How to More Effectively Obtain Ginsenoside Rg5: Understanding Pathways of Conversion
Abstract
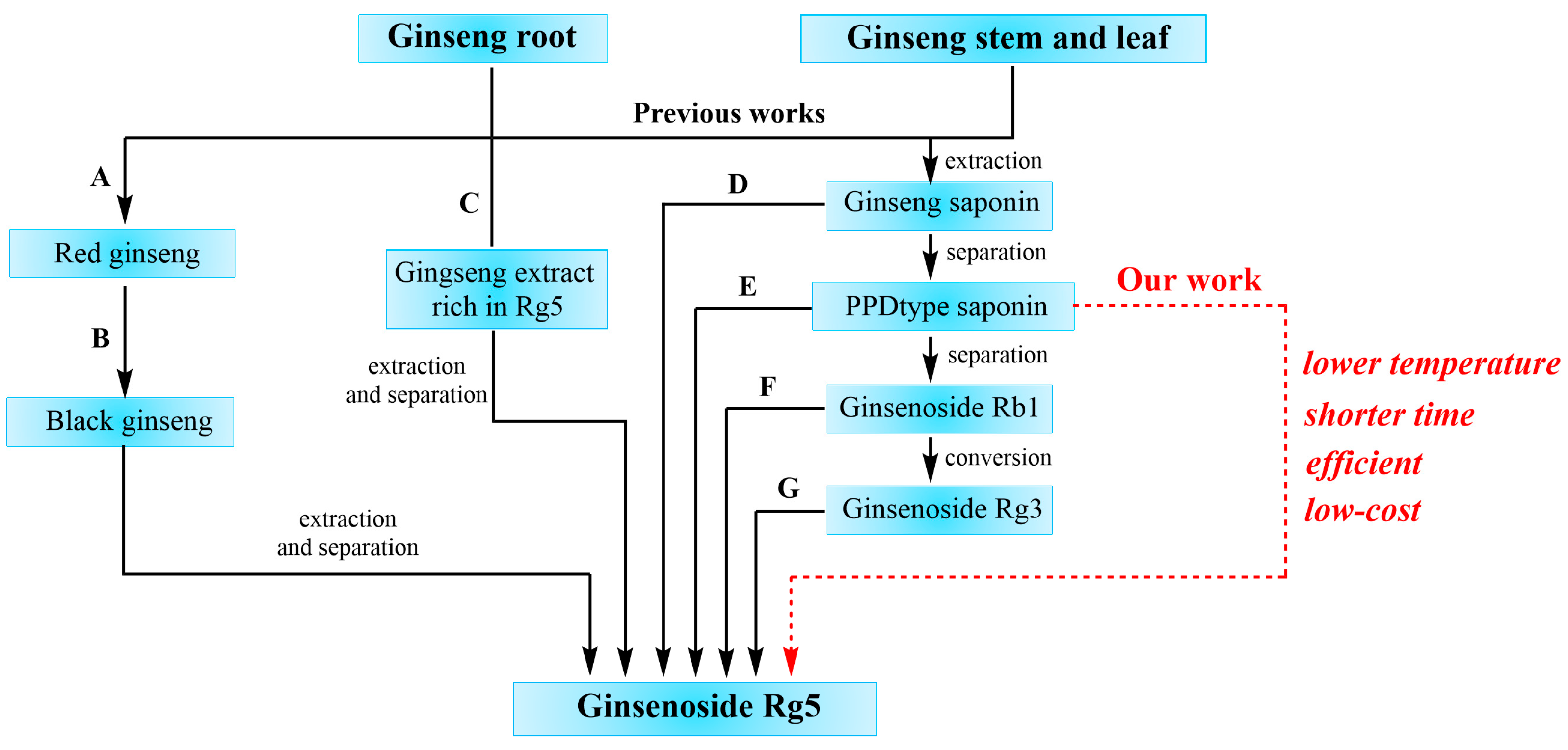
:1. Introduction
2. Results
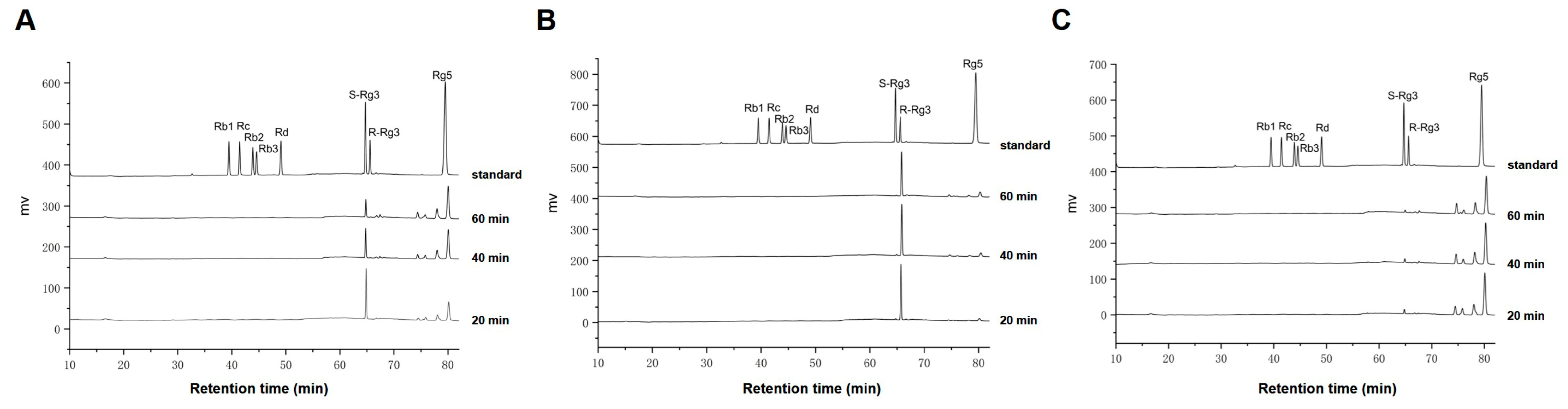
2.1. Preparation of Ginsenoside Rg5 from Single Ginsenoside S-Rg3, R-Rg3 and Rb1
2.2. Preparation of Ginsenoside Rg5 from PPD-Type Saponin Mixture
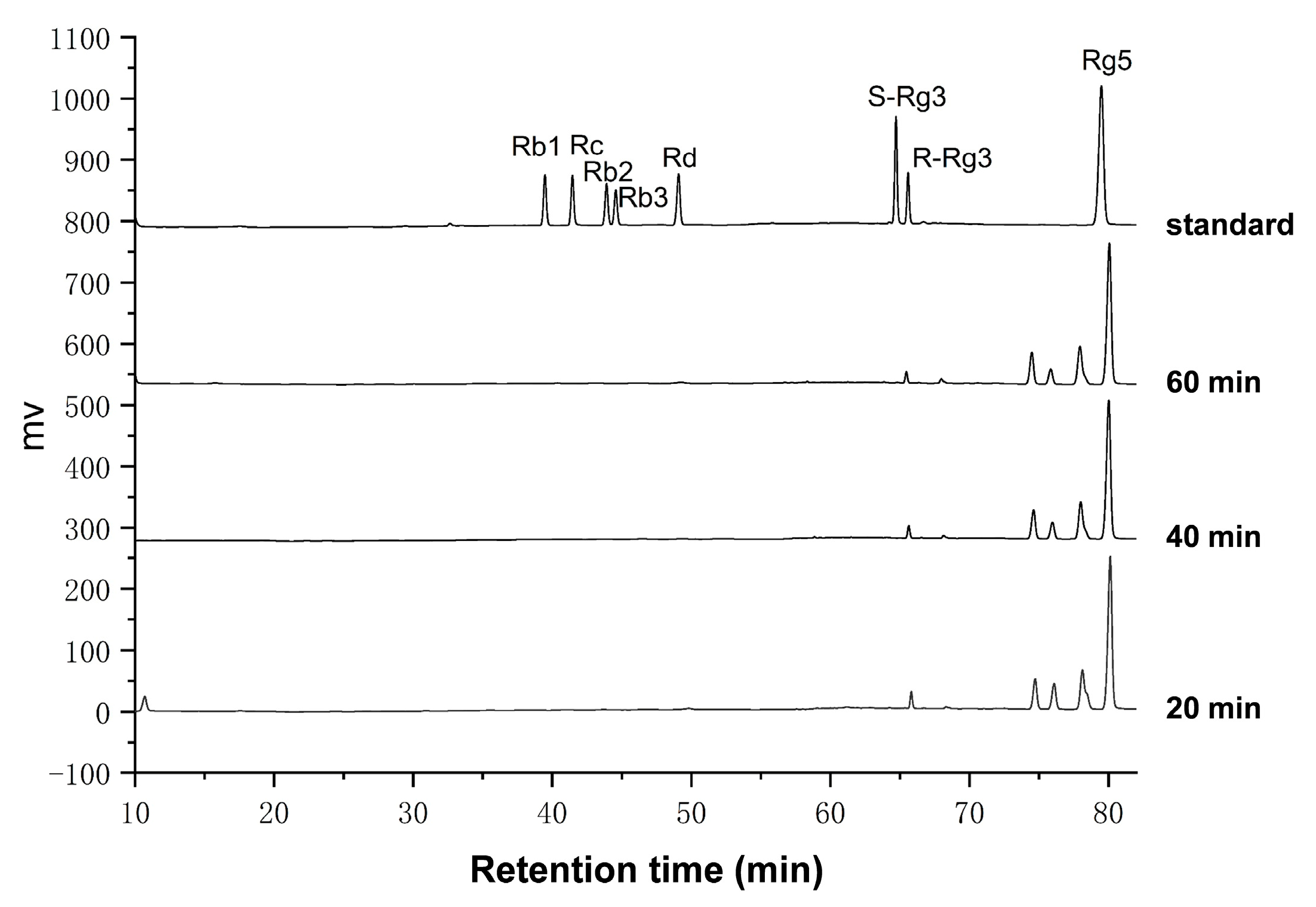
2.3. Amplification Experiment of Prepared Rg5
3. Discussion
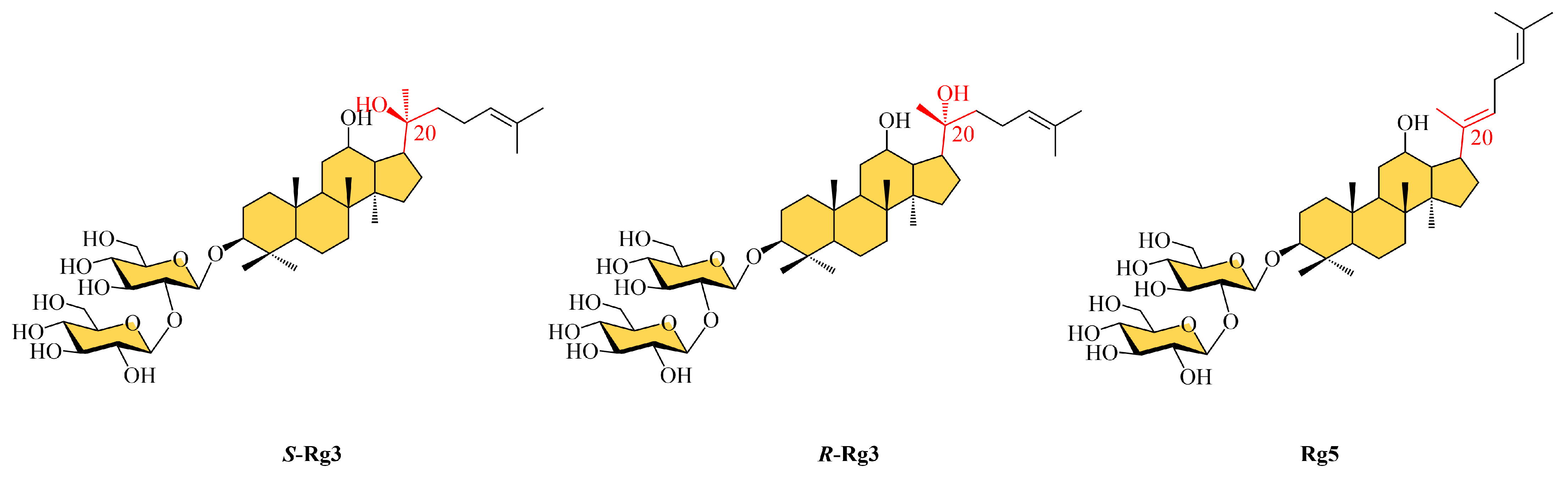
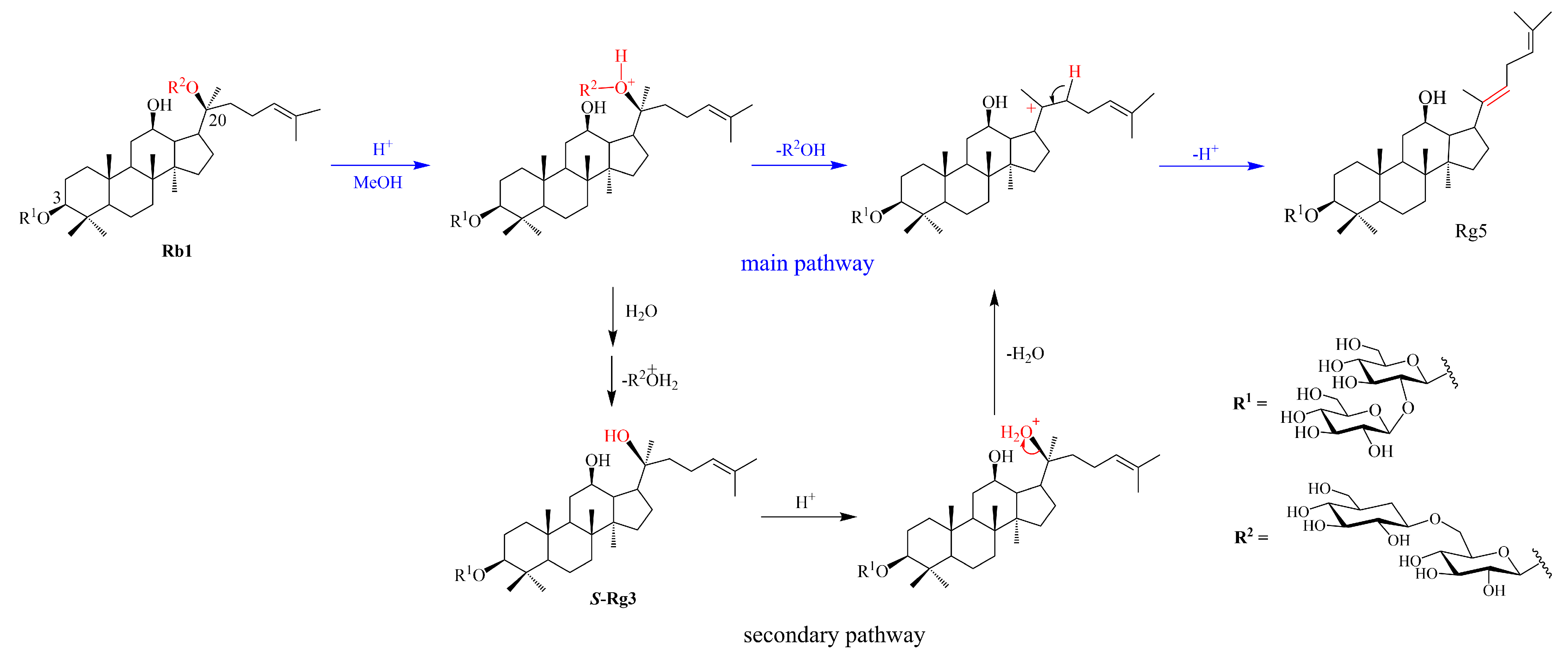
3.1. Conversion Pathways Proposed for Ginsenoside Rg5
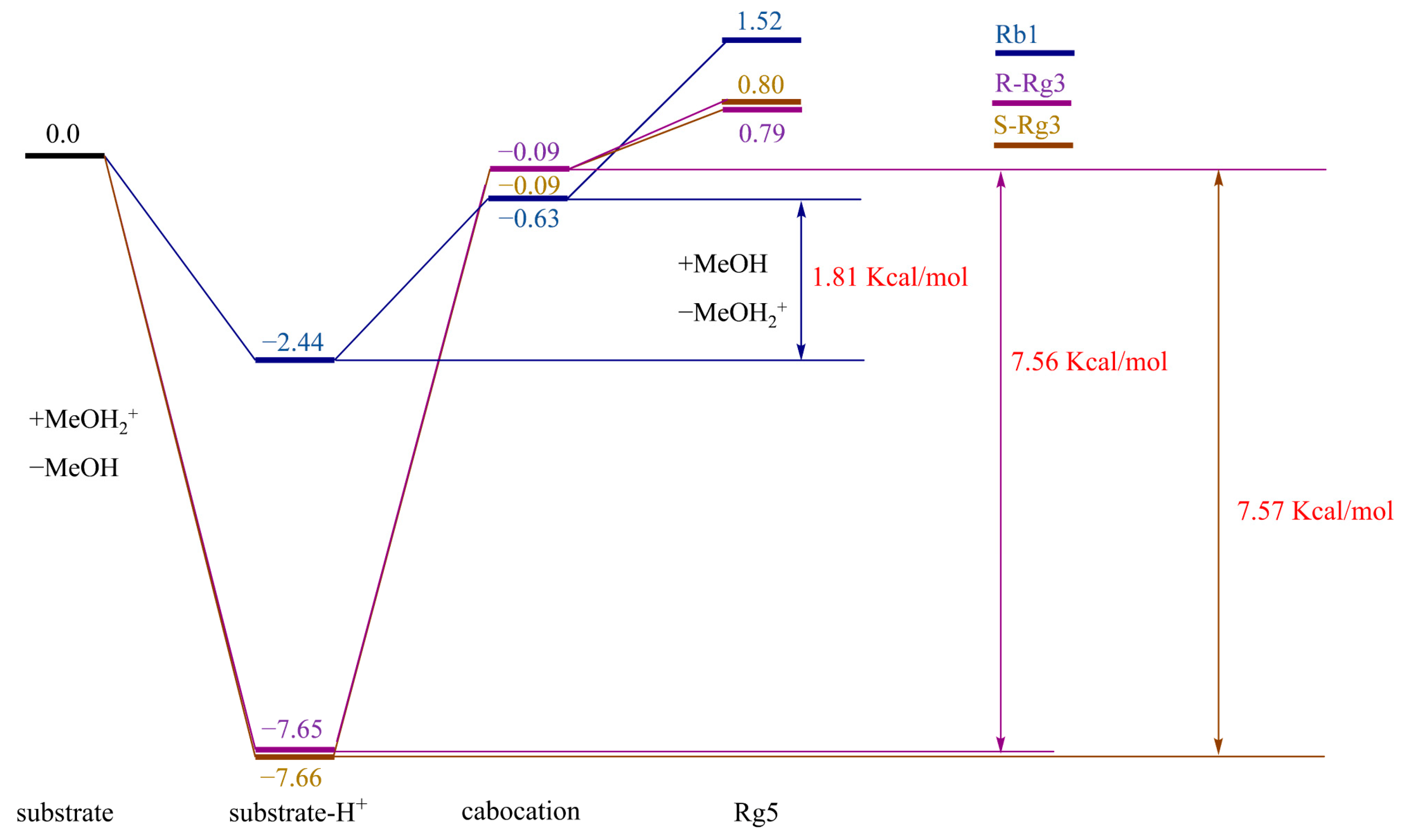
3.2. Theoretical Analysis of the Conversion Paths of Rg5
3.2.1. Density Functional Theory (DFT) Calculations
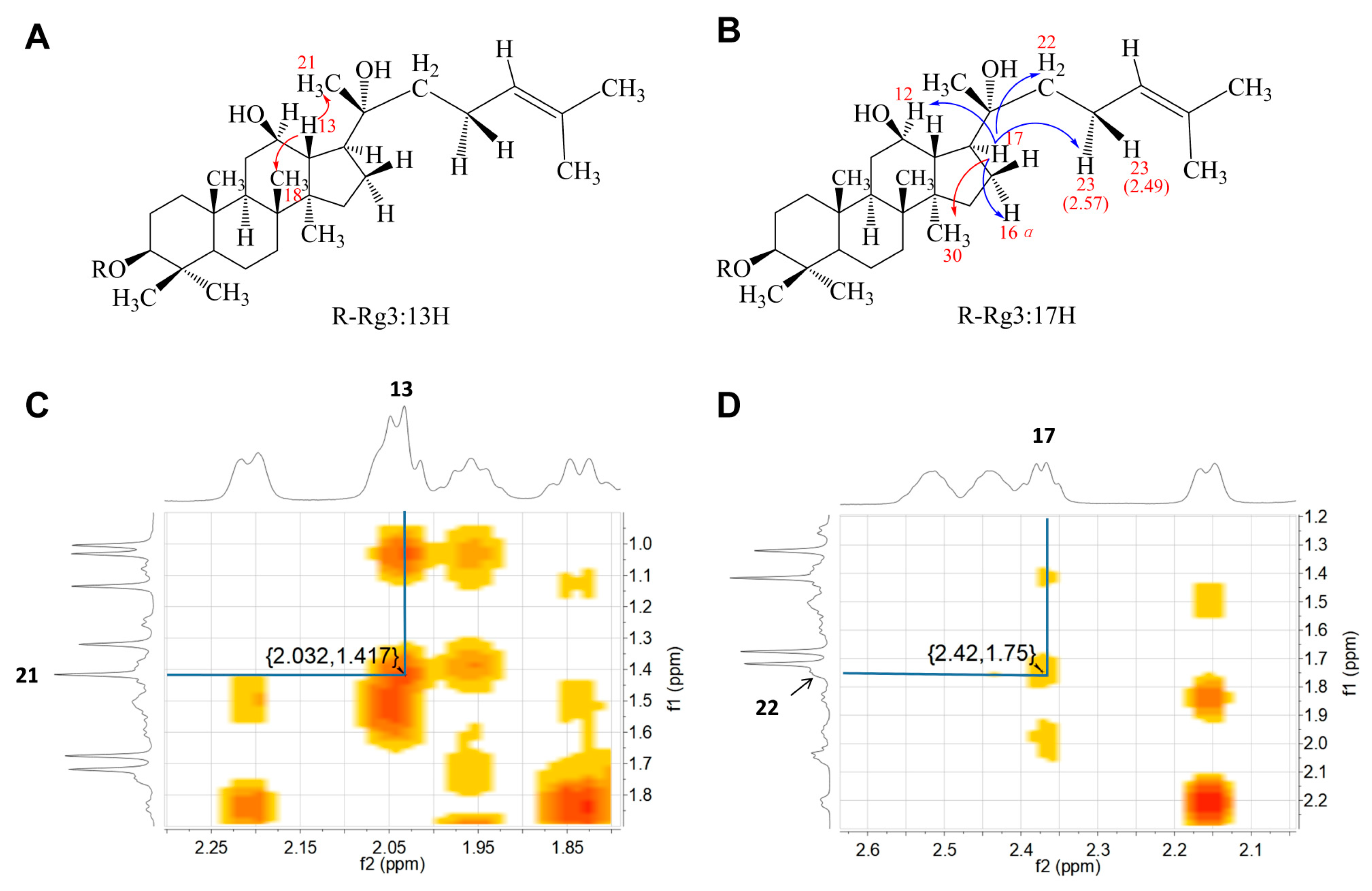
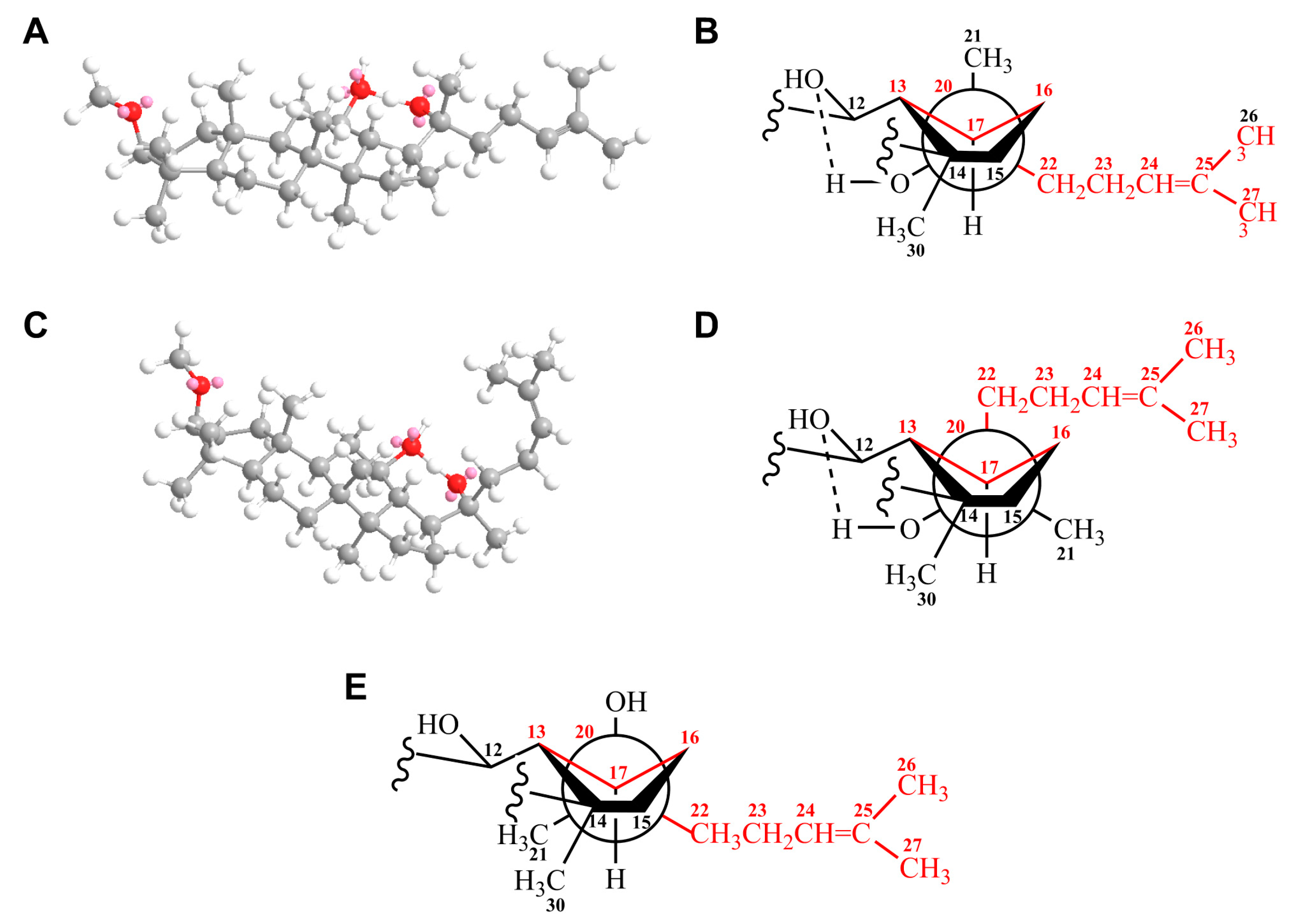
3.2.2. Structural Analysis by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Instruments
4.2. Preparation Method for Ginsenoside Rg5
4.3. TLC Analyzing Method
4.4. HPLC Analyzing Method
4.5. Density Functional Theory (DFT) Analyzing Method
4.6. Amplification Experiment for Preparation of Ginsenoside Rg5
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, J.H.; Yi, Y.-S.; Kim, M.-Y.; Cho, J.Y. Role of ginsenosides, the main active components of panax ginseng, in inflammatory responses and diseases. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luong Huynh, D.; Nguyen, N.H.; Nguyen, C.T. Pharmacological properties of ginsenosides in inflammation-derived cancers. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2021, 476, 3329–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhou, X.; Yang, W.; Lin, Y. Pharmacological effects of natural medicine ginsenosides against alzheimer’s disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 952332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thai, H.; Tran, D.L.; Thach, T.L.; Le, D.G.; Do Tran, M.T.; Vu, Q.T.; Nguyen, T.A.; Nguyen, D.T.; Nguyen, T.C. Effect of both lovastatin and ginsenoside Rb1 on some properties and in-vitro drug release of alginate/chitosan/lovastatin/ginsenoside Rb1 composite films. J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 2728–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Ko, C.-N.; Li, D.; Yang, C. The anti-aging mechanism of ginsenosides with medicine and food homology. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 9123–9136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhu, C.; Deng, J.; Fan, D. Ginsenoside Rg5 relieves type 2 diabetes by improving hepatic insulin resistance in db/db mice. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 71, 104014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Cho, S.-H. The effect of ginsenosides on depression in preclinical studies: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Ginseng Res. 2021, 45, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Ruan, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Hu, P. Tartaric acid induced conversion of protopanaxadiol to ginsenosides Rg3 and Rg5 and their in situ recoveries by integrated expanded bed adsorption chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 2995–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, K.; Liu, Q.; Wan, J.Y.; Zhao, Y.J.; Guo, R.Z.; Alolga, R.N.; Li, P.; Qi, L.W. Rapid preparation of rare ginsenosides by acid transformation and their structure-activity relationships against cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Balan, P.; Popovich, D.G. Changes of ginsenoside composition in the creation of black ginseng leaf. Molecules 2020, 25, 2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, X.M.; Huo, Y.; Kang, J.P.; Mathiyalagan, R.; Zhang, H.; Yang, D.U.; Kim, M.; Yang, D.C.; Kang, S.C.; Wang, Y.P. Diversity of ginsenoside profiles produced by various processing technologies. Molecules 2020, 25, 4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Ma, M.; Wu, Z.; Liang, X.; Zheng, Q.; Li, D.; An, T.; Wang, G. Advances in the biosynthesis and metabolic engineering of rare ginsenosides. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 3391–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Lyu, W.; Duan, C.; Ma, F.; Li, X.; Li, D. Preparation and bioactivity of the rare ginsenosides Rg3 and Rh2: An updated review. Fitoterapia 2023, 167, 105514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.I.; Park, J.H.; Ryu, J.H.; Park, J.D.; Lee, Y.H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, J.M.; Baek, N.I. Ginsenoside Rg5, a genuine dammarane glycoside from Korean red ginseng. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 1996, 19, 551–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.D.; He, T.; Du, T.W.; Fan, Y.G.; Chen, D.S.; Wang, Y. Ginsenoside-Rg5 induces apoptosis and DNA damage in human cervical cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.Y.; Liu, F.; Li, Y.J.; Yin, J.N.; Gao, Y.L.; Wang, X.Y.; Yang, C.; Liu, J.G.; Li, H.J. Ginsenoside Rg5 inhibits human osteosarcoma cell proliferation and induces cell apoptosis through PI3K/Akt/mTORC1-related LC3 autophagy pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 5040326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Fan, D. Ginsenoside Rg5 induces G2/M phase arrest, apoptosis and autophagy via regulating ROS-mediated MAPK pathways against human gastric cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 168, 285–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fan, D. Ginsenoside Rg5 induces apoptosis and autophagy via the inhibition of the PI3K/Akt pathway against breast cancer in a mouse model. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 5513–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnuraj, S.P.; Siraj, F.; Kang, S.; Noh, H.Y.; Min, J.W.; Kim, Y.J.; Yang, D.C. Amelioration of insulin resistance by Rk1 + Rg5 complex under endoplasmic reticulum stress conditions. Pharmacogn. Res. 2014, 6, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.L.; Hur, S.M.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, D.K.; Choe, J.; Won, M.H.; Ha, K.S.; Jeoung, D.; Han, S.; et al. Specific activation of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor by ginsenoside Rg5 promotes angiogenesis and vasorelaxation. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Xu, X.; Wei, J.; Xu, J.; Luo, W.; Li, A.; Liang, G.; Wang, M. Ginsenoside Rg5 alleviates Ang II-induced cardiac inflammation and remodeling by inhibiting the JNK/AP-1 pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 120, 110408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, H.Y.; Zhang, J.; Yeo, S.J.; Myung, C.S.; Kim, H.M.; Kim, J.M.; Park, J.H.; Cho, J.; Kang, J.S. Memory enhancing and neuroprotective effects of selected ginsenosides. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2005, 28, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Fan, D. The preparation of ginsenoside Rg5, its antitumor activity against breast cancer cells and its targeting of PI3K. Nutrients 2020, 12, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Qi, L.W.; Wan, J.Y. Preparation Method of C20-Position Dehydroxydama Alkane Rare Ginsenoside and Its Glycogen. Chinese patents CN102911238A, 26 November 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, T.H.; Park, H.M.; Kim, Y.B.; Kim, H.; Kim, N.; Do, J.H.; Kang, C.; Cho, Y.; Kim, S.Y. Effects of red ginseng extract on UVB irradiation-induced skin aging in hairless mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 123, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.-S.; Gu, L.-J.; Fang, Z.M.; Wang, C.y.; Wang, Z.; Lee, M.R.; Li, Z.; Li, J.J.; Sung, C.K. Simultaneous quantification of 19 ginsenosides in black ginseng developed from panax ginseng by HPLC–ELSD. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2009, 50, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, D.P.; Wang, H.; Li, W.; Liu, W.C.; Wang, Y.P.; Wang, J.; Zheng, Y.N. Optimization of preparing technology of ginsenoside Rk1 and Rg5 by high-temperature pyrolysis. Shanghai J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2015, 49, 91–95. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, D.D.; Cheng, L.Q.; Zhang, Y.W.; Zheng, H.C.; Ma, H.Y.; Li, L. An improved method for the preparation of Ginsenoside Rg5 from ginseng fibrous root powder. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, M.; Huo, X.; Li, Z.; Qu, D.; Sha, J.; Sun, Y. A novel process for one-step separation and cyclodextrin inclusion of ginsenoside Rg5 from ginseng stem–leaf saponins (GSLS): Preparation, characterization, and evaluation of storage stability and bioactivity. Foods 2023, 12, 2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.Q.; Ye, A.q.; Zhang, H.R.; Zhang, Y.W.; Ling, L. An efficient synthesis of ginsenoside Rg5 via conversion of PPD type saponins: Unusual application of 4A molecular sieves. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2021, 16, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Yang, J.; Xu, L.; Li, G.; Song, J.; Jin, F. Conversion of ginsenoside Rb1 into six types of highly bioactive ginsenoside Rg3 and its derivatives by FeCl3 catalysis. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 66, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, B.; Lambert Eugene, P.; Mazzola Ridge, C.D. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy: An introduction to principles, applications, and experimental methods, 2nd ed.WILEY: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–480. ISBN 978-1-119-29528-0. [Google Scholar]
- Khodov, I.A.; Belov, K.V.; Krestyaninov, M.A.; Sobornova, V.V.; Dyshin, A.A.; Kiselev, M.G. Does DMSO affect the conformational changes of drug molecules in supercritical CO2 media? J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 384, 122230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodov, I.A.; Belov, K.V.; Sobornova, V.V.; Dyshin, A.A.; Kiselev, M.G. Exploring the temperature-dependent proportions of lidocaine conformers equilibria in supercritical carbon dioxide via NOESY. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 387, 122620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronina, Y.A.; Stepakov, A.V.; Popova, E.A.; Boitsov, V.M.; Baichurin, R.I.; Selivanov, S.I. Diastereomers of cyclopropa[a]pyrrolizine spiro-fused with a benzo [4,5]imidazo [1,2-a]indole fragment: Structure determinations using NMR methods. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2023, 54, 999–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.; et al. Gaussian 09, revision D. 01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Schultz, N.E.; Truhlar, D.G. Design of density functionals by combining the method of constraint satisfaction with parametrization for thermochemistry, thermochemical kinetics, and noncovalent interactions. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2006, 2, 364–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Truhlar, D.G. The M06 suite of density functionals for main group thermochemistry, thermochemical kinetics, noncovalent interactions, excited states, and transition elements: Two new functionals and systematic testing of four M06-class functionals and 12 other functionals. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2008, 120, 215–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigend, F.; Ahlrichs, R. Balanced basis sets of split valence, triple zeta valence and quadruple zeta valence quality for H to Rn: Design and assessment of accuracy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2005, 7, 3297–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marenich, A.V.; Cramer, C.J.; Truhlar, D.G. Universal solvation model based on solute electron density and on a continuum model of the solvent defined by the bulk dielectric constant and atomic surface tensions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 6378–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| No. C | 13C-NMR | No. H | 1H-NMR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R-Rg3 | S-Rg3 | R-Rg3 | S-Rg3 | ||
| 1 | 39.20 | 39.20 | 1α 1β | 0.75 m 1.51 m | 0.75 m 1.50 m |
| 2 | 26.82 | 26.81 | 2α 2β | 2.21 m 1.84 m | 2.20 m 1.83 m |
| 3 | 88.91 | 89.01 | 3 | 3.31 dd (3.0, 11.4) | 3.30 dd (4.2,12) |
| 4 | 39.79 | 39.79 | 4 | - | - |
| 5 | 56.34 | 56.43 | 5 | 0.70 br d (11.4) | 0.68 br d (11.4) |
| 6 | 18.53 | 18.51 | 6α 6β | 1.51 m 1.39 m | 1.49 m 1.36 m |
| 7 | 35.26 | 35.23 | 7α 7β | 1.25 m 1.48 m | 1.22 m 1.46 m |
| 8 | 40.09 | 40.06 | 8 | - | - |
| 9 | 50.45 | 50.45 | 9 | 1.43 m | 1.40 m |
| 10 | 36.99 | 36.99 | 10 | - | - |
| 11 | 32.25 | 32.12 | 11α 11β | 2.05 m 1.57 m | 2.03 m 1.52 m |
| 12 | 70.97 | 71.10 | 12 | 3.95 m | 3.93 m |
| 13 | 49.30 | 48.64 | 13 | 2.03 m | 2.04 m |
| 14 | 51.86 | 51.79 | 14 | - | - |
| 15 | 31.50 | 31.42 | 15α 15β | 1.08 m 1.60 m | 1.05 m 1.59 m |
| 16 | 26.71 | 26.92 | 16α 16β | 1.96 m 1.38 m | 1.91 m 1.40 m |
| 17 | 50.69 | 54.88 | 17 | 2.42 m | 2.37 m |
| 18 | 15.82 | 15.90 | 18 | 1.03 s | 0.97 s |
| 19 | 16.48 | 16.45 | 19 | 0.84 s | 0.80 s |
| 20 | 73.06 | 73.05 | 20 | - | - |
| 21 | 22.80 | 27.15 | 21 | 1.42 s | 1.44 s |
| 22 | 43.35 | 35.96 | 22 | 1.75 m (2H) | 1.71 m 2.05 m |
| 23 | 22.70 | 23.08 | 23 | 2.49 m 2.57 m | 2.30 m 2.62 m |
| 24 | 126.05 | 126.40 | 24 | 5.35 m | 5.33 m |
| 25 | 130.89 | 130.86 | 25 | - | - |
| 26 | 25.85 | 25.92 | 26 | 1.72 s | 1.66 s |
| 27 | 17.80 | 17.78 | 27 | 1.68 s | 1.63 s |
| 28 | 28.11 | 28.20 | 28 | 1.32 s | 1.30 s |
| 29 | 16.69 | 16.70 | 29 | 1.13 s | 1.12 s |
| 30 | 17.38 | 17.08 | 30 | 1.00 s | 0.96 s |
| 1′ | 105.2 | 105.21 | 1′ | 4.96 d (7.2) | 4.95 d (7.8) |
| 2′ | 83.54 | 83.48 | 2′ | 4.27 m | 4.26 m |
| 3′ | 78.05 | 78.05 | 3′ | 4.28 m | 4.27 m |
| 4′ | 71.70 | 71.70 | 4′ | 4.18 m | 4.17 m |
| 5′ | 78.25 | 78.23 | 5′ | 3.96 m | 3.95 m |
| 6′ | 62.92 | 62.91 | 6′ | 4.38 m 4.59 d (9.6) | 4.37 m 4.58 d (9.6) |
| 1′′ | 106.1 | 106.14 | 1′′ | 5.41 (7.8) | 5.40 d (7.8) |
| 2′′ | 77.28 | 77.25 | 2′′ | 4.17 m | 4.16 m |
| 3′′ | 78.43 | 78.44 | 3′′ | 4.35 m | 4.34 m |
| 4′′ | 71.69 | 71.68 | 4′′ | 4.38 m | 4.36 m |
| 5′′ | 78.41 | 78.41 | 5′′ | 3.96 m | 3.95 m |
| 6′′ | 62.75 | 62.76 | 6′′ | 4.52 m | 4.51 m |
| 12-OH | 7.36 | 7.29 | |||
| 20-OH | 7.15 | 7.03 | |||
| 3′-OH | 7.34 | 7.35 | |||
| 4′-OH | 7.45 | 7.44 | |||
| 6′-OH | 6.42 | 6.43 | |||
| 2′′-OH | 7.65 | 7.64 | |||
| 3′′-OH | 8.11 | 8.08 | |||
| 4′′-OH | 7.26 | 7.25 | |||
| 6′′-OH | 5.86 | 5.87 | |||
| No. | R-Rg3 | S-Rg3 | △δ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22-C | 43.35 | 35.96 | 7.39 |
| 21-C | 22.80 | 27.15 | −4.35 |
| 17-C | 50.69 | 54.88 | −4.19 |
| No. | R-Rg3 | S-Rg3 | △δ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22-H | 1.75 m(2H) | 1.71 m (1H) | 0.04 |
| 2.05 m (1H) | −0.30 | ||
| 23-H | 2.49 m (1H) | 2.30 m (1H) | 0.19 |
| 2.57 m (1H) | 2.62 m (1H) | −0.05 | |
| 20-OH | 7.15 (1H) | 7.03 (1H) | 0.12 |
| 12-OH | 7.36 (1H) | 7.29 (1H) | 0.07 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, L.; Luo, W.; Ye, A.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Xie, H. How to More Effectively Obtain Ginsenoside Rg5: Understanding Pathways of Conversion. Molecules 2023, 28, 7313. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217313
Cheng L, Luo W, Ye A, Zhang Y, Li L, Xie H. How to More Effectively Obtain Ginsenoside Rg5: Understanding Pathways of Conversion. Molecules. 2023; 28(21):7313. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217313
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Leqin, Wei Luo, Anqi Ye, Yuewei Zhang, Ling Li, and Haijiao Xie. 2023. "How to More Effectively Obtain Ginsenoside Rg5: Understanding Pathways of Conversion" Molecules 28, no. 21: 7313. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217313
APA StyleCheng, L., Luo, W., Ye, A., Zhang, Y., Li, L., & Xie, H. (2023). How to More Effectively Obtain Ginsenoside Rg5: Understanding Pathways of Conversion. Molecules, 28(21), 7313. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28217313






