Towards Developing Novel Prostate Cancer Recurrence Suppressors: Acute Toxicity of Pseurotin A, an Orally Active PCSK9 Axis-Targeting Small-Molecule in Swiss Albino Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. In Vitro Cytotoxicity of Pseurotin A
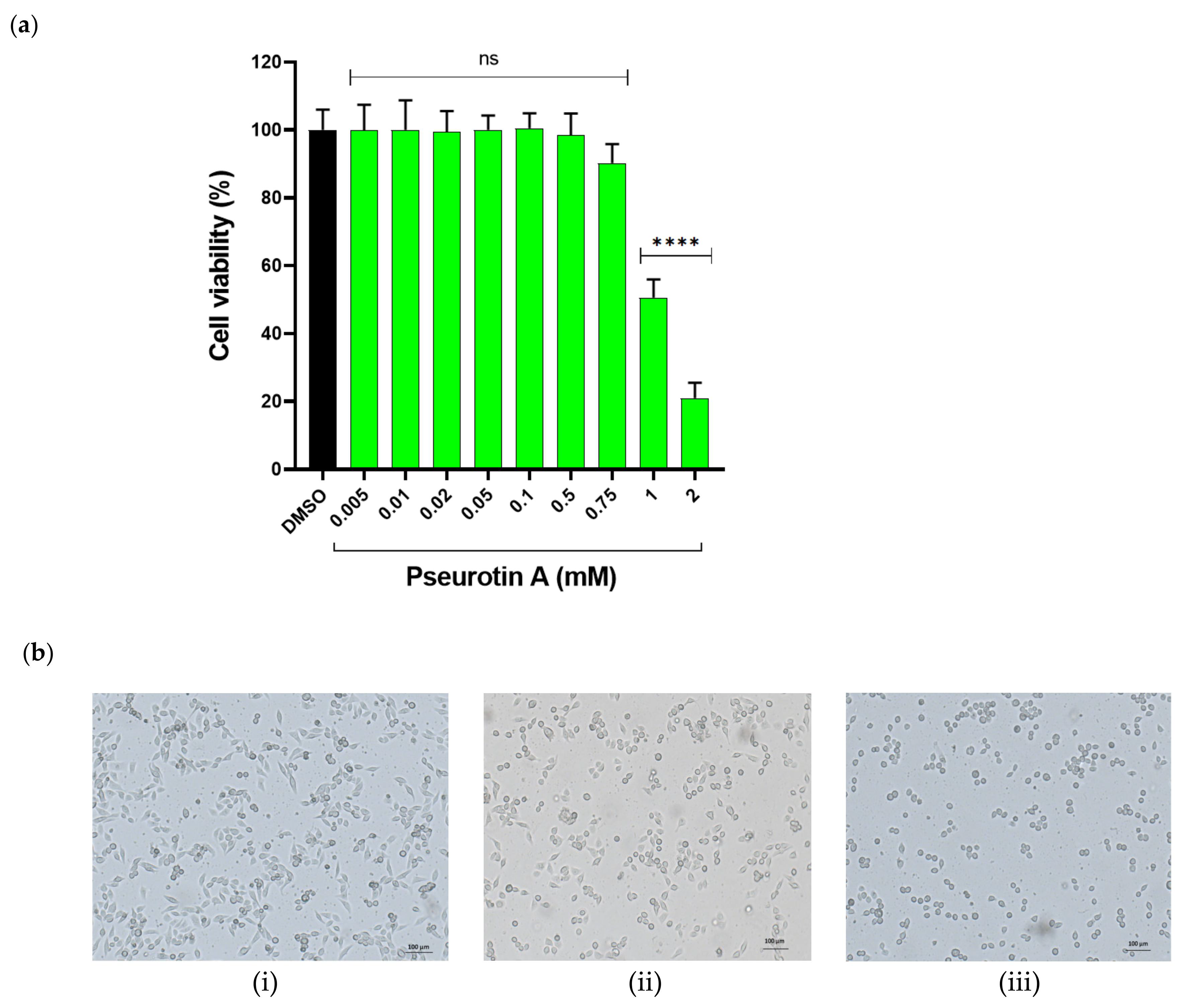
2.1.1. The Effect of PsA on the Viability of Human Non-Tumorigenic Prostate and Colon Cells Using MTT-Based Cell Cytotoxicity
2.1.2. The Effect of PsA on Mitochondrial Functionality in Human Normal Prostatic RWPE-1 Cells
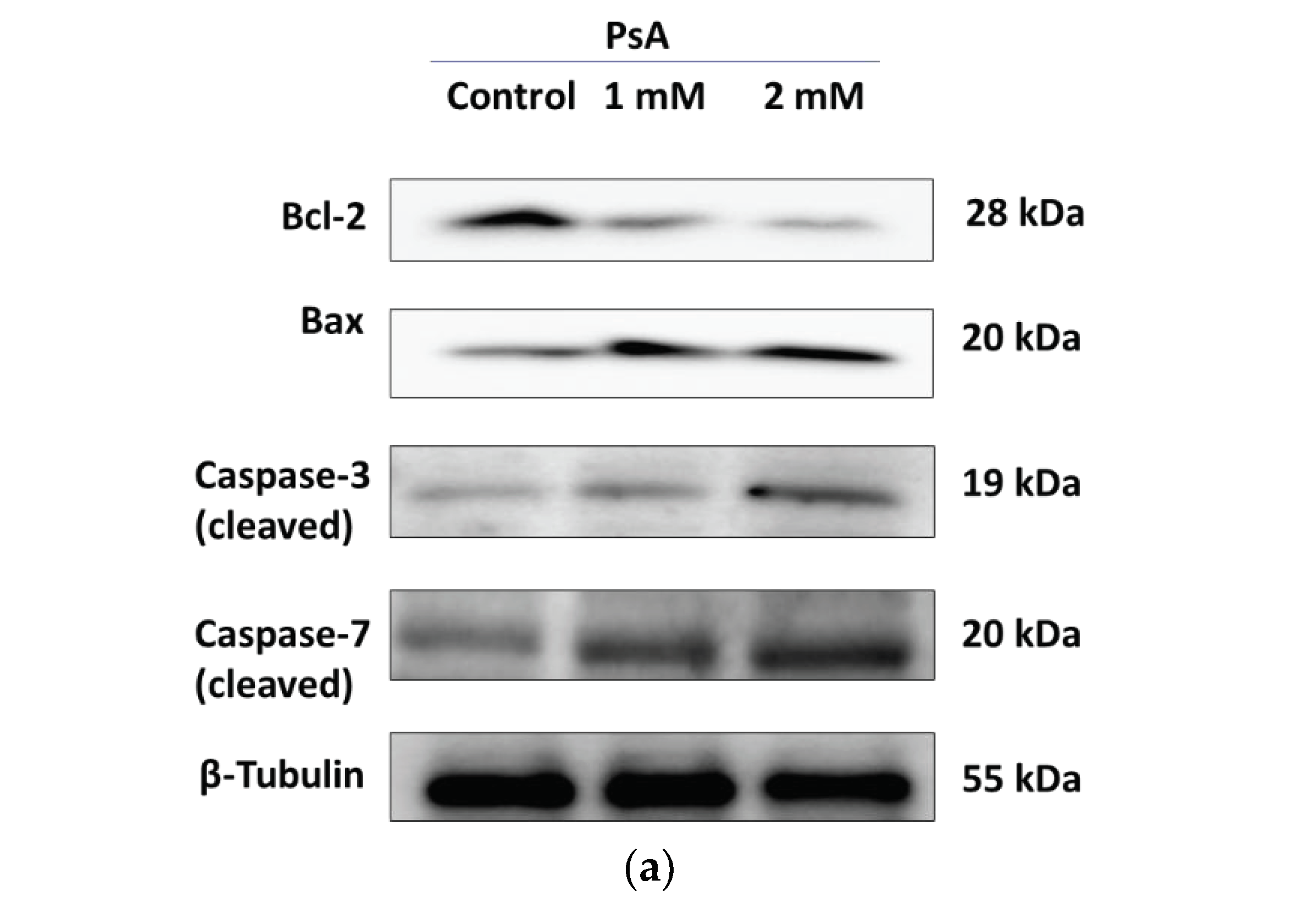
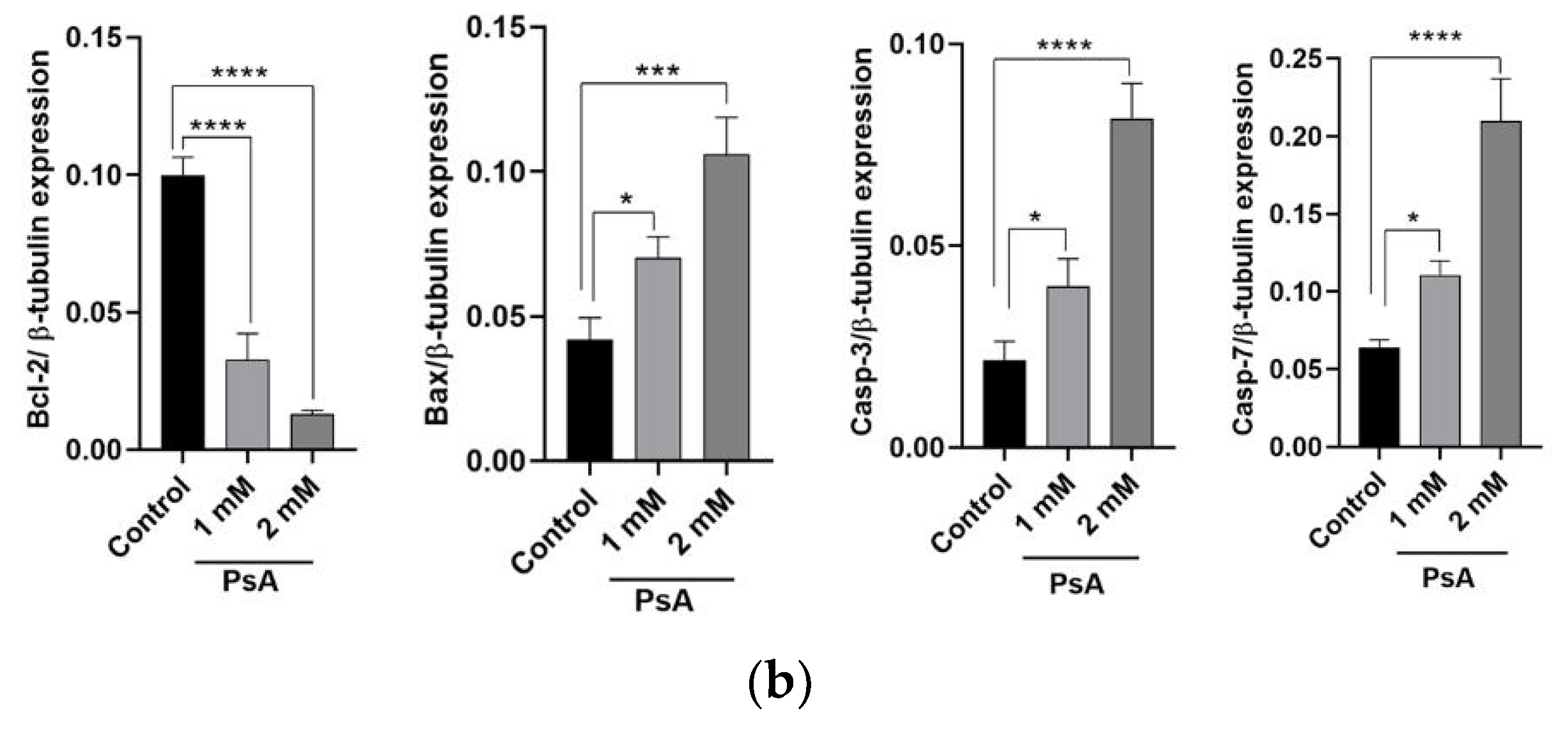
2.1.3. The Effect of PsA on the Apoptotic Signaling Pathway in Human Normal Prostatic RWPE-1 Cells
2.2. Determination of LD50 of Pseurotin A
2.3. 14-Day Acute Toxicity Assay of Pseurotin A
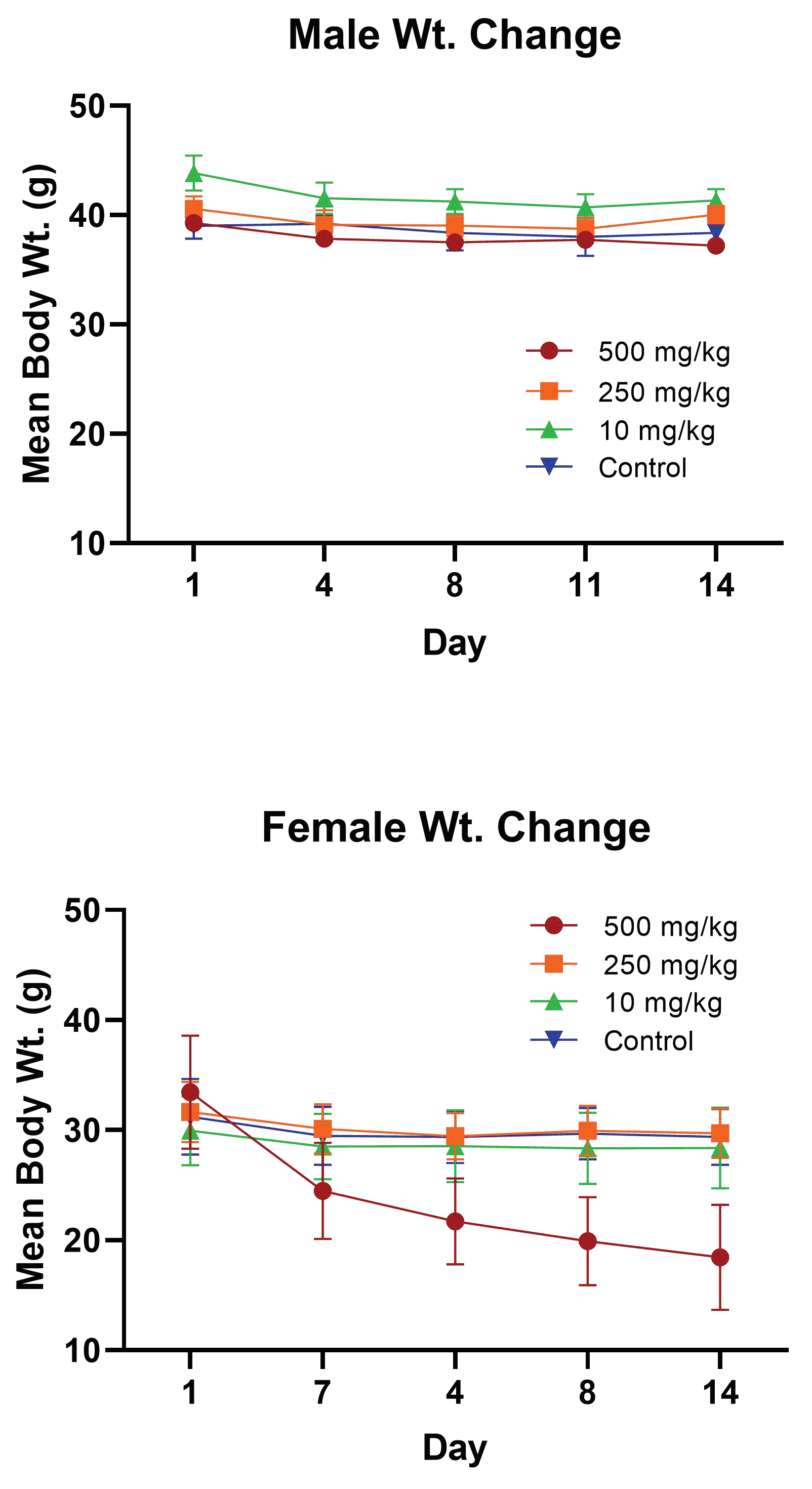
2.3.1. PsA Effects on Mouse Body Weight
2.3.2. The Effects of PsA Treatments on Swiss Albino Mice Behavior
2.3.3. Evaluation of Relative Animal Organ Weight
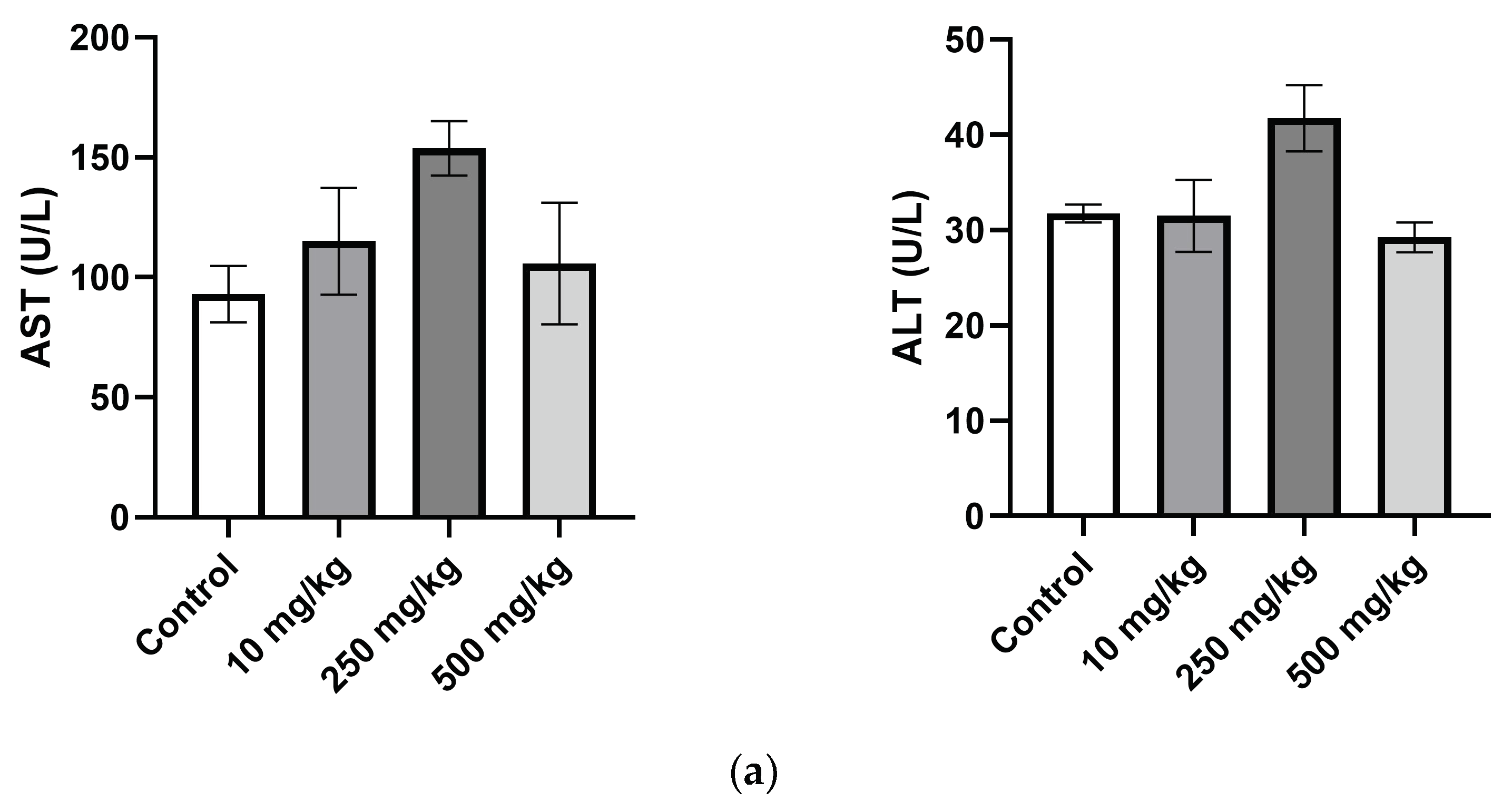
2.3.4. Analysis of Mice Hematological Biochemical Parameters after PsA Single Oral Dose
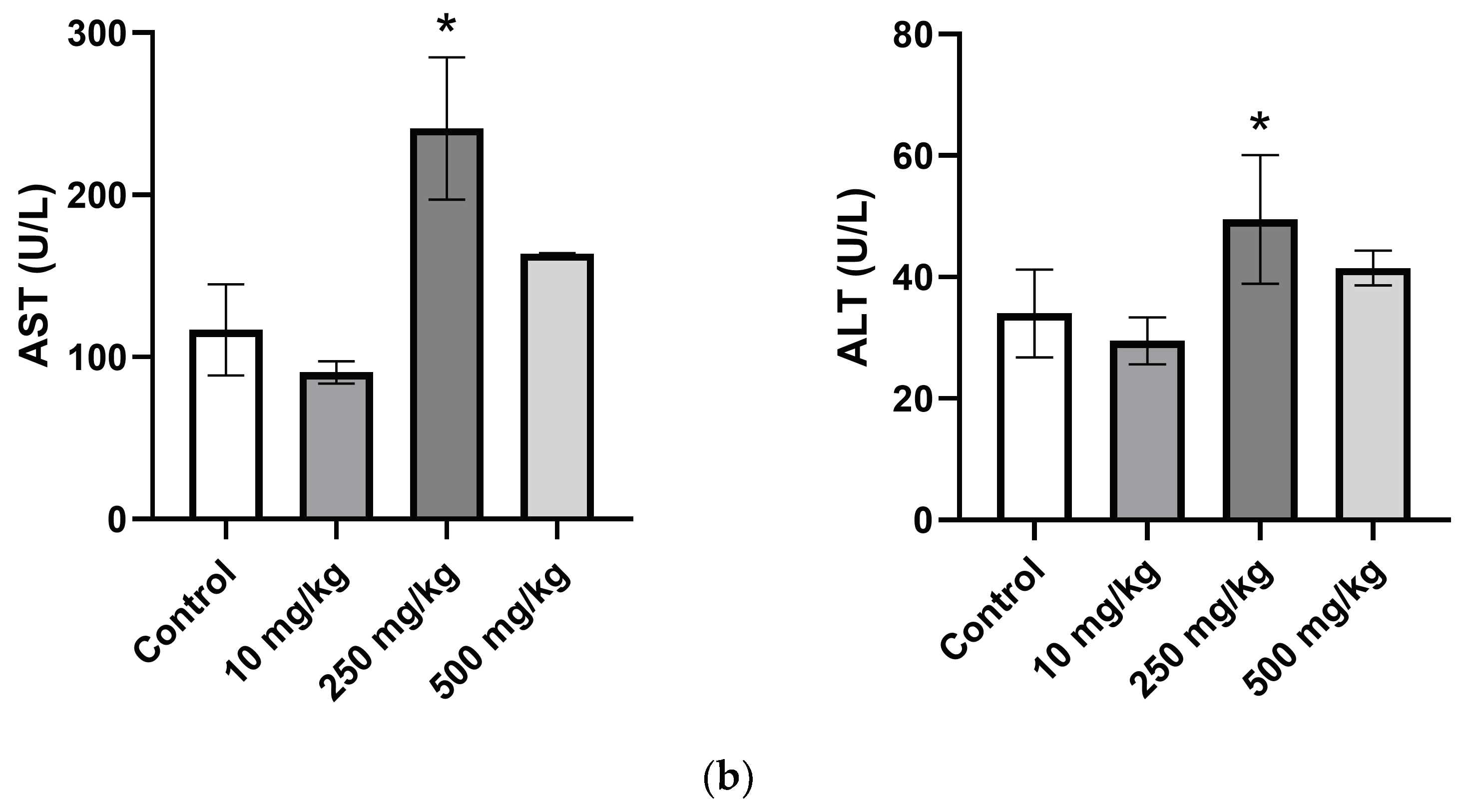
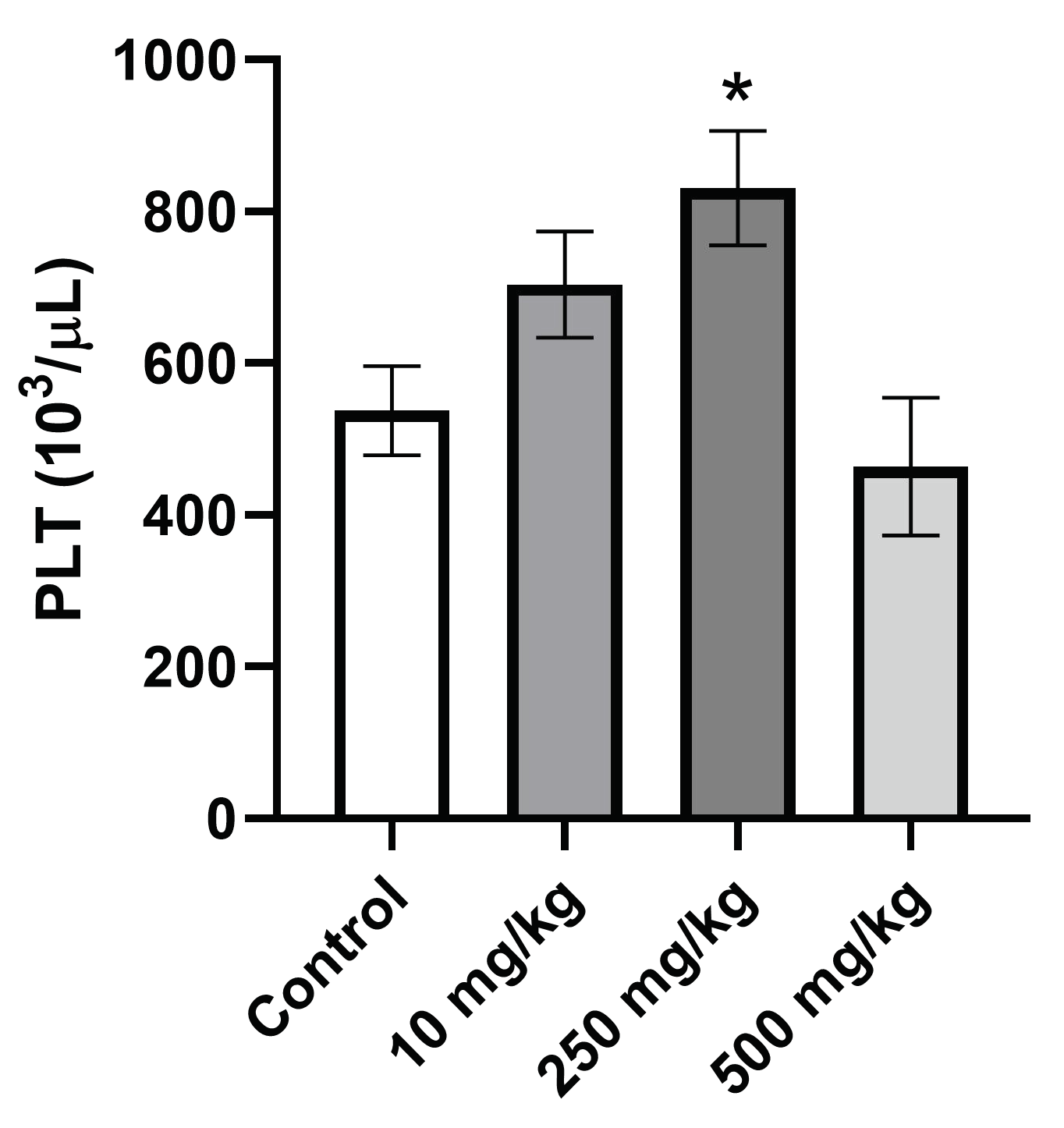
2.3.5. Analysis of Hematological Parameters after Single Oral Dose PsA Treatment
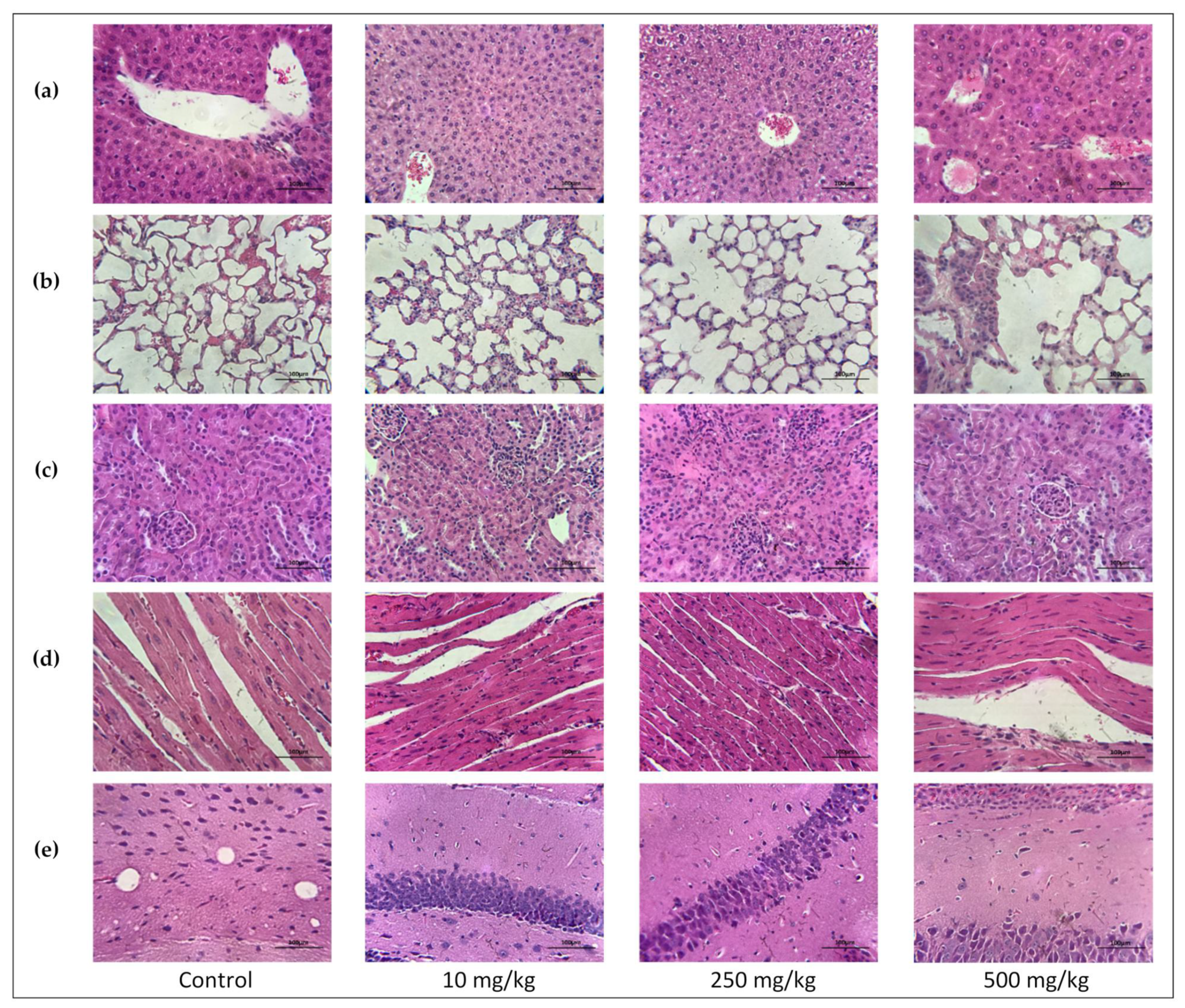
2.3.6. Single Oral Dose PsA Effects on Swiss Albino Mouse Organs Histopathology
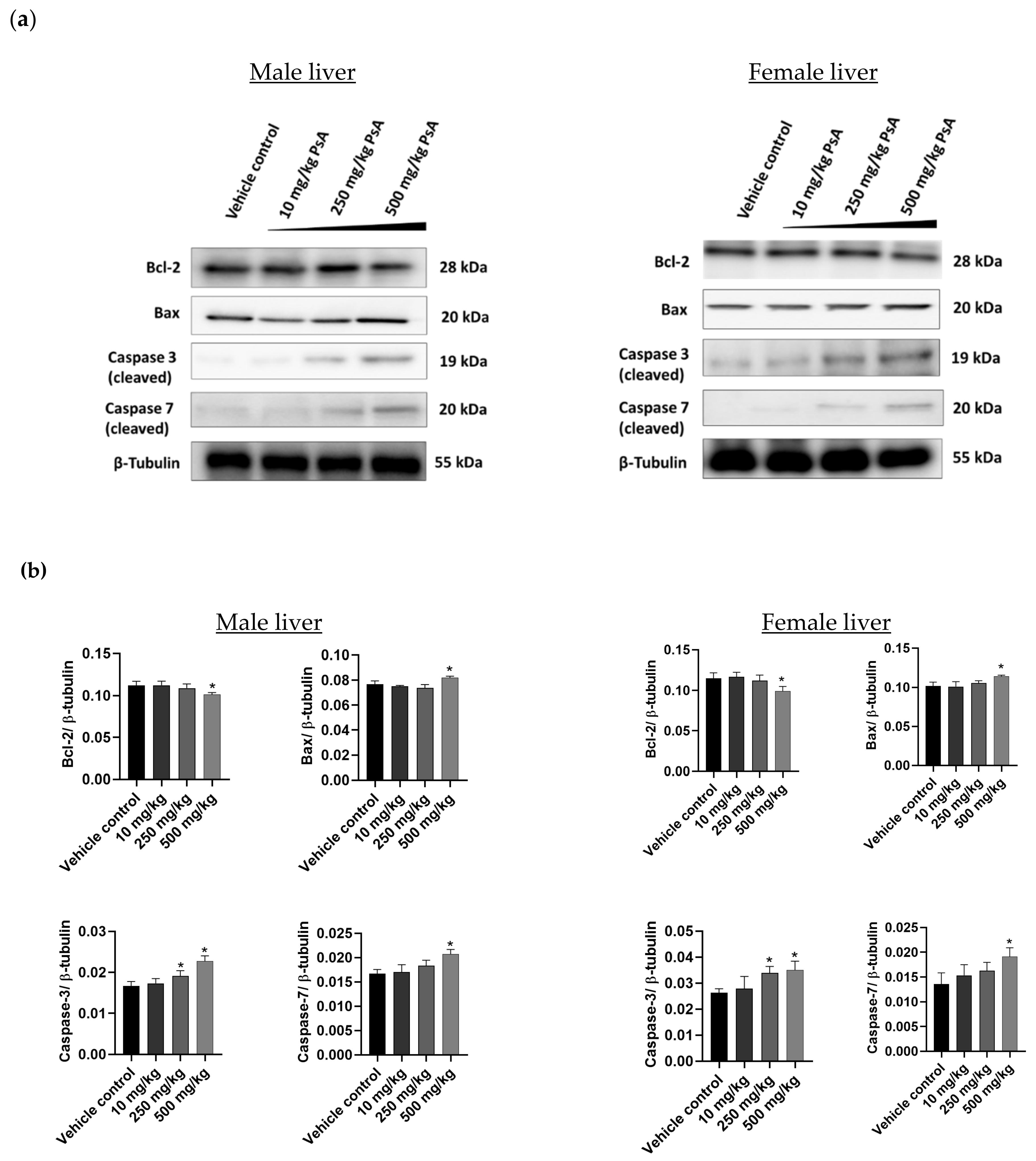
2.3.7. The Effect of PsA on the Apoptotic Signaling Pathway in Liver Tissues of Swiss Albino Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
4.2. In Vitro Cytotoxicity of Pseurotin A
4.2.1. MTT-Based Cell Cytotoxicity Assay
4.2.2. ATP-Based Cell Cytotoxicity Assay
4.2.3. Western Blot Analysis
4.3. Experimental Animals
4.4. Up-and-Down Procedure
4.5. 14-Day Single Oral Dose PsA Acute Toxicity Study Design
4.6. Hematological and Biochemical Evaluation
4.7. Data Analysis
4.8. Paraffin Embedding and Staining
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seidah, N.G.; Prat, A. The biology and therapeutic targeting of the proprotein convertases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 367–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochholzer, W.; Giugliano, R.P. Lipid lowering goals: Back to nature? Ther. Adv. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2010, 4, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaRosa, J.C.; Pedersen, T.R.; Somaratne, R.; Wasserman, S.M. Safety and effect of very low levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol on cardiovascular events. Am. J. Cardiol. 2013, 111, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietschy, J.M.; Turley, S.D. Thematic review series: Brain Lipids. Cholesterol metabolism in the central nervous system during early development and in the mature animal. J. Lipid Res. 2004, 45, 1375–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousselet, E.; Marcinkiewicz, J.; Kriz, J.; Zhou, A.; Hatten, M.E.; Prat, A.; Seidah, N.G. PCSK9 reduces the protein levels of the LDL receptor in mouse brain during development and after ischemic stroke. J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moşteoru, S.; Gaiţă, D.; Banach, M. An update on PCSK9 inhibitors—Pharmacokinetics, drug interactions, and toxicity. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2020, 16, 1199–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora, C.; Tittensor, D.P.; Adl, S.; Simpson, A.G.; Worm, B. How many species are there on Earth and in the ocean? PLoS Biol. 2011, 9, e1001127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copmans, D.; Rateb, M.; Tabudravu, J.N.; Pérez-Bonilla, M.; Dirkx, N.; Vallorani, R.; Diaz, C.; Pérez del Palacio, J.; Smith, A.J.; Ebel, R.; et al. Zebrafish-Based Discovery of Antiseizure Compounds from the Red Sea: Pseurotin A2 and Azaspirofuran A. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 1652–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaspars, M.; De Pascale, D.; Andersen, J.H.; Reyes, F.; Crawford, A.D.; Ianora, A. The marine biodiscovery pipeline and ocean medicines of tomorrow. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2016, 96, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloch, P.; Tamm, C.; Bollinger, P.; Petcher, T.J.; Weber, H.P. Pseurotin, a new metabolite of Pseudeurotium ovalis Stolk having an unusual hetero-spirocyclic system. Helv. Chim. Acta 1976, 59, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelwahed, K.S.; Siddique, A.B.; Mohyeldin, M.M.; Qusa, M.H.; Goda, A.A.; Singh, S.S.; Ayoub, N.M.; King, J.A.; Jois, S.D.; El Sayed, K.A. Pseurotin A as a novel suppressor of hormone dependent breast cancer progression and recurrence by inhibiting PCSK9 secretion and interaction with LDL receptor. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 158, 104847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, Y.; Shoji, M.; Yamaguchi, S.; Mukaiyama, T.; Yamaguchi, J.; Kakeya, H.; Osada, H. Asymmetric Total Synthesis of Pseurotin A. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 2287–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radišauskas, R.; Kuzmickienė, I.; Milinavičienė, E.; Everatt, R. Hypertension, serum lipids and cancer risk: A review of epidemiological evidence. Medicina 2016, 52, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murai, T. Cholesterol lowering: Role in cancer prevention and treatment. Biol. Chem. 2015, 396, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emberson, J.R.; Kearney, P.M.; Blackwell, L.; Newman, C.; Reith, C.; Bhala, N.; Holland, L.; Peto, R.; Keech, A.; Collins, R.; et al. Lack of effect of lowering LDL cholesterol on cancer: Meta-analysis of individual data from 175,000 people in 27 randomized trials of statin therapy. PloS ONE 2012, 7, e29849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravnskov, U.; McCully, K.S.; Rosch, P.J. The statin-low cholesterol-cancer conundrum. QJM Mon. J. Assoc. Physicians 2012, 105, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelton, K.; Freeman, M.R.; Solomon, K.R. Cholesterol and prostate cancer. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2012, 12, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, L.; Kim, J.; Adam, R.M.; Solomon, K.R.; Freeman, M.R. Cholesterol targeting alters lipid raft composition and cell survival in prostate cancer cells and xenografts. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, B.; Wei, L.; Jian, X.; Shan, K.; He, Q.; Huang, F.; Ge, X.; Gao, X.; Feng, N.; et al. Cholesterol and saturated fatty acids synergistically promote the malignant progression of prostate cancer. Neoplasia 2022, 24, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, F.; Mader, S.; Philip, A. Cholesterol as an endogenous ligand of ERRα promotes ERRα-mediated cellular proliferation and metabolic target gene expression in breast cancer cells. Cells 2020, 9, 1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Estevez, L.; Moreno-Bueno, G. Updating the role of obesity and cholesterol in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2019, 21, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Yang, L.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, W. Systematic review and meta-analysis suggest that dietary cholesterol intake increases risk of breast cancer. Nutr. Res. 2016, 36, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelwahed, K.S.; Siddique, A.B.; Qusa, M.H.; King, J.A.; Souid, S.; Abd Elmageed, Z.Y.; El Sayed, K.A. PCSK9 Axis-targeting pseurotin A as a novel prostate cancer recurrence suppressor lead. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2021, 4, 1771–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, J.G.; Farnier, M.; Krempf, M.; Bergeron, J.; Luc, G.; Averna, M.; Stroes, E.S.; Langslet, G.; Raal, F.J.; El Shahawy, M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of alirocumab in reducing lipids and cardiovascular events. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1489–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabrizi, M.; Bornstein, G.G.; Suria, H. Biodistribution mechanisms of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies in health and disease. AAPS J. 2010, 12, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, M.J.; Sabatine, M.S.; Giugliano, R.P.; Langslet, G.; Wiviott, S.D.; Ruzza, A.; Ma, Y.; Hamer, A.W.; Wasserman, S.M.; Raal, F.J. Long-Term Efficacy and Safety of Evolocumab in Patients with Hypercholesterolemia. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 2132–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test No. 425: Acute Oral Toxicity: Up-and-Down Procedure; OECD: Paris, France, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langford, D.J.; Bailey, A.L.; Chanda, M.L.; Clarke, S.E.; Drummond, T.E.; Echols, S.; Glick, S.; Ingrao, J.; Klassen-Ross, T.; Lacroix-Fralish, M.L.; et al. Coding of facial expressions of pain in the laboratory mouse. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 447–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaid, A.; Roubtsova, A.; Essalmani, R.; Marcinkiewicz, J.; Chamberland, A.; Hamelin, J.; Tremblay, M.; Jacques, H.; Jin, W.; Davignon, J.; et al. Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9): Hepatocyte-specific low-density lipoprotein receptor degradation and critical role in mouse liver regeneration. Hepatology 2008, 48, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Dalt, L.; Castiglioni, L.; Baragetti, A.; Audano, M.; Svecla, M.; Bonacina, F.; Pedretti, S.; Uboldi, P.; Benzoni, P.; Giannetti, F.; et al. PCSK9 deficiency rewires heart metabolism and drives heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3078–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Toxicology Program (Ed.) The Digitized Atlas of Mouse Liver Lesions; National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences: Durham, NC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gartner, L.; Hiatt, J. Color Atlas of Histology, 2nd ed.; Coryell, P., Ed.; Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1994; p. 397. [Google Scholar]
- Hesketh, E.E.; Czopek, A.; Clay, M.; Borthwick, G.; Ferenbach, D.; Kluth, D.; Hughes, J. Renal ischaemia reperfusion injury: A mouse model of injury and regeneration. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 88, 51816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdeva, J.; Dai, W.; Kloner, R.A. Functional and histological assessment of an experimental model of Takotsubo’s cardiomyopathy. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2014, 3, e000921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, W.H.; Young, J.K.; Hyten, M.J.; Hall, D.G. Preparation and analysis of the central nervous system. Toxicol. Pathol. 2011, 39, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, B.A.; Thompson, P.D. Statin-associated muscle disease: Advances in diagnosis and management. Neurotherapeutics 2018, 15, 1006–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabernilla, A.; Dos Santos Rodrigues, B.; Pieters, A.; Caufriez, A.; Leroy, K.; Van Campenhout, R.; Cooreman, A.; Gomes, A.R.; Arnesdotter, E.; Gijbels, E.; et al. In vitro liver toxicity testing of chemicals: A Pragmatic approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomakina, G.Y.; Modestova, Y.A.; Ugarova, N.N. Bioluminescence assay for cell viability. Biochemistry/Biokhimiia 2015, 80, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, V.L.; Thurston, S.E.; Lofgren, J.L. Using Cageside measures to evaluate analgesic efficacy in mice (Mus musculus) after Surgery. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2018, 57, 186–201. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins, P.; Morton, D.B.; Burman, O.; Dennison, N.; Honess, P.; Jennings, M.; Lane, S.; Middleton, V.; Roughan, J.V.; Wells, S.; et al. A guide to defining and implementing protocols for the welfare assessment of laboratory animals: Eleventh report of the BVAAWF/FRAME/RSPCA/UFAW Joint Working Group on Refinement. Lab. Anim. 2011, 45, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.V.; Norinder, U.; Liiv, E.; Platzack, B.; Öberg, M.; Törnqvist, E. Associations between clinical signs and pathological findings in toxicity testing. Altex 2021, 38, 198–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, S.R.; Biernot, S.; Bleich, A.; van Dijk, R.M.; Ernst, L.; Häger, C.; Helgers, S.O.A.; Koegel, B.; Koska, I.; Kuhla, A.; et al. Defining body-weight reduction as a humane endpoint: A critical appraisal. Lab. Anim. 2020, 54, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Parliament; The Council of The European Union. Directive 2010/63/Eu of The European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2010 on the Protection of Animals Used for Scientific Purposes. Off. J. Eur. Union 2010, 276, 33–79. [Google Scholar]
- Amgen. Double-blind, Randomized, Multicenter, Placebo-Controlled Study to Characterize the Efficacy, Safety, and Tolerability of 24 Weeks of Evolocumab for LDL-C Reduction in Pediatric Subjects 10 to 17 Years of Age with HeFH. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?cond=Double-blind%2C+Randomized%2C+Multicenter%2C+Placebo-Controlled+Study+to+Characterize+the+Efficacy%2C+Safety%2C+and+Tolerability+of+24+Weeks+of+Evolocumab+for+LDL-C+Reduction+in+Pediatric+Subjects+10+to+17+Years+of+Age+with+HeFH&term=&cntry=&state=&city=&dist= (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- Giboney, P.T. Mildly elevated liver transaminase levels in the asymptomatic patient. Am. Fam. Physician 2005, 71, 1105–1110. [Google Scholar]
- Silva-Santana, G.; Bax, J.C.; Fernandes, D.C.S.; Bacellar, D.T.L.; Hooper, C.; Dias, A.; Silva, C.B.; de Souza, A.M.; Ramos, S.; Santos, R.A.; et al. Clinical hematological and biochemical parameters in Swiss, BALB/c, C57BL/6 and B6D2F1 Mus musculus. Anim. Model. Exp. Med. 2020, 3, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, G.P.; Rathkolb, B.; Oestereicher, M.A.; Lengger, C.J.; Moerth, C.; Micklich, K.; Fuchs, H.; Gailus-Durner, V.; Wolf, E.; Hrabě de Angelis, M. Clinical Chemistry Reference Intervals for C57BL/6J, C57BL/6N, and C3HeB/FeJ Mice (Mus musculus). J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2016, 55, 375–386. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.G.; Mukamal, K.; Tapper, E.; Robson, S.C.; Tsugawa, Y. Low LDL-C and high HDL-C levels are associated with elevated serum transaminases amongst adults in the United States: A cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zainal, Z.; Ong, A.; Yuen May, C.; Chang, S.K.; Abdul Rahim, A.; Khaza’ai, H. Acute and subchronic oral toxicity of oil palm puree in Sprague-Dawley rats. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, H.; Betton, G.; Robinson, D.; Thomas, K.; Monro, A.; Kolaja, G.; Lilly, P.; Sanders, J.; Sipes, G.; Bracken, W.; et al. Concordance of the toxicity of pharmaceuticals in humans and in animals. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2000, 32, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morowski, M.; Vögtle, T.; Kraft, P.; Kleinschnitz, C.; Stoll, G.; Nieswandt, B. Only severe thrombocytopenia results in bleeding and defective thrombus formation in mice. Blood 2013, 121, 4938–4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J. When to Worry About High Platelet Count; Verywell Health: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Test No. 423: Acute Oral toxicity—Acute Toxic Class Method; OECD: Paris, France, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameters | Control | 10 mg/kg | 250 mg/kg | 500 mg/kg |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liver | 1819 ± 107.3 | 1968 ± 330.1 | 1705 ± 196.9 | 1664 ± 306.5 |
| Kidneys | 858.4 ± 57.3 | 730.8 ± 106.4 | 714.6 ± 44.4 | 756.0 ± 148.3 |
| Spleen | 133.4 ± 20.4 | 124.4 ± 7.4 | 117.2 ± 13.2 | 141.3 ± 32.4 |
| Lungs | 263.0 ± 40.0 | 350.2 ± 80.1 | 278.8 ± 57.8 | 341.5 ± 62.8 |
| Heart | 223.4 ± 9.2 | 285.8 ± 86.2 | 220.6 ± 18.4 | 295.3 ± 25.4 |
| Brain | 346.5 ± 68.9 | 405.2 ± 63.1 | 397.8 ± 72.2 | 458.0 ± 24.2 |
| Parameters | Control | 10 mg/kg | 250 mg/kg | 500 mg/kg |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liver | 1150 ± 90.6 | 1157 ± 119.0 | 1227 ± 18.0 | 1145 ± 240.4 |
| Kidneys | 435.6 ± 47.9 | 408.5 ± 33.1 | 437.2 ± 28.4 | 391.8 ± 50.9 |
| Spleen | 107.0 ± 28.2 | 123.0 ± 11.4 | 118.4 ± 6.1 | 104.4 ± 22.6 |
| Lungs | 258.4 ± 79.8 | 233.3 ± 39.1 | 248.2 ± 73.4 | 209.0 ± 51.6 |
| Heart | 165.4 ± 24.5 | 171.0 ± 51.2 | 184.4 ± 29.6 | 180.4 ± 26.8 |
| Brain | 443.6 ± 50.9 | 392.0 ± 12.7 | 428.0 ± 72.7 | 378.8 ± 33.5 |
| Parameters | Control | 10 mg/kg | 250 mg/kg | 500 mg/kg |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLU (mg/dL) | 224.0 ± 4.8 | 294.0 ± 15.8 | 234.3 ± 11.8 | 236.8 ± 7.7 |
| AST (U/L) | 93.0 ± 10.2 | 115.0 ± 17.3 | 153.8 ± 8.8 | 105.8 ± 19.7 |
| ALT (U/L) | 31.8 ± 0.8 | 31.5 ± 2.9 | 41.8 ± 2.7 | 29.3 ± 1.2 |
| ALP (U/L) | 74.8 ± 1.4 | 70.8 ± 5.0 | 79.5 ± 4.1 | 76.8 ± 9.1 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 24.3 ± 0.2 | 21.0 ± 1.6 | 22.8 ± 1.5 | 20.3 ± 0.5 |
| CREAT (mg/dL) | 0.2 ± 0.0 | 0.2 ± 0.0 | <0.2 ± 0.0 | 0.2 ± 0.0 |
| Parameters | Control | 10 mg/kg | 250 mg/kg | 500 mg/kg |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLU (mg/dL) | 198.5 ± 17.2 | 222.5 ± 20.5 | 221.5 ± 6.3 | 191.7 ± 4.0 |
| AST (U/L) | 78.0 ± 28.1 | 90.5 ± 5.9 | 241.0 ± 35.0 | 158.3 ± 4.5 |
| ALT (U/L) | 28.5 ± 3.6 | 29.5 ± 1.5 | 49.5 ± 4.1 | 40.5 ± 2.5 |
| ALP (U/L) | 111.0 ± 8.0 | 95.0 ± 5.2 | 68.5 ± 4.7 | 87.0 ± 8.5 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 17.5 ± 1.2 | 19.3 ± 1.4 | 23.0 ± 1.3 | 21.7 ± 0.5 |
| CREAT (mg/dL) | <0.2 ± 0.0 | 0.2 ± 0.0 | <0.2 ± 0.0 | <0.2 ± 0.0 |
| Parameters | Control | 10 mg/kg | 250 mg/kg | 500 mg/kg |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WBC (103/μL) | 5.3 ± 1.2 | 6.0 ± 0.8 | 6.3 ± 1.9 | 4.1 ± 1.6 |
| RBC (106/μL) | 9.0 ± 0.7 | 8.9 ± 0.4 | 9.0 ± 0.9 | 8.6 ± 3.4 |
| HGB (g/dL) | 13.2 ± 0.5 | 13.2 ± 0.6 | 13.2 ± 0.7 | 12.8 ± 1.2 |
| HCT (%) | 44.3 ± 4.8 | 45.1 ± 3.1 | 44.7 ± 5.3 | 41.3 ± 4.6 |
| MCV (fL) | 49.1 ± 2.1 | 50.5 ± 2.7 | 49.6 ± 2.8 | 48.0 ± 2.6 |
| MCHC (g/dL) | 30.0 ± 2.3 | 29.3 ± 2.1 | 29.7 ± 2.3 | 30.9 ± 2.2 |
| PLT (103/μL) | 537.8 ± 117.6 | 679.7 ± 139.7 | 768.5 ± 133.2 | 547.3 ± 159.9 |
| Parameters | Control | 10 mg/kg | 250 mg/kg | 500 mg/kg |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WBC (103/μL) | 4.1 ± 1.2 | 4.6 ± 0.8 | 5.2 ± 1.9 | 3.1 ± 1.1 |
| RBC (106/μL) | 9.1 ± 0.7 | 9.1 ± 0.4 | 9.5 ± 0.9 | 10.0 ± 0.3 |
| HGB (g/dL) | 13.5 ± 0.5 | 13.4 ± 0.6 | 14.1 ± 0.7 | 15.0 ± 0.5 |
| HCT (%) | 47.3 ± 4.8 | 45.0 ± 3.1 | 46.3 ± 5.3 | 50.7 ± 2.8 |
| MCV (fL) | 51.8 ± 2.1 | 49.5 ± 2.7 | 48.7 ± 2.8 | 50.6 ± 1.3 |
| MCHC (g/dL) | 28.7 ± 2.3 | 30.0 ± 2.1 | 30.5 ± 2.3 | 29.6 ± 0.9 |
| PLT (103/μL) | 514.0 ± 117.6 | 587.5 ± 139.7 | 635.0 ± 133.2 | 409.0 ± 129.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McGehee, O.C.; Ebrahim, H.Y.; Rad, A.H.; Abdelwahed, K.S.; Mudhish, E.A.; King, J.A.; Helal, I.E.; Meyer, S.A.; El Sayed, K.A. Towards Developing Novel Prostate Cancer Recurrence Suppressors: Acute Toxicity of Pseurotin A, an Orally Active PCSK9 Axis-Targeting Small-Molecule in Swiss Albino Mice. Molecules 2023, 28, 1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031460
McGehee OC, Ebrahim HY, Rad AH, Abdelwahed KS, Mudhish EA, King JA, Helal IE, Meyer SA, El Sayed KA. Towards Developing Novel Prostate Cancer Recurrence Suppressors: Acute Toxicity of Pseurotin A, an Orally Active PCSK9 Axis-Targeting Small-Molecule in Swiss Albino Mice. Molecules. 2023; 28(3):1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031460
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcGehee, Oliver C., Hassan Y. Ebrahim, Ashkan H. Rad, Khaldoun S. Abdelwahed, Ethar A. Mudhish, Judy A. King, Iman E. Helal, Sharon A. Meyer, and Khalid A. El Sayed. 2023. "Towards Developing Novel Prostate Cancer Recurrence Suppressors: Acute Toxicity of Pseurotin A, an Orally Active PCSK9 Axis-Targeting Small-Molecule in Swiss Albino Mice" Molecules 28, no. 3: 1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031460
APA StyleMcGehee, O. C., Ebrahim, H. Y., Rad, A. H., Abdelwahed, K. S., Mudhish, E. A., King, J. A., Helal, I. E., Meyer, S. A., & El Sayed, K. A. (2023). Towards Developing Novel Prostate Cancer Recurrence Suppressors: Acute Toxicity of Pseurotin A, an Orally Active PCSK9 Axis-Targeting Small-Molecule in Swiss Albino Mice. Molecules, 28(3), 1460. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031460







