Surface Properties of Graffiti Coatings on Sensitive Surfaces Concerning Their Removal with Formulations Based on the Amino-Acid-Type Surfactants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Preparation, Characterization and RSM Optimization of w/o Nanoemulsions
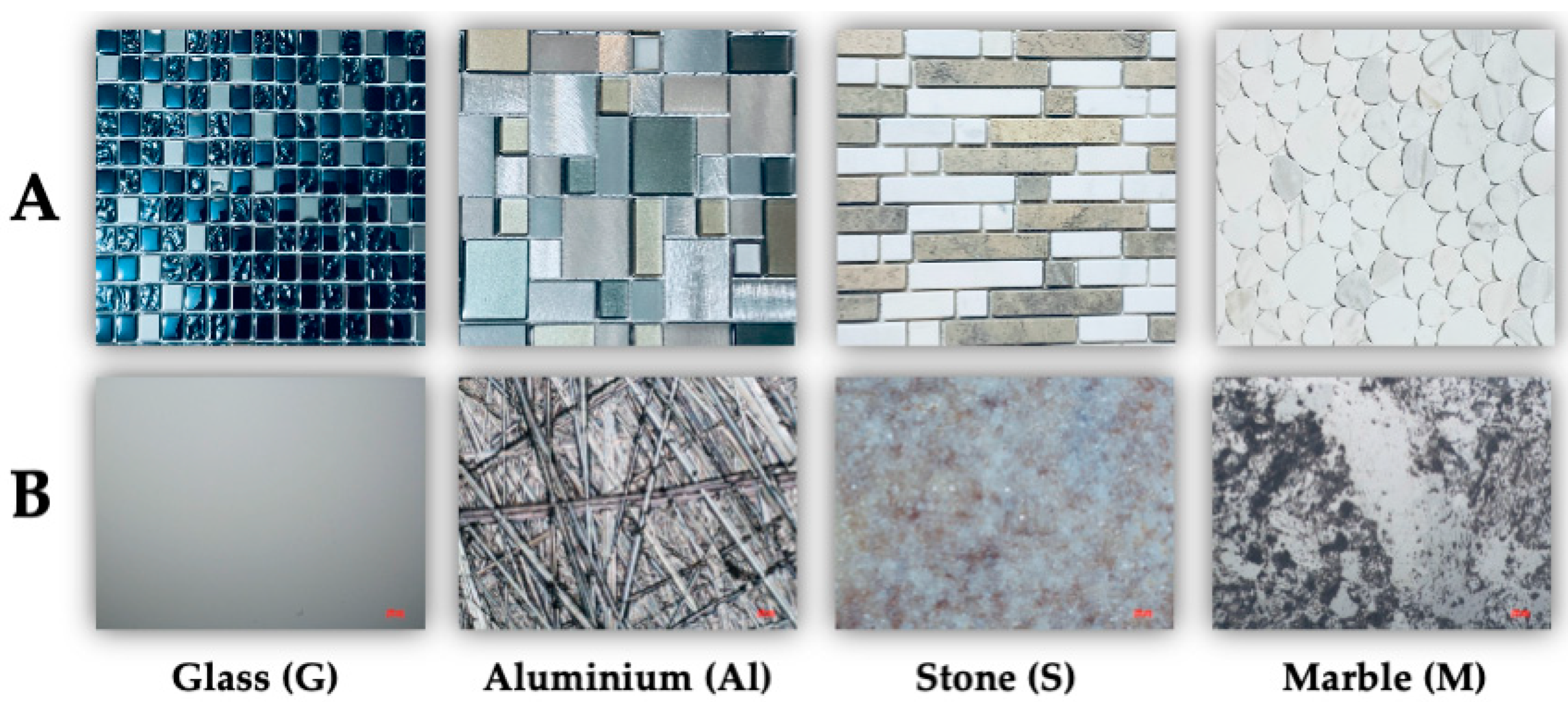
2.2. Surface Properties of Sensitive Surfaces
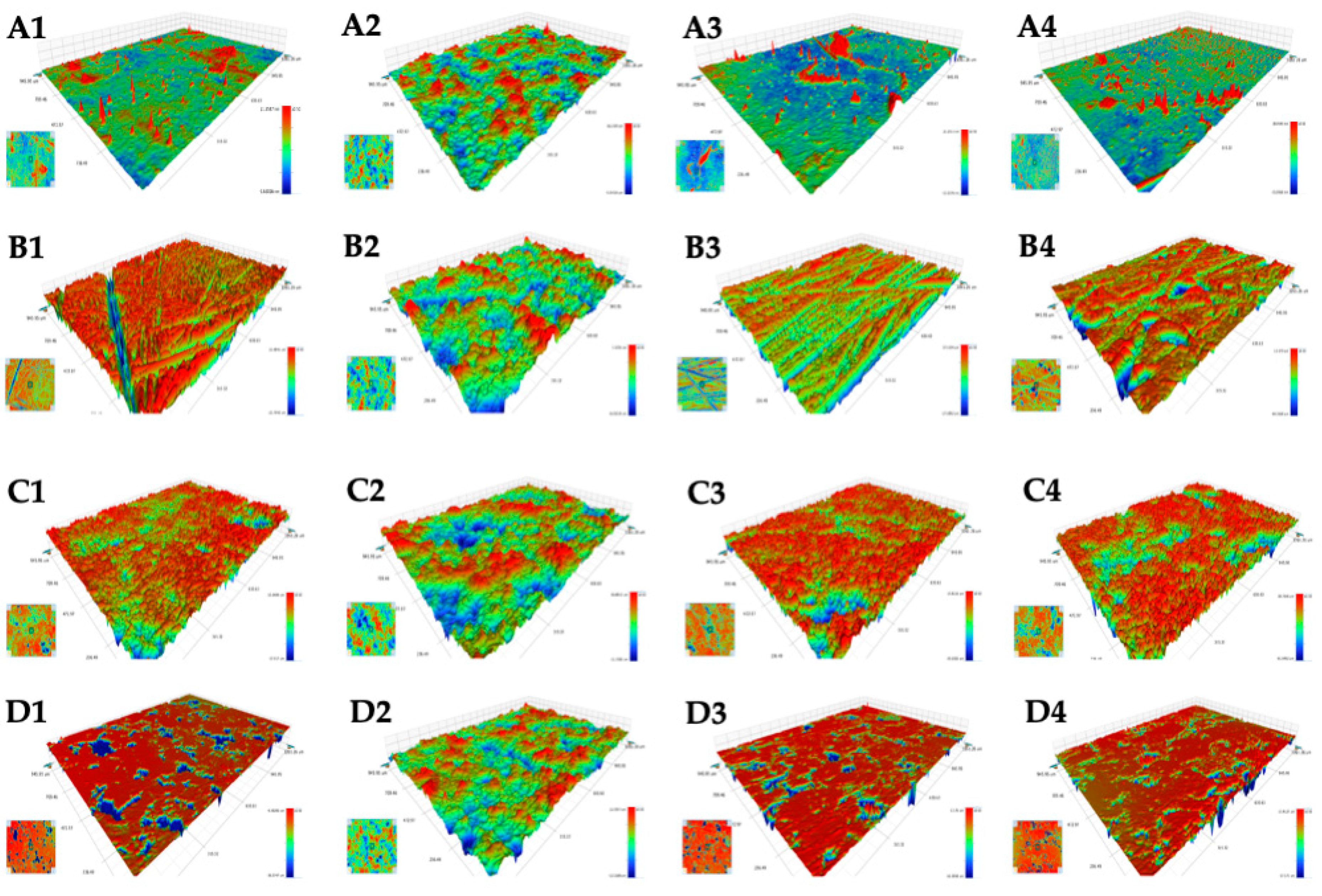
2.2.1. Surface Structure Analysis
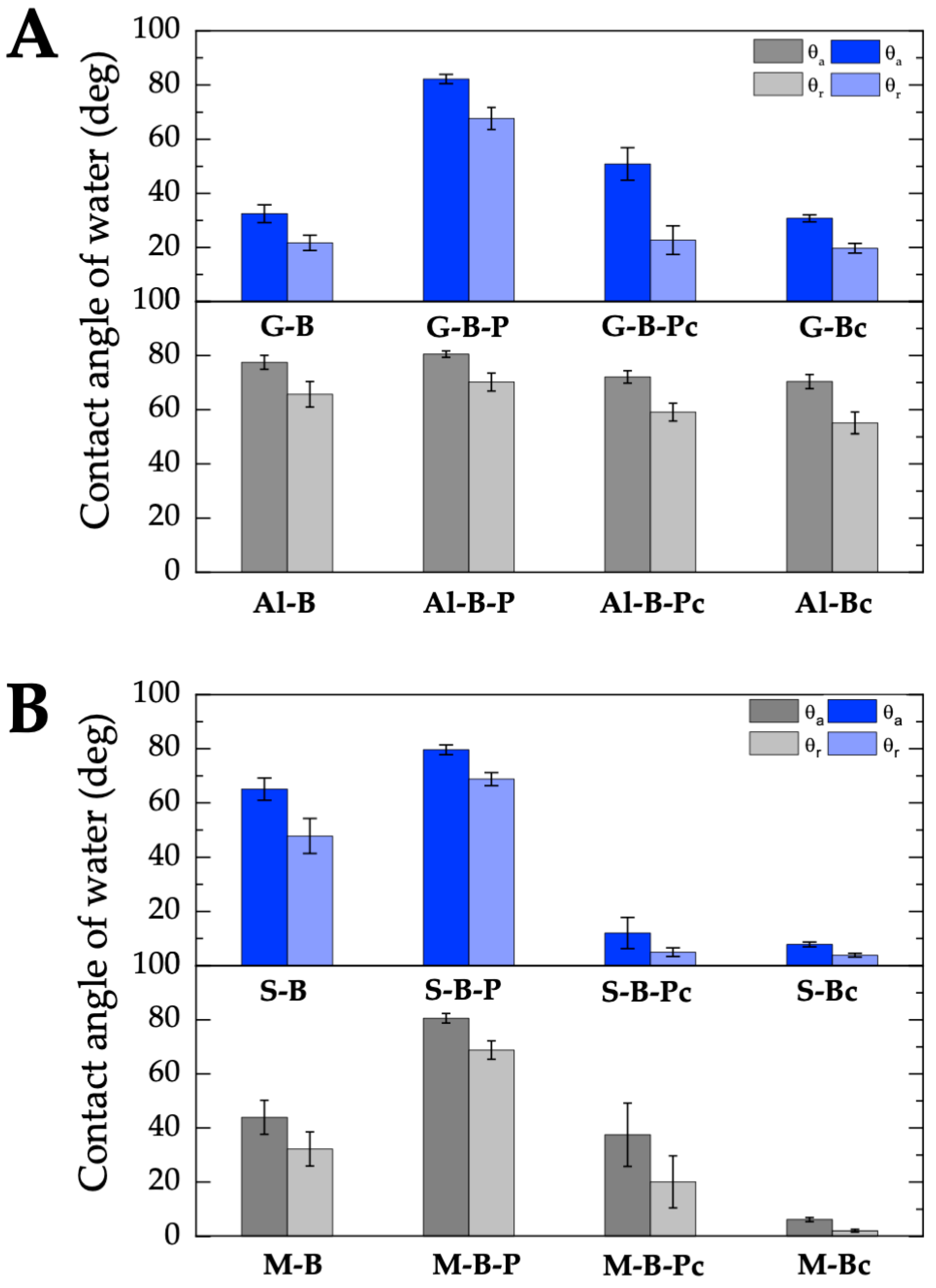
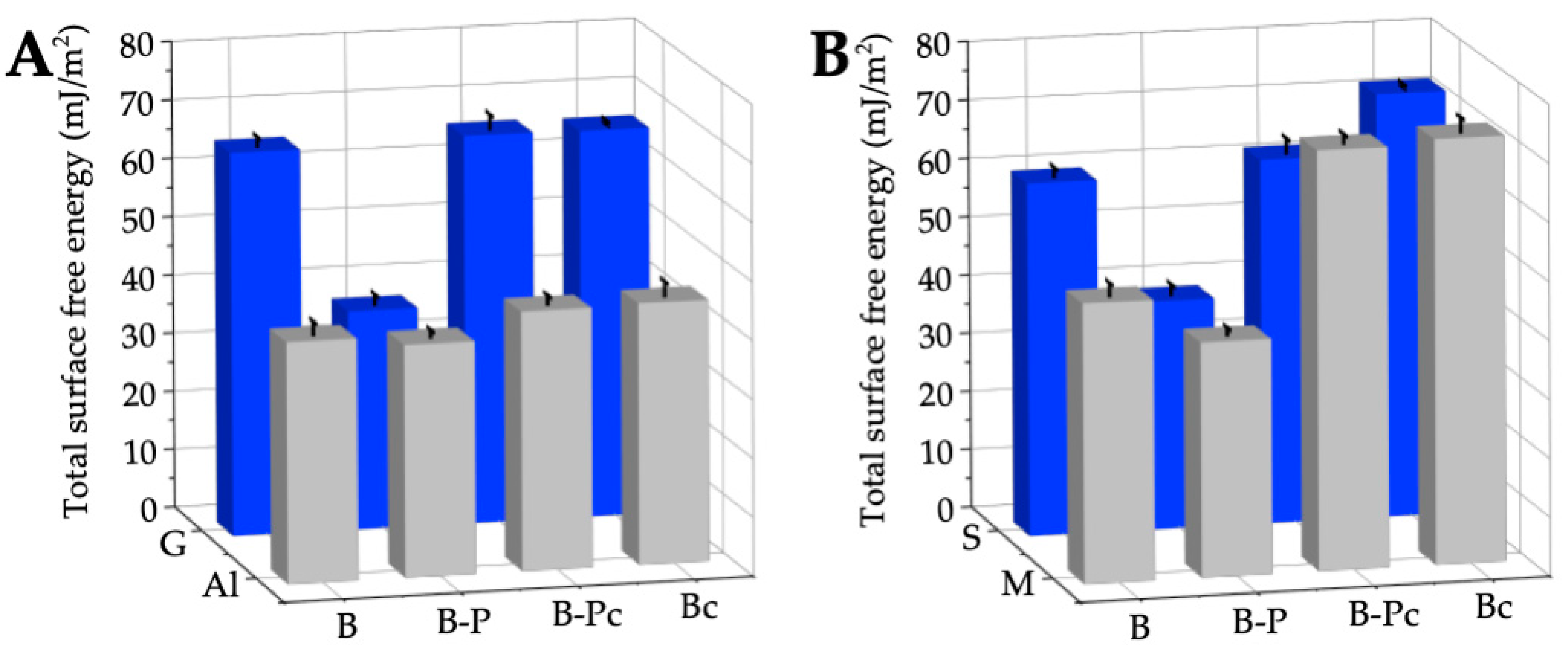
2.2.2. Wettability and Surface Free Energy
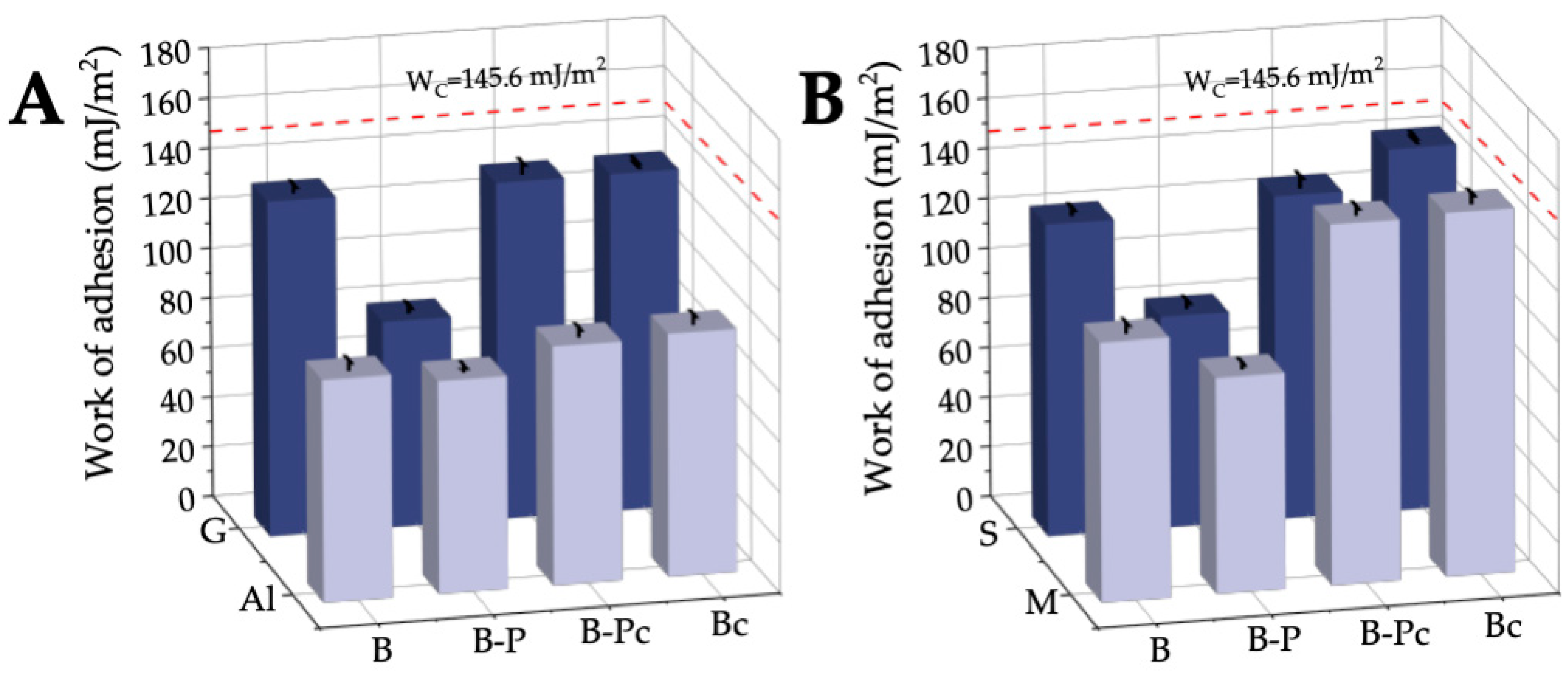
2.2.3. Work of Adhesion
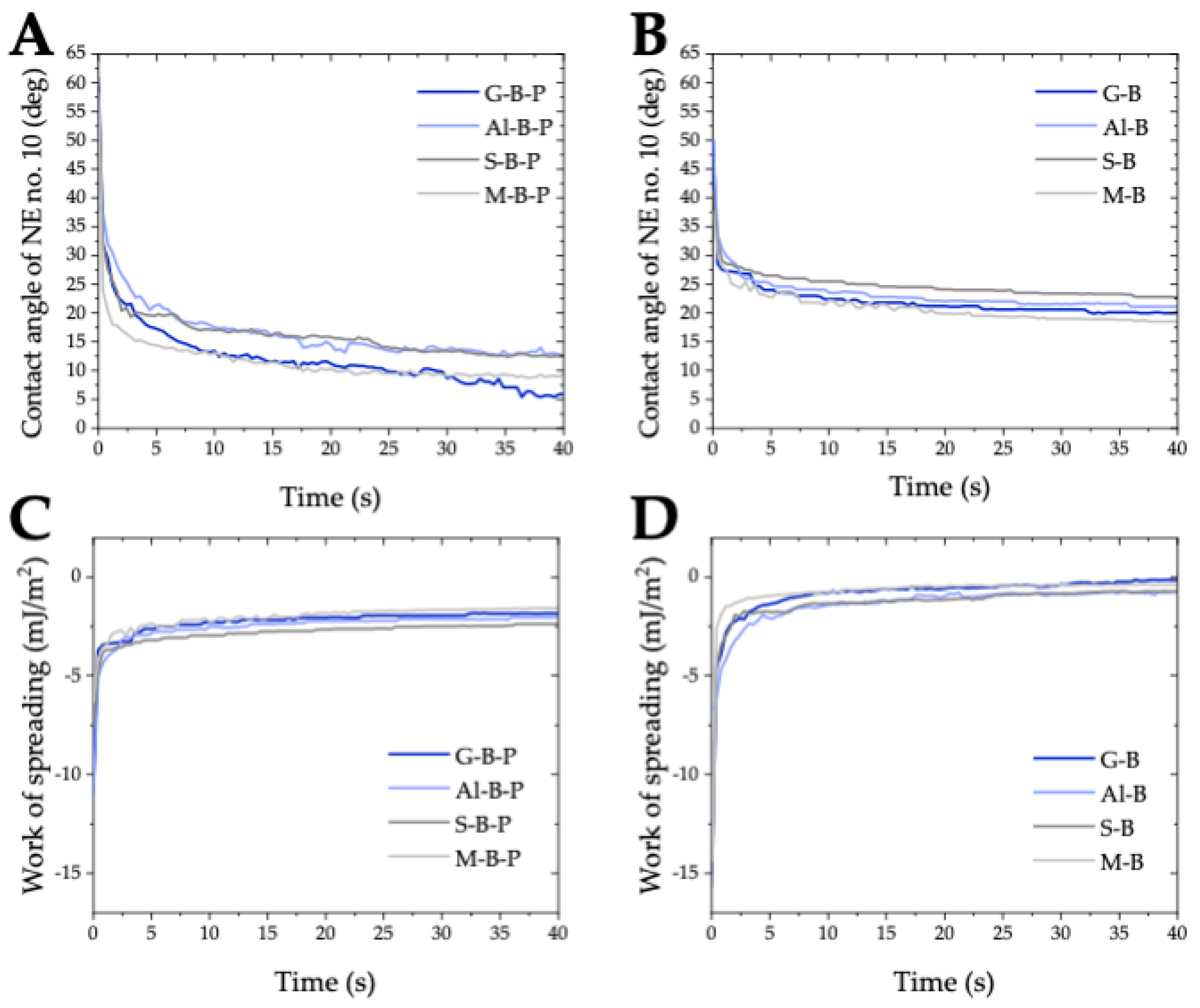
2.3. “Brush on, Wipe off” Method for Testing Graffiti Removers
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Fabrication of NSFs
3.3. Physicochemical Characterization Measurements and RSM Optimization
3.3.1. Surface Tension Measurements
3.3.2. Contact Angle Measurements
3.3.3. Surface Free Energy Determination
3.3.4. Surface Topography
3.3.5. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
3.3.6. Turbidimetric Measurements
3.3.7. RSM Optimization
3.3.8. Optical Microscopy Analysis
3.3.9. Laboratory “Brush on, Wipe off” Detergent Tests
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Wilhelm, K.; Longman, J.; Orr, S.A.; Viles, H. Stone-built heritage as a proxy archive for long-term historical air quality: A study of weathering crusts on three generations of stone sculptures on Broad Street, Oxford. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Florentino, C.; Maguregui, M.; Ciantelli, C.; Sardella, A.; Bonazza, A.; Queralt, I.; Carrero, J.A.; Natali, C.; Morillas, H.; Madariaga, J.M.; et al. Deciphering past and present atmospheric metal pollution of urban environments: The role of black crusts formed on historical constructions. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 243, 118594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanmartín, P.; Cappitelli, F.; Mitchell, R. Current methods of graffiti removal: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 71, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanmartín, P.; Mitchell, R.; Cappitelli, F. Evaluation of cleaning methods for graffiti removal. In Urban Pollution and Changes to Materials and Building Surfaces; Brimblecombe, P., Ed.; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2016; Chapter 11; pp. 291–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feltes, J.; Borsoi, G.; Caiado, P.; Dionísio, A.; Parracha, J.; Flores-Colen, I. Graffiti removal on external thermal insulation composite systems through chemical-mechanical methods: A feasible protocol? J. Build. Eng. 2023, 66, 105872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, C.; Gambino, F.; Nervo, M.; Piccirillo, A.; Scarcella, A.; Zenucchini, F.; Ramil, A.; Pozo-Antonio, J.S. Enhancement of graffiti removal from heritage stone by combining laser ablation and application of a solvent mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 119934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattò, C.; Sanmartín, P.; Gulotta, D.; Troiano, F.; Cappitelli, F. Bioremoval of graffiti using novel commercial strains of bacteria. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 144075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechikh, A.; Klinkova, O.; Maalej, Y.; Tawfiq, I.; Nasri, R. Sandblasting parameter variation effect on galvanized steel surface chemical composition, roughness and free energy. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2020, 102, 102653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicks, Z.W., Jr.; Jones, F.N.; Pappas, S.P.; Wicks, D.A. Adhesion. Chapter 6. In Organic Coatings: Science and Technology, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 121–136. ISBN 13: 9780471698067. [Google Scholar]
- Weldon, D.G. Why coatings work? In Failure Analysis of Paints and Coatings; John Wiley and Sons, Ltd.: PA, New York, USA, 2009; pp. 9–23. ISBN 978-0-470-69753-5. [Google Scholar]
- Emelyanenko, K.A.; Emelyanenko, A.M.; Boinovich, L.B. water and ice adhesion to solid surfaces: Common and specific, the impact of temperature and surface wettability. Coatings 2020, 10, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, R.-H.; Mao, L. Application of Extended DLVO Theory, IV. Derivation of Flotation Rate Equation from First Principles. J Colloid Interface Sci 1996, 181, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Flores, A.; Bradford, S.A.; Hwang, G.; Heyes, G.W.; Kim, H. Particle–bubble Interaction Energies for Particles with Physical and Chemical Heterogeneities. Min. Eng. 2020, 155, 106472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamson, A.W.; Gast, A.P. Physical Chemistry of Surfaces, 6th ed.; Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1997; ISBN 0471148733. [Google Scholar]
- van Dam, J.P.B.; Abrahami, S.T.; Yilmaz, A.; Gonzalez-Garcia, Y.; Terryn, H.; Mol, J.M.C. Effect of surface roughness and chemistry on the adhesion and durability of a steel-epoxy adhesive interface. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2020, 96, 102450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Q. Insight into the Influence of Surface Roughness on the Wettability of Apatite and Dolomite. Minerals 2020, 10, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Fu, Y.; Yin, W.; Sun, H.; Chen, K.; Tang, Y.; Yang, B. Role of surface roughness in the magnesite flotation and its mechanism. Particuology 2022, 62, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vineeth, P.; Peethan, A.; George, S.D. Special wettability for sensing: Drawing inspiration from nature. J. Chem. Eng. 2023, 459, 141615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-T.; Chu, K.-C.; Tsao, H.-K.; Sheng, Y.-J. Size-dependent behavior and failure of young’s equation for wetting of two-component nanodroplets. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 578, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drelich, J.W.; Boinovich, L.; Chibowski, E.; Della Volpe, C.; Hołysz, L.; Marmur, A.; Siboni, S. Contact angles: History of over 200 years of open questions. Surf. Innov. 2020, 8, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmur, A. A guide to the equilibrium contact angles maze. In Contact Angle, Wettability and Adhesion; Mittal, K.L., Ed.; Koninklijke Brill NV: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2009; Volume 6, pp. 3–18. ISBN 9780429088384. [Google Scholar]
- Shardt, N.; Elliott, J.A.W. Gibbsian Thermodynamics of Wenzel Wetting (Was Wenzel Wrong? Revisited). Langmuir. 2020, 36, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Bilal, M.; Khan, A.; Ali, F.; Ibrahim, M.N.M.; Gao, X.; Zhang, S.; Hong, K.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Engineered Hybrid Materials with Smart Surfaces for Effective Mitigation of Petroleum-Originated Pollutants. Engineering 2021, 7, 1492–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruel, C.; Queffeulou, S.; Darlow, T.; Virgilio, N.; Tavares, J.R.; Patience, G.S. Experimental methods in chemical engineering: Contact angles. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 97, 832–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogorzelski, S.; Boniewicz-Szmyt, K.; Grzegorczyk, M.; Rochowski, P. Wettability of metal surfaces affected by paint layer covering. Materials 2022, 15, 1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, B.; Tian, Y.; Di, J.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, L.; Yu, J. Modulation of solid surface with desirable under-liquid wettability based on molecular hydrophilic–lipophilic balance. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 6136–6142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvate, S.; Dixit, P.; Chattopadhyay, S. Superhydrophobic Surfaces: Insights from Theory and Experiment. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 1323–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Oss, C.J.; Good, R.J.; Chaudhury, M.K. Additive and nonadditive surface-tension components and the interpretation of contact angles. Langmuir 1988, 4, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibowski, E.; Perea-Carpio, R. Problems of contact angle and solid surface free energy determination. Adv. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2002, 98, 245–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chibowski, E. Surface free energy of a solid from contact angle hysteresis. Adv. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2003, 103, 149–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chibowski, E. On some relations between advancing, receding and Young’s contact angles. Adv. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2007, 133, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bormashenko, E.Y. Wetting of Real Surfaces; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2013; ISBN 987-3-1-025853-0. [Google Scholar]
- Erbil, H.Y. The debate on the dependence of apparent contact angles on drop contact area or 3-phase contact line: A review. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2014, 69, 325–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbil, H.Y. Dependency of contact angles on three-phase contact line: A review. Colloids Interfaces 2021, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, K.-Y. Contact Angle Hysteresis on Smooth/Flat and Rough Surfaces. Interpretation, Mechanism, and Origin. Acc. Mater. Res. 2022, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghishov, I.; Abeykoon, G.A.; Wang, M.; Oyenowo, O.P.; Argüelles-Vivas, F.J.; Okuno, R. A mechanistic comparison of formate, acetate, and glycine as wettability modifiers for carbonate and shale formations. Colloids Surf. A 2022, 652, 129849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yu, S.; Wei, J.; Qiao, W. Cleaning efficiency of amino-acid surfactants with polyoxyethylene ether and isopropanol in liquid carbon dioxide. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2018, 21, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freese, S.; Diraoui, S.; Mateescu, A.; Frank, P.; Theodorakopoulos, C.; Jonas, U. Polyolefin-supported hydrogels for selective cleaning treatments of paintings. Gels 2020, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atta, D.Y.; Negash, B.M.; Yekeen, N.; Habte, A.D.; Abdul Malik, A.B. Influence of natural L-amino acids on the interfacial tension of an oil-water system and rock wettability alterations. J. Petrol. Sci. Engin. 2021, 199, 108241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara Orozco, R.A.; Abeykoon, R.A.; Wang, M.; Arguelles-Vivas, F.; Okuno, R.; Lake, L.W.; Ayirala, S.C.; AlSofi, A.M. Amino acid as a novel wettability modifier for enhanced waterflooding in carbonate reservoirs. SPE Res. Eval. & Eng. 2020, 23, 741–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartman, M.; Balicki, S.; Wilk, K.A. Formulation of environmentally safe graffiti remover containing esterified plant oils and sugar surfactant. Molecules 2021, 26, 4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartman, M.; Balicki, S.; Hołysz, L.; Wilk, K.A. Graffiti coating eco-remover developed for sensitive surfaces by using an optimized high-pressure homogenization process. Colloid Surf. A 2023, 659, 130792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglioni, M.; Sekine, F.H.; Ogura, T.; Chen, S.-H.; Baglioni, P. Nanostructured fluids for polymeric coatings removal: Surfactants affect the polymer glass transition temperature. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 606, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglioni, M.; Poggi, G.; Giorgi, R.; Rivella, P.; Ogura, T.; Baglioni, P. Selective removal of over-paintings from “Street Art” using an environmentally friendly nanostructured fluid loaded in highly retentive hydrogels. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 595, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglioni, M.; Poggi, G.; Benavides, Y.J.; Martínez Camacho, F.; Giorgi, R.; Baglioni, P. Nanostructured fluids for the removal of graffiti–A survey on 17 commercial spray-can paints. J. Cult. Herit. 2018, 34, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; Liu, X.-M.; Yang, Q.-X.; Luo, X.-D.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S.-Y. Effect of hydrophile–lipophile balance of the linker in Gal/GalNAc ligands on high-affinity binding of galactosylated liposomes by the asialoglycoprotein receptor. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 624, 121967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilk, K.A.; Syper, L.; Burczyk, B.; Maliszewska, I.; Jon, M.; Domagalska, B.W. Preparation and Properties of New Lactose–Derived Surfactants. J. Surf. Deterg. 2001, 4, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilk, K.A.; Zielińska, K.; Jezierski, A. Structural aspects in saccharide-derived micelles studied by a spin probe technique. Colloid Surf. A 2009, 343, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglioni, M.; Alterini, M.; Chelazzi, D.; Giorgi, R.; Baglioni, P. Removing polymeric coatings with nanostructured fluids: Influence of substrate, nature of the film, and application methodology. Front. Mater. 2019, 6, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredda, N.; Buscaglia, P.; Gallo, P.; Borla, M.; Aicardi, S.; Poggi, G.; Baglioni, P.; Nervo, M.; Scalarone, D.; Borghi, A.; et al. An ancient Egyptian multilayered polychrome wooden sculpture belonging to the museo Egizio of Torino: Characterization of painting materials and design of cleaning processes by means of highly retentive hydrogels. Coatings 2021, 11, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglioni, M.; Guaragnone, T.; Mastrangelo, R.; Sekine, F.H.; Ogura, T.; Baglioni, P. Nonionic surfactants for the cleaning of works of art: Insights on acrylic polymer films dewetting and artificial soil removal. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 26704–26716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglioni, M.; Montis, C.; Brandi, F.; Guaragnone, T.; Meazzini, I.; Baglioni, P.; Berti, D. Dewetting acrylic polymer films with water/propylene carbonate/surfactant mixtures–implications for cultural heritage conservation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 23723–23732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, M.; Huang, M.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, T.; Huang, M. Effect of ultrasound assisted emulsification in the production of Pickering emulsion formulated with chitosan self-assembled particles: Stability, macro, and micro rheological properties. LWT 2022, 154, 112595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukuyama, M.N.; Ghisleni, D.D.M.; Pinto, T.J.A.; Bou-Chacra, N.A. Nanoemulsion: Process selection and application in cosmetics—A review. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2016, 38, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, N.; Singh, M.; Om, H.; Sachin, K.M.; Sharma, D. Study of surface and bulk physicochemical properties of biocompatible nanoemulsions at T = (293.15, 303.15 and 313.15 K). J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 305, 112744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananthapadmanabhan, K.P. Amino-acid surfactants in personal cleansing (Review). Tenside Surfactants Deterg. 2019, 56, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piętka-Ottlik, M.; Lewińska, A.; Jaromin, A.; Krasowska, A.; Wilk, K.A. Antifungal organoselenium compound loaded nanoemulsions stabilized by bifunctional cationic surfactants. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 510, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, K.; Matamala, C.; Martínez, N.; Zúñiga, R.N.; Troncoso, E. Comparative Study of physicochemical properties of nanoemulsions fabricated with natural and synthetic surfactants. Processes 2021, 9, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, M.; Inoue, M.; Fukami, T. Novel amino acid-based surfactant for silicone emulsification and its application in hair care products: A promising alternative to quaternary ammonium cationic surfactants. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2017, 39, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croll, S.G. Surface roughness profile and its effect on coating adhesion and corrosion protection: A review. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 148, 105847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, C.G.J.; Prasanth, R. Approaches to design a surface with tunable wettability: A review on surface properties. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 108–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubiak, K.J.; Wilson, M.C.T.; Mathia, T.G.; Carval, P. Wettability versus roughness of engineering surfaces. Wear 2011, 271, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudawska, A.; Miturska-Barańska, I.; Doluk, E.; Olewnik-Kruszkowska, E. Assessment of surface treatment degree of steel sheets in the bonding process. Materials 2022, 15, 5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, S.; Jiang, L. Nature-inspired superwettability systems. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 17036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edachery, V.; Swamybabu, V.; Adarsh, D.; Kailas, S.V. Influence of surface roughness frequencies and roughness parameters on lubricant wettability transitions in micro-nano scale hierarchical surfaces. Tribol. Int. 2022, 165, 107316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.Q.; Yan, X.P.; Peng, Z. Prediction of surface features of wear components based on surface characteristics of wear Derbis. Wear 2007, 263, 1513–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurak, M.; Gołąbek, M.; Hołysz, L.; Chibowski, E. Properties of Langmuir and solid supported lipid films with sphingomyelin. Adv. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2014, 222, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymczyk, K.; Zdziennicka, A.; Jańczuk, B. Adsorption and wetting properties of cationic, anionic and nonoionic surfactants in the glass-aqueous solution of surfactant-air system. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 162, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terpiłowski, K.; Rymuszka, D. Surface properties of glass plates activated by air, oxygen, nitrogen and argon plasma. Glass Phys. Chem. 2016, 42, 53–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charola, A.E. Stone deterioration in historic buildings and monuments. In Proceedings of the 10th International Congress on Deterioration and Conservation of Stone, ICOMOS, Stockholm, Sweden, 27 June 27–2 July 2004; Kwiatkowski, D., Löfvendahl, R., Eds.; pp. 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Terpiłowski, K.; Rymuszka, D.; Hołysz, L.; Ilnicki, M. Surface properties of metal alloys used in aviation after plasma treatment. Surf. Interface Anal. 2017, 49, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrisi, L.; Scolaro, C. Treatment techniques on aluminum to modify the surface wetting properties. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2015, 128, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, M.; Fojan, P.; Gurevich, L.; Afshari, A. Effects of aluminium surface morphology and chemical modification on wettability. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 296, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, M.; Afshari, A.; Thormann, E. Effect of aluminum substrate surface modification on wettability and freezing delay of water droplet at subzero temperatures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 11147–11153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çıra, S.C.; Daĝ, A.; Karakuş, A. Investigation of the effects of marble material properties on the surface quality. Adv. Mater. Sci. Engin. 2018, 2018, 6514785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somlyai-Sipos, L.; Baymli, P. Wettability of metals by water. Metals 2022, 12, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibowski, E.; Hołysz, L.; Szcześ, A. Wettability of powders. In Adhesion in Pharmaceutical, Biomedical and Dental Fields; Mittal, K., Etzler, F., Eds.; Scrivener Publishing LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Chapter 2; pp. 23–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starov, V.M.; Velarde, M.G. Surface forces and wetting phenomena. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2009, 21, 464121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibowski, E.; Jurak, M. Comparison of contact angle hysteresis of different probe liquids on the same solid surface. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2013, 291, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radelczuk, H.; Hołysz, L.; Chibowski, E. Comparison of the Lifshitz-van der Waals/acid-base and contact hysteresis approaches for determination of solid surface free energy. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2002, 16, 1547–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibowski, E.; Jurak, M.; Hołysz, L. Preparation, investigation techniques, and surface free energy of solid-supported phospholipid layers. In The Encyclopedia of Surface and Colloid Science, 2nd ed.; Somasundaran, P., Ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; pp. 1–22. ISBN 0-8493-9615-8. [Google Scholar]
- Gołąbek (Mirosław), M.; Hołysz, L. Changes in wetting and energetic properties of glass caused by deposition of different lipid layers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 5463–5469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krainer, S.; Hirn, U. Contact angle measurement on porous substrates: Effect of liquid absorption and drop size. Colloids Surf. A 2021, 619, 126503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Oss, C.J.; Good, R.J.; Busscher, H.J. Estimation of dipolar surface tension parameters of glycerol and formamide for use in contact angle measurements on polar solids. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 1990, 11, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Oss, C.J.; Giese, R.F.; Wu, W. On the degree to which the contact angle is affected by the adsorption onto a solid surface of vapor molecules originating from the liquid drop. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 1998, 19, 1221–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibowski, E.; Carpio, R.; Ontiveros–Ortega, A. On the interpretation of contact angle hysteresis. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2002, 16, 1283–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamińska, A.; Kaczmarek, H.; Kowalonek, J. The influence of side groups and polarity of polymers on the kind and effectiveness of their surface modification by air plasma action. Eur. Polym. J. 2002, 38, 1915–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.; Lu, F.; Li, B.; Kwok, D.Y. Wettability interpretation of oxygen plasma modified poly(methyl methacrylate). Langmuir 2004, 20, 10919–10927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibowski, E.; Hołysz, L.; Terpiłowki, K.; Jurak, M. Investigation of super–hydrophobic effect of PMMA layers with different fillers deposited on glass support. Colloids Surf. A 2006, 291, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basri, E.; Martha, R.; Damayanti, R.; Rahayu, I.; Darmawan, W.; Gerardin, P. Durability and wettability of varnishes on the modified and aged surfaces of short rotation teak wood. Pigm. Resin. Technol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuningsih, I.; Rahayu, I.S.; Dumasari, L.; Darmawan, W. Wettability and adherence of acrylic paints on long and short rotation teaks. Wood Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 15, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Fedel, M.; Petrolli, S.; Deflorian, F. Behaviour of different removers on permanent anti-graffiti organic coatings. J. Build. Eng. 2016, 5, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khwanmuang, P.; Naparswad, C.; Archakunakorn, S.; Waicharoen, C.; Chitichotpanya, C. Optimization of in situ synthesis of Ag/PU nanocomposites using response surface methodology for self-disinfecting coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 110, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balicki, S. Unit process optimization in the organic technology. Przem. Chem. 2021, 100, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balicki, S.; Pawlaczyk-Graja, I.; Gancarz, R.; Capek, P.; Wilk, K.A. Optimization of Ultrasound Assisted Extraction of Functional Food Fiber from Canadian Horseweed (Erigeron canadensis L.). ACS Omega 2020, 5, 20854–20862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| No. | Structure | INCI | Abb. | Mw (M) | 1 (mN/m) | HLBm 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amino-acid-type surfactants (AAS) | ||||||
| 1 | 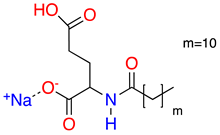 | Sodium Lauroyl Glutamate | SLG | 356 | 35.7 | 9.7 |
| 2 | 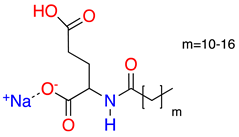 | Sodium Cocoyl Glutamate | SCCG | 359 | 29.9 | 8.3 |
| 3 | 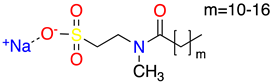 | Sodium Methyl Cocoyl Taurate | SMCT | 363 | 35.3 | 6.1 |
| 4 |  | Sodium Cocoyl Glycinate | SCG | 273 | 26.4 | 7.5 |
| Solvents | ||||||
| 1 | 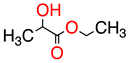 | Ethyl lactate | EL | 118.1 | 28.7 | 8.3 |
| 2 | 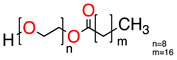 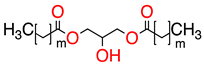 | UCO-Oil-PEG 8 | UCO-Oil-PEG 8 | 636.9 625.0 | 32.6 | 3.5 0.9 |
| Type of AAS: | SLG | SCCG | SCMT | SCG | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NE No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| Concentration (mol/dm3) | 0.05 | 0.075 | 0.1 | 0.05 | 0.075 | 0.1 | 0.05 | 0.075 | 0.1 | 0.05 | 0.075 | 0.1 |
| 0 days storage | ||||||||||||
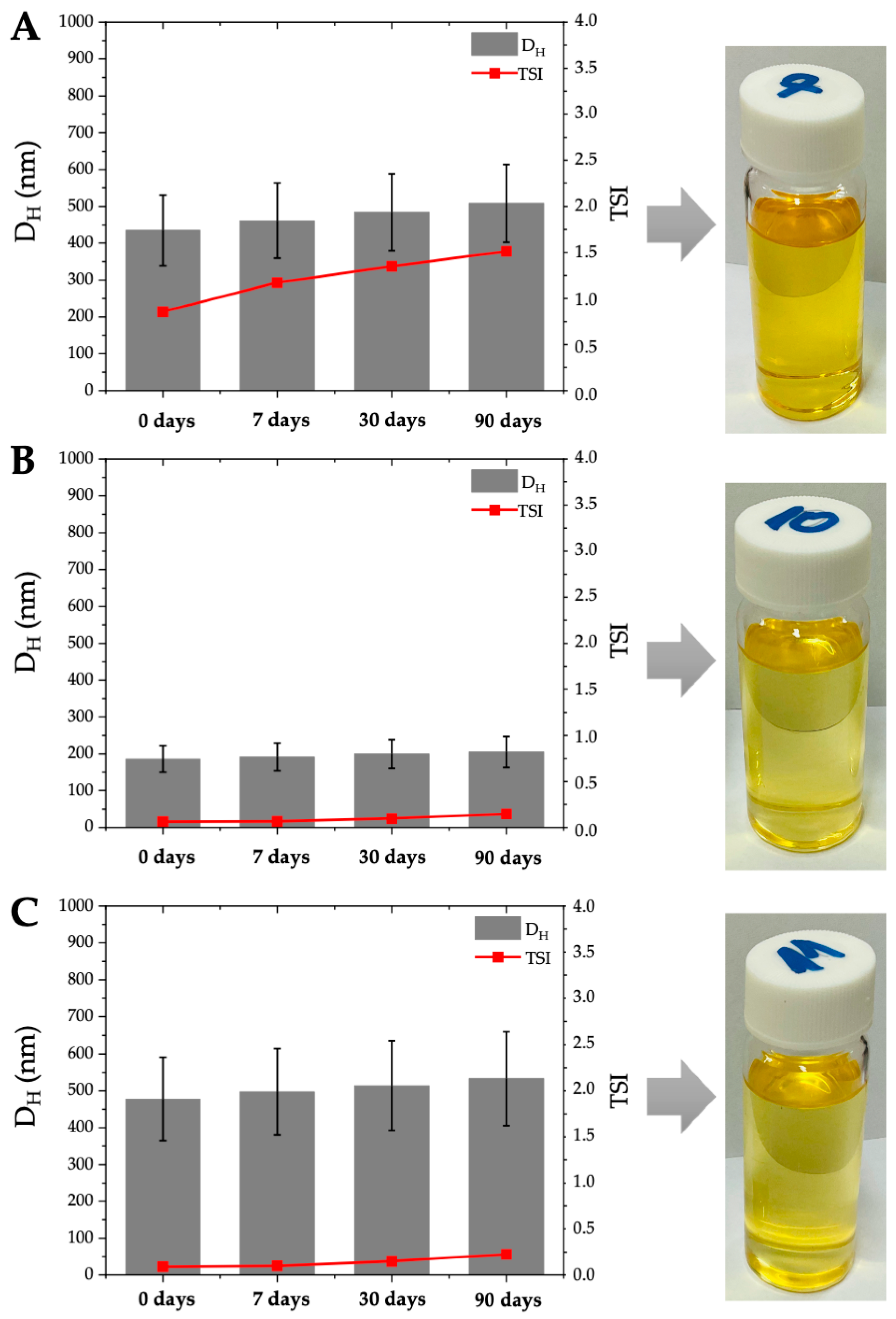
| DH (nm) | 749 | 1042 | 1424 | 1328 | 1963 | 2247 | 435 1 | 776 | 817 | 186 | 478 | 761 |
| DH S.D. ± (nm) | 143 | 190 | 253 | 297 | 460 | 695 | 96 | 150 | 152 | 36 | 113 | 198 |
| PDI | 0.036 | 0.033 | 0.032 | 0.050 | 0.055 | 0.096 | 0.049 | 0.037 | 0.035 | 0.037 | 0.056 | 0.068 |
| TSI | 1.01 | 1.57 | 2.40 | 1.74 | 1.89 | 2.27 | 0.86 | 1.53 | 1.56 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.11 |
| 7 days storage | ||||||||||||
| DH (nm) | 779 | 1137 | 1524 | - 2 | - | - | 461 | 864 | 906 | 192 | 497 | 799 |
| DH S.D. ± (nm) | 144 | 209 | 281 | - | - | - | 102 | 167 | 175 | 38 | 117 | 208 |
| PDI | 0.034 | 0.034 | 0.034 | - | - | - | 0.049 | 0.037 | 0.037 | 0.038 | 0.055 | 0.068 |
| TSI | 1.67 | 3.05 | 5.04 | 31.32 | 34.02 | 31.78 | 1.17 | 2.74 | 2.84 | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.20 |
| 1 month storage | ||||||||||||
| DH (nm) | 812 | 1194 | 1618 | - | - | - | 484 | 916 | 961 | 200 | 514 | 833 |
| DH S.D. ± (nm) | 146 | 215 | 292 | - | - | - | 104 | 178 | 187 | 39 | 122 | 219 |
| PDI | 0.032 | 0.032 | 0.033 | - | - | - | 0.046 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.038 | 0.057 | 0.069 |
| TSI | 2.12 | 4.69 | 8.42 | - | - | - | 1.35 | 3.39 | 3.80 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.78 |
| 3 months storage | ||||||||||||
| DH (nm) | 843 | 253 | 1681 | - | - | - | 508 | 971 | 1018 | 205 | 533 | 868 |
| DH S.D. ± (nm) | 147 | 221 | 304 | - | - | - | 106 | 91 | 209 | 42 | 127 | 238 |
| PDI | 0.030 | 0.031 | 0.033 | - | - | - | 0.044 | 0.039 | 0.042 | 0.042 | 0.057 | 0.075 |
| TSI | 2.35 | 5.44 | 10.02 | - | - | - | 1.51 | 4.17 | 4.76 | 0.15 | 0.22 | 1.64 |
| No. | NE No. | Type of AAS | Diameter (nm) | PDI | TSI (0 Days) | TSI (7 Days) | TSI (30 Days) | Desirability | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P 3 | A 4 | P | A | P | A | P | A | P | A | ||||
| 1 | 10 1 | SLG | 207 | 186 | 0.042 | 0.037 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 1.66 | 0.07 | 0.34 | 0.10 | 0.964 |
| 2 | 11 2 | SLG | 380 | 478 | 0.043 | 0.057 | 0.20 | 0.09 | 1.56 | 0.10 | 5.53 | 0.15 | 0.950 |
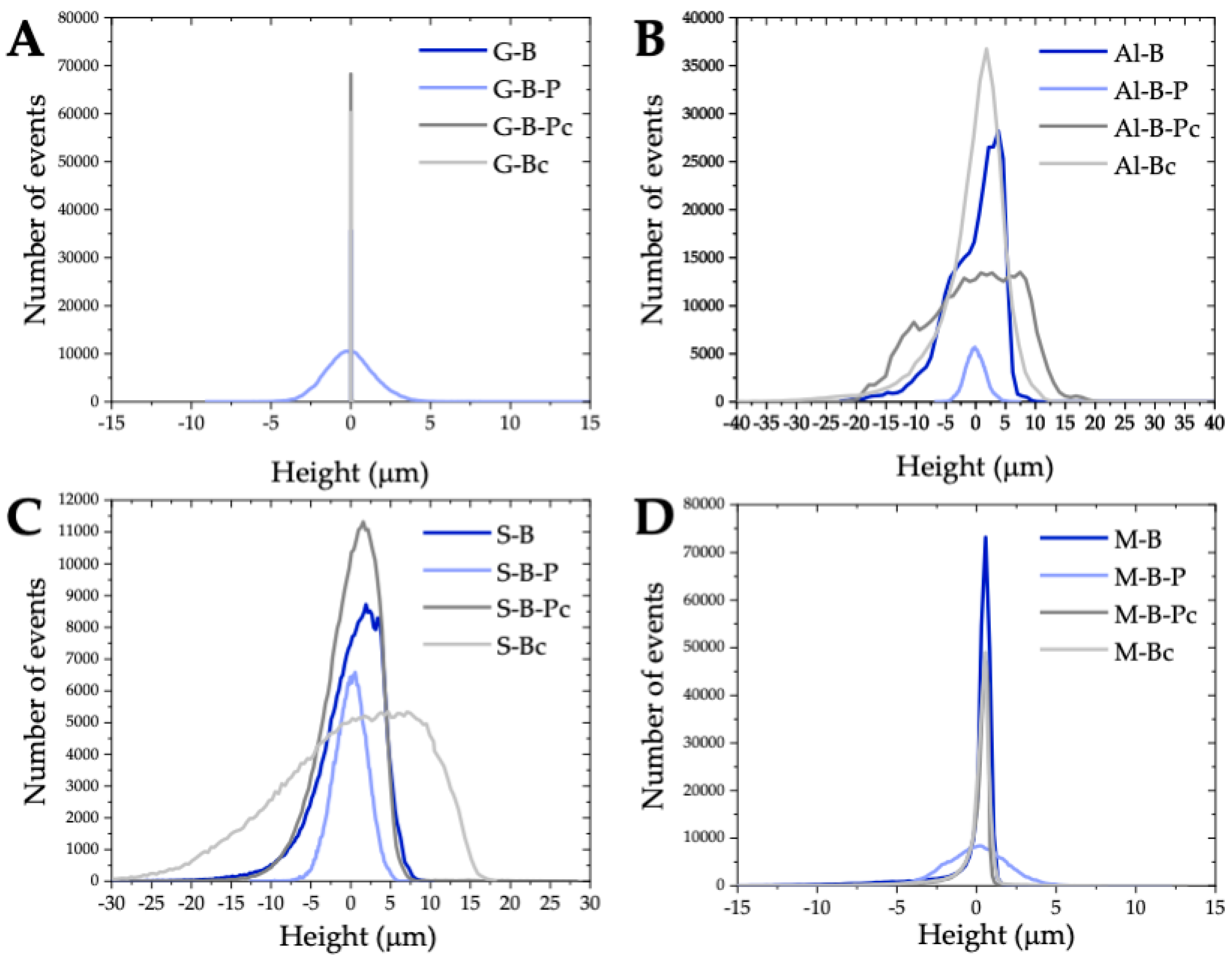
| Sample | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| (nm) | |||
| G-B | 0.37 ± 0.02 | 0.62 ± 0.07 | 28.9 ± 17.1 |
| G-B-P | 1.16 ± 0.02 μm | 1.48 ± 0.01 μm | 19.2 ± 4.5 μm |
| G-B-Pc | 0.74 ± 0.07 | 1.60 ± 0.39 | 99.5 ± 52.2 |
| G-Bc | 0.73 ± 1.63 | 1.34 ± 0.29 | 47.6 ± 16.7 |
| (μm) | |||
| Al-B | 3.95 ± 0.39 | 5.01 ± 0.56 | 46.0 ± 4.1 |
| Al-B-P | 1.36 ± 0.07 | 1.69 ± 0.04 | 14.3 ± 0.9 |
| Al-B-Pc | 5.42 ± 0.24 | 6.72 ± 0.22 | 44.4 ± 4.5 |
| Al-Bc | 3.97 ± 0.24 | 5.69 ± 0.38 | 179.0 ± 19.5 |
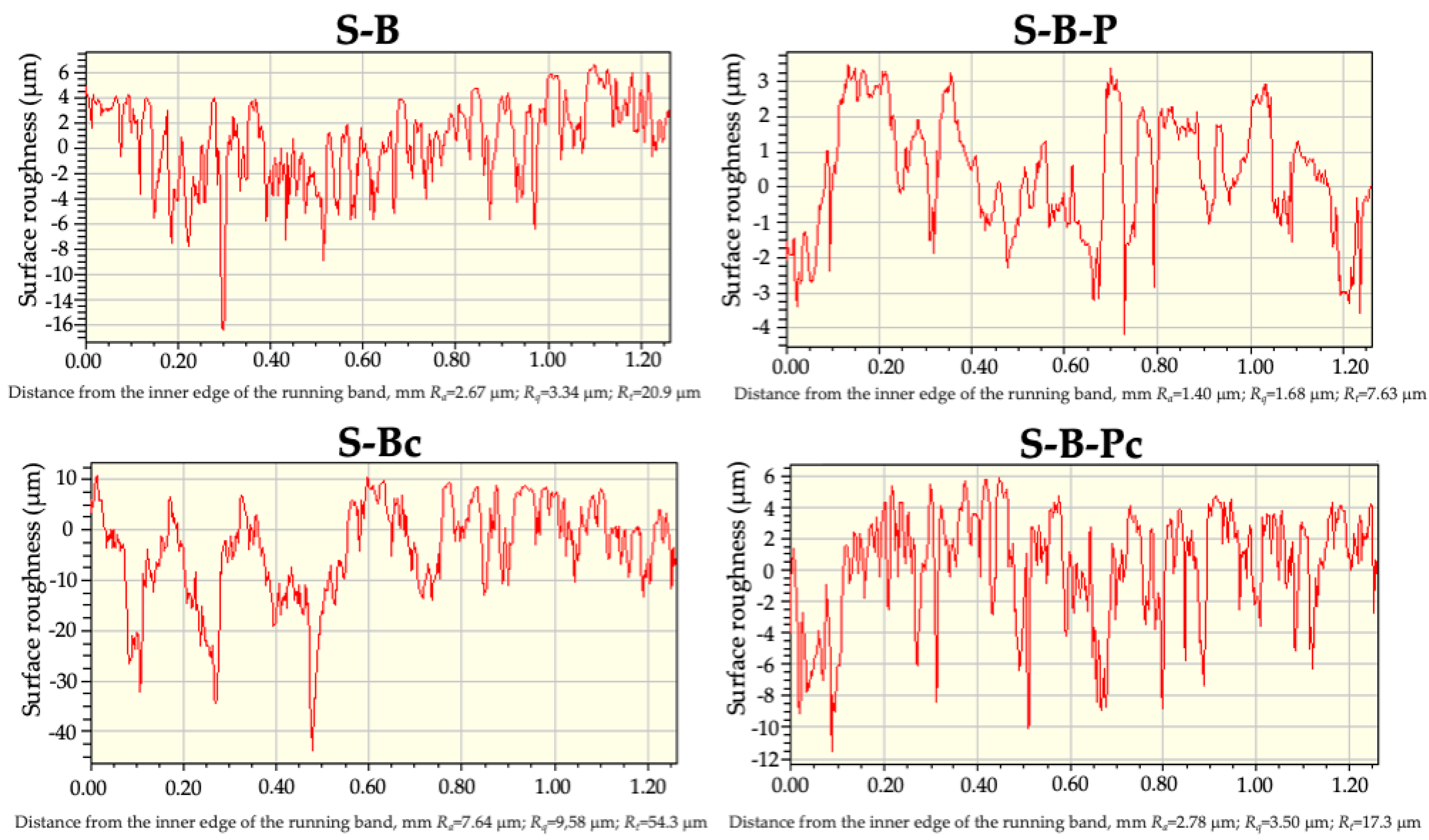
| S-B | 3.78 ± 1.40 | 5.08 ± 1.90 | 49.2 ± 9.7 |
| S-B-P | 1.62 ± 0.04 | 2.05 ± 0.06 | 17.1 ± 0.7 |
| S-B-Pc | 2.72 ± 0.30 | 3.50 ± 0.38 | 51.8 ± 8.3 |
| S-Bc | 6.55 ± 0.82 | 8.56 ± 1.04 | 72.4 ± 1.4 |
| M-B | 1.12 ± 0.20 | 1.86 ± 0.13 | 32.8 ± 12.8 |
| M-B-P | 1.50 ± 0.16 | 1.92 ± 0.22 | 20.8 ± 3.70 |
| M-B-Pc | 0.69 ± 0.05 | 1.38 ± 0.26 | 23.2 ± 5.50 |
| M-Bc | 0.81 ± 0.05 | 1.27 ± 0.35 | 20.1 ± 17.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bartman, M.; Balicki, S.; Hołysz, L.; Wilk, K.A. Surface Properties of Graffiti Coatings on Sensitive Surfaces Concerning Their Removal with Formulations Based on the Amino-Acid-Type Surfactants. Molecules 2023, 28, 1986. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041986
Bartman M, Balicki S, Hołysz L, Wilk KA. Surface Properties of Graffiti Coatings on Sensitive Surfaces Concerning Their Removal with Formulations Based on the Amino-Acid-Type Surfactants. Molecules. 2023; 28(4):1986. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041986
Chicago/Turabian StyleBartman, Marcin, Sebastian Balicki, Lucyna Hołysz, and Kazimiera A. Wilk. 2023. "Surface Properties of Graffiti Coatings on Sensitive Surfaces Concerning Their Removal with Formulations Based on the Amino-Acid-Type Surfactants" Molecules 28, no. 4: 1986. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041986
APA StyleBartman, M., Balicki, S., Hołysz, L., & Wilk, K. A. (2023). Surface Properties of Graffiti Coatings on Sensitive Surfaces Concerning Their Removal with Formulations Based on the Amino-Acid-Type Surfactants. Molecules, 28(4), 1986. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041986






