Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles Using Morus alba (White Mulberry) Leaf Extract as Potential Antibacterial and Anticancer Agents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Gas Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry (GC–MS) Analysis of an Aqueous Morus alba Leaf Extract (MLE) Revealed the Presence of Significant Bioactive Compounds
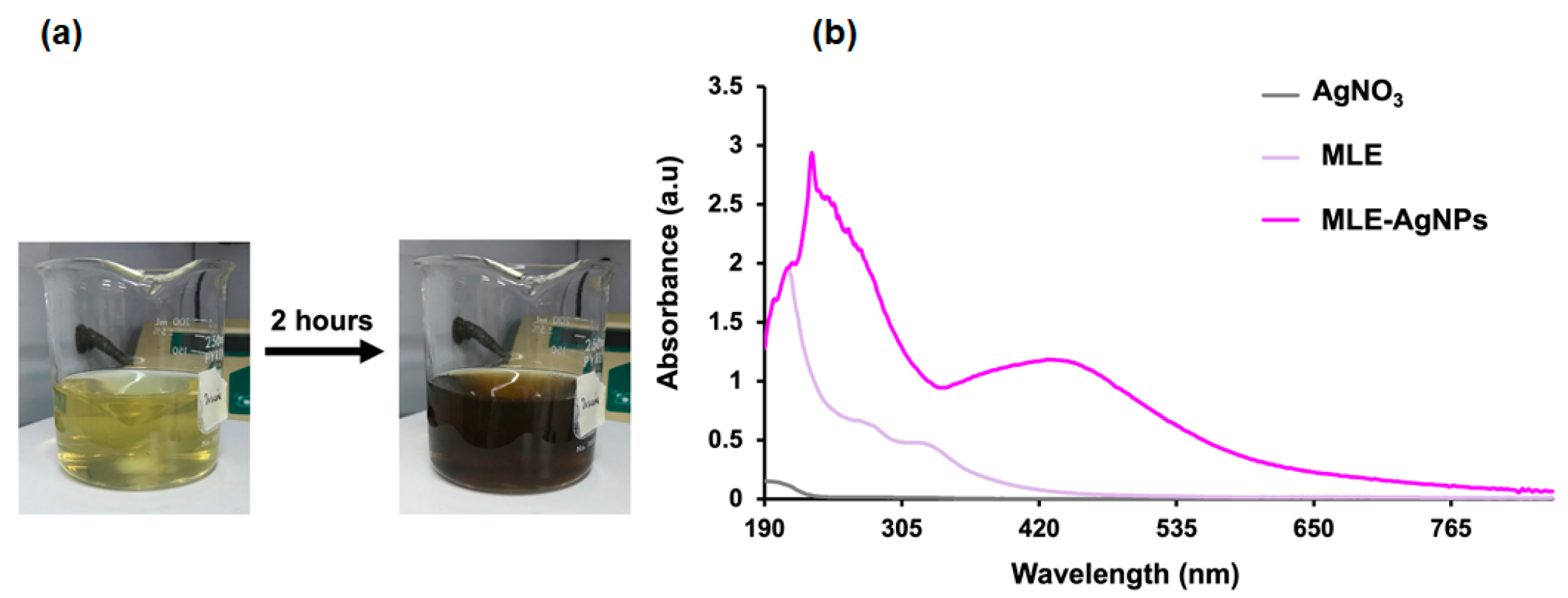
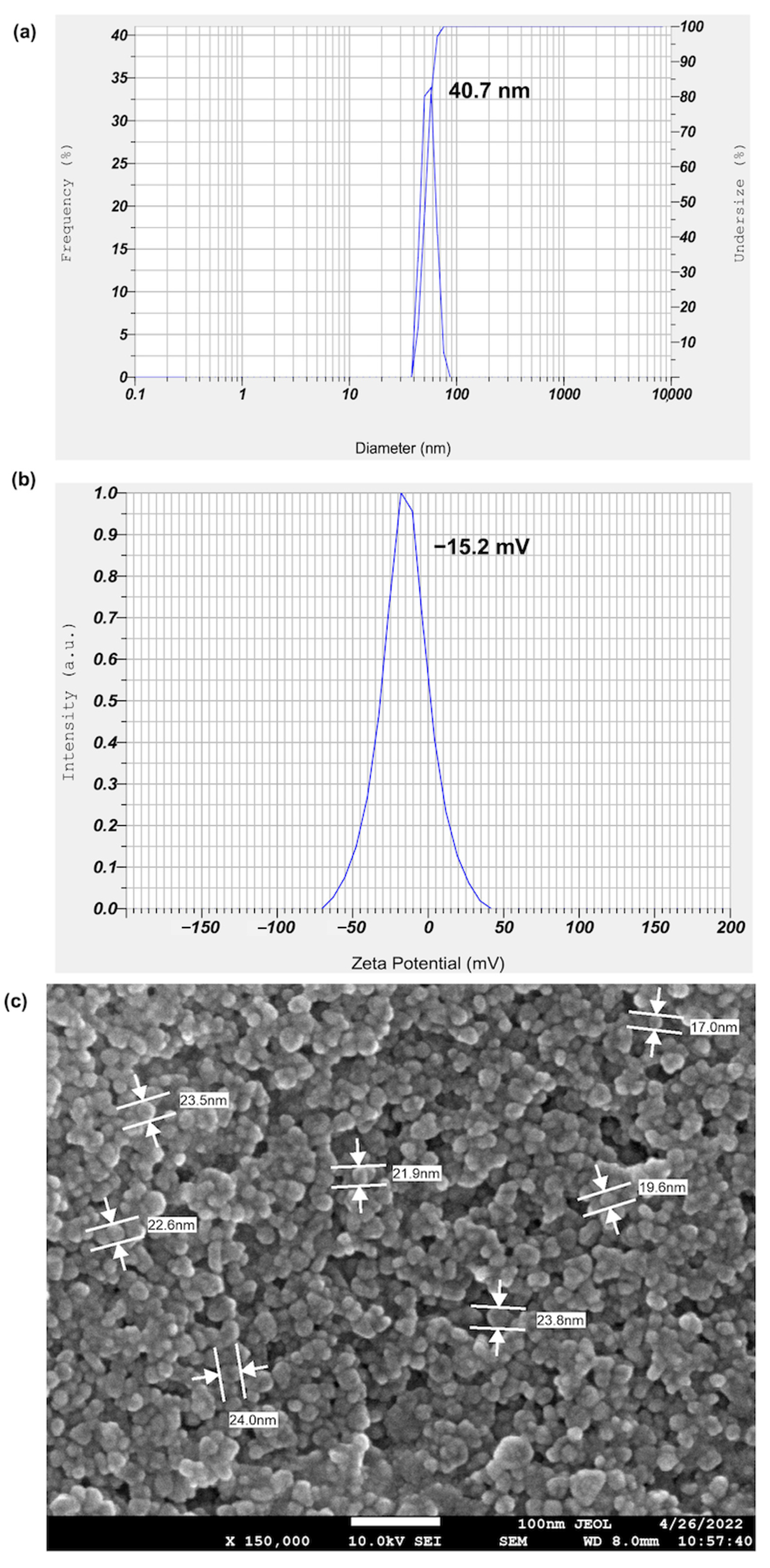
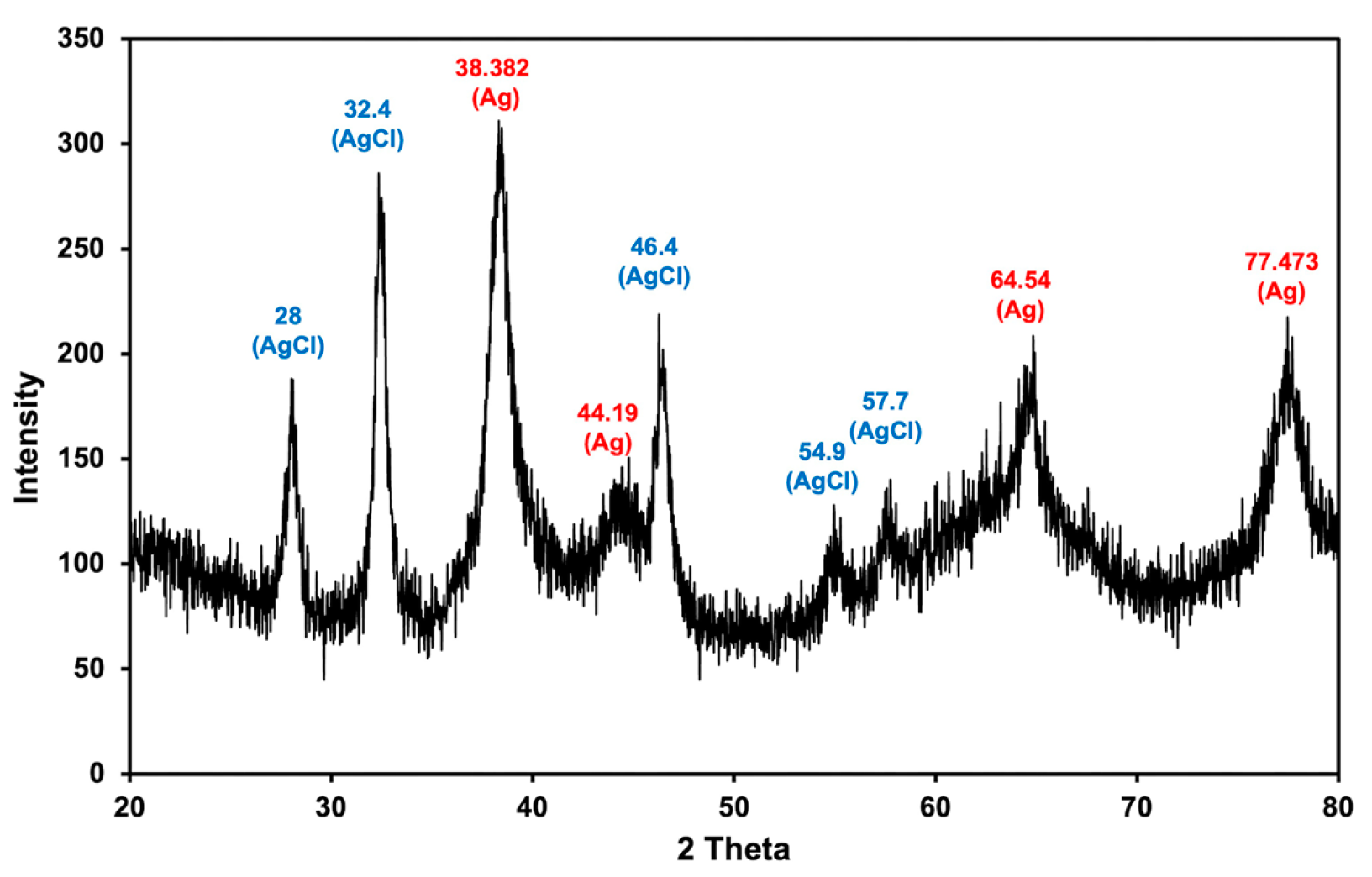
2.2. Biological Synthesis and Characterization of MLE-AgNPs
2.3. MLE-AgNPs Exhibited Antibacterial Activity against Gram-Negative and Gram-Positive Bacteria
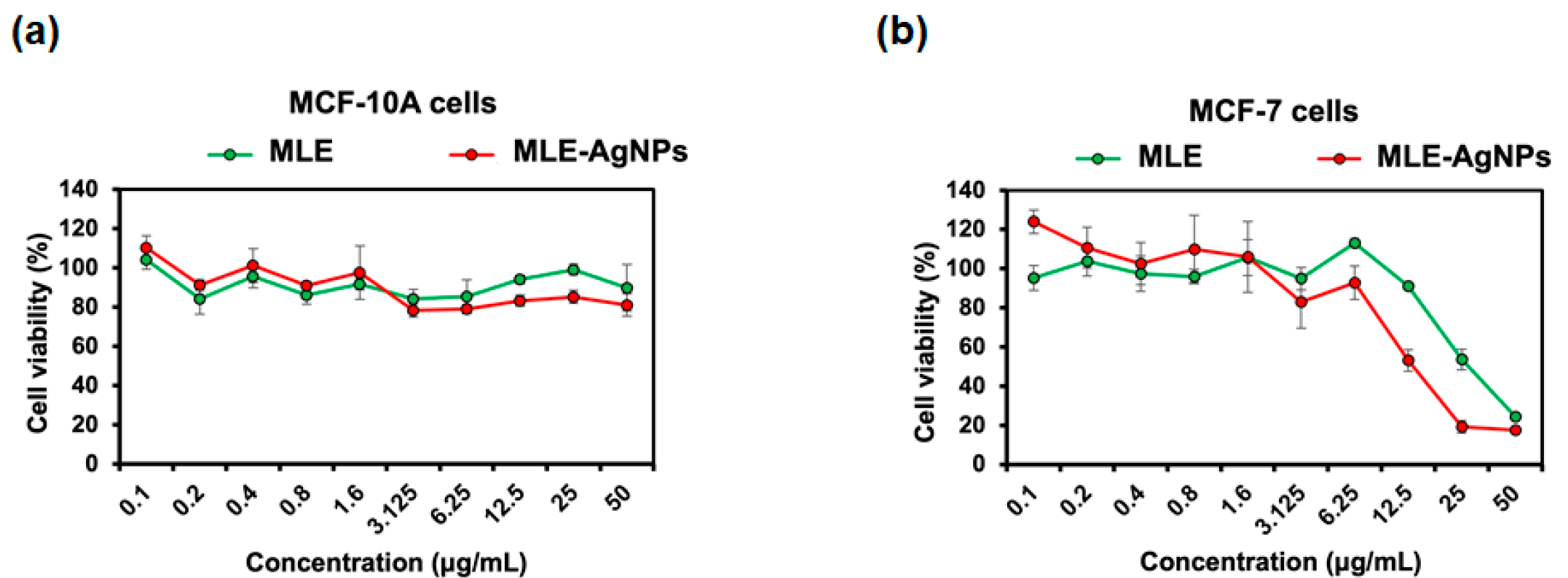
2.4. MLE and MLE-AgNPs Exhibited Anticancer Activity against Breast Cancer Cells
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Bacteria Strains
3.2. Collection and Preparation of Aqueous Extract of Morus alba Leaves
3.3. Gas Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry (GC–MS) Analysis
3.4. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles (MLE-AgNPs)
3.5. Characterization of MLE-AgNPs
3.5.1. UV–Visible Absorbance Spectroscopy
3.5.2. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
3.5.3. Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FE-SEM) Coupled with Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDX), Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR), and X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analyses
3.6. Determination of the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) of MLE and MLE-AgNPs
3.7. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
3.7.1. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
3.7.2. Antiproliferative Analysis
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Pugazhendhi, A.; Edison, T.; Karuppusamy, I.; Kathirvel, B. Inorganic nanoparticles: A potential cancer therapy for human welfare. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 539, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, N.; Gugleva, V.; Dobreva, M.; Pehlivanov, I.; Stefanov, S.; Andonova, V. Silver nanoparticles as multi-functional drug delivery systems. In Nanomedicines; InTech Open: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.; Fawcett, D.; Sharma, S.; Tripathy, S.K.; Poinern, G.E.J. Green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles via biological entities. Materials 2015, 8, 7278–7308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Bulut, O.; Some, S.; Mandal, A.K.; Yilmaz, M.D. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Biomolecule-nanoparticle organizations targeting antimicrobial activity. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 2673–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedefoglu, N.; Zalaoglu, Y.; Bozok, F. Green synthesized ZnO nanoparticles using Ganoderma lucidum: Characterization and in vitro nanofertilizer effects. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 918, 165695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, N.; Muddapur, U. Biosynthesis of metal nanoparticles: A review. J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 2014, 510246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, E.W.-C.; Phui-Yan, L.; Siu-Kuin, W. Phytochemistry, pharmacology, and clinical trials of Morus alba. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2016, 14, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Memete, A.R.; Timar, A.V.; Vuscan, A.N.; Miere Groza, F.; Venter, A.C.; Vicas, S.I. Phytochemical composition of different botanical parts of Morus species, health benefits and application in food industry. Plants 2022, 11, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaipitakwong, T.; Numhom, S.; Aramwit, P. Mulberry leaves and their potential effects against cardiometabolic risks: A review of chemical compositions, biological properties and clinical efficacy. Pharm. Biol. 2018, 56, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, H.Y.; Son, K.H.; Kwon, C.S.; Kwon, G.S.; Kang, S.S. Antimicrobial and cytotoxic activity of 18 prenylated flavonoids isolated from medicinal plants: Morus alba L., Morus mongolica Schneider., Broussnetia papyrifera (L.) Vent, Sophora flavescens Ait and Echinosophora koreensis Nakai. Phytomedicine 2004, 11, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naowaratwattana, W.; De-Eknamkul, W.; De Mejia, E.G. Phenolic-containing organic extracts of mulberry (Morus alba L.) leaves inhibit HepG2 hepatoma cells through G2/M phase arrest, induction of apoptosis, and inhibition of topoisomerase IIα activity. J. Med. Food 2010, 13, 1045–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xiang, L.; Wang, C.; Tang, C.; He, X. Antidiabetic and antioxidant effects and phytochemicals of mulberry fruit (Morus alba L.) polyphenol enhanced extract. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deepa, M.; Sureshkumar, T.; Satheeshkumar, P.K.; Priya, S. Antioxidant rich Morus alba leaf extract induces apoptosis in human colon and breast cancer cells by the downregulation of nitric oxide produced by inducible nitric oxide synthase. Nutr. Cancer 2013, 65, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, A.H.M.K.; Hossain, A.S.M.S.; Khan, M.A.; Kabir, S.R.; Reza, M.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Islam, M.S.; Rahman, M.A.A.; Rashid, M.; Sadik, M.G. The antioxidative fraction of white mulberry induces apoptosis through regulation of p53 and NFκB in EAC cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Mohamad Razali, U.H.; Saikim, F.H.; Mahyudin, A.; Mohd Noor, N.Q.I. Morus alba L. plant: Bioactive compounds and potential as a functional food ingredient. Foods 2021, 10, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, K.B.; Rizvi, S.I. Plant polyphenols as dietary antioxidants in human health and disease. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2009, 2, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, E.W.C.; Wong, S.K.; Tangah, J.; Inoue, T.; Chan, H.T. Phenolic constituents and anticancer properties of Morus alba (white mulberry) leaves. J. Integr. Med. 2020, 18, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Sharma, A.R.; Aniemena, C.; Roedel, K.; Henry, F.; Moussou, P.; Samuga, A.; Medina-Bolivar, F. Elicitation of stilbenes and benzofuran derivatives in hairy root cultures of white mulberry (Morus alba). Plants 2023, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, L.; Iori, R.; Rollin, P.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E. Isothiocyanates: An overview of their antimicrobial activity against human infections. Molecules 2018, 23, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahey, J.W.; Wehage, S.L.; Holtzclaw, W.D.; Kensler, T.W.; Egner, P.A.; Shapiro, T.A.; Talalay, P. Protection of humans by plant glucosinolates: Efficiency of conversion of glucosinolates to isothiocyanates by the gastrointestinal microflora. Cancer Prev. Res. 2012, 5, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.G.; Lee, H.S. Growth-inhibiting activities of phenethyl isothiocyanate and its derivatives against intestinal bacteria. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, M467–M471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traka, M.; Mithen, R. Glucosinolates, Isothiocyanates and human health. Phytochem. Rev. 2009, 8, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patharakorn, T.; Arpornsuwan, T.; Wetprasit, N.; Promboon, A.; Ratanapo, S. Antibacterial activity and cytotoxicity of the leaf essential oil of Morus rotunbiloba Koidz. J. Med. Plant Res. 2010, 4, 837–843. [Google Scholar]
- Erdogan, O.; Abbak, M.; Demirbolat, G.M.; Birtekocak, F.; Aksel, M.; Pasa, S.; Cevik, O. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles via Cynara scolymus leaf extracts: The characterization, anticancer potential with photodynamic therapy in MCF7 cells. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.M. Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using banana peel extract and their antimicrobial activity against representative microorganisms. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2015, 8, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Li, W.; Shi, Q.; Li, H.; Yang, Z.; Liao, D.; Li, L.; Yang, X.; Zhang, J. Synthesis of mulberry leaf extract mediated gold nanoparticles and their ameliorative effect on Aluminium intoxicated and diabetic retinopathy in rats during perinatal life. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2019, 196, 111502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, P.A.; Rana, S.; Verma, G. Making sense of Brownian motion: Colloid characterization by dynamic light scattering. Langmuir 2015, 31, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stetefeld, J.; McKenna, S.A.; Patel, T.R. Dynamic light scattering: A practical guide and applications in biomedical sciences. Biophys. Rev. 2016, 8, 409–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourdikoudis, S.; Pallares, R.M.; Thanh, N.T. Characterization techniques for nanoparticles: Comparison and complementarity upon studying nanoparticle properties. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 12871–12934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, P.; Maheshwari, S.K. Preparation of sliver and selenium nanoparticles and its characterization by dynamic light scattering and scanning electron microscopy. J. Microsc. Ultrastruct. 2018, 6, 182–187. [Google Scholar]
- Syafiuddin, A.; Salmiati Hadibarata, T.; Salim, M.R.; Kueh, A.B.H.; Sari, A.A. A purely green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Carica papaya, Manihot esculenta, and Morinda citrifolia: Synthesis and antibacterial evaluations. Bioprocess. Biosyst. Eng. 2017, 40, 1349–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.S.U.; Salam, A.B.; Yates, C.; Willian, K.; Jaynes, J.; Turner, T.; Abdalla, M.O. Double-receptor-targeting multifunctional iron oxide nanoparticles drug delivery system for the treatment and imaging of prostate cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 6973–6984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riaz Ahmed, K.B.; Nagy, A.M.; Brown, R.P.; Zhang, Q.; Malghan, S.G.; Goering, P.L. Silver nanoparticles: Significance of physicochemical properties and assay interference on the interpretation of in vitro cytotoxicity studies. Toxicol. Vitr. 2017, 38, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, A.K.; Islam, M.R.; Choudhury, Z.S.; Mostafa, A.; Kadir, M.F. Nanotechnology based approaches in cancer therapeutics. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 043001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Singh, N.; Rathi, A.; Kukkar, D.; Rawat, M. Facile approach to synthesize and characterization of silver nanoparticles by using mulberry leaves extract in aqueous medium and its application in antimicrobial activity. J. Nanostruct. 2017, 7, 134–140. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, S.; Mathew, B. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles by microwave irradiation and investigation of their catalytic activity. Res. J. Recent Sci. 2014, 3, 185–191. [Google Scholar]
- Liem, L.N.; The, N.P.; Nguyen, D. Microwave assisted green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using mulberry leaves extract and silver nitrate solution. Technologies 2019, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Raman, J.; Abd Malek, S.N.; John, P.A.; Vikineswary, S. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Ganoderma neo-japonicum Imazeki: A potential cytotoxic agent against breast cancer cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 4399. [Google Scholar]
- Awwad, A.M.; Salem, N.M. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by mulberry leaves extract. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 2, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghkheiratia, E.K.; Bagherieh-Najjar, M.B.; Fadafanb, H.K.; Abdolzadeha, A. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of stable bio-conjugated nanoparticles mediated by walnut (Juglans regia) green husk extract. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2015, 11, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakal, T.C.; Kumar, A.; Majumdar, R.S.; Yadav, V. Mechanistic basis of antimicrobial actions of silver nanoparticles. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer-Jones, M.A.; Mousavi, M.P.S.; Chen, L.D.; Buhlmann, P.; Haynes, C.L. Characterization of silver ion dissolution from silver nanoparticles using fluorous-phase ion-selective electrodes and assessment of resultant toxicity to Shewanella oneidensis. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 2564–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molleman, B.; Hiemstra, T. Surface structure of silver nanoparticles as a model for understanding the oxidative dissolution of silver ions. Langmuir 2015, 31, 13361–13372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dat, N.T.; Binh, P.T.X.; Quynh, L.T.P.; Minh, C.V.; Huong, H.T.; Lee, J.J. Cytotoxic prenylated flavonoids from Morus alba. Fitoterapia 2010, 81, 1224–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepa, M.; Sureshkumar, T.; Satheeshkumar, P.K.; Priya, S. Purified mulberry leaf lectin (MLL) induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in human breast cancer and colon cancer cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2012, 200, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Dar, M.Y.; Joshi, B.; Sharma, B.; Shrivastava, S.; Shukla, S. Phytofabrication of silver nanoparticles: Novel drug to overcome hepatocellular ailments. Toxicol. Rep. 2018, 5, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.-J.; Yi, J.; Kim, Y.; Choi, K.; Park, K. Silver nanoparticles induce cytotoxicity by a Trojan-horse type mechanism. Toxicol. Vitr. 2010, 24, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressan, E.; Ferroni, L.; Gardin, C.; Rigo, C.; Stocchero, M.; Vindigni, V.; Cairns, W.; Zavan, B. Silver nanoparticles and mitochondrial interaction. Int. J. Dent. 2013, 2013, 312747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumai Selvan, D.; Mahendiran, D.; Senthil Kumar, R.; Kalilur Rahiman, A. Garlic, green tea and turmeric extracts-mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Phyto-chemical, antioxidant and in vitro cytotoxicity studies. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2018, 180, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, P.P.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Harsha, S.N.; Policegoudra, R.S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Karak, N.; Chattopadhyay, A. Mentha arvensis (Linn.)-mediated green silver nanoparticles trigger caspase 9-dependent cell death in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells. Breast Cancer Targets Ther. 2017, 9, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathishkumar, G.; Gobinath, C.; Wilson, A.; Sivaramakrishnan, S. Dendrophthoe falcata (L.f) Ettingsh (Neem mistletoe): A potent bioresource to fabricate silver nanoparticles for anticancer effect against human breast cancer cells (MCF-7). Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 128, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonejuie, P.; Burkart, M.; Pogliano, K.; Pogliano, J. Bacterial cytological profiling rapidly identifies the cellular pathways targeted by antibacterial molecules. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 16169–16174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| S. No. | RT (min) | Compound Name | Formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6.953 | Benzoyl isothiocyanate | C8H5NOS |
| 2 | 25.080 | Phenol, 3,5-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl) | C14H22O |
| 3 | 25.554 | 2(4H)-Benzofuranone, 5,6,7,7a tetrahydro-4,4,7a-trimethyl | C11H16O2 |
| 4 | 27.038 | Megastigmatrienone | C13H18O |
| Bacterial Strain | MIC (µg/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| MLE | MLE-AgNPs | ||
| Gram-negative | Acinetobacter baumannii (ATCC 17978) | >64 | 2 |
| Acinetobacter baumannii (ATCC 19606) | >64 | 2 | |
| Escherichia coli (ATCC 25922) | >64 | 32 | |
| Salmonella typhimurium (DMST 562) | >64 | 32 | |
| Gram-positive | Bacillus subtilis (PY59) | >64 | 32 |
| Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 29213) | >64 | 32 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumkoon, T.; Srisaisap, M.; Boonserm, P. Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles Using Morus alba (White Mulberry) Leaf Extract as Potential Antibacterial and Anticancer Agents. Molecules 2023, 28, 1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031213
Kumkoon T, Srisaisap M, Boonserm P. Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles Using Morus alba (White Mulberry) Leaf Extract as Potential Antibacterial and Anticancer Agents. Molecules. 2023; 28(3):1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031213
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumkoon, Tipaporn, Monrudee Srisaisap, and Panadda Boonserm. 2023. "Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles Using Morus alba (White Mulberry) Leaf Extract as Potential Antibacterial and Anticancer Agents" Molecules 28, no. 3: 1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031213
APA StyleKumkoon, T., Srisaisap, M., & Boonserm, P. (2023). Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles Using Morus alba (White Mulberry) Leaf Extract as Potential Antibacterial and Anticancer Agents. Molecules, 28(3), 1213. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031213








