Abstract
Neurodegenerative diseases are associated with oxidative stress, due to an imbalance in the oxidation-reduction reactions at the cellular level. Various treatments are available to treat these diseases, although they often do not cure them and have many adverse effects. Therefore, it is necessary to find complementary and/or alternative drugs that replace current treatments with fewer side effects. It has been demonstrated that natural products derived from plants, specifically phenolic compounds, have a great capacity to suppress oxidative stress and neutralize free radicals thus, they may be used as alternative alternative pharmacological treatments for pathological conditions associated with an increase in oxidative stress. The plant species that dominate the Mediterranean ecosystems are characterized by having a wide variety of phenolic compound content. Therefore, these species might be important sources of neuroprotective biomolecules. To evaluate this potential, 24 typical plant species of the Mediterranean ecosystems were selected, identifying the most important compounds present in them. This set of plant species provides a total of 403 different compounds. Of these compounds, 35.7% are phenolic acids and 55.6% are flavonoids. The most relevant of these compounds are gallic, vanillic, caffeic, chlorogenic, p-coumaric, and ferulic acids, apigenin, kaempferol, myricitrin, quercetin, isoquercetin, quercetrin, rutin, catechin and epicatechin, which are widely distributed among the analyzed plant species (in over 10 species) and which have been involved in the literature in the prevention of different neurodegenerative pathologies. It is also important to mention that three of these plant species, Pistacea lentiscus, Lavandula stoechas and Thymus vulgaris, have most of the described compounds with protective properties against neurodegenerative diseases. The present work shows that the plant species that dominate the studied geographic area can provide an important source of phenolic compounds for the pharmacological and biotechnological industry to prepare extracts or isolated compounds for therapy against neurodegenerative diseases.
1. Introduction
1.1. Brief Description of Neurodegenerative Diseases and Their Causes
Neurodegenerative diseases, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, sarcopenia, and cancer are associated with the “free radical theory” of aging [1,2,3]. This theory is based on the structural damage-based hypothesis claiming that tissue dysfunction due to aging can be attributed to the accumulation of oxidative damage of macromolecules by free radicals [1]. Oxidative stress results from an imbalance in reduction and oxidation reactions at the cellular level. The consequence of this imbalance is the formation of reactive oxygen or nitrogen species (ROS/RNS) and sometimes it can be attributed to a decrease in the level of antioxidant defense [4,5]. In particular, the excessive production of ROS contributes to oxidative stress leading to neuronal cell death and an alteration of brain function [2,6]. The central nervous system is vulnerable to oxidative stress since it has a large requirement for oxygen and has a lower amount of antioxidant enzymes, compared with other tissues [7,8].
Harman et al. [1] extended the “free radical theory” of aging to the “mitochondrial theory of aging”, which states that ROS accumulation induces mitochondrial dysfunction, which contributes to aging and the development of related diseases [9,10,11]. Over the last decade, a connection between mitochondria and longevity has become increasingly evident. Mitochondria are also regulators of some types of cell death, such as apoptosis, and thus, their mitochondrial dysfunction might affect the lifespan of individuals presenting defects in this organelle [11].
Neurodegenerative diseases are frequently associated with neuroinflammation, which is a process related to oxidative and nitrosative stress. The inflammatory response is further propagated by the activation of glial cells and the modulation of constitutively expressed extracellular matrix proteins [12,13].
Many neurodegenerative diseases have been described to be highly prevalent in the population and have a high socioeconomic impact. Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Parkinson’s disease (PD), Huntington’s disease (HD), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and frontotemporal dementia are some examples [14,15]. All these diseases, specifically AD and PD, are associated with high morbidity and mortality and represent a primary health problem, especially in the aged population [16]. These disorders share common pathological characteristics, such as the induction of oxidative stress, abnormal protein aggregation, perturbed Ca2+ homeostasis, excitotoxicity, inflammation and apoptosis [17,18].
AD is a progressive neurological condition and the world’s most common form of dementia [19]. The pathological characteristics include extracellular deposits of amyloid β, (Aβ), intracellular formation of neurofibrillary tangles and loss of neuronal synapses and pyramidal neurons [20]. Aβ deposits derive from amyloid precursor protein and the neurofibrillary tangles containing an abnormally phosphorylated form of tau, which is a microtubule-associated protein [21]. A growing body of research supports that Aβ aggregation and decreased Aβ clearance are the leading causes of this disease onset.
Different studies indicate that oxidative stress plays a fundamental role in the development and evolution of AD. For example, elevated ROS production has been shown to initiate toxic amyloid beta precursor protein processing, thereby triggering Aβ generation [22]. These ROS are primarily generated via NADPH oxidase 2, which is well associated with inflammation and amyloid plaque deposition, leading to mitochondrial dysfunction and decreased glutathione levels. Neurons contain a high amount of polyunsaturated fatty acids that can interact with ROS, leading to a self-propagating cascade of lipid peroxidation and molecular destruction [23]. Products of lipid peroxidation have also been shown to be elevated in blood samples and brains of AD patients at autopsy [24]. It has also been correlated with the initial stage of the disease DNA oxidative damage in the AD brains, due to increased expression of ERCC-80 and 89 genes related to DNA repair activity [25].
On the other hand, the “cholinergic hypothesis of AD” is based on acetylcholine deficiency [26,27]. This neurotransmitter is involved in cognition and memory processes that are known to be decreased in AD. Thus, cholinesterase inhibitors are the first line of therapy for the management of AD [28,29].
PD is the second most common age-related neurodegenerative disorder in the central nervous system. This disease is a clinical syndrome characterized by motor impairments, including bradykinesia, resting tremor, muscle rigidity, loss of postural reflexes, freezing phenomenon and flexed posture. PD involves the loss of dopaminergic neurons of the pars compacta region of the substantia nigra and the accumulation of intracellular proteins (synucleins), leading to cognitive and motor deterioration in people who suffer from it [30,31,32,33].
It is possible that processes, such as oxidation, may be responsible for the gradual dysfunction that can be manifested throughout the disease. Previous publications have reported evidence of this oxidative stress through the detection of oxidized DNA, lipids, and proteins in the brain tissues of PD patients [34]. Dopaminergic neurons contain large amounts of ROS derived from dopamine’s enzymatic and non-enzymatic metabolism. Dopamine may be catabolized by monoamine oxidase (MAO) in a process that generates 3,4-dihydroxyphenyl-acetaldehyde, ammonia and H2O2, which reacts with Fe2+ to form hydroxyl radical. In addition, dopamine oxidation may spontaneously generate 6-hydroxydopamine, which is subsequently transformed into reactive electrophilic molecules in the presence of oxygen [35]. On the other hand, several studies suggest that the overexpression or misfolding of α-synuclein increases ROS production and cell susceptibility to oxidative stress [36,37].
In general, the treatments for neurodegenerative diseases tend to be limited in their therapeutic approach, due to their symptom management but non-curative nature [38], and the continuous use of certain conventional drugs generates many adverse effects, such as nausea, diarrhea, eating disorders and kidney and liver affectations [39]. Therefore, it is necessary to find complementary and/or alternative treatments. Several clinical trials have proved the implication of natural products as antioxidant agents (e.g., ferulic and p-coumaric acids, resveratrol, catechin, epi-catechin, quercetin, ginsenosides.) [40,41,42,43] and, given the role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases, these compounds can be a good therapeutic alternative against these diseases.
1.2. Phenolic Compounds: Their Importance and Implication in Neurodegenerative Diseases
Many studies have focused on natural phytocomponents as important bioactive molecules against aging-related chronic diseases, including neurodegenerative diseases [44,45,46]. The wide and countless number of natural compounds from plants, animals, fungi and microorganisms provide a rich and unique source for new drug search [47], with plants being the main source of these compounds. In most cases, the biological activity attributed to plant extracts derives from secondary metabolites, which include two extensive categories: nitrogen-containing and non-nitrogen-containing compounds [48,49]. In the latter category, phenols are one of the most extensive groups of secondary metabolites in the plant kingdom [50]. Structurally, they are characterized by the presence of at least one hydroxyl functional group (-OH) linked to an aromatic ring [51]. Polyphenol classification is based on the number of phenol rings in the molecule, and the main subgroups include phenolic acids, coumarins, stilbenes, flavonoids, tannins and lignans [50]. These compounds exert different biological activities, including antioxidant, antiallergic, anti-inflammatory, antiviral, antiproliferative and anticarcinogenic effects [52,53].
One of the most remarkable functions of phenols is their capacity to suppress oxidative stress and neutralize free radicals. They can act as reducing agents, metal chelators, free-radical scavengers, enzyme modulators and regulators of diverse proteins and transcriptional factors (Figure 1) [54,55]. The antioxidant potential of these compounds confers therapeutic activities for a wide variety of diseases, such as cardiovascular diseases, cancer, liver diseases, diabetes and neurodegenerative disorders [56,57].
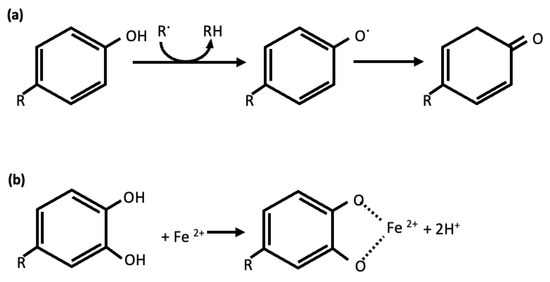
Figure 1.
Mechanism of scavenging of ROS (a) and metal chelation (b) by phenolic compounds antioxidants.
It has been demonstrated that phenols can inhibit the aggregation of proteins involved in various neurodegenerative pathologies in which cognitive deterioration occurs, including AD, PD, dementia with Lewy bodies, and multiple system atrophy [58]. In fact, studies conducted with flavonoids show that these compounds would be involved in preventing neurodegeneration [59]. Their bioactivity is attributed to their antioxidant effect and their capacity to inhibit acetylcholinesterase (AChE)/butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) [19] and the GABA receptor [60], alleviate mitochondrial dysfunction [61], modulate neuronal signaling pathways critical for the control of neuronal resistance to neurotoxic oxidants, inhibition inflammatory mediators [62] and chelation of transition metal ions [59].
It has been shown that the interaction of flavonoids with these receptors depends on the structure [63], implying that not all phenols have the same activity and importance as agents to prevent or treat neurodegenerative diseases. It has been suggested that B-ring hydroxylation is a differentiating element in the action exerted by flavonoids, particularly the positive contribution of 5-dehydroxylation and 3′,4′-ortho-dihydroxylation on the B-ring [64]. Furthermore, a study on flavonoid-PI3-kinase interaction has further confirmed the pivotal role of B-ring hydroxylation [65], and highly sensitive allosteric modulation has been proposed [60].
Other studies have reported the direct involvement of phenolic compounds in preventing various pathologies associated with oxidative stress. One of these compounds is resveratrol, a phenol that can directly target multiple signaling cascades involved in neurodegenerative diseases, such as anti-inflammatory activity and inhibiting the aggregation of toxic Aβ amyloid protein [66]. Another example is 3,4,5–trihydroxybenzoic acid, a phenol that inhibits the plasma membrane Pdr5p efflux pump in AD124567 yeast strain overexpressing the PDR5 gene [67]. Another study demonstrated that 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde represses translation in yeast, as concluded by the accumulation of processing bodies and stress granules composed of non-translating mRNAs and proteins after 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde exposure [68].
In studies conducted in Saccharomyces, Sunthonkun et al. [69] observed the positive effects of 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid against aging. In this sense, 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid positively modulated the life span of Saccharomyces by reducing ROS, conferring cells greater resistance against free radicals. According to these authors, regarding the reduction of ROS levels, 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid seems to imitate the effect of the inactivation of proteins such as Sir2 (silent information regulator 2), Tor1 (protein kinase) or Sch9 (protein kinase).
Considering all this information and the multifactor origin of neurodegenerative disorders, it is interesting and necessary to delve into the study of natural multitarget compounds and their bioavailability [70,71].
Mediterranean ecosystems show a great diversity of plant species derived from the specific climatic conditions and the heterogeneity of their habitats [72]. The species that dominate these habitats endure harsh conditions due to the frequency of wild fires, high temperatures, water stress in summer and herbivory [73]. These unfavorable conditions stimulate the production of compounds derived from secondary metabolism, specifically phenolic compounds [74,75], which play an important ecological role in the adaptive response to these unfavorable conditions. Therefore, the species of these ecosystems may constitute an important and diverse source of compounds that should be studied.
This work aimed to evaluate the potential of Mediterranean shrub species as a source of phenolic compounds. To this end, we selected the shrub species that dominate a particular geographic area of the Iberian Peninsula.
2. Description of the Study Area and Article Search Strategy
The study area selected was Extremadura, a region of the Western Iberian Peninsula with a surface of 41,635 km2. From a biogeographic perspective, it is in the Mediterranean region and is characterized by a diverse set of plant associations that result from the interaction of its biotic and abiotic factors. The bioclimatic floors and levels that may be found in the region of Extremadura are mesomediterranean, supramediterranean and orosubmediterranean [76], and they are associated with a rainfall of 200–2000 mm/year and an average annual temperature of 4–19 °C. These conditions are responsible for the wide variability of the plant landscape of this region, which is represented by the vegetation sets described in “Plant Landscape and Dynamics in Extremadura” [77], with the following dominating shrub formations: orophilous laburnum and creeping juniper, heath and rock rose, broom and rotem, thyme and cantuesar, gorse and basophilic rock rose, wild olive and mastic, strawberry tree, arborescent juniper, kermes oaks, and garrigues and thorny bushes (brambles and thorns). These groupings are characterized and dominated by the following 24 species: Cistus ladanifer, Cistus salviifolius, Cistus monspeliensis, Cistus crispus, Cistus albidus, Cistus populifoius, Cytisus multiflorus, Cytisus scoparius, Cytisus striatus, Erica multiflora, Erica scoparia, Erica australis, Calluna vulgaris, Myrtus communis, Pistacea lentiscus, Pistacea terebinthus, Rosmarinus officinalis, Quercus ilex, Quercus suber, Arbutus unedo, Lavandula stoechas, Thymus mastichina, Thymus vulgaris and Rubus ulmifolius.
In this study, we reviewed the works conducted on the identification of phenolic compounds in the 24 selected species. The data reflect the compounds identified in studies published between 1996 and 2022 in the Pubmed, ScienceDirect and Scopus databases. We selected the articles where the identification of these compounds was supported, at least, by techniques such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)–photodiode array detection (DAD)–mass spectrometry (MS), which provide reliable information about the constitution of phenolic compounds. Articles that were not available in full-text were not considered. Moreover, articles without a clear experimental procedure were also excluded.
3. Description and Classification of the Phenolic Compounds Present in the Selected Species
Table 1 presents the list of phenolic compounds that have been identified by different authors in the 24 species selected for this study. A total of 403 different phenolic compounds can be found in this entire set of species. These compounds belong to different classes or groups: phenolic acids, flavonoids, other polyphenols, lignans and stilbenes. Each of these groups accounts for 35.7%, 55.6%, 5.7%, 2% and 0.7%, respectively (Table 2). As can be observed, the largest group is constituted by flavonoids; thus, these species are an important and diverse source of these phenols.

Table 2.
Number and percentage of phenolic compounds, grouped by class and subclass, found in the 24 species selected in this study.

Table 1.
Phenolic compounds identified in the 24 species selected in this study.
Table 1.
Phenolic compounds identified in the 24 species selected in this study.
| Species | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cl | Cs | Cm | Cc | Ca | Cp | Cym | Cys | Cyst | Em | Es | Ea | Cv | Mc | Pl | Pt | Ro | Qi | Qs | Au | Ls | Tm | Tv | Ru | |
| Class: Phenolic acid. Sub Class: Hydroxybenzoic acids | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Acetovanillone | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Anisic acid | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Benzoic acid | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Benzyl benzoate | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Methyl benzoate | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Castalagin | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cornusilin | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-hydroxybenzoic acid | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-hydroxybenzoic acid | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| 4-hydroxybenzoic acid glucuronide | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Glucose p-hydroxy benzoate | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dihydroxy-methoxybenzoic acid | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dihydroxybenzoic acid di-pentoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dihydroxybenzoic acid hexoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ducheside A | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3,4′-dihydroxypropiofenone-3-glucoside | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-O-galloylquinic acid (Theogallin) | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-O-galloylshikimic acid | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3,4-Di-O-galloylquinic acid | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-O-galloylquinic acid | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-O-galloylshikimic acid | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Galloyl arbutin | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Galloyl glucose | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Galloyl glucuronide | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Galloyl hexoside | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Galloyl-bis-HHDP glucose | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Galloyl-HHDP-DHHDP-hexoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Galloyl-HHDP-hexoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Digallic acid | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Digalloyl glucose | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Digalloyl shikimic acid | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Digalloyl-HHDP-hexoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Digalloylarbutin | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Digalloylquinic shikimic acid | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tetra-galloyl-hexoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Trigalloylquinic acid | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Trigalloylshikimic acid | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pentagalloyl glucose | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ellagic acid | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||
| Ellagic acid-7-xyloside | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Ellagic acid arabinoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ellagic acid diglucoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ellagic acid glucoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ellagic acid glucuronide | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ellagic acid hexoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ellagic acid mannopyranoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ellagic acid pentoside | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ellagic acid xylofuranoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ellagitannin | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Methylellagic acid rhamnoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3,3′-di-O-Methylellagic acid 4-O-β-D-(2″-acetyl) glucoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gallic acid (3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid) | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||
| Gallic acid dihexoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gallic acid glucoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gallic acid hexoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gallotannin | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ethyl gallate | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Methyl gallate | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gentisic acid | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Gentisoyl glucoside | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Gentisoyl hexoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Glucogallin | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Hexahydroxydiphenoyl-glucose | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
| Isoeugenol | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lambertianin C | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Methoxysalicylic acid | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Protocatechualdehyde (3,4-dihidroxy-benzaldehyde) | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Protocatechuic acid (3,4-dihydroxy-benzoic acid) | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||
| Protocatechuic acid glucoside | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Punicalagin | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Punicalin | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Punicalagin-gallate | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Sanguiin H-10 | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sanguiin H-10 isomer | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shikimic acid gallate | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shikimic acid dimer | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Strictinin ellagitannin | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Syringic acid | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||
| Syringyl-shikimic acid | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| TriGG-dehydrohexahydroxydiphenoyl (DHHDP)-glucose | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uralenneoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vanillic acid | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||
| Vanillic acid sulfoquinovoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class: Phenolic acid. Sub Class: Hydroxycinnamic acids | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Caffeic acid (3,4-dihydroxycinnamic acid) | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||
| caffeic acid 4-O-glucoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Caffeic acid derivate | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Caffeic acid hexoside | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Caffeic acid trimer | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dihydrocaffeic acid | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Caffeoyl arbutin | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Caffeoyl ferulic acid | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Caffeoyl feruloyl tartaric acid | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Caffeoyl hexoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Caffeoyl hexoside derivative | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-O-Caffeoyl quinic acid | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Caffeoyl quinic acid glucoside | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Caffeoyl quinic acid derivative | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Caffeoyl tartaric acid (caftaric acid) | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Dicaffeoyl shikimic acid | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1,4-dicaffeoyl quinic acid | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3,5-dicaffeoyl quinic acid | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6-Caffeoyl sucrose | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chlorogenic acid (3-O-caffeoylquinic acid) | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||
| Methyl caffeate | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cinnamic acid | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||
| Cinnamic acid derivative | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Methoxycinnamic acid | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cinnamic acid-O xylosyl hexoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrocinnamic acid | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrocinnamic acid glucoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydroxycinnamoyl-quinic acid | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| p-Coumaric acid | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||
| p-Coumaricacid derivate | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Coumaroyl quinic acid | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||
| Coumaroyl quinic acid derivative | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Coumaric acid hexoside | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chicoric acid | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ferulic acid | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||
| Ferulic acid derivative | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-O-Feruloylquinic acid | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Feruloylquinic glucoside | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Feruloyl-glucoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydroxy-ferulic acid hexoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydroxy-ferulic acid rhamnoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Feruloyl tartaric acid (fertaric acid) | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 6′-O-Sinapoylsucrose | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3,4-Dihydroxyphenyllactic acid hexoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-2-hydroxypropanoic acid | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rosmarinic acid | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||
| Rosmarinic acid hexoside | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rosmarinic acid-3-O-glucoside | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dihydroxy-dihydro feruloyl methyl rosmarinic acid | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Methylrosmaric acid | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
| p-Hydroxybenzylrosmarinic acid | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isosalvianolic acid A | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Methyl melitrate | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Salvianolic acid A | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Salvianolic acid B | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Salvianolic acid C | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sinapaldehyde | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3-Sinapoylquinic acid | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sinapic acid | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Yunnaneic acid F | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Verbascoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class: Phenolic acid. Sub Class: Hydroxyphenylacetic acids | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| p-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetic acid | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3,4-dihydroxyphenyllactic acid hexoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class: Flavonoid. Sub Class: Flavanones | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Eriodictyol | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Eriodictyol 7-O-rutinoside | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Eriodictyol-7-O-glucuronide | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Eriodictyol-O-di-hexoside | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Eriodictyol-O-hexoside | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Eriodictyol-O-hexuronide | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Glucodistylin | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Glucodistylin isomer | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hesperetin 7-O-rutinoside (Hesperidin) | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||
| Methyleriodictyol-O-pentosylhexoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Naringenin | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||
| Naringenin-di-hexoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Naringenin 7-O-glucoside (Naringin-Prunina) | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||
| Pinocembrin | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class: Flavonoid. Sub Class: Flavones | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Apigenin | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||
| Apigenin 7-O-glucuronide | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Apigenin glucuronide hexoside | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Apigenin 6,8-di-C-glucoside | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Apigenin 7-O-glucoside | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
| Apigenin C-hexoside | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Apigenin pentoside | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Apigenin-7-O-rutinoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Apigenin-O-hexoside | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Apigenin-O-hexoside derivative | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isovitexin 7-O-glucoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Apigenin 8-C-glucoside (Vitexin) | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2″-O-pentosyl-6-C-hexosyl-apigenin | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2″-O-Pentosyl-8-C-hexoside apigenin isomer I | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2″-O-Pentosyl-8-C-hexoside apigenin isomer II | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2″-O-pentosyl-8-C-hexosyl-apigenin | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2″-O-Pentoxide-8-C-hexoside apigenin | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4′-O-Rutinoside of 7-O-methylated apigenin | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6″-O-(3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaroyl)-2″-O-pentosyl-C-hexosyl-apigenin | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Apigenin 4′-methyl ether | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Apigenin 7-methyl ether (Genkwanin) | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Apigenin 4′,7-dimethyl ether | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Chalcone | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chrysin derivative | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chrysin-7-O-glucoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Circimaritin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hispidulin (Scutellarein 6-methyl ether) | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hispidulin 7-O-glucose (homoplantaginin) | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6″-O-(E)-feruloylhomoplantaginin | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hispidulin-rutinoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hypolaetin di-glucuronide | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hypolaetin 8-O-glucuronide | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isoscutellarein 7-O-glucoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isoscutellarein 8-O-glucuronide | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ladanein (5,6-dihydroxy-7,4′-dimethoxyflavone) | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Luteolin (3′.4′.5.7-Tetrahydroxyflavone) | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||
| Chrysoeriol-O-hexoside (Luteolin 3′-methyl ether) | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diosmetin (Luteolin 4′-methyl ether) | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cirsilineol (6-Methoxyluteolin 3′,7-dimethyl ether) | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Luteolin 7,3-dimethyl ether | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Luteolin 3′-O-glucuronide | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Luteolin-7-O-glucuronide | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Luteolin 7,4′-di-glucuronide | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Luteolin 4-O-glucoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Luteolin 7-O-glucoside | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||
| Luteolin-5-O-glucoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Luteolin 8-C-glucoside (Orientin) | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Luteolin 6-C-glucoside (Isoorientin) | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Luteolin-O-hexorunide | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Luteolin-7-O-rutinoside | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
| Luteolin-hexoside | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Luteolin 6-hydroxy-7-O-glucoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Luteolin-O-malonyl-hexoside) | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 2″-O-Pentosyl-8-C-hexoside luteolin | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2″-O-pentosyl-6-C-hexosyl-luteolin | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2″-O-pentosyl-8-C-hexosyl-luteolin | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6″-O-(3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaroyl)-2″-O-pentosyl-C-hexosyl-luteolin | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nepitrin (Nepetin 7-O-glucoside) | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6″-O-(E)-feruloylnepitrin | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Salvigenin (5-Hydroxy-6,7,4′-trimethoxyflavone) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Techtochrysin | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class: Flavonoid. Sub Class: Flavonols | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isorhamnetin | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isorhamnetin 3-O-glucoside | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Isorhamnetin 3-O-rutinoside | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Isorhamnetin-3-O-hexoside | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Isorhamnetin-O-(6″-caffeoyl)hexoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isorhamnetin-O-deoxyhexosyl-hexoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isorhamnetin-O-hexoside-O-rhamnoside | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Galangin (3,5,7-Trihydroxyflavone) | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kaempferol | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||
| 6-Hydroxykaempferol | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dihydrokaempferol 3-O-glucoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kaempferol 3-methyl ether | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Kaempferol 3 4′-dimethyl ether | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kaempferol 3 7-dimethyl ether | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| kaempferol 3,7,4′-trimmethyl ether | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| kaempferol methylether O-rutinoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kaempferol dimethylether hexoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kaempferol 3-O-(6″-galloyl) glucoside | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| kaempferol-3-O-(6″-feruloyl)-β-D-glucopyranoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kaempferol 3-O-(6″-p-coumaroyl) glucoside | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| kaempferol-3-O-(2′′,6′′-di-p-coumaroyl)glucoside isomers | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| kaempferol-3-O-(2″,6″-di-E-p-coumaroyl)-glucopyranoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| kaempferol-3-O-(3′′-acetyl-2″,6′′-di-p-coumaroyl)glucoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| kaempferol-3-O-(3′′,4′′-diacetyl-2′′,6′′-di-p-coumaroyl)glucoside isomers | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| kaempferol-3-O-(6″-p-coumaroyl) glucopyranoside(Tiliroside) | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Kaempferol-3-galactoside-6″-rhamnoside-3′″- rhamnoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| kaempferol malonyl glucoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| kaempferol 3-O-ramnopyranoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kaempferol-O-rhamnoside | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Kaempferol 7-O-(6″-rhamnosyl) glucoside | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| kaempferol 3-O-arabinofuranoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| kaempferol-3-O-arabinopyranoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kaempferol 3-O-glucoside (Astragalin) | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Kaempferol 3-O-rutinoside | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Kaempferol-acetyl-O-rutinoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| kaempferol-acetyl-O-rahmnoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kaempferol-acetyl-O-hexoside | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Kaempferol O-glucuronide | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kaempferol 7-O-hexuronide | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kaempferol 3-O-pentoside | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kaempferol O-hexoside | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||
| Kaempferol O-pentosyl hexoside | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kaempferol-3-O-hydroxybenzoyl glucoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| kaempferol-3-O-galactoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kaempferol xyloside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kaempferol-O-di-hexoside | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Morin | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Myricetin (3.3′.4′.5.5′.7-Hexahydroxyflavone) | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||
| Myricetin 3-O-(6″-rhamnosyl) glucoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Myricetin-O-(6″-benzoyl) hexoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Myricetin-O-(6″-cinnamoyl) hexoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Myricetin-O-(6″-p-coumaroyl) hexoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Myricetin-O-(galloyl) hexoside | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Methoxy-myricetin-O-rhamnoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Myricetin 3,7,4′,5′-tetramethyl ether | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Myricetin-3-arabinoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| myricetin 3-O-arabinofuranoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Myricetin-3-O-galactoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Myricetin-3-O-glucoside | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Myricetin-3-O-glucuronide | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Myricetin 3-O-hexoside | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
| Myricetin 7-O-hexuronide | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Myricetin 3-O-pentoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Myricetin 7-O-pentoside | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Myricetin-O-rhamnoside (Myricitrin) | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||
| Myricitrin-2′′-O-gallate (Desmanthin) | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Myricetin-O-rutinoside | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||
| Myricetin 3-O-xyloside | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pinobanksin (bioflavonoide) | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Quercetin (3.3′.4′.5.7-Pentahydroxyflavone) | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||||
| Quercetin-(acetyl) rutinoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Quercetin-(acetyl) hexoside | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Quercetin-(acetyl)-O-rhamnoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Quercetin-O-(6″-cinnamoyl) hexoside | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| quercetin 3-O-(2′-coumaroyl) rutinoside | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Quercetin 3-O-(6″-p-coumaroyl) hexoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Quercetin 3-O-(6″-galloyl) hexoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Quercetin-O-(6″-p-hydroxybenzoyl) hexoside | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Quercetin-O-(malonyl) hexoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Quercetrin-O-gallate | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Quercertin methyl ether-3-O-galactoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Quercetin 4′,5′-dimethyl ether | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Quercetin 3,7,4′,5′-tetramethyl ether | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Quercetin 3-O-arabinoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| quercetin 3-O-arabinofuranoside | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Quercetin 3-O-galactoside (Hyperoside) | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Quercetin 3-O-glucoside (Isoquercetin) | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||
| Quercetin 3-O-glucuronide | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Quercetin-O-hexoside | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||
| Quercetin 3-O-hexuronide | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Quercetin hexose protocatechuic acid | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Quercetin-O-rhamnoside (Quercetrin) | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||
| Quercetin 3-O-rutinoside (Rutin) | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||
| Quercetin 3-O-pentoside | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Quercetin 3-O-xyloside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Quercetin 3-O-rhamnoside-7-O-glucoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Quercetin 3,4-diglucoside | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Quercetin-O-deoxyhexosyl-hexoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Quercetin-O-dihexoside | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Quercetin-pentosyl-hexoside | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taxifolin (dihydroquercetin) | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Taxifolin-3-O-glucoside | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taxifolin 3-O-rhamnoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taxifolin-O-hexoside | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taxifolin pentoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class: Flavonoid. Sub Class: Flavanols | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Catechin | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||
| Catechin 3-gallate | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4,3′,4′-Trimethylcatechin | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Catechin derivates | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Catechin glucose | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Catechin-( 4α→8)-Catechin (Procyanidin B3) | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dehydrodicatechin A | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Epicatechin | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||
| Epicatechin derivatives | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Epicatechin methyl gallate | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Epicatechin gallate | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||
| epicatechin-4,6-catechin | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| epicatechin-4,8-catechin | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| epicatechin-4,8-epicatechin-4,8-catechin | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Epicatechin-4,8-epicatechin-4,8-Epicatechin | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Epicatechin-A-epicatechin | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Epicatechin-B-epicatechin-A-epicatechin | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Epicatechin-epicatechin 3-O gallate | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Epicatechin-epigallocatechin | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Epigallocatechin | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Epigallocatechin gallate(Teatannin II) | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Epigallocatechin–catechin | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Epigallocatechin–epicatechin | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Epigallocatechin–epigallocatechin | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Fzelechin-catechin-3-O-rhamnoside (proanthocyanidin) | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gallocatechin | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Gallocatechin-4,8-catechin | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Procyanidin B2 | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tannic acid | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class: Flavonoid. Sub Class: Anthocyanins | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cyanidin 3-O-arabinoside | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cyanidin-3-galactoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cyanidin 3-O-glucoside | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||
| Cyanidin-3-O-rutinoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cyanidin 3-O-xyloside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cyanidin dihexoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cyanidin-3,5-diglucoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Delphinidin 3-O-galactoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Delphinidin 3-O-glucoside | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Malvidin-3-O-glucoside/Oenin | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Pelargonidin 3-O-(6″-malonyl) glucoside | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pelargonidin-3-O-glucoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pelargonidin 3-rutinoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Peonidin 3-O-(6″-p-coumaroyl) glucoside | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Peonidin-3-O-glucoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Petunidin | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Petunidin-3-O-glucoside | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class: Flavonoid. Sub Class: Isoflavonoids | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Daidzein | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3′-Hydroxydaidzein | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Genistein | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2′-Hydroxygenistein | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Glycitin 6″-O-malonate | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class: Other polyphenols. Sub Class: Hydroxybenzaldehydes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-hydroxybenzoic acid 4-(6-O-sulfo)glucoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Syringaldehyde | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vanillin | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Class: Other polyphenol. Sub Class: Hydroxycoumarins | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4-methylumbelliferone | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6,7-Dihydroxycoumarin 3O-glucoside (Aesculin) | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Coumarin | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class: Other polyphenol. Sub Class: Tyroslos | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oleuropein | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class: Lignans. Sub Class: Lignans | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carnosic acid | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carnosol | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Isolariciresinol 3-glucoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Methyl carnosic acid | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pinoresinol | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rosmanol | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rosmanol derivate | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sagerinic acid | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thymol | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class: Other polyphenols. Sub Class: Other polyphenols | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-Nonadecylresorcinol | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Arbutin | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Catechol | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Coniferaldehyde | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydroquinone derivative | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Salvianolic acid | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Salvianolic acid A | + | + | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| salvianolic acid B (lithospermic acid B) | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Salvianolic acid B/E/L | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Salvianolic acid C | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Salvianolic acid C isomer | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Salvianolic acid F | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Salvianolic acid K | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Salvianolic acid I | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sculetin | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class: Stilbenes. Sub Class: Stilbenes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Piceid | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Resveratrol | + | + | + | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Stilbericoside | + | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | [75,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86] | [81,87,88] | [81,83,88,89,90] | [81] | [81,88,91] | [81,82] | [92,93,94,95,96] | [97,98,99] | [100] | [100] | [101] | [102,103] | [101] | [83,104] | [105,106,107] | [108,109] | [110,111,112,113,114,115] | [116,117,118] | [117] | [119,120,121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128,129,130,131,132,133] | [134,135,136,137,138,139] | [140,141,142] | [143,144,145,146,147,148,149,150,151,152] | [92,153,154,155,156,157,158,159,160,161,162] |
Cl: C. ladanifer; Cs: C. salviifolius; Cm: C. monspeliensis; Cc: C. crispus; Ca: C. albidus; Cp: C. populifolius; Cym: C. multiflorus; Cys: C. scoparius; Cyst: C. striatus; Em: E. multiflora; Es: E. scoparia; Ea: E. australis; Cv: C. vulgaris; Mc: M. communis; Pl: P. lentiscus; Pt: P. terebinthus; Ro: R. officinalis; Qi: Q. ilex; Qs: Q. suber; Au: A. unedo; Ls: L. stoechas; Tm: T. mastichina; Tv: T. vulgaris; Ru: R. ulmifolius.
There is a clear difference in the number of compounds identified in each species. The species with the largest number of compounds is A. unedo (142 compounds), whereas only 5 to 8 compounds have been identified in C. crispus, C. striatus and C. vulgaris. The identification of more or fewer compounds in a species is due to the number of studies conducted on each, which is determined by their commercial interest. Some of them, such as A. unedo, have a high commercial interest, which explains the existence of many studies on this species and, therefore, a larger number of compounds identified in it.
Furthermore, the compounds are unequally represented. Some phenols have only been cited in one species, while others have been reported in many species (Table 1). Considering the compounds that appear in more than 5 species (Table 3), 38 phenolic compounds are found in these species, 15 of which are phenolic acids and 23 are flavonoids.

Table 3.
Identified phenolic compounds in more than 5 species among the 24 species selected in this study. The percentage of representation in these species is also shown.
4. Neuroprotective Effect of the Most Represented Phenolic Compounds in the Selected Species
The most distributed phenolic compounds among the selected species belong to two classes (Table 3): phenolic acids and flavonoids. Activity against neurodegenerative disorders has been attributed to most of these compounds. In fact, one of the activities most strongly associated with phenolic acids is their antioxidant capacity. This activity depends on the number of hydroxyl moieties attached to the aromatic ring of benzoic or cinnamic acid molecules. For example, Rice-Evans et al. [163] reported that the total antioxidant activity of phenolic acids, in decreasing order, is gallic > p-coumaric > ferulic > vanillic > syringic > caffeic > m-coumaric > protocatechuic > gentisic > o-coumaric > salicylic > p-hydroxybenzoic. Free-radical scavenging is the activity that confers them with the protective function against neurodegenerative disorders.
Six phenolic acids (gallic, chlorogenic, ferulic, caffeic, vanillic and p-coumaric acids) are represented in more than 40% of the species studied. These compounds have been assigned neuroprotective functions (Figure 2). Some of the properties attributed to them are described below.
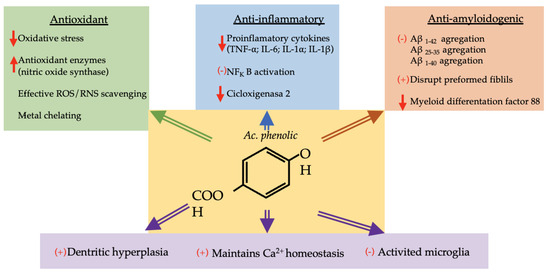
Figure 2.
Diagram with neuroprotective mechanisms of phenolic acid. ↑: increase, ↓: decrease, (+): activation, (−): inhibition, ROS: reactive oxygen species, RNS: reactive nitrogen species, TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-alfa, IL: interleukin, NFkB: nuclear factor kappa B, AB: amyloid beta-peptide.
Gallic acid (GA) is present in 70% of the species that dominate the ecosystems of Extremadura. GA is a well-known 5,4,3-trihydroxybenzoic acid found abundantly in free and conjugated (hydrolyzable tannins) or esterified forms in many plants [164]. It is a phenol with great interest for the treatment of patients with AD and PD, due to its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-amyloidogenic properties [165]. Different studies have shown its application as a therapy to interact with amyloid (Aβ) monomers and fibrils. These studies have proved that GA-loaded transferrin-functionalized liposomes could inhibit Aβ1–42 aggregation and fibrillation and disrupt preformed fibrils, and thus it could be considered for AD therapy [166]. GA has been demonstrated to reduce memory deficit and cerebral oxidative stress in a unilateral 6-hydroxydopamine-induced PD model in rats [167]. Moreover, its neuroprotective effect has been shown in models of traumatic brain injury [168] and glutamate-induced neurotoxicity in rats [169], due to the improvement in the antioxidant profile and the inhibition of proinflammatory cytokine generation [168,169].
The mechanisms by which GA exerts its prophylactic action in these processes have been analyzed in several studies. For instance, refs. [170,171] reported that, in animals with multiple sclerosis (MS), the administration of GA improved the oxidative and inflammatory response and induced dendritic hyperplasia. This causes an increase in the number of dendritic spines, which could explain the positive response in the dendritic morphology of the three regions (CA1-CA3-DG) of the rat hippocampus with MS. It has been indicated that GA inhibits Aβ-induced neurotoxicity via suppressing microglial-mediated neuroinflammation and decreasing cytokine generation [172]. Studies conducted by [173] show that GA treatment maintains Ca2+ homeostasis and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) expression and protects neurons from glutamate-induced neurotoxicity.
A recent study conducted by [174] estimated the neuroprotective effects of (GA) against aluminum chloride-induced AD in adult Wistar rats. The trials performed showed that there was a significant decrease in antioxidant enzymes, serum electrolyte and neurotransmitter levels with a corresponding increase in stress markers (MDA, H2O2 and NO) among the rats treated with aluminum, which were restored to nearly normal levels after GA administration. Histological observation showed neurofibrillary tangles and amyloid plaques in the external granular layer of the rats treated with aluminum, although this effect disappeared after GA administration [174].
These studies suggest that structural and functional alterations in the neurons of animals with neurodegenerative diseases are reverted after GA treatment; consequently, neurochemical processes are restored, improving recognition memory [175].
Chlorogenic acid (CGA) is another type of polyphenol that has demonstrated potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities [176]. CGA is present in 54.1% of the species analyzed in this study. Its mechanism of action could be related to the attenuation of mRNA and protein expression levels of proinflammatory and profibrotic mediators, and the reduction of the levels of serum proinflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor-alfa) IL-6 (interleukin-6) and IL-1β, as is reported in studies conducted in female rats [177]. CGA treatment also suppressed CCl4-induced NF-κB (nuclear factor kappa-B) activation and reduced the expression levels of Toll-like receptor 4, myeloid differentiation factor 88, inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase in rats exposed to CCl4 [178].
Ferulic acid (FA) is present in 50% of the 24 species selected in this study. This compound has been reported to increase neuronal survival, enhance antioxidant enzyme function, modulate multiple neuronal signal transduction, and impair cholinesterase activity (ChAT) [179].
FA has been identified as an effective ROS and RNS scavenger, reducing the likelihood of attack of radicals on proteins and thereby preventing oxidative changes. The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential of FA could be due to its ability to suppress leukotriene synthesis and reduce oxidative stress in the brain [180].
Several studies have highlighted the anti-inflammatory effects of FA [181,182]. Particularly, FA has been shown to reduce the neuroinflammation induced by chronic unpredictable mild stress in the prefrontal cortex through the inhibition of NF-κB activation [183].
The potential role of FA against AD has also been investigated in cell models. In particular, Kikugawa et al. [184] showed that the pretreatment of primary cerebral cortical neurons with FA exerted a protective effect toward Aβ25–35-induced cytotoxicity; moreover, FA was able to inhibit the aggregation of Aβ25–35, Aβ1–40 and Aβ1–42 and to destabilize pre-aggregated Aβ.
It is worth highlighting that the potential usefulness of FA in AD has also been investigated in in vivo studies [185]. Yan et al. [186] reported that IL-1β production, neuroinflammation and gliosis, induced by the intracerebroventricular injection of Aβ in the mouse hippocampus, were counteracted by pretreatment with FA, and this phenolic acid was able to improve memory loss. Kim et al. [41] also showed that FA prevented the Aβ1–42-induced increase in endothelial nitric oxide synthase and 3-nitrotyrosine and suppressed IL-1α immunoreactivity in the hippocampus [187]. Along with the amelioration of Aβ plaque deposition, Wang et al. [188] recently found that FA prevented the reduction in the density and diameter of hippocampal capillaries, thus favoring the oxygen and nutrient supply and the removal of metabolic wastes from the brain, which finally led to improved spatial memory.
Caffeic acid (CA) is another phenol that is present among 50% of the selected species. It has been shown that CA reduces elevated oxidative stress and neuroinflammation and improves synaptic/memory dysfunctions in AD mice [189]. Studies conducted in mice have reported that CA has strong antioxidative and anti-inflammatory properties and prevents the mice brain from AB-induced oxidative stress and neuroinflammation [190]. These findings suggest that CA significantly reduces activated microglia and astrocytes in the brains of AD mice.
There are markers clearly related to neurodegenerative conditions and memory dysfunctions, such as phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase /protein kinase b signaling pathway, and downregulation of neuronal growth factors, such as brain-derived neurotrophic factor [191,192,193]. It has been proved that CA considerably upregulates the expression of these markers in the brains of Aβ-injected mice, and a significant improvement was observed with CA treatment [194].
Vanillic acid (VA) is present in 42% of the species analyzed in this study, and this phenolic acid has been reported to have a clear anti-inflammatory function [195]. Studies conducted with VA have shown that this compound significantly increases neurite outgrowth after 48 h in culture. This compound significantly reduces the expression of cyclooxygenase-2, NF-κB, tenascin-C, chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans and glial fibrillary acidic protein in astrocytes in the LPC-induced model of inflammation. This study supports the hypothesis that VA has anti-inflammatory activities, and, since axonal and synaptic damage is present in most and possibly all neurodegenerative diseases, including AD, PD, and HD [196], the effects of VA on neurite outgrowth make it a potential candidate to encourage the regeneration of neurites after demyelination.
p-coumaric acid (PCA) is present in over 40% of the studied species. In recent years, this compound has been the focus of numerous studies due to its wide variety of biological activities: antioxidant [197], anti-inflammatory [198], neuroprotective [199] and memory-ameliorating effects [200]. Authors such as Rashno et al. [201] explored the effects of oral administration of PCA on passive avoidance memory function, LTP (long-term potentiation) induction in the hippocampal dentate gyrus and hippocampal Aβ plaque formation following AlCl3 exposure in male rats, a condition that resembles the symptoms of AD. The results obtained by this group demonstrated that treatment with PCA alleviated passive avoidance deficit, improved hippocampal LTP impairment and prevented Aβ plaque formation in the AlCl3-exposed rats. Cognitive-improving effects of PCA have been reported in various neuropathological conditions, such as cerebral ischemia [202], lipopolysaccharide-induced neurological changes [200] and scopolamine-induced neurotoxicity [42].
In addition to the group of phenolic acids, the other group of phenols widely distributed among these species is that of flavonoids. Of the 224 different flavonoids that can be found in the entire set of species selected in this study, 23 are present in over 20% of them. Within this group, quercetin and its derivatives quercetin 3-O-rutinoside and quercetin 3-O-glucoside (isoquercetin) stand out, as they are present in over 60% of the selected species. Other flavonols and flavones that are also widely distributed include quercetin-O-rhamnoside (quercetrin), apigenin, kaempferol and myricetin-O-rhamnoside (myricitrin), being present in 45–55% of the selected species.
Different in vitro and in vivo experiments found that these polyphenols may exert a beneficial effect in the prevention and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases associated with oxidative stress, shown in Figure 3, and that the activity of flavonoids such as galangin, kaempferol, quercetin, myricetin, fisetin, apigenin, luteolin and rutin was correlated with the number of OH groups and their side on their phenyl ring [63,203]. It is worth highlighting that these phenolic compounds and their metabolites can enter the brain at detectable levels in mammals, which supports their direct neurological action [204].
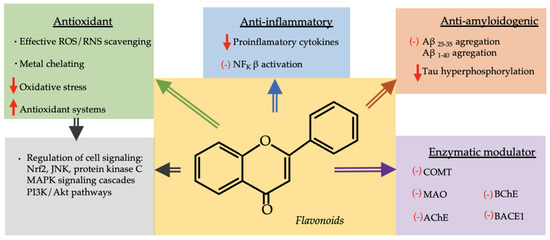
Figure 3.
Diagram with neuroprotective mechanisms of flavonoids. ↑: increase, ↓: decrease, (−): inhibition, ROS: reactive oxygen species, RNS: reactive nitrogen species, NFkB: nuclear factor kappa B, AB: amyloid beta-peptide, Nrf2: nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2, JNK (Jun-NH2-terminal kinase), MAPK (the mitogen-activated protein kinase), PI3K/Akt (phosphoinositide 3-kinase), COMT (catechol-O-methyltransferase), MAO (monoamine oxidase), AChE (acetylcholinesterase), BchE (butyrylcholinesterase), BACE1 (amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme I).
Flavonoids, depending on the degree of oxidation and saturation in the heterocyclic C-ring, can be divided into different subclasses, varying in their bioavailability. Thus, flavanols, flavanones and flavonol glycosides have intermediate rates of absorption and bioavailability, while proanthocyanidins, flavanol gallates and anthocyanins have the lowest absorption [205]. According to different studies, epicatechin metabolites seem to reach the brain of rodents at levels that might be physiologically effective [206], and some conjugated forms of quercetin can also accumulate in the brain after oral administration [207,208].
Among flavonoids, flavonols and flavones constitute the largest group and have been associated with a clear neuroprotective role [70,209,210,211,212,213]. It has been demonstrated in numerous studies that flavonols such as quercetin, myricetin and kaempferols, as well as their derivatives, have strong antioxidant activity [209] and also demonstrate that their glucosylated derivatives have greater activity than the corresponding aglycones [213]. The radical scavenging and metal chelating activity of flavonols contribute to ameliorating oxidative stress [167,214]; in turn, this activity depends on the number of the hydroxyl and the sugar moiety associated [213,215].
In addition to the antioxidant capacity of these compounds as free-radical scavengers, the mechanisms involved in the neuroprotector effect of these compounds would be associated with their capacity to inhibit Aβ aggregation, the amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme (BACE1) [216] and AChE [217]. Studies on AChE inhibition in the brain of oxidative stress-induced rats report that AChE activity significantly decreases [218,219]. Specifically, treatment with flavonol quercetin in hippocampal neurons has resulted in the elevation of neurogenesis, synaptogenesis, and cell proliferation, as well as restoration of Aβ-induced synaptic loss [220]. This flavonol also exerts positive effects on PD, as it can inhibit the activity of catechol-O-methyltransferase and monoamine oxidase enzymes, which can lead to an increase in the bioavailability of L-dopa in the brain [4]. Quercetin has also been attributed to the capacity to act through different signaling pathways, including regulation of cytokines via Nrf2 (nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2), JNK (Jun-NH2-terminal kinase), protein kinase C, MAPK (the mitogen-activated protein kinase) signaling cascades, and PI3K/Akt (phosphoinositide 3-kinase) pathways [221].
Another flavonoid with clear antioxidant functions is flavan-3-ol catechin [222], which, along with its isomers and/or conjugates of gallic acid, is a naturally occurring constituent in plants [223]. This has been observed among the studied species, as this flavonoid is present in 46% of the species. Different studies report the neuroprotective properties of catechins, mostly through antioxidative and anti-inflammatory effects, mainly involving Nrf2 and NF-kB signaling pathways [222,224,225]. One in vivo study has revealed that it can improve cognitive impairment induced by doxorubicin via increasing antioxidant defense, preventing neuroinflammation and inhibiting AChE [226]. Catechin has also been indicated to inhibit the late stages of Aβ-soluble aggregate growth change in the fibrillar form of Aβ [227]. It has also prevented neurotoxin-induced dopamine neuron loss in substantia nigra in a mouse model of PD [228]. The other flavanol with a high representation among the studied species is epicatechin, which is present in 42% of them. It has been demonstrated that epicatechin treatment prevents oxidative damage to the hippocampus induced by Aβ25–35 [229]. This flavanol may reduce Tau hyperphosphorylation, downregulate BACE1 and Aβ1–42 expression and boost AD rats’ antioxidant system, as well as their cognition and memory [230,231].
5. Main Species with Neuroprotective Activity
As can be observed, the species considered in this study can be an important source of phenolic compounds with activity against neurodegenerative diseases. However, focusing on the most represented compounds (in over 40% of the analyzed species) and the species that contain all or most of these compounds (Table 4), 7 of these species stand out: C. multiflorus, P. lentiscus, A. unedo, L. stoechas, R. ulmifolius and T. vulgaris contain the 6 most frequent phenolic acids (gallic, chlorogenic, ferulic, caffeic, vanillic and p-coumaric acids) and C. salviifolius and P. lentiscus contain the main flavonoids.

Table 4.
Species with the most represented phenolic compounds (present in over 10 of the 24 analyzed species).
Of these 7 species, studies have been conducted with extracts of P. lentiscus, L. stoechas and T. vulgaris to demonstrate their activity against neurodegenerative diseases [107,136,138,151,232]. These studies have reported the in vitro AChE inhibitory activity of P. lentiscus and its extract exhibited a significant dose-related AChE inhibitory activity. This extract also showed the ability to prevent neurodegeneration and improve memory and cognitive function. This indicates that P. lentiscus inhibited Al-induced neurodegeneration of neurons in the brain cortex, which is known to be susceptible in AD and to play an important role in learning and memory functions [107,233,234]. These findings explain the protective effects of P. lentiscus on cognitive deficit. Moreover, the capability of the extract to correct the in vivo disorders may be explained by its ability to inhibit oxidative stress and lipid oxidation induced by Al [213,235].
The extracts of L. stoechas also significantly (p < 0.001) enhanced the retention power and learning capacity of mice brains. Similarly, treatment of animals with extracts of la- vender showed a significant (p < 0.001) reduction in the level of AChE and relieved the patient of memory loss [136,139].
On their part, studies conducted with the extract of T. vulgaris also indicate that this species can present neuroprotective effects [151,152]. The results obtained by [236] suggest that the antiamnesic effect of T. vulgaris extract on scopolamine-induced memory impairment may be related to the antioxidant activity of the extract or mediation of the cholinergic nervous system [148,150].
The protective activities attributed to these species can be inherent to the presence of these phenolic compounds (flavonoids and phenolic acids), where the presence of all of them may exert a synergistic effect as neuroprotective agents.
6. Conclusions
This review highlights the relevance of the species of Mediterranean ecosystems as a diverse source of phenolic compounds. Among these compounds, phenolic acids and flavonoids stand out. The most represented compounds among the species studied are gallic, vanillic, caffeic, chlorogenic, p-coumaric and ferulic acids, apigenin, kaempferol, myricitrin, quercetin, isoquercetin, quercetrin, rutin, catechin and epicatechin, which have been attributed neuroprotective functions. Given this information, these Mediterranean scrub species could be considered as sources of compounds for use in therapy against neurodegenerative diseases such as AD and PD.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.C., L.N., I.M.-F., J.B.-S. and J.C.A.; methodology, N.C.; validation, N.C., L.N., I.M.-F., J.B.-S. and J.C.A.; investigation, N.C.; data curation, N.C. and J.C.A.; writing—original draft preparation, N.C. and J.C.A.; writing—review and editing, N.C., L.N., I.M.-F., J.B.-S. and J.C.A.; visualization, N.C., L.N., I.M.-F., J.B.-S. and J.C.A.; supervision, N.C.; project administration, N.C.; funding acquisition, N.C., J.B.-S. and J.C.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research has been financed by the project titled “Direct subsidy to the University of Extremadura for the implementation of the LA4 lines of action of the I+D+i program in the area of Biodiversity. LIA4:Evaluation and mitigation of the impact of global change on biodiversity—FEDER Funds”/LIA4 Complementary Plan, co-financed by the Ministry of Economy, Science and Digital Agenda of the Government of Extremadura and by the European Regional Development Fund (FEDER) of Extremadura corresponding to the 2021–2027 programming period.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Harman, D. Aging: A theory based on free radical and radiation chemistry. J. Gerontol. 1956, 11, 298–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liguori, I.; Russo, G.; Curcio, F.; Bulli, G.; Aran, L.; Della-Morte, D.; Gargiulo, G.; Testa, G.; Cacciatore, F.; Bonaduce, D. Oxidative stress, aging, and diseases. Clin. Interv. Aging 2018, 13, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costanzo, P.; Oliverio, M.; Maiuolo, J.; Bonacci, S.; De Luca, G.; Masullo, M.; Arcone, R.; Procopio, A. Novel hydroxytyrosol-donepezil hybrids as potential antioxidant and neuroprotective agents. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 741444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, E.; Devasahayam, G. Neurodegeneration by oxidative stress: A review on prospective use of small molecules for neuroprotection. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 3133–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilberger, B.; Weppler, S.; Eckert, G.P. Phenolic acid metabolites of polyphenols act as inductors for hormesis in C. elegans. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2021, 198, 111518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Kukreti, R.; Saso, L.; Kukreti, S. Oxidative stress: A key modulator in neurodegenerative diseases. Molecules 2019, 24, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouayed, J.; Rammal, H.; Dicko, A.; Younos, C.; Soulimani, R. Chlorogenic acid, a polyphenol from Prunus domestica (Mirabelle), with coupled anxiolytic and antioxidant effects. J. Neurol. Sci. 2007, 262, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, I.; Inaba, M.; Inoue, D.; Uenishi, K.; Saito, M.; Shiraki, M.; Suzuki, A.; Takeuchi, Y.; Hagino, H.; Fujiwara, S.; et al. Executive summary of clinical practice guide on fracture risk in lifestyle diseases. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2020, 38, 746–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harman, D. The Biologic Clock: The Mitochondria? J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1972, 20, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzetti, E.; Csiszar, A.; Dutta, D.; Balagopal, G.; Calvani, R.; Leeuwenburgh, C. Role of mitochondrial dysfunction and altered autophagy in cardiovascular aging and disease: From mechanisms to therapeutics. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2013, 305, H459–H476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilberger, B.; Baumanns, S.; Schmitt, F.; Schmiedl, T.; Hardt, M.; Wenzel, U.; Eckert, G.P. Mitochondrial oxidative stress impairs energy metabolism and reduces stress resistance and longevity of C. elegans. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 6840540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Mehta, V.; Raj, U.; Varadwaj, P.K.; Udayabanu, M.; Yennamalli, R.M.; Singh, T.R. Computational and in-vitro validation of natural molecules as potential acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and neuroprotective agents. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2019, 16, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khazdair, M.R.; Anaeigoudari, A.; Hashemzehi, M.; Mohebbati, R. Neuroprotective potency of some spice herbs, a literature review. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2019, 9, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, P. The Potential of Flavonoids for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prince, M.; Bryce, R.; Albanese, E.; Wimo, A.; Ribeiro, W.; Ferri, C.P. The global prevalence of dementia: A systematic review and metaanalysis. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2013, 9, 63–75.e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, S.-C.; Providencia, R.; Sofat, R.; Pujades-Rodriguez, M.; Torralbo, A.; Fatemifar, G.; Fitzpatrick, N.K.; Taylor, J.; Li, K.; Dale, C.; et al. Incidence, morbidity, mortality and disparities in dementia: A population linked electronic health records study of 4.3 million individuals. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2023, 19, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, J.; Chen, Z.; Cai, P.; Wang, R.; Yang, Q.; Li, L.; Yang, H.; Zhu, R. Targeting microRNA-125b promotes neurite outgrowth but represses cell apoptosis and inflammation via blocking PTGS2 and CDK5 in a FOXQ1-dependent way in Alzheimer disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 587747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, C.; Kim, S.R. Linking oxidative stress and proteinopathy in Alzheimer’s disease. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhan, I.E.; Senol, F.S.; Ercetin, T.; Kahraman, A.; Celep, F.; Akaydin, G.; Sener, B.; Dogan, M. Assessment of anticholinesterase and antioxidant properties of selected sage (Salvia) species with their total phenol and flavonoid contents. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 41, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Pozo, A.; Frosch, M.P.; Masliah, E.; Hyman, B.T. Neuropathological alterations in Alzheimer disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2011, 1, a006189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, K.; Alonso, A.d.C.; Chen, S.; Chohan, M.O.; El-Akkad, E.; Gong, C.-X.; Khatoon, S.; Li, B.; Liu, F.; Rahman, A. Tau pathology in Alzheimer disease and other tauopathies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2005, 1739, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamagno, E.; Parola, M.; Bardini, P.; Piccini, A.; Borghi, R.; Guglielmotto, M.; Santoro, G.; Davit, A.; Danni, O.; Smith, M. β-Site APP cleaving enzyme up-regulation induced by 4-hydroxynonenal is mediated by stress-activated protein kinases pathways. J. Neurochem. 2005, 92, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunomura, A.; Castellani, R.J.; Zhu, X.; Moreira, P.I.; Perry, G.; Smith, M.A. Involvement of oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2006, 65, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeandel, C.; Nicolas, M.B.; Dubois, F.; Nabet-Belleville, F.; Penin, F.; Cuny, G. Lipid peroxidation and free radical scavengers in Alzheimer’s disease. Gerontology 1989, 35, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabbita, S.P.; Lovell, M.A.; Markesbery, W.R. Increased nuclear DNA oxidation in the brain in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 1998, 71, 2034–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, L.A.; Hong, N.S.; McDonald, R.J. Revisiting the cholinergic hypothesis in the development of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2011, 35, 1397–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; Mesulam, M.-M.; Cuello, A.C.; Khachaturian, A.S.; Vergallo, A.; Farlow, M.; Snyder, P.; Giacobini, E.; Khachaturian, Z.; Cholinergic System Working Group, and for the Alzheimer Precision Medicine Initiative (APMI). Revisiting the cholinergic hypothesis in Alzheimer’s disease: Emerging evidence from translational and clinical research. J. Prev. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2019, 6, 2–15. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, K.-X.; Tan, M.-S.; Tan, C.-C.; Cao, X.-P.; Hou, X.-H.; Guo, Q.-H.; Tan, L.; Mok, V.; Yu, J.-T. Comparative safety and effectiveness of cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine for Alzheimer’s disease: A network meta-analysis of 41 randomized controlled trials. Alzheimer’s Res.Ther. 2018, 10, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marucci, G.; Buccioni, M.; Ben, D.D.; Lambertucci, C.; Volpini, R.; Amenta, F. Efficacy of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropharmacology 2021, 190, 108352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poewe, W.; Seppi, K.; Tanner, C.M.; Halliday, G.M.; Brundin, P.; Volkmann, J.; Schrag, A.E.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Casacuberta, I.; Juárez-Flores, D.L.; Morén, C.; Garrabou, G. Bioenergetics and Autophagic Imbalance in Patients-Derived Cell Models of Parkinson Disease Supports Systemic Dysfunction in Neurodegeneration. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacabelos, R. Parkinson’s Disease: From pathogenesis to pharmacogenomics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naveen, K.; Bhattacharjee, A. Medicinal herbs as neuroprotective agents. WJPPS 2021, 10, 675–689. [Google Scholar]
- Nakabeppu, Y.; Tsuchimoto, D.; Yamaguchi, H.; Sakumi, K. Oxidative damage in nucleic acids and Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci. Res. 2007, 85, 919–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, S.M.; Xie, Z.; Stout, K.A.; Zampese, E.; Burbulla, L.F.; Shih, J.C.; Kondapalli, J.; Patriarchi, T.; Tian, L.; Brichta, L.; et al. Dopamine metabolism by a monoamine oxidase mitochondrial shuttle activates the electron transport chain. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junn, E.; Mouradian, M.M. Human alpha-synuclein over-expression increases intracellular reactive oxygen species levels and susceptibility to dopamine. Neurosci. Lett. 2002, 320, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- . Perfeito, R.; Ribeiro, M.; Rego, A.C. Alpha-synuclein-induced oxidative stress correlates with altered superoxide dismutase and glutathione synthesis in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 1245–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, L.A.; Tovar, H.C.; Agudelo, C. Utilización de servicios de salud y perfiles epidemiológicos como parámetros de adecuación del Plan Obligatorio de Salud en Colombia. Rev. Salud Pública 2003, 5, 246–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Locanto, Ó. Tratamiento farmacológico de la enfermedad de Alzheimer y otras demencias. Arch. Med. Interna 2015, 37, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Blesa, J.; Lanciego, J.; Obeso, J.A. Editorial: Parkinson’s disease: Cell vulnerability and disease progression. Front. Neuroanat. 2015, 9, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, H.-S.; Cho, J.-y.; Kim, D.-H.; Yan, J.-J.; Lee, H.-K.; Suh, H.-W.; Song, D.-K. Inhibitory Effects of Long-Term Administration of Ferulic Acid on Microglial Activation Induced by Intracerebroventricular Injection of β-Amyloid Peptide (1—42) in Mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 27, 120–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-B.; Lee, S.; Hwang, E.-S.; Maeng, S.; Park, J.-H. p-Coumaric acid enhances long-term potentiation and recovers scopolamine-induced learning and memory impairments. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 492, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Lee, D.; Lee, H.L.; Kim, C.E.; Jung, K.; Kang, K.S. Beneficial effects of Panax ginseng for the treatment and prevention of neurodegenerative diseases: Past findings and future directions. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelsey, N.A.; Wilkins, H.M.; Linseman, D.A. Nutraceutical antioxidants as novel neuroprotective agents. Molecules 2010, 15, 7792–7814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vauzour, D.; Buonfiglio, M.; Corona, G.; Chirafisi, J.; Vafeiadou, K.; Angeloni, C.; Hrelia, S.; Hrelia, P.; Spencer, J.P.E. Sulforaphane protects cortical neurons against 5-S-cysteinyl-dopamine-induced toxicity through the activation of ERK1/2, NrF-2 and the upregulation of detoxification enzymes. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarozzi, A.; Angeloni, C.; Malaguti, M.; Morroni, F.; Hrelia, S.; Hrelia, P. Sulforaphane as a Potential protective phytochemical against neurodegenerative diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 415078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs from 1981 to 2014. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheynier, V.; Comte, G.; Davies, K.M.; Lattanzio, V.; Martens, S. Plant phenolics: Recent advances on their biosynthesis, genetics, andecophysiology. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 72, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnuolo, C.; Napolitano, M.; Tedesco, I.; Moccia, S.; Milito, A.; Russo, G.L. Neuroprotective role of natural polyphenols. Curr.Top. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 1943–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueira, I.; Garcia, G.; Pimpão, R.C.; Terrasso, A.; Costa, I.; Almeida, A.; Tavares, L.; Pais, T.; Pinto, P.; Ventura, M. Polyphenols journey through blood-brain barrier towards neuronal protection. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, R. Chemistry and biochemistry of dietary polyphenols. Nutrients 2010, 2, 1231–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eastwood, M.A. Interaction of dietary antioxidants in vivo: How fruit and vegetables prevent disease? QJM 1999, 92, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollman, P.C.H.; Katan, M.B. Health effects and bioavailability of dietary flavonols. Free Radic. Res. 1999, 31, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prior, R.L.; Cao, G.; Martin, A.; Sofic, E.; McEwen, J.; O’Brien, C.; Lischner, N.; Ehlenfeldt, M.; Kalt, W.; Krewer, G.; et al. Antioxidant Capacity as Influenced by Total Phenolic and Anthocyanin Content, Maturity, and Variety of Vaccinium Species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 2686–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Jeong, T.-S.; Lee, M.-K.; Park, Y.B.; Choi, M.-S. Lipid-lowering efficacy of hesperetin metabolites in high-cholesterol fed rats. Clin. Chim. Acta 2003, 327, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soobrattee, M.A.; Neergheen, V.S.; Luximon-Ramma, A.; Aruoma, O.I.; Bahorun, T. Phenolics as potential antioxidant therapeutic agents: Mechanism and actions. Mutat. Res. 2005, 579, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Lin, H.S. Antioxidant activity in fruits and leaves of blackberry, raspberry, and strawberry varies with cultivar and developmental stage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghorn, L.F.; Hoestgaard-Jensen, K.; Kongstad, K.T.; Bay, T.; Higgins, D.; Frølund, B.; Wellendorph, P. Positive allosteric modulation of the GHB high-affinity binding site by the GABAA receptor modulator monastrol and the flavonoid catechin. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freyssin, A.; Page, G.; Fauconneau, B.; Bilan, A.R. Natural polyphenols effects on protein aggregates in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s prion-like diseases. Neural Regen. Res. 2018, 13, 955. [Google Scholar]
- Gopinath, K.; Sudhandiran, G. Naringin modulates oxidative stress and inflammation in 3-nitropropionic acid-induced neurodegeneration through the activation of nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor-2 signalling pathway. Neuroscience 2012, 227, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhir, R.; Mehrotra, A. Quercetin supplementation is effective in improving mitochondrial dysfunctions induced by 3-nitropropionic acid: Implications in Huntington’s disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2013, 1832, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, H.; Jing, X.; Wei, X.; Shi, H.; Ren, D.; Zhang, X. Naringenin protects against 6-OHDA-induced neurotoxicity via activation of the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway. Neuropharmacology 2014, 79, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katalinić, M.; Rusak, G.; Barović, J.D.; Šinko, G.; Jelić, D.; Antolović, R.; Kovarik, Z. Structural aspects of flavonoids as inhibitors of human butyrylcholinesterase. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, N.; Choi, J.H.; Yang, H.; Jeong, E.J.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, Y.C.; Sung, S.H. Neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of flavonoids isolated from Rhus verniciflua in neuronal HT22 and microglial BV2 cell lines. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 1940–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, J.P.; Vafeiadou, K.; Williams, R.J.; Vauzour, D. Neuroinflammation: Modulation by flavonoids and mechanisms of action. Mol. Asp. Med. 2012, 33, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiciński, M.; Domanowska, A.; Wódkiewicz, E.; Malinowski, B. Neuroprotective Properties of Resveratrol and Its Derivatives—Influence on Potential Mechanisms Leading to the Development of Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.R.; Fritzen, M.; Yunes, R.A.; Leal, P.C.; Creczynski-Pasa, T.B.; Pereira, A.F. Inhibitory effects of gallic acid ester derivatives on Saccharomyces cerevisiae multidrug resistance protein Pdr5p. FEMS Yeast Res. 2010, 10, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaki, A.; Ohnuki, S.; Suga, Y.; Izawa, S.; Ohya, Y. Vanillin inhibits translation and induces messenger ribonucleoprotein (mRNP) granule formation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Application and validation of high-content, image-based profiling. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunthonkun, P.; Palajai, R.; Somboon, P.; Suan, C.L.; Ungsurangsri, M.; Soontorngun, N. Life-span extension by pigmented rice bran in the model yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.G.; Garrick, J.M.; Roquè, P.J.; Pellacani, C. Mechanisms of neuroprotection by quercetin: Counteracting oxidative stress and more. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 2986796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Lin, Q.; Liang, Y. Plant-derived antioxidants protect the nervous system from aging by inhibiting oxidative stress. Front. aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scognamiglio, M.; Fiumano, V.; D’Abrosca, B.; Esposito, A.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R.; Fiorentino, A. Chemical interactions between plants in Mediterranean vegetation: The influence of selected plant extracts on Aegilops geniculata metabolome. Phytochemistry 2014, 106, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scognamiglio, M.; Graziani, V.; Tsafantakis, N.; Esposito, A.; Fiorentino, A.; D’Abrosca, B. NMR-based metabolomics and bioassays to study phytotoxic extracts and putative phytotoxins from Mediterranean plant species. Phytochem. Anal. 2019, 30, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chengxu, W.; Mingxing, Z.; Xuhui, C.; Bo, Q. Review on allelopathy of exotic invasive plants. Procedia Eng. 2011, 18, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, N.; Alías, J.; Sosa, T. Phytotoxicity of Cistus ladanifer L.: Role of allelopathy. Allelopath. J. 2016, 38, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas-Martínez, S. Memoria y Mapas de la Series de Vegetación de España.1:400.000; ICONA. Serie Técnica; MAPA: Madrid, Spain, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Plan Forestal de Extremadura. Análisis y Estudio del Paisaje Vegetal y su Dinámica en la región de Extremadura. Available online: http://extremambiente.juntaex.es/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=3609&Itemid=307 (accessed on 8 November 2023).
- Chaves, N.; Ríos, J.J.; Gutierrez, C.; Escudero, J.C.; Olías, J.M. Analysis of secreted flavonoids of Cistus ladanifer L. by high-performance liquid chromatography–particle beam mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 1998, 799, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, N.; Sosa, T.; Alías, J.C.; Escudero, J.C. Identification and effects of interaction phytotoxic compounds from exudate of Cistus ladanifer leaves. J. Chem. Ecol. 2001, 27, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einhellig, F.A.; Galindo, J.C.G.; Molinillo, J.M.G.; Cutler, H.G. Mode of allelochemical action of phenolic compounds. In Allelopathy: Chemistry and Mode of Action of Allelochemicals; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; pp. 217–238. [Google Scholar]
- Barrajõn-Catalán, E.; Fernández-Arroyo, S.; Roldán, C.; Guillén, E.; Saura, D.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Micol, V. A systematic study of the polyphenolic composition of aqueous extracts deriving from several Cistus genus species: Evolutionary relationship. Phytochem. Anal. 2011, 22, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrajón-Catalán, E.; Fernández-Arroyo, S.; Saura, D.; Guillén, E.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, A.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Micol, V. Cistaceae aqueous extracts containing ellagitannins show antioxidant and antimicrobial capacity, and cytotoxic activity against human cancer cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 2273–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viuda-Martos, M.; Sendra, E.; Alvarez, J.A.P.; Fernández-López, J.; Amensour, M.; Abrini, J. Identification of flavonoid content and chemical composition of the essential oils of moroccan herbs: Myrtle (Myrtus communis L.), rockrose (Cistus ladanifer L.) and montpellier cistus (Cistus monspeliensis L.). J. Essent. Oil Res. 2011, 23, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, L.; Dueñas, M.; Alves, C.T.; Silva, S.; Henriques, M.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Antifungal activity and detailed chemical characterization of Cistus ladanifer phenolic extracts. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 41, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaweł-Bęben, K.; Kukula-Koch, W.; Hoian, U.; Czop, M.; Strzępek-Gomółka, M.; Antosiewicz, B. Characterization of Cistus × incanus L. and Cistus ladanifer L. extracts as potential multifunctional antioxidant ingredients for skin protecting cosmetics. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves-Ferreira, J.; Miranda, I.; Duarte, L.C.; Roseiro, L.B.; Lourenço, A.; Quilhó, T.; Cardoso, S.; Fernandes, M.C.; Carvalheiro, F.; Pereira, H. Cistus ladanifer as a source of chemicals: Structural and chemical characterization. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2020, 10, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carev, I.; Maravić, A.; Ilić, N.; Čulić, V.Č.; Politeo, O.; Zorić, Z.; Radan, M. UPLC-MS/MS phytochemical analysis of two Croatian Cistus species and their biological activity. Life 2020, 10, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastino, P.M.; Marchetti, M.; Costa, J.; Juliano, C.; Usai, M. Analytical Profiling of Phenolic Compounds in Extracts of Three Cistus Species from Sardinia and Their Potential Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activity. Chem. Biodivers. 2021, 18, e2100053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Jemia, M.; Kchouk, M.E.; Senatore, F.; Autore, G.; Marzocco, S.; De Feo, V.; Bruno, M. Antiproliferative activity of hexane extract from Tunisian Cistus libanotis, Cistus monspeliensis and Cistus villosus. Chem. Cent. J. 2013, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomé-Abarca, L.F.; Mandrone, M.; Sanna, C.; Poli, F.; van der Hondel, C.A.M.J.J.; Klinkhamer, P.G.L.; Choi, Y.H. Metabolic variation in Cistus monspeliensis L. ecotypes correlated to their plant-fungal interactions. Phytochemistry 2020, 176, 112402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahiri, O.; Atmani-Kilani, D.; Sanchez-Fidalgo, S.; Aparicio-Soto, M.; Alarcón-de-la-Lastra, C.; Barrajón-Catalán, E.; Micol, V.; Atmani, D. The flavonol-enriched Cistus albidus chloroform extract possesses in vivo anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive activity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 209, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luís, Â.; Domingues, F.; Duarte, A.P. Bioactive compounds, RP-HPLC analysis of phenolics, and antioxidant activity of some Portuguese shrub species extracts. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2011, 6, 1863–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, L.; Dueñas, M.; Carvalho, A.M.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Santos-Buelga, C. Characterization of phenolic compounds in flowers of wild medicinal plants from Northeastern Portugal. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 1576–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, O.R.; Silva, A.M.S.; Domingues, M.R.M.; Cardoso, S.M. Identification of phenolic constituents of Cytisus multiflorus. Food Chem. 2012, 131, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, O.R.; Macias, R.I.R.; Perez, M.J.; Marin, J.J.G.; Cardoso, S.M. Protective effects of phenolic constituents from Cytisus multiflorus, Lamium album L. and Thymus citriodorus on liver cells. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Oliveira, P.; Carreira-Casais, A.; Pereira, E.; Dias, M.I.; Pereira, C.; Calhelha, R.C.; Stojković, D.; Sokovic, M.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Prieto, M.A.; et al. From Tradition to Health: Chemical and Bioactive Characterization of Five Traditional Plants. Molecules 2022, 27, 6495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, N.; Ribeiro, D.; Fernandes, E.; Nogueira, D.R.; Conde, E.; Moure, A.; Vinardell, M.P.; Mitjans, M.; Domínguez, H. Potential use of Cytisus scoparius extracts in topical applications for skin protection against oxidative damage. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2013, 125, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lores, M.; Pájaro, M.; Álvarez-Casas, M.; Domínguez, J.; García-Jares, C. Use of ethyl lactate to extract bioactive compounds from Cytisus scoparius: Comparison of pressurized liquid extraction and medium scale ambient temperature systems. Talanta 2015, 140, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, N.; Otero, A.; Conde, E.; Falqué, E.; Moure, A.; Domínguez, H. Extraction of phenolics from broom branches using green technologies. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2017, 92, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, A.C.; Coqueiro, A.; Sultan, A.R.; Lemmens, N.; Kim, H.K.; Verpoorte, R.; Van Wamel, W.J.; Simões, M.; Choi, Y.H. Looking to nature for a new concept in antimicrobial treatments: Isoflavonoids from Cytisus striatus as antibiotic adjuvants against MRSA. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekkai, D.; El Majdoub, Y.O.; Bekkai, H.; Cacciola, F.; Miceli, N.; Taviano, M.F.; Cavò, E.; Errabii, T.; Vinci, R.L.; Mondello, L. Determination of the phenolic profile by liquid chromatography, evaluation of antioxidant activity and toxicity of moroccan Erica multiflora, Erica scoparia, and Calluna vulgaris (Ericaceae). Molecules 2022, 27, 3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márquez-García, B.; Fernández, M.A.; Córdoba, F. Phenolics composition in Erica sp. differentially exposed to metal pollution in the Iberian Southwestern Pyritic Belt. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caleja, C.; Finimundy, T.C.; Pereira, C.; Barros, L.; Calhelha, R.C.; Sokovic, M.; Ivanov, M.; Carvalho, A.M.; Rosa, E.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Challenges of traditional herbal teas: Plant infusions and their mixtures with bioactive properties. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 5939–5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yangui, I.; Younsi, F.; Ghali, W.; Boussaid, M.; Messaoud, C. Phytochemicals, antioxidant and anti-proliferative activities of Myrtus communis L. genotypes from Tunisia. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 137, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amel, Z.; Nabila, B.B.; Nacéra, G.; Fethi, T.; Fawzia, A.B. Assessment of phytochemical composition and antioxidant properties of extracts from the leaf, stem, fruit and root of Pistacia lentiscus L. Int. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. Res. 2016, 8, 627–633. [Google Scholar]
- Yemmen, M.; Landolsi, A.; Ben Hamida, J.; Mégraud, F.; Trabelsi Ayadi, M. Antioxidant activities, anticancer activity and polyphenolics profile, of leaf, fruit and stem extracts of Pistacia lentiscus from Tunisia. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2017, 63, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehaki, C.; Jullian, N.; Ayati, F.; Fernane, F.; Gontier, E. A Review of Pistacia lentiscus Polyphenols: Chemical Diversity and Pharmacological Activities. Plants 2023, 12, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özcan, M.M.; Al Juhaimi, F.; Uslu, N.; Ahmed, I.A.M.; Babiker, E.E.; Osman, M.A.; Gassem, M.A.; Alqah, H.A.S.; Ghafoor, K. Effect of sonication process of terebinth (Pistacia terebinthus L.) fruits on antioxidant activity, phenolic compounds, fatty acids and tocopherol contents. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 2017–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, S.; Sinan, K.I.; Jekő, J.; Cziáky, Z.; Zengin, G. Chemical characterization, comprehensive antioxidant capacity, and enzyme inhibitory potential of leaves from Pistacia terebinthus L. (Anacardiaceae). Food Biosci. 2022, 48, 101820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena, P.; Cirlini, M.; Tassotti, M.; Herrlinger, K.A.; Dall’Asta, C.; Del Rio, D. Phytochemical Profiling of Flavonoids, Phenolic Acids, Terpenoids, and Volatile Fraction of a Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) Extract. Molecules 2016, 21, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falade, A.O.; Omolaiye, G.I.; Adewole, K.E.; Agunloye, O.M.; Ishola, A.A.; Okaiyeto, K.; Oboh, G.; Oguntibeju, O.O. Aqueous Extracts of Bay Leaf (Laurus nobilis) and Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis) Inhibit Iron-Induced Lipid Peroxidation and Key-Enzymes Implicated in Alzheimer’s Disease in Rat Brain-in Vitro. Am. J. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 18, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellumori, M.; Innocenti, M.; Congiu, F.; Cencetti, G.; Raio, A.; Menicucci, F.; Mulinacci, N.; Michelozzi, M. Within-plant variation in Rosmarinus officinalis L. Terpenes and phenols and their antimicrobial activity against the rosemary phytopathogens Alternaria alternata and Pseudomonas viridiflava. Molecules 2021, 26, 3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, E.W.C.; Wong, S.K.; Chan, H.T. An overview of the chemistry and anticancer properties of rosemary extract and its diterpenes. J. HerbMed Pharmacol. 2022, 11, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaymaa, M.H.; Adnan, M.M.; Muthanna, J.M. The Effect of Extracts and Phenolic Compounds Isolation from Rosmarinus officinalis Plant Leaves on Tribolium castaneum Mortality. Int. J. Drug Deliv. Technol. 2022, 12, 814–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama, K.S.; Monteiro, M.C.; Saito, P.; Pinto, I.C.; Nakano, C.T.; Martinez, R.M.; Thomaz, D.V.; Verri, W.A.; Baracat, M.M.; Arakawa, N.S. Rosmarinus officinalis extract-loaded emulgel prevents UVB irradiation damage to the skin. Anais Acad. Brasil. Ciências 2022, 94, e20201058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karioti, A.; Sokovic, M.; Ciric, A.; Koukoulitsa, C.; Bilia, A.R.; Skaltsa, H. Antimicrobial properties of Quercus ilex L. proanthocyanidin dimers and simple phenolics: Evaluation of their synergistic activity with conventional antimicrobials and prediction of their pharmacokinetic profile. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 6412–6422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Custódio, L.; Patarra, J.; Alberício, F.; Neng, N.R.; Nogueira, J.M.F.; Romano, A. Extracts from Quercus sp. acorns exhibit in vitro neuroprotective features through inhibition of cholinesterase and protection of the human dopaminergic cell line SH-SY5Y from hydrogen peroxide-induced cytotoxicity. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 45, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadidi, L.; Babou, L.; Zaidi, F.; Valentão, P.; Andrade, P.B.; Grosso, C. Quercus ilex L.: How season, Plant Organ and Extraction Procedure Can Influence Chemistry and Bioactivities. Chem. Biodivers. 2017, 14, e1600187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlowska, A.M.; De Leo, M.; Braca, A. Phenolics of Arbutus unedo L.(Ericaceae) fruits: Identification of anthocyanins and gallic acid derivatives. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 10234–10238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorentino, A.; Castaldi, S.; D’Abrosca, B.; Natale, A.; Carfora, A.; Messere, A.; Monaco, P. Polyphenols from the hydroalcoholic extract of Arbutus unedo living in a monospecific Mediterranean woodland. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2007, 35, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallauf, K.; Rivas-Gonzalo, J.C.; Del Castillo, M.; Cano, M.P.; de Pascual-Teresa, S. Characterization of the antioxidant composition of strawberry tree (Arbutus unedo L.) fruits. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2008, 21, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, R.; Barros, L.; Dueñas, M.; Carvalho, A.M.; Queiroz, M.J.R.P.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Characterisation of phenolic compounds in wild fruits from Northeastern Portugal. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 3721–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleš, Ž.; Šarić, D.; Bojić, M. Quantitative determination of flavonoids and chlorogenic acid in the leaves of Arbutus unedo L. using thin layer chromatography. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2013, 2013, 385473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachkoul, R.; Housseini, T.S.; Mohim, M.; El Habbani, R.; Miyah, Y.; Lahrichi, A. Chemical compounds as well as antioxidant and litholytic activities of Arbutus unedo L. leaves against calcium oxalate stones. J. Integr. Med. 2019, 17, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldini, M.; D’Urso, G.; Pagliuca, G.; Petretto, G.L.; Foddai, M.; Gallo, F.R.; Multari, G.; Caruso, D.; Montoro, P.; Pintore, G. HPTLC-PCA complementary to HRMS-PCA in the case study of Arbutus unedo antioxidant phenolic profiling. Foods 2019, 8, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenuta, M.C.; Deguin, B.; Loizzo, M.R.; Dugay, A.; Acquaviva, R.; Malfa, G.A.; Bonesi, M.; Bouzidi, C.; Tundis, R. Contribution of flavonoids and iridoids to the hypoglycaemic, antioxidant, and nitric oxide (NO) inhibitory activities of Arbutus unedo L. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Cadi, H.; El Cadi, A.; Kounnoun, A.; El Majdoub, Y.O.; Lovillo, M.P.; Brigui, J.; Dugo, P.; Mondello, L.; Cacciola, F. Wild strawberry (Arbutus unedo): Phytochemical screening and antioxidant properties of fruits collected in northern Morocco. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 6299–6311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitouni, H.; Hssaini, L.; Messaoudi, Z.; Ourradi, H.; Viuda-Martos, M.; Hernández, F.; Ercisli, S.; Hanine, H. Phytochemical components and bioactivity assessment among twelve strawberry (Arbutus unedo L.) genotypes growing in Morocco using chemometrics. Foods 2020, 9, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coimbra, A.T.; Luís, Â.F.; Batista, M.T.; Ferreira, S.M.; Duarte, A.P.C. Phytochemical characterization, bioactivities evaluation and synergistic effect of Arbutus unedo and Crataegus monogyna extracts with Amphotericin B. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 2143–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macchioni, V.; Santarelli, V.; Carbone, K. Phytochemical profile, antiradical capacity and α-glucosidase inhibitory potential of wild Arbutus unedo L. Fruits from central italy: A chemometric approach. Plants 2020, 9, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izcara, S.; Morante-Zarcero, S.; Casado, N.; Sierra, I. Study of the Phenolic Compound Profile of Arbutus unedo L. Fruits at Different Ripening Stages by HPLC-TQ-MS/MS. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.; Batista, T.; Pinto, G.; Canhoto, J. Seasonal variation of phenolic compounds in Strawberry tree (Arbutus unedo L.) leaves and inhibitory potential on Phytophthora cinnamomi. Trees 2021, 35, 1571–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brčić Karačonji, I.; Jurica, K.; Gašić, U.; Dramićanin, A.; Tešić, Ž.; Milojković Opsenica, D. Comparative study on the phenolic fingerprint and antioxidant activity of strawberry tree (Arbutus unedo L.) leaves and fruits. Plants 2022, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, M.D.M.; Algieri, F.; Rodriguez-Nogales, A.; Gálvez, J.; Segura-Carretero, A. Phytochemical profiling of anti-inflammatory Lavandula extracts via RP–HPLC–DAD–QTOF–MS and –MS/MS: Assessment of their qualitative and quantitative differences. Electrophoresis 2018, 39, 1284–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karan, T. Metabolic profile and biological activities of Lavandula stoechas L. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2018, 64, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobros, N.; Zawada, K.D.; Paradowska, K. Phytochemical Profiling, Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Plants Belonging to the Lavandula Genus. Molecules 2023, 28, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriti, J.; Fares, N.; Msaada, K.; Zarroug, Y.; Boulares, M.; Djebbi, S.; Selmi, S.; Limam, F. Phenological stage effect on phenolic composition, antioxidant, and antibacterial activity of Lavandula stoechas extract. Riv. Ital. Sostanze Grasse 2022, 99, 225–234. [Google Scholar]
- Karabagias, I.K.; Karabagias, V.K.; Riganakos, K.A. Physico-Chemical Parameters, Phenolic Profile, In Vitro Antioxidant Activity and Volatile Compounds of Ladastacho (Lavandula stoechas) from the Region of Saidona. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingues, J.; Delgado, F.; Gonçalves, J.C.; Zuzarte, M.; Duarte, A.P. Mediterranean Lavenders from Section Stoechas: An Undervalued Source of Secondary Metabolites with Pharmacological Potential. Metabolites 2023, 13, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Vioque, R.; Polissiou, M.; Astraka, K.; Mozos-Pascual, M.D.L.; Tarantilis, P.; Herraiz-Peñalver, D.; Santana-Méridas, O. Polyphenol composition and antioxidant and metal chelating activities of the solid residues from the essential oil industry. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 49, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, T.; Marinero, P.; Asensio-S.-Manzanera, M.C.; Asensio, C.; Herrero, B.; Pereira, J.A.; Ramalhosa, E. Antioxidant activity of twenty wild Spanish Thymus mastichina L. populations and its relation with their chemical composition. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 57, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Tovar, I.; Sponza, S.; Asensio-S-Manzanera, M.C.; Novak, J. Contribution of the main polyphenols of Thymus mastichina subsp: Mastichina to its antioxidant properties. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 66, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; Al-Raqmi, K.A.S.; Al-Mijizy, Z.H.; Weli, A.M.; Al-Riyami, Q. Study of total phenol, flavonoids contents and phytochemical screening of various leaves crude extracts of locally grown Thymus vulgaris. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2013, 3, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara-Salinas, J.R.; Pérez-Jiménez, J.; Torres, J.L.; Agosin, E.; Pérez-Correa, J.R. Effects of temperature and time on polyphenolic content and antioxidant activity in the pressurized hot water extraction of deodorized thyme (Thymus vulgaris). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 10920–10929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roby, M.H.H.; Sarhan, M.A.; Selim, K.A.H.; Khalel, K.I. Evaluation of antioxidant activity, total phenols and phenolic compounds in thyme (Thymus vulgaris L.), sage (Salvia officinalis L.), and marjoram (Origanum majorana L.) extracts. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 43, 827–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliora, A.C.; Kogiannou, D.A.A.; Kefalas, P.; Papassideri, I.S.; Kalogeropoulos, N. Phenolic profiles and antioxidant and anticarcinogenic activities of Greek herbal infusions; Balancing delight and chemoprevention? Food Chem. 2014, 142, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, E.; Barros, L.; Antonio, A.L.; Cabo Verde, S.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Infusions from Thymus vulgaris L. treated at different gamma radiation doses: Effects on antioxidant activity and phenolic composition. LWT 2016, 74, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, E.; Pimenta, A.I.; Barros, L.; Calhelha, R.C.; Antonio, A.L.; Cabo Verde, S.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Effects of gamma radiation on the bioactivity of medicinal and aromatic plants: Mentha × piperita L., Thymus vulgaris L. and Aloysia citrodora Paláu as case studies. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 5150–5161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonmezdag, A.S.; Kelebek, H.; Selli, S. Characterization of bioactive and volatile profiles of thyme (Thymus vulgaris L.) teas as affected by infusion times. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2018, 12, 2570–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlili, N.; Sarikurkcu, C. Bioactive compounds profile, enzyme inhibitory and antioxidant activities of water extracts from five selected medicinal plants. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 151, 112448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.M.; Ramu, R.; Shirahatti, P.S.; Shivamallu, C.; Amachawadi, R.G. A systematic review on ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacological aspects of Thymus vulgaris Linn. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, R.; Kazemi Fard, M.; Rezaei, M.; Moftakharzadeh, S.A.; Mohseni, A. Antioxidant, Antimicrobial Activities, and Characterization of Phenolic Compounds of Thyme (Thymus vulgarisL.), Sage (Salvia officinalis L.), and Thyme–Sage Mixture Extracts. J. Food Qual. 2023, 2602454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, S.; D’Addario, C.; Colacevich, A.; Focardi, S.; Borghini, F.; Santucci, A.; Figura, N.; Rossi, C. Antimicrobial activity against Helicobacter pylori strains and antioxidant properties of blackberry leaves (Rubus ulmifolius) and isolated compounds. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2009, 34, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quave, C.L.; Estévez-Carmona, M.; Compadre, C.M.; Hobby, G.; Hendrickson, H.; Beenken, K.E.; Smeltzer, M.S. Ellagic acid derivatives from Rubus ulmifolius inhibit Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation and improve response to antibiotics. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e28737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazio, A.; Plastina, P.; Meijerink, J.; Witkamp, R.F.; Gabriele, B. Comparative analyses of seeds of wild fruits of Rubus and Sambucus species from Southern Italy: Fatty acid composition of the oil, total phenolic content, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of the methanolic extracts. Food Chem. 2013, 140, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Rodríguez, B.M.; Sánchez-Moreno, C.; Ancos, B.D.; Sánchez-Mata, M.D.; Fernández-Ruíz, V.; Cámara, M.; Tardío, J. Wild Arbutus unedo L. and Rubus ulmifolius Schott fruits are underutilized sources of valuable bioactive compounds with antioxidant capacity. Fruits 2014, 69, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.; Barros, L.; Carvalho, A.M.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Fernandes, I.P.; Barreiro, F.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Phenolic extracts of Rubus ulmifolius Schott flowers: Characterization, microencapsulation and incorporation into yogurts as nutraceutical sources. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabarki, S.; Aouadhi, C.; Mechergui, K.; Hammi, K.M.; Ksouri, R.; Raies, A.; Toumi, L. Comparison of Phytochemical Composition and Biological Activities of Rubus ulmifolius Extracts Originating from Four Regions of Tunisia. Chem. Biodivers. 2017, 14, e1600168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, L.P.; Pereira, E.; Pires, T.C.S.P.; Alves, M.J.; Pereira, O.R.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Rubus ulmifolius Schott fruits: A detailed study of its nutritional, chemical and bioactive properties. Food Res. Int. 2019, 119, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, M.; Seraglio, S.K.T.; Della Betta, F.; Nehring, P.; Valese, A.C.; Daguer, H.; Gonzaga, L.V.; Costa, A.C.O.; Fett, R. Blackberry (Rubus ulmifolius Schott): Chemical composition, phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacity in two edible stages. Food Res. Int. 2019, 122, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.A.; Nicácio, A.E.; Boeing, J.S.; Garcia, F.P.; Nakamura, C.V.; Visentainer, J.V.; Maldaner, L. Rapid extraction method followed by a d-SPE clean-up step for determination of phenolic composition and antioxidant and antiproliferative activities from berry fruits. Food Chem. 2020, 309, 125694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candela, R.G.; Lazzara, G.; Piacente, S.; Bruno, M.; Cavallaro, G.; Badalamenti, N. Conversion of organic dyes into pigments: Extraction of flavonoids from blackberries (Rubus ulmifolius) and stabilization. Molecules 2021, 26, 6278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice-Evans, C.A.; Miller, N.J.; Paganga, G. Structure-antioxidant activity relationships of flavonoids and phenolic acids. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1996, 20, 933–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daglia, M.; Di Lorenzo, A.; F Nabavi, S.; S Talas, Z.; M Nabavi, S. Polyphenols: Well beyond the antioxidant capacity: Gallic acid and related compounds as neuroprotective agents: You are what you eat! Curr. Pharm.Biotechnol. 2014, 15, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabani, S.; Rabiei, Z.; Amini-Khoei, H. Exploring the multifaceted neuroprotective actions of gallic acid: A review. Int. J. Food Prop. 2020, 23, 736–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, S.; Loureiro, J.A.; Pereira, M.C. Transferrin-functionalized liposomes for the delivery of gallic acid: A therapeutic approach for Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansouri, M.T.; Farbood, Y.; Sameri, M.J.; Sarkaki, A.; Naghizadeh, B.; Rafeirad, M. Neuroprotective effects of oral gallic acid against oxidative stress induced by 6-hydroxydopamine in rats. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 1028–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirshekar, M.A.; Sarkaki, A.; Farbood, Y.; Gharib Naseri, M.K.; Badavi, M.; Mansouri, M.T.; Haghparast, A. Neuroprotective effects of gallic acid in a rat model of traumatic brain injury: Behavioral, electrophysiological, and molecular studies. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2018, 21, 1056–1063. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maya, S.; Prakash, T.; Goli, D. Effect of wedelolactone and gallic acid on quinolinic acid-induced neurotoxicity and impaired motor function: Significance to sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. NeuroToxicology 2018, 68, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.-X.; Shan, J.-L.; Hu, W.-Q.; Zeng, J.-X.; Shu, J.-C. Gallic acid activates hippocampal BDNF-Akt-mTOR signaling in chronic mild stress. Metab. Brain Dis. 2019, 34, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, A.; Muñoz-Arenas, G.; Caporal-Hernandez, K.; Vázquez-Roque, R.; Lopez-Lopez, G.; Kozina, A.; Espinosa, B.; Flores, G.; Treviño, S.; Guevara, J. Gallic acid improves recognition memory and decreases oxidative-inflammatory damage in the rat hippocampus with metabolic syndrome. Synapse 2021, 75, e22186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-J.; Seong, A.-R.; Yoo, J.-Y.; Jin, C.-H.; Lee, Y.-H.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.; Jun, W.J.; Yoon, H.-G. Gallic acid, a histone acetyltransferase inhibitor, suppresses β-amyloid neurotoxicity by inhibiting microglial-mediated neuroinflammation. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 1798–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maya, S.; Prakash, T.; Goli, D. Evaluation of neuroprotective effects of wedelolactone and gallic acid on aluminium-induced neurodegeneration: Relevance to sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 835, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunlade, B.; Adelakun, S.A.; Agie, J.A. Nutritional supplementation of gallic acid ameliorates Alzheimer-type hippocampal neurodegeneration and cognitive impairment induced by aluminum chloride exposure in adult Wistar rats. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 45, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samad, N.; Jabeen, S.; Imran, I.; Zulfiqar, I.; Bilal, K. Protective effect of gallic acid against arsenic-induced anxiety−/depression-like behaviors and memory impairment in male rats. Metab. Brain Dis. 2019, 34, 1091–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabavi, S.F.; Tejada, S.; Setzer, W.N.; Gortzi, O.; Sureda, A.; Braidy, N.; Daglia, M.; Manayi, A.; Nabavi, S.M. Chlorogenic acid and mental diseases: From chemistry to medicine. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2017, 15, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Dong, L.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, G.; Dang, X.; Lu, X.; Jia, M. Chlorogenic acid reduces liver inflammation and fibrosis through inhibition of toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway. Toxicology 2013, 303, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimifard, M.; Maqbool, F.; Moeini-Nodeh, S.; Niaz, K.; Abdollahi, M.; Braidy, N.; Nabavi, S.M.; Nabavi, S.F. Targeting the TLR4 signaling pathway by polyphenols: A novel therapeutic strategy for neuroinflammation. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 36, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Dhiman, M.; Mantha, A.K. Ferulic Acid: A Natural Antioxidant with Application towards Neuroprotection against Alzheimer’s Disease. In Functional Food and Human Health; Rani, V., Yadav, U.C.S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 575–586. [Google Scholar]
- Gulcin, İ. Antioxidants and antioxidant methods: An updated overview. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 651–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, C.; Santangelo, R. Ferulic acid: Pharmacological and toxicological aspects. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 65, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Rui, Y.; Guo, S.-D.; Luan, F.; Liu, R.; Zeng, N. Ferulic acid: A review of its pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and derivatives. Life Sci. 2021, 284, 119921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-M.; Shen, J.-D.; Xu, L.-P.; Li, H.-B.; Li, Y.-C.; Yi, L.-T. Ferulic acid inhibits neuro-inflammation in mice exposed to chronic unpredictable mild stress. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 45, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikugawa, M.; Tsutsuki, H.; Ida, T.; Nakajima, H.; Ihara, H.; Sakamoto, T. Water-soluble ferulic acid derivatives improve amyloid-β-induced neuronal cell death and dysmnesia through inhibition of amyloid-β aggregation. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2016, 80, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.-J.; Wu, M.-Y.; Lu, J.-H. Ferulic Acid in Animal Models of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review of Preclinical Studies. Cells 2021, 10, 2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.-J.; Cho, J.-Y.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, K.-L.; Jung, J.-S.; Huh, S.-O.; Suh, H.-W.; Kim, Y.-H.; Song, D.-K. Protection against β-amyloid peptide toxicity in vivo with long-term administration of ferulic acid. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 133, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.-Y.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, D.-H.; Yan, J.-J.; Suh, H.-W.; Song, D.-K. Inhibitory effects of long-term administration of ferulic acid on astrocyte activation induced by intracerebroventricular injection of β-amyloid peptide (1–42) in mice. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2005, 29, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.-Y.; Li, J.-N.; Liu, W.-L.; Huang, Q.; Li, W.-X.; Tan, Y.-H.; Liu, F.; Song, Z.-H.; Wang, M.-Y.; Xie, N.; et al. Ferulic Acid Ameliorates Alzheimer’s Disease-like Pathology and Repairs Cognitive Decline by Preventing Capillary Hypofunction in APP/PS1 Mice. Neurotherapeutics 2021, 18, 1064–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AAlikhani, M.; Khalili, M.; Jahanshahi, M. The natural iron chelators’ ferulic acid and caffeic acid rescue mice’s brains from side effects of iron overload. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 951725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, U.J.; Lee, M.K.; Park, Y.B.; Jeon, S.M.; Choi, M.S. Antihyperglycemic and antioxidant properties of caffeic acid in db/db mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 318, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maass, A.; Düzel, S.; Brigadski, T.; Goerke, M.; Becke, A.; Sobieray, U.; Neumann, K.; Lövdén, M.; Lindenberger, U.; Bäckman, L.; et al. Relationships of peripheral IGF-1, VEGF and BDNF levels to exercise-related changes in memory, hippocampal perfusion and volumes in older adults. NeuroImage 2016, 131, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Na, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, L. Roles of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling pathways in neurodegenerative diseases and tumours. Cell Biosci. 2020, 10, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.M.; Chauhan, L.; Bhardwaj, A.; Sharma, A.; Fayaz, F.; Kumar, B.; Alhashmi, M.; AlHajri, N.; Alam, M.S.; Pottoo, F.H. Brain-Derived Neurotropic Factor in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.; Huang, D.; Lo, Y.M.; Tee, Q.; Kuo, P.; Wu, J.S.; Huang, W.; Shen, S. Protective effect of caffeic acid against Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis via modulating cerebral insulin signaling, β-amyloid accumulation, and synaptic plasticity in hyperinsulinemic rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 7684–7693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.; Kamal, A.; Khan, F.; Jamali, K.S.; Saify, Z.S. Gallic and vanillic acid suppress inflammation and promote myelination in an in vitro mouse model of neurodegeneration. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 997–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesan, R.; Ji, E.; Kim, S.Y. Phytochemicals that regulate neurodegenerative disease by targeting neurotrophins: A comprehensive review. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 814068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamula, R.; Thong-asa, W. Neuroprotective effect of p-coumaric acid in mice with cerebral ischemia reperfusion injuries. Metab. Brain Dis. 2018, 33, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.-H.; Youn, K.; Ho, C.-T.; Karwe, M.V.; Jeong, W.-S.; Jun, M. p-Coumaric Acid and Ursolic Acid from Corni fructus Attenuated β-Amyloid25–35-Induced Toxicity through Regulation of the NF-κB Signaling Pathway in PC12 Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 4911–4916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, D.-R.; Kim, M.-J.; Choi, E.-J.; Kim, Y.; Lee, H.-S.; Bae, D.; Choi, C. Protective Effects of p-Coumaric Acid Isolated from Vaccinium bracteatum Thunb. Leaf Extract on Corticosterone-Induced Neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y Cells and Primary Rat Cortical Neurons. Processes 2021, 9, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daroi, P.A.; Dhage, S.N.; Juvekar, A.R. p-Coumaric acid mitigates lipopolysaccharide induced brain damage via alleviating oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2021, 74, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashno, M.; Gholipour, P.; Salehi, I.; Komaki, A.; Rashidi, K.; Esmaeil Khoshnam, S.; Ghaderi, S. p-Coumaric acid mitigates passive avoidance memory and hippocampal synaptic plasticity impairments in aluminum chloride-induced Alzheimer’s disease rat model. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 94, 105117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Chen, S.; Tsoi, B.; Qi, S.; Gu, B.; Wang, Z.; Peng, C.; Shen, J. Alpinia oxyphylla Miq. and Its Active Compound P-Coumaric Acid Promote Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Signaling for Inducing Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Improving Post-cerebral Ischemic Spatial Cognitive Functions. Front. Cell Develop. Biol. 2021, 8, 577790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mughal, E.U.; Sadiq, A.; Ashraf, J.; Zafar, M.N.; Sumrra, S.H.; Tariq, R.; Javed, C.O. Flavonols and 4-thioflavonols as potential acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors: Synthesis, structure-activity relationship and molecular docking studies. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 91, 103124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueira, I.; Menezes, R.; Macedo, D.; Costa, I.; dos Santos, C.N. Polyphenols beyond barriers: A glimpse into the brain. Curr. Neuropharmacol.. 2017, 15, 562–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manach, C.; Williamson, G.; Morand, C.; Scalbert, A.; Rémésy, C. Bioavailability and bioefficacy of polyphenols in humans. I. Review of 97 bioavailability studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renaud, J.; Martinoli, M.-G. Considerations for the use of polyphenols as therapies in neurodegenerative diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishisaka, A.; Ichikawa, S.; Sakakibara, H.; Piskula, M.K.; Nakamura, T.; Kato, Y.; Ito, M.; Miyamoto, K.-I.; Tsuji, A.; Kawai, Y. Accumulation of orally administered quercetin in brain tissue and its antioxidative effects in rats. Free Rad. Biol. Med. 2011, 51, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dajas, F.; Abin-Carriquiry, J.A.; Arredondo, F.; Blasina, F.; Echeverry, C.; Martínez, M.; Rivera, F.; Vaamonde, L. Quercetin in brain diseases: Potential and limits. Neurochem. Int. 2015, 89, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dajas, F. Life or death: Neuroprotective and anticancer effects of quercetin. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 143, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zhuang, J.; Li, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zheng, X. Myricitrin protects against peroxynitrite-mediated DNA damage and cytotoxicity in astrocytes. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreca, D.; Bellocco, E.; DOnofrio, G.; Fazel Nabavi, S.; Daglia, M.; Rastrelli, L.; Mohammad Nabavi, S. Neuroprotective effects of quercetin: From chemistry to medicine. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2016, 15, 964–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanzadeh, E.; Esmaeili, A.; Rahgozar, S.; Nourbakhshnia, M. Application of quercetin in neurological disorders: From nutrition to nanomedicine. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 30, 555–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azib, L.; Debbache-Benaida, N.; Costa, G.D.; Atmani-Kilani, D.; Saidene, N.; Ayouni, K.; Richard, T.; Atmani, D. Pistacia lentiscus L. leaves extract and its major phenolic compounds reverse aluminium-induced neurotoxicity in mice. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 137, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moneim, A.E.A. Antioxidant activities of Punica granatum (pomegranate) peel extract on brain of rats. J. Med. Plants Res. 2012, 6, 195–199. [Google Scholar]
- Martín, S.; González-Burgos, E.; Carretero, M.E.; Gómez-Serranillos, M.P. Neuroprotective properties of Spanish red wine and its isolated polyphenols on astrocytes. Food Chem. 2011, 128, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabogal-Guáqueta, A.M.; Munoz-Manco, J.I.; Ramírez-Pineda, J.R.; Lamprea-Rodriguez, M.; Osorio, E.; Cardona-Gómez, G.P. The flavonoid quercetin ameliorates Alzheimer’s disease pathology and protects cognitive and emotional function in aged triple transgenic Alzheimer’s disease model mice. Neuropharmacol. 2015, 93, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdalla, F.H.; Schmatz, R.; Cardoso, A.M.; Carvalho, F.B.; Baldissarelli, J.; de Oliveira, J.S.; Rosa, M.M.; Nunes, M.A.G.; Rubin, M.A.; da Cruz, I.B. Quercetin protects the impairment of memory and anxiogenic-like behavior in rats exposed to cadmium: Possible involvement of the acetylcholinesterase and Na+, K+-ATPase activities. Physiol. Behav. 2014, 135, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.T.H.; Orhan, I.; Şenol, F.; Kartal, M.; Şener, B.; Dvorská, M.; Šmejkal, K.; Šlapetová, T. Cholinesterase inhibitory activities of some flavonoid derivatives and chosen xanthone and their molecular docking studies. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2009, 181, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, B.S.; Cuong, T.D.; Lee, J.-S.; Shin, B.-S.; Woo, M.H.; Hung, T.M. Cholinesterase inhibitors from Cleistocalyx operculatus buds. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2010, 33, 1665–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeini, R.; Memariani, Z.; Asadi, F.; Bozorgi, M.; Gorji, N. Pistacia Genus as a Potential Source of Neuroprotective Natural Products. Planta Med. 2019, 85, 1326–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaplatic, E.; Bule, M.; Shah, S.Z.A.; Uddin, M.S.; Niaz, K. Molecular mechanisms underlying protective role of quercetin in attenuating Alzheimer’s disease. Life Sci. 2019, 224, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervin, M.; Unno, K.; Ohishi, T.; Tanabe, H.; Miyoshi, N.; Nakamura, Y. Beneficial effects of green tea catechins on neurodegenerative diseases. Molecules 2018, 23, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, G.A.C.; da Rocha, C.Q.; Veloso, W.B.; Fernandes, R.N.; da Silva, I.S.; Tanaka, A.A. Determination of the catechin contents of bioactive plant extracts using disposable screen-printed carbon electrodes in a batch injection analysis (BIA) system. Microchem. J. 2019, 146, 1249–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzaei, M.H.; Bahramsoltani, R.; Abbasabadi, Z.; Braidy, N.; Nabavi, S.M. Role of green tea catechins in prevention of age-related cognitive decline: Pharmacological targets and clinical perspective. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 2447–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkhondeh, T.; Yazdi, H.S.; Samarghandian, S. The protective effects of green tea catechins in the management of neurodegenerative diseases: A review. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2019, 16, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheruku, S.P.; Ramalingayya, G.V.; Chamallamudi, M.R.; Biswas, S.; Nandakumar, K.; Nampoothiri, M.; Gourishetti, K.; Kumar, N. Catechin ameliorates doxorubicin-induced neuronal cytotoxicity in in vitro and episodic memory deficit in in vivo in Wistar rats. Cytotechnology 2018, 70, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ide, K.; Matsuoka, N.; Yamada, H.; Furushima, D.; Kawakami, K. Effects of tea catechins on Alzheimer’s disease: Recent updates and perspectives. Molecules 2018, 23, 2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levites, Y.; Weinreb, O.; Maor, G.; Youdim, M.B.; Mandel, S. Green tea polyphenol (–)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate prevents N-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3, 6-tetrahydropyridine-induced dopaminergic neurodegeneration. J. Neurochem. 2001, 78, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuevas, E.; Limón, D.I.; Pérez-Severiano, F.; Díaz, A.; Ortega, L.; Zenteno, E.; Guevara, J. Antioxidant effects of epicatechin on the hippocampal toxicity caused by amyloid-beta 25-35 in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 616, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, S.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, J. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Provides Protection Against Alzheimer’s Disease-Induced Learning and Memory Impairments in Rats. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2021, 13, 2013–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.A.; Abd El-Fattah, A.I.; Abu-Elfotuh, K.; Elariny, H.A. Natural antioxidants enhance the power of physical and mental activities versus risk factors inducing progression of Alzheimer’s disease in rats. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 96, 107729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ez zoubi, Y.; Farah, A.; Zaroual, H.; El Ouali Lalami, A. Antimicrobial activity of Lavandula stoechas phenolic extracts against pathogenic bacteria isolated from a hospital in Morocco. Vegetos 2020, 33, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.R.; Wani, W.Y.; Sunkaria, A.; Kandimalla, R.J.; Verma, D.; Cameotra, S.S.; Gill, K.D. Quercetin protects against chronic aluminum-induced oxidative stress and ensuing biochemical, cholinergic, and neurobehavioral impairments in rats. Neurotox. Res. 2013, 23, 336–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyahya, A.; Bakri, Y.; Et-Touys, A.; Assemian, I.C.C.; Abrini, J.; Dakka, N. In vitro antiproliferative activity of selected medicinal plants from the North-West of Morocco on several cancer cell lines. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2018, 18, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyahya, A.; Dakka, N.; Talbaoui, A.; Moussaoui, N.E.; Abrini, J.; Bakri, Y. Phenolic contents and antiradical capacity of vegetable oil from Pistacia lentiscus (L). J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2018, 9, 1518–1524. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemi Pirbalouti, A.; Emami Bistghani, Z.; Malekpoor, F. An overview on genus Thymus. J. Med. Herb 2015, 6, 93–100. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).