Chemical Profiling, Quantitation, and Bioactivities of Ginseng Residue
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Analysis of Chemical Composition in Ginseng Residue Using UPLC-Q-TOF/MS
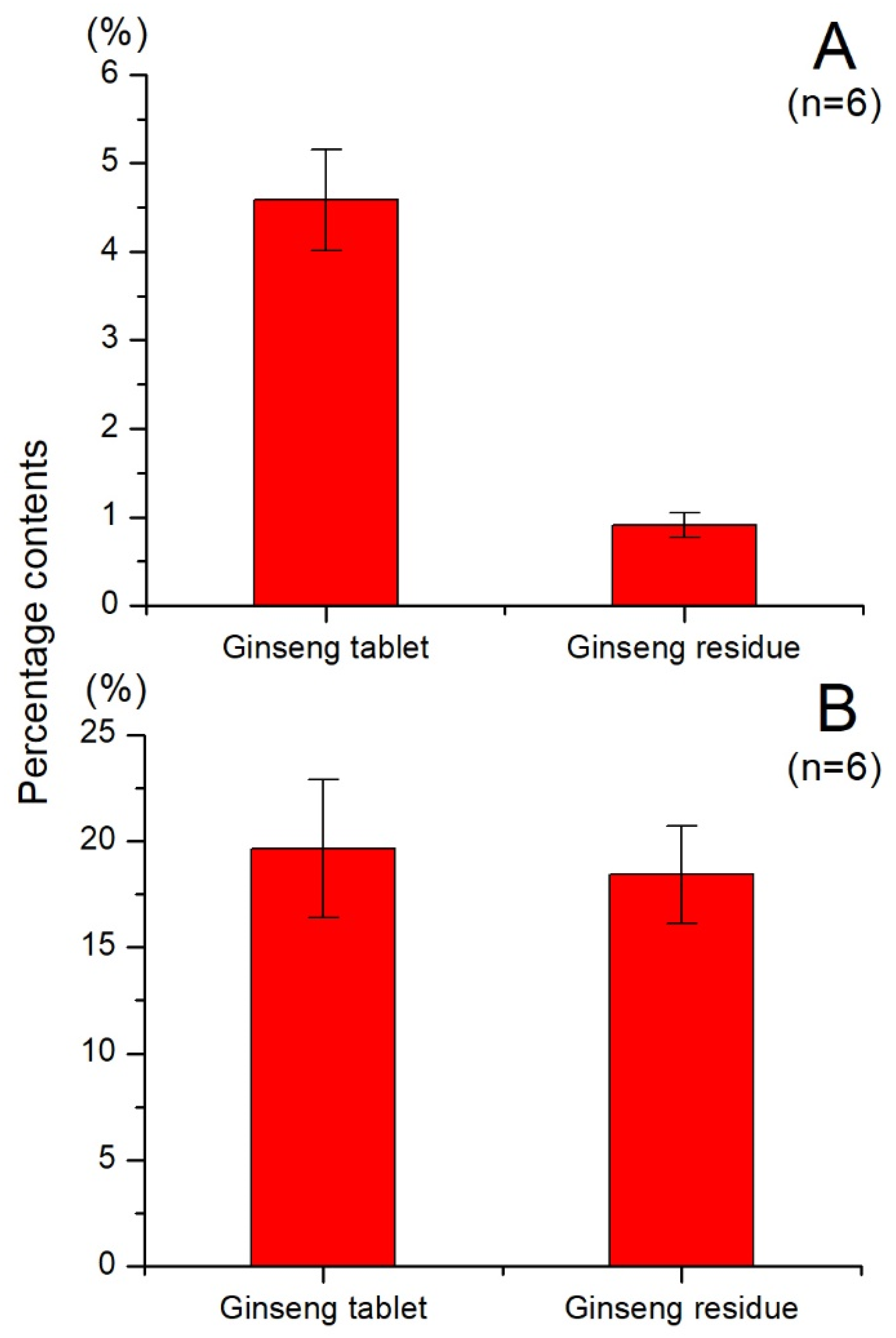
2.2. Quantitative Analysis of Total Ginsenosides and Total Polysaccharides in Ginseng Residue and Ginseng Tablet
2.3. Evaluation of Antioxidant Activities of Ginseng Residue
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemical Reagents and Materials
3.2. UPLC-Q-TOF/MS Analysis
3.3. Quantitative Analysis
3.3.1. Quantitative Analysis of Total Ginsenosides
3.3.2. Quantitative Analysis of Total Polysaccharides
3.4. ABTS+ Radical Scavenging Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, C.-X.; Xiao, P.G. Recent advances on ginseng research in China. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1992, 36, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Song, F.; Guo, D.; Mi, J.; Qin, Q.; Yu, Q.; Liu, S. Mass Spectrometry-Based Approach in Ginseng Research: A Promising Way to Metabolomics. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2012, 8, 43–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Kim, Y.-J.; Jeon, J.-N.; Wang, C.; Min, J.-W.; Noh, H.-Y.; Yang, D.-C. Effect of White, Red and Black Ginseng on Physicochemical Properties and Ginsenosides. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2015, 70, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.-R.; Yun, B.-S.; Sung, C.-K. Comparative Study of White and Steamed Black Panax ginseng, P. quinquefolium, and P. notoginseng on Cholinesterase Inhibitory and Antioxidative Activity. J. Ginseng Res. 2012, 36, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.-J.; Shin, Y.-W.; Chang, H.; Shin, H.-R.; Kim, W.-W.; Jung, S.-W.; Kim, M.; Nah, S.-Y. Safety and efficacy of dietary supplement (gintonin-enriched fraction from ginseng) in subjective memory impairment: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. Integr. Med. Res. 2021, 11, 100773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocak, M.Z.; Aktas, G.; Bilgin, S.; Duman, T.T.; Kurtkulagi, O.; Atak, B.; Demirkol, M.E.; Yilmaz, E.B. An unusual immune thrombocytopenia case associated with dietary supplements containing 3G (Green tea, Ginseng and Guarana). Russ. Open Med. J. 2020, 9, e307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, M.; Rahman, N.U.; Zia-Ul-Haq, M.; Jaffar, H.Z.; Manea, R. Ginseng: A dietary supplement as immune-modulator in various diseases. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 83, 12–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, V.-L.; Jeong, W.-S. Red ginseng (Panax ginseng Meyer) oil: A comprehensive review of extraction technologies, chemical composition, health benefits, molecular mechanisms, and safety. J. Ginseng Res. 2021, 46, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, S.; Ebihara, A.; Zhou, X.; Fan, L.; Li, P.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Y. The current research progress of ginseng species: The cultivation and application. Cogent Food Agric. 2023, 9, e2216483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Lu, K.; Zong, G.; Xia, Y.; Han, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, Z.; Lu, Y. Ginseng polysaccharides: Potential antitumor agents. J. Ginseng Res. 2023, 47, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Lu, X.; Han, Y.; Xing, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Cui, C. Ginseng polysaccharide reduces autoimmune hepatitis inflammatory response by inhibiting PI3K/AKT and TLRs/NF-κB signaling pathways. Phytomedicine 2023, 116, 154859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Lv, C.; Lu, J. Studies on laccase mediated conversion of lignin from ginseng residues for the production of sugars. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 317, 123945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Zhong, X.; Sun, D.; Cao, X.; Yao, F.; Shi, L.; Liu, Y. Structural characterization of polysaccharides recovered from extraction residue of ginseng root saponins and its fruit nutrition preservation performance. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 934927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Gao, X.; Zhang, A.; Qin, X.; Du, G. Characterization of multiple chemical components of GuiLingJi by UHPLC-MS and 1H NMR analysis. J. Pharm. Anal. 2021, 12, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, P.; Zhong, F.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, X.; Xue, W.; Wang, Y.; Song, X.; Tang, W.; Fan, D. Thermosensitive molecularly imprinted polymer coupled with HPLC for selective enrichment and determination of matrine in traditional Chinese medicine. J. Chromatogr. B 2022, 1191, 123130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Ma, L.; Guo, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S. Analysis of oligosaccharides from Panax ginseng by using solid-phase permethylation method combined with ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-Q-Orbitrap/mass spectrometry. J. Ginseng Res. 2019, 44, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-T.; Zhang, F.-X.; Fan, C.-L.; Ye, M.-N.; Chen, W.-W.; Yao, Z.-H.; Yao, X.-S.; Dai, Y. Discovery of potential Q-marker of traditional Chinese medicine based on plant metabolomics and network pharmacology: Periplocae Cortex as an example. Phytomedicine 2021, 85, 153535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Luo, S.; Zhong, K.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Z. Chemical profiling, quantitation, and bioactivities of Du-Zhong tea. Food Chem. 2022, 394, 133552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Yang, W.-Z.; Shi, X.-J.; Yao, C.-L.; Yang, M.; Liu, X.; Jiang, B.-H.; Wu, W.-Y.; Guo, D.-A. A green protocol for efficient discovery of novel natural compounds: Characterization of new ginsenosides from the stems and leaves of Panax ginseng as a case study. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 893, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Liu, S. Profiling and multivariate statistical analysis of Panax ginseng based on ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 107, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Huang, G. Antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from different sources of ginseng. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 125, 906–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.M.; Song, Y.; Hyun, G.H.; Long, N.P.; Park, J.H.; Hsieh, Y.S.; Kwon, S.W. Characterization and Antioxidant Activity Determination of Neutral and Acidic Polysaccharides from Panax Ginseng C. A. Meyer. Molecules 2020, 25, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, D.; Wei, E.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Z.; Qi, L.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, J. Microwave-assisted extraction, structural elucidation, and in vitro anti-glioma and immunostimulatory activity of polysaccharide from Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2022, 189, 115729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, K.F.; Mumin, A.; Lui, E.M.; Charpentier, P.A. Fabrication of fluorescent labeled ginseng polysaccharide nanoparticles for bioimaging and their immunomodulatory activity on macrophage cell lines. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, F.-G.; Liang, Q.-C.; Wu, Y.-Y.; Liu, J.-W. Red ginseng polysaccharide exhibits anticancer activity through GPX4 downregulation-induced ferroptosis. Pharm. Biol. 2022, 60, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, R.; Li, N.; Zheng, F.; Dai, Y.; Ge, Y.; Yue, H.; Yu, S. Mechanism of antidiabetic and synergistic effects of ginseng polysaccharide and ginsenoside Rb1 on diabetic rat model. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 158, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, A.W.B.; Simborio, H.L.T.; Hop, H.T.; Arayan, L.T.; Min, W.G.; Lee, H.J.; Rhee, M.H.; Chang, H.H.; Kim, S. Inhibitory effect of red ginseng acidic polysaccharide from Korean red ginseng on phagocytic activity and intracellular replication of Brucella abortus in RAW 264.7 cells. J. Vet.-Sci. 2016, 17, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
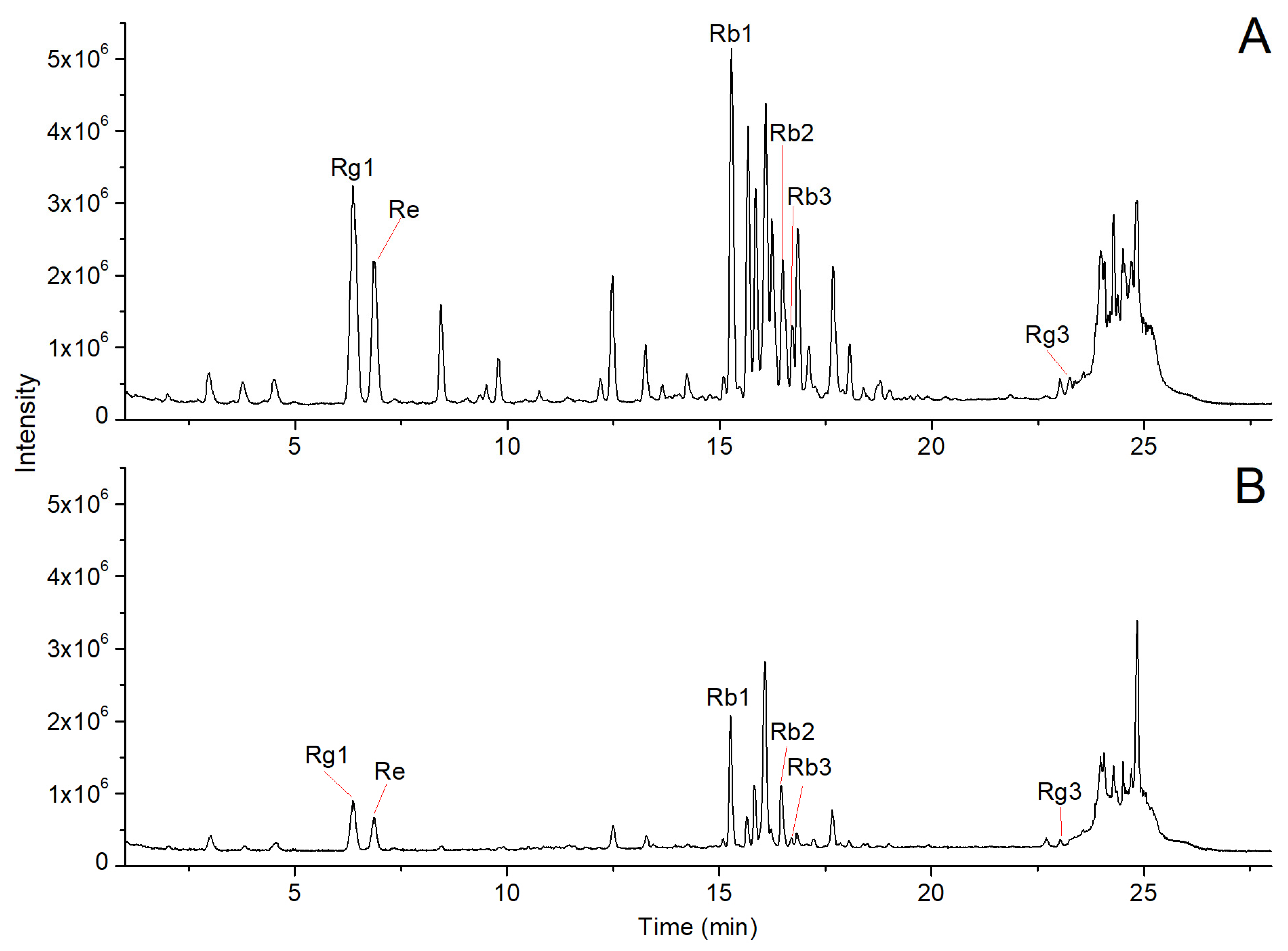
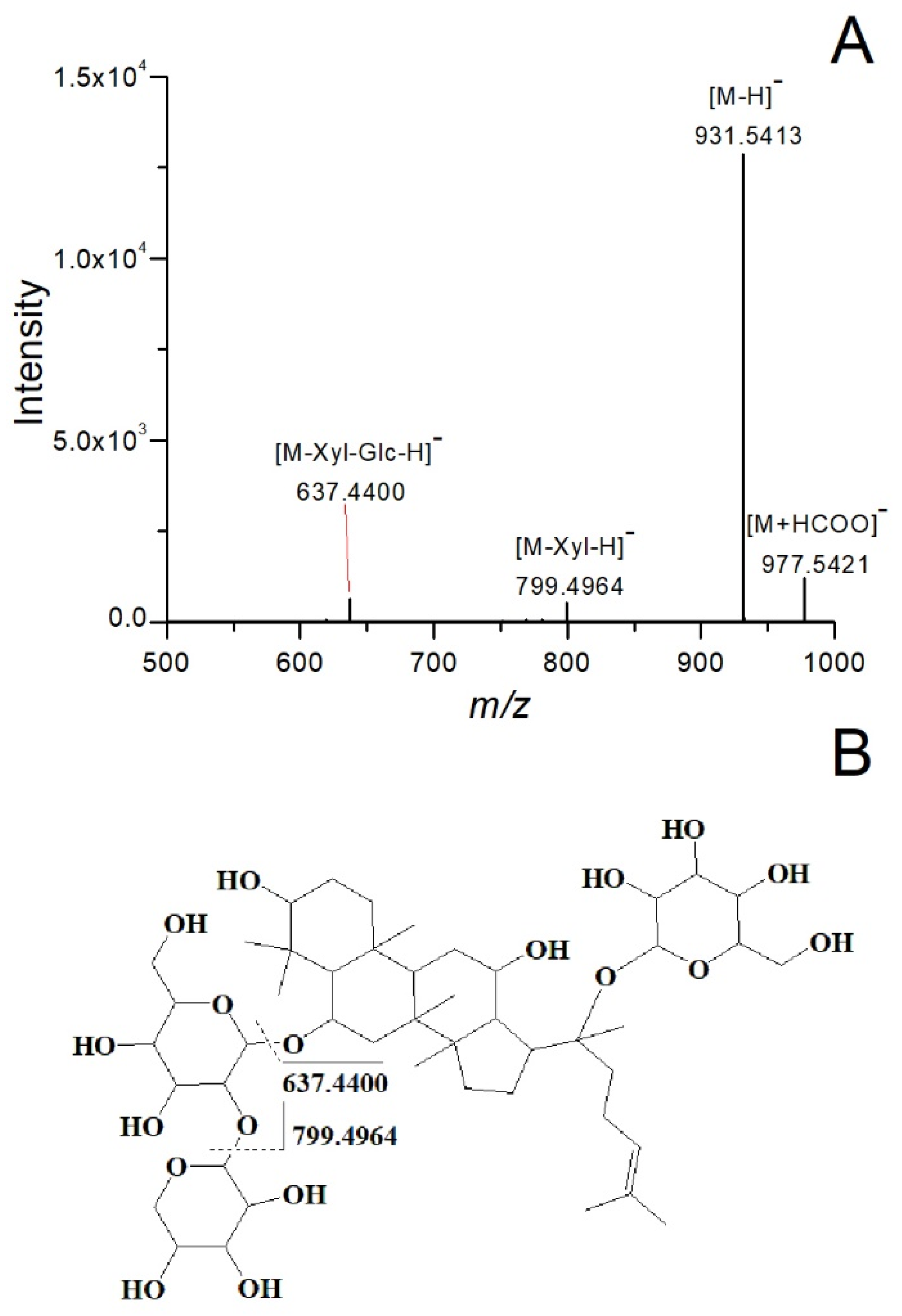
| No. | RT (min) | Measured m/z | Mass Deviation (ppm) | Adducts | Product Ions | Compounds | Formula | Peak Area of Ginseng Residue/Ginseng Tablet (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.79 | 1007.5534 | 10.12 | [M+HCOO]− | 961.5574, 799.4996, 637.4438 | 20-Glc-Rf | C48H82O19 | 19.82 |
| 2 | 4.52 | 977.5421 | 9.62 | [M+HCOO]− | 931.5450, 799.4996, 637.4402 | Noto R1 | C47H80O18 | 24.54 |
| 3 * | 6.37 | 845.4956 | 6.15 | [M+HCOO]− | 799.5001, 637.4424, 475.3846 | Rg1 | C42H72O14 | 17.78 |
| 4 * | 6.86 | 991.5559 | 7.66 | [M+HCOO]− | 945.5588, 799.4996, 783.5050, 637.4418 | Re | C48H82O18 | 18.59 |
| 5 | 8.43 | 827.4838 | 4.83 | [M+HCOO]− | 781.4884, 619.4333 | Rg9/Rg8 | C42H70O13 | 3.60 |
| 6 | 9.82 | 1031.5517 | 8.24 | [M-H]− | 987.5748, 945.5434, 927.5525, 799.5008 | mRe | C51H84O21 | 5.44 |
| 7 | 12.48 | 845.496 | 6.62 | [M+HCOO]− | 799.4997, 637.4435, 475.3860 | Rf | C42H72O14 | 17.50 |
| 8 | 13.08 | 913.5222 | 6.13 | [M+HCOO]− | 867.5276, 799.5000, 781.4883 | Re6 | C46H76O15 | 46.35 |
| 9 | 13.27 | 815.4847 | 6.01 | [M+HCOO]− | 769.4891, 637.4419, 475.3846 | Noto R2 | C41H70O13 | 23.06 |
| 10 | 13.95 | 1285.656 | 9.8 | [M+HCOO]− | 1239.6656, 1077.6281 | Ra3 | C59H100O27 | 37.64 |
| 11 | 14.07 | 683.4413 | 5.41 | [M+HCOO]− | 637.4407, 475.3801 | F1 | C36H62O9 | 17.09 |
| 12 | 14.24 | 829.4988 | 3.98 | [M+HCOO]− | 783.5053, 637.4469, 475.3846 | Rg2 | C42H72O13 | 13.50 |
| 13 | 14.33 | 1325.6462 | 4.67 | [M-H]− | 1325.6462 | mRa3 | C62H102O30 | 10.05 |
| 14# | 14.59 | 811.491 | 7.52 | [M+HCOO]− | 769.4871, 619.4269, 475.3824 | Rg6 | C42H70O12 | 0 |
| 15 | 15.08 | 1255.6408 | 6.37 | [M+HCOO]− | 1209.5873, 1077.6061 | Ra1 | C58H98O26 | 32.97 |
| 16 * | 15.27 | 1153.6123 | 9.71 | [M+HCOO]− | 1107.6182, 945.5630, 783.5052 | Rb1 | C54H92O23 | 26.63 |
| 17 | 15.65 | 1193.6003 | 3.52 | [M-H]− | 1149.6313, 1107.6206, 1089.6096, 945.5598, 783.5021 | mRb1 | C57H94O26 | 10.00 |
| 18 | 15.83 | 1123.6002 | 8.54 | [M+HCOO]− | 1077.6097, 945.5621 | Rc | C53H90O22 | 27.39 |
| 19 | 15.96 | 1255.6428 | 7.96 | [M+HCOO]− | 1209.6536, 1077.6084 | Ra2 | C58H98O26 | 54.38 |
| 20 | 16.07 | 1001.5011 | 4.79 | [M+HCOO]− | 955.5147, 793.4542 | Ro | C48H76O19 | 49.06 |
| 21 | 16.21 | 1163.5952 | 8.34 | [M-H]− | 1119.6217, 1077.6107, 1059.5996 | mRc | C56H92O25 | 6.49 |
| 22 | 16.22 | 1165.6098 | 7.46 | [M+HCOO]− | 1119.6184, 1077.6069, 1059.5966 | Rs1 | C55H92O23 | 3.74 |
| 23 | 16.29 | 1295.6326 | 3.7 | [M-H]− | - | m Ra1/m Ra2 | C61H100O29 | 7.26 |
| 24 * | 16.45 | 1123.6003 | 8.63 | [M+HCOO]− | 1077.6072, 945.5597, 915.5481, 783.5034 | Rb2 | C53H90O22 | 46.33 |
| 25 * | 16.69 | 1123.6009 | 9.17 | [M+HCOO]− | 1077.6079, 945.5579, 915.5535, 783.5058 | Rb3 | C53H90O22 | 15.42 |
| 26 | 16.82 | 1163.5913 | 4.98 | [M-H]− | 1119.6184, 1077.6080, 1059.5979 | mRb2 | C56H92O25 | 6.45 |
| 27 | 17.07 | 1163.5911 | 4.81 | [M-H]− | 1119.6178, 1077.6052, 1059.5935 | mRb3 | C56H92O25 | 5.03 |
| 28 | 17.66 | 991.5568 | 8.57 | [M+HCOO]− | 945.5615, 783.5049, 621.4464 | Rd | C48H82O18 | 25.23 |
| 29 | 18.04 | 1031.5512 | 7.76 | [M-H]− | 987.5718, 945.5615, 927.5497 | mRd | C51H84O21 | 12.77 |
| 30 # | 20.56 | 811.4897 | 5.92 | [M+HCOO]− | 765.4939, 619.4329 | F4 | C42H70O12 | 0 |
| 31 | 20.91 | 665.4322 | 7.81 | [M+HCOO]− | 619.3430, 341.1122, 295.2295 | Rh4 | C36H60O8 | 47.37 |
| 32 | 21.1 | 811.4905 | 6.9 | [M+HCOO]− | 765.4932, 619.4310, 570.7531 | Rk1 | C42H70O12 | 7.91 |
| 33 | 21.85 | 829.5016 | 7.35 | [M+HCOO]− | 783.5039, 621.4471 | F2 | C42H72O13 | 3.79 |
| 34 | 23.03 | 839.4473 | 4.53 | [M+HCOO]− | 793.4514 | zingibroside | C42H66O14 | 40.93 |
| 35 * | 23.37 | 829.5008 | 6.39 | [M+HCOO]− | 783.5044, 621.4603 | Rg3 | C42H72O13 | 26.88 |
| 36 # | 23.45 | 871.5122 | 6.99 | [M-H]− | 825.5154, 783.5054 | Rs3 | C44H74O14 | 0 |
| 37 # | 24.06 | 667.4484 | 8.54 | [M+HCOO]− | 621.4453 | Rh2 | C36H62O8 | 0 |
| 38 | 24.11 | 811.4878 | 3.57 | [M+HCOO]− | 765.4916, 603.4352 | Rg5 | C42H70O12 | 38.56 |
| 39 # | 24.83 | 667.4473 | 6.89 | [M+HCOO]− | 333.2319, 275.1532 | Compound K | C36H62O8 | 0 |
| Sample | Trolox (mM) | Ginseng Tablet Extracts (mg Dried Raw Material Equivalents/mL) | Ginseng Residue Extracts (mg Dried Raw Material Equivalents/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 values | 0.91 ± 0.04 | 18.51 ± 2.38 | 23.46 ± 3.62 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ge, S.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Song, J.; Wu, H.; Li, L.; Zhu, H.; Feng, B. Chemical Profiling, Quantitation, and Bioactivities of Ginseng Residue. Molecules 2023, 28, 7854. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28237854
Ge S, Liu J, Liu Y, Song J, Wu H, Li L, Zhu H, Feng B. Chemical Profiling, Quantitation, and Bioactivities of Ginseng Residue. Molecules. 2023; 28(23):7854. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28237854
Chicago/Turabian StyleGe, Shengyu, Jinlong Liu, Yang Liu, Jiaqi Song, Hongfeng Wu, Lele Li, Heyun Zhu, and Bo Feng. 2023. "Chemical Profiling, Quantitation, and Bioactivities of Ginseng Residue" Molecules 28, no. 23: 7854. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28237854
APA StyleGe, S., Liu, J., Liu, Y., Song, J., Wu, H., Li, L., Zhu, H., & Feng, B. (2023). Chemical Profiling, Quantitation, and Bioactivities of Ginseng Residue. Molecules, 28(23), 7854. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28237854








