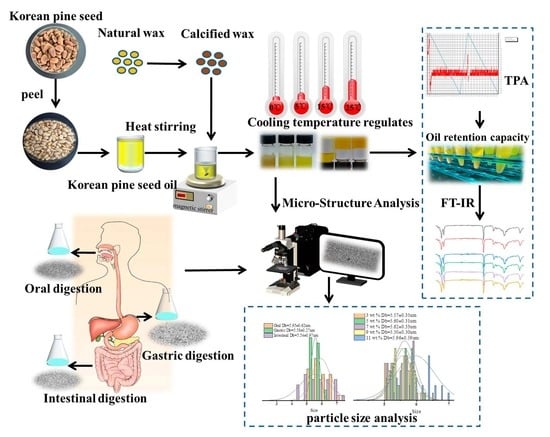
Formation and In Vitro Simulated Digestion Study of Gelatinized Korean Pine Seed Oil Encapsulated with Calcified Wax
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
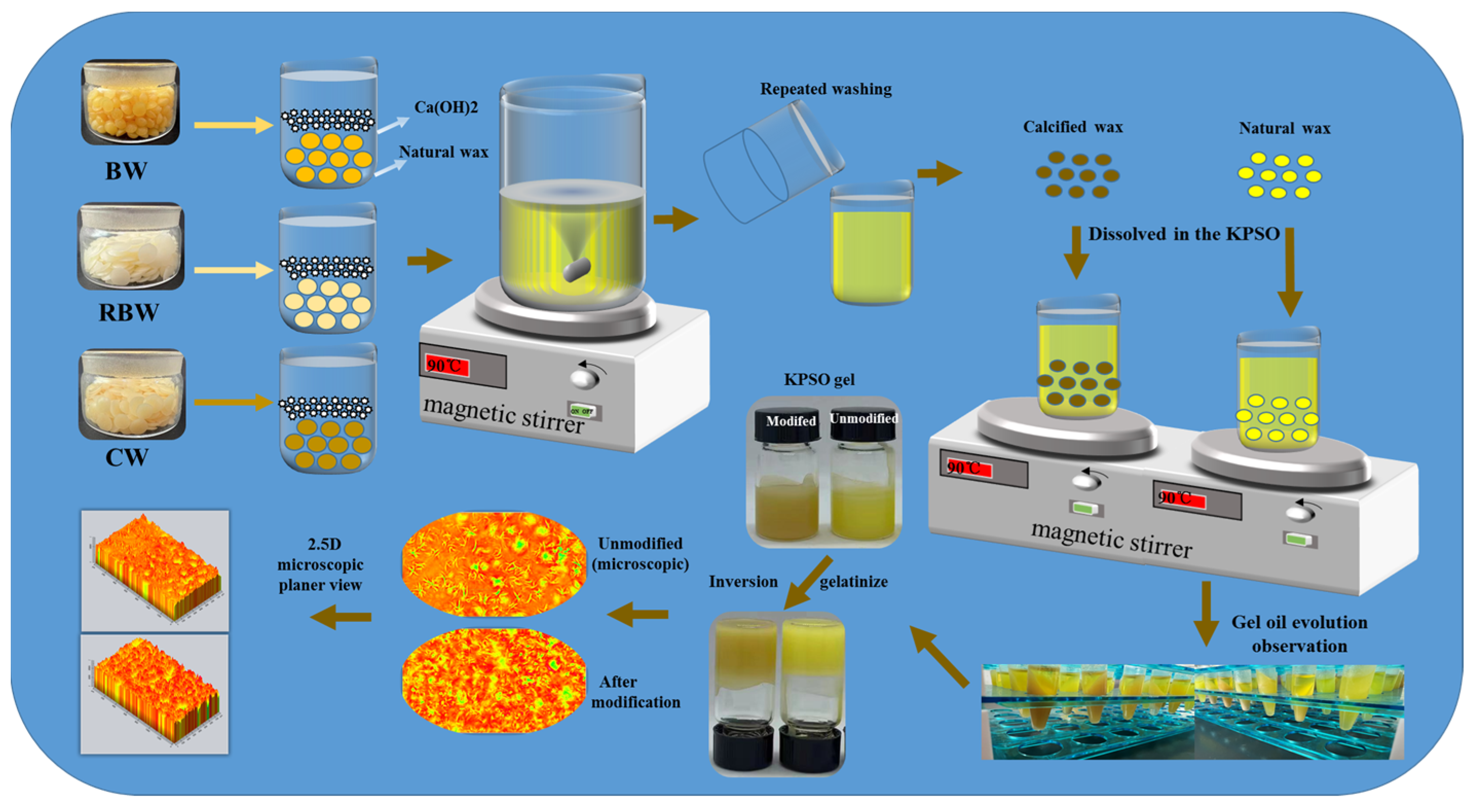
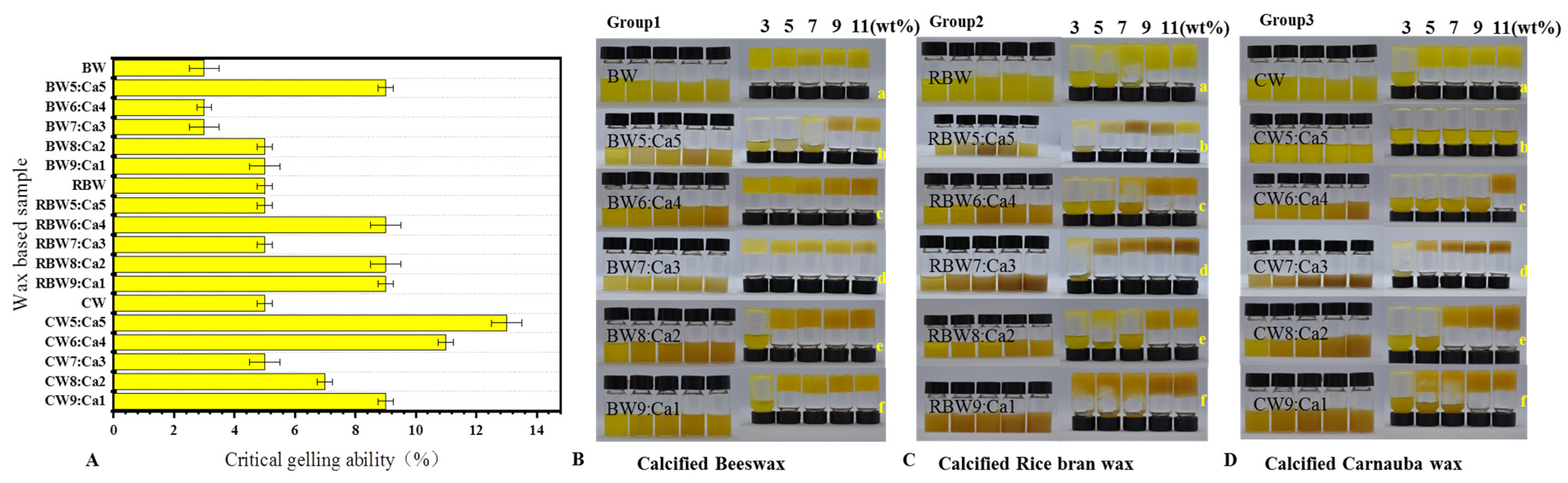
2.1. Physical Characterization of KPSO Gel
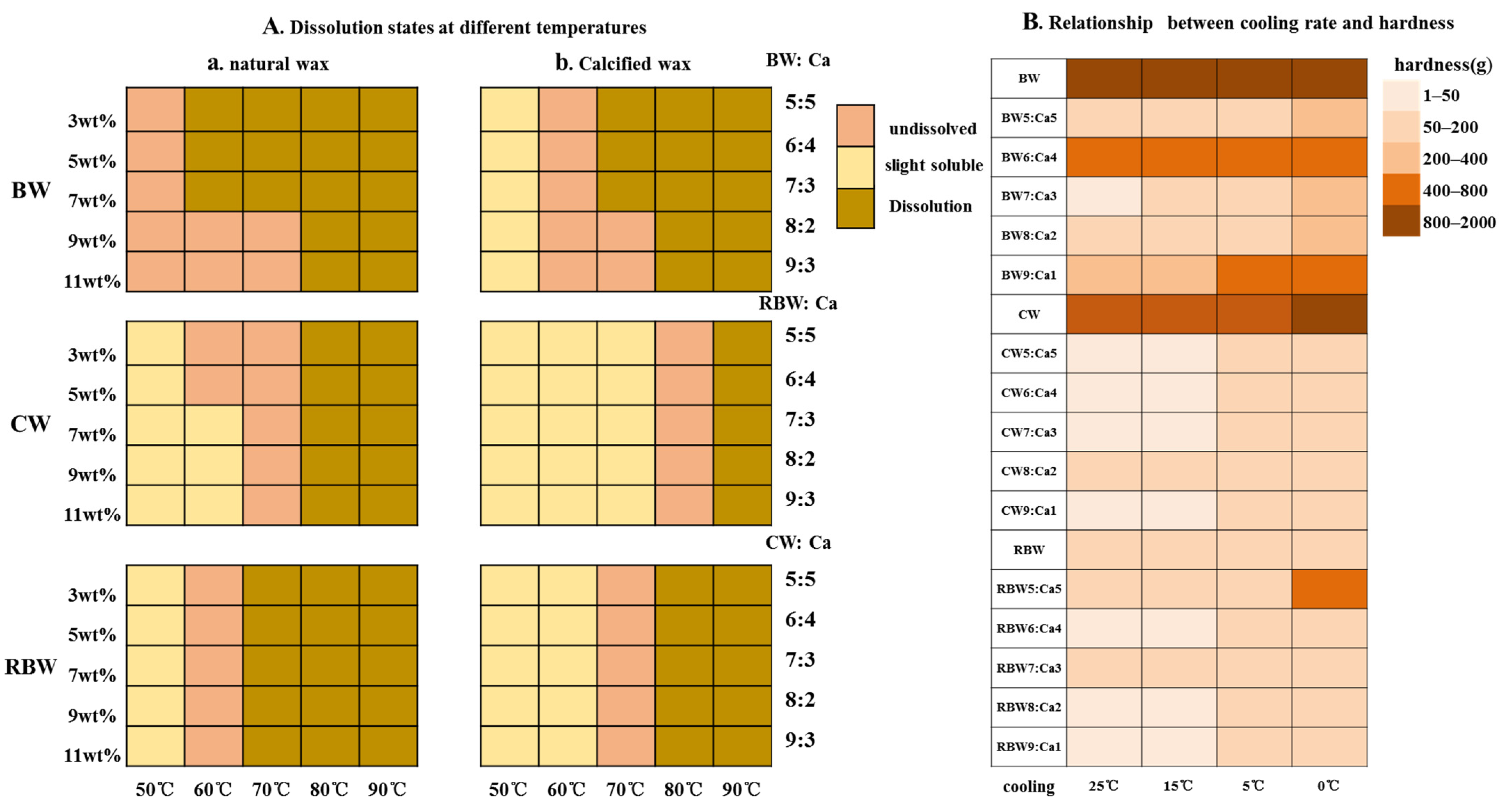
2.2. Influence of Temperature on Gel Strength of KPSO Gel
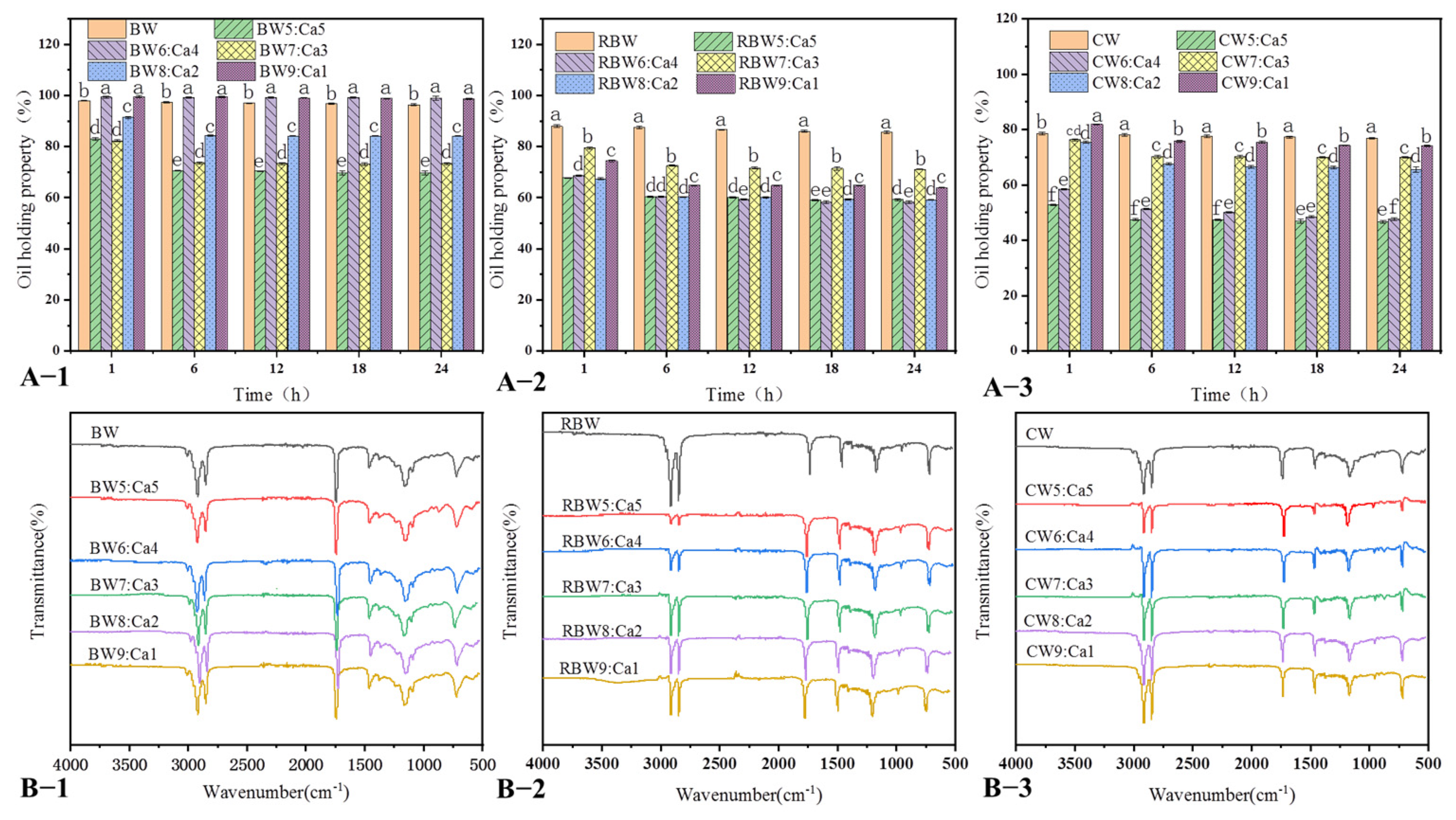
2.3. KPSO Gel Oil-Binding Capacity and FT-IR Scanning
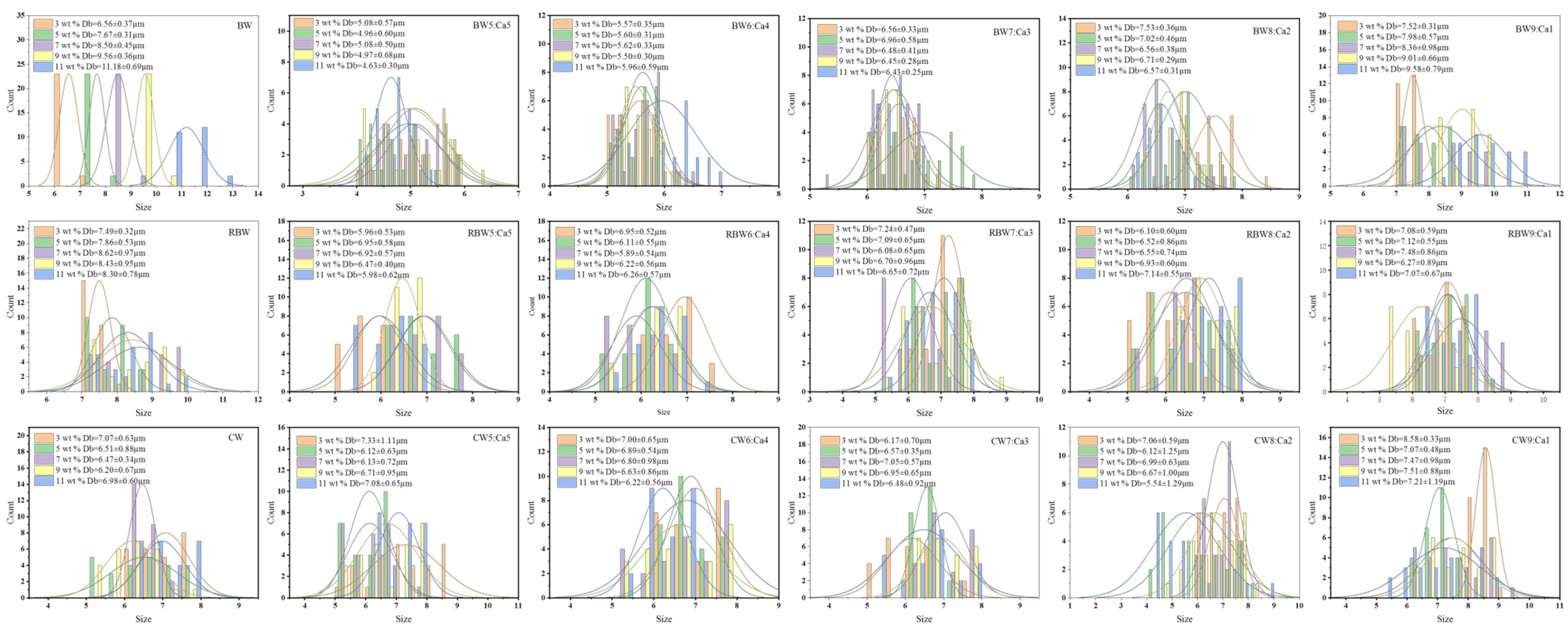
2.4. Microstructure Observation of KPSO Gel
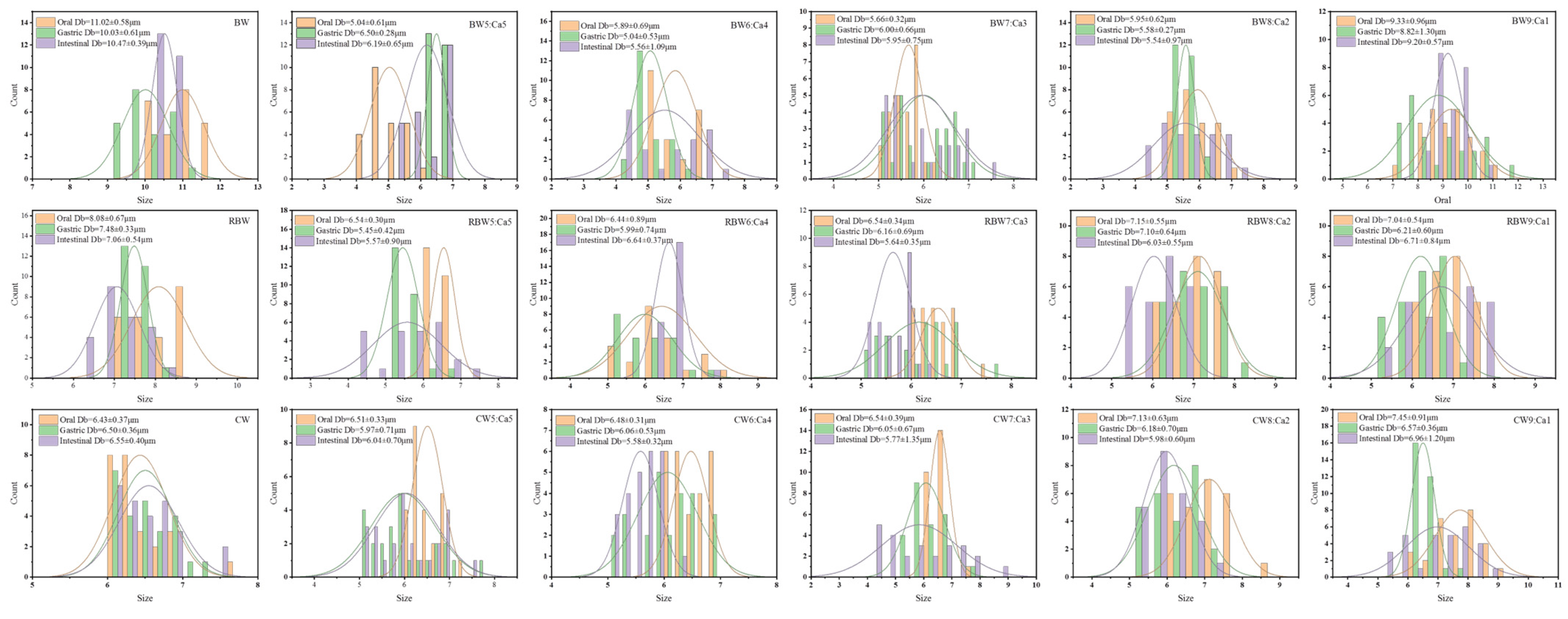
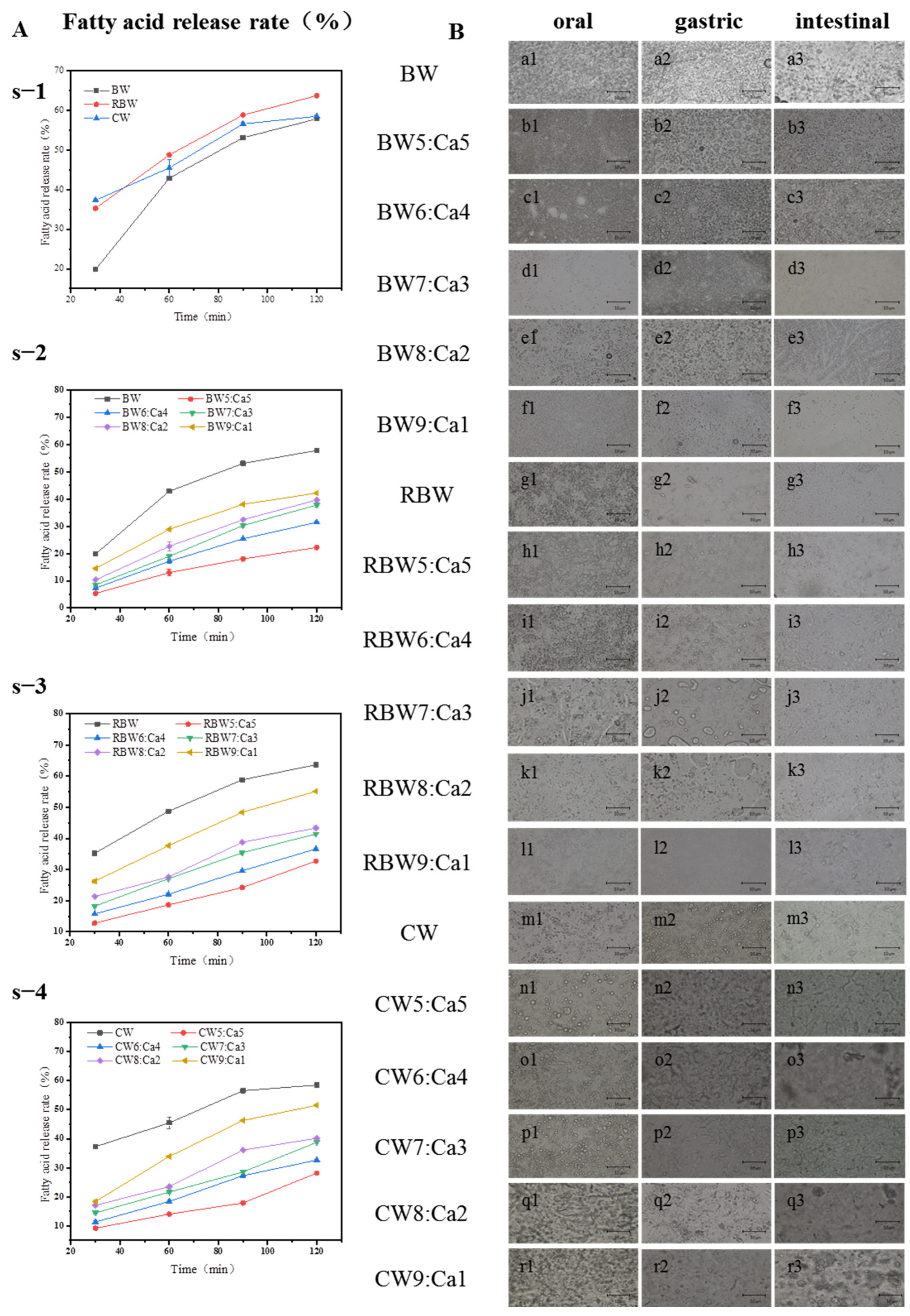
2.5. Analysis of KPSO Gel by Digestive Model
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Chemicals and Reagents
4.3. Preparation of Calcified Wax
4.4. Preparation of KPSO Gel
4.5. Characterization of KPSO Gel Properties
4.5.1. Critical Gelling Ability (C*) Analysis
4.5.2. Texture Profile Analysis
4.5.3. Analysis of Temperature Intervention Gel Strength Change
4.5.4. Oil-Holding Capacity Measurement
4.5.5. Determination of Molecular Forces by Fourier Spectroscopy
4.5.6. Micro Structure Analysis
4.6. Construction of Digestive Model In Vitro
4.6.1. Simulated Oral Digestion
4.6.2. Simulated Gastric Digestion
4.6.3. Simulated Intestinal Digestion
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
Appendix A
Appendix B
References
- Toro-Vazquez, J.F.; Mauricio-Pérez, R.; González-Chávez, M.M.; Sánchez-Becerril, M.; Ornelas-Paz, J.D.; Pérez-Martínez, J.D. Physical properties of organogels and water in oil emulsions structured by mixtures of candelilla wax and monoglycerides. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 1360–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.T.; Liu, D.; Yao, Y.P.; Li, C.M. Effects of Low-melting-point Fractions of Cocoa Butter on Rice Bran Wax-corn Oil Mixtures: Thermal, Crystallization and Rheological Properties. J. Oleo Sci. 2021, 70, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, A.I.; Marangoni, A.G. The Use of Cooling Rate to Engineer the Microstructure and Oil Binding Capacity of Wax Crystal Networks. Food Biophys. 2015, 10, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.K.; Keum, Y.S. Omega-3 and omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids: Dietary sources, metabolism, and significance—A review. Life Sci. 2018, 203, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, A.J.; Cerqueira, M.A.; Fasolin, L.H.; Cunha, R.L.; Vicente, A.A. Beeswax organogels: Influence of gelator concentration and oil type in the gelation process. Food Res. Int. 2016, 84, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagaratnam, S.; Hoque, M.E.; Sahri, M.M.; Spowage, A. Investigating the effect of deforming temperature on the oil-binding capacity of palm oil based shortening. J. Food Eng. 2013, 118, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkisyan, V.; Frolova, Y.; Sobolev, R.; Kochetkova, A. On the Role of Beeswax Components in the Regulation of Sunflower Oil Oleogel Properties. Food Biophys. 2023, 18, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagalowicz, L.; Michel, M.; Blank, I.; Schafer, O.; Leser, M.E. Self-assembly in food—A concept for structure formation inspired by Nature. Curr. Opin. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2017, 28, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimanian, Y.; Goli, S.A.H.; Shirvani, A.; Elmizadeh, A.; Marangoni, A.G. Wax-based delivery systems: Preparation, characterization, and food applications. Compr. Rev. Food. Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2994–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, H.S.; Kim, S.; Winkler-Moser, J.K.; Lee, S.; Liu, S.X. Feasibility of hemp seed oil oleogels structured with natural wax as solid fat replacement in margarine. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2022, 99, 1055–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler-Moser, J.K.; Anderson, J.; Felker, F.C.; Hwang, H.S. Physical Properties of Beeswax, Sunflower Wax, and Candelilla Wax Mixtures and Oleogels. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2019, 96, 1125–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badem, S.; Bastürk, A. Oxidative stability and characterization of oleogels obtained from safflower oil-based beeswax and rice bran wax and their effect on the quality of cake samples. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2023, 100, 635–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botega, D.C.Z.; Marangoni, A.G.; Smith, A.K.; Goff, H.D. The Potential Application of Rice Bran Wax Oleogel to Replace Solid Fat and Enhance Unsaturated Fat Content in Ice Cream. J. Food Sci. 2013, 78, C1334–C1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, C.D.; To, C.M.; De Vrieze, M.; Lynen, F.; Danthine, S.; Brown, A.; Dewettinck, K.; Patel, A.R. Chemical profiling of the major components in natural waxes to elucidate their role in liquid oil structuring. Food Chem. 2017, 214, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandolsook, S.; Kupongsak, S. Influence of bleached rice bran wax on the physicochemical properties of organogels and water-in-oil emulsions. J. Food Eng. 2017, 214, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, D.; Singh, A.; Suhag, R.; Dhiman, A.; Chauhan, D.S. Oleogelation based on plant waxes: Characterization and food applications. J. Food Sci. Technol.-Mysore 2023, 60, 2927–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brykczynski, H.; Wettlaufer, T.; Flöter, E. Revisiting pure component wax esters as basis of wax-based oleogels. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2022, 99, 925–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, E.; Ögütcü, M.; Yüceer, Y.K. Physical Properties, Volatiles Compositions and Sensory Descriptions of the Aromatized Hazelnut Oil-Wax Organogels. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, S2035–S2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, A.I.; Co, E.D.; Marangoni, A.G. Structure and Physical Properties of Plant Wax Crystal Networks and Their Relationship to Oil Binding Capacity. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2014, 91, 885–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayaz, G.; Goli, S.A.H.; Kadivar, M. A Novel Propolis Wax-Based Organogel: Effect of Oil Type on Its Formation, Crystal Structure and Thermal Properties. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2017, 94, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, B.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, J. Physicochemical properties and oxidative stability of oleogels made of carnauba wax with canola oil or beeswax with grapeseed oil. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 26, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, S.; Bhattacharya, A.; Singh, R.; Tabor, R.F. Rheological behavior of high internal phase water-in-oil emulsions: Effects of droplet size, phase mass fractions, salt concentration and aging. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 174, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.D.; Hallinan, R.; Maleky, F. Comparison of different oleogels in processed cheese products formulation. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 2525–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, X.H.; Yuan, T.L.; Jin, Q.Z.; Wei, W.; Wang, X.G. Digestion of Medium- and Long-Chain Triacylglycerol and sn-2 Palmitate in Infant Formula: A Study Based on Dynamic In Vitro Simulation of Infant Gastrointestinal Lipolysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 3263–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cheng, W.; Yao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Cao, X. GC-MS analysis of aliphatic acid extracted from red pine seeds using cold pressing technology. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2014, 35, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shen, N.; Xin, H.W.; Yu, L.L.; Xu, Q.; Cui, Y.L. Unsaturated fatty acids in natural edible resources, a systematic review of classification, resources, biosynthesis, biological activities and application. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 102790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Cong, Y.; Wang, X. Preparation of High-Hardness Oxidized Wax. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2011, 29, 1825–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.F.; Liu, C.H.; Zheng, Z.J.; Chai, X.H.; Han, W.J.; Liu, Y.F. Gelation behavior and crystal network of natural waxes and corresponding binary blends in high-oleic sunflower oil. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 3987–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.Y.; Meng, Z.; Liu, C.H.; Liu, Y.F. Structural and mechanical behavior of colloidal fat crystal networks of fully hydrogenated lauric acid-rich fats and rapeseed oils mixtures. Food Chem. 2019, 288, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baümler, E.R.; Carelli, A.A.; Martini, S. Preparation and physical properties of calcium pectinate films modified with sunflower wax. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2014, 116, 1534–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Wijarnprecha, K.; Sonwai, S.; Rousseau, D. Oleogelation of emulsified oil delays in vitro intestinal lipid digestion. Food Res. Int. 2019, 119, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hur, S.J.; Lim, B.O.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. In vitro human digestion models for food applications. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazani, S.M.; Dobson, S.; Marangoni, A.G. Hardness, plasticity, and oil binding capacity of binary mixtures of natural waxes in olive oil. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.C.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.R.; Li, Z.K.; Guo, Y.X.; He, H.J.; Liang, B.; Li, X.L.; Ji, C.J. Design of protein-polysaccharide multi-scale composite interfaces to modify lipid digestion. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 127, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.L.; Lu, Y.C.; Yu, N.X.; Nie, X.H.; Meng, X.H. A depth-insight on reduced lipolysis of diacylglycerol (DAG) oleogels with the gelation of diosgenin (DSG). Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 58, 2934–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, L.; Ménard, O.; Baumann, C.; Duerr, D.; Schlegel, P.; Stoll, P.; Vergères, G.; Dupont, D.; Portmann, R. Digestion of milk proteins: Comparing static and dynamic in vitro digestion systems with in vivo data. Food Res. Int. 2019, 118, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, L.; Ménard, O.; Delgado-Andrade, C.; Alvito, P.; Assuncao, R.; Balance, S.; Barberá, R.; Brodkorb, A.; Cattenoz, T.; Clemente, A.; et al. The harmonized INFOGEST in vitro digestion method: From knowledge to action. Food Res. Int. 2016, 88, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaucel, S.; Trelea, I.C.; Le Feunteun, S. Comment on New Mathematical Model for Interpreting pH-Stat Digestion Profiles: Impact of Lipid Droplet Characteristics on in Vitro Digestibility. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 10352–10353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakir, M.; Özer, C.O.; Var, G.B. Utilization of Sunflower Oil-based Oleogel for Deep-Fried Coated Chicken Products. J. Oleo Sci. 2023, 72, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.H.; Hu, J.L.; Zuo, S.; Zhang, S.S.; Li, M.Z.; Nie, S.P. In vitro gastrointestinal digestion and fermentation models and their applications in food carbohydrates. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 5349–5371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLoid, G.M.; Sohal, I.S.; Lorente, L.R.; Molina, R.M.; Pyrgiotakis, G.; Stevanovic, A.; Zhang, R.J.; McClements, D.J.; Geitner, N.K.; Bousfield, D.W.; et al. Reducing Intestinal Digestion and Absorption of Fat Using a Nature-Derived Biopolymer: Interference of Triglyceride Hydrolysis by Nanocellulose. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 6469–6479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, S.J.; Kim, D.H.; Chun, S.C.; Lee, S.K.; Keum, Y.S. Effects of biopolymer encapsulation on trans fatty acid digestibility in an in vitro human digestion system. Food Funct. 2013, 4, 1827–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.X.; Ritzoulis, C.; Jin, Z.X.; Cui, W.N.; Li, X.Y.; Han, J.Z.; Liu, W.L. Yellow and Black Soybean Pellet Degradation and Nutrients Hydrolysis During In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion. Food Biophys. 2022, 17, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, L.; Wu, G.; Qi, X.; Zhang, H. Effect of interfacial composition on the stability and sustained release in vitro digestion of emulsions. Food Ferment. Ind. 2021, 47, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matalanis, A.; McClements, D.J. Impact of Encapsulation Within Hydrogel Microspheres on Lipid Digestion: An In Vitro Study. Food Biophys. 2012, 7, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidinejad, A.; Birch, E.J.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Everett, D.W. Effect of liposomal encapsulation on the recovery and antioxidant properties of green tea catechins incorporated into a hard low-fat cheese following in vitro simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Food Bioprod. Process. 2016, 100, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakseresht, S.; Tehrani, M.M.; Farhoosh, R.; Koocheki, A. Rheological and thermal properties of reinforced monoglyceride-carnauba wax oleogels. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 4184–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.L.; Liu, G.Q. Corn oil-based oleogels with different gelation mechanisms as novel cocoa butter alternatives in dark chocolate. J. Food Eng. 2019, 263, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.R.; Babaahmadi, M.; Lesaffer, A.; Dewettinck, K. Rheological Profiling of Organogels Prepared at Critical Gelling Concentrations of Natural Waxes in a Triacylglycerol Solvent. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 4862–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, C.D.; Tavernier, I.; Okuro, P.K.; Dewettinck, K. Internal and external factors affecting the crystallization, gelation and applicability of wax-based oleogels in food industry. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2018, 45, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | Hardness (g) | Adhesive Force (g) | Cohesiveness (mj) | Elasticity (mm) | Adhesion (g) | Mastication (mj) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group1 | |||||||
| BW | 1479.04 ± 6.04 a | 373.33 ± 10.12 a | 0.72 ± 0.11 b | 6.77 ± 1.39 a | 14.67 ± 0.59 c | 43.36 ± 1.28 a | |
| BW:Ca | BW5:Ca5 | 112.18 ± 4.22 f | 5.51 ± 0.51 ef | 0.13 ± 0.02 ef | 0.43 ± 0.02 e | 13.33 ± 1.53 d | 0.38 ± 0.07 e |
| BW6:Ca4 | 529.10 ± 14.55 b | 153.53 ± 8.72 b | 0.13 ± 0.06 e | 1.76 ± 0.11 c | 33.83 ± 1.35 a | 0.46 ± 0.14 c | |
| BW7:Ca3 | 480.01 ± 5.02 c | 18.19 ± 0.25 d | 0.25 ± 0.06 d | 0.12 ± 0.02 f | 12.33 ± 0.43 e | 0.43 ± 0.04 d | |
| BW8:Ca2 | 268.10 ± 7.40 e | 5.86 ± 5.80 e | 1.92 ± 2.52 a | 3.20 ± 4.49 b | 20.25 ± 9.74 b | 14.53 ± 14.35 b | |
| BW9:Ca1 | 340.38 ± 15.79 d | 116.33 ± 0.47 c | 0.61 ± 0.48 c | 1.64 ± 0.50 d | 9.92 ± 0.09 f | 0.17 ± 0.03 f | |
| Group2 | |||||||
| RBW | 143.26 ± 16.68 f | 25.00 ± 2.06 a | 0.31 ± 0.31 f | 0.52 ± 0.06 e | 17.09 ± 0.93 e | 0.22 ± 0.14 f | |
| RBW:Ca | RBW5:Ca5 | 269.04 ± 15.29 d | 15.33 ± 0.47 e | 0.90 ± 0.05 a | 0.87 ± 0.11 a | 27.92 ± 1.09 b | 0.65 ± 0.43 a |
| RBW6:Ca4 | 258.59 ± 37.97 e | 16.97 ± 0.31 d | 0.62 ± 0.19 b | 0.69 ± 0.26 b | 46.42 ± 0.60 a | 0.46 ± 0.36 d | |
| RBW7:Ca3 | 318.46 ± 9.18 c | 14.09 ± 3.14 f | 0.49 ± 0.23 e | 0.65 ± 0.30 c | 26.22 ± 10.68 c | 0.54 ± 0.24 c | |
| RBW8:Ca2 | 327.33 ± 6.14 b | 19.19 ± 0.25 c | 0.53 ± 0.32 d | 0.46 ± 0.07 f | 18.81 ± 5.45 d | 0.61 ± 0.20 b | |
| RBW9:Ca1 | 365.22 ± 7.98 a | 22.42 ± 2.68 b | 0.54 ± 0.27 c | 0.63 ± 0.23 d | 16.83 ± 1.82 f | 0.45 ± 0.16 e | |
| Group3 | |||||||
| CW | 1066.92 ± 24.32 a | 253.67 ± 10.69 a | 0.31 ± 0.31 bc | 3.28 ± 0.26 a | 65.09 ± 2.60 a | 5.25 ± 0.27 a | |
| CW:Ca | CW5:Ca5 | 33.92 ± 1.24 d | 3.06 ± 0.24 e | 0.54 ± 0.30 ab | 0.36 ± 0.03 d | 7.59 ± 0.34 e | 0.18 ± 0.06 f |
| CW6:Ca4 | 14.99 ± 0.36 e | 1.26 ± 0.20 f | 0.36 ± 0.40 b | 0.33 ± 0.19 e | 5.47 ± 0.33 f | 0.67 ± 0.14 b | |
| CW7:Ca3 | 126.68 ± 13.82 b | 5.12 ± 0.10 b | 0.05 ± 0.03 d | 0.26 ± 0.17 f | 13.22 ± 2.43 d | 0.37 ± 0.01 e | |
| CW8:Ca2 | 120.46 ± 7.58 bc | 4.39 ± 0.34 c | 0.15 ± 0.13 c | 0.51 ± 0.14 c | 19.81 ± 4.90 c | 0.48 ± 0.31 d | |
| CW9:Ca1 | 69.89 ± 2.77 c | 3.36 ± 0.31 d | 0.77 ± 0.14 a | 1.43 ± 0.41 b | 31.31 ± 2.05 b | 0.62 ± 0.27 c | |
| Samples | Effect of Wax Base Concentration (wt%) on Average Particle Size (μm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 wt% | 5 wt% | 7 wt% | 9 wt% | 11 wt% | ||
| Group1 | ||||||
| BW | 6.56 ± 0.37 b | 7.67 ± 0.31 a | 8.50 ± 0.45 a | 9.56 ± 0.36 a | 11.18 ± 0.69 a | |
| BW:Ca | BW5:Ca5 | 5.08 ± 0.57 d | 4.96 ± 0.60 d | 5.08 ± 0.50 e | 4.97 ± 0.68 f | 4.63 ± 0.30 e |
| BW6:Ca4 | 5.57 ± 0.35 c | 5.60 ± 0.31 c | 5.62 ± 0.33 d | 5.50 ± 0.30 e | 5.96 ± 0.59 d | |
| BW7:Ca3 | 6.56 ± 0.33 b | 6.96 ± 0.58 b | 6.48 ± 0.41 c | 6.45 ± 0.28 d | 6.43 ± 0.25 c | |
| BW8:Ca2 | 7.53 ± 0.36 b | 7.02 ± 0.46 b | 6.56 ± 0.38 c | 6.71 ± 0.29 c | 6.57 ± 0.31 c | |
| BW9:Ca1 | 7.52 ± 0.31 a | 7.98 ± 0.57 a | 8.36 ± 0.98 b | 9.01 ± 0.66 b | 9.58 ± 0.79 b | |
| Group2 | ||||||
| RBW | 7.49 ± 0.32 a | 7.86 ± 0.53 a | 8.62 ± 0.97 a | 8.43 ± 0.95 a | 8.30 ± 0.78 a | |
| RBW:Ca | RBW5:Ca5 | 5.96 ± 0.53 d | 6.95 ± 0.58 b | 6.92 ± 0.57 c | 6.47 ± 0.40 cd | 5.98 ± 0.62 d |
| RBW6:Ca4 | 6.95 ± 0.52 c | 6.11 ± 0.55 d | 5.89 ± 0.54 e | 6.22 ± 0.56 d | 6.26 ± 0.57 d | |
| RBW7:Ca3 | 7.24 ± 0.47 ab | 7.09 ± 0.65 b | 6.08 ± 0.65 e | 6.70 ± 0.96 bc | 6.65 ± 0.72 c | |
| RBW8:Ca2 | 6.10 ± 0.60 d | 6.52 ± 0.86 c | 6.55 ± 0.74 d | 6.93 ± 0.60 b | 7.14 ± 0.55 b | |
| RBW9:Ca1 | 7.08 ± 0.59 bc | 7.12 ± 0.55 b | 7.48 ± 0.86 b | 6.27 ± 0.89 d | 7.07 ± 0.67 b | |
| Group3 | ||||||
| CW | 7.07 ± 0.63 b | 6.51 ± 0.88 cd | 6.47 ± 0.34 cd | 6.20 ± 0.67 c | 6.98 ± 0.60 a | |
| CW:Ca | CW5:Ca5 | 7.24 ± 1.14 b | 6.09 ± 0.61 e | 6.17 ± 0.69 d | 6.66 ± 0.94 b | 7.08 ± 0.65 a |
| CW6:Ca4 | 7.00 ± 0.65 b | 6.89 ± 0.54 ab | 6.80 ± 0.98 bc | 6.63 ± 0.86 bc | 6.22 ± 0.56 b | |
| CW7:Ca3 | 6.17 ± 0.70 c | 6.57 ± 0.35 bc | 7.05 ± 0.57 ab | 6.95 ± 0.65 b | 6.48 ± 0.92 b | |
| CW8:Ca2 | 7.12 ± 0.56 b | 6.16 ± 1.19 de | 7.03 ± 0.64 ab | 6.62 ± 1.03 bc | 5.65 ± 1.36 c | |
| CW9:Ca1 | 8.58 ± 0.33 a | 7.07 ± 0.48 a | 7.47 ± 0.98 a | 7.51 ± 0.88 a | 7.21 ± 1.19 a | |
| Sample | Average Particle Size/μm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oral | Gastric | Intestinal | ||
| Group1 | ||||
| BW | 10.99 ± 0.60 a | 10.03 ± 0.61 a | 10.47 ± 0.39 a | |
| BW:Ca | BW5:Ca5 | 5.04 ± 0.61 d | 6.50 ± 0.28 c | 6.19 ± 0.65 c |
| BW6:Ca4 | 5.89 ± 0.69 c | 5.04 ± 0.53 f | 5.56 ± 1.09 d | |
| BW7:Ca3 | 5.66 ± 0.32 c | 6.00 ± 0.66 d | 5.95 ± 0.75 c | |
| BW8:Ca2 | 5.95 ± 0.62 c | 5.58 ± 0.27 e | 5.54 ± 0.97 d | |
| BW9:Ca1 | 9.33 ± 0.96 b | 8.82 ± 1.30 b | 9.20 ± 0.57 b | |
| Group2 | ||||
| RBW | 8.08 ± 0.67 a | 7.48 ± 0.33 a | 7.06 ± 0.54 a | |
| RBW:Ca | RBW5:Ca5 | 6.54 ± 0.30 c | 5.45 ± 0.42 d | 5.57 ± 0.90 d |
| RBW6:Ca4 | 6.44 ± 0.89 c | 5.99 ± 0.74 c | 6.64 ± 0.37 b | |
| RBW7:Ca3 | 6.54 ± 0.34 c | 6.16 ± 0.69 c | 5.64 ± 0.35 d | |
| RBW8:Ca2 | 7.15 ± 0.55 b | 7.10 ± 0.64 b | 6.03 ± 0.55 c | |
| RBW9:Ca1 | 7.04 ± 0.54 b | 6.21 ± 0.60 c | 6.71 ± 0.84 b | |
| Group3 | ||||
| CW | 6.43 ± 0.37 c | 6.50 ± 0.36 a | 6.55 ± 0.40 a | |
| CW:Ca | CW5:Ca5 | 6.51 ± 0.33 c | 5.97 ± 0.71 b | 6.04 ± 0.70 b |
| CW6:Ca4 | 6.48 ± 0.31 c | 6.06 ± 0.53 b | 5.58 ± 0.32 c | |
| CW7:Ca3 | 6.55 ± 0.37 c | 6.12 ± 0.69 b | 6.13 ± 1.15 bc | |
| CW8:Ca2 | 7.13 ± 0.63 b | 6.18 ± 0.70 ab | 5.98 ± 0.60 bc | |
| CW9:Ca1 | 7.44 ± 0.91 a | 6.54 ± 0.34 a | 6.66 ± 1.07 a | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, P.; Wang, H.; Hou, Y.; Wang, J.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, N.; Guo, Q. Formation and In Vitro Simulated Digestion Study of Gelatinized Korean Pine Seed Oil Encapsulated with Calcified Wax. Molecules 2023, 28, 7334. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217334
Wang P, Wang H, Hou Y, Wang J, Fan Y, Zhang N, Guo Q. Formation and In Vitro Simulated Digestion Study of Gelatinized Korean Pine Seed Oil Encapsulated with Calcified Wax. Molecules. 2023; 28(21):7334. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217334
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Peng, Honglu Wang, Yanli Hou, Jingyi Wang, Yue Fan, Na Zhang, and Qingqi Guo. 2023. "Formation and In Vitro Simulated Digestion Study of Gelatinized Korean Pine Seed Oil Encapsulated with Calcified Wax" Molecules 28, no. 21: 7334. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217334
APA StyleWang, P., Wang, H., Hou, Y., Wang, J., Fan, Y., Zhang, N., & Guo, Q. (2023). Formation and In Vitro Simulated Digestion Study of Gelatinized Korean Pine Seed Oil Encapsulated with Calcified Wax. Molecules, 28(21), 7334. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217334