Effect of Nano-Selenium on Nutritional Quality of Cowpea and Response of ABCC Transporter Family
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
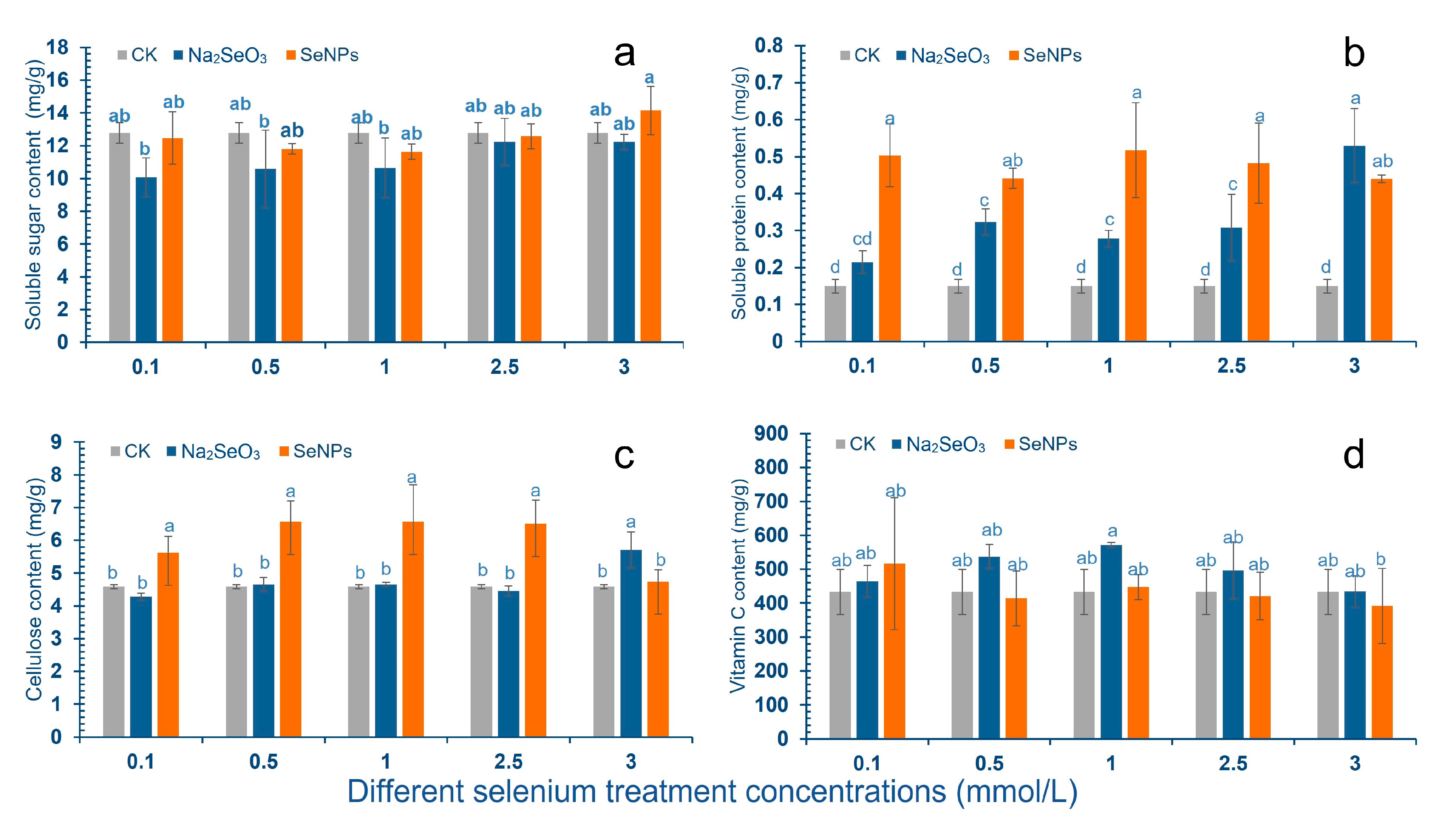
2.1. Physiological Indexes of Cowpea Pods
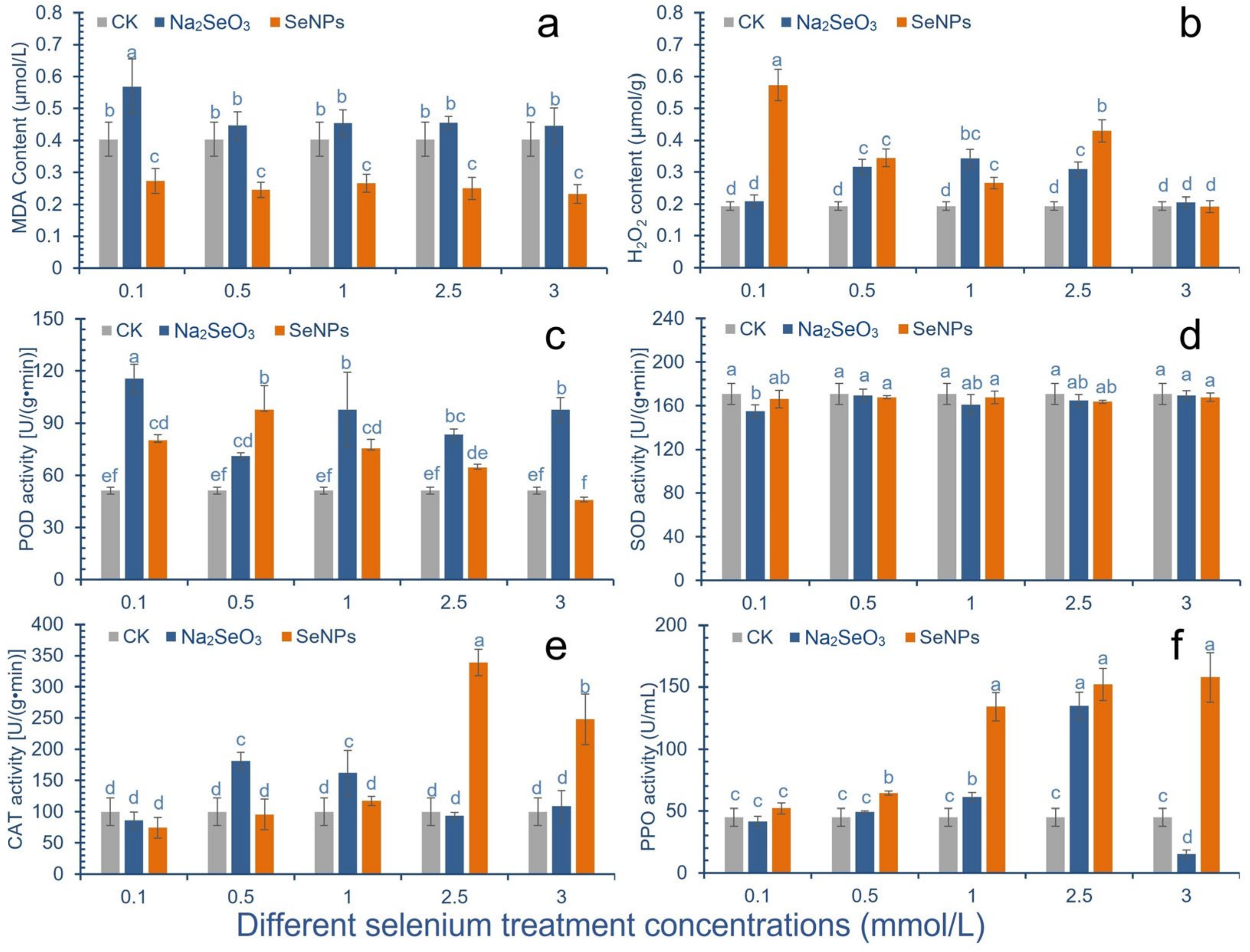
2.2. Effect of Se on Antioxidant System
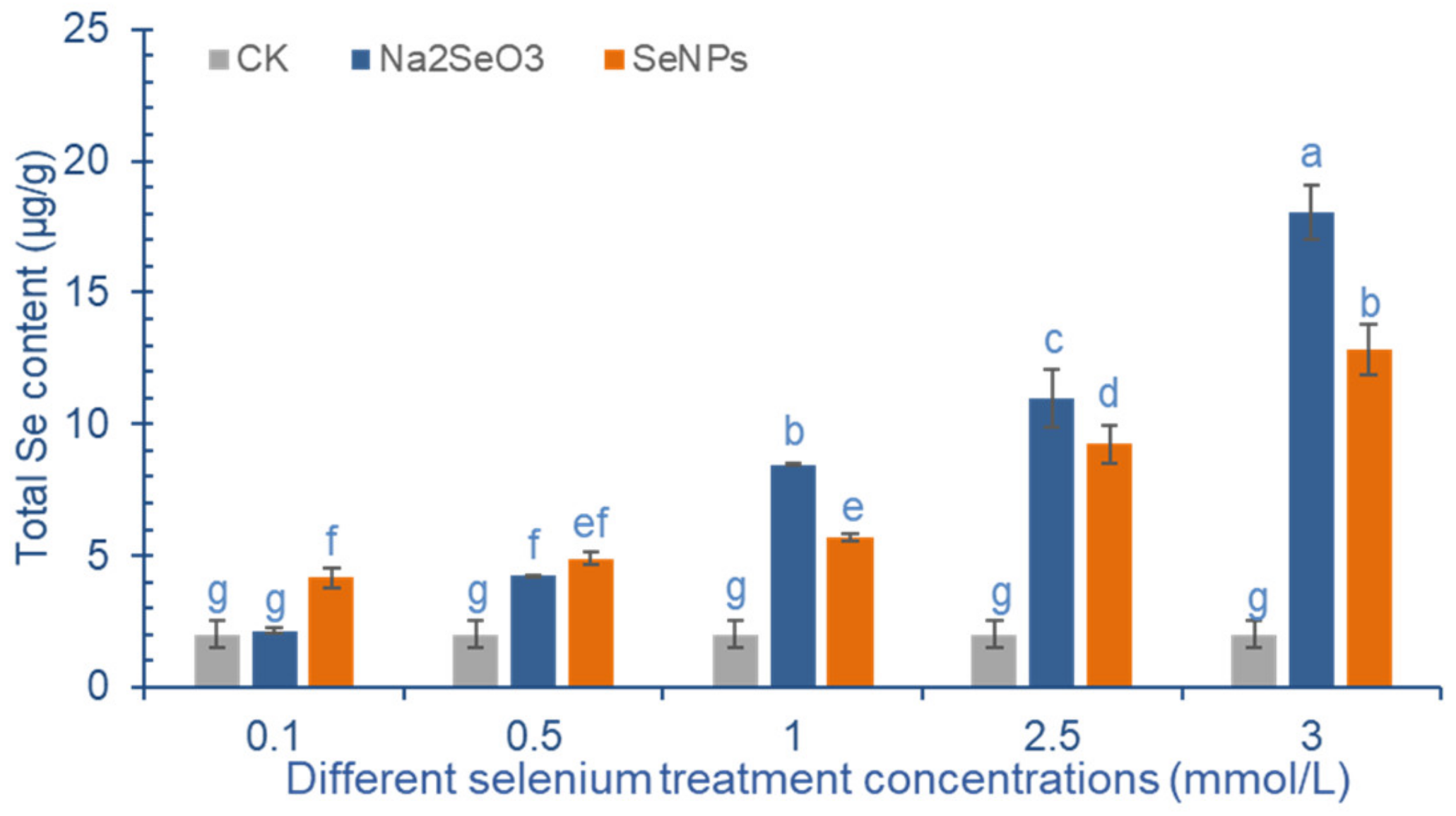
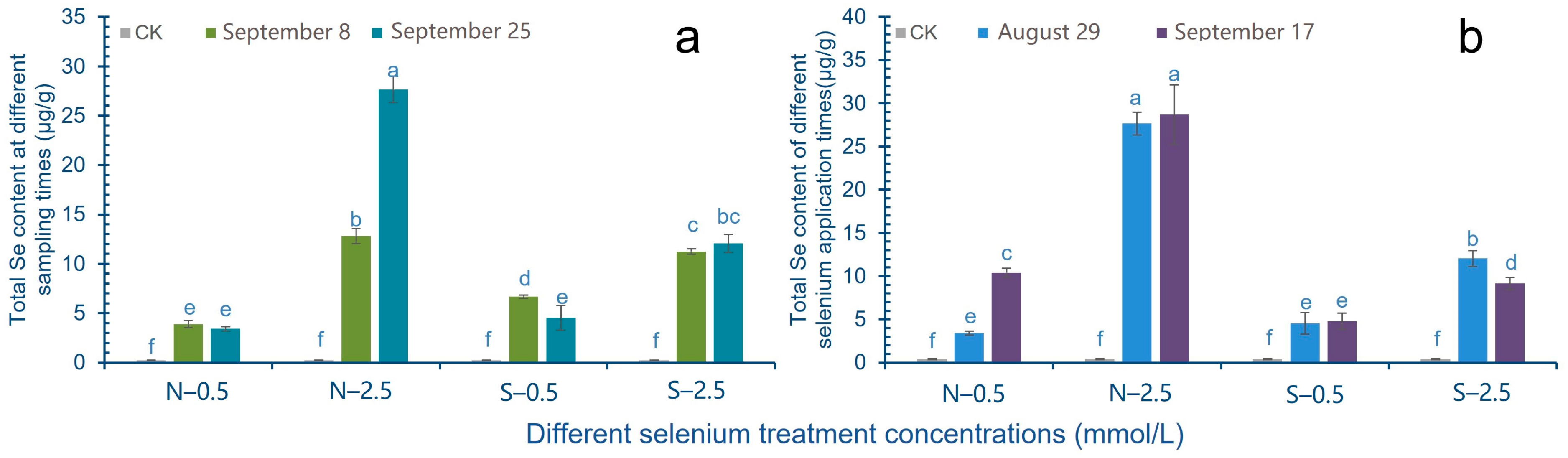
2.3. Effect of Exogenous Se Treatment on Total Se Content in Cowpea Pods
2.4. Effects of Se Application on the Forms and Contents of Se in Cowpea Pods
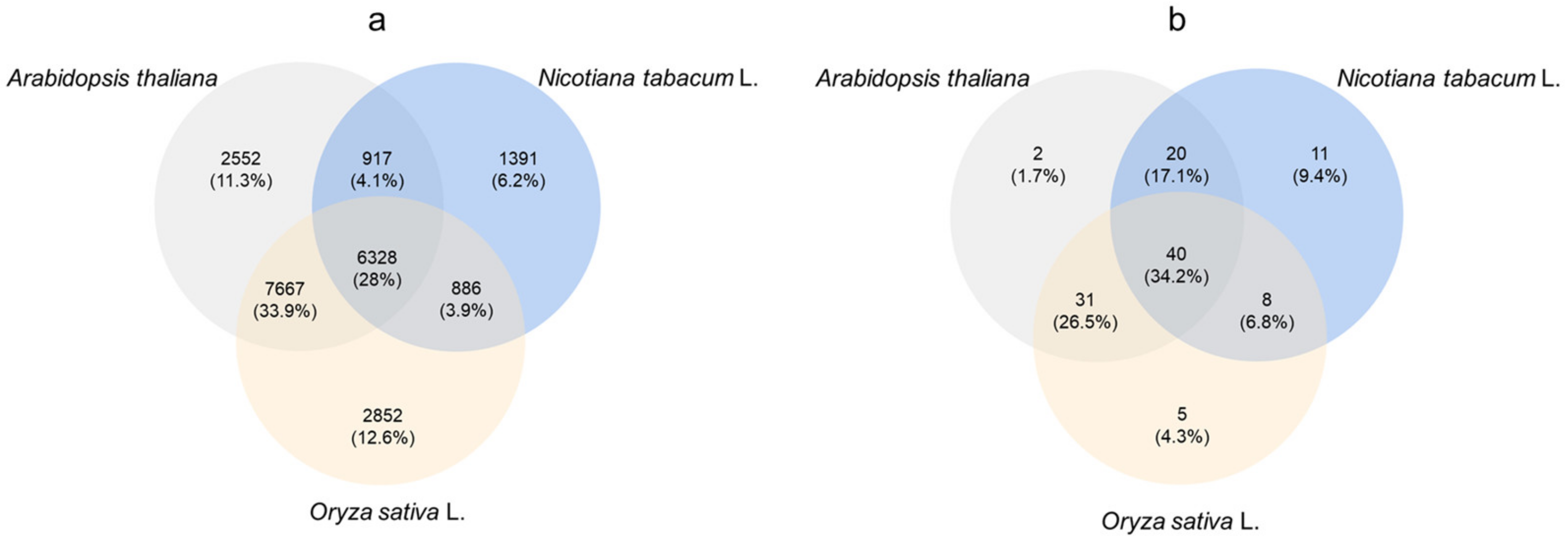
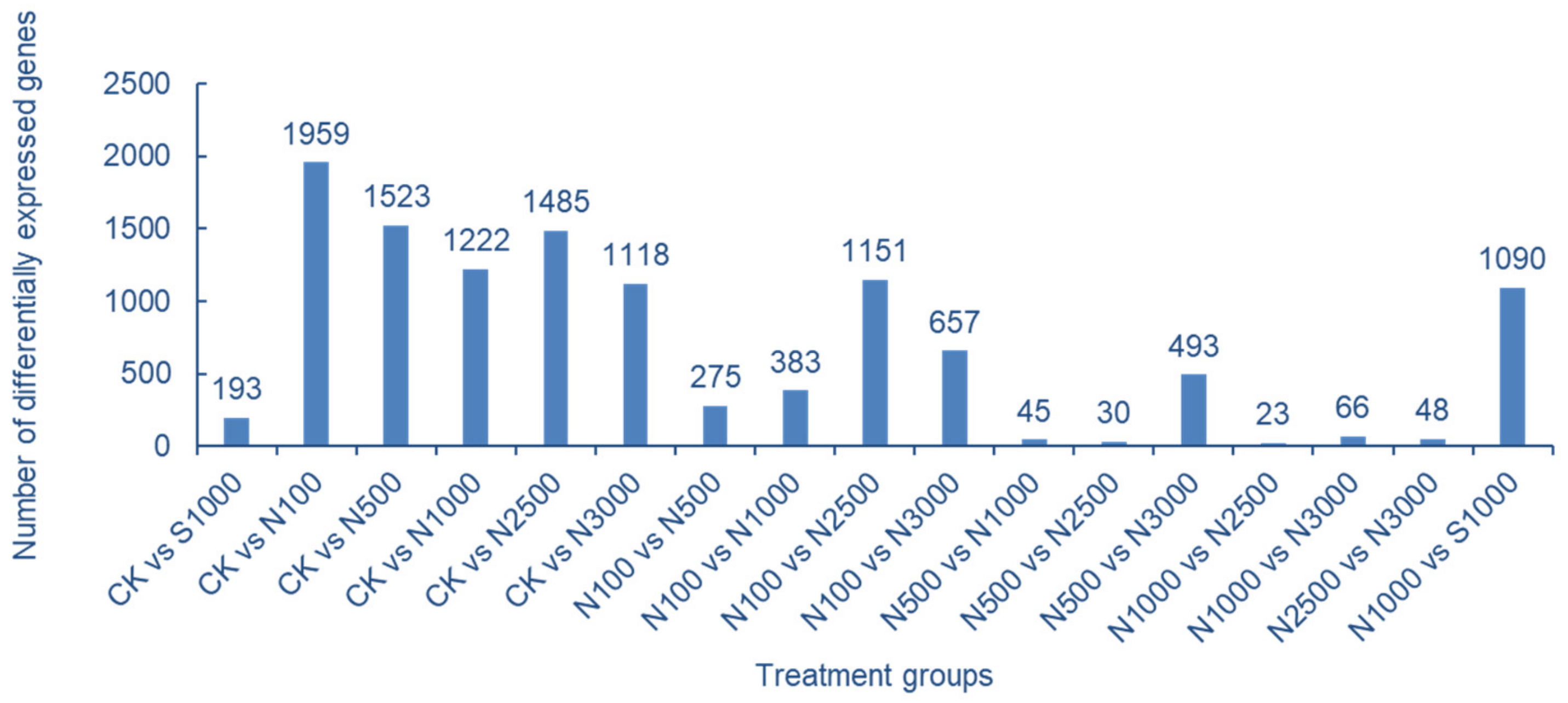
2.5. Analysis of Transcriptome Data of Cowpea Treated with Se
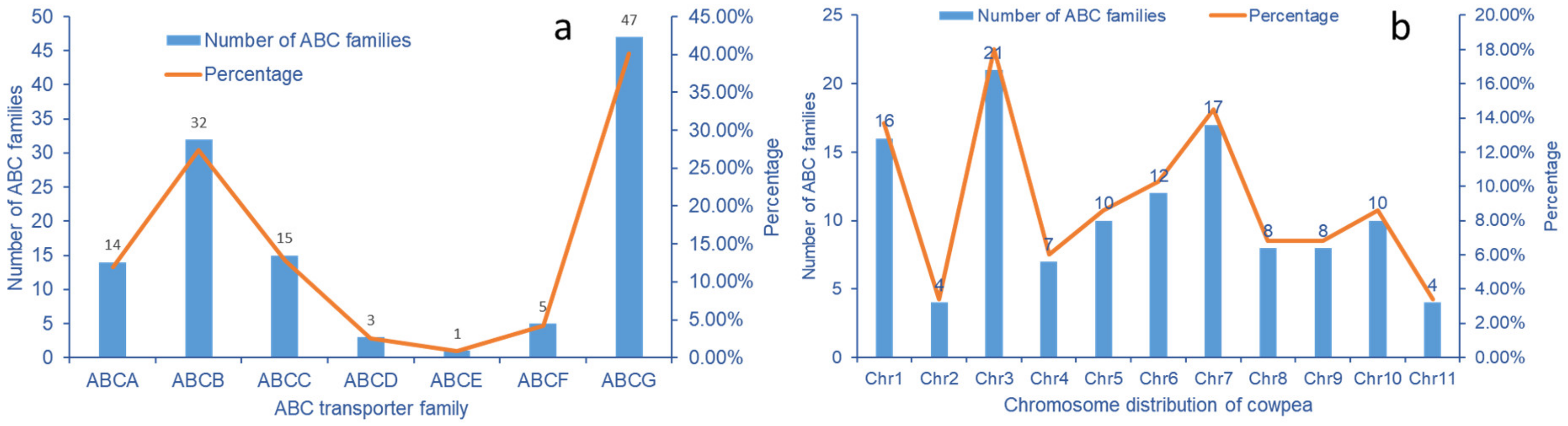
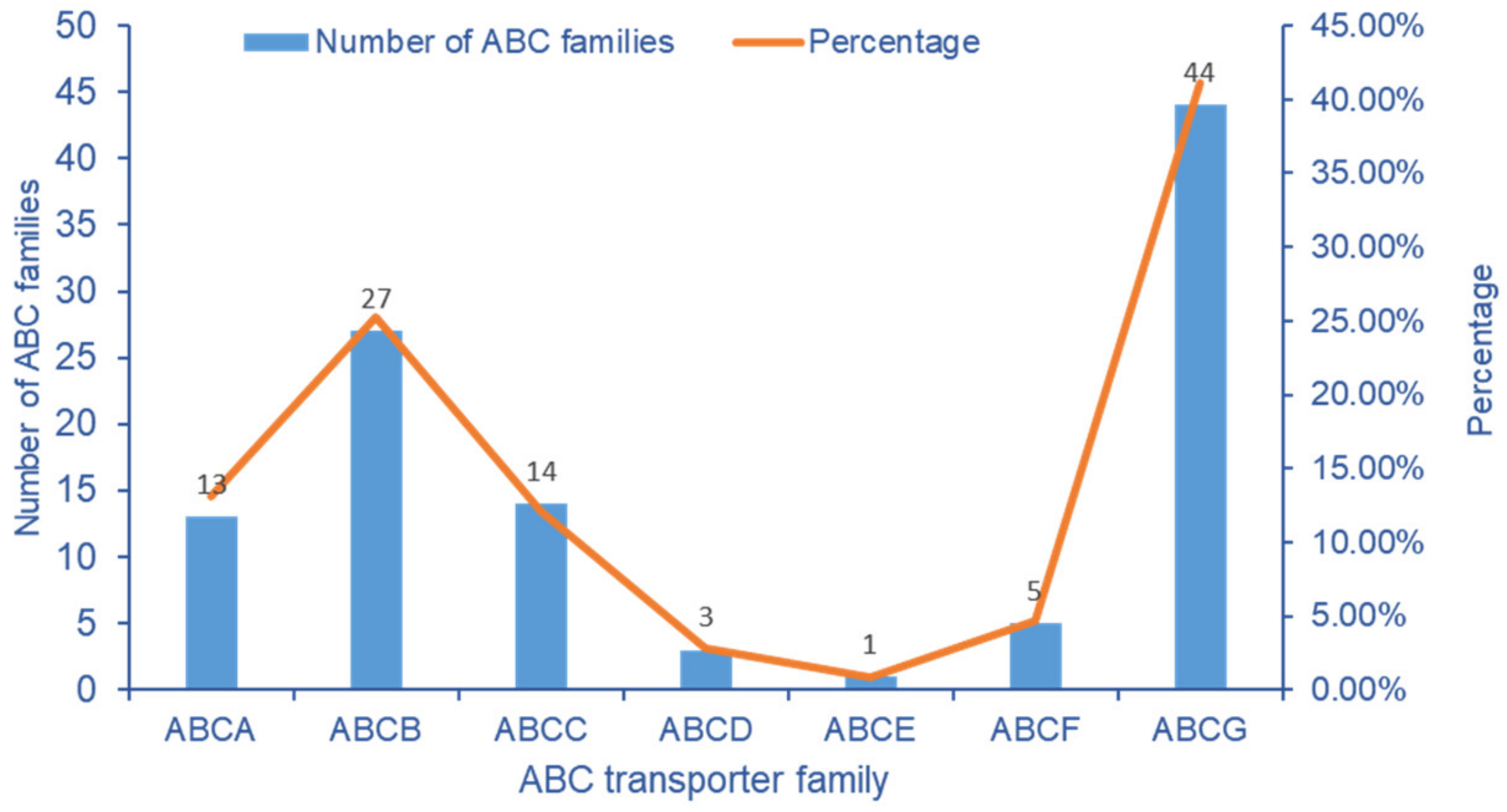
2.6. Analysis of Transcriptome ABC Transporter Gene
2.7. Differential Expression Analysis of ABC Transporter Gene
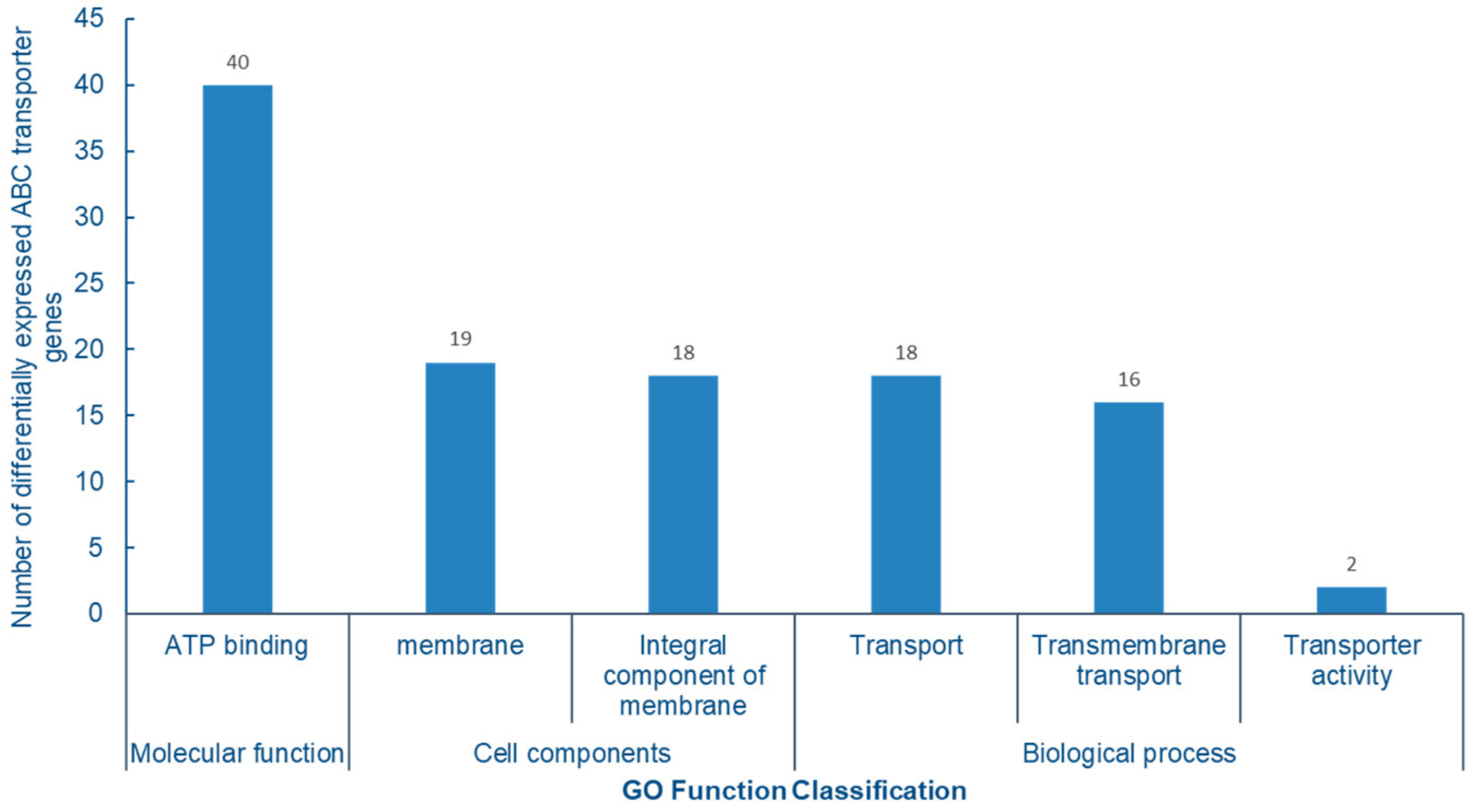
2.8. GO Enrichment Analysis of ABC Transporters
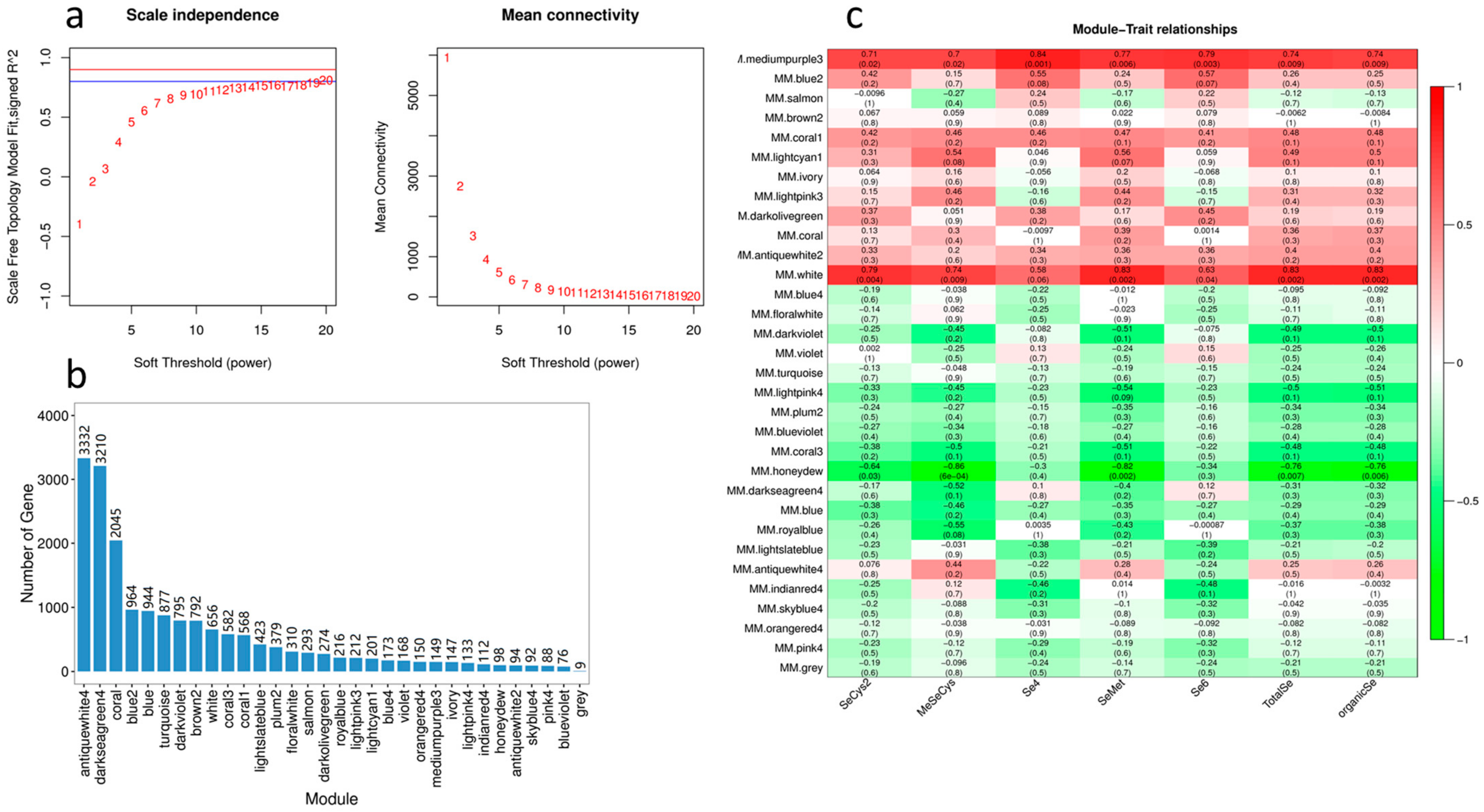
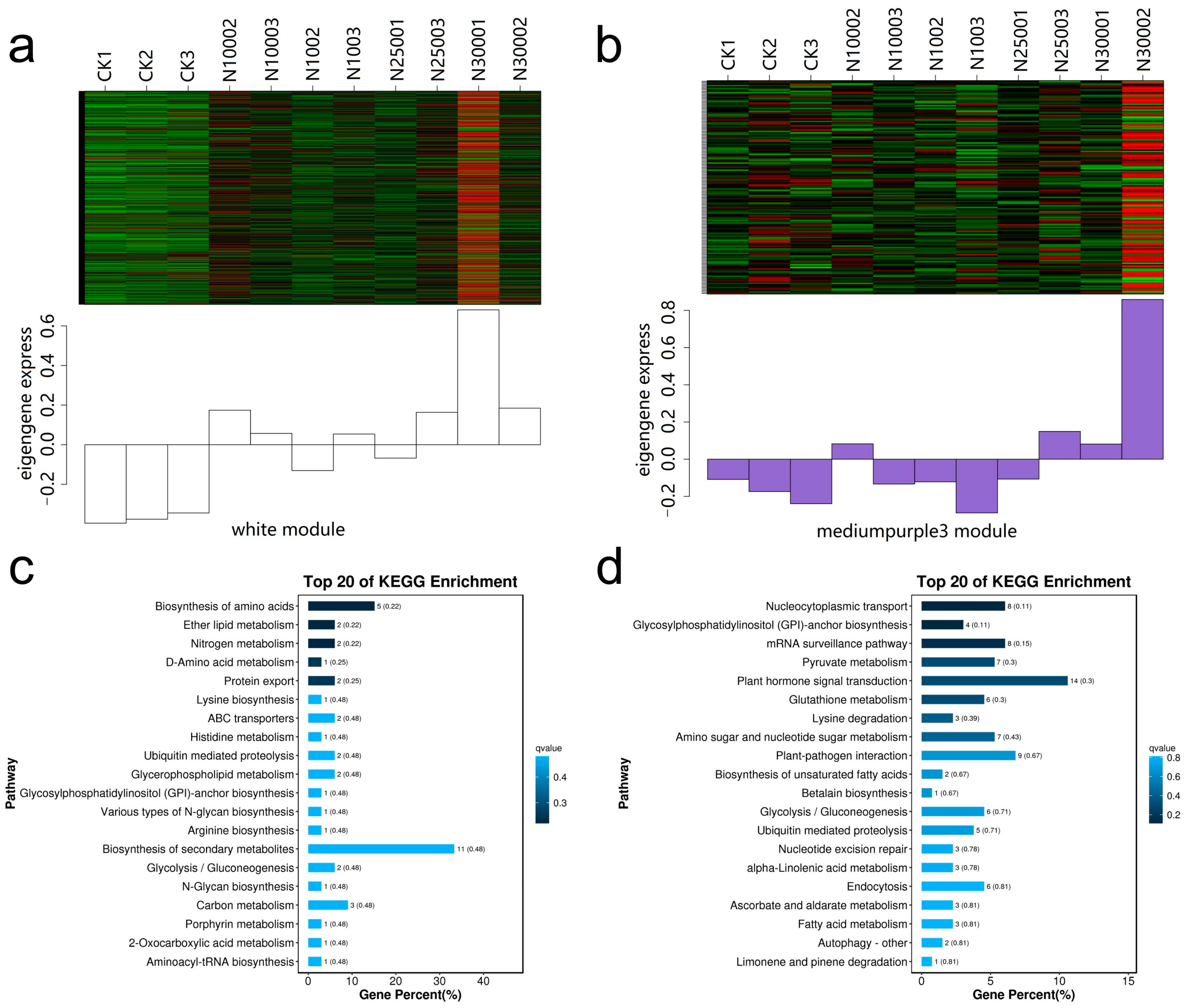
2.9. WGCNA Analysis of DEGs
3. Discussion
3.1. Effect of Se on Physiological Indexes of Cowpea Pods
3.2. Effect of Exogenous Se Treatment on Total Se Content in Cowpea Pods
3.3. Effect of Se on Antioxidant Capacity of Cowpea
3.4. Effect of Se Treatment on Se Species in Cowpea
3.5. ABC Transporters and Se Absorption
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Treatment of Cowpea with Se
4.3. Chlorophyll, Cellulose, Soluble Sugar and Protein, Free Amino Acid, and Vc Contents
4.4. Determination of Antioxidant Index of Cowpea Pods
4.5. Total Se and Se Species Concentrations
4.6. Transcriptome Sequencing and Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Roman, M.; Jitaru, P.; Barbante, C. Selenium biochemistry and its role for human health. Metallomics 2014, 6, 25–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, N.; Cheng, Q.; Arnér, E.S.J.; Davies, M.J. Inhibition and crosslinking of the selenoprotein thioredoxin reductase-1 by p-benzoquinone. Redox Biol. 2020, 28, 101335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, B.R.; Roberts, B.R.; Bush, A.I.; Hare, D.J. Selenium, selenoproteins and neurodegenerative diseases. Metallomics 2015, 7, 1213–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kipp, A.P.; Strohm, D.; Brigelius-Flohé, R.; Schomburg, L.; Bechthold, A.; Leschik-Bonnet, E.; Heseker, H.; German Nutrition, S. Revised reference values for selenium intake. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2015, 32, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krinsky, N.I.; Beecher, G.R.; Burk, R.F.; Chan, A.C.; Erdman, J.J.; Jacob, R.A.; Jialal, I.; Kolonel, L.N.; Marshall, J.R.; Taylor Mayne, P.R. Dietary reference intakes for vitamin C, vitamin E, selenium, and carotenoids. Inst. Med. 2000, 19, 95–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.J. Selenium metabolism in plants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Gen. Subj. 2018, 1862, 2333–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, C.T.; Elizabeth, A.H.P.-S. Selenium transport and metabolism in plants: Phytoremediation and biofortification implications. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404, 124178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, R.; Fontanella, M.C.; Falcinelli, B.; Beone, G.M.; Bravi, E.; Marconi, O.; Benincasa, P.; Businelli, D. Selenium biofortification in rice (Oryza sativa L.) sprouting: Effects on Se yield and nutritional traits with focus on phenolic acid profile. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 4082–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, R.; Proietti, P.; Onofri, A.; Regni, L.; Esposto, S.; Servili, M.; Businelli, D.; Selvaggini, R. Biofortification (Se): Does it increase the content of phenolic compounds in virgin olive oil (VOO)? PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Rao, S.; Yu, T.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, X.; Xue, H.; Gou, Y.; Cheng, S.; Xu, F. Selenium yeast promoted the Se accumulation, nutrient quality and antioxidant system of cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata L.). Plant Signal. Behav. 2021, 16, 1907042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.; Gou, Y.; Yu, T.; Cong, X.; Gui, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Liao, Y.; Ye, J.; Cheng, S. Effects of selenate on Se, flavonoid, and glucosinolate in broccoli florets by combined transcriptome and metabolome analyses. Food Res. Int. 2021, 146, 110463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.; Yu, T.; Cong, X.; Lai, X.; Xiang, J.; Cao, J.; Liao, X.; Gou, Y.; Chao, W.; Xue, H.; et al. Transcriptome, proteome, and metabolome reveal the mechanism of tolerance to selenate toxicity in Cardamine violifolia . J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.M.; Boleta, E.H.M.; Lanza, M.G.D.B.; Lavres, J.; Martins, J.T.; Santos, E.F.; dos Santos, F.L.M.; Putti, F.F.; Junior, E.F.; White, P.J.; et al. Physiological, biochemical, and ultrastructural characterization of selenium toxicity in cowpea plants. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2018, 150, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.E. Phenotyping cowpeas for adaptation to drought. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzeke, M.G.; Mtambanengwe, F.; Nezomba, H.; Watts, M.J.; Broadley, M.R.; Mapfumo, P. Zinc fertilization increases productivity and grain nutritional quality of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata [L.] Walp.) under integrated soil fertility management. Field Crops Res. 2017, 213, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavon, M.; Pilon-Smits, E.A.H. The fascinating facets of plant selenium accumulation–biochemistry, physiology, evolution and ecology. New Phytol. 2017, 213, 1582–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Reis, A.R.; El-Ramady, H.; Santos, E.F.; Gratão, P.L.; Schomburg, L. Overview of selenium deficiency and toxicity worldwide: Affected areas, selenium-related health issues, and case studies. In Selenium in Plants; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 209–230. [Google Scholar]
- Lanza, M.G.D.B.; Silva, V.M.; Montanha, G.S.; Lavres, J.; de Carvalho, H.W.P.; Dos Reis, A.R. Assessment of selenium spatial distribution using μ-XFR in cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.) plants: Integration of physiological and biochemical responses. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 207, 111216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hu, B.; Li, W.; Che, R.; Deng, K.; Li, H.; Yu, F.; Ling, H.; Li, Y.; Chu, C. OsPT2, a phosphate transporter, is involved in the active uptake of selenite in rice. New Phytol. 2014, 201, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, S.L.; Durandeau, K.; Nagy, I.; Barth, S. Identification of ABC transporters from Lolium perenne L. that are regulated by toxic levels of selenium. Planta 2010, 231, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrier, P.J.; Bird, D.; Burla, B.; Dassa, E.; Forestier, C.; Geisler, M.; Klein, M.; Kolukisaoglu, Ü.; Lee, Y.; Martinoia, E. Plant ABC proteins a unified nomenclature and updated inventory. Trends Plant Sci. 2008, 13, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Q.; Mitani, N.; Yamaji, N.; Shen, R.F.; Ma, J.F. Involvement of silicon influx transporter OsNIP2; 1 in selenite uptake in rice. Plant Physiol. 2010, 153, 1871–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.F.; McGrath, S.P.; Zhao, F.J. Selenium uptake, translocation and speciation in wheat supplied with selenate or selenite. New Phytol. 2008, 178, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Q.; Li, F.; Qin, L.; Chen, E.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Guan, Y. Screening and analysis of Se responsive genes in leaves of foxtail millet. Mol. Plant Breed. 2021, 19, 2798–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, H.; Batieno, B.J.; Fatokun, C.; Boukar, O. A high plant density and the split application of chemical fertilizer increased the grain and protein content of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) in Burkina Faso, West Africa. Agriculture 2022, 12, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lin, C.; Luo, H.; Jin, C.; Yu, Z.; Qian, C. Impact of precooling time on quality and physio-biochemical characteristics of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) and cowpea (Vigna sinensis) under controlled atmosphere storage conditions. Food Sci. 2018, 39, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, R.; Hettiarachchy, N.S.; Jalaluddin, M. High-performance liquid chromatography determination of phenolic constituents in 17 varieties of cowpeas. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 1623–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.; Wu, J.; Qin, H.; Yang, Q.; Liu, C.; Guo, X.; Sun, J. Content and antioxidant activity of polyphenols and flavonoids from 4 food beans. J. Chin. Cereals Oils Assoc. 2017, 32, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, R.; Regni, L.; Falcinelli, B.; Mattioli, S.; Benincasa, P.; Dal Bosco, A.; Pacheco, P.; Proietti, P.; Troni, E.; Santi, C.; et al. Current knowledge on selenium biofortification to improve the nutraceutical profile of food: A comprehensive review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 4075–4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manaf, H.H. Beneficial effects of exogenous selenium, glycine betaine and seaweed extract on salt stressed cowpea plant. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2016, 61, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, P.; Li, Y.; Ren, X.; Wang, J. Effects of sodium selenite treatment on quality and active oxygen of cowpea. J. Gansu Agric. Univ. 2020, 55, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Shan, W.; Zhu, G. Effect of foliar application selenium on the yield and quality of soybean. Xinjiang Agric. Sci. 2009, 46, 506–509. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, H.-A.A.; Darwesh, O.M.; Mekki, B.B. Environmentally friendly nano-selenium to improve antioxidant system and growth of groundnut cultivars under sandy soil conditions. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 18, 101080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, J.A.; Kumar, S.; Thakur, P.; Sharma, S.; Kaur, N.; Kaur, R.; Pathania, D.; Bhandhari, K.; Kaushal, N.; Singh, K. Promotion of growth in mungbean (Phaseolus aureus Roxb.) by selenium is associated with stimulation of carbohydrate metabolism. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2011, 143, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Guo, D.; Gao, W. Effects of Na2SeO3 sprayed at different time on growth and selenium accumulation of pea seedling. Seed 2008, 27, 40–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, S.; Huang, Y.; Liu, K.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, H. Effect of application of sodium selenite to soil on the growth and physiological indexes and selenium accumulation of Astragalus sinicus . Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2016, 47, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, Z.; Soós, Á.; Kovács, B.; Kaszás, L.; Elhawat, N.; Bákonyi, N.; Razem, M.; Fári, M.G.; Prokisch, J.; Domokos-Szabolcsy, É. Uptake dynamics of ionic and elemental selenium forms and their metabolism in multiple-harvested alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Plants 2021, 10, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, S.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Gao, W. Effect of sodium selenite on plant growth and selenium accumulation in pea sprout. Guangdong Trace Elem. Sci. 2004, 11, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Zhao, G.; Wu, W.; Liu, L.; Wang, Q.; Guo, Y. Absorption and bio-transformation of selenium nanoparticles by wheat seedlings (Triticum aestivum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Li, K.; Wan, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhuang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Li, H. Uptake, translocation and biotransformation of selenium nanoparticles in rice seedlings (Oryza sativa L.). J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, N.; Liang, X.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.-F.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, J. A comparative study on the accumulation, translocation and transformation of selenite, selenate, and SeNPs in a hydroponic-plant system. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 189, 109955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rady, M.M.; Desoky, E.-S.M.; Ahmed, S.M.; Majrashi, A.; Ali, E.F.; Arnaout, S.M.A.I.; Selem, E. Foliar nourishment with nano-selenium dioxide promotes physiology, biochemistry, antioxidant defenses, and salt tolerance in phaseolus vulgaris. Plants 2021, 10, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qados, A.M.S.A. Effects of salicylic acid on growth, yield and chemical contents of pepper (Capsicum annuum L) plants grown under salt stress conditions. Int. J. Agric. Crop Sci. 2015, 8, 107–113. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, V.M.; Tavanti, R.F.R.; Gratão, P.L.; Alcock, T.D.; Dos Reis, A.R. Selenate and selenite affect photosynthetic pigments and ROS scavenging through distinct mechanisms in cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) walp) plants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 201, 110777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, H.P.G.; de Queiroz Barcelos, J.P.; Junior, E.F.; Santos, E.F.; Silva, V.M.; Moraes, M.F.; Putti, F.F.; dos Reis, A.R. Agronomic biofortification of upland rice with selenium and nitrogen and its relation to grain quality. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 79, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Qi, Z.; Li, M.; Ahammed, G.J.; Chu, X.; Zhou, J. Selenium forms and methods of application differentially modulate plant growth, photosynthesis, stress tolerance, selenium content and speciation in Oryza sativa L. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 169, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jóźwiak, W.; Politycka, B. Effect of selenium on alleviating oxidative stress caused by a water deficit in cucumber roots. Plants 2019, 8, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, T.; Chang, S.; Li, S.; Pang, X.; Zheng, L.; Kang, Y. Effect of nano-selenium spraying on the growth characteristics, nutritional quality, phenolics content and antioxidant activity of mung bean sprouts. J. China Agric. Univ. 2019, 24, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Dernovics, M.; Long, S. Study on the forms of selenium in Enshi selenium rich beans. J. Miner. 2015, 35, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y. Identification and Analysis of Genes Related to Selenium Assimilation and Metabolism in Tea Plant Roots; Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences: Hangzhou, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Xu, J.; Zhang, D. Molecular evolution, expression and functional network prediction analysis of ABC transporter gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. J. 2012, 48, 1151–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X. Identification and Functional Characterization of Nicotiana Tabacum Abc Transporters Involved in The Transport of Secondary Metabolites; Chongqing University: Chongqing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Sun, W.; Ma, Y.; Han, E.; Han, L.; Sun, L.; Peng, Z.; Wang, B. Research progress of ABC transporters in Arabidopsis thaliana . Plant Physiol. J. 2017, 53, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Li, H.; Song, Z.; Dong, B.; Cao, H.; Liu, T.; Du, T.; Yang, W.; Amin, R.; Wang, L. The functional analysis of ABCG transporters in the adaptation of pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan) to abiotic stresses. PeerJ 2021, 9, e10688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, T.H.T.; Martinoia, E.; Lee, Y. Functions of ABC transporters in plant growth and development. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2018, 41, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, W. Functional prediction and expression analysis of GmABCG40. Soybean Sci. 2017, 36, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, E.; Wang, H.; Han, L.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, B. Cloning and functional analysis of GmABCG1 gene in Glycine max . Mol. Plant Breed. 2018, 16, 7925–7932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Guo, H.; Wang, S.; Xu, L.; Li, C.; Qian, Q.; Chen, F.; Geisler, M.; Qi, Y.; et al. OsABCB14 functions in auxin transport and iron homeostasis in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant J. 2014, 79, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.F.; Yamaji, N.; Mitani, N.; Yano, M.; Nagamura, Y.; Ma, J.F. A bacterial-type ABC transporter is involved in aluminum tolerance in rice. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneda, M.; Schuetz, M.; Lin, B.S.P.; Chanis, C.; Hamberger, B.; Western, T.L.; Ehlting, J.; Samuels, A.L. ABC transporters coordinately expressed during lignification of Arabidopsis stems include a set of ABCBs associated with auxin transport. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 2063–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Bovet, L.; Kushnir, S.; Noh, E.W.; Martinoia, E.; Lee, Y. AtATM3 is involved in heavy metal resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, P.B.; Cancel, J.; Rounds, M.; Ochoa, V. Arabidopsis ALS1 encodes a root tip and stele localized half type ABC transporter required for root growth in an aluminum toxic environment. Planta 2007, 225, 1447–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Wu, Z.; Li, Y.; Shen, Z.; Feng, X.; Zhang, M.; Ye, H. Mitochondrial ABC transporter ATM3 is essential for cytosolic iron-sulfur cluster assembly. Plant Physiol. 2017, 173, 2096–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefèvre, F.; Boutry, M. Towards identification of the substrates of ATP-binding cassette transporters. Plant Physiol. 2018, 178, 18–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raichaudhuri, A.; Peng, M.; Naponelli, V.; Chen, S.; Sánchez-Fernández, R.; Gu, H.; Gregory, J.F.; Hanson, A.D.; Rea, P.A. Plant vacuolar ATP-binding cassette transporters that translocate folates and antifolates in vitro and contribute to antifolate tolerance in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 8449–8460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Sánchez-Fernández, R.; Li, Z.-S.; Rea, P.A. Enhanced multispecificity of Arabidopsis vacuolar multidrug resistance-associated protein-type ATP-binding cassette transporter, AtMRP2. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 8648–8656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Song, W.Y.; Ko, D.; Eom, Y.; Hansen, T.H.; Schiller, M.; Lee, T.G.; Martinoia, E.; Lee, Y. The phytochelatin transporters AtABCC1 and AtABCC2 mediate tolerance to cadmium and mercury. Plant J. 2012, 69, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; He, X.; Zhuo, R.; Qiao, G.; Han, X.; Qiu, W.; Chi, L.; Zhang, D.; Liu, M. Identification and functional characterization of ABCC transporters for Cd tolerance and accumulation in Sedum alfredii Hance. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Yamaki, T.; Yamaji, N.; Ko, D.; Jung, K.; Fujii-Kashino, M.; An, G.; Martinoia, E.; Lee, Y.; Ma, J.F. A rice ABC transporter, OsABCC1, reduces arsenic accumulation in the grain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 15699–15704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Yu, Q.; Wang, J.; Han, H.; Mao, L.; Nyporko, A.; Maguza, A.; Fan, L.; Bai, L.; Powles, S. An ABCC-type transporter endowing glyphosate resistance in plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2100136118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.; Li, L.; Li, L.; Xu, F.; Yuan, H.; Zha, S.; Xiao, X.; Yu, J.; Cheng, S.; Cheng, H. Molecular mechanism of selenium affecting the synthesis of flavonoids in G. biloba leaves. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 40, 232–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Deng, J.; Wang, Q.; Yi, T.; Dong, X.; Cheng, S.; He, Y.; et al. Highly efficient biotransformation and production of selenium nanoparticles and polysaccharides using potential probiotic Bacillus subtilis T5. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, F. Experiments in Plant Physiology; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2022; pp. 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Gui, J.Y.; Rao, S.; Gou, Y.; Xu, F.; Cheng, S. Comparative study of the effects of selenium yeast and sodium selenite on selenium content and nutrient quality in broccoli florets (Brassica oleracea L. var. italica). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 1707–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G.M.; Antonescu, C.M.; Chang, T.C.; Mendell, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Content of Different Se Forms | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SeNP Treatment Concentration (mM) | SeCys2 (μg/g) DW | MeSeCys (μg/g) DW | SeMet (μg/g) DW | Se4+ (μg/g) DW | Se6+ (μg/g) DW |
| CK | - | - | 0.1187 ± 0.0059 e 100.00% | - | - |
| 0.1 | - | - | 0.2666 ± 0.0028 e 100.00% | - | - |
| 0.5 | - | 0.1509 ± 0.0116 d 28.65% | 0.3758 ± 0.0061 d 71.35% | - | - |
| 1.0 | 0.0183 ± 0.0057 c 2.17% | 0.2274 ± 0.0195 c 26.93% | 0.5988 ± 0.0084 c 70.90% | - | - |
| 2.5 | 0.0587 ± 0.0066 b 4.45% | 0.4261 ± 0.0167 b 32.31% | 0.8338 ± 0.0749 b 63.24% | - | - |
| 3.0 | 0.1478 ± 0.0095 a 6.88% | 0.5206 ± 0.0127 a 24.24% | 1.1813 ± 0.0272 a 55.00% | 0.0084 ± 0.0032 a 0.39% | 0.2897 ± 0.0254 a 13.49% |
| Content of Different Se Forms | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na2SeO3 Treatment Concentration (mM) | SeCys2 (μg/g) DW | MeSeCys (μg/g) DW | SeMet (μg/g) DW | Se4+ (μg/g) DW | Se6+ (μg/g) DW |
| CK | - | - | 0.1035 ± 0.0059 e 100.00% | - | - |
| 0.1 | - | - | 0.1545 ± 0.0119 e 100.00% | - | - |
| 0.5 | 0.0136 ± 0.0016 c 1.21% | 0.1672 ± 0.0073 c 14.82% | 0.9473 ± 0.0799 c 83.97% | - | - |
| 1.0 | 0.0459 ± 0.0083 c 3.53% | 0.2872 ± 0.0348 bc 22.09% | 0.9671 ± 0.0967 c 74.38% | - | - |
| 2.5 | 0.1323 ± 0.0213 b 4.68% | 0.4095 ± 0.0304 b 14.50% | 2.2833 ± 0.1101 b 80.82% | - | - |
| 3.0 | 0.2990 ± 0.0121 a 6.28% | 0.8859 ± 0.0517 a 18.61% | 3.4273 ± 0.2747 a 71.99% | 0.1485 ± 0.0412 a 3.12% | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Xiao, C.; Wang, S.; Cheng, S.; Cheng, H. Effect of Nano-Selenium on Nutritional Quality of Cowpea and Response of ABCC Transporter Family. Molecules 2023, 28, 1398. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031398
Li L, Xiong Y, Wang Y, Wu S, Xiao C, Wang S, Cheng S, Cheng H. Effect of Nano-Selenium on Nutritional Quality of Cowpea and Response of ABCC Transporter Family. Molecules. 2023; 28(3):1398. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031398
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Li, Yuzhou Xiong, Yuan Wang, Shuai Wu, Chunmei Xiao, Shiyan Wang, Shuiyuan Cheng, and Hua Cheng. 2023. "Effect of Nano-Selenium on Nutritional Quality of Cowpea and Response of ABCC Transporter Family" Molecules 28, no. 3: 1398. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031398
APA StyleLi, L., Xiong, Y., Wang, Y., Wu, S., Xiao, C., Wang, S., Cheng, S., & Cheng, H. (2023). Effect of Nano-Selenium on Nutritional Quality of Cowpea and Response of ABCC Transporter Family. Molecules, 28(3), 1398. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031398








