Ionic Liquid-Based Green Emulsion Liquid Membrane for the Extraction of the Poorly Soluble Drug Ibuprofen
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
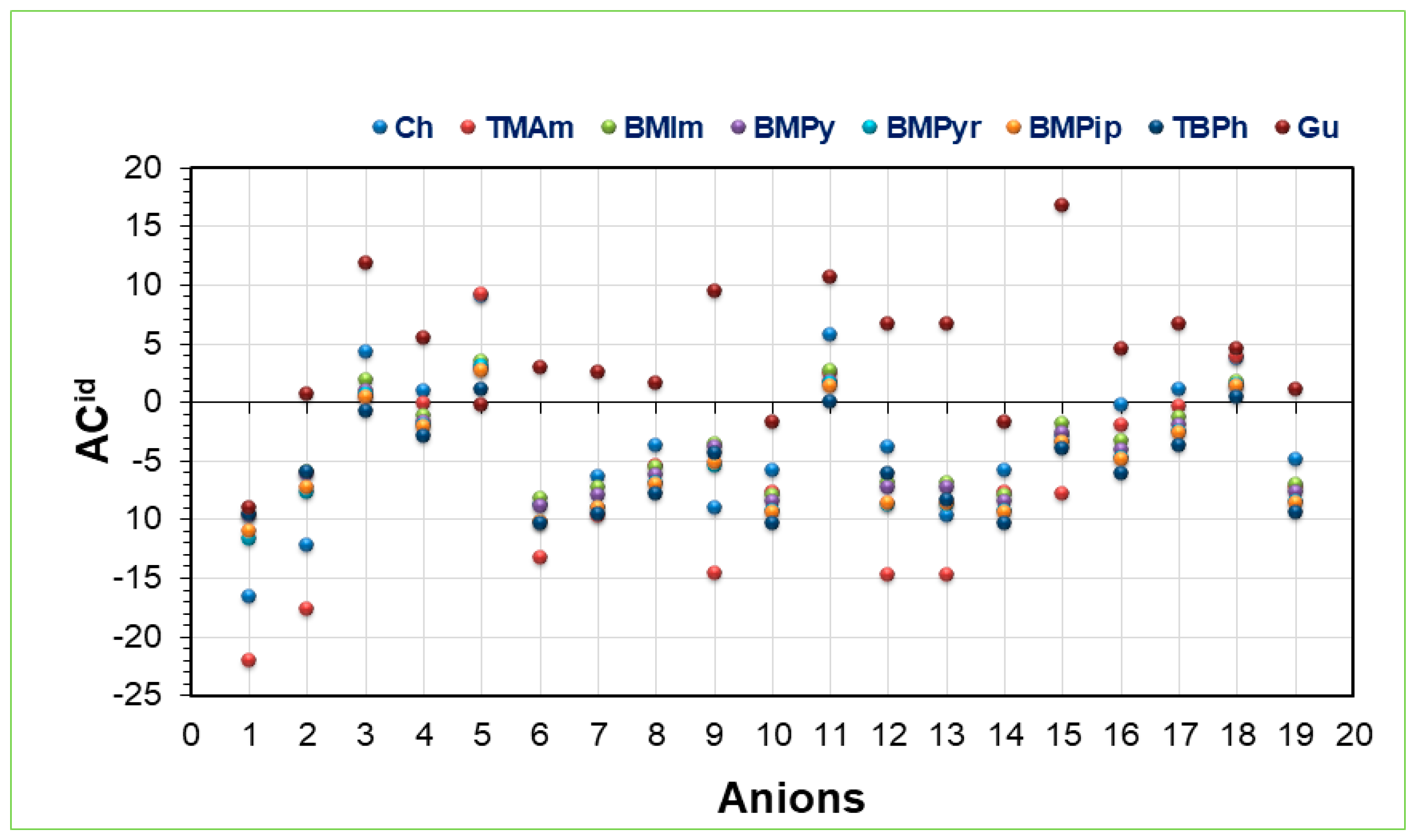
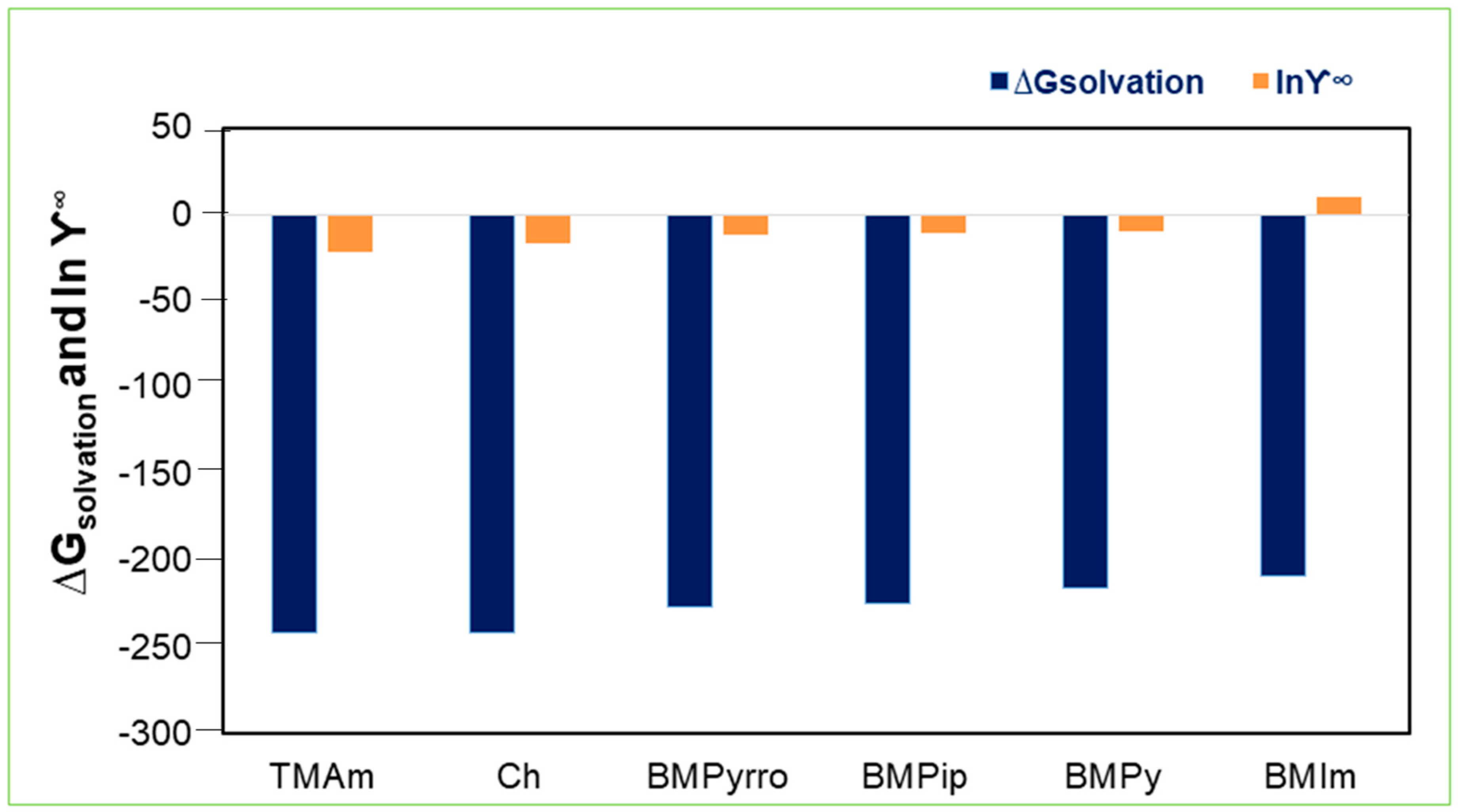
2.1. Activity Coefficient at Infinite Dilution
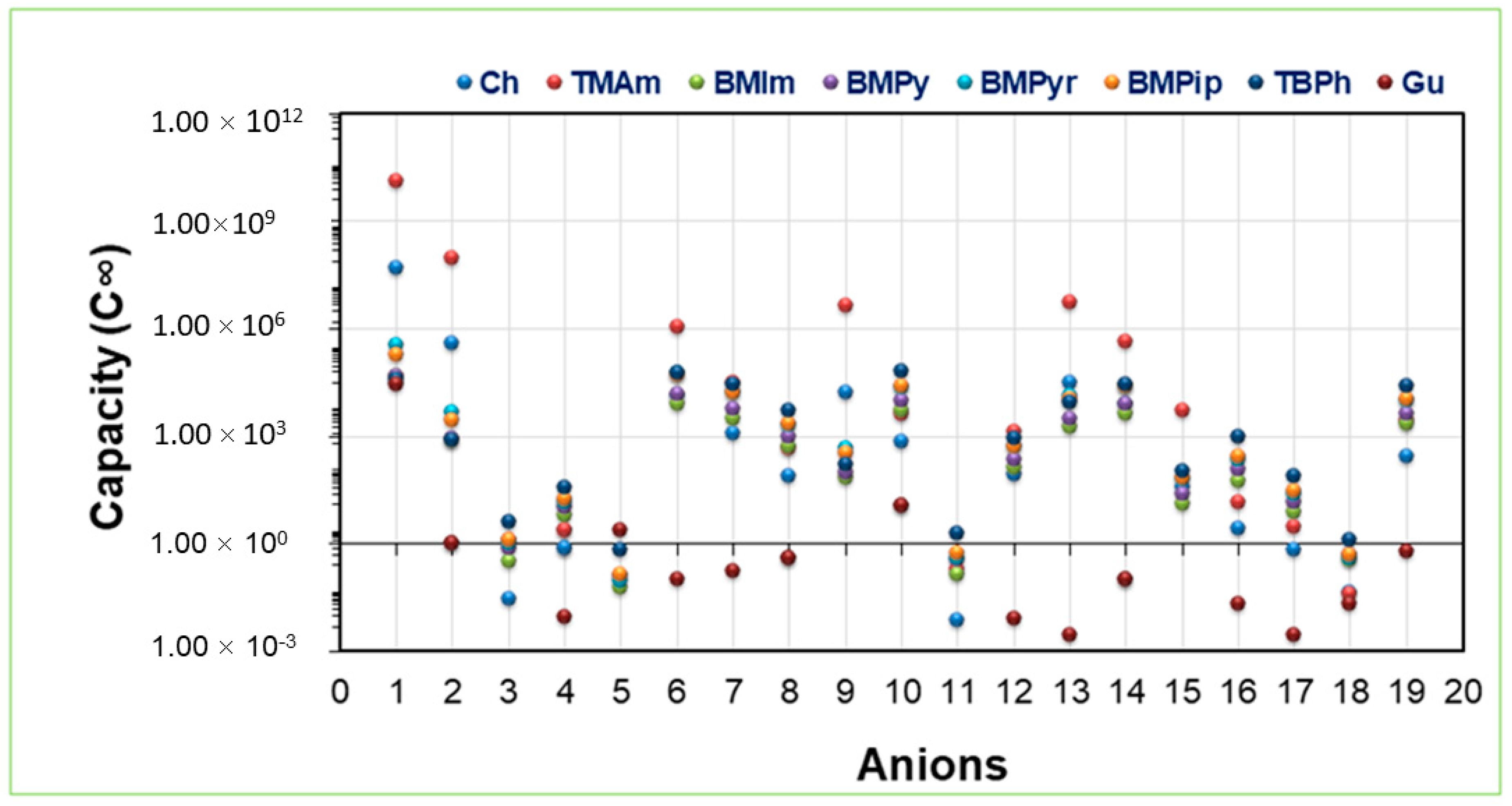
2.2. IL Capacity towards Ibf
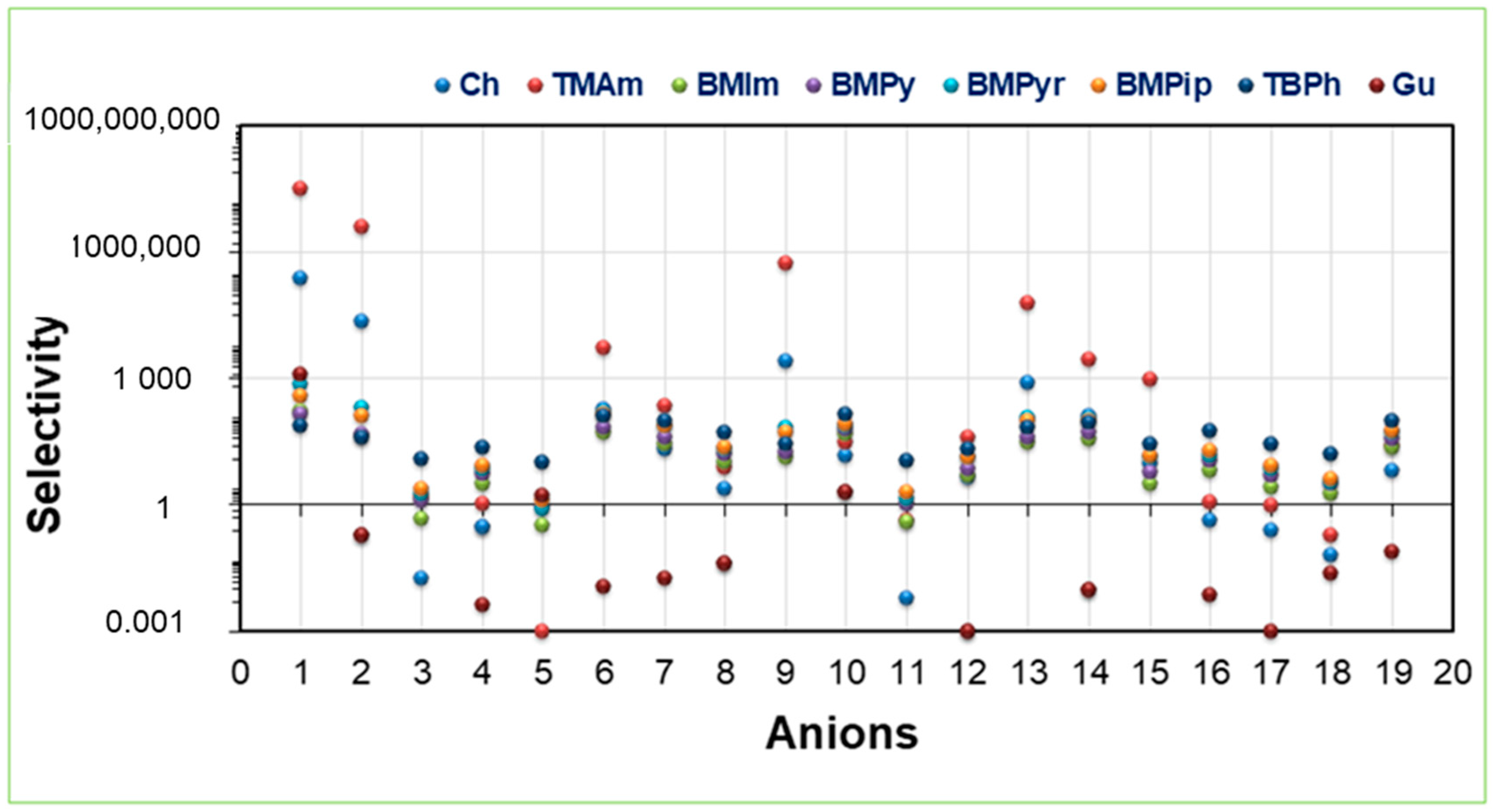
2.3. Selectivity at Infinite Dilution
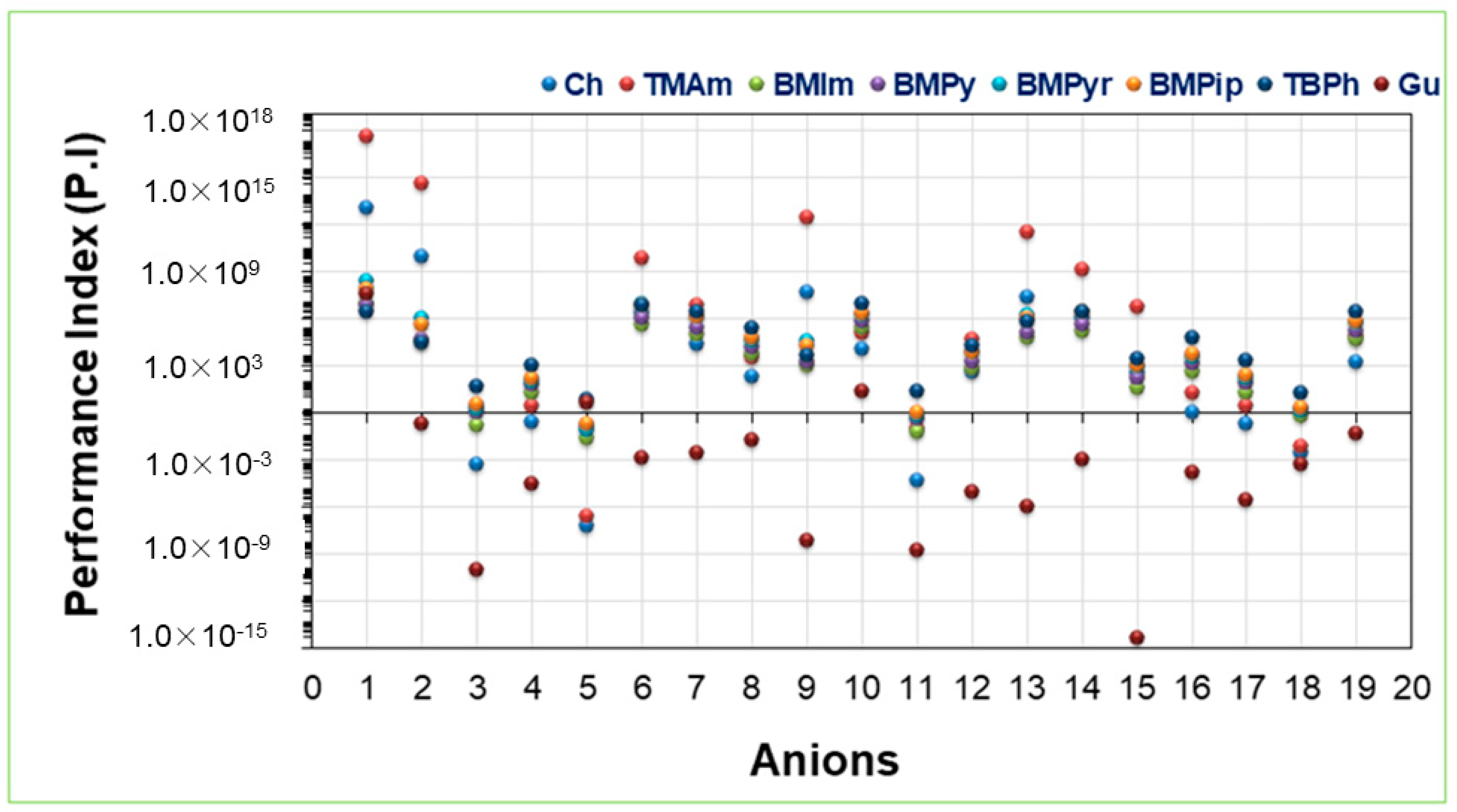
2.4. Performance Index
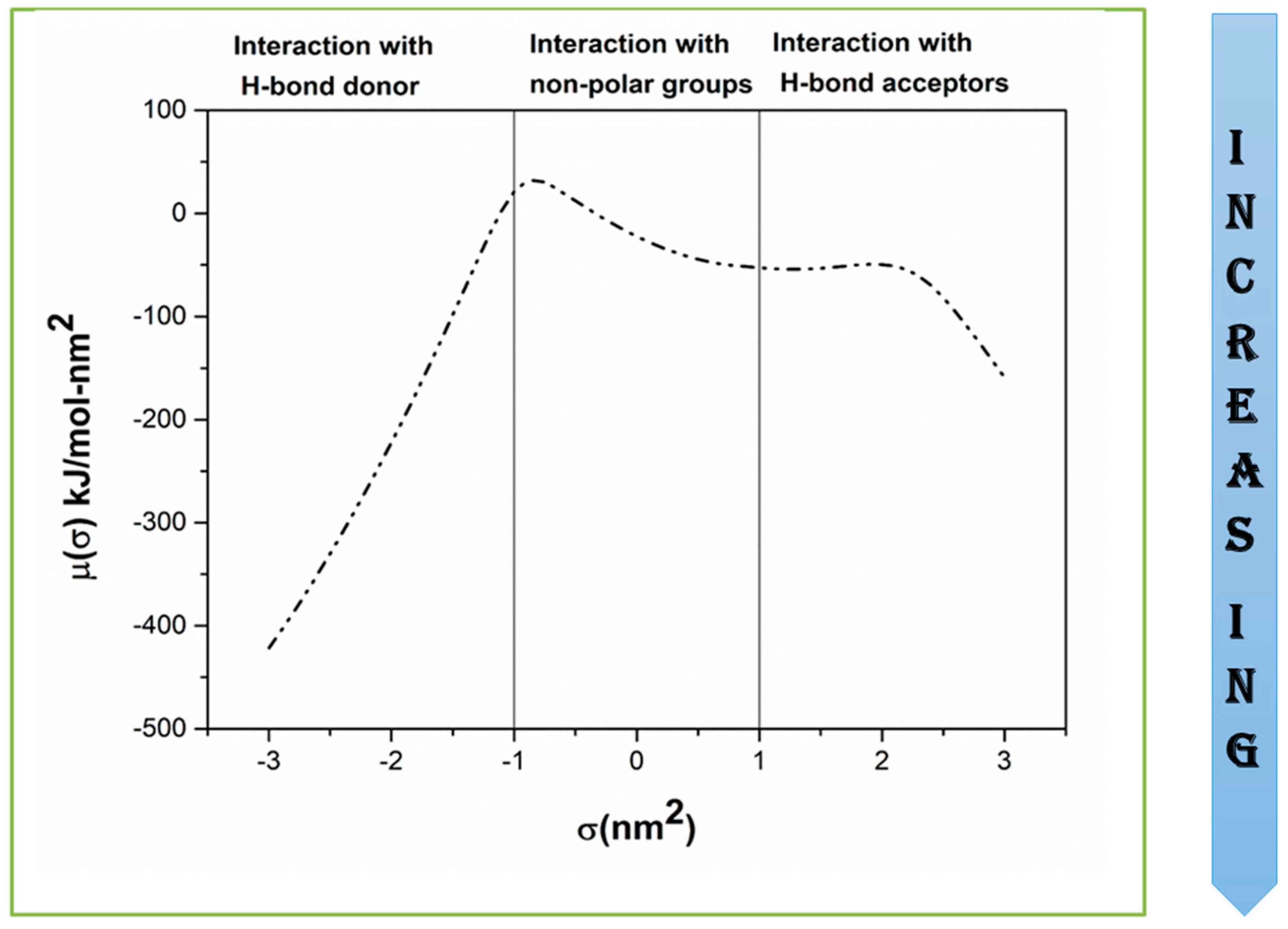
2.5. Solvation Free Energies
2.6. Effect of Alkyl Chain Length upon ACid, Capacity, and Selectivity
2.7. Extraction Performance
2.8. ILGELM Extraction for Ibf and Experimental Verification
2.9. COSMO-RS Experimental Validation Using the ILGELM
3. Materials and Methodology
3.1. Materials
3.2. COSMO-RS Simulation Study
- µ = are the chemical potential of the IL
- µo = chemical potential of the pure compound
3.3. ILGELM Development
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| [TBPPyri][Br] | 4-Tert-butyl-1-propylpyridinium bromide |
| [EMIm][Trif] | 1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium trifluoromethane-sulfonate (triflate), |
| [BMIm][Trif] | 1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium trifluoromethanesulfonate (triflate), |
| [BMIm][Tos] | 1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium tosylate |
| [TIBMPh][Tos] | Tri(isobutyl)methylphosphonium tosylate, |
| [TBPh][Cl] | Tetrabutylphosphonium chloride |
| [TBAm][Cl] | Tetrabutylammonium chloride |
| [VBIm][PF6] | 1-Vinyl-3-butylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate |
| [BMIm][PF6] | 1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate |
| [BMIm][BF4] | 1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate |
| [OMIm][PF6] | 1-Octyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate |
| [D2EHPA] | Di-(2-ethylhexyl)phosphoric acid |
References
- Madikizela, L.M.; Chimuka, L. Simultaneous determination of naproxen, ibuprofen and diclofenac in wastewater using solid-phase extraction with high-performance liquid chromatography. Water Sa 2017, 43, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo-Neira, C.; Álvarez-Lueje, A. Ionic liquids for improving the extraction of NSAIDs in water samples using dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction by high performance liquid chromatography-diode array–fluorescence detection. Talanta 2015, 134, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chopra, S.; Kumar, D. Ibuprofen as an emerging organic contaminant in environment, distribution and remediation. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñiz-González, A.B. Ibuprofen as an emerging pollutant on non-target aquatic invertebrates: Effects on Chironomus riparius. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 81, 103537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulahcene, L.; Kebiche-Senhadji, O.; Skiba, M.; Lahiani-Skiba, M.; Oughlis-Hammache, F.; Benamor, M. Cyclodextrin polymers for ibuprofen extraction in aqueous solution: Recovery, separation, and characterization. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 11392–11402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, S.I.; Gumus, E.; Cetinkaya, A.; Zor, E.; Ozkan, S.A. Trends in on-site removal, treatment, and sensitive assay of common pharmaceuticals in surface waters. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 149, 116556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Shams, D.F.; Khan, W.; Ijaz, A.; Qasim, M.; Saad, M.; Hafeez, V.; Baig, S.A.; Ahmed, N. Prevalence of selected pharmaceuticals in surface water receiving untreated sewage in northwest Pakistan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Odaini, N.A.; Zakaria, M.P.; Yaziz, M.I.; Surif, S.; Abdulghani, M. The occurrence of human pharmaceuticals in wastewater effluents and surface water of Langat River and its tributaries, Malaysia. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2013, 93, 245–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Du, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y. Rapid analysis of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in tap water and drinks by ionic liquid dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction coupled to ultra-high performance supercritical fluid chromatography. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 7294–7304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Ivars, J.; Martella, L.; Massella, M.; Carbonell-Alcaina, C.; Alcaina-Miranda, M.I.; Iborra-Clar, M.I. Nanofiltration as tertiary treatment method for removing trace pharmaceutically active compounds in wastewater from wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 2017, 125, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; An, X. Spherical activated carbon modified by polymerized ionic liquid for the removal of ibuprofen from water. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2016, 91, 794–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dâas, A.; Hamdaoui, O. Removal of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs ibuprofen and ketoprofen from water by emulsion liquid membrane. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 2154–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astrid, G. Three-phase hollow fiber liquid-phase microextraction and parallel artificial liquid membrane extraction. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 113, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Jusoh, N.; Othman, N.; Nasruddin, N.A. Emulsion liquid membrane technology in organic acid purification. Malays. J. Anal. Sci. 2016, 20, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Kusumastuti, A.; Derek, C.J.C.; Ooi, B.S. Emulsion liquid membrane for cadmium removal: Studies on emulsion diameter and stability. Desalination 2012, 287, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.W.; Reddy, A.V.B.; Bustam, M.A.; Goto, M.; Moniruzzaman, M. Development and optimization of ionic liquid-based emulsion liquid membrane process for efficient recovery of lactic acid from aqueous streams. Biochem. Eng. J. 2021, 176, 108216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, N.; Noah, N.F.; Shu, L.Y.; Ooi, Z.Y.; Jusoh, N.; Idroas, M.; Goto, M. Easy removing of phenol from wastewater using vegetable oil-based organic solvent in emulsion liquid membrane process. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 25, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaulkiflee, N.D.; Ahmad, A.L.; Sugumaran, J.; Lah, N.F. Stability Study of Emulsion Liquid Membrane via Emulsion Size and Membrane Breakage on Acetaminophen Removal from Aqueous Solution Using TOA. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 23892–23897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, R.K.; Jayakumar, N.S.; Hashim, M.A. Chromium removal by emulsion liquid membrane using [BMIM]+[NTf2]− as stabilizer and TOMAC as extractant. Desalination 2011, 278, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, P.A.; Johl, S.K.; Akhtar, S. Vinculum of Sustainable Development Goal Practices and Firms’ Financial Performance: A Moderation Role of Green Innovation. J. Risk Financ. Manag. 2022, 15, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, P.A.; Johl, S.K.; Johl, S.K. Does adoption of ISO 56002-2019 and green innovation reporting enhance the firm sustainable development goal performance? An emerging paradigm. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2021, 30, 2922–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavir, K.; Konieczna, K.; Marcinkowski, L.; Kloskowski, A. Ionic liquids in the microextraction techniques: The influence of ILs structure and properties. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 130, 115994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, P.A.; Singh, S.K.; Johl, S.K.; Shamim, A.; Nurhayadi, Y.; Wijiharjono, N.; Al-Azizah, U.S. Injecting Green Innovation Reporting into Sustainability Reporting. EDP Sci. 2021, 124, 05003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, P.A.; Johl, S.K. Firm Performance from the Lens of Comprehensive Green Innovation and Environmental Management System ISO. Processes 2020, 8, 1152. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, P.A.; Johl, S.K.; Akhtar, S. Firm Sustainable Development Goals and Firm Financial Performance through the Lens of Green Innovation Practices and Reporting: A Proactive Approach. J. Risk Financ. Manag. 2021, 14, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delińska, K.; Yavir, K.; Kloskowski, A. Ionic liquids in extraction techniques: Determination of pesticides in food and environmental samples. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 143, 116396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniruzzaman, M.; Tahara, Y.; Tamura, M.; Kamiya, N.; Goto, M. Ionic liquid-assisted transdermal delivery of sparingly soluble drugs. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 1452–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, S.P.; e Silva, F.A.; Quental, M.V.; Mondal, D.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A. Ionic-liquid-mediated extraction and separation processes for bioactive compounds: Past, present, and future trends. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6984–7052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.W.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Nasef, M.M.E.; Khalil, M.A.B. Ionic liquid assisted cellulose aerogels for cleaning an oil spill. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 31, 217–220. [Google Scholar]
- Anantharaj, R.; Banerjee, T. COSMO-RS-based screening of ionic liquids as green solvents in denitrification studies. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 8705–8725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.W.; Elgharbawy, A.A.M.; Bustam, M.A.; Moniruzzaman, M. Design and Selection of Ionic Liquids via COSMO for Pharmaceuticals and Medicine. In Application of Ionic Liquids in Drug Delivery; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 137–164. [Google Scholar]
- Jeliński, T.; Cysewski, P. Screening of ionic liquids for efficient extraction of methylxanthines using COSMO-RS methodology. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2017, 122, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.S.; Ibrahim, T.H.; Rashid, Z.; Khamis, M.I.; Nancarrow, P.; Jabbar, N.A. COSMO-RS based screening of ionic liquids for extraction of phenolic compounds from aqueous media. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 328, 115387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.W.; Reddy, A.V.B.; Nasef, M.M.E.; Bustam, M.A.; Goto, M.; Moniruzzaman, M. Screening of ionic liquids for the extraction of biologically active compounds using emulsion liquid membrane: COSMO-RS prediction and experiments. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 309, 113122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cysewski, P. Prediction of ethenzamide solubility in organic solvents by explicit inclusions of intermolecular interactions within the framework of COSMO-RS-DARE. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 290, 111163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardar, S.; Wilfred, C.D.; Mumtaz, A.; Rashid, Z.; Leveque, J.M. Synthesis, thermophysical properties, Hammett acidity and COSMO-RS study of camphor sulfonate-based Brönsted acidic ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 271, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Song, Z.; Jin, C.; Nijhuis, J.; Zhou, T.; Noël, T.; Gröger, H.; Sundmacher, K.; van Hest, J.; Hessel, V. Screening of functional solvent system for automatic aldehyde and ketone separation in aldol reaction: A combined COSMO-RS and experimental approach. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallanza, M.; González-Miquel, M.; Elia, R.; Alfredo, O.; Gorri, D.; Palomar, J.; Ortiz, I. Screening of RTILs for propane/propylene separation using COSMO-RS methodology. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 220, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, H.C.; Khan, H.W.; Reddy, A.V.B.; Goto, M.; Moniruzzaman, M. Extraction of salicylic acid from wastewater using ionic liquid-based green emulsion liquid membrane: COSMO-RS prediction and experimental verification. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 347, 118280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, M.; Ouyang, D. How imidazolium-based ionic liquids solubilize the poorly soluble ibuprofen? A theoretical study. AIChE J. 2020, 66, 16940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellaoui, L.; Guedidi, H.; Masson, S.; Reinert, L.; Levêque, J.M.; Knani, S.; Lamine, A.B.; Khalfaoui, M.; Duclaux, L. Steric and energetic interpretations of the equilibrium adsorption of two new pyridinium ionic liquids and ibuprofen on a microporous activated carbon cloth: Statistical and COSMO-RS models. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2016, 414, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- e Silva, F.A.; Caban, M.; Stepnowski, P.; Coutinho, J.A.; Ventura, S.P. Recovery of ibuprofen from pharmaceutical wastes using ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 3749–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, H.F.; Marrucho, I.M.; Freire, M.G. Removal of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs from aqueous environments with reusable ionic-liquid-based systems. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2428–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, H.; Khan, H.W.; Shah, M.U.; Ahmad, M.I.; Khan, I.; Al-Kahtani, A.A.; Sillanpaa, M. Screening of ionic liquids as green entrainers for ethanol water separation by extractive distillation: COSMO-RS prediction and aspen plus simulation. Chemosphere 2023, 311, 136901. [Google Scholar]
- Haron, G.A.; Mahmood, H.; Noh, M.H.; Moniruzzaman, M. Ionic liquid assisted nanocellulose production from microcrystalline cellulose: Correlation between cellulose solubility and nanocellulose yield via COSMO-RS prediction. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 368, 120591. [Google Scholar]
- Kurnia, K.A.; Harimurti, S.; Yung, H.K.; Baraheng, A.; Alimin, M.A.; Dagang, N.S.; Fadhilah, A.; Rosyadi, R.; Yahya, W.Z.; Bustam, M.A. Understanding the effect of pH on the solubility of Gamavuton-0 in the aqueous solution: Experimental and COSMO-RS modelling. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 296, 111845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, N.; Khan, H.W.; Gari, A.A.; Yusuf, M.; Irshad, K. Screening of ionic liquids as sustainable greener solvents for the capture of greenhouse gases using COSMO-RS approach: Computational study. Fuel 2022, 330, 125540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunov-Kruse, A.J.; Weber, C.C.; Rogers, R.D.; Myerson, A.S. A priori design and selection of ionic liquids as solvents for active pharmaceutical ingredients. Chem. —Eur. J. 2017, 23, 5498–5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Tang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Song, S. Hofmeister series: Insights of ion specificity from amphiphilic assembly and interface property. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 6229–6239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.B.; Bridson, R.H.; Leeke, G.A. Solubilities of pharmaceutical compounds in ionic liquids. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2011, 5, 2039–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei Motlagh, S.; Harun, R.; Awang Biak, D.R.; Hussain, S.A.; Wan Ab Karim Ghani, W.A.; Khezri, R.; Wilfred, C.D.; Elgharbawy, A.A. Screening of suitable ionic liquids as green solvents for extraction of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) from microalgae biomass using COSMO-RS model. Molecules 2019, 4, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei Motlagh, S.; Harun, R.; Awang Biak, D.R.; Hussain, S.A.; Omar, R.; Elgharbawy, A.A. COSMO-RS based prediction for alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) extraction from microalgae biomass using room temperature ionic liquids (RTILs). Mar. Drugs 2020, 2, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei Motlagh, S.; Harun, R.; Awang Biak, D.R.; Hussain, S.A.; Omar, R.; Elgharbawy, A.A. Prediction of potential ionic liquids (ILS) for the solidâ liquid extraction of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) from microalgae using COSMO-RS screening model. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1149. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, S.A.; Yahya, W.Z.; Bustam, M.A.; Kibria, M.G.; Masri, A.N.; Kamonwel, N.D. Study of the ionic liquids electrochemical reduction using experimental and computational methods. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 359, 119219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.W.; Elgharbawy, A.A.; Bustam, M.A.; Goto, M.; Moniruzzaman, M. Vegetable Oil–Ionic Liquid-Based Emulsion Liquid Membrane for the Removal of Lactic Acid from Aqueous Streams: Emulsion Size, Membrane Breakage, and Stability Study. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 32176–32183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diedenhofen, M.; Klamt, A. COSMO-RS as a tool for property prediction of IL mixtures—A review. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2010, 294, 31–38. [Google Scholar]

| Cation | Acronym |
|---|---|
| Choline | Ch |
| Tetramethylammonium | TMAm |
| 1-Butyl-3-methyl-imidazolium | BMIm |
| 1-Butyl-3-methyl pyridinium | BMPy |
| 1-Butyl-1-methyl pyrrolidiniumtoledo | BMPyr |
| 1-Butyl-1-methyl piperidinium | BMPip |
| Tetrabutylphosphonium | TBPh |
| Gunadinium | Gu |
| Anion | Acronym |
|---|---|
| Sulphate | SO42− |
| Chloride | Cl− |
| Tetrafluoroborate | BF4− |
| Butylsulfate | C4H9O4S− |
| Hexfluorophosphate | PF6− |
| Acetate | CH3COO− |
| Alaninate | C3H6NO2− |
| Arginitate | C16H13N4O2− |
| Bromide | Br− |
| Decanoate | C10H19O2− |
| Perchlorate | ClO4− |
| Glutamate | C5H9NO4− |
| Formate | HCOO− |
| Glycinate | C2H4NO2− |
| Nitrite | NO3− |
| salicylate | C7H5O3− |
| sachcharinate | C7H5NO3S− |
| bis(trifluoromethyl)sulfonylimide | Ntf2− |
| valinate | C5H11N2O3− |
| IL Concentration (wt.%) | Breakage (%) | Extraction Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5.2 | 28.5 |
| 0.1 | 3.6 | 56.2 |
| 0.15 | 3.15 | 64.5 |
| 0.2 | 2.36 | 81.8 |
| 0.25 | 1.2 | 93.5 |
| 0.3 | 1.64 | 87.6 |
| 0.35 | 2.25 | 78.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, H.W.; Elgharbawy, A.A.M.; Bustam, M.A.; Goto, M.; Moniruzzaman, M. Ionic Liquid-Based Green Emulsion Liquid Membrane for the Extraction of the Poorly Soluble Drug Ibuprofen. Molecules 2023, 28, 2345. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052345
Khan HW, Elgharbawy AAM, Bustam MA, Goto M, Moniruzzaman M. Ionic Liquid-Based Green Emulsion Liquid Membrane for the Extraction of the Poorly Soluble Drug Ibuprofen. Molecules. 2023; 28(5):2345. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052345
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Huma Warsi, Amal A. M. Elgharbawy, Mohamed Azmi Bustam, Masahiro Goto, and Muhammad Moniruzzaman. 2023. "Ionic Liquid-Based Green Emulsion Liquid Membrane for the Extraction of the Poorly Soluble Drug Ibuprofen" Molecules 28, no. 5: 2345. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052345
APA StyleKhan, H. W., Elgharbawy, A. A. M., Bustam, M. A., Goto, M., & Moniruzzaman, M. (2023). Ionic Liquid-Based Green Emulsion Liquid Membrane for the Extraction of the Poorly Soluble Drug Ibuprofen. Molecules, 28(5), 2345. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052345







