(S)-N-Benzyl-1-phenyl-3,4-dihydroisoqunoline-2(1H)-carboxamide Derivatives, Multi-Target Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase and Cholinesterase: Design, Synthesis, and Biological Activity
Abstract
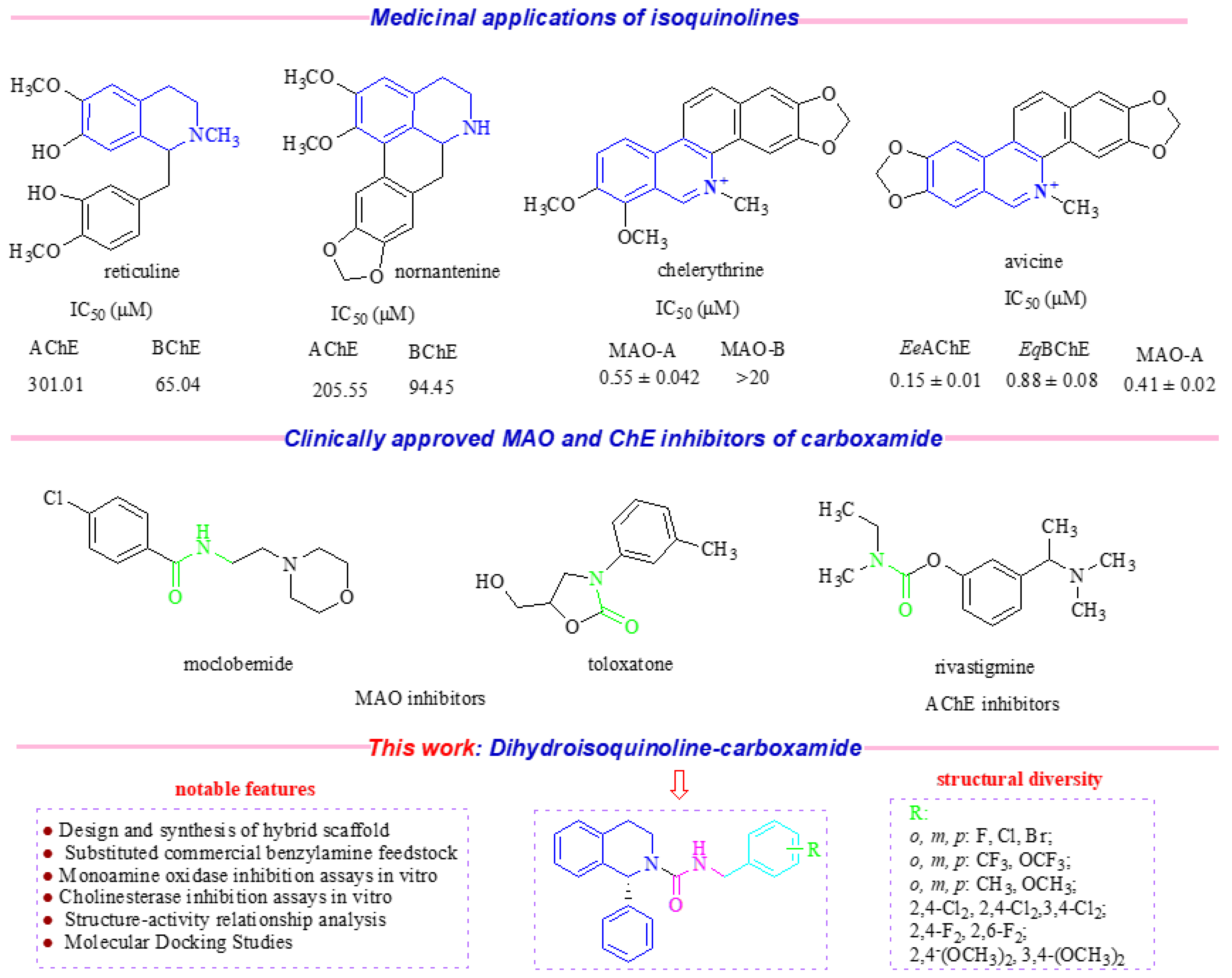
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Design of Analogs
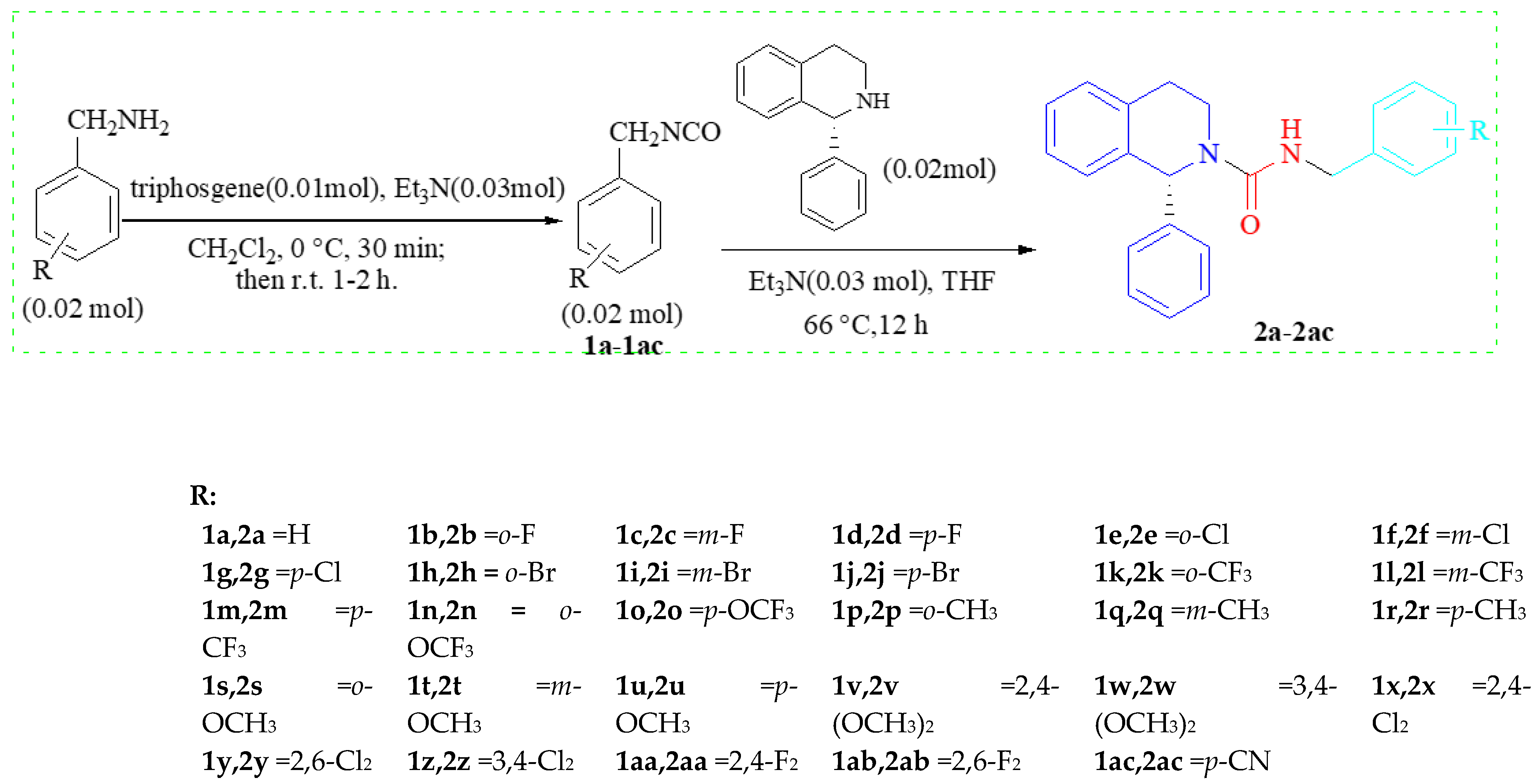
2.2. Synthetic Chemistry
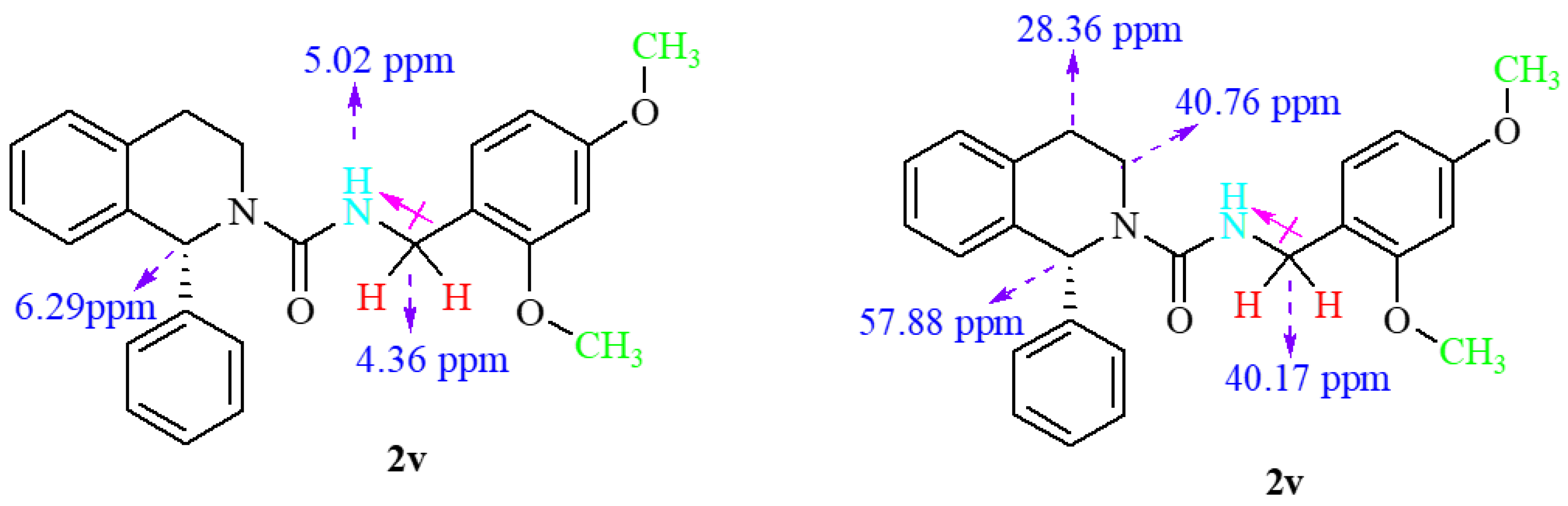
2.3. Spectroscopic Characterization
2.4. In Vitro Biological Evaluation
2.4.1. Inhibitory Activity of Compounds 2a–2ac on MAO
2.4.2. In Vitro Cholinesterase Inhibition of Compounds 2a–2ac
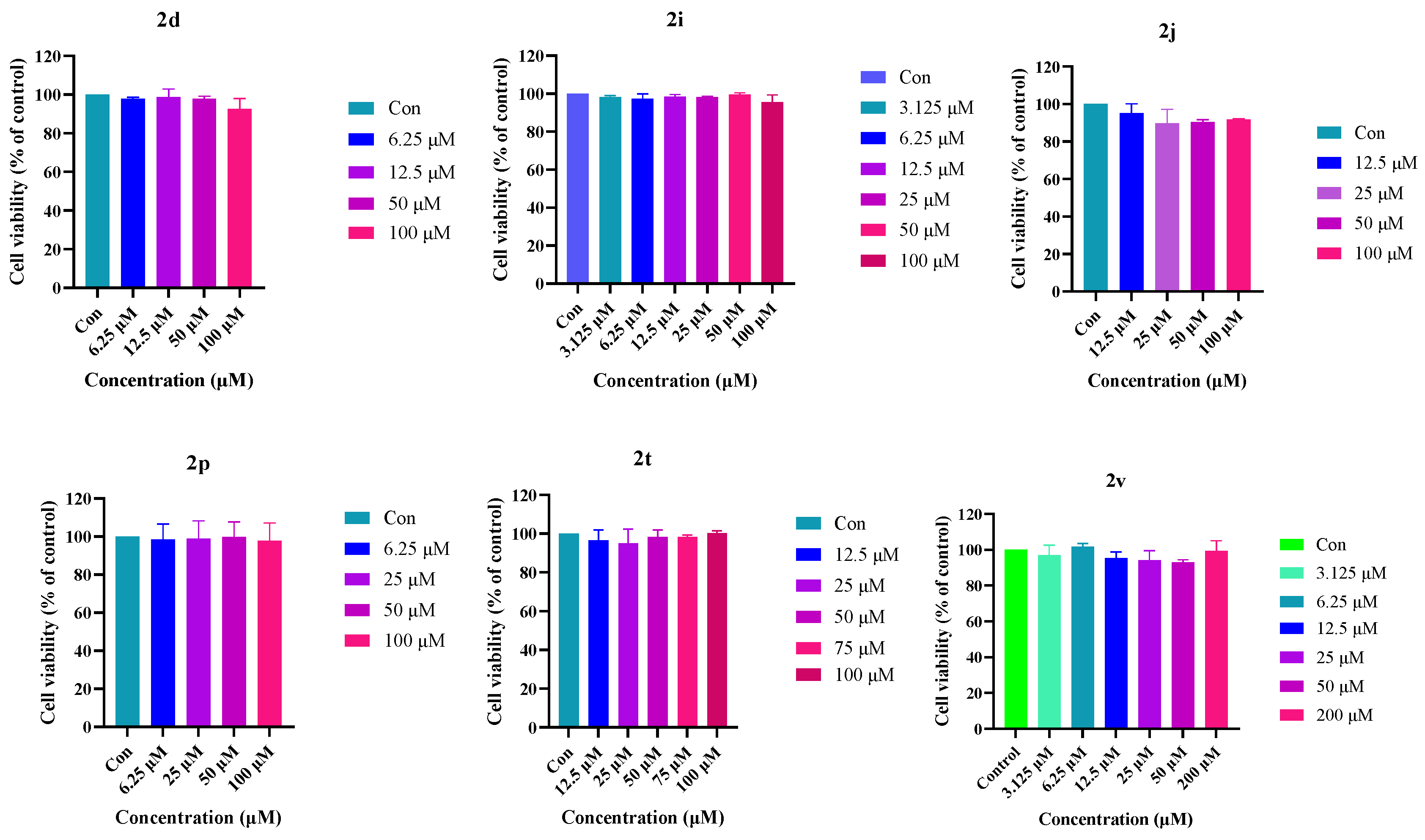
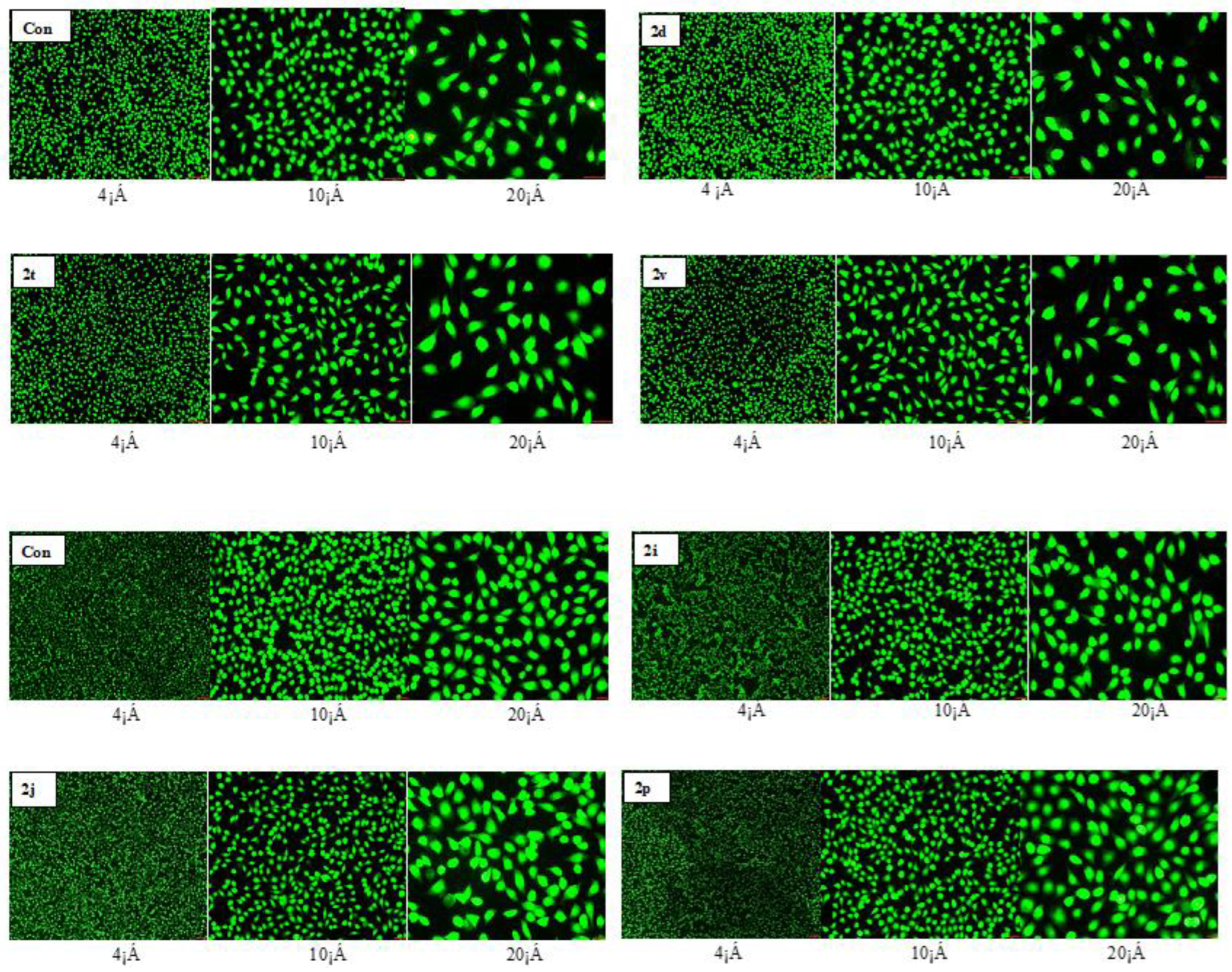
2.5. Cellular Toxicity
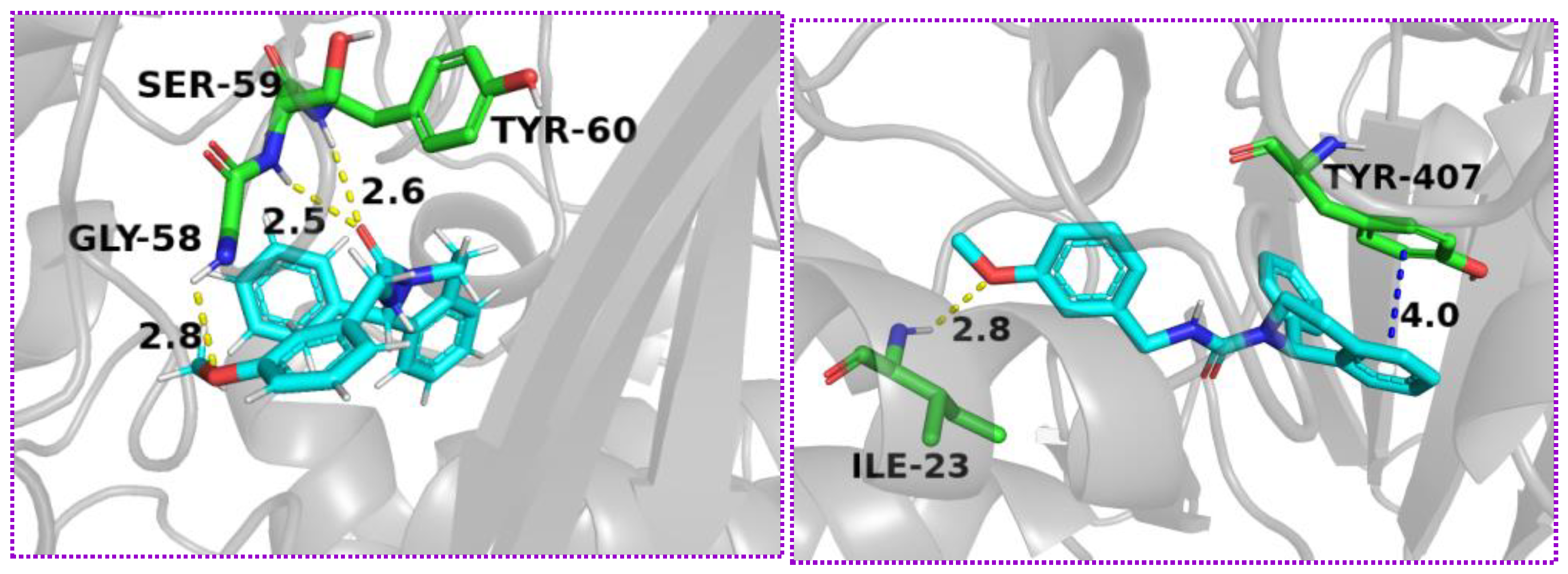
2.6. Molecular DockingTest
3. Experimental Protocols
3.1. Reagents and Instruments
3.2. Synthesis of the Compounds
3.2.1. Preparation of Substituted 1-(Isocyanatomethyl)benzene (1a–1ac)
3.2.2. Preparation of 3,4-Dihydroisoquinoline Carboxamide Derivatives 2a–2ac
3.3. Spectral Data of 3,4-Dihydroisoquinoline Carboxamide Derivatives 2a–2ac
4. Biological Activity
4.1. MAO Activity Assay
4.2. In Vitro Cholinesterase Inhibition Assay
4.3. Cytotoxicity Test
4.3.1. MTT Assay to Detect Cell Viability
4.3.2. Analysis of Cell Viability by AO Fluorescent Staining
4.4. Molecular Docking Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Sanabria, A.; Alvarado, I.; Monge, C. Molecular Pathogennesis of Alzheimer’s Disease: An update. Ann. Neurosci. 2017, 24, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaurasiya, N.D.; Leon, F.; Muhammad, I.; Tekwani, B.L. Natural Products Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidases-Potential New Drug Leads for Neuroprotection, Neurological Disorders, and Neuroblastoma. Molecules 2022, 27, 4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bautista-Aguilera, Ó.M.; Alonso, J.M.; Catto, M.; Iriepa, I.; Knez, D.; Gobec, S.; Marco-Contelles, J. N-Hydroxy-N-Propargylamide Derivatives of Ferulic Acid: Inhibitors of Cholinesterases and Monoamine Oxidases. Molecules 2022, 27, 7437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reitz, C. Genetic Diagnosis and Prognosis of Alzheimer’sDisease: Challenges and Opportunities. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2015, 15, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakir, M.N.; Dugger, B.N. Advances in Deep Nneuropathlogical Phenotyping of Alzheimer Disease: Past, Present, and Future. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2022, 81, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, K. Cholinesteras Inhibitors as Alzheimer’s Therpeutics (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yang, H.; Chen, Y.; Sun, H.P. Recent Progress in the Identification of Selective Butyrylcholinesterase Inhibitors for Alzheimer’s Disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 132, 294–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak-Nowicka, Ł.J.; Herbet, M. Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors in the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases and the Role of Acetylcholinesterase in their Pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, R.; Ziaur-rehman, M.; Murtaza, S.; Zaib, S.; Javid, N.; Awan, S.J.; Iftikhar, K.; Athar, M.M.; Khan, I. Microwave-assisted Synthesis of (Piperidin-1-yl)Quinolin-3-yl)Methylene)Hydrazine Carbothioamides as Potent Inhibitors of Cholinesterases: A Biochemical and in Silico approach. Molecules 2021, 26, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.K.; Plitman, E.; Nakajima, S.; Chakravarty, M.M.; Caravaggio, F.; Gerretsen, P.; Iwata, Y.; Graff-Guerrero, A. Cortical Amyloid β Deposition and Current Depressive Symptoms in Alzheimer Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry Neurol. 2016, 29, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaherian, K.; Newman, B.M.; Weng, H.; Hassenstab, J.; Xiong, C.J.; Coble, D.; Fagan, A.M.; Benzinger, T.; Morris, J.C. Examining the Complicated Relationship Between Depressive Symptoms and Cognitive Impairment in Preclinical Alzheimer Disease. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2019, 33, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.K.; Plitman, E.; Nakajima, S.; Chakravarty, M.M.; Caravaggio, F.; Takeuchi, H.; Gerretsen, P.; Iwat, Y.; Patel, R.; Mulsant, B.H.; et al. Depressive Symptoms and Small Hippocampal Volume Accelerate the Progression to Dementia from Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2016, 49, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, C.S.; Li, J.J.; Tipoe, G.L.; Youdim, M.B.H.; Fung, M.L. Monoamine Oxidase A Upregulated by Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia Activates Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase and Neurodegeneration. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavich, G.M.; Sacher, J. Stress, Sex Hormones, Inflammation, and Major Depressive Disorder: Extending Social Signal Transduction Theory of Depression to Account for Sex Differences in Mood Disorders. Psychopharmacol. 2019, 236, 3063–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors: Promising Therapeutic Agents for Alzheimer’s Disease (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 9, 1533–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behl, T.; Kaur, D.; Sehgal, A.; Singh, S.; Sharma, N.; Zengin, G.; Andronie-Cioara, F.L.; Toma, M.M.; Bungau, S.; Bumbu, A.G. Role of Monoamine Oxidase Activity in Alzheimer’s Disease: An Insight into the Therapeutic Potential of Inhibitors. Molecules 2021, 26, 3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, S.J.; Khan, A.; Kazmi, I.; Rashid, U. Design, Synthesis, and Bioevaluation of Indole Core Containing 2-Arylidine Derivatives of Thiazolopyrimidine as Multitarget Inhibitors of Cholinesterases and Monoamine Oxidase A/B for the Treatment of Alzheimer Disease. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 9369–9379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartey, M.O.; Nyarko, J.N.K.; Pennington, P.R.; Heistad, R.M.; Klassen, P.C.; Baker, G.B.; Mousseau, D.D. Alzheimer Disease and Selected Risk Factors Disrupt a Co-regulation of Monoamine Oxidase-A/B in the Hippocampus, but Not in the Cortex. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, R.R.; Tipton, K.F. Assessment of Enzyme Inhibition: A Review with Examples from the Development of Monoamine Oxidase and Cholinesterase Inhibitory Drugs. Molecules 2017, 22, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, M.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Guo, L.K.; Wang, Q.Q.; Gao, Z.R.; Kang, J.R.; Zhang, M.B.; Feng, J.Q.; Guo, Q.; et al. Polypharmacology of Berberine Based on Multi-Target Binding Motifs. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2016 Neurology Collaborators. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Alzheimer’s Disease and other Dementias, 1990–2016: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 459–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsay, R.R.; Majekova, M.; Medina, M.; Valoti, M. Key Targets for Multi-Target Ligands Designed to Combat Neurodegeneration. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 375–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patsenka, A.; Antkiewicz-Michaluk, L. Inhibition of Rodent Brain Monoamine Oxidase and Tyrosine Hydroxylase by Endogenous Compounds-1,2,3,4-Tetrahydroisoquinoline Alkaloids. Pol. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 56, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bembenek, M.E.; Abell, C.W.; Chrisey, L.A.; Rozwadowska, M.D.; Gessner, W.; Brossi, A. Inhibition of Monoamine Oxidases A and B by Simple Isoquinoline Alkaloids: Racemic and Optically Active 1,2,3,4-Tetrahydro-3,4-Dihydro-, and Fully Aromatic Isoquinolines. J. Med. Chem. 1990, 33, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.; Wahab, A.T.; Wajid, S.; Khan, M.A.; Yousuf, S.; Shaikh, M.; Laghari, G.H.; Rahman, A.U.; Choudhary, M.I. Isolation, Derivatization, in-vitro, and in-silico Studies of Potent Butyrylcholinesterase Inhibitors from Berberis parkeriana Schneid. Bioorganic Chem. 2022, 127, 105944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan Othman, W.N.N.; Liew, S.Y.; Khaw, K.Y.; Murugaiyah, V.; Litaudon, M.; Awang, K. Cholinesterase Inhibitory Activity of Isoquinoline Alkaloids from three Cryptocarya species (Lauraceae). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 4464–4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.C.; Ryu, H.W.; Kang, M.G.; Lee, H.; Park, D.; Cho, M.L.; Oh, S.R.; Kim, H. Selective Inhibition of Monoamine Oxidase A by Chelerythrine, Anisoquinoline Alkaloid. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 2403–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, E.P.; Hagenow, S.; Murillo, M.A.; Stark, H.; Suarez, L.C. Isoquinoline Alkaloids from the Roots of Zanthoxylumrigidum as Multi-target Inhibitors of Cholinesterase, Monoamine Oxidase A and Aβ1-42 Aggregation. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 98, 103722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.Y.; Jin, Q.H.; Xia, Y.N.; Jiang, H.Y.; Guan, L.P. Study on Synthesis and Biological Effects of a Series of 3,4-Dihydroisoquinoline-2(1H)-Carboxamide Derivatives. Med. Chem. Res. 2019, 28, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan-Zitouni, G.; Hussein, W.; Sağlık, B.N.; Tabbi, A.; Korkut, B. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of novel N-Pyridy-l-Hydrazone Derivatives as Potential Monoamine Oxidase (MAO) Inhibitors. Molecules 2018, 23, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaurasiya, N.D.; Midiwo, J.; Pandey, P.; Bwire, R.N.; Doerksen, R.J.; Muhammad, I.; Tekwani, B.L. Selective Interactions of O-Methylated Flavonoid Natural Products with Human Monoamine Oxidase-A and -B. Molecules 2020, 25, 5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knez, D.; Colettis, N.; Iacovino, L.G.; Sova, M.; Pišlar, A.; Konc, J.; Lešnik, S.; Higgs, J.; Kamecki, F.; Mangialavori, I.; et al. Stereoselective Activity of 1-Propargyl-4-Styryl Piperidine-like Analogues that Can Discriminate Between Monoamine Oxidase Isoforms A and B. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 1361–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, S.; Hoda, N. A Comprehensive Review of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors as Anti-Alzheimer’s Disease Agents: A Review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 206, 112787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.; Andres, V.; Featherstone, R.M. A New and Rapid Colorimetric Determination of Acetylcholinesterase Activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalili-Baleh, L.; Babaei, E.; Abdpour, S.; Bukhari, S.N.A.; Foroumadi, A.; Ramazani, A.; Sharifzadeh, M.; Abdollahi, M.; Khoobi, M. A Review on Flavonoid-based Scaffolds as Multi-Target-Directed Ligands (MTDLs) for Alzheimer’s Disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 152, 570–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croaker, A.; Davis, A.; Carroll, A.; Liu, L.; Myers, S.P. Understanding of Black Salve Toxicity by Multi-Compound Cytotoxicity Assays. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2022, 22, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El–Gaber, M.K.; Hassan, H.Y.; Mahfouz, N.M.; Farag, H.H.; Bekhit, A.A. Synthesis, Biological Investigation and Molecular Docking Study of N-Malonyl-1,2-Dihydroisoquinoline Derivatives as Brain Specific and Shelf-Stable MAO Inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 93, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, C.E.; Villalpando, A.; Nguyen, A.L.; McCandless, G.T.; Kartika, R. Chlorination of Aliphatic Primary Alcohols via Triphosgene-Triethylamine Activation. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 3676–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolaka, N.; Akocaka, S.; Buab, S.; Supuran, C.T. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of novel Ureido Benzenesulfonamides Incorporating 1,3,5-Triazine Moieties as Potent Carbonic Anhydrase IX Inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 82, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compds | Inhibition Rate for MAO a (%) | IC50 (μM) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAO | MAO-A | MAO-B | ||
| 2a | 29.2 | - c | - | - |
| 2b | N.A. b | - | - | - |
| 2c | N.A. | - | - | - |
| 2d | 71.8 | 5.78 | 1.38 | >100 |
| 2e | 41.4 | - | - | - |
| 2f | 24. 5 | - | - | - |
| 2g | 21.2 | - | - | - |
| 2h | N.A. | - | - | - |
| 2i | 58.5 | 1.34 | 1.56 | 4.30 |
| 2j | 57.4 | 1.93 | 2.48 | >100 |
| 2k | 33.0 | - | - | - |
| 2l | N.A. | - | - | - |
| 2m | 35.8 | - | - | - |
| 2n | 33.0 | - | - | - |
| 2o | 31.1 | - | - | - |
| 2p | 59.4 | 0.774 | 2.92 | 3.88 |
| 2q | N.A. | - | - | - |
| 2r | N.A. | - | - | - |
| 2s | N.A. | - | - | - |
| 2t | 53.7 | 2.08 | 2.50 | 1.61 |
| 2u | N.A. | - | - | - |
| 2v | 52.0 | 0.958 | 3.51 | 3.52 |
| 2w | N.A. | - | - | - |
| 2x | 44.7 | - | - | - |
| 2y | 37.7 | - | - | - |
| 2z | 7.40 | - | - | - |
| 2aa | 32.1 | - | - | - |
| 2ab | 33.0 | - | - | - |
| 2ac | N.A. | - | - | - |
| Rasagiline | 91.75 | 0.338 | 0.64 | 0.97 |
| Compds | R | Inhibition Rate a (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| AChE | BChE | ||
| 2b | o-F | N.A. b | 49.0 |
| 2f | m-Cl | N.A. | 3.4 |
| 2j | p-Br | N.A. | 34.5 |
| 2l | m-CF3 | N.A. | 49.1 |
| 2q | m-CH3 | N.A. | 8.7 |
| 2s | o-OCH3 | N.A. | 39.6 |
| 2t | m-OCH3 | N.A. | 55.0 |
| 2u | p-OCH3 | N.A. | 40.7 |
| 2w | 3,4-(OCH3)2 | N.A. | 9.4 |
| 2z | 3,4-Cl2 | N.A. | 12.1 |
| 2ab | 2,6-F2 | N.A. | 24.9 |
| 2ac | p-CN | N.A. | 17.7 |
| donepezil | - | 62.7 | - c |
| tacolin | - | - | 98.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, Q.-H.; Zhang, L.-P.; Zhang, S.-S.; Zhuang, D.-N.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Zheng, Z.-J.; Guan, L.-P. (S)-N-Benzyl-1-phenyl-3,4-dihydroisoqunoline-2(1H)-carboxamide Derivatives, Multi-Target Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase and Cholinesterase: Design, Synthesis, and Biological Activity. Molecules 2023, 28, 1654. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041654
Jin Q-H, Zhang L-P, Zhang S-S, Zhuang D-N, Zhang C-Y, Zheng Z-J, Guan L-P. (S)-N-Benzyl-1-phenyl-3,4-dihydroisoqunoline-2(1H)-carboxamide Derivatives, Multi-Target Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase and Cholinesterase: Design, Synthesis, and Biological Activity. Molecules. 2023; 28(4):1654. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041654
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Qing-Hao, Li-Ping Zhang, Shan-Shan Zhang, Dai-Na Zhuang, Chu-Yu Zhang, Zhou-Jun Zheng, and Li-Ping Guan. 2023. "(S)-N-Benzyl-1-phenyl-3,4-dihydroisoqunoline-2(1H)-carboxamide Derivatives, Multi-Target Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase and Cholinesterase: Design, Synthesis, and Biological Activity" Molecules 28, no. 4: 1654. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041654
APA StyleJin, Q.-H., Zhang, L.-P., Zhang, S.-S., Zhuang, D.-N., Zhang, C.-Y., Zheng, Z.-J., & Guan, L.-P. (2023). (S)-N-Benzyl-1-phenyl-3,4-dihydroisoqunoline-2(1H)-carboxamide Derivatives, Multi-Target Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase and Cholinesterase: Design, Synthesis, and Biological Activity. Molecules, 28(4), 1654. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041654






