Green Extraction and Preliminary Biological Activity of Hydrolyzed Collagen Peptides (HCPs) Obtained from Whole Undersized Unwanted Catches (Mugil cephalus L.)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Preliminary Characterization of Samples
2.2. Pre-Treatment and Recovery of the Isolated Intermediate Fractions
2.3. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Hydrolyzed Collagen Peptides (HCPs)
2.4. Sircol and Hydroxyproline Tests
2.5. Spectrophotometric Characterization of HCPs Extracts
2.5.1. UltraViolet (UV) Spectra
2.5.2. Fourier-Transform Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.6. Cellular Activity
2.6.1. Cell Viability (MTT)
2.6.2. T-Scratch Test
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Samples
3.2. Chemicals
3.3. Preliminary Characterization of Samples
3.4. Pre-Treatment
3.5. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Hydrolyzed Collagen Peptides (HCPs)
3.6. Purification, Formulation and Calculation of the HCP Ponderal Yields
3.7. Sircol Collagen Quantification Assay
3.8. Hydroxyproline Content Assay
3.9. Spectrophotometric Analyses
3.9.1. UV Spectra
3.9.2. FT-IR Spectroscopy
3.10. Cell Viability
3.11. T-Scratch Assay
4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. In Brief to The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022; ISBN 9789251363645. [Google Scholar]
- Alfio, V.G.; Manzo, C.; Micillo, R. From Fishwaste to Value: An Overview of the Sustainable Recovery of Omega-3 for Food Supplements. Molecules 2021, 26, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thirukumaran, R.; Anu Priya, V.K.; Krishnamoorthy, S.; Ramakrishnan, P.; Moses, J.A.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Resource Recovery from Fish Waste: Prospects and the Usage of Intensified Extraction Technologies. Chemosphere 2022, 299, 134361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, G. Fishery Wastes and By-Products: A Resource to Be Valorised. J. Fish. Sci. 2015, 9, 080–083. [Google Scholar]
- Discarding in Fisheries. Available online: Https://Oceans-and-Fisheries.Ec.Europa.Eu/Fisheries/Rules/Discarding-Fisheries_en (accessed on 1 September 2023).
- European Commission European Green Deal: Developing a Sustainable Blue Economy in the European Union. 2022. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/commission/presscorner/detail/en/ip_21_2341 (accessed on 1 September 2023).
- Coppola, D.; Lauritano, C.; Esposito, F.P.; Riccio, G.; Rizzo, C.; de Pascale, D. Fish Waste: From Problem to Valuable Resource. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messina, C.M.; Arena, R.; Manuguerra, S.; La Barbera, L.; Curcuraci, E.; Renda, G.; Santulli, A. Valorization of Side Stream Products from Sea Cage Fattened Bluefin Tuna (Thunnus Thynnus): Production and In Vitro Bioactivity Evaluation of Enriched ω-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laasri, I.; Bakkali, M.; Mejias, L.; Laglaoui, A. Marine collagen: Unveiling the blue resource-extraction techniques and multifaceted applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenoy, M.; Abdul, N.S.; Qamar, Z.; Al Bahri, B.M.; Al Ghalayini, K.Z.K.; Kakti, A. Collagen Structure, Synthesis, and Its Applications: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e24856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M. Processing of Collagen Based Biomaterials and the Resulting Materials Properties. Biomed. Eng. Online 2019, 18, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.H.; Moreira-Silva, J.; Marques, A.L.P.; Domingues, A.; Bayon, Y.; Reis, R.L. Marine Origin Collagens and Its Potential Applications. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5881–5901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlowska, J.; Sionkowska, A.; Skopinska-Wisniewska, J.; Piechowicz, K. Northern Pike (Esox Lucius) Collagen: Extraction, Characterization and Potential Application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felician, F.F.; Xia, C.; Qi, W.; Xu, H. Collagen from Marine Biological Sources and Medical Applications. Chem. Biodivers. 2018, 15, e1700557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, A.L.; Penaloza, A.M.; Juarez, V.M.M.; Torres, A.V.; Zeugolis, D.I.; Alvarez, G.A. Hydrolyzed Collagen-Sources and Applications. Molecules 2019, 24, 4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Yang, P.; Zhou, C.; Li, S.; Hong, P. Marine Collagen Peptides from the Skin of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis Niloticus): Characterization and Wound Healing Evaluation. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Value, A.; Simpson, B.K. Byproducts from Agriculture and Fisheries; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; ISBN 9781119383994. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Li, L.; Yi, R.; Xu, N.; Gao, R.; Hong, B. Extraction and Characterization of Acid-Soluble Collagen from Scales and Skin of Tilapia (Oreochromis Niloticus). LWT 2016, 66, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecoefishent. Demonstrable and Replicable Cluster Implementing Systemic Solutions through Multilevel Circular Value Chains for Eco-Efficient Valorization of Fishing and Fish Industries Side Streams. Available online: https://ecoefishent.eu/ (accessed on 30 September 2023).
- Suvanich, V.; Ghaedian, R.; Chanamai, R.; Decker, E.A.; Mcclements, D.J. Prediction of Proximate Fish Composition from Ultrasonic Properties: Catfish, Cod, Flounder, Mackerel and Salmon. J. Food Sci. 2006, 63, 966–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedes, F. Determination of Total Lipid Using Non-Chlorinated Solvents. Analyst 1999, 124, 1711–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haedrich, J.; Stumpf, C.; Denison, M.S. Rapid Extraction of Total Lipids and Lipophilic POPs from All EU-Regulated Foods of Animal Origin: Smedes’ Method Revisited and Enhanced. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A Rapid Method of Total Lipid Extraction and Purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque de Castro, M.D.; Priego-Capote, F. Soxhlet Extraction: Past and Present Panacea. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 2383–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Benjakul, S.; Prodpran, T.; Kishimura, H. Extraction and Characterisation of Collagen from the Skin of Golden Carp (Probarbus Jullieni), a Processing By-Product. Waste Biomass Valorization 2018, 9, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, H.; Lista, A.; Siekapen, M.M.; Ghaffari-Bohlouli, P.; Nie, L.; Alimoradi, H.; Shavandi, A. Fish Collagen: Extraction, Characterization, and Applications for Biomaterials Engineering. Polymers 2020, 12, 2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vate, N.K.; Undeland, I.; Abdollahi, M. Resource Efficient Collagen Extraction from Common Starfish with the Aid of High Shear Mechanical Homogenization and Ultrasound. Food Chem. 2022, 393, 133426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Verma, A.K.; Patel, R. Collagen Extraction and Recent Biological Activities of Collagen Peptides Derived from Sea-Food Waste: A Review. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2020, 18, 100315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, L.; Gallo, N.; Natali, M.L.; Campa, L.; Lunetti, P.; Madaghiele, M.; Blasi, F.S.; Corallo, A.; Capobianco, L.; Sannino, A. Marine Collagen and Its Derivatives: Versatile and Sustainable Bio-Resources for Healthcare. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 113, 110963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.M.M.; Kishimura, H.; Benjakul, S. Extraction Efficiency and Characteristics of Acid and Pepsin Soluble Collagens from the Skin of Golden Carp (Probarbus Jullieni) as Affected by Ultrasonication. Process Biochem. 2018, 66, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Fan, H.; Chalamaiah, M.; Wu, J. Preparation of Low-Molecular-Weight, Collagen Hydrolysates (Peptides): Current Progress, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Food Chem. 2019, 301, 125222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, T.Y.; Shaik, M.I.; Sarbon, N.M. Isolation and Characterization of Acid and Pepsin Soluble Collagen Extracted from Sharpnose Stingray (Dasyatis Zugei) Skin. Food Res. 2021, 5, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojha, K.S.; Mason, T.J.; O’Donnell, C.P.; Kerry, J.P.; Tiwari, B.K. Ultrasound Technology for Food Fermentation Applications. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 34, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lionetto, F.; Esposito Corcione, C. Recent Applications of Biopolymers Derived from Fish Industry Waste in Food Packaging. Polymers 2021, 13, 2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hk, M.; Acharya, P.P.; Bhat, G.G.; More, S.S.; Fasim, A. Biophysical and in Vitro Wound Healing Assessment of Collagen Peptides Processed from Fish Skin Waste. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2022, 38, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, D.; Oliviero, M.; Vitale, G.A.; Lauritano, C.; D’Ambra, I.; Iannace, S.; de Pascale, D. Marine Collagen from Alternative and Sustainable Sources: Extraction, Processing and Applications. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minh Thuy, L.T.; Okazaki, E.; Osako, K. Isolation and Characterization of Acid-Soluble Collagen from the Scales of Marine Fishes from Japan and Vietnam. Food Chem. 2014, 149, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweat, F.; Puchtler, H.; Rosenthal, S.I. Sirius red F3BA as a stain for connective tissue. Arch. Pathol. 1964, 78, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Constantine, V.S.; Mowry, R.W. Selective Staining of Human Dermal Collagen. II. The Use of Picrosirius Red F3BA with Polarization Microscopy. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1968, 50, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratky, R.G.; Ivey, J.; Roach, M.R. Collagen Quantitation by Video-Microdensitometry in Rabbit Atherosclerosis. Matrix Biol. 1996, 15, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brotchie, D.; Birch, M.; Roberts, N.; Howard, C.V.; Smith, V.A.; Grierson, I. Localisation of Connective Tissue and Inhibition of Autofluorescence in the Human Optic Nerve and Nerve Head Using a Modified Picrosirius Red Technique and Confocal Microscopy. J. Neurosci. Methods 1999, 87, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Figueiredo Borges, L.; Gutierrez, P.S.; Marana, H.R.C.; Taboga, S.R. Picrosirius-Polarization Staining Method as an Efficient Histopathological Tool for Collagenolysis Detection in Vesical Prolapse Lesions. Micron 2007, 38, 580–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lareu, R.R.; Zeugolis, D.I.; Abu-Rub, M.; Pandit, A.; Raghunath, M. Essential Modification of the Sircol Collagen Assay for the Accurate Quantification of Collagen Content in Complex Protein Solutions. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 3146–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capella-Monsonís, H.; Coentro, J.Q.; Graceffa, V.; Wu, Z.; Zeugolis, D.I. An Experimental Toolbox for Characterization of Mammalian Collagen Type I in Biological Specimens. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 507–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piez, K.A. Characterization of a Collagen from Codfish Skin Containing Three Chromatographically Different Alpha Chains. Biochemistry 1965, 4, 2590–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeruraj, A.; Arumugam, M.; Balasubramanian, T. Isolation and Characterization of Thermostable Collagen from the Marine Eel-Fish (Evenchelys Macrura). Process Biochem. 2013, 48, 1592–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, G.K.; Nidheesh, T.; Suresh, P.V. Comparative Study on Characteristics and in Vitro Fibril Formation Ability of Acid and Pepsin Soluble Collagen from the Skin of Catla (Catla Catla) and Rohu (Labeo Rohita). Food Res. Int. 2015, 76, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, T.; Manna, P.J.; Raja, S.T.K.; Gnanamani, A.; Kundu, P.P. Curcumin Loaded Nano Graphene Oxide Reinforced Fish Scale Collagen—A 3D Scaffold Biomaterial for Wound Healing Applications. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 98653–98665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampath Kumar, N.S.; Nazeer, R.A.; Jaiganesh, R. Wound Healing Properties of Collagen from the Bone of Two Marine Fishes. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2012, 18, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampitiya, A.G.D.M.; Gonapinuwala, S.T.; Fernando, C.A.N.; de Croos, M.D.S.T. Extraction and Characterisation of Type I Collagen from the Skin Offcuts Generated at the Commercial Fish Processing Centres. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 60, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León-López, A.; Fuentes-Jiménez, L.; Hernández-Fuentes, A.D.; Campos-Montiel, R.G.; Aguirre-álvarez, G. Hydrolysed Collagen from Sheepskins as a Source of Functional Peptides with Antioxidant Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsuwan, K.; Patil, U.; Tu, C.; Zhang, B.; Benjakul, S. Salmon Skin Acid-Soluble Collagen Produced by A Simplified Recovery Process: Yield, Compositions, and Molecular Characteristics. Fishes 2022, 7, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Hou, H.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y. Characterization of Acid- and Pepsin-Soluble Collagen Extracted from the Skin of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis Niloticus). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 99, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyonga, J.H.; Cole, C.G.B.; Duodu, K.G. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopic Study of Acid Soluble Collagen and Gelatin from Skins and Bones of Young and Adult Nile Perch (Lates Niloticus). Food Chem. 2004, 86, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.R.; Wang, B.; Chi, C.F.; Zhang, Q.H.; dan Gong, Y.; Tang, J.J.; Luo, H.Y.; Ding, G. fang Isolation and Characterization of Acid Soluble Collagens and Pepsin Soluble Collagens from the Skin and Bone of Spanish Mackerel (Scomberomorous Niphonius). Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 31, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.J.; Ha, G.H.; Seo, W.Y.; Kim, C.K.; Kim, K.J.; Lee, S.B. Human Collagen Alpha-2 Type I Stimulates Collagen Synthesis, Wound Healing, and Elastin Production in Normal Human Dermal Fibroblasts (HDFs). BMB Rep. 2020, 53, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davison-Kotler, E.; Marshall, W.S.; García-Gareta, E. Sources of Collagen for Biomaterials in Skin Wound Healing. Bioengineering 2019, 6, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demori, I.; El Rashed, Z.; De Negri Atanasio, G.; Parodi, A.; Millo, E.; Salis, A.; Costa, A.; Rosa, G.; Zanotti Russo, M.; Salvidio, S.; et al. First Evidence of Anti-Steatotic Action of Macrotympanain A1, an Amphibian Skin Peptide from Odorrana Macrotympana. Molecules 2022, 27, 7417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambruschini, C.; Demori, I.; El Rashed, Z.; Rovegno, L.; Canessa, E.; Cortese, K.; Grasselli, E.; Moni, L. Synthesis, Photoisomerization, Antioxidant Activity, and Lipid-Lowering Effect of Ferulic Acid and Feruloyl Amides. Molecules 2021, 26, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

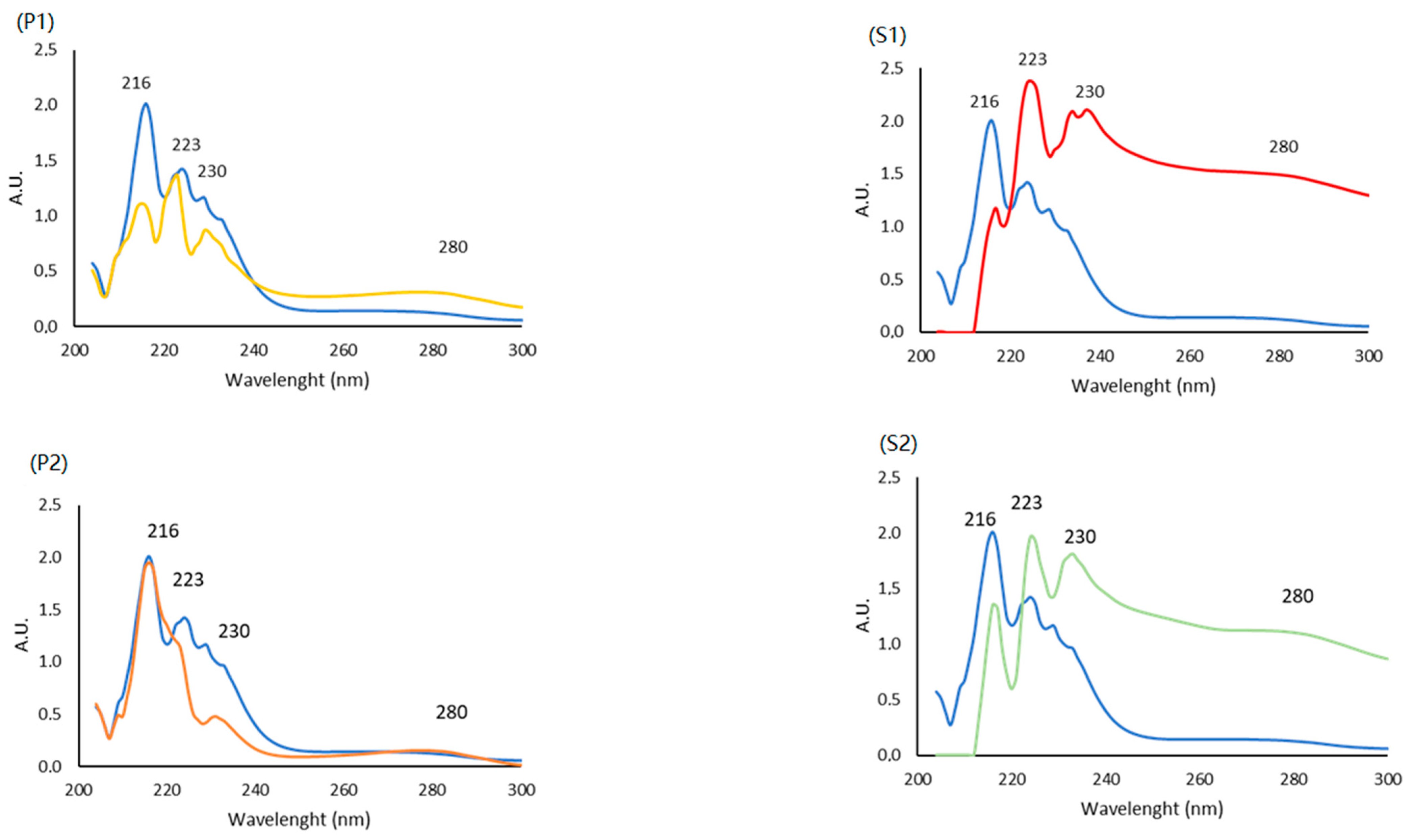
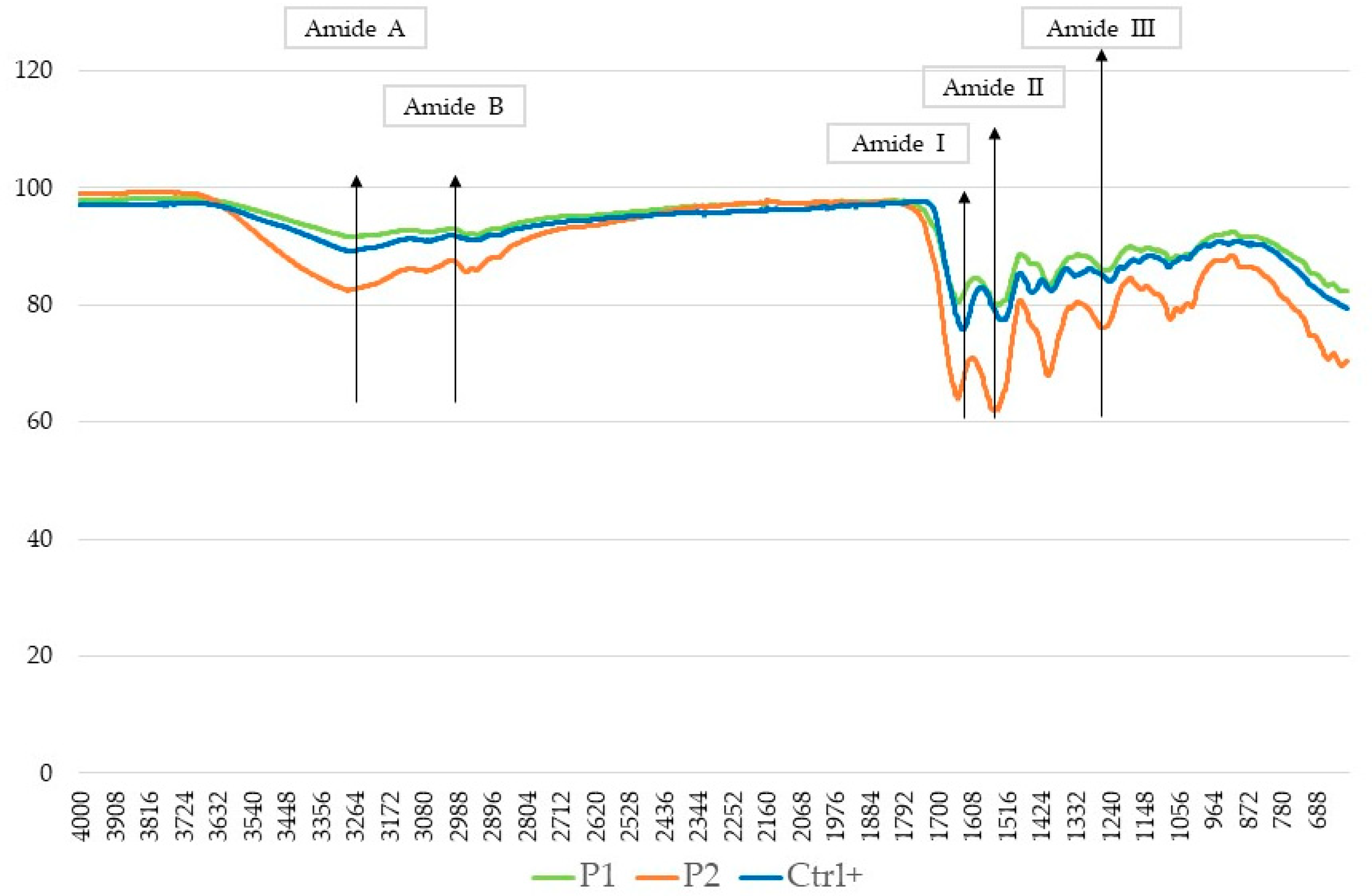
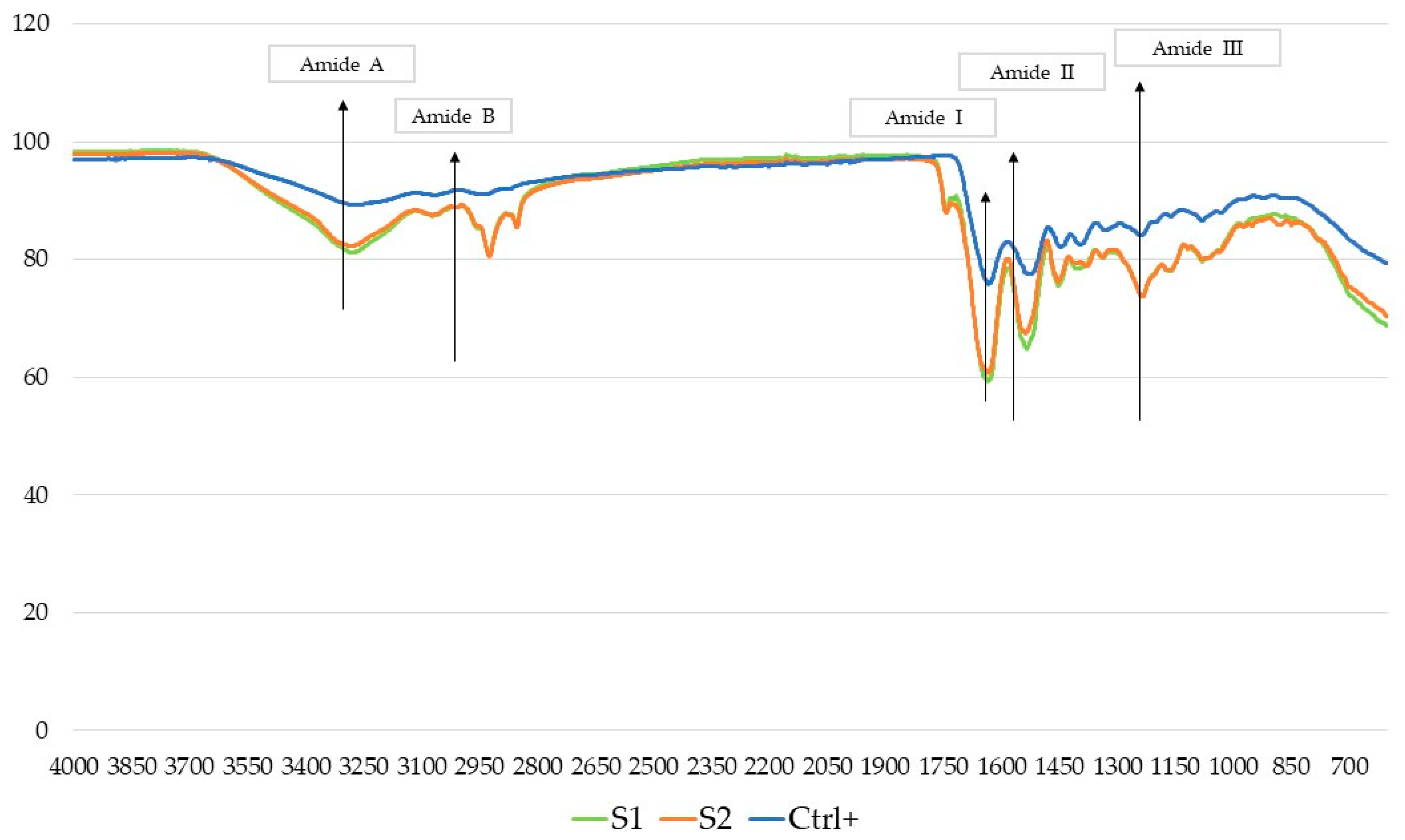
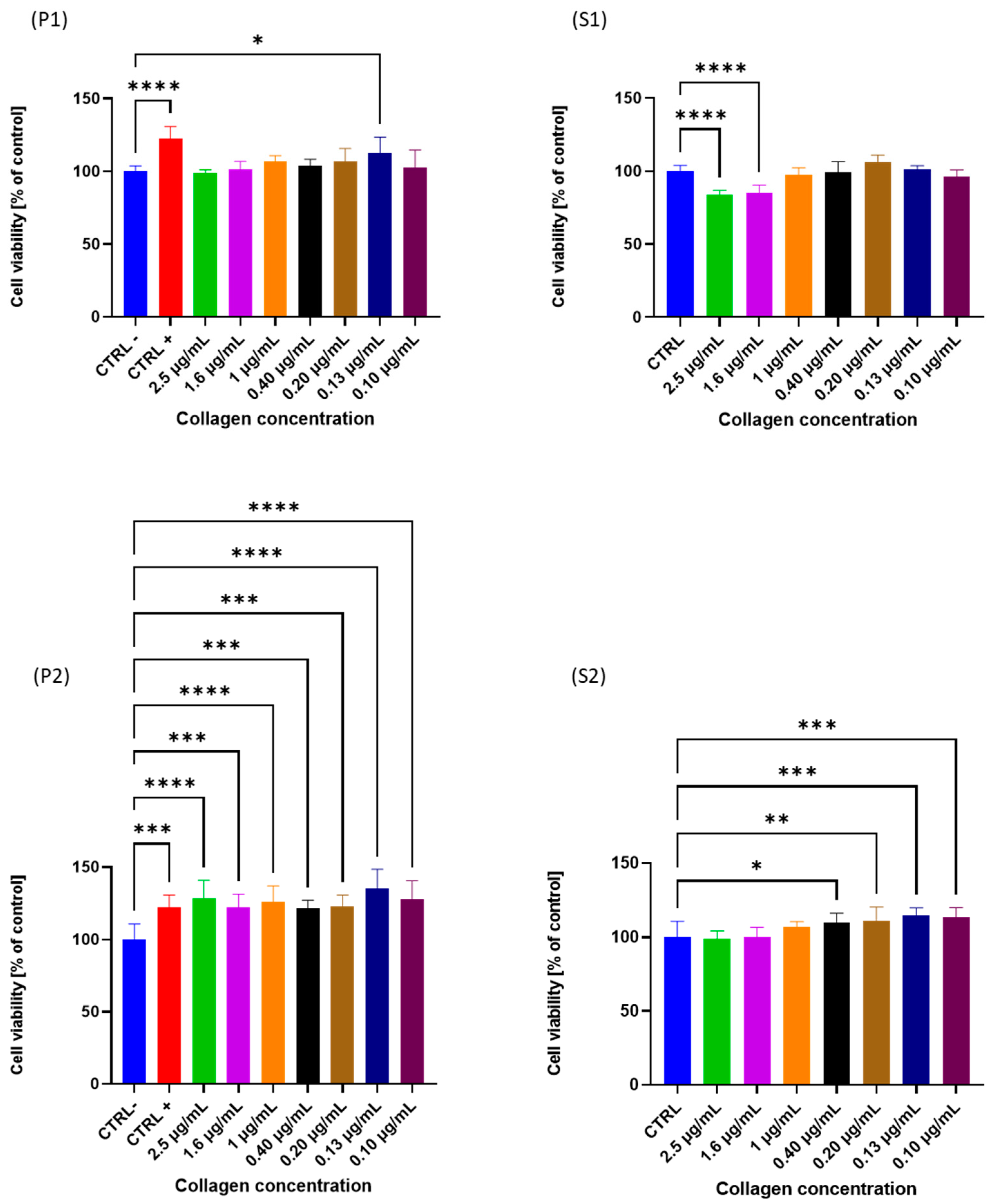

| Sample | Residual Moisture (g/100 g) | Crude Proteins (g/100 g) | Ashes (g/100 g) | Lipids (g/100 g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 (whole fishes) | 4.4 ± 0.8 | 68.7 ± 4.9 | 16.9 ± 0.5 | 10.1 ± 0.7 |
| F2 (skin, fins and tails) | 4.7 ± 0.3 | 63.9 ± 2.7 | 20.6 ± 0.6 | 8.1 ± 0.4 |
| Edible portion (fillet) | 4.0 ± 0.1 | 75.3 ± 0.9 | 11.2 ± 0.2 | 9.0 ± 0.4 |
| Sample | NCPs/Total Sample Weight (g/100 g) | NCPs/Total Protein Weight (g/100 g) |
|---|---|---|
| F1 (whole fishes) | 16.3 ± 0.9 | 23.7 ± 1.0 |
| F2 (skin, fins and tails) | 17.3 ± 0.8 | 27.1 ± 0.8 |
| Edible portion (fillet) | 23.0 ± 0.5 | 30.5 ± 0.5 |
| Ponderal Yield | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Extract Code | Description | HCPs/Total Sample Weight (g/100 g) | HCPs/Total Protein Weight (g/100 g) |
| P1 | <3 KDa (obtained from F1, whole fishes) | 5.2 ± 0.3 | 7.6 ± 0.4 |
| P2 | <3 KDa (obtained from F2, skin, fins and tails) | 5.0 ± 0.3 | 7.8 ± 0.3 |
| S1 | >3 KDa (obtained from F1, whole fishes) | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.6 ± 0.1 |
| S2 | >3 KDa (obtained from F2, skin, fins and tails) | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 3.9 ± 0.3 |
| Extract Code | SCA (µg/mL) | Hydroxyproline (µg/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| CTRL+ P1 | 60.24 ± 37.30 74.70 ± 0.73 | 49.32 ± 7.75 3.22 ± 0.45 |
| P2 | 73.45 ± 3.43 | 2.41 ± 0.22 |
| S1 | 141.81 ± 3.83 | 21.93 ± 7.98 |
| S2 | 184.02 ± 10.87 | 33.06 ± 0.68 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Orlandi, V.; Dondero, L.; Turrini, F.; De Negri Atanasio, G.; Grasso, F.; Grasselli, E.; Boggia, R. Green Extraction and Preliminary Biological Activity of Hydrolyzed Collagen Peptides (HCPs) Obtained from Whole Undersized Unwanted Catches (Mugil cephalus L.). Molecules 2023, 28, 7637. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28227637
Orlandi V, Dondero L, Turrini F, De Negri Atanasio G, Grasso F, Grasselli E, Boggia R. Green Extraction and Preliminary Biological Activity of Hydrolyzed Collagen Peptides (HCPs) Obtained from Whole Undersized Unwanted Catches (Mugil cephalus L.). Molecules. 2023; 28(22):7637. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28227637
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrlandi, Valentina, Lorenzo Dondero, Federica Turrini, Giulia De Negri Atanasio, Federica Grasso, Elena Grasselli, and Raffaella Boggia. 2023. "Green Extraction and Preliminary Biological Activity of Hydrolyzed Collagen Peptides (HCPs) Obtained from Whole Undersized Unwanted Catches (Mugil cephalus L.)" Molecules 28, no. 22: 7637. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28227637
APA StyleOrlandi, V., Dondero, L., Turrini, F., De Negri Atanasio, G., Grasso, F., Grasselli, E., & Boggia, R. (2023). Green Extraction and Preliminary Biological Activity of Hydrolyzed Collagen Peptides (HCPs) Obtained from Whole Undersized Unwanted Catches (Mugil cephalus L.). Molecules, 28(22), 7637. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28227637









