Amino Acid Derivatives of Ginsenoside AD-2 Induce HepG2 Cell Apoptosis by Affecting the Cytoskeleton
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of AD-2 Amino Acid Derivatives on the Proliferation of HepG2 Cells
2.2. Effect of AD-2 Derivative 6b on Cytotoxicity of Normal Cells
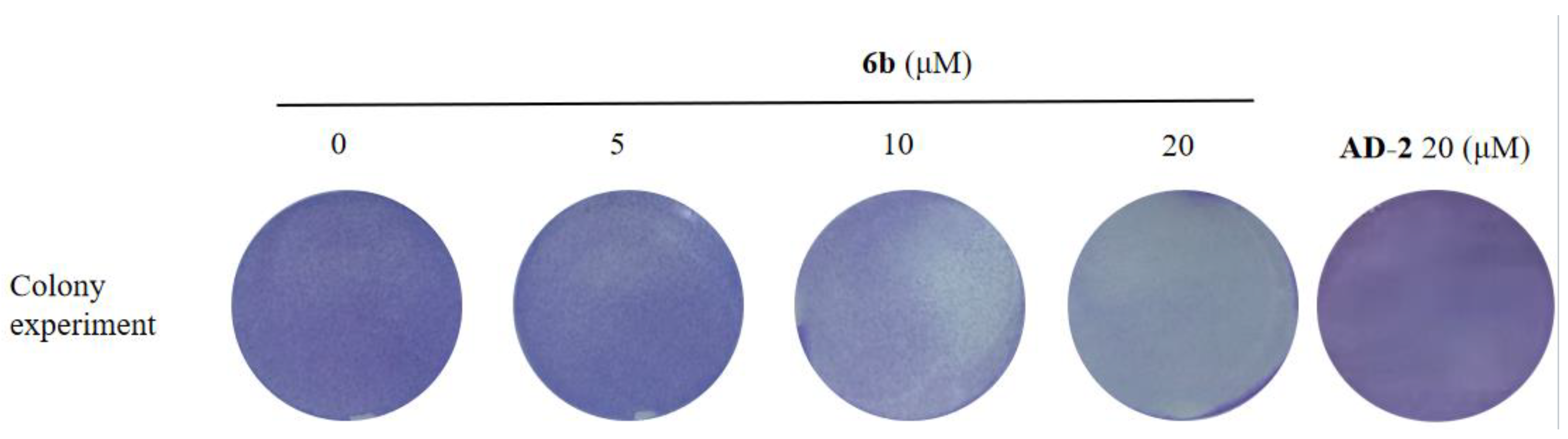
2.3. Effect of Amino Acid Derivative 6b of AD-2 on Colony Formation of HepG2 Cells
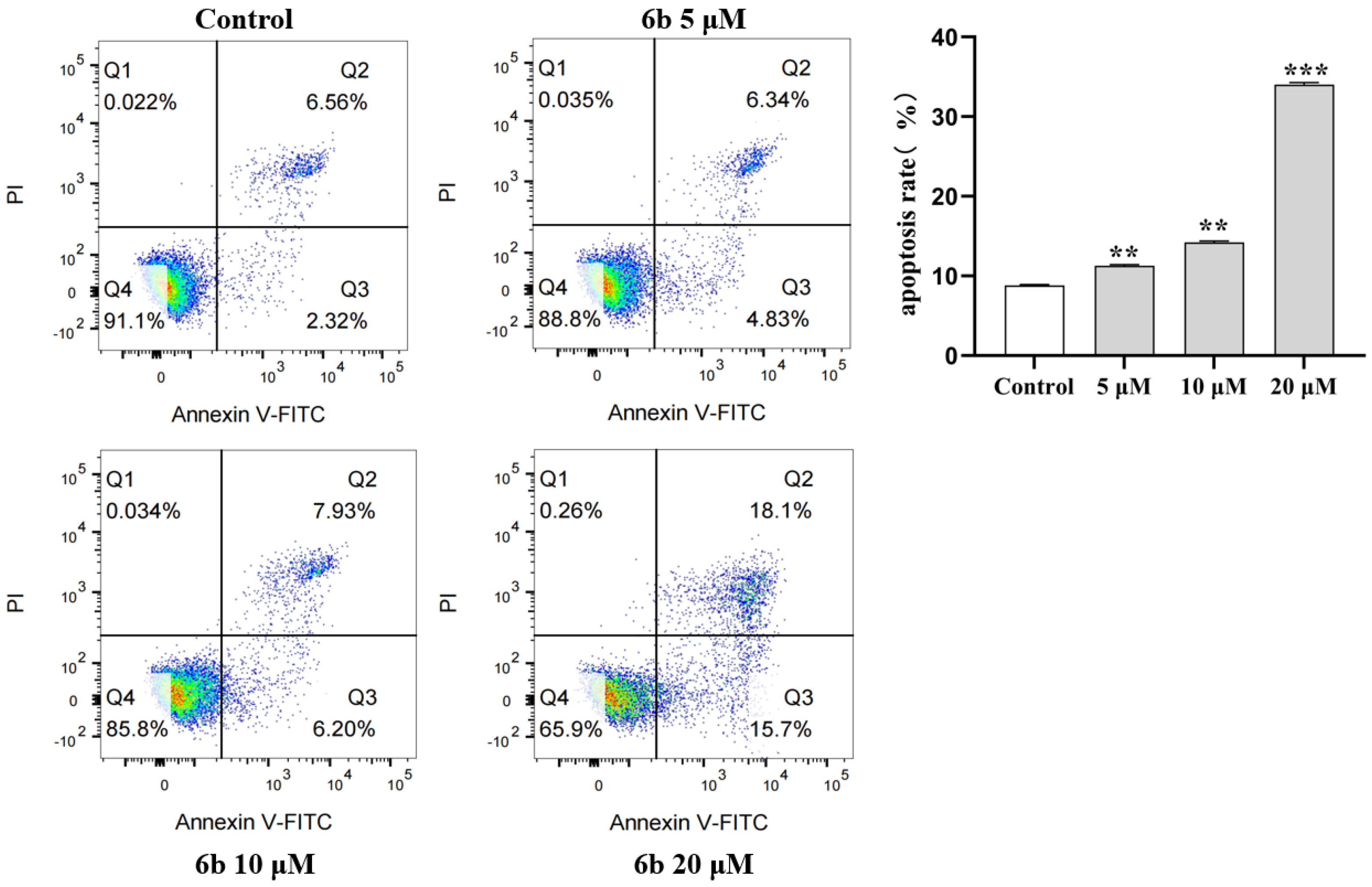
2.4. Effects of AD-2 Amino Acid Derivative 6b on Apoptosis of HepG2 Cells
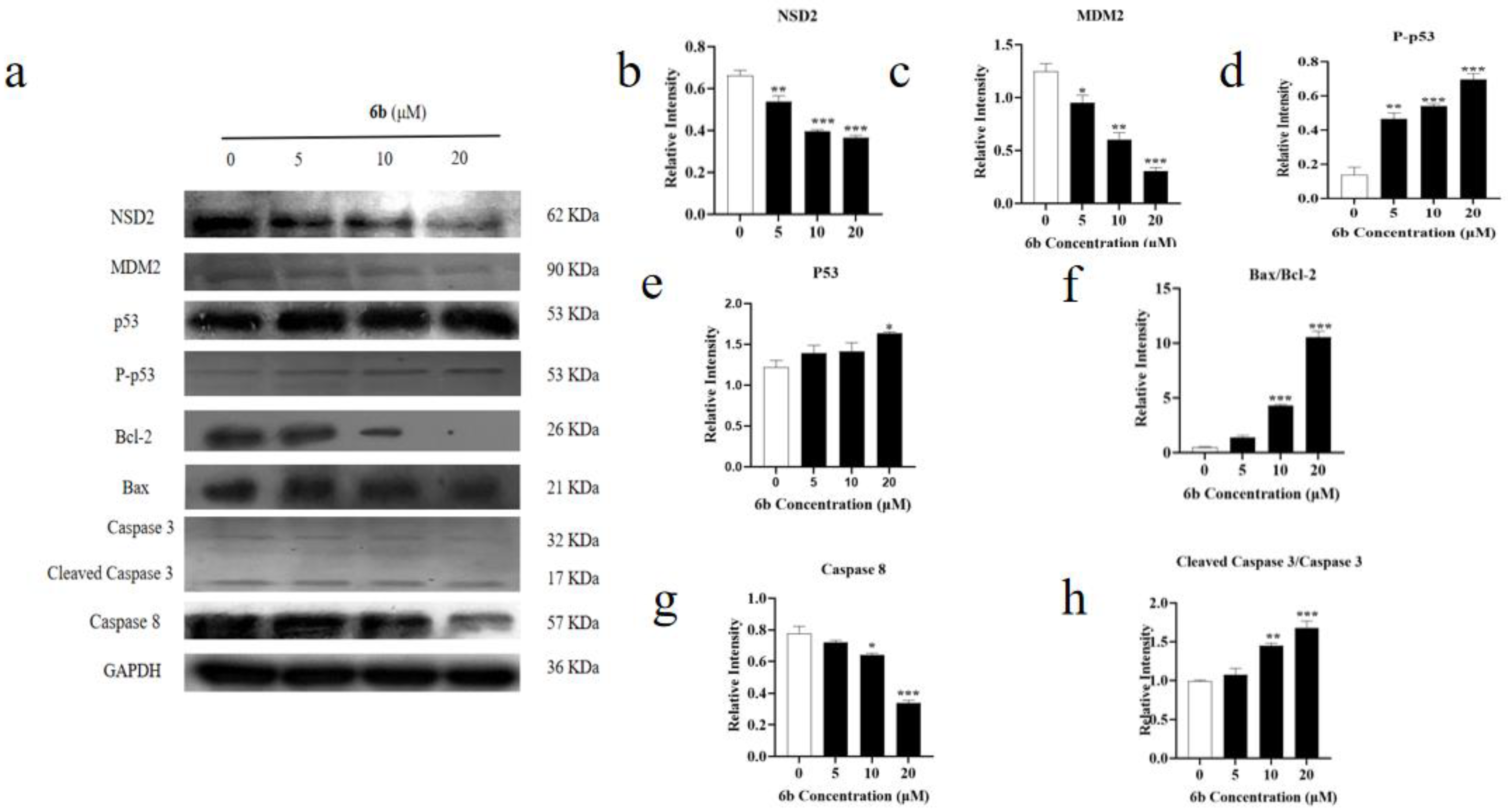
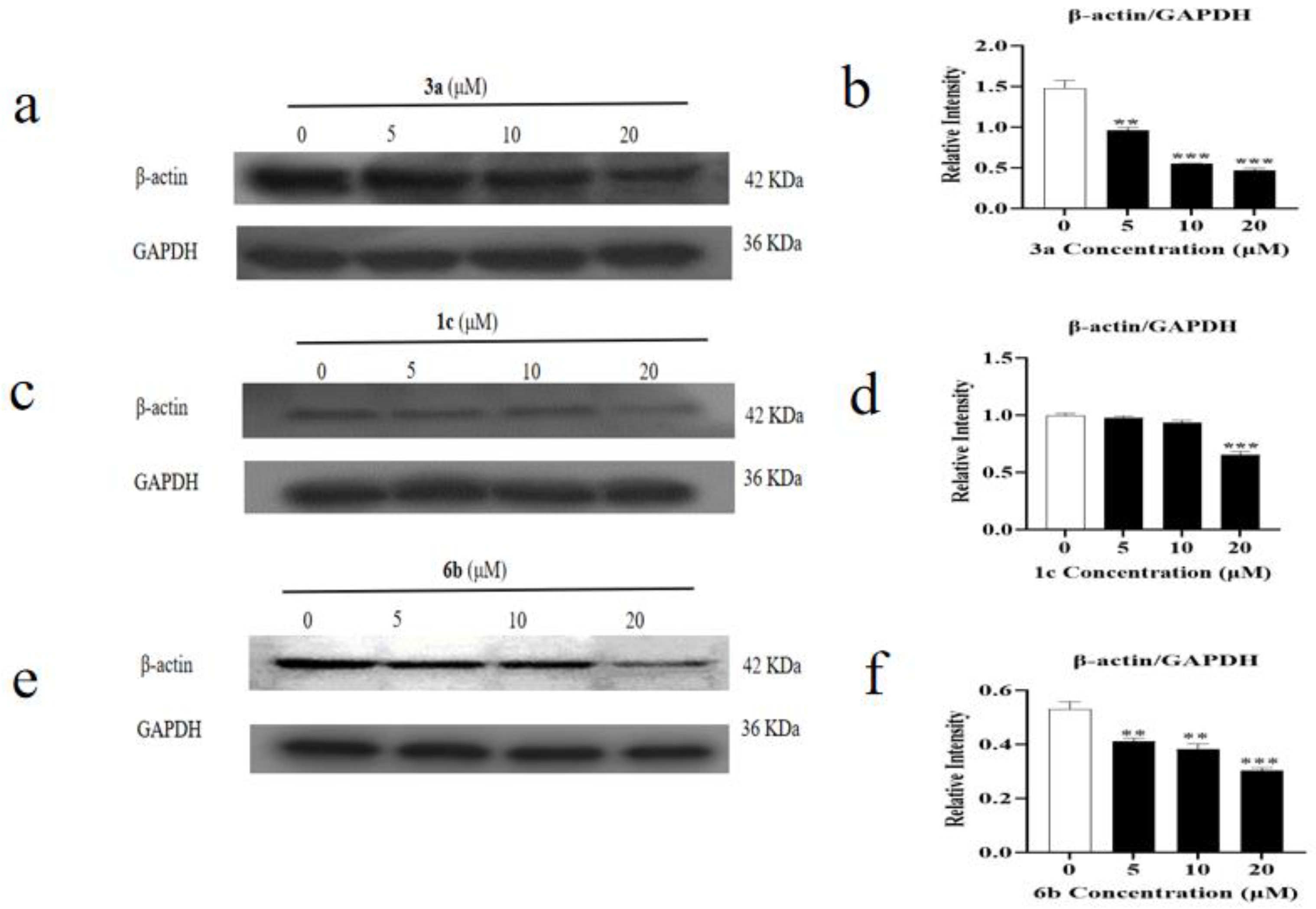
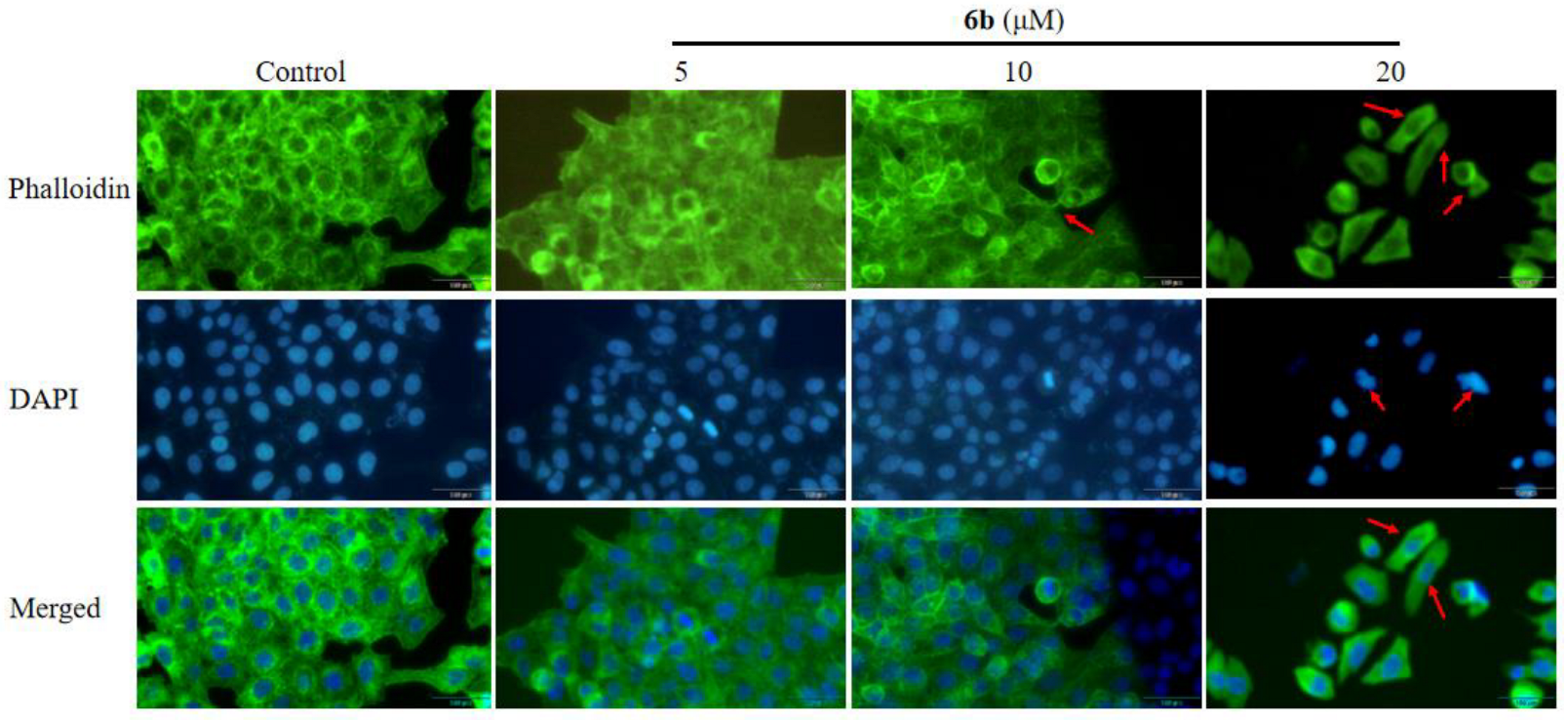
2.5. Effect of Amino Acid Derivative 6b of AD-2 on Cytoskeleton
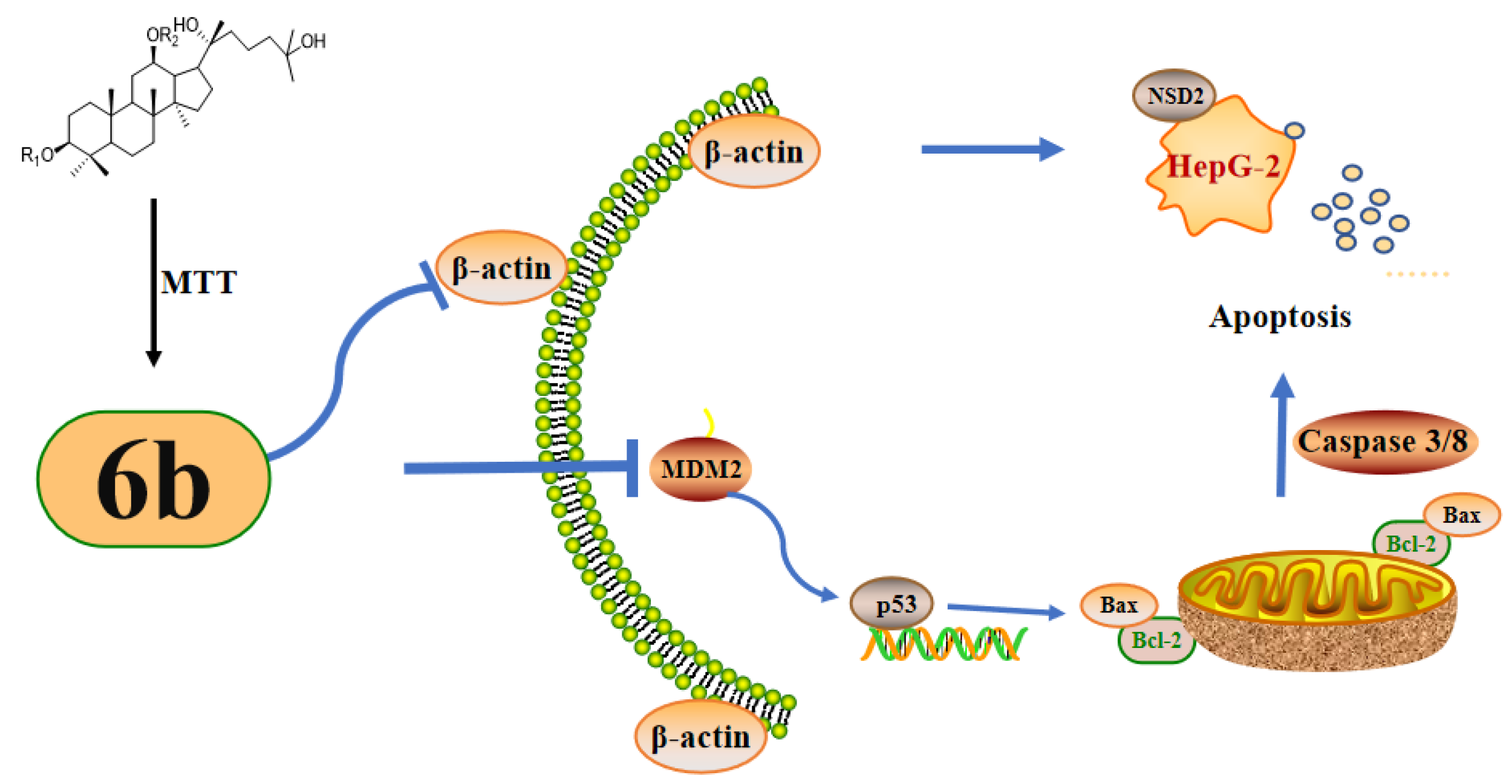
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemical and Reagents
4.2. Cell Cultures
4.3. Cell Viability Assay
4.4. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.5. Colony Formation Analysis
4.6. Western Blotting Analysis
4.7. Flow Cytometry
4.8. Phalloidin Staining
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Xu, G.; Han, C.; Xing, G. lncRNA MIR4435-2HG promotes the progression of liver cancer by upregulating B3GNT5 expression. Mol. Med. Rep. 2022, 25, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwanwan, D.; Singh, S.K.; Singh, S.; Saikam, V.; Singh, R. Challenges in liver cancer and possible treatment approaches. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2020, 1873, 188314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Cui, H.T.; Bian, Y.H.; Li, Y.T.; Wang, Y.X.; Peng, Y.F.; Wen, W.B.; Li, K.; Wang, H.W.; Zhang, Z.Y.; et al. Ethanol extract of Ardisiae Japonicae Herba inhibits hepatoma carcinoma cell proliferation in vitro through regulating lipid metabolism. Chin. Herb. Med. 2021, 13, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Saviano, A.; Erstad, D.J.; Hoshida, Y.; Fuchs, B.C.; Baumert, T.; Tanabe, K.K. Risk Factors, Pathogenesis, and Strategies for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Prevention: Emphasis on Secondary Prevention and Its Translational Challenges. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, N.; Friedman, S.L.; Goossens, N.; Hoshida, Y. Risk factors and prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma in the era of precision medicine. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 526–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, N.C.; Huang, R.L.; Huang, X.F.; Chang, K.F.; Lee, C.J.; Hsiao, C.Y.; Lee, S.C.; Tsai, N.M. Evaluation of anticancer effects of Juniperus communis extract on hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Biosci. Rep. 2021, 41, BSR20211143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Lv, Q.; Li, Y.; Jin, Y.H. The Anti-Tumor Effect and Underlying Apoptotic Mechanism of Ginsenoside Rk1 and Rg5 in Human Liver Cancer Cells. Molecules 2021, 26, 3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, M.; Wang, R.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Z. Ginsenosides in Panax genus and their biosynthesis. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 1813–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vig, B.S.; Huttunen, K.M.; Laine, K.; Rautio, J. Amino acids as promoieties in prodrug design and development. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1370–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, W.; Guo, J.; Wang, X.; Su, G.; Zhao, Y. Non-protein amino acid derivatives of 25-methoxylprotopanaxadiol/25-hydroxyprotopanaxadioland their anti-tumour activity evaluation. Steroids 2018, 129, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Huang, H.; Ma, Y.; Wu, C.; Yang, X.; Choi, H.Y. Davidone C Induces the Death of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Promoting Apoptosis and Autophagy. Molecules 2021, 26, 5219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jannus, F.; Medina-O'Donnell, M.; Rivas, F.; Diaz-Ruiz, L.; Rufino-Palomares, E.E.; Lupianez, J.A.; Parra, A.; Reyes-Zurita, F.J. A Diamine-PEGylated Oleanolic Acid Derivative Induced Efficient Apoptosis through a Death Receptor and Mitochondrial Apoptotic Pathway in HepG2 Human Hepatoma Cells. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, P.; Zhai, Z.; Hao, Z.; Zhang, H.; He, J. CircWHSC1 serves as an oncogene to promote hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 51, e13487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshatwi, A.A.; Subash-Babu, P.; Antonisamy, P. Violacein induces apoptosis in human breast cancer cells through up regulation of BAX, p53 and down regulation of MDM2. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2016, 68, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Ha, S.E.; Lee, H.J.; Rampogu, S.; Vetrivel, P.; Kim, H.H.; Venkatarame Gowda Saralamma, V.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, G.S. Sinensetin Induces Autophagic Cell Death through p53-Related AMPK/mTOR Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma HepG2 Cells. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, M.M.; Eissa, N.; Althobaiti, F.; Fayad, E.; Abu Almaaty, A.H. Nomad Jellyfish Rhopilema nomadica Venom Induces Apoptotic Cell Death and Cell Cycle Arrest in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma HepG2 Cells. Molecules 2021, 26, 5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haronikova, L.; Bonczek, O.; Zatloukalova, P.; Kokas-Zavadil, F.; Kucerikova, M.; Coates, P.J.; Fahraeus, R.; Vojtesek, B. Resistance mechanisms to inhibitors of p53-MDM2 interactions in cancer therapy: Can we overcome them? Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 2021, 26, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, Y.Y.; Jia, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, F.J.; Dong, N.; Feng, Y.W.; Wu, M.; Tong, Y.L.; Yao, Y.M. The potential mechanism of extracellular high mobility group box-1 protein mediated p53 expression in immune dysfunction of T lymphocytes. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 112959–112971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, G.; Qu, L.; Jiang, L.; Dai, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; et al. Structures of p53/BCL-2 complex suggest a mechanism for p53 to antagonize BCL-2 activity. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.Y.; Zang, E.H.; Lv, L.J.; Li, Q.Y.; Zhang, C.H.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, L.; Dang, L.S.; Li, M.H. Flavonoids in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: Therapeutic effects and mechanisms. Chin. Herb. Med. 2021, 13, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, J.; Yuan, W.; Hao, S.; Wang, M.; Wang, F.; Xuan, H. Bioactive components and mechanisms of poplar propolis in inhibiting proliferation of human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 144, 112364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.J.; Chiu, C.C.; Hsiao, M.H.; Yow, J.L.; Tzang, B.S.; Hsu, T.C. Potential of antiviral drug oseltamivir for the treatment of liver cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2021, 59, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Tang, S.; Wang, Z.; Cai, L.; Lian, H.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, Y. A pan-cancer analysis of the prognostic and immunological role of β-actin (ACTB) in human cancers. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 6166–6185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.D.; Su, G.Y.; Zhao, C.; Qu, F.Z.; Wang, P.; Zhao, Y.Q. Anticancer activity and potential mechanisms of 1C, a ginseng saponin derivative, on prostate cancer cells. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Bi, X.L.; Xu, J.; Yuan, H.N.; Piao, H.R.; Zhao, Y.Q. Synthesis and anti-tumor evaluation of novel 25-hydroxyprotopanaxadiol analogs incorporating natural amino acids. Steroids 2013, 78, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.N.; Bao, N.R.; Wang, S.; Xi, M.; Zhang, T.H.; Chen, F.S. Ketamine Induces Ferroptosis of Liver Cancer Cells by Targeting lncRNA PVT1/miR-214-3p/GPX4. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 3965–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Fang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Le, J.; Zhang, B.; Huang, R.; Chen, Z.; Shao, J. Evolution in medicinal chemistry of sorafenib derivatives for hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 179, 916–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, X.; Zhang, H.; Kang, J.P.; Yang, D.U.; Li, Y.; Pang, S.; Jin, Y.; Yang, D.C.; Wang, Y. Advances in Saponin Diversity of Panax ginseng. Molecules 2020, 25, 3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, K.; Liu, Q.; Wan, J.Y.; Zhao, Y.J.; Guo, R.Z.; Alolga, R.N.; Li, P.; Qi, L.W. Rapid preparation of rare ginsenosides by acid transformation and their structure-activity relationships against cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieu, E.L.; Nguyen, T.; Rhyne, S.; Kim, J. Amino acids in cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoni, A.; Capone, M.; Ramazzotti, M.; Vanni, A.; Locatello, L.G.; Gallo, O.; De Palma, R.; Cosmi, L.; Liotta, F.; Annunziato, F.; et al. IL4I1 Is Expressed by Head-Neck Cancer-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and Contributes to Suppress T Cell Proliferation. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.F.; Yuan, H.N.; Bi, X.L.; Piao, H.R.; Cao, J.Q.; Li, W.; Wang, P.; Zhao, Y.Q. 25-Methoxylprotopanaxadiol derivatives and their anti-proliferative activities. Steroids 2013, 78, 1305–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Qu, F.; Liu, Y.; Lu, J.; Su, G.; Zhao, Y. Conjugation of Ginsenoside with Dietary Amino Acids: A Promising Strategy to Suppress Cell Proliferation and Induce Apoptosis in Activated Hepatic Stellate Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 10245–10255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.; Wang, X.; Xu, L.; Miao, D.; Li, T.; Su, G.; Zhao, Y. Novel ginsenoside derivatives have shown their effects on PC-3 cells by inducing G1-phase arrest and reactive oxygen species-mediate cell apoptosis. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 112, 104864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.; Guo, R.; Chai, J.; Wu, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Abdel-Rahman, M.A.; Xia, H.; Xu, X. Smp24, a Scorpion-Venom Peptide, Exhibits Potent Antitumor Effects against Hepatoma HepG2 Cells via Multi-Mechanisms In Vivo and In Vitro. Toxins 2022, 14, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Liu, J.; Chai, J.; Gao, Y.; Abdel-Rahman, M.A.; Xu, X. Scorpion Peptide Smp24 Exhibits a Potent Antitumor Effect on Human Lung Cancer Cells by Damaging the Membrane and Cytoskeleton In Vivo and In Vitro. Toxins 2022, 14, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostuni, A.; Carmosino, M.; Miglionico, R.; Abruzzese, V.; Martinelli, F.; Russo, D.; Laurenzana, I.; Petillo, A.; Bisaccia, F. Inhibition of ABCC6 Transporter Modifies Cytoskeleton and Reduces Motility of HepG2 Cells via Purinergic Pathway. Cells 2020, 9, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Franca, M.N.F.; Isidorio, R.G.; Bonifacio, J.H.O.; Dos Santos, E.W.P.; Santos, J.F.; Ottoni, F.M.; de Lucca Junior, W.; Scher, R.; Alves, R.J.; Correa, C.B. Anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic activity of glycosidic derivatives of lawsone in melanoma cancer cell. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Rayburn, E.R.; Hao, M.; Zhao, Y.; Hill, D.L.; Zhang, R.; Wang, H. Experimental therapy of prostate cancer with novel natural product anti-cancer ginsenosides. Prostate 2008, 68, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.F.; Gong, Y.X.; Li, H.F.; Sun, F.L.; Li, W.L.; Chen, D.Q.; Xie, D.P.; Ren, C.X.; Guo, X.Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; et al. Curcumin Activates ROS Signaling to Promote Pyroptosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma HepG2 Cells. In Vivo 2021, 35, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kui, X.Y.; Gao, Y.; Liu, X.S.; Zeng, J.; Yang, J.W.; Zhou, L.M.; Liu, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Pei, Z.J. Comprehensive Analysis of SLC17A9 and Its Prognostic Value in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 809847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Bai, X.; Hou, Y. 1,4,5,6,7,8-Hexahydropyrido[4,3-d]pyrimidine inhibits HepG2 cell proliferation, migration and invasion, and induces apoptosis through the upregulation of miR-26b-5p by targeting CDK8. Oncol. Lett. 2023, 25, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Dong, X.; Liu, Y.; Ni, B.; Sai, N.; You, L.; Sun, M.; Yao, Y.; Qu, C.; Yin, X.; et al. Itraconazole exerts anti-liver cancer potential through the Wnt, PI3K/AKT/mTOR, and ROS pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 131, 110661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, C.Z.; Liu, Y.F.; Zhang, L.L.; Chen, S.H.; Hu, C.Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.T. Polyphenols from Broussonetia papyrifera Induce Apoptosis of HepG2 Cells via Inactivation of ERK and AKT Signaling Pathways. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 8841706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.; Shin, N.R.; Kim, S.H.; Park, S.C.; Lee, H.J. Fibrinogen-Like Protein 1 Modulates Sorafenib Resistance in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.D.; Zhu, A.; Li, L.D.; Zhang, T.; Wang, S.; Shan, D.P.; Li, Y.Z.; Wang, Q. Cytotoxicity and underlying mechanism of evodiamine in HepG2 cells. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2021, 53, 1107–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.H.; Bi, J.H.; Wu, M.R.; Ye, S.J.; Hu, L.; Li, L.J.; Yi, Y.; Wang, H.X.; Wang, L.M. In vitro anti-hepatocellular carcinogenesis of 1,2,3,4,6-Penta-O-galloyl-beta-D-glucose. Food Nutr. Res. 2023, 67, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lintao, R.C.V.; Medina, P.M.B. Screening for Anticancer Activity of Leaf Ethanolic Extract of Alpinia elegans ("tagbak") on Human Cancer Cell Lines. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2021, 22, 3781–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.J.; Hwang, S.K.; Magae, J.; Chang, Y.C. Ascofuranone suppresses invasion and F-actin cytoskeleton organization in cancer cells by inhibiting the mTOR complex 1 signaling pathway. Cell Oncol. 2020, 43, 793–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
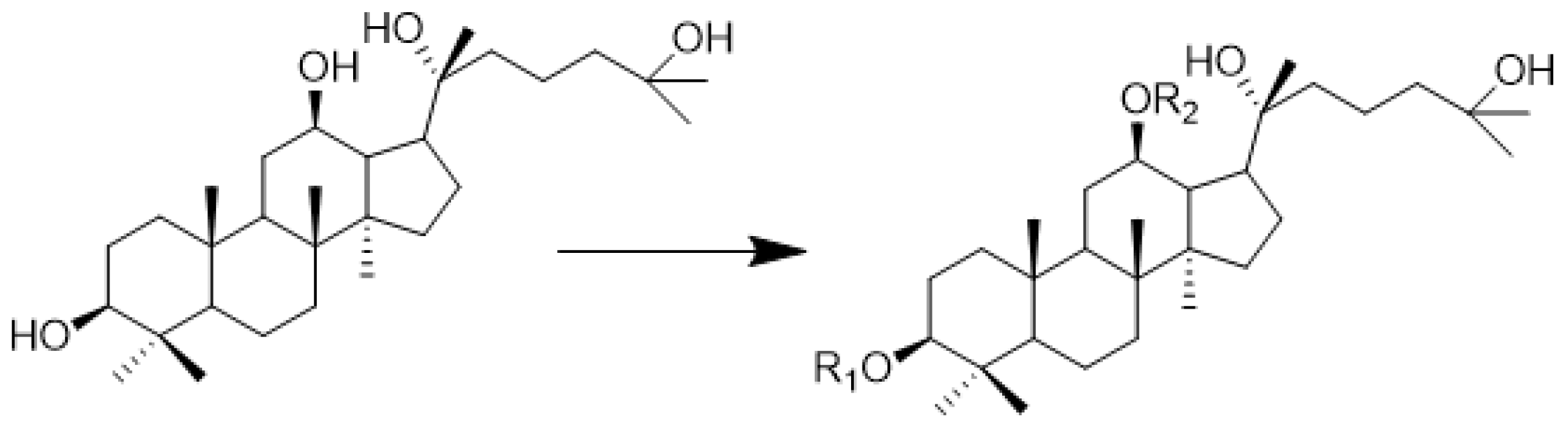

| Number | Compound | R1 | R2 | IC50 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1b | Boc-Ala | H | 13.44 ± 0.38 |
| 2 | 1c | Ala | H | 26.84 ± 4.45 |
| 3 | 2b | Boc-Val | H | 20.68 ± 2.36 |
| 4 | 2c | Val | H | 13.22 ± 2.52 |
| 5 | 3a | H | Boc-Gly | 7.05 ± 1.27 |
| 6 | 3b | Boc-Gly | H | 17.09 ± 4.1 |
| 7 | 3c | Gly | H | 11.47 ± 1.58 |
| 8 | 4b | Boc-Pro | H | 6.97 ± 2.71 |
| 9 | 4c | Pro | H | 15.50 ± 2.70 |
| 10 | 5a | H | Boc-Met | 11.28 ± 1.99 |
| 11 | 5b | Boc-Met | H | 9.79 ± 1.92 |
| 12 | 5c | Met | H | 20.14 ± 4.01 |
| 13 | 6a | H | Boc-Phe | 8.30 ± 3.86 |
| 14 | 6b | Boc-Phe | H | 8.25 ± 2.93 |
| 15 | 6c | Phe | H | 11.23 ± 1.36 |
| 16 | AD-2 | H | H | >100 |
| 17 | 5-FU | - | - | 43.8 ± 1.93 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, T.; Liang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Meng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Su, G. Amino Acid Derivatives of Ginsenoside AD-2 Induce HepG2 Cell Apoptosis by Affecting the Cytoskeleton. Molecules 2023, 28, 7400. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217400
Lin L, Zhao Y, Wang P, Li T, Liang Y, Chen Y, Meng X, Zhang Y, Su G. Amino Acid Derivatives of Ginsenoside AD-2 Induce HepG2 Cell Apoptosis by Affecting the Cytoskeleton. Molecules. 2023; 28(21):7400. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217400
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Lizhen, Yuqing Zhao, Peng Wang, Tao Li, Yuhang Liang, Yu Chen, Xianyi Meng, Yudong Zhang, and Guangyue Su. 2023. "Amino Acid Derivatives of Ginsenoside AD-2 Induce HepG2 Cell Apoptosis by Affecting the Cytoskeleton" Molecules 28, no. 21: 7400. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217400
APA StyleLin, L., Zhao, Y., Wang, P., Li, T., Liang, Y., Chen, Y., Meng, X., Zhang, Y., & Su, G. (2023). Amino Acid Derivatives of Ginsenoside AD-2 Induce HepG2 Cell Apoptosis by Affecting the Cytoskeleton. Molecules, 28(21), 7400. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217400








