Licochalcone A Inhibits Prostaglandin E2 by Targeting the MAPK Pathway in LPS Activated Primary Microglia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
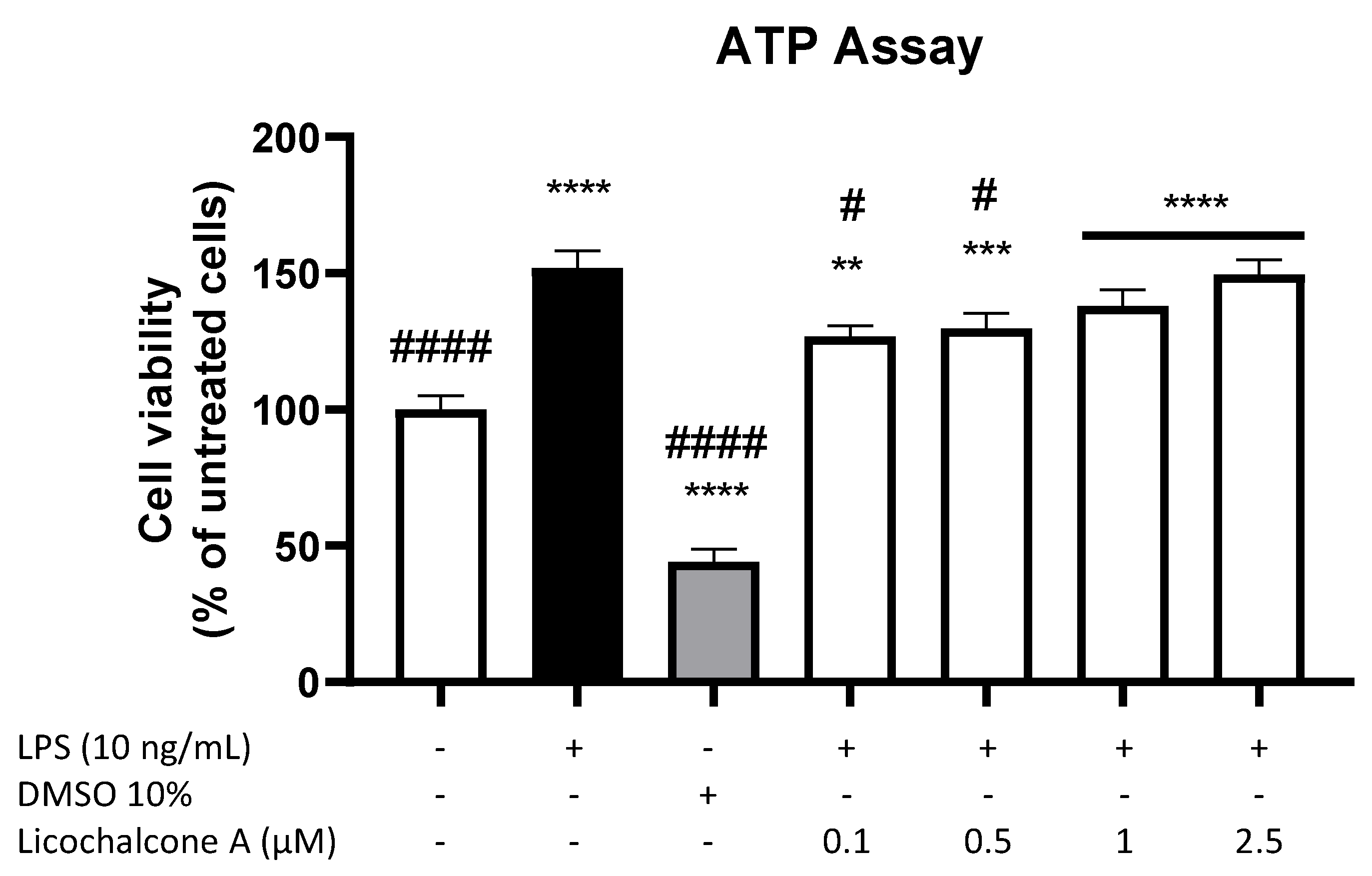
2.1. Cytotoxic Effects of Licochalcone A in Primary Rat Microglia
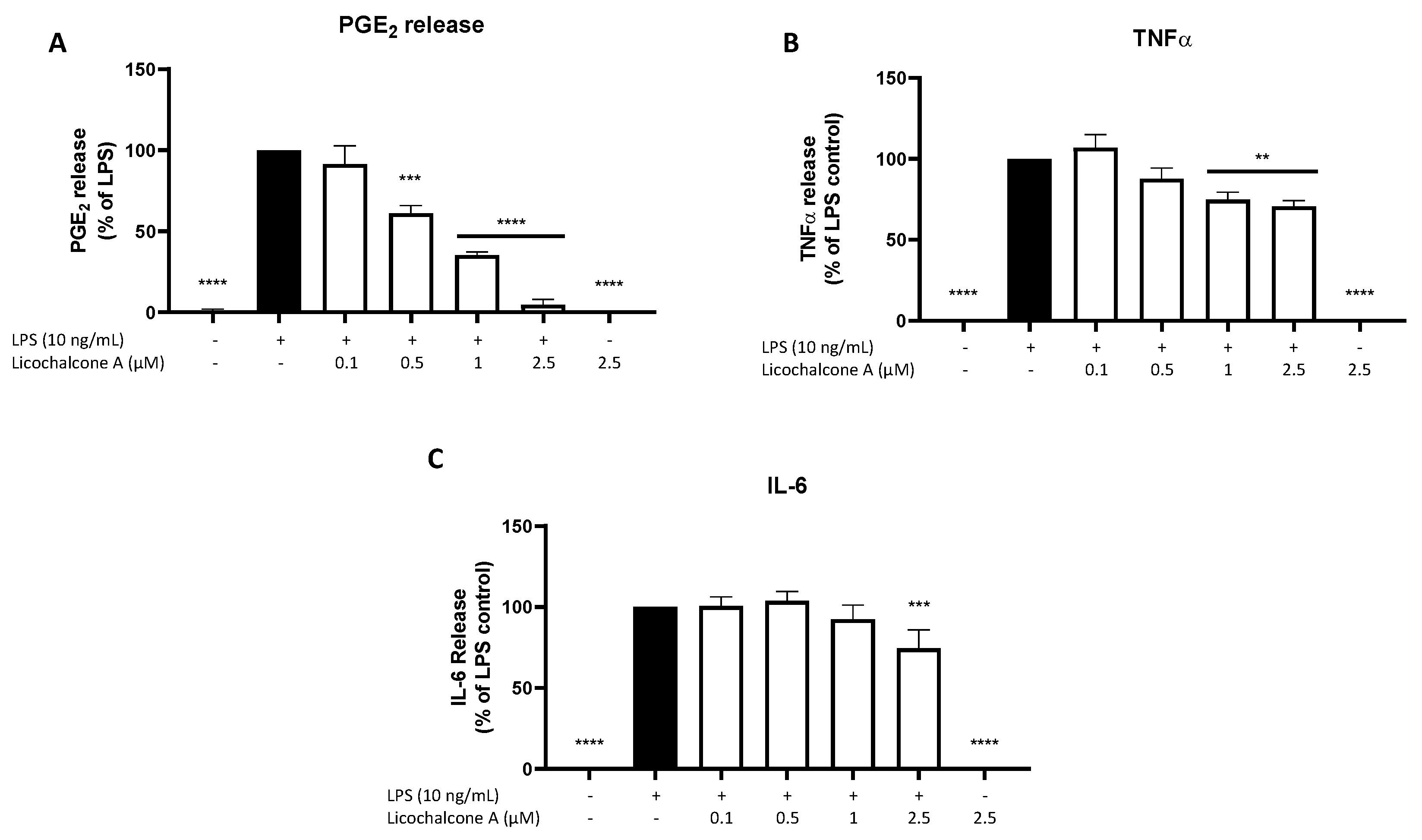
2.2. Effects of Licochalcone A on PGE2, TNFα, and IL-6 Release
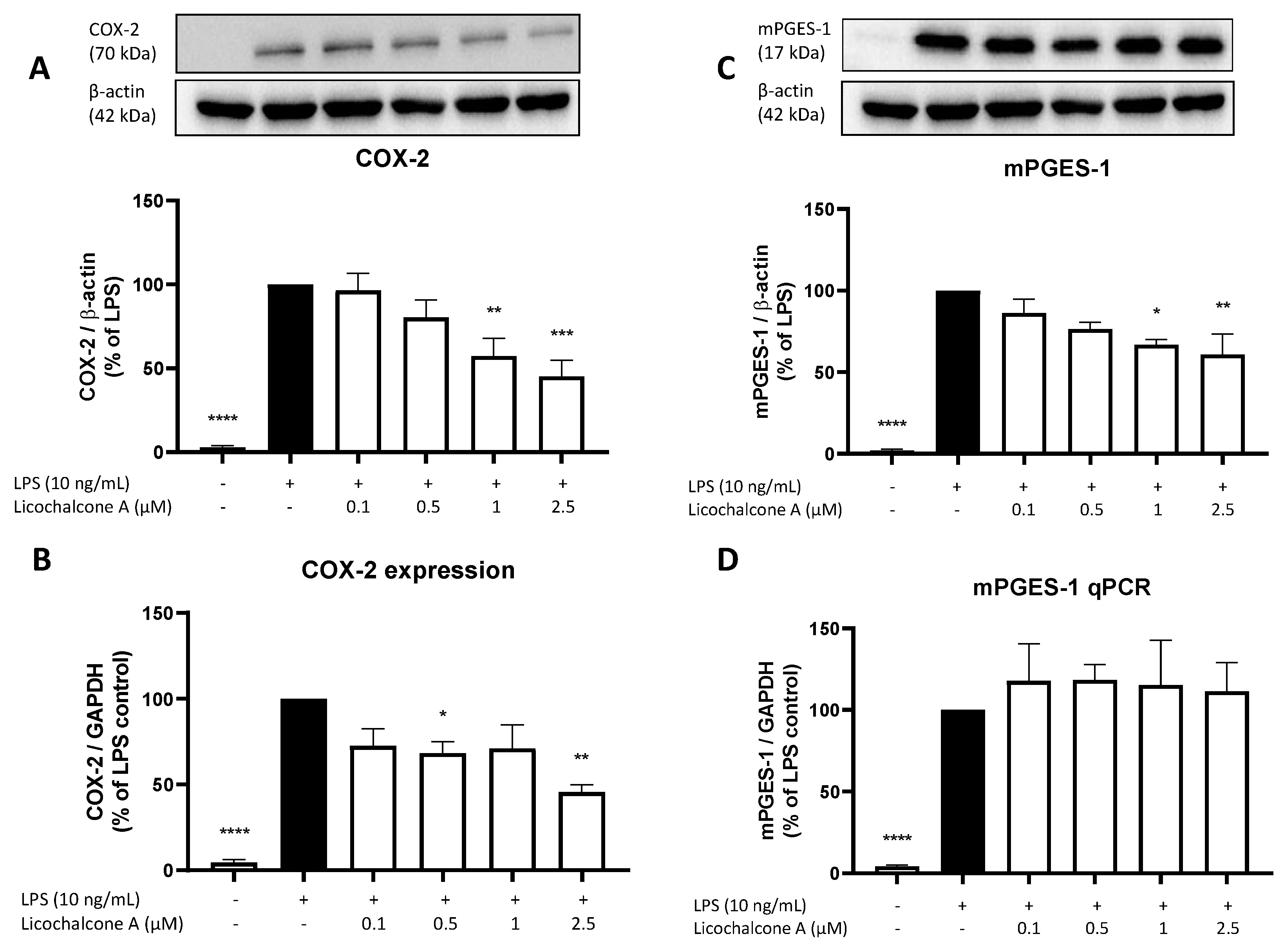
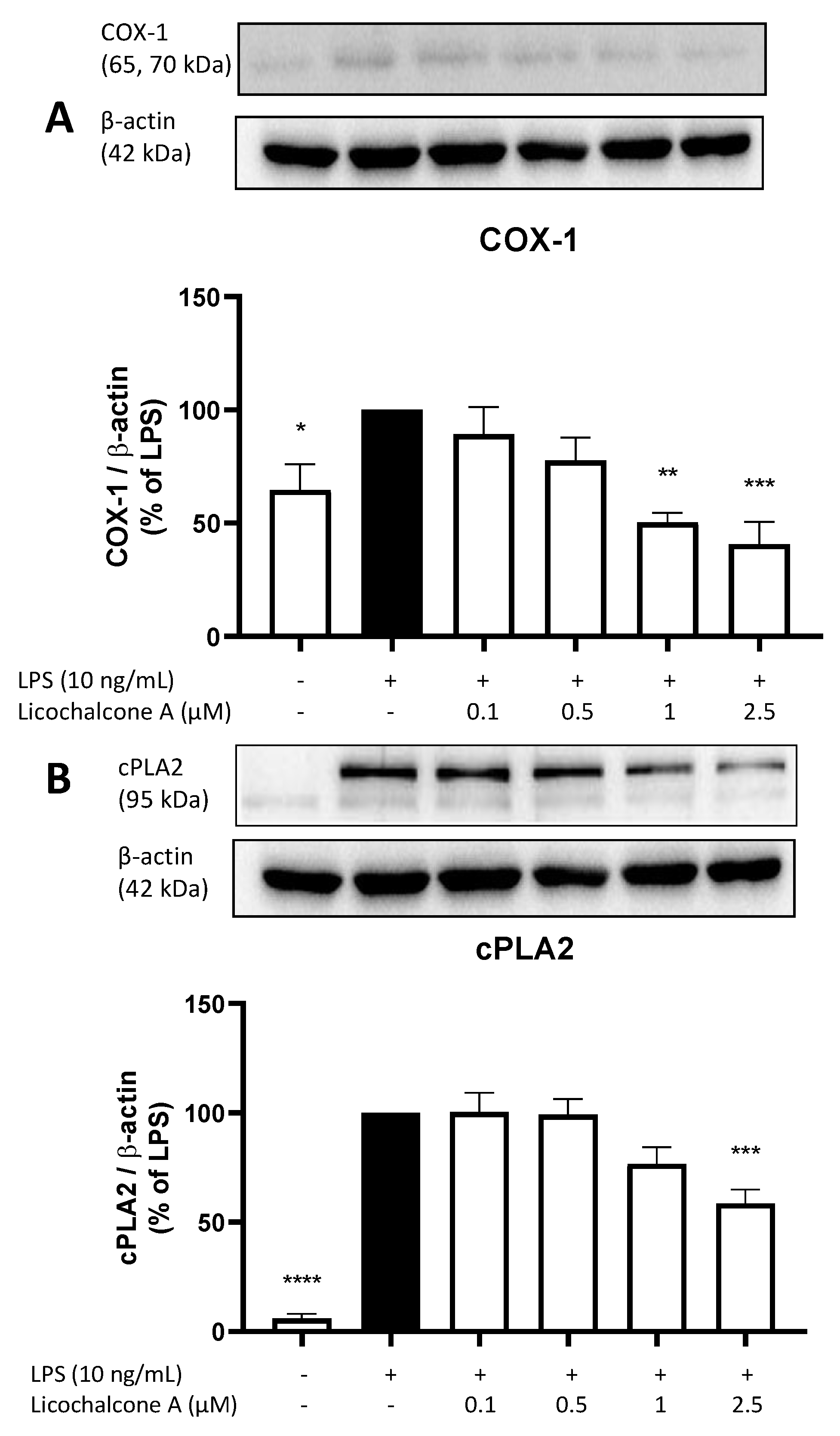
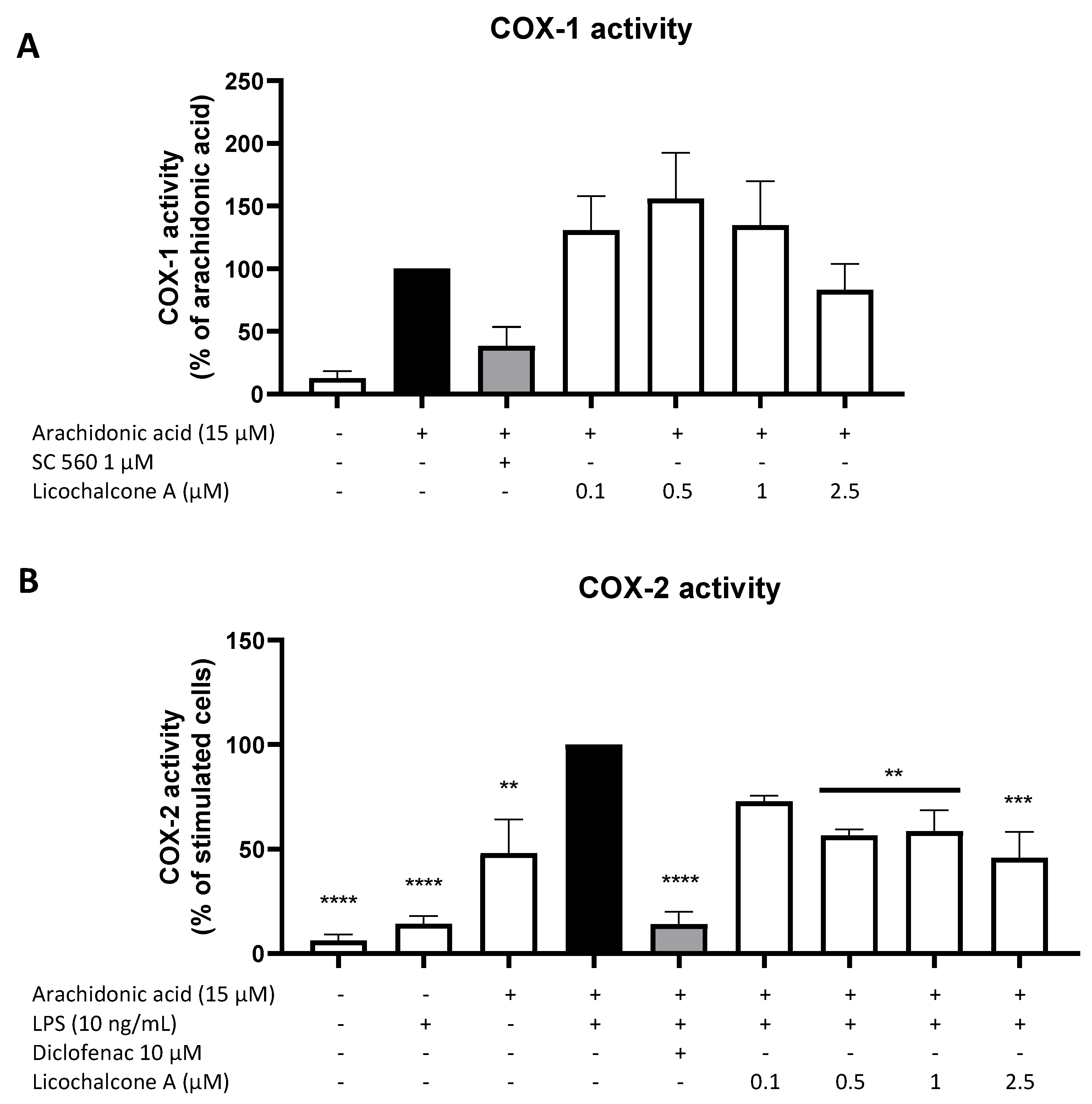
2.3. Effects of Licochalcone A on the AA/COX/PGE2 Pathway
2.4. Effects of Licochalcone A on Oxidative Markers
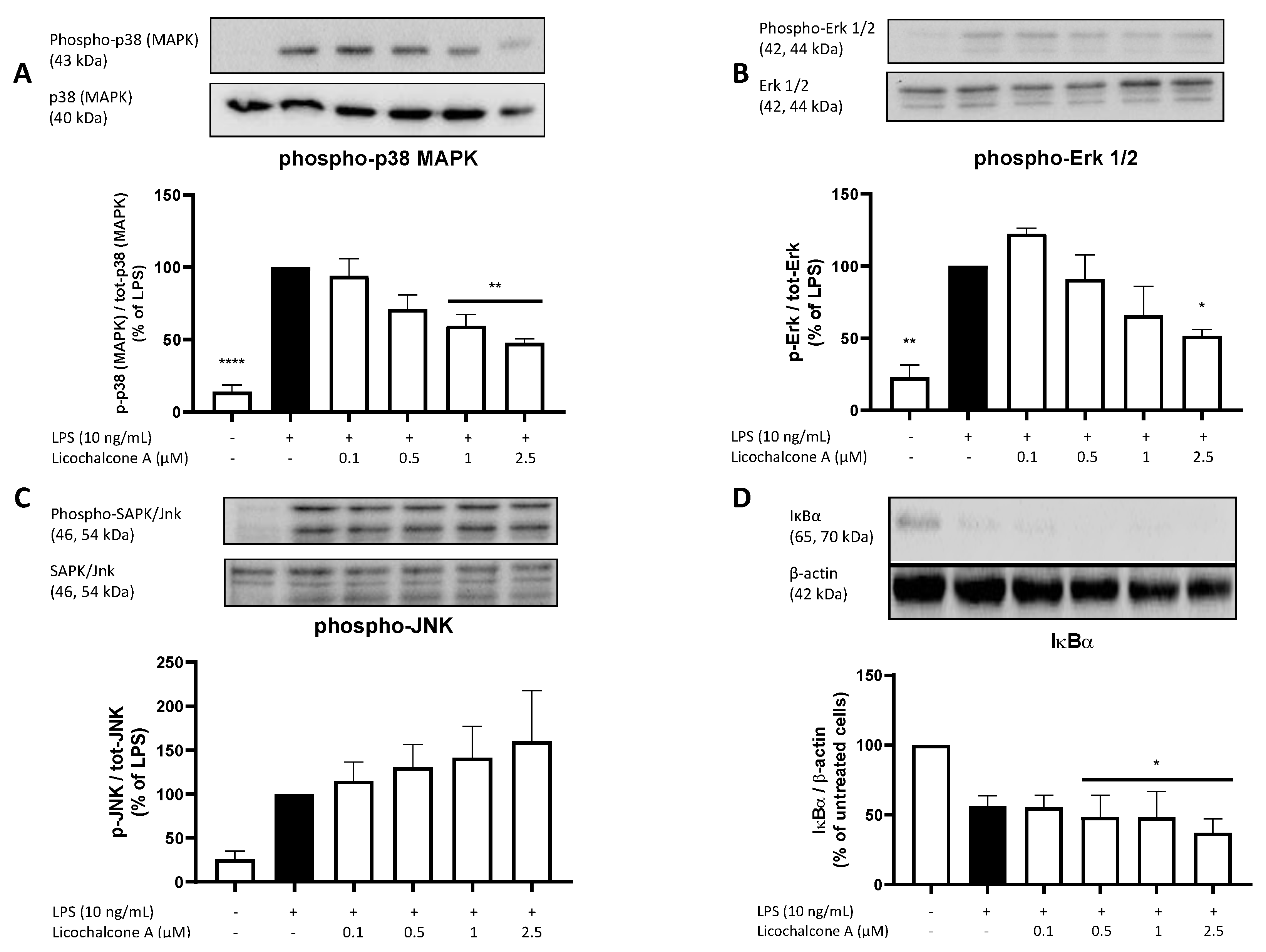
2.5. Molecular Targets
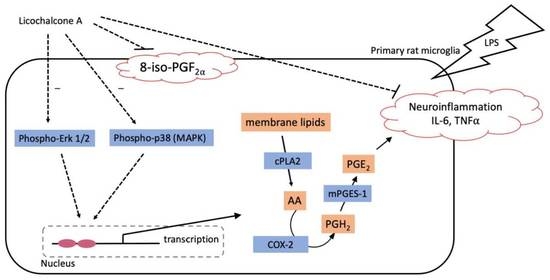
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Compound Preparation
4.2. Primary Microglia Cultures
4.2.1. Ethics Statement
4.2.2. Primary Rat Microglia Cultures
4.3. Cell Viability Assay
4.4. Determination of PGE2, 8-iso-PGF2α, IL-6, and TNFα Production from LPS Activated Primary Microglia by ELISA
4.5. Western Blot
4.6. Real-Time PCR
4.7. Cyclooxygenase Activity Assay
4.8. NO Release Assay
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J. Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s Disease and Its Potential as Therapeutic Target. Transl. Neurodegener. 2015, 4, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philips, T.; Robberecht, W. Neuroinflammation in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Role of Glial Activation in Motor Neuron Disease. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heneka, M.T.; Carson, M.J.; Khoury, J.E.; Landreth, G.E.; Brosseron, F.; Feinstein, D.L.; Jacobs, A.H.; Wyss-Coray, T.; Vitorica, J.; Ransohoff, R.M.; et al. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s Disease. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 388–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craft, J.M.; Watterson, D.M.; Van Eldik, L.J. Neuroinflammation: A Potential Therapeutic Target. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2005, 9, 887–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subhramanyam, C.S.; Wang, C.; Hu, Q.; Dheen, S.T. Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 94, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinz, M.; Masuda, T.; Wheeler, M.A.; Quintana, F.J. Microglia and Central Nervous System–Associated Macrophages—From Origin to Disease Modulation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 39, 251–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherry, J.D.; Olschowka, J.A.; O’Banion, M.K. Neuroinflammation and M2 Microglia: The Good, the Bad, and the Inflamed. J. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 11, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, J.K. Oxidative Stress in Neurodegeneration: Cause or Consequence? Nat. Med. 2004, 10, S18–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiebich, B.L.; Akter, S.; Akundi, R.S. The Two-Hit Hypothesis for Neuroinflammation: Role of Exogenous ATP in Modulating Inflammation in the Brain. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, H.S.; Baron, J.; Hagl, S.; Eckert, G.P.; Fiebich, B.L. Rice Bran Derivatives Alleviate Microglia Activation: Possible Involvement of MAPK Pathway. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickman, S.; Izzy, S.; Sen, P.; Morsett, L.; El Khoury, J. Microglia in Neurodegeneration. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1359–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.-F.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.-A.; Zhu, H.-L. A Review: The Anti-Inflammatory, Anticancer and Antibacterial Properties of Four Kinds of Licorice Flavonoids Isolated from Licorice. CMC 2020, 27, 1997–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-H.; Yang, M.; Xu, J.-G.; Yu, X.; Qian, X.-J. Role of Licochalcone A on Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin Expression: Implications for Asthma. Exp. Biol. Med. 2015, 240, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Maegawa, S.; Yang, Y.; Gopalakrishnan, V.; Zheng, G.; Cheng, D. Licochalcone A Is a Natural Selective Inhibitor of Arginine Methyltransferase 6. Biochem. J. 2021, 478, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Liu, B.; Yin, Y.; Kan, X.; Gong, Q.; Li, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, D.; Ma, H.; et al. Licochalcone A Protects the Blood–Milk Barrier Integrity and Relieves the Inflammatory Response in LPS-Induced Mastitis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, Z.; Koh, Y.-S. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases in Inflammation. J. Bacteriol. Virol. 2012, 42, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Ci, X.; Wei, M.; Yang, X.; Cao, Q.; Guan, M.; Li, H.; Deng, Y.; Feng, H.; Deng, X. Licochalcone A Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Response in Vitro and in Vivo. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 3947–3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Liu, J.; Ju, C.; Yang, D.; Chen, G.; Xu, S.; Zeng, Y.; Yan, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, D.; et al. Licochalcone A Prevents the Loss of Dopaminergic Neurons by Inhibiting Microglial Activation in Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Parkinson’s Disease Models. IJMS 2017, 18, 2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, H. Licochalcone A Improves the Cognitive Ability of Mice by Regulating T- and B-Cell Proliferation. Aging 2021, 13, 8895–8915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousif, N.M.; de Oliveira, A.C.P.; Brioschi, S.; Huell, M.; Biber, K.; Fiebich, B.L. Activation of EP 2 Receptor Suppresses Poly(I: C) and LPS-Mediated Inflammation in Primary Microglia and Organotypic Hippocampal Slice Cultures: Contributing Role for MAPKs. Glia 2018, 66, 708–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannunzio, A.; Coluccia, M. Cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) and COX-1 Inhibitors in Cancer: A Review of Oncology and Medicinal Chemistry Literature. Pharmaceuticals 2018, 11, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoozemans, J.; O’Banion, M. The Role of COX-1 and COX-2 in Alzheimers Disease Pathology and the Therapeutic Potentials of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. CDTCNSND 2005, 4, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, C.; Narumiya, S. Prostaglandin-Cytokine Crosstalk in Chronic Inflammation: PGs in Chronic Inflammation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akundi, R.S.; Candelario-Jalil, E.; Hess, S.; Hüll, M.; Lieb, K.; Gebicke-Haerter, P.J.; Fiebich, B.L. Signal Transduction Pathways Regulating Cyclooxygenase-2 in Lipopolysaccharide-Activated Primary Rat Microglia. Glia 2005, 51, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Li, Q. Prostaglandin EP2 Receptor: Novel Therapeutic Target for Human Cancers (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 1203–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishimoto, K.; Li, R.-C.; Zhang, J.; Klaus, J.A.; Kibler, K.K.; Doré, S.; Koehler, R.C.; Sapirstein, A. Cytosolic Phospholipase A2alpha Amplifies Early Cyclooxygenase-2 Expression, Oxidative Stress and MAP Kinase Phosphorylation after Cerebral Ischemia in Mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2010, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Cai, J.; Wan, Z.; Gao, H.; Sun, Y. Pathophysiological Role of Prostaglandin E Synthases in Liver Diseases. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2021, 154, 106552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, A.C.P.; Candelario-Jalil, E.; Bhatia, H.S.; Lieb, K.; Hüll, M.; Fiebich, B.L. Regulation of Prostaglandin E2 Synthase Expression in Activated Primary Rat Microglia: Evidence for Uncoupled Regulation of MPGES-1 and COX-2. Glia 2008, 56, 844–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, O.; Terada, S.; Ishizu, H.; Ishihara, T.; Ujike, H.; Nakashima, H.; Nakashima, Y.; Kugo, A.; Checler, F.; Kuroda, S. Cyclooxygenase-2 in the Hippocampus Is up-Regulated in Alzheimer’s Disease but Not in Variant Alzheimer’s Disease with Cotton Wool Plaques in Humans. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 343, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-M.; Yang, L.-H.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Niu, C.-L.; Cui, Y.; Feng, W.-S.; Wang, G.-F. BDNF and COX-2 Participate in Anti-Depressive Mechanisms of Catalpol in Rats Undergoing Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 151, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, N.; Myint, A.-M.; Krause, D.; Weidinger, E.; Schwarz, M.J. Anti-Inflammatory Treatment in Schizophrenia. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 42, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minghetti, L. Role of COX-2 in Inflammatory and Degenerative Brain Diseases. In Inflammation in the Pathogenesis of Chronic Diseases; Harris, R.E., Bittman, R., Dasgupta, D., Engelhardt, H., Flohe, L., Herrmann, H., Holzenburg, A., Nasheuer, H.-P., Rottem, S., Wyss, M., et al., Eds.; Subcellular Biochemistry; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 42, pp. 127–141. ISBN 978-1-4020-5687-1. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrer, M.D.; Busquets-Cortés, C.; Capó, X.; Tejada, S.; Tur, J.A.; Pons, A.; Sureda, A. Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibitors as a Therapeutic Target in Inflammatory Diseases. CMC 2019, 26, 3225–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, J.S.C.; Ley, S.C. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases in Innate Immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, C.A.; Baker, K.J.; McCaffrey, A.; AuCoin, D.P.; Dechert, M.A.; Gerthoffer, W.T. P38 MAPK and NF-ΚB Mediate COX-2 Expression in Human Airway Myocytes. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2003, 285, L1087–L1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van ’t Erve, T.J.; Lih, F.B.; Kadiiska, M.B.; Deterding, L.J.; Eling, T.E.; Mason, R.P. Reinterpreting the Best Biomarker of Oxidative Stress: The 8-Iso-PGF(2α)/PGF(2α) Ratio Distinguishes Chemical from Enzymatic Lipid Peroxidation. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 83, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, J.; Ripperger, A.; Frantz, S.; Ergün, S.; Schwedhelm, E.; Benndorf, R.A. Pathophysiology of Isoprostanes in the Cardiovascular System: Implications of Isoprostane-Mediated Thromboxane A2 Receptor Activation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 3115–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picca, A.; Calvani, R.; Coelho-Junior, H.J.; Landi, F.; Bernabei, R.; Marzetti, E. Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Oxidative Stress, and Neuroinflammation: Intertwined Roads to Neurodegeneration. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandley, M.J.; Szebeni, A.; Szebeni, K.; Wang-Heaton, H.; Garst, J.; Stockmeier, C.A.; Lewis, N.H.; Ordway, G.A. Markers of Elevated Oxidative Stress in Oligodendrocytes Captured from the Brainstem and Occipital Cortex in Major Depressive Disorder and Suicide. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2022, 117, 110559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiurchiù, V.; Orlacchio, A.; Maccarrone, M. Is Modulation of Oxidative Stress an Answer? The State of the Art of Redox Therapeutic Actions in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osimo, E.F.; Cardinal, R.N.; Jones, P.B.; Khandaker, G.M. Prevalence and Correlates of Low-Grade Systemic Inflammation in Adult Psychiatric Inpatients: An Electronic Health Record-Based Study. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2018, 91, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasi, E.; Barluzzi, R.; Bocchini, V.; Mazzolla, R.; Bistoni, F. Immortalization of Murine Microglial Cells by a V-Raf/v-Myc Carrying Retrovirus. J. Neuroimmunol. 1990, 27, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apweiler, M.; Streyczek, J.; Saliba, S.W.; Collado, J.A.; Hurrle, T.; Gräßle, S.; Muñoz, E.; Normann, C.; Hellwig, S.; Bräse, S.; et al. Functional Selectivity of Coumarin Derivates Acting via GPR55 in Neuroinflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheray, M.; Joseph, B. Epigenetics Control Microglia Plasticity. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hämäläinen, M.; Nieminen, R.; Asmawi, M.; Vuorela, P.; Vapaatalo, H.; Moilanen, E. Effects of Flavonoids on Prostaglandin E 2 Production and on COX-2 and MPGES-1 Expressions in Activated Macrophages. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 1504–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, D.T.; Lemere, C.A.; Selkoe, D.J.; Clemens, J.A. Cytosolic Phospholipase A2(CPLA2) Immunoreactivity Is Elevated in Alzheimer’s Disease Brain. Neurobiol. Dis. 1996, 3, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliba, S.W.; Marcotegui, A.R.; Fortwängler, E.; Ditrich, J.; Perazzo, J.C.; Muñoz, E.; de Oliveira, A.C.P.; Fiebich, B.L. AM404, Paracetamol Metabolite, Prevents Prostaglandin Synthesis in Activated Microglia by Inhibiting COX Activity. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, R.N.; Jana, M.; Pahan, K. MAPK P38 Regulates Transcriptional Activity of NF-ΚB in Primary Human Astrocytes via Acetylation of P65. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 7101–7109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, N.; Malemud, C.J. Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase: A Regulator of Cell Growth, Inflammation, Chondrocyte and Bone Cell Receptor-Mediated Gene Expression. IJMS 2019, 20, 3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Das, S.; Murthy, K.S. Erk1/2- and P38 MAP Kinase-Dependent Phosphorylation and Activation of CPLA 2 by M3 and M2 Receptors. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2003, 284, G472–G480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, M.K.A.; Lieb, K.; Schulze-Osthoff, K.; Berger, M.; Gebicke-Haerter, P.J.; Bauer, J.; Fiebich, B.L. Expression and Regulation of Cyclooxygenase-2 in Rat Microglia. Eur. J. Biochem. 1997, 243, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, A.S. THE NF-ΚB AND IκB PROTEINS: New Discoveries and Insights. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1996, 14, 649–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Yin, S.; Nie, D.; He, Z.; Xie, S.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Xiao, J.; Liu, H.; et al. Regulation of MPGES-1 Composition and Cell Growth via the MAPK Signaling Pathway in Jurkat Cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 3211–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degousee, N.; Angoulvant, D.; Fazel, S.; Stefanski, E.; Saha, S.; Iliescu, K.; Lindsay, T.F.; Fish, J.E.; Marsden, P.A.; Li, R.-K.; et al. C-Jun N-Terminal Kinase-Mediated Stabilization of Microsomal Prostaglandin E2 Synthase-1 MRNA Regulates Delayed Microsomal Prostaglandin E2 Synthase-1 Expression and Prostaglandin E2 Biosynthesis by Cardiomyocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 16443–16452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Trott, J.S.; Haque, S.; McCormick, S.; Chiorazzi, N.; Mongini, P.K.A. A Cyclooxygenase-2/Prostaglandin E Pathway Augments Activation-Induced Cytosine Deaminase Expression within Replicating Human B Cells. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 5300–5314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apweiler, M.; Streyczek, J.; Saliba, S.W.; Ditrich, J.; Muñoz, E.; Fiebich, B.L. Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Oxidative Effects of AM404 in IL-1β-Stimulated SK-N-SH Neuroblastoma Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 789074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apweiler, M.; Saliba, S.W.; Streyczek, J.; Hurrle, T.; Gräßle, S.; Bräse, S.; Fiebich, B.L. Targeting Oxidative Stress: Novel Coumarin-Based Inverse Agonists of GPR55. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altmann, D.M. Neuroimmunology and Neuroinflammation in Autoimmune, Neurodegenerative and Psychiatric Disease. Immunology 2018, 154, 167–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.; Bhatia, H.S.; Kumar, A.; de Oliveira, A.C.P.; Fiebich, B.L. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Valproic Acid and Sodium Butyrate Enhance Prostaglandins Release in Lipopolysaccharide-Activated Primary Microglia. Neuroscience 2014, 265, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiebich, B.L.; Lieb, K.; Hüll, M.; Aicher, B.; van Ryn, J.; Pairet, M.; Engelhardt, G. Effects of Caffeine and Paracetamol Alone or in Combination with Acetylsalicylic Acid on Prostaglandin E2 Synthesis in Rat Microglial Cells. Neuropharmacology 2000, 39, 2205–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliba, S.W.; Gläser, F.; Deckers, A.; Keil, A.; Hurrle, T.; Apweiler, M.; Ferver, F.; Volz, N.; Endres, D.; Bräse, S.; et al. Effects of a Novel GPR55 Antagonist on the Arachidonic Acid Cascade in LPS-Activated Primary Microglial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiebich, B.L.; Lieb, K.; Kammerer, N.; Hüll, M. Synergistic Inhibitory Effect of Ascorbic Acid and Acetylsalicylic Acid on Prostaglandin E2 Release in Primary Rat Microglia: Inhibition of PGE2 Synthesis by Ascorbic Acid. J. Neurochem. 2004, 86, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bhatia, H.S.; Apweiler, M.; Sun, L.; Baron, J.; Tirkey, A.; Fiebich, B.L. Licochalcone A Inhibits Prostaglandin E2 by Targeting the MAPK Pathway in LPS Activated Primary Microglia. Molecules 2023, 28, 1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041927
Bhatia HS, Apweiler M, Sun L, Baron J, Tirkey A, Fiebich BL. Licochalcone A Inhibits Prostaglandin E2 by Targeting the MAPK Pathway in LPS Activated Primary Microglia. Molecules. 2023; 28(4):1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041927
Chicago/Turabian StyleBhatia, Harsharan Singh, Matthias Apweiler, Lu Sun, Julian Baron, Ashwini Tirkey, and Bernd L. Fiebich. 2023. "Licochalcone A Inhibits Prostaglandin E2 by Targeting the MAPK Pathway in LPS Activated Primary Microglia" Molecules 28, no. 4: 1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041927
APA StyleBhatia, H. S., Apweiler, M., Sun, L., Baron, J., Tirkey, A., & Fiebich, B. L. (2023). Licochalcone A Inhibits Prostaglandin E2 by Targeting the MAPK Pathway in LPS Activated Primary Microglia. Molecules, 28(4), 1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041927