Molecular Dynamics Investigation of Wettability Alteration of Quartz Surface under Thermal Recovery Processes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Methodology
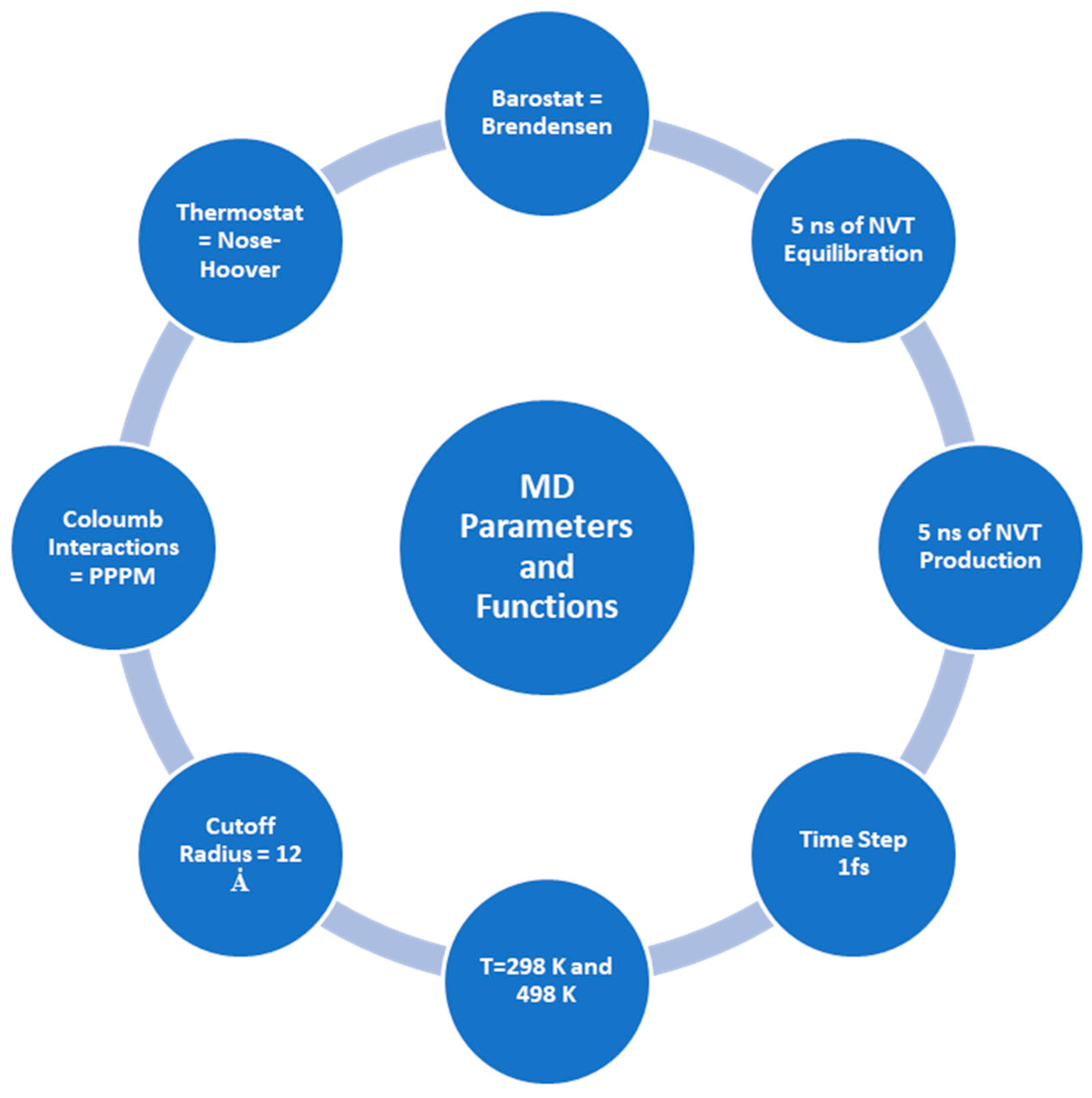
3.1. Force Field and Simulation Initialization
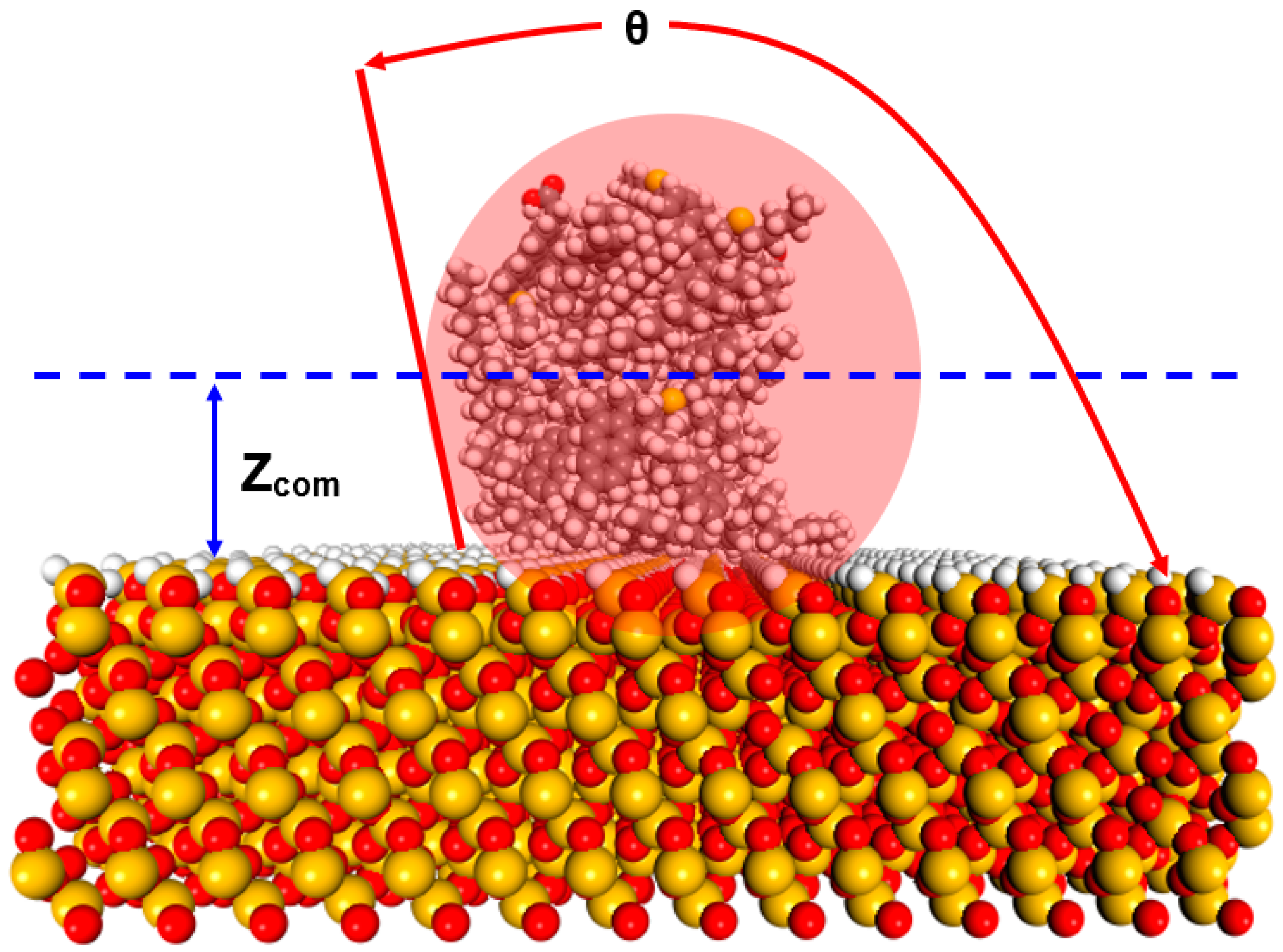
3.2. Contact Angle Calculations
3.3. Adsorption Energy (AE)
4. Conclusions
- Increasing the temperature from the ambient temperature (298 K) to a typical steam chamber temperature (498 K) can significantly increase the adsorption energy between heavy oil droplets and the quartz surface. In other words, heavy oil droplets tend to adsorb onto the quartz surface at higher temperatures than ambient conditions.
- Increasing the asphaltene content of the heavy oil can also increase the adsorption energy significantly, and this behavior was intensified at a higher temperature. However, the rate of change of the adsorption energy is not linearly correlated with the asphaltene content of the heavy oil.
- According to the adsorption energy calculations, a coulombic interaction was the main contributor to an adsorption process due to the polarity of the asphaltene and resin molecules since they have heteroatoms in their structures.
- Based on the contact angle calculations, at ambient temperature, a quartz surface tends to be water-wet due to the lower adsorption energy of the heavy oil at that temperature; however, at temperatures well beyond the water boiling temperature, the quartz surface became more oil-wet thanks to higher energy adsorption.
- The results of this study are specific to the quartz surfaces and one type of asphaltene and resin; further research may be needed to understand the wettability alteration on different rock types and various types of asphaltenes and resins.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mohr, S.; Wang, J.; Ellem, G.; Ward, J.; Giurco, D. Projection of world fossil fuels by country. Fuel 2015, 141, 120–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Chen, Z. Challenges and future of chemical assisted heavy oil recovery processes. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 275, 102081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.; Fishwick, R.; Wood, J.; Leeke, G.; Rigby, S.; Greaves, M. A review of novel techniques for heavy oil and bitumen extraction and upgrading. Energy Environ. Sci. 2010, 3, 700–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huc, A.-Y. Heavy Crude Oils: From Geology to Upgrading: An Overview; Technip: Paris, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, K.; Li, H.; Yu, Z. In-situ heavy and extra-heavy oil recovery: A review. Fuel 2016, 185, 886–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Liu, H.; Chen, Z.; Wu, K.; Lu, N.; Zhang, Q. Enhanced oil recovery techniques for heavy oil and oilsands reservoirs after steam injection. Appl. Energy 2019, 239, 1190–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J. Enhanced Oil Recovery Field Case Studies; Gulf Professional Publishing: Houston, TX, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Nie, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, B.; Wu, W.; Chen, Z. A critical review of reservoir simulation applications in key thermal recovery processes: Lessons, opportunities, and challenges. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 7387–7405. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Li, X.; Fang, Z.; Wei, N.; Li, Q. Small-molecule gas sorption and diffusion in coal: Molecular simulation. Energy 2010, 35, 2939–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Z.; Wang, S.; Peng, F.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y. Dissipative particle dynamics investigation of microencapsulated thermal energy storage phase change materials. Energy 2012, 44, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raaen, S.; Ramstad, A. Monte-Carlo simulations of thermal desorption of adsorbed molecules from metal surfaces. Energy 2005, 30, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjelstrup, S.; Bedeaux, D.; Inzoli, I.; Simon, J.-M. Criteria for validity of thermodynamic equations from non-equilibrium molecular dynamics simulations. Energy 2008, 33, 1185–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, S.; Tao, W. A study on thermodynamic and transport properties of carbon dioxide using molecular dynamics simulation. Energy 2019, 179, 1094–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klonos, P.A.; Goncharuk, O.V.; Pakhlov, E.M.; Sternik, D.; Deryło-Marczewska, A.; Kyritsis, A.; Gun’ko, V.M.; Pissis, P. Morphology, molecular dynamics, and interfacial phenomena in systems based on silica modified by grafting polydimethylsiloxane chains and physically adsorbed polydimethylsiloxane. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 2863–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Lu, G.; Shao, C.; Li, X. Molecular dynamics simulation of hydrocarbon molecule adsorption on kaolinite (0 0 1) surface. Fuel 2019, 237, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.-L.; Gao, S.; Jiang, Z.-W.; Su, D.; Liu, G.-S. Monolayer adsorption of dodecylamine surfactants at the mica/water interface. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2014, 114, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestri, A.; Ataman, E.; Budi, A.; Stipp, S.; Gale, J.D.; Raiteri, P. Wetting Properties of the CO2–Water–Calcite System via Molecular Simulations: Shape and Size Effects. Langmuir 2019, 35, 16669–16678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perilla, J.R.; Goh, B.C.; Cassidy, C.K.; Liu, B.; Bernardi, R.C.; Rudack, T.; Yu, H.; Wu, Z.; Schulten, K. Molecular dynamics simulations of large macromolecular complexes. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2015, 31, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ziebarth, J.; Wang, Y. Molecular dynamics simulations of DNA-polycation complex formation. Biophys. J. 2009, 97, 1971–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.-L.; Tu, J.-F. Characterizing mechanical properties of graphite using molecular dynamics simulation. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 194–199. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, J.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Hu, S.; Zhang, J. Adsorption mechanism of oil components on water-wet mineral surface: A molecular dynamics simulation study. Energy 2013, 59, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikjoo, H.; O’Neill, P.; Wilson, W.; Goodhead, D. Computational approach for determining the spectrum of DNA damage induced by ionizing radiation. Radiat. Res. 2001, 156, (577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Miller, J. A molecular dynamics simulation study of water structure and adsorption states at talc surfaces. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2007, 84, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hu, Y.; Sun, W.; Sun, Y. Molecular dynamics simulation study of the interaction of mixed cationic/anionic surfactants with muscovite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 327, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepehrinia, K.; Mohammadi, A. Wettability alteration properties of fluorinated silica nanoparticles in liquid-loaded pores: An atomistic simulation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 371, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yao, G.; Ramisetti, S.B.; Hammond, R.B.; Wen, D. Molecular dynamics investigation of substrate wettability alteration and oil transport in a calcite nanopore. Fuel 2019, 239, 1149–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S.; Li, B. Effects of hydrophilic groups of nonionic surfactants on the wettability of lignite surface: Molecular dynamics simulation and experimental study. Fuel 2018, 231, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naser, M.A.; Permadi, A.K.; Bae, W.; Ryoo, W.S.; Yunsun, P.; Dang, S.T.; Kim, S. Steam-Induced Wettability Alteration Through Contact Angle Measurement, a Case Study in X Field, Indonesia. Proceedings of the SPE International Heavy Oil Conference and Exhibition, Mangaf, Kuwait, 8–10 December 2014, OnePetro: Richardson, TX, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tipler, P.A.; Mosca, G. Physics for scientists and engineers. Macmillan: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Yaseen, S.; Mansoori, G.A. Molecular dynamics studies of interaction between asphaltenes and solvents. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2017, 156, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Chen, Z. Comprehensive molecular scale modeling of anionic surfactant-asphaltene interactions. Fuel 2021, 288, 119729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BIOVIA, D.S. Materials Studio, 2020th ed.; Dassault Systèmes: San Diego, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Ren, P.; Fried, J. The COMPASS force field: Parameterization and validation for phosphazenes. Comput. Theor. Polym. Sci. 1998, 8, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H. COMPASS: An ab initio force-field optimized for condensed-phase applications overview with details on alkane and benzene compounds. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 7338–7364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkermans, R.L.; Spenley, N.A.; Robertson, S.H. COMPASS III: Automated fitting workflows and extension to ionic liquids. Mol. Simul. 2021, 47, 540–551. [Google Scholar]
- Pacheco-Sánchez, J.; Zaragoza, I.; Martínez-Magadán, J. Asphaltene aggregation under vacuum at different temperatures by molecular dynamics. Energy Fuels 2003, 17, 1346–1355. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, S.-M.; Liu, Q.-K.; Wang, K.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, P.-Q.; Cheng, Z.-M.; Yuan, W.-K. Solvation of asphaltenes in supercritical water: A molecular dynamics study. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 146, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunte, S.W.; Sun, H. Molecular modeling of energetic materials: The parameterization and validation of nitrate esters in the COMPASS force field. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 2477–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQuaid, M.J.; Sun, H.; Rigby, D. Development and validation of COMPASS force field parameters for molecules with aliphatic azide chains. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Hou, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z. Interfacial and molecular interactions between fractions of heavy oil and surfactants in porous media: Comprehensive review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 102242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Jin, Z.; Yang, C.; Akkermans, R.L.; Robertson, S.H.; Spenley, N.A.; Miller, S.; Todd, S.M. COMPASS II: Extended coverage for polymer and drug-like molecule databases. J. Mol. Model. 2016, 22, (2), 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; LeBoeuf, E.J. A molecular dynamics study of natural organic matter: 1. Lignin, kerogen and soot. Org. Geochem. 2009, 40, 1132–1142. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.; Zhu, X.; Ji, H.; Chen, D. Molecular modeling of interactions between heavy crude oil and the soil organic matter coated quartz surface. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuefen, Z.; Guiwu, L.; Xiaoming, W.; Hong, Y. Molecular dynamics investigation into the adsorption of oil–water–surfactant mixture on quartz. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 6493–6498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; He, L.; Chen, D. Sorption and distribution of asphaltene, resin, aromatic and saturate fractions of heavy crude oil on quartz surface: Molecular dynamic simulation. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 1465–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Chen, Z. Molecular dynamics simulation of oil detachment from hydrophobic quartz surfaces during steam-surfactant Co-injection. Energy 2022, 254, 124434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xue, Q.; Zhu, L.; Jin, Y.; Wu, T.; Guo, Q.; Zheng, H.; Lu, S. How to select an optimal surfactant molecule to speed up the oil-detachment from solid surface: A computational simulation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 147, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Fang, T.; Xiong, W.; Ding, B.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, J. Oil detachment by modified nanoparticles: A molecular dynamics simulation study. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2019, 170, 109177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Zhang, H.; Liang, S.; Zhao, S.; Guo, Z.; Hang, Y. Behavior of carbon nanotube-asphalt composites for dioxide capture based on molecular simulation. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2022, 802, 139756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Chan, M.; Froehlich, W. Steam injection pressure and the sagd ramp-up process. J. Can. Pet. Technol. 2009, 48, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.; Polikar, M. New economic indicator to evaluate SAGD performance. Proceedings of the SPE Western Regional Meeting, Irvine, CA, USA, 30 March–1 April 2005, Society of Petroleum Engineers: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hautman, J.; Klein, M.L. Microscopic wetting phenomena. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1991, 67, 1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treiber, L.; Owens, W. A laboratory evaluation of the wettability of fifty oil-producing reservoirs. Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 1972, 12, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Liu, G.; Xing, X.; Chen, L.; Lu, X.; Teng, H.; Wang, J. Molecular dynamics simulation of CO2 dissolution in heavy oil resin-asphaltene. J. CO2 Util. 2019, 33, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
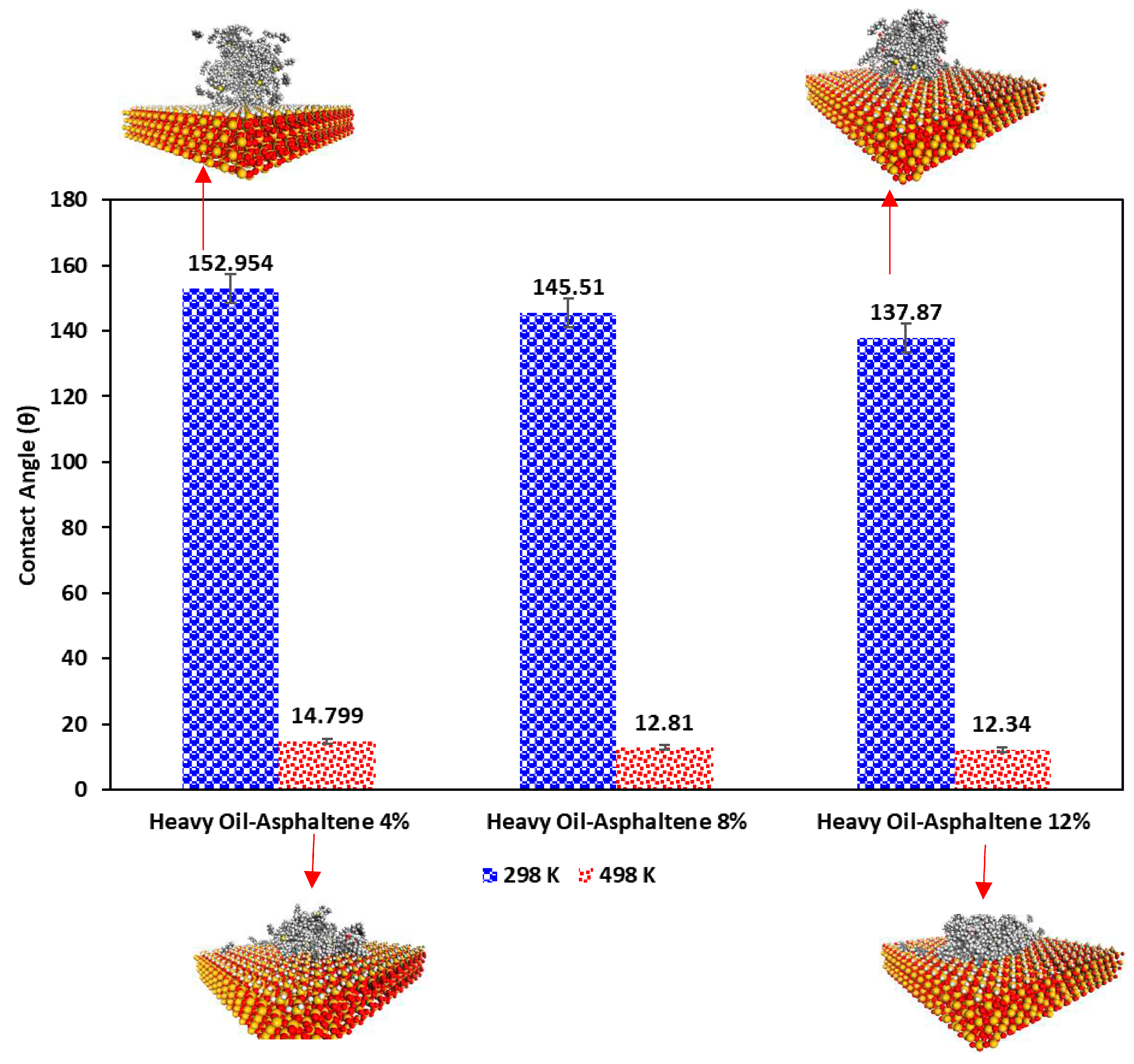
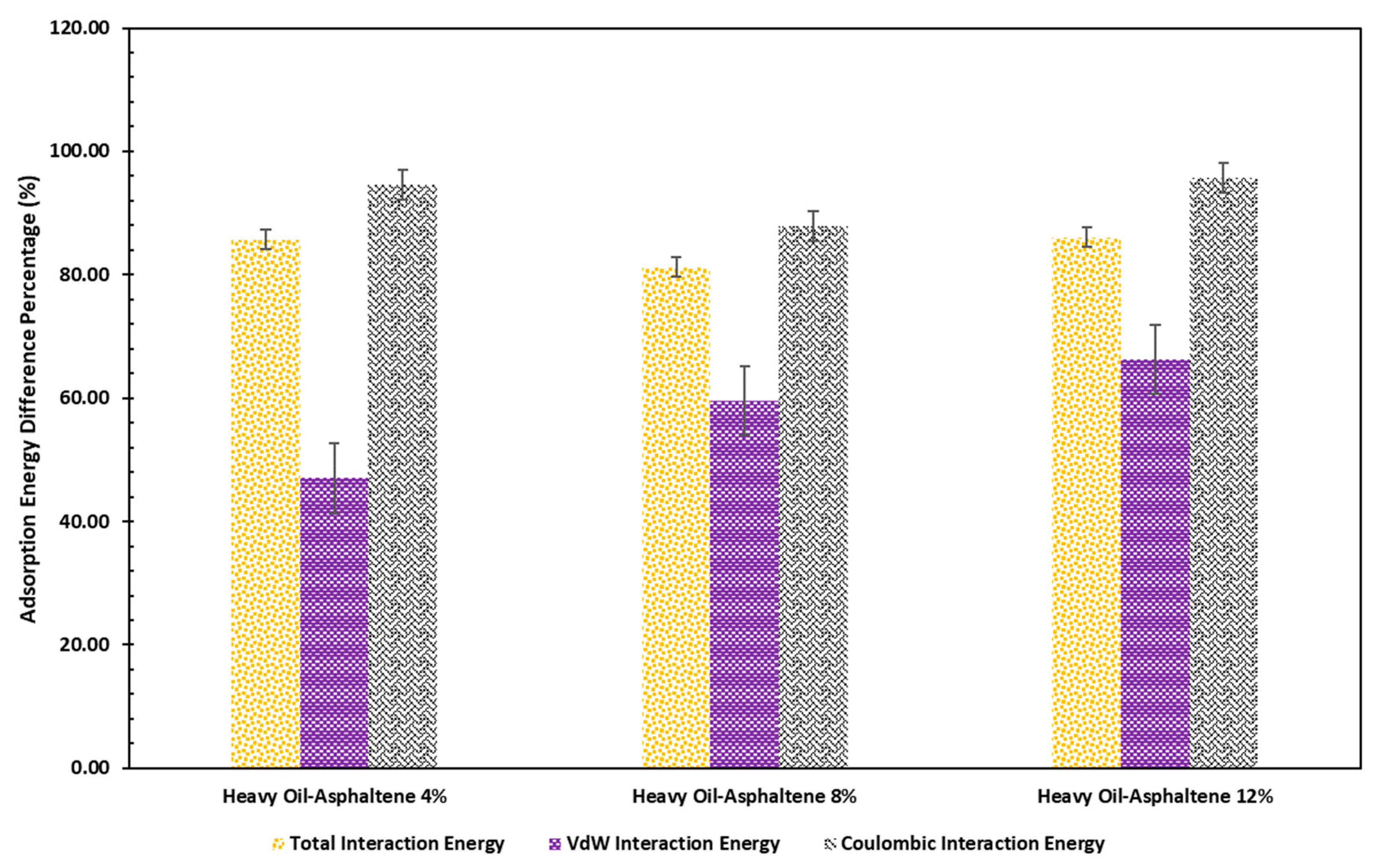

| Temperature (K) | EAdsorption (Kcal/mol) | Evdw (Kcal/mol) | Ecoulombic (Kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy Oil with 4% Asphaltene | |||
| 298 | −1308.71 | −285.65 | −991.33 |
| 498 | −2430.74 | −419.99 | −1929.02 |
| Heavy Oil with 8% Asphaltene | |||
| 298 | −1423.86 | −306.18 | −1096.85 |
| 498 | −2580.69 | −488.59 | −2061.27 |
| Heavy Oil with 12% Asphaltene | |||
| 298 | −1484.39 | −320.82 | −1144.11 |
| 498 | −2762.26 | −533.33 | −2239.47 |
| Heptane | Toluene | Resin | Asphaltene | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy Oil ID | 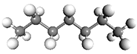 | 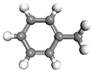 | 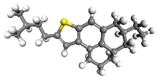 |  |
| 4% Asphaltene | 120 | 120 | 30 | 3 |
| 8% Asphaltene | 120 | 120 | 30 | 5 |
| 12% Asphaltene | 120 | 120 | 30 | 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmadi, M.; Chen, Z. Molecular Dynamics Investigation of Wettability Alteration of Quartz Surface under Thermal Recovery Processes. Molecules 2023, 28, 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031162
Ahmadi M, Chen Z. Molecular Dynamics Investigation of Wettability Alteration of Quartz Surface under Thermal Recovery Processes. Molecules. 2023; 28(3):1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031162
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmadi, Mohammadali, and Zhangxin Chen. 2023. "Molecular Dynamics Investigation of Wettability Alteration of Quartz Surface under Thermal Recovery Processes" Molecules 28, no. 3: 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031162
APA StyleAhmadi, M., & Chen, Z. (2023). Molecular Dynamics Investigation of Wettability Alteration of Quartz Surface under Thermal Recovery Processes. Molecules, 28(3), 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031162







