaled by AI-2/LsrR: Effects on Small RNA and Biofilm Architecture. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 6011–6020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, J.-H.; Eo, Y.; Grishaev, A.; Guo, M.; Smith, J.A.I.; Sintim, H.O.; Kim, E.-H.; Cheong, H.-K.; Bentley, W.E.; Ryu, K.-S. Crystal Structures of the LsrR Proteins Complexed with Phospho-AI-2 and Two Signal-Interrupting Analogues Reveal Distinct Mechanisms for Ligand Recognition. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 15526–15535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linciano, P.; Cavalloro, V.; Martino, E.; Kirchmair, J.; Listro, R.; Rossi, D.; Collina, S. Tackling Antimicrobial Resistance with Small Molecules Targeting LsrK: Challenges and Opportunities. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 15243–15257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, K.B.; Bassler, B.L. Regulation of uptake and processing of the quorum-sensing autoinducer AI-2 in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, V.; Fernandes, R.; Tsao, C.-Y.; Bentley, W.E. Cross Species Quorum Quenching Using a Native AI-2 Processing Enzyme. ACS Chem. Biol. 2010, 5, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medarametla, P.; Kronenberger, T.; Laitinen, T.; Poso, A. Structural Characterization of LsrK as a Quorum Sensing Target and a Comparison between X-ray and Homology Models. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 1346–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stotani, S.; Gatta, V.; Medarametla, P.; Padmanaban, M.; Karawajczyk, A.; Giordanetto, F.; Tammela, P.; Laitinen, T.; Poso, A.; Tzalis, D.; et al. DPD-Inspired Discovery of Novel LsrK Kinase Inhibitors: An Opportunity to Fight Antimicrobial Resistance. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 2720–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatta, V.; Ilina, P.; Porter, A.; McElroy, S.; Tammela, P. Targeting quorum sensing: High-throughput screening to identify novel lsrk inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, J.H.; Hauk, P.; Cho, K.; Eo, Y.; Ma, X.; Stephens, K.; Cha, S.; Jeong, M.; Suh, J.Y.; Sintim, H.O.; et al. Evidence of link between quorum sensing and sugar metabolism in Escherichia coli revealed via cocrystal structures of LsrK and HPr. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar7063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghisaidoobe, A.; Chung, S. Intrinsic Tryptophan Fluorescence in the Detection and Analysis of Proteins: A Focus on Förster Resonance Energy Transfer Techniques. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 22518–22538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yammine, A.; Gao, J.; Kwan, A. Tryptophan Fluorescence Quenching Assays for Measuring Protein-ligand Binding Affinities: Principles and a Practical Guide. BIO-PROTOCOL 2019, 9, e3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosanić, M.; Ranković, B. Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties of Some Lichens and Their Constituents. J. Med. Food 2011, 14, 1624–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Htun, T. A Negative Deviation from Stern–Volmer Equation in Fluorescence Quenching. J. Fluoresc. 2004, 14, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehrer, S.S. Solute perturbation of protein fluorescence. The quenching of the tryptophyl fluorescence of model compounds and of lysozyme by iodide ion. Biochemistry 1971, 10, 3254–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehlen, M.H. The centenary of the Stern-Volmer equation of fluorescence quenching: From the single line plot to the SV quenching map. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2020, 42, 100338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mátyus, L.; Szöllősi, J.; Jenei, A. Steady-state fluorescence quenching applications for studying protein structure and dynamics. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2006, 83, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Quenching of Fluorescence. In Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2006; pp. 277–330. [Google Scholar]
- Samworth, C.M.; Esposti, M.D.; Lenaz, G. Quenching of the intrinsic tryptophan fluorescence of mitochondrial ubiquinol-cytochrome-c reductase by the binding of ubiquinone. Eur. J. Biochem. 1988, 171, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrocola, G.; Valtulina, V.; Rindi, S.; Jost, B.H.; Speziale, P. Functional and structural properties of CbpA, a collagen-binding protein from Arcanobacterium pyogenes. Microbiology 2007, 153, 3380–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geethanjali, H.S.; Nagaraja, D.; Melavanki, R.M.; Kusanur, R.A. Fluorescence quenching of boronic acid derivatives by aniline in alcohols—A Negative deviation from Stern–Volmer equation. J. Lumin. 2015, 167, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.F.; Varshney, S.; Khan, M.A.; Laskar, A.A.; Younus, H. In vitro DNA binding studies of therapeutic and prophylactic drug citral. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvijetić, I.N.; Petrović, D.D.; Verbić, T.Ž.; Juranić, I.O.; Drakulić, B.J. Human Serum Albumin Binding of 2-[(Carboxymethyl)sulfanyl]-4-oxo-4-(4-tert-butylphenyl)butanoic Acid and its Mono-Me Ester. ADMET DMPK 2014, 2, 126–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phopin, K.; Ruankham, W.; Prachayasittikul, S.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Tantimongcolwat, T. Insight into the Molecular Interaction of Cloxyquin (5-chloro-8-hydroxyquinoline) with Bovine Serum Albumin: Biophysical Analysis and Computational Simulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, O.; Amorim, A.; Castro, L.; Sant’Anna, C.; de Oliveira, M.; Cesarin-Sobrinho, D.; Netto-Ferreira, J.; Ferreira, A. Fluorescence and Docking Studies of the Interaction between Human Serum Albumin and Pheophytin. Molecules 2015, 20, 19526–19539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genovese, D.; Cingolani, M.; Rampazzo, E.; Prodi, L.; Zaccheroni, N. Static quenching upon adduct formation: A treatment without shortcuts and approximations. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 8414–8427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malacrida, A.; Cavalloro, V.; Martino, E.; Costa, G.; Ambrosio, F.A.; Alcaro, S.; Rigolio, R.; Cassetti, A.; Miloso, M.; Collina, S. Anti-Multiple Myeloma Potential of Secondary Metabolites from Hibiscus sabdariffa—Part 2. Molecules 2021, 26, 6596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel-Moral, S.; Borrás-Linares, I.; Lozano-Sánchez, J.; Arráez-Román, D.; Martínez-Férez, A.; Segura-Carretero, A. Microwave-assisted extraction for Hibiscus sabdariffa bioactive compounds. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 156, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malacrida, A.; Cavalloro, V.; Martino, E.; Cassetti, A.; Nicolini, G.; Rigolio, R.; Cavaletti, G.; Mannucci, B.; Vasile, F.; Di Giacomo, M.; et al. Anti-multiple myeloma potential of secondary metabolites from hibiscus sabdariffa. Molecules 2019, 24, 2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, D.; Ahmed, K.; Gaggeri, R.; Della Volpe, S.; Maggi, L.; Mazzeo, G.; Longhi, G.; Abbate, S.; Corana, F.; Martino, E.; et al. (R)-(−)-Aloesaponol III 8-Methyl Ether from Eremurus persicus: A Novel Compound against Leishmaniosis. Molecules 2017, 22, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collina, S.; Azzolina, O.; Vercesi, D.; Sbacchi, M.; Scheideler, M.A.; Barbieri, A.; Lanza, E.; Ghislandi, V. Synthesis and antinociceptive activity of pyrrolidinylnaphthalenes. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2000, 8, 1925–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghislandi, V.; Collina, S.; Azzolina, O.; Barbieri, A.; Lanza, E.; Tadini, C. Preparation and configuration of racemic and optically active analgesic cycloaminoalkylnaphthalenes. Chirality 1999, 11, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Volpe, S.; Listro, R.; Parafioriti, M.; Di Giacomo, M.; Rossi, D.; Ambrosio, F.A.; Costa, G.; Alcaro, S.; Ortuso, F.; Hirsch, A.K.H.; et al. BOPC1 Enantiomers Preparation and HuR Interaction Study. From Molecular Modeling to a Curious DEEP-STD NMR Application. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Volpe, S.; Nasti, R.; Queirolo, M.; Unver, M.Y.; Jumde, V.K.; Dömling, A.; Vasile, F.; Potenza, D.; Ambrosio, F.A.; Costa, G.; et al. Novel Compounds Targeting the RNA-Binding Protein HuR. Structure-Based Design, Synthesis, and Interaction Studies. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasti, R.; Rossi, D.; Amadio, M.; Pascale, A.; Unver, M.Y.; Hirsch, A.K.H.; Collina, S. Compounds Interfering with Embryonic Lethal Abnormal Vision (ELAV) Protein–RNA Complexes: An Avenue for Discovering New Drugs. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 8257–8267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, M.; Rossi, D.; Marra, A.; Paolillo, M.; Schinelli, S.; Curti, D.; Tesei, A.; Cortesi, M.; Zamagni, A.; Laurini, E.; et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of new aryl-alkyl(alkenyl)-4-benzylpiperidines, novel Sigma Receptor (SR) modulators, as potential anticancer-agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 124, 649–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, D.M.; Jasim, S.B.; Dyer, N.T.; Auvray, F.; Réfrégiers, M.; Hirst, J.D. Electronic Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy of Proteins. Chem 2019, 5, 2751–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodger, A.; Marrington, R.; Roper, D.; Windsor, S. Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy for the Study of Protein-Ligand Interactions. In Protein-Ligand Interactions; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 343–363. [Google Scholar]
- Micsonai, A.; Wien, F.; Kernya, L.; Lee, Y.-H.; Goto, Y.; Réfrégiers, M.; Kardos, J. Accurate secondary structure prediction and fold recognition for circular dichroism spectroscopy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E3095–E3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friesner, R.A.; Banks, J.L.; Murphy, R.B.; Halgren, T.A.; Klicic, J.J.; Mainz, D.T. Glide: A new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 1. Method and assessment of docking accuracy. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrödinger. Schrödinger Release 2021-3: Maestro 2021; Schrödinger LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.; Wu, C.; Ghoreishi, D.; Chen, W.; Wang, L.; Damm, W.; Ross, G.A.; Dahlgren, M.K.; Russell, E.; Von Bargen, C.D.; et al. OPLS4: Improving Force Field Accuracy on Challenging Regimes of Chemical Space. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2021, 17, 4291–4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).