A Study of Pigment, Adhesive, and Firing Temperature in Pottery Figurines Excavated from the Tomb of Qibi Ming, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Surface Morphology of the Pigments
2.2. Composition of the Pigments
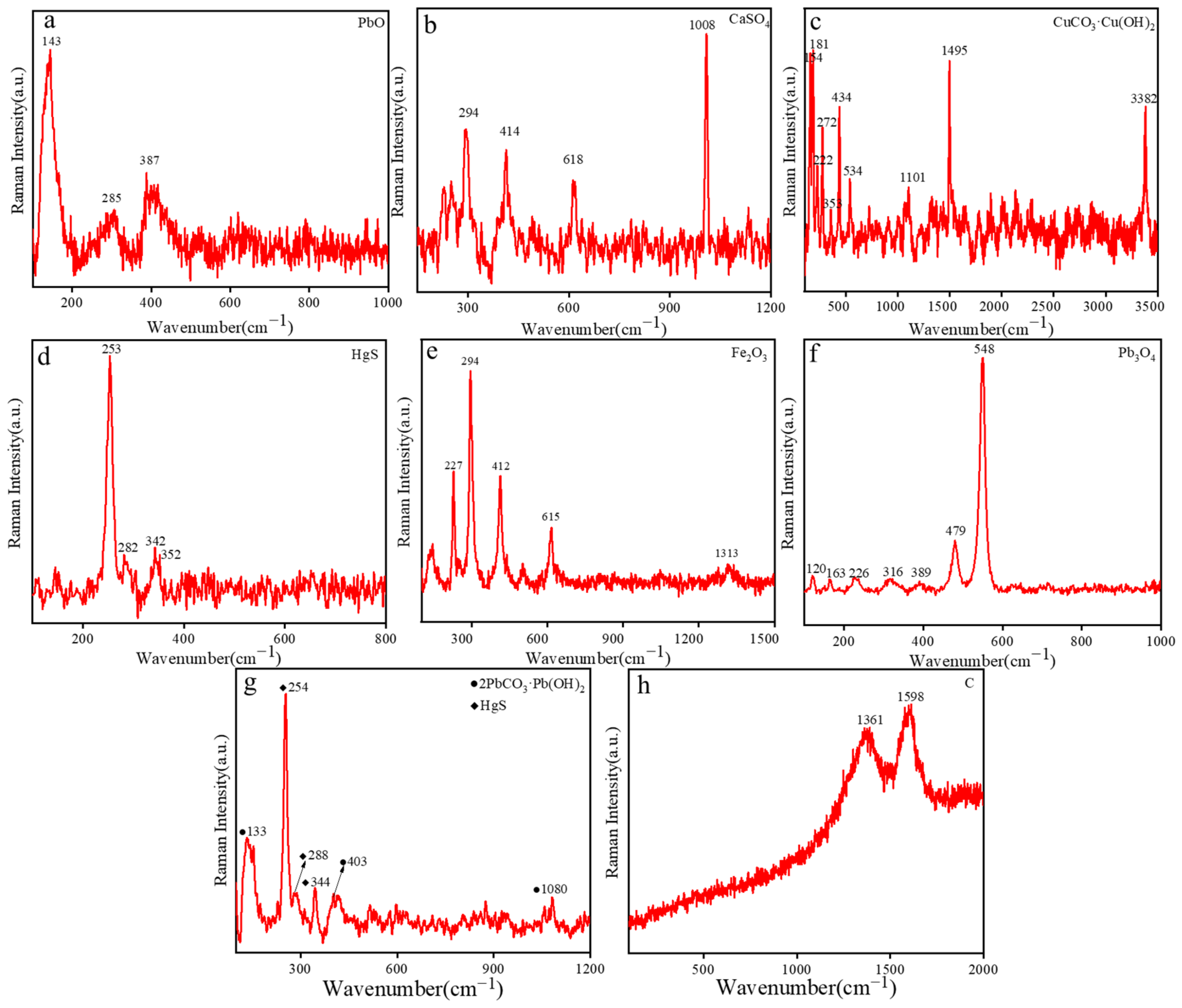
2.2.1. Yellow Pigment Analysis
2.2.2. White Pigment
2.2.3. Green Pigment
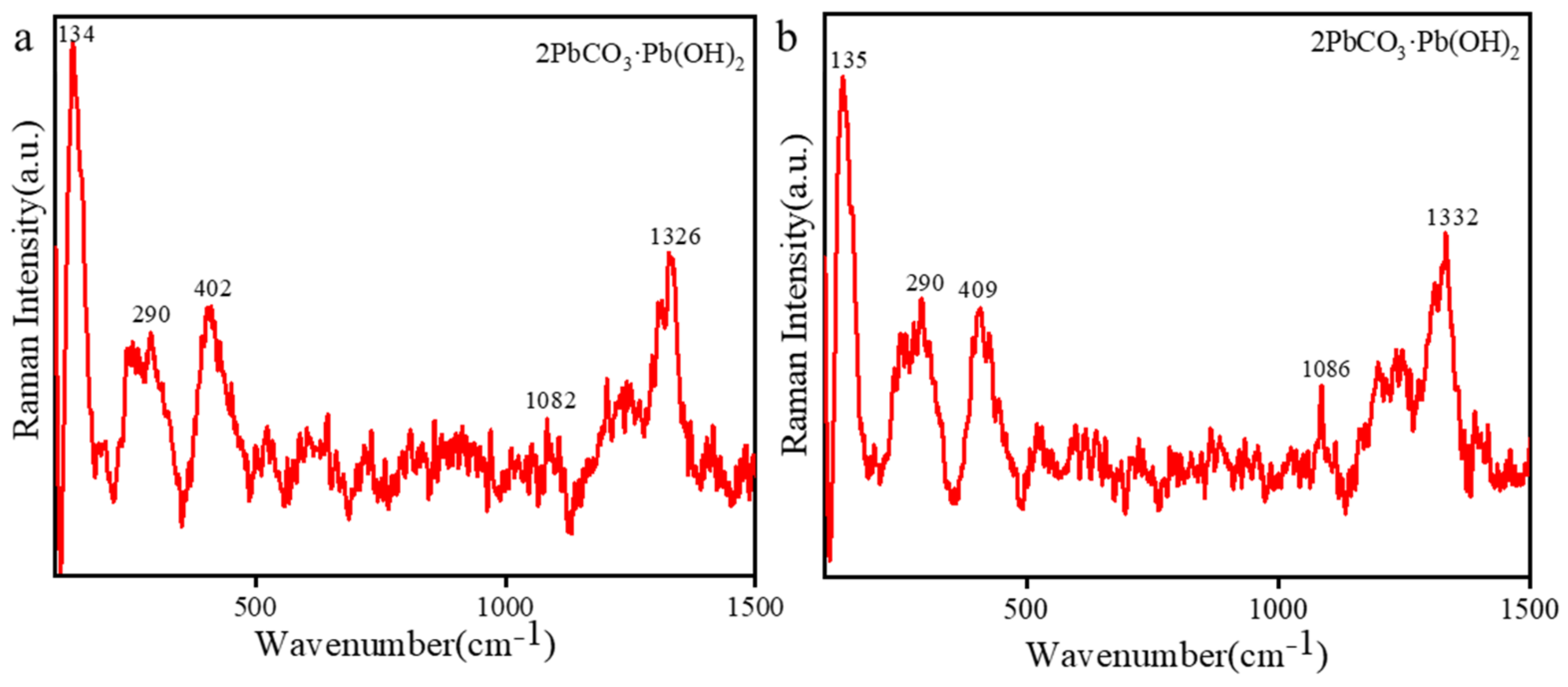
2.2.4. Red Pigment
2.2.5. Pink Pigment
2.2.6. Black Pigment
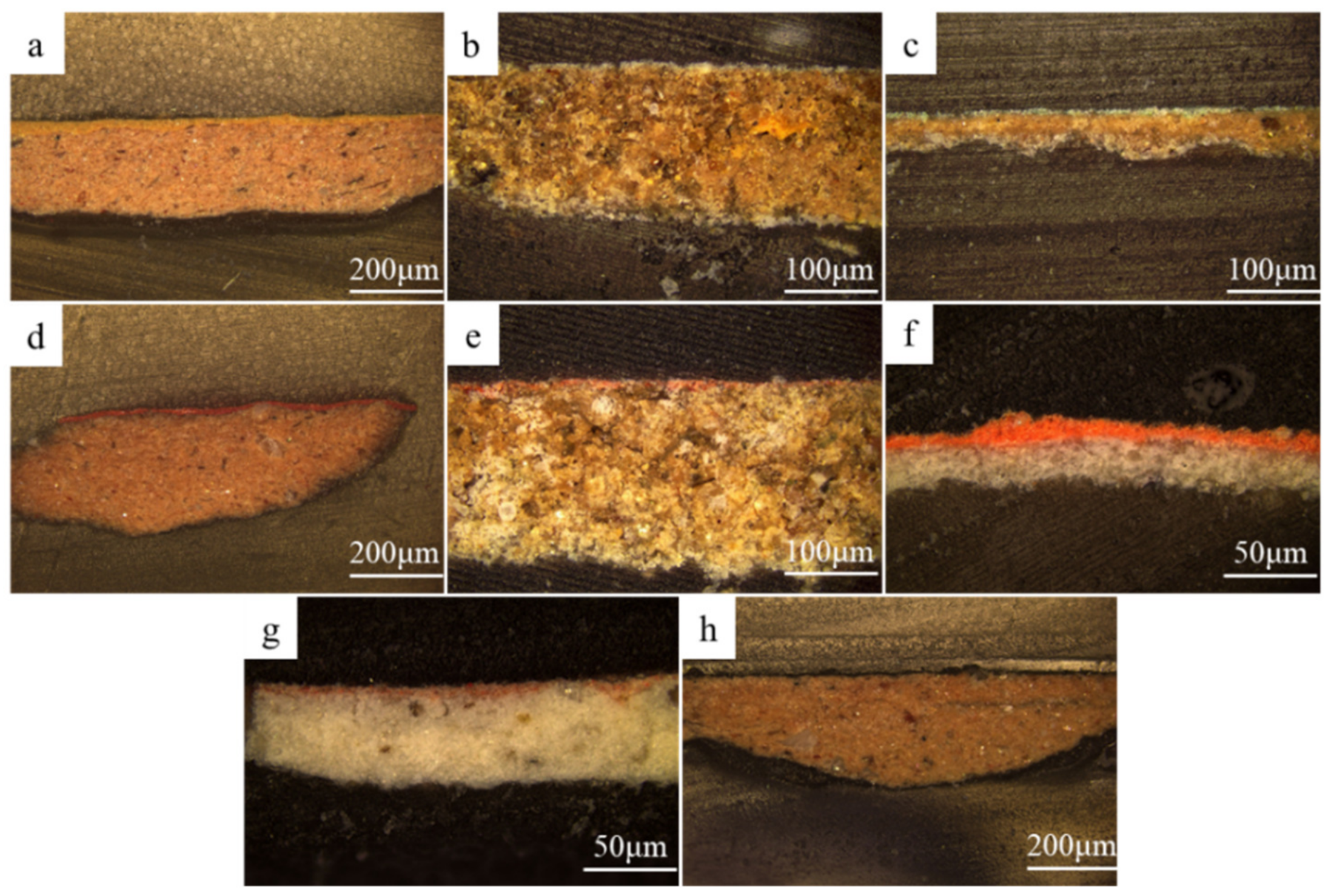
2.3. Analysis of the Cross-Sections
2.4. Analysis of Adhesives
2.5. Determining the Firing Temperature of the Pottery Figurines
3. Materials and Methods
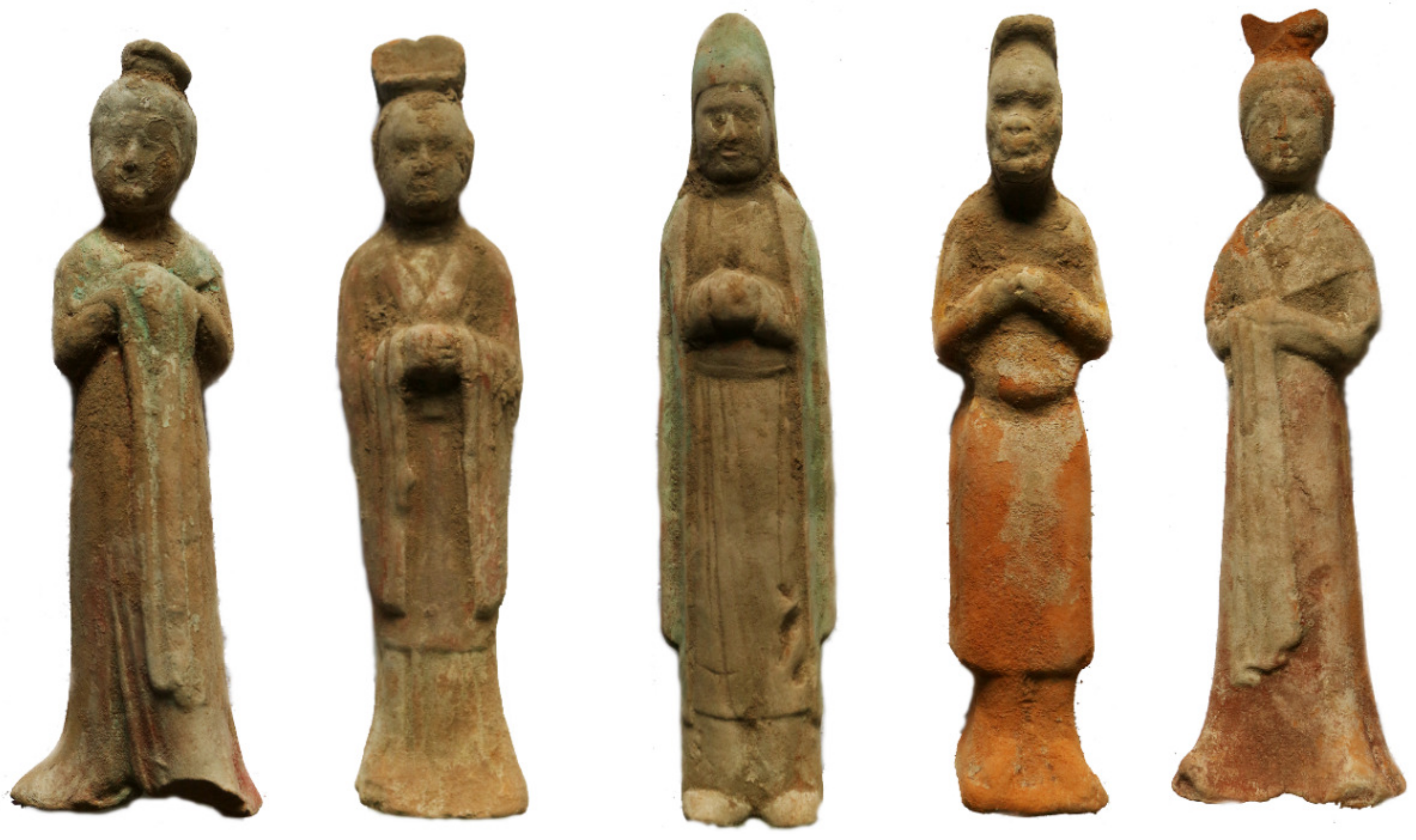
3.1. Samples
3.2. Cross-Section Sample Preparation
3.3. Experimental Methods and Instrumentation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jie, F.; Ma, X. Excavation of Qibi Ming’s Tomb. Relics Museolgy 1998, 5, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, X. The Rare Tang Tri-Colored Glazed Pottery Unearthed from the Tomb of Qibi Ming. Collections 2011, 224, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, P.; Huang, W.; Jianhua, W.; Zhao, G.; Wang, X. The Identification of the Pigments Used to Paint Statues of Feixiange Cliff in China in Late 19th Century by Micro-Raman Spectroscopy and Scanning Electron Microscopy/Energy Dispersive X-ray Analysis. J. Mol. Struct. 2010, 983, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, D.; Lee, N.; Lee, E. Ancient Pigments in Afrasiab Murals: Characterization by Xrd, Sem, and Raman Spectroscopy. Minerals 2021, 11, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Ye, L.; Gu, L.; Chang, L.; Wang, W.; Dai, Y.; Bai, J. Multi-Analytical Investigations on a Tomb Mural Painting of the Yuan Dynasty in Chongqing, China. Vib. Spectrosc. 2023, 124, 103475–103484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasini, E.; Rodríguez, D.C.; Gómez, B.A.; Faria, D.L.A.; Landa, C.R.; Siracusano, G.; Maier, M.S. A Multi-Analytical Investigation of the Materials and Painting Technique of a Wall Painting from the Church of Copacabana De Andamarca (Bolivia). Microchem. J. 2016, 128, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaviva, S.; Lecci, S.; Puiu, A.; Spizzichino, V.; Fantoni, R.; Falconieri, M.; Gagliardi, S.; Chiari, M.; Mazzinghi, A.; Ruberto, C.; et al. Raman/Xrf/Edx Microanalysis of 2nd-Century Stuccoes from Domus Valeriorum in Rome. J. Cult. Herit. 2019, 37, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.; Teri, G.; Li, J.; Huo, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, Y. Analysis of an Ancient Architectural Painting from the Jiangxue Palace in the Imperial Museum, Beijing, China. Anal. Lett. 2020, 54, 684–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.; Lee, S. Identification of Natural Inorganic Pigments Used on 18th Century Korean Traditional Mural Paintings by Using a Portable X-ray Fluorescence. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 28, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhen, G.; Hao, X.; Zhou, P.; Wang, Z.; Jia, J.; Gao, Y.; Dong, S.; Tong, H. Micro-Raman, Xrd and Thm-Py-Gc/Ms Analysis to Characterize the Materials Used in the Eleven-Faced Guanyin of the Du Le Temple of the Liao Dynasty, China. Microchem. J. 2021, 171, 106828–106836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hao, X.; Zhao, Y.; Tong, T.; Wu, H.; Ma, L.; Shen, X.; Tong, H. Systematic Study of the Material, Structure and Lacquering Techniques of Lacquered Wooden Coffins from the Eastern Regius Tombs of the Qing Dynasty, China. Microchem. J. 2021, 168, 106369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franquelo, M.L.; Duran, A.; Herrera, L.K.; Jimenez, M.C.; Perez-Rodriguez, J.L. Comparison between Micro-Raman and Micro-Ftir Spectroscopy Techniques for the Characterization of Pigments from Southern Spain Cultural Heritage. J. Mol. Struct. 2009, 924–926, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, E.A.; Perez, F.R.; Garcia, J.M.; Edwards, H.G.M. Raman Spectroscopic Analysis of an Important Visigothic Historiated Manuscript. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2016, 374, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosano, D.; Esquivel, D.; Costa, C.M.; Jimenez-Sanchidrian, C.; Ruiz, J.R. Identification of Pigments in the Annunciation Sculptural Group (Cordoba, Spain) by Micro-Raman Spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta A 2019, 214, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Han, Y.; Han, L.; Cheng, Y.; Ma, Y.; Fang, L. Micro-Raman Analysis of the Pigments on Painted Pottery Figurines from Two Tombs of the Northern Wei Dynasty in Luoyang. Spectrochim. Acta A 2013, 109, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čukovska, L.R.; Minčeva–Šukarova, B.; Lluveras-Tenorio, A.; Andreotti, A.; Colombini, M.P.; Nastova, I. Micro-Raman and Gc/Ms Analysis to Characterize the Wall Painting Technique of Dicho Zograph in Churches from Republic of Macedonia. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2012, 43, 1685–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribechini, E.; Orsini, S.; Silvano, F.; Colombini, M.P. Py-Gc/Ms, Gc/Ms and Ftir Investigations on Late Roman-Egyptian Adhesives from Opus Sectile: New Insights into Ancient Recipes and Technologies. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 638, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Gu, A.; Li, G.; Lei, Y. Rapid Evaluation of Uv and Thermal Aging of Boiled Tung Oil by Micro-Uv/Py-Gc/Ms System. Microchem. J. 2023, 187, 108414–108425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Xiang, J.; Ji, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Fu, P.; Han, J.; Li, L. Multi-Method Analysis of Painting Materials in Murals of the North Mosque (Linqing, China). Coatings 2023, 13, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Xu, C.; Li, W. Application Research on Measuring the Firing Temperature of Ancient Ceramics by the Top Rod Thermal Expansion Method. Sci. Conserv. Archaeol. 2020, 32, 70–80. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Wang, C. Application and Exploration of the Thermal Expansion Technology in Determination of the Firing Temperature of Ancient Ceramics. J. Guangxi Univ. Natl. 2017, 23, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, T.; Li, J. Firing Temperature Analysis of Early Pottery from Nanzhuangtou Site. Rock Miner. Anal. 2010, 29, 148–152. [Google Scholar]
- Ravindran, T.R.; Arora, A.K.; Ramya, S.; Subba Rao, R.V.; Raj, B. Raman Spectroscopic Study of Medieval Indian Art of 17th Century. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2010, 42, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, H. A Study on Yellow Pigments in Dunhuang Art of the Tang Dynasty. Art Panor. 2015, 62–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Němečková, K.; Jehlička, J.; Culka, A. Fast Screening of Carotenoids of Gypsum Endoliths Using Portable Raman Spectrometer (Messinian Gypsum, Sicily). J. Raman Spectrosc. 2020, 51, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Němečková, K.; Culka, A.; Jehlička, J. Detecting Pigments from Gypsum Endoliths Using Raman Spectroscopy: From Field Prospection to Laboratory Studies. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2021, 53, 630–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge-Villar, S.E.; Edwards, H.G.M. Green and Blue Pigments in Roman Wall Paintings: A Challenge for Raman Spectroscopy. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2021, 52, 2190–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hou, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Teri, G.; Han, K.; Jia, Z.; Chao, X.; Xing, H.; et al. Analytical Characterization of Wooden Figurines Excavated from the Tomb of Princess Yongtai, Qianling Tomb, China. Anal. Lett. 2023, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Gong, D.; Yao, Z.; Xu, L.; Zhu, Z.; Eckfeld, T. Characterization of a Mahamayuri Vidyarajni Sutra Excavated in Lu’an, China. Herit. Sci. 2019, 7, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teri, G.; Han, K.; Huang, D.; Li, Y.; Tian, Y.; Chao, X.; Jia, Z.; Fu, P.; Li, Y. A Study on the Materials Used in the Ancient Architectural Paintings from the Qing Dynasty Tibetan Buddhist Monastery of Puren, China. Materials 2023, 16, 6404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, I.; GarcÍA-Borja, P.; RoldÁN, C. Identification, Processing and Use of Red Pigments (Hematite and Cinnabar) in the Valencian Early Neolithic (Spain). Archaeometry 2012, 54, 868–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilmi, M.M.; Nurdini, N.; Maryanti, E.; Saiyasombat, C.; Setiawan, P.; Kadja, G.T.M. Ismunandar; Multi-Analytical Characterizations of Prehistoric Rock Art Pigments from Karim Cave, Sangkulirang–Mangkalihat Site, East Kalimantan, Indonesia. Microchem. J. 2020, 155, 104738–104746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Gu, W.; Zhong, L.; Liu, B.; Huang, F.; Chang, Y.; Li, M.; Jing, Y.; Chen, G. Investigation of Asian Dyes and Pigments from the Artifact of “Murongzhi” and the Silk Road in China. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 2508–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faurel, X.; Vanderperre, A.; Colomban, P. Pink Pigment Optimization by Resonance Raman Spectroscopy. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2003, 34, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcaida, I.; Maguregui, M.; Morillas, H.; García-Florentino, C.; Knuutinen, U.; Carrero, J.A.; Fdez-Ortiz, S.; Pitarch Martí, A.; Castro, K.; Madariaga, J.M. Multispectroscopic and Isotopic Ratio Analysis to Characterize the Inorganic Binder Used on Pompeian Pink and Purple Lake Pigments. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 6395–6402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarta, G.; D’Elia, M.; Paparella, S.; Serra, A.; Calcagnile, L. Characterisation of Lead Carbonate White Pigments Submitted to Ams Radiocarbon Dating. J. Cult. Herit. 2020, 46, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrote, M.A.; Robador, M.D.; Perez-Rodriguez, J.L. Analytical Investigation of Mudejar Polychrome on the Carpentry in the Casa De Pilatos Palace in Seville Using Non-Destructive Xrf and Complementary Techniques. Spectrochim. Acta A 2017, 173, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Ma, Q.; Schreiner, M. The Identification of Binding Media Used in the Polychromy of Western Han Dynasty Terracotta Army from Qingzhou. Wenbo 2009, 6, 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, B.; Wei, S.; Song, Y. Application of Thermally Assisted Methylation Thermolysis Gas Chromatography (THM-Py-Gc/Ms) for the Analysis and Identification of Protein Binding Materials in Murals. China Cult. Herit. Sci. Res. 2018, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Dong, X.; Lou, Z. Uhplc-Q-Tof/Ms in Rapid Aeparation and Identification of Chemical Components in Veraturm Nigrum. Acad. J. Second Mil. Med. Univ. 2012, 33, 536–540. [Google Scholar]
- Tite, M.S. Determination of the Firing Temperature of Ancient Ceramics by Measurement of Thermal Expansion: A Reassessment. Archaeometry 1969, 11, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Wang, C. Study on Firing Temperature of the Song Dynasty (960–1279ad) Greenish-White Porcelain in Guangxi, China by Thermal Expansion Method. Herit. Sci. 2019, 7, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhao, C.; Yu, J.; Glascock, M.; Wang, C. Determining the Firing Temperature of Low-Fired Ancient Pottery: An Example from the Donghulin Site, Beijing, China. Archaeometry 2014, 56, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
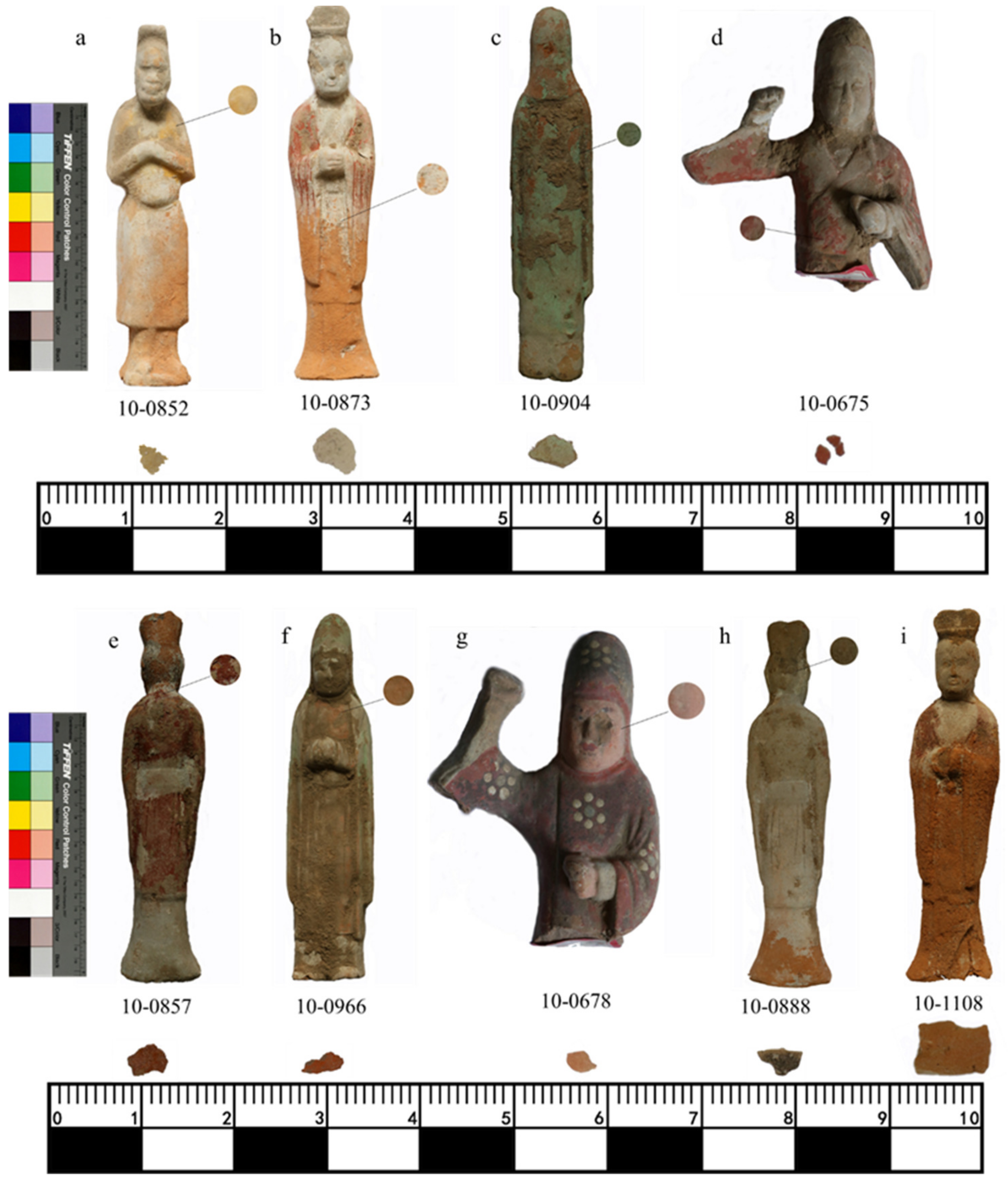







| Sample | Color | Elements |
|---|---|---|
| 10-0852 | Yellow | Pb, Si, Ca, Fe, K, Mn |
| 10-0873 | White | Ca, Si, Fe, Pb, S, K |
| 10-0904 | Green | Cu, Si, Ca, Fe, K, S, Pb, Ti |
| 10-0675 | Red | Si, Hg, S, Ca, Fe, K, Pb, Ba |
| 10-0857 | Fe, Si, Ca, Pb, K, Ti | |
| 10-0966 | Pb, Si, Ca, K | |
| 10-0678 | Pink | Pb, Ca, Si, Hg |
| 10-0888 | Black | Si, Al, Fe, Ca, K, S |
| Peak Number | Retention Time (min) | Peak Area | Identified Compound |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.739 | 562,115 | N-Methyl pyrrole |
| 2 | 4.174 | 1,941,906 | Toluene |
| 3 | 4.768 | 619,003 | Alpha-methyl-gamma-butyrolactone |
| 4 | 5.746 | 361,143 | 2-Octyne |
| 5 | 6.552 | 561,330 | 1,7-Octanediyne |
| 6 | 14.108 | 512,429 | 3,4-Dimethoxytoluene |
| 7 | 15.514 | 1,048,921 | Isoeugenol |
| 8 | 16.635 | 2,368,855 | Veratraldehyde |
| 9 | 17.342 | 1,147,657 | 2,4-Dimethoxyacetophenone |
| 10 | 17.514 | 2,133,439 | 3,4-Dimethoxybenzoate methyl ester |
| 11 | 17.812 | 773,318 | 2,3-Dimethoxycinnamic acid |
| 12 | 18.683 | 808,835 | Methyl palmitate |
| 13 | 19.875 | 368,136 | Methyl stearate |
| 14 | 21.183 | 460,770 | 2,2,5,5-Tetramethoxybiphenyl |
| 15 | 21.513 | 263,101 | Menthol |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Guo, H.; Xiao, K.; Liu, P.; Chao, X.; Fu, P.; Xing, H.; Li, Y. A Study of Pigment, Adhesive, and Firing Temperature in Pottery Figurines Excavated from the Tomb of Qibi Ming, China. Molecules 2023, 28, 7739. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28237739
Li Y, Guo H, Xiao K, Liu P, Chao X, Fu P, Xing H, Li Y. A Study of Pigment, Adhesive, and Firing Temperature in Pottery Figurines Excavated from the Tomb of Qibi Ming, China. Molecules. 2023; 28(23):7739. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28237739
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yanli, Haiqiang Guo, Ke Xiao, Panpan Liu, Xiaolian Chao, Peng Fu, Huiping Xing, and Yuhu Li. 2023. "A Study of Pigment, Adhesive, and Firing Temperature in Pottery Figurines Excavated from the Tomb of Qibi Ming, China" Molecules 28, no. 23: 7739. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28237739
APA StyleLi, Y., Guo, H., Xiao, K., Liu, P., Chao, X., Fu, P., Xing, H., & Li, Y. (2023). A Study of Pigment, Adhesive, and Firing Temperature in Pottery Figurines Excavated from the Tomb of Qibi Ming, China. Molecules, 28(23), 7739. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28237739






