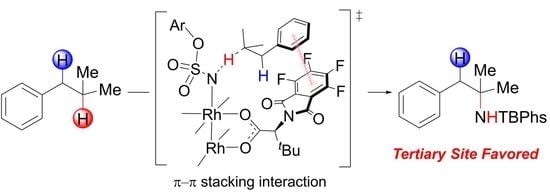
Computational Exploration of Dirhodium Complex-Catalyzed Selective Intermolecular Amination of Tertiary vs. Benzylic C−H Bonds
Abstract
Share and Cite
Su, X.-X.; Chen, X.-H.; Ding, D.-B.; She, Y.-B.; Yang, Y.-F. Computational Exploration of Dirhodium Complex-Catalyzed Selective Intermolecular Amination of Tertiary vs. Benzylic C−H Bonds. Molecules 2023, 28, 1928. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041928
Su X-X, Chen X-H, Ding D-B, She Y-B, Yang Y-F. Computational Exploration of Dirhodium Complex-Catalyzed Selective Intermolecular Amination of Tertiary vs. Benzylic C−H Bonds. Molecules. 2023; 28(4):1928. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041928
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Xing-Xing, Xia-He Chen, De-Bo Ding, Yuan-Bin She, and Yun-Fang Yang. 2023. "Computational Exploration of Dirhodium Complex-Catalyzed Selective Intermolecular Amination of Tertiary vs. Benzylic C−H Bonds" Molecules 28, no. 4: 1928. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041928
APA StyleSu, X.-X., Chen, X.-H., Ding, D.-B., She, Y.-B., & Yang, Y.-F. (2023). Computational Exploration of Dirhodium Complex-Catalyzed Selective Intermolecular Amination of Tertiary vs. Benzylic C−H Bonds. Molecules, 28(4), 1928. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041928