Biodistribution of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Labeled with [89Zr]Zr-Oxine in Local Radiation Injuries in Laboratory Animals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
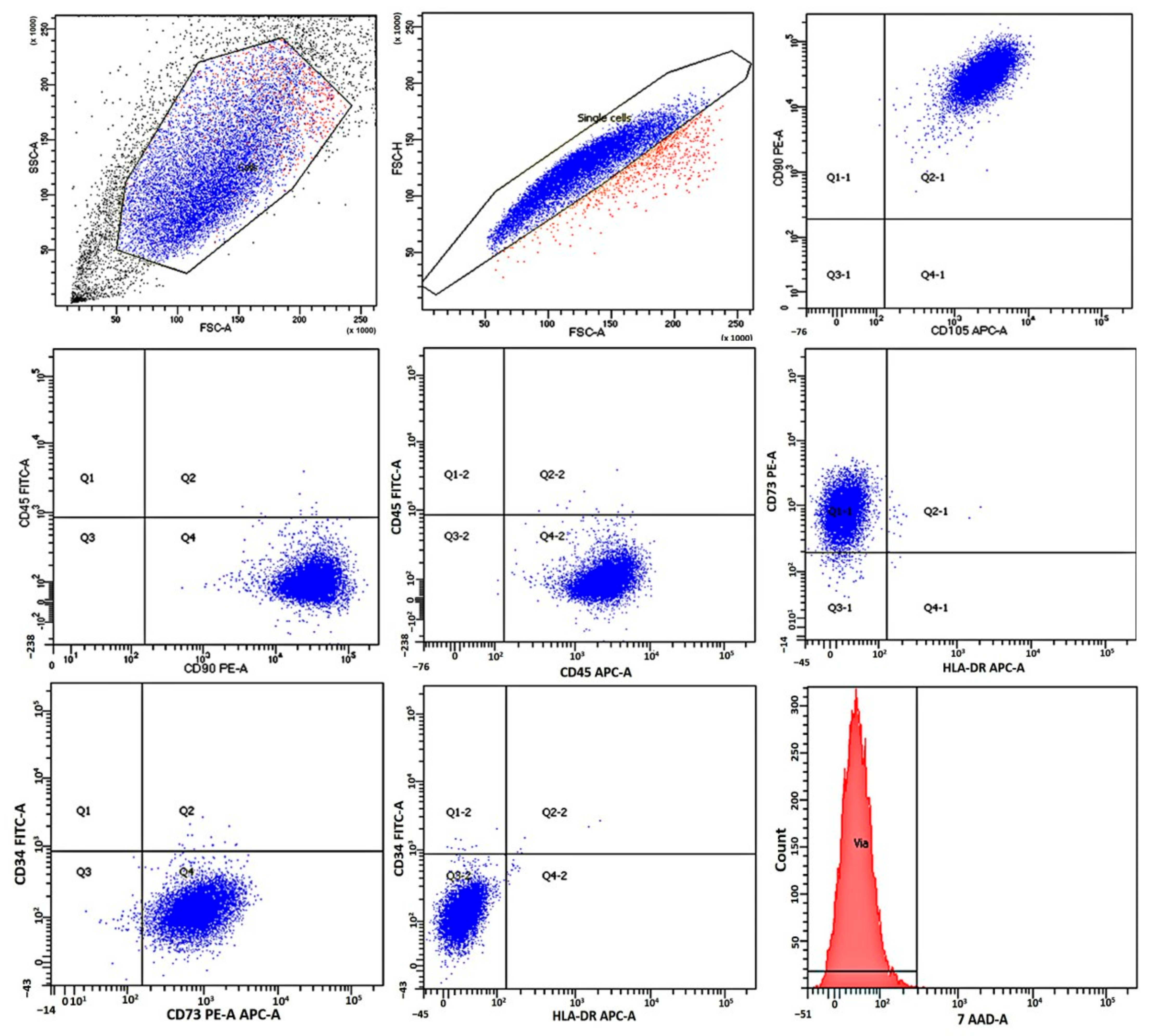
2.1. Immunological Characteristics and Viability of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells
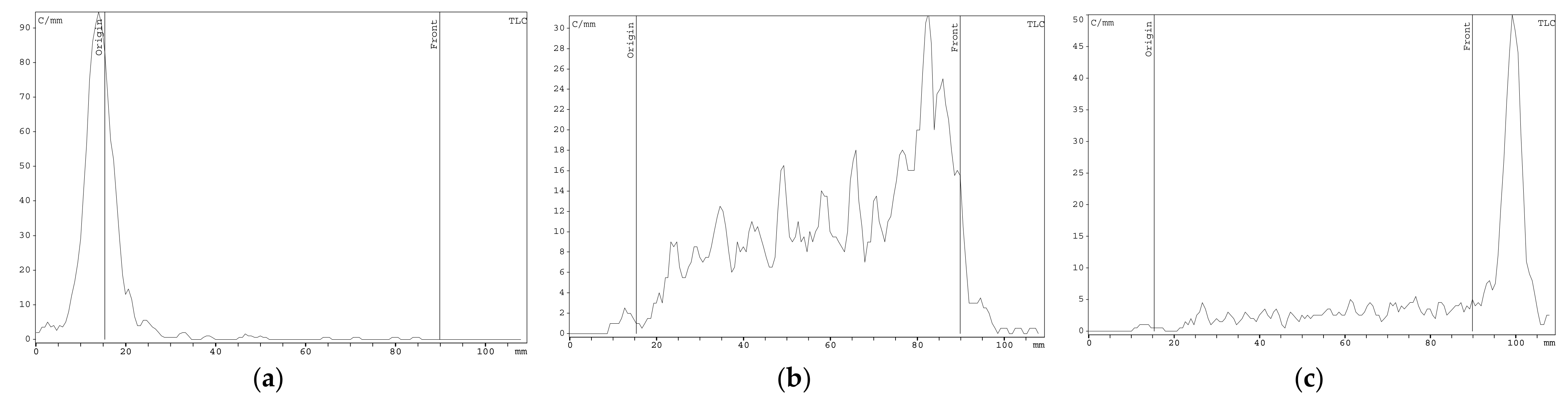
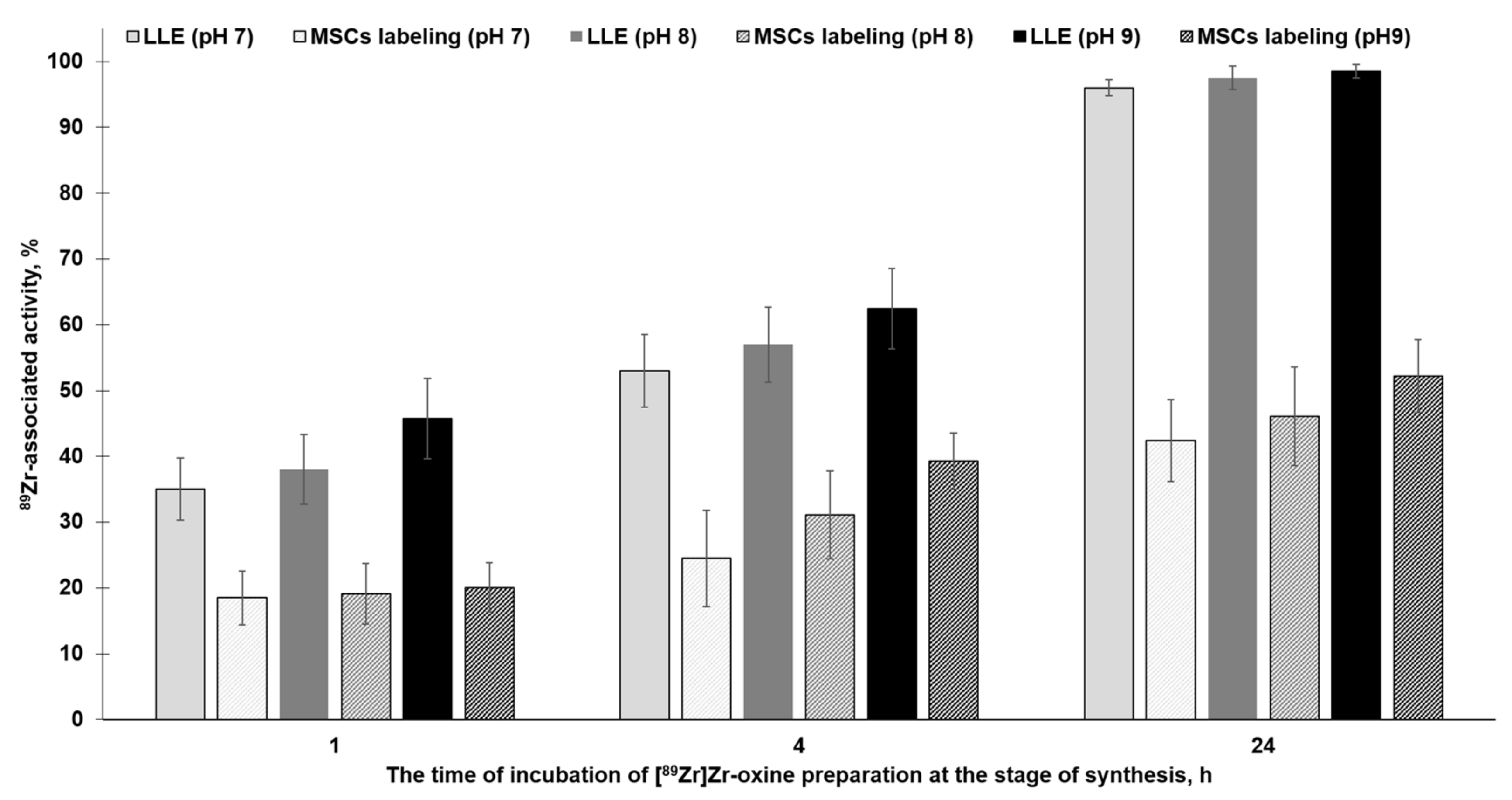
2.2. [89Zr]Zr-Oxine Synthesis, QC, and Cell Labeling Efficiency
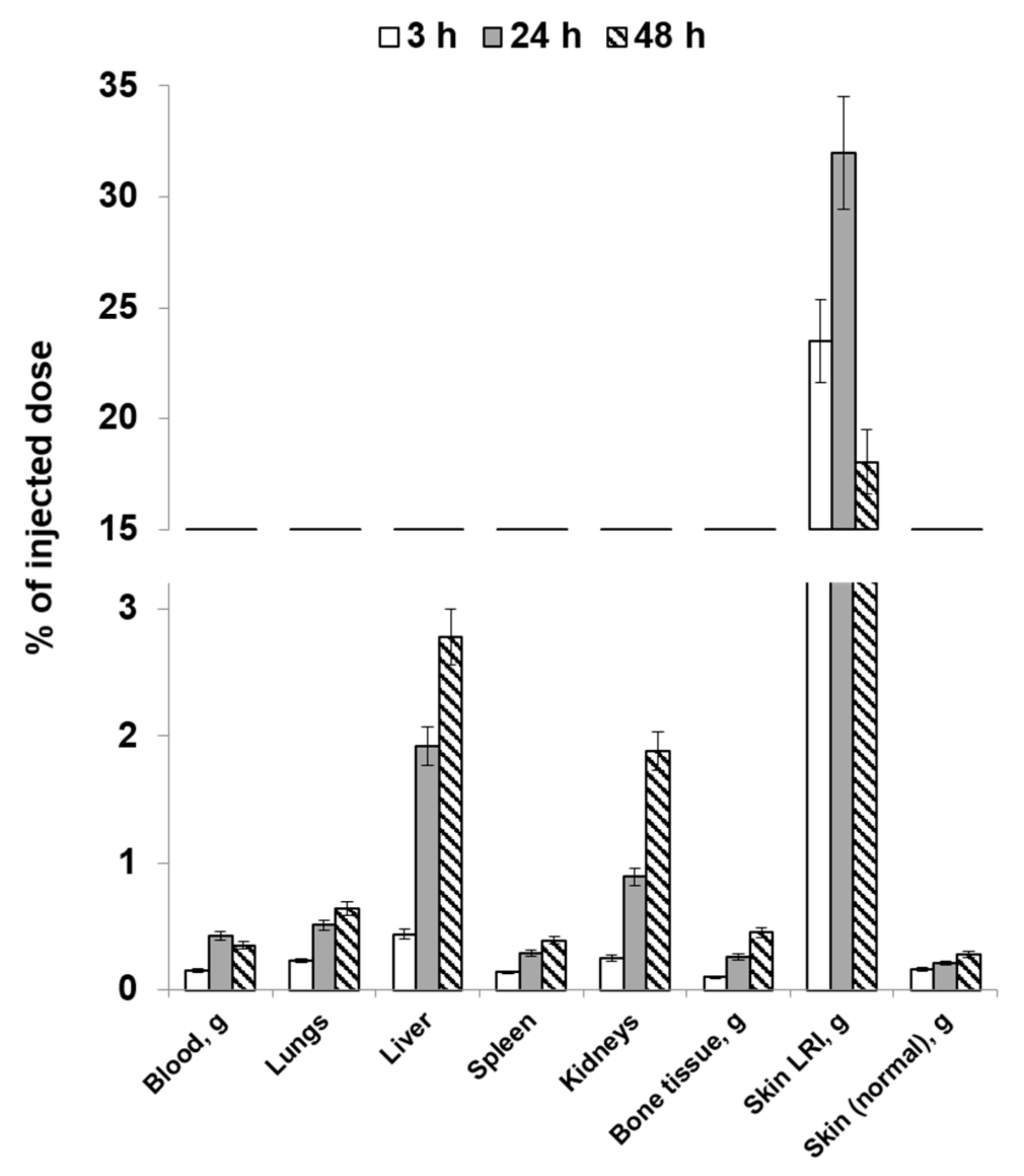
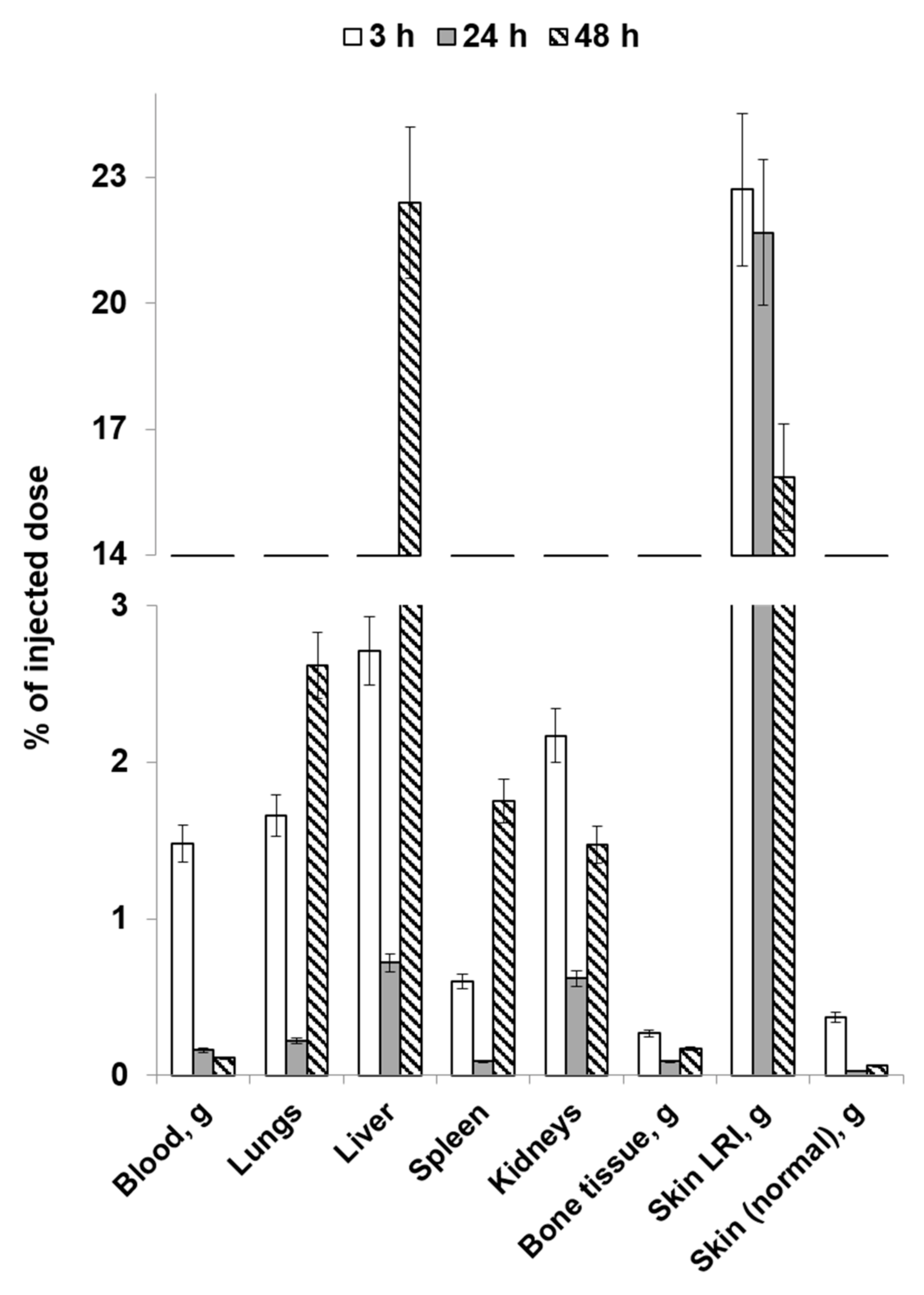
2.3. Study of the Distribution Dynamics of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Labeled with [89Zr]Zr-Oxine in Animals on the Post-Irradiation Day
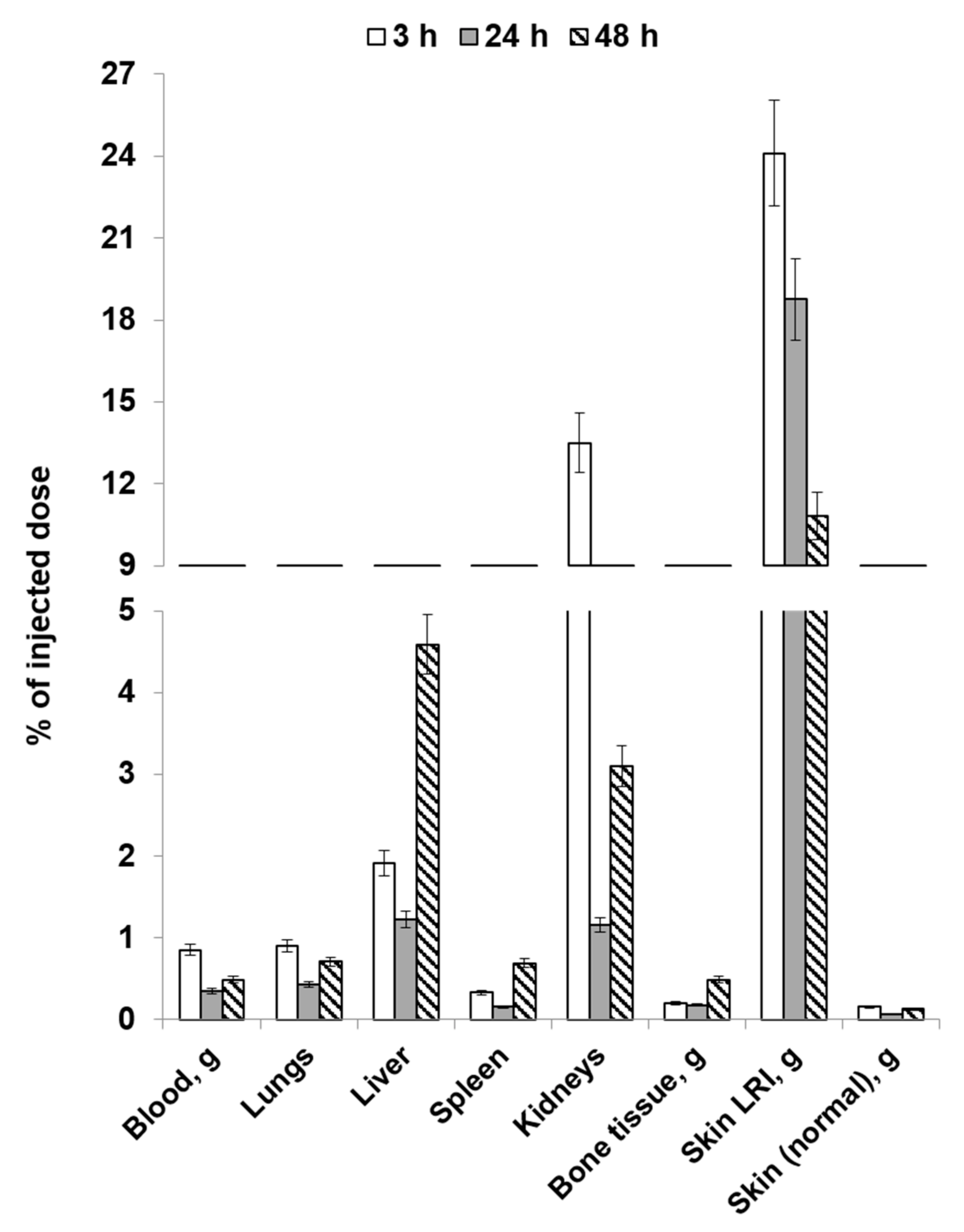
2.4. Study of the Distribution Dynamics of Animals on Post-Irradiation Day 14
- (a)
- the LRI focus can be clearly visualized using PET, and
- (b)
- effective therapy through the local administration of cells is possible.
2.5. Study of the Distribution Dynamics of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Labeled with [89Zr]Zr-Oxine in Wistar Rats with Chronic Radiation-Induced Ulcers
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Groups
- Group 1—irradiated rats that received an intradermal injection of [89Zr]Zr-oxine-labeled allogeneic MSCs of human mucosal tissue into the ulcerated surface on day 1 after LRI modeling;
- Group 2—irradiated rats that received an intradermal injection of [89Zr]Zr-oxine-labeled allogeneic MSCs of human mucosal tissue into the ulcerated surface on day 14 after LRI modeling;
- Group 3—irradiated rats that received an intradermal injection of [89Zr]Zr-oxine-labeled allogeneic MSCs of human mucosal tissue into the ulcerated surface after chronic ulcer formation after LRI modeling (six months);
- Group 4—irradiated rats that received intravenous infusion of [89Zr]Zr-oxine-labeled allogeneic MSCs of human mucosal tissue on day 1 after LRI modeling;
- Group 5—irradiated rats that received intravenous infusion of [89Zr]Zr-oxine-labeled allogeneic MSCs of human mucosal tissue on day 14 after LRI modeling;
- Group 6—irradiated rats that received intravenous infusion of [89Zr]Zr-oxine-labeled allogeneic MSCs of human mucosal tissue after chronic ulcer formation six months after LRI modeling.
4.2. Modeling of Local Radiation Injuries
4.3. Cultivation of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells
4.4. Immunological Characteristics and Viability of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells
4.5. Synthesis of [89Zr]Zr-Oxine
4.6. Radiolabeling of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells
4.7. Injection of Radiolabeled Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in the Animals
4.8. Radiometry
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Puncher, M.R.; Blower, P.J. Autoradiography and Density Gradient Separation of Technetium-99m-Exametazime (HMPAO) Labelled Leucocytes Reveals Selectivity for Eosinophils. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 1994, 21, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukawska, J.J.; Livieratos, L.; Sawyer, B.M.; Lee, T.; O’Doherty, M.; Blower, P.J.; Kofi, M.; Ballinger, J.R.; Corrigan, C.J.; Gnanasegaran, G.; et al. Real-Time Differential Tracking of Human Neutrophil and Eosinophil Migration in Vivo. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 233–239.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharif-Paghaleh, E.; Sunassee, K.; Tavaré, R.; Ratnasothy, K.; Koers, A.; Ali, N.; Alhabbab, R.; Blower, P.J.; Lechler, R.I.; Smyth, L.A.; et al. In Vivo SPECT Reporter Gene Imaging of Regulatory T Cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griessinger, C.M.; Kehlbach, R.; Bukala, D.; Wiehr, S.; Bantleon, R.; Cay, F.; Schmid, A.; Braumüller, H.; Fehrenbacher, B.; Schaller, M.; et al. In Vivo Tracking of Th1 Cells by PET Reveals Quantitative and Temporal Distribution and Specific Homing in Lymphatic Tissue. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruparelia, P.; Szczepura, K.R.; Summers, C.; Solanki, C.K.; Balan, K.; Newbold, P.; Bilton, D.; Peters, A.M.; Chilvers, E.R. Quantification of Neutrophil Migration into the Lungs of Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2011, 38, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavaré, R.; Sagoo, P.; Varama, G.; Tanriver, Y.; Warely, A.; Diebold, S.S.; Southworth, R.; Schaeffter, T.; Lechler, R.I.; Razavi, R.; et al. Monitoring of In Vivo Function of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Labelled Murine Dendritic Cells during Anti-Tumour Vaccination. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, A.W.; Arnot, R.N.; Thakur, M.L.; Lavender, J.P. Indium-111-Labelled Leucocytes for Localisation of Abscesses. Lancet Lond. Engl. 1976, 2, 1056–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Zhuang, H.; Torigian, D.A.; Rosenbaum, J.; Chen, W.; Alavi, A. Functional Imaging of Inflammatory Diseases Using Nuclear Medicine Techniques. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2009, 39, 124–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intenzo, C.M.; Desai, A.G.; Thakur, M.L.; Park, C.H. Comparison of Leukocytes Labeled with Indium-111-2-Mercaptopyridine-N-Oxide and Indium-111 Oxine for Abscess Detection. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 1987, 28, 438–441. [Google Scholar]
- Kotzé, H.F.; Heyns, A.D.; Lötter, M.G.; Pieters, H.; Roodt, J.P.; Sweetlove, M.A.; Badenhorst, P.N. Comparison of Oxine and Tropolone Methods for Labeling Human Platelets with Indium-111. J. Nucl. Med. 1991, 32, 62–66. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, B.L.; Sampson, C.B.; Abeysinghe, R.D.; Porter, J.B.; Hider, R.C. 6-Alkoxymethyl-3-Hydroxy-4H-Pyranones: Potential Ligands for Cell-Labelling with Indium. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 1999, 26, 1400–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, A.M. The Utility of [99mTc]HMPAO-Leukocytes for Imaging Infection. Semin. Nucl. Med. 1994, 24, 110–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, M.L.; Coleman, R.E.; Welch, M.J. Indium-111-Labeled Leukocytes for the Localization of Abscesses: Preparation, Analysis, Tissue Distribution, and Comparison with Gallium-67 Citrate in Dogs. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1977, 89, 217–228. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmim, A.; Zaidi, H. PET versus SPECT: Strengths, Limitations and Challenges. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2008, 29, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherry, S.R.; Jones, T.; Karp, J.S.; Qi, J.; Moses, W.W.; Badawi, R.D. Total-Body PET: Maximizing Sensitivity to Create New Opportunities for Clinical Research and Patient Care. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weist, M.R.; Starr, R.; Aguilar, B.; Chea, J.; Miles, J.K.; Poku, E.; Gerdts, E.; Yang, X.; Priceman, S.J.; Forman, S.J.; et al. PET of Adoptively Transferred Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells with 89 Zr-Oxine. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, F.; Lim, L.; Volpe, A.; Gabizon, A.; Shmeeda, H.; Draper, B.; Parente-Pereira, A.C.; Maher, J.; Blower, P.J.; Fruhwirth, G.O.; et al. In Vivo PET Tracking of 89Zr-Labeled Vγ9Vδ2 T Cells to Mouse Xenograft Breast Tumors Activated with Liposomal Alendronate. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, N.; Wu, H.; Asiedu, K.O.; Szajek, L.P.; Griffiths, G.L.; Choyke, P.L. 89 Zr-Oxine Complex PET Cell Imaging in Monitoring Cell-Based Therapies. Radiology 2015, 275, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temnov, A.; Astrelina, T.; Rogov, K.; Lebedev, V.; Nasonova, T.; Lyrshchikova, A.; Deshevoy Yu Dobrynina, O.; Melerzanov, A.; Samoylov, A.S.; Bushmanov, A.; et al. Investigation of the Influence of the Conditioning Medium Factors Obtained During the Cultivation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells on the Course of Severe Local Radiation Injuries of Skin in Rats. Med. Radiol. Radiat. Saf. 2018, 63, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, F.; Khan, A.A.; Carrascal-Miniño, A.; Blower, P.J.; de Rosales, R.T.M. A Kit Formulation for the Preparation of [89Zr]Zr(Oxinate)4 for PET Cell Tracking: White Blood Cell Labelling and Comparison with [111In]In(Oxinate)3. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2020, 90–91, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoenphun, P.; Meszaros, L.K.; Chuamsaamarkkee, K.; Sharif-Paghaleh, E.; Ballinger, J.R.; Ferris, T.J.; Went, M.J.; Mullen, G.E.D.; Blower, P.J. [89Zr]Oxinate4 for Long-Term in Vivo Cell Tracking by Positron Emission Tomography. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2015, 42, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Pharmacopoeia 8.0 (v. 1). In Monograph “Indium (111In) Oxine Solution”; European Pharmacopoeia: Strasbourg, France, 2014; p. 1066.
- van Santen, R.T.; Schlewitz, J.H.; Toy, C.H. The Spectrophotometric Determination of Zirconium with 8-Hydroxyquinoline. Anal. Chim. Acta 1965, 33, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, P.S.; Kolluri, K.K.; Thin, M.Z.; Edwards, A.; Sage, E.K.; Sanderson, T.; Weil, B.D.; Dickson, J.C.; Kalber, T.L. 89Zr-oxine labelling and PET imaging shows lung delivery of a cell/gene cancer therapy. bioRxiv 2019, 736967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraitchman, D.L.; Tatsumi, M.; Gilson, W.D.; Ishimori, T.; Kedziorek, D.; Walczak, P.; Segars, W.P.; Chen, H.H.; Fritzges, D.; Izbudak, I.; et al. Dynamic Imaging of Allogeneic Mesenchymal Stem Cells Trafficking to Myocardial Infarction. Circulation 2005, 112, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.H.; Pulin, A.A.; Seo, M.J.; Kota, D.J.; Ylostalo, J.; Larson, B.L.; Semprun-Prieto, L.; Delafontaine, P.; Prockop, D.J. Intravenous hMSCs Improve Myocardial Infarction in Mice Because Cells Embolized in Lung Are Activated to Secrete the Anti-Inflammatory Protein TSG-6. Cell Stem Cell 2009, 5, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devine, S.M.; Cobbs, C.; Jennings, M.; Bartholomew, A.; Hoffman, R. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Distribute to a Wide Range of Tissues Following Systemic Infusion into Nonhuman Primates. Blood 2003, 101, 2999–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.-W.; Ahn, J.H.; Kwon, E.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, H.; Jang, J.-J.; Kim, W.H.; Kim, J.H.; Han, S.; Kim, J.T.; et al. Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Acute Liver Injury: Hepatoprotective Efficacy, Subchronic Toxicity, Tumorigenicity, and Biodistribution. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 81, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Kong, W.H.; Kim, H.; Hahn, S.K. Targeted Systemic Mesenchymal Stem Cell Delivery Using Hyaluronate—Wheat Germ Agglutinin Conjugate. Biomaterials 2016, 106, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Lv, H.; An, Y.; Wei, X.; Yi, X.; Yi, H. Tracking of Transplanted Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Labeled with Fluorescent Probe in a Mouse Model of Acute Lung Injury. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 2527–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibacher, J.; Dauber, K.; Ehser, S.; Brixner, V.; Kollar, K.; Vogel, A.; Spohn, G.; Schäfer, R.; Seifried, E.; Henschler, R. Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Undergo Apoptosis and Fragmentation after Intravenous Application in Immune-Competent Mice. Cytotherapy 2017, 19, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; An, G.; Wang, Y.; Liang, D.; Zhu, Z.; Tian, L. Targeted Migration of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Inhibits Silica-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Witte, S.F.H.; Luk, F.; Sierra Parraga, J.M.; Gargesha, M.; Merino, A.; Korevaar, S.S.; Shankar, A.S.; O’Flynn, L.; Elliman, S.J.; Roy, D.; et al. Immunomodulation By Therapeutic Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (MSC) Is Triggered Through Phagocytosis of MSC By Monocytic Cells. Stem Cells 2018, 36, 602–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Li, J.; Xin, L.; Xie, J. In Vivo Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Iron Oxide-Labeled, Intravenous-Injected Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Kidneys of Rabbits with Acute Ischemic Kidney Injury: Detection and Monitoring at 1.5 T. Ren. Fail. 2015, 37, 1363–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnberg, F.; Lundberg, J.; Olsson, A.; Samén, E.; Jaff, N.; Jussing, E.; Dahlén, U.; Nava, S.; Axelsson, R.; Ringdén, O.; et al. Intra-Arterial Administration of Placenta-Derived Decidual Stromal Cells to the Superior Mesenteric Artery in the Rabbit: Distribution of Cells, Feasibility, and Safety. Cell Transplant. 2016, 25, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dave, M.; Menghini, P.; Sugi, K.; Somoza, R.A.; Lee, Z.; Jain, M.; Caplan, A.; Cominelli, F. Ultrasound-Guided Intracardiac Injection of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Increase Homing to the Intestine for Use in Murine Models of Experimental Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 127, e55367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.-N.; Lim, T.S.; Yoon, J.-K.; An, Y.-S. In Vivo Tracking of Intravenously Injected Mesenchymal Stem Cells in an Alzheimer’s Animal Model. Cell Transplant. 2018, 27, 1203–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrhart, J.; Darlington, D.; Kuzmin-Nichols, N.; Sanberg, C.D.; Sawmiller, D.R.; Sanberg, P.R.; Tan, J. Biodistribution of Infused Human Umbilical Cord Blood Cells in Alzheimer’s Disease-Like Murine Model. Cell Transplant. 2016, 25, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Jeong, C.H.; Woo, J.S.; Ryu, C.H.; Lee, J.-H.; Jeun, S.-S. In Vivo Near-Infrared Imaging for the Tracking of Systemically Delivered Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Tropism for Brain Tumors and Biodistribution. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, Y.; Hamaguchi, A.; Ootaki, M.; Watanabe, M.; Takeba, Y.; Iiri, T.; Matsumoto, N.; Takenaga, M. Intravenous Infusion of Adipose-Derived Stem/Stromal Cells Improves Functional Recovery of Rats with Spinal Cord Injury. Cytotherapy 2017, 19, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Jo, S.; Kim, W.H.; Kweon, O.-K. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Intravenously Injected Adipose Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Dogs with Acute Spinal Cord Injury. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015, 6, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, T.G.; Rosado-de-Castro, P.H.; Campos, R.M.P.; Vasques, J.F.; Rangel-Junior, W.S.; Mattos, R.S.d.A.R.d.; Puig-Pijuan, T.; Foerster, B.U.; Gutfilen, B.; Souza, S.A.L.; et al. Intravenous Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Administration in Models of Moderate and Severe Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Stem Cells Dev. 2020, 29, 586–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Zhuo, L.; Cai, J.; He, X.; Liu, B.; Feng, C.; Zhang, L. In vivo Monitoring of Magnetically Labeled Mesenchymal Stem Cells Homing to Rabbit Hepatic VX2 Tumors Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 17, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Cook, T.; Poirier, C.; Merfeld-Clauss, S.; Petrache, I.; March, K.L.; Bogatcheva, N.V. Pulmonary Retention of Adipose Stromal Cells Following Intravenous Delivery Is Markedly Altered in the Presence of ARDS. Cell Transplant. 2016, 25, 1635–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramowski, P.; Krasemann, S.; Ernst, T.; Lange, C.; Ittrich, H.; Schweizer, M.; Zander, A.R.; Martin, R.; Fehse, B. Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells Do Not Ameliorate Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis and Are Not Detectable in the Central Nervous System of Transplanted Mice. Stem Cells Dev. 2016, 25, 1134–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, W.-Z.; Lin, Y.-H.; Su, L.-J.; Wu, M.-S.; Jeng, H.-Y.; Chang, H.-C.; Huang, Y.-H.; Ling, T.-Y. Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cell-Based Therapy: Mechanism, Systemic Safety and Biodistribution for Precision Clinical Applications. J. Biomed. Sci. 2021, 28, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harting, M.T.; Jimenez, F.; Cox, C.S. The Pulmonary First-Pass Effect, Xenotransplantation and Translation to Clinical Trials—A Commentary. Brain 2008, 131, e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schmuck, E.G.; Koch, J.M.; Centanni, J.M.; Hacker, T.A.; Braun, R.K.; Eldridge, M.; Hei, D.J.; Hematti, P.; Raval, A.N. Biodistribution and Clearance of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Quantitative Three-Dimensional Cryo-Imaging After Intravenous Infusion in a Rat Lung Injury Model. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2016, 5, 1668–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, R.; Sann, J.; Frueh, J.; Ullrich, E.; Geiger, H.; Baer, P. Tracking of Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells in a Model of Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury: Comparison of Bioluminescence Imaging versus qRT-PCR. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crop, M.J.; Baan, C.C.; Korevaar, S.S.; Ijzermans, J.N.M.; Weimar, W.; Hoogduijn, M.J. Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Induce Explosive T-Cell Proliferation. Stem Cells Dev. 2010, 19, 1843–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholamrezanezhad, A.; Mirpour, S.; Bagheri, M.; Mohamadnejad, M.; Alimoghaddam, K.; Abdolahzadeh, L.; Saghari, M.; Malekzadeh, R. In Vivo Tracking of 111In-Oxine Labeled Mesenchymal Stem Cells Following Infusion in Patients with Advanced Cirrhosis. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2011, 38, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koç, O.N.; Gerson, S.L.; Cooper, B.W.; Dyhouse, S.M.; Haynesworth, S.E.; Caplan, A.I.; Lazarus, H.M. Rapid Hematopoietic Recovery After Coinfusion of Autologous-Blood Stem Cells and Culture-Expanded Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Advanced Breast Cancer Patients Receiving High-Dose Chemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 18, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokal, E.M.; Lombard, C.A.; Roelants, V.; Najimi, M.; Varma, S.; Sargiacomo, C.; Ravau, J.; Mazza, G.; Jamar, F.; Versavau, J.; et al. Biodistribution of Liver-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells After Peripheral Injection in a Hemophilia A Patient. Transplantation 2017, 101, 1845–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratheesh, M.D.; Gade, N.E.; Nath, A.; Dubey, P.K.; Sivanarayanan, T.B.; Madhu, D.N.; Sreekumar, T.R.; Amarpal, S.G.; Sharma, G.T. Evaluation of Persistence and Distribution of Intra-Dermally Administered PKH26 Labelled Goat Bone Marrow Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Cutaneous Wound Healing Model. Cytotechnology 2017, 69, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Santalla, M.; Mancheño-Corvo, P.; Escolano, A.; Menta, R.; DelaRosa, O.; Abad, J.L.; Büscher, D.; Redondo, J.M.; Bueren, J.A.; Dalemans, W.; et al. Biodistribution and Efficacy of Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Following Intranodal Administration in Experimental Colitis. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, A.; Pandey, M.K.; Demirhan, Y.E.; Nesbitt, J.J.; Crespo-Diaz, R.J.; Terzic, A.; Behfar, A.; DeGrado, T.R. Novel 89Zr Cell Labeling Approach for PET-Based Cell Trafficking Studies. EJNMMI Res. 2015, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunev, K.A.; Lunev, A.S.; Klementieva, O.E.; Ternovskaya, K.E.; Astrelina, T.A. Study of the ways of mesenchimal stem cells migration in animals with experimental radiation skin burns. Drug Dev. Regist. 2018, 2, 130–134. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Henriksson, H.B.; Papadimitriou, N.; Hingert, D.; Baranto, A.; Lindahl, A.; Brisby, H. The Traceability of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells After Injection Into Degenerated Discs in Patients with Low Back Pain. Stem Cells Dev. 2019, 28, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, P.S.; Kolluri, K.K.; Zaw Thin, M.; Edwards, A.; Sage, E.K.; Sanderson, T.; Weil, B.D.; Dickson, J.C.; Lythgoe, M.F.; Lowdell, M.; et al. Lung Delivery of MSCs Expressing Anti-Cancer Protein TRAIL Visualised with 89Zr-Oxine PET-CT. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osanov, D.P. Dosimetry and Radiation Biophysics of the Skin; Energoatomizdat: Moscow, Russia, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Brunchukov, V.; Astrelina, T.; Usupzhanova, D.; Rastorgueva, A.; Kobzeva, I.; Nikitina, V.; Lishchuk, S.; Dubova, E.; Pavlov, K.; Brumberg, V.; et al. Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Mesenchymal Stem Cells of the Placenta and Their Conditioned Medium in Local Radiation Injuries. Cells 2020, 9, 2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larenkov, A.; Bubenshchikov, V.; Makichyan, A.; Zhukova, M.; Krasnoperova, A.; Kodina, G. Preparation of Zirconium-89 Solutions for Radiopharmaceutical Purposes: Interrelation Between Formulation, Radiochemical Purity, Stability and Biodistribution. Molecules 2019, 24, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besiadovsky, R.A.; Ivanov, K.V.; Kozyura, A.K. Reference Guide for Radiobiologists; Atomizdat: Moscow, Russia, 1978; p. 128. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Astrelina, T.A.; Brunchukov, V.A.; Kodina, G.E.; Bubenshchikov, V.B.; Larenkov, A.A.; Lunev, A.S.; Petrosova, K.A.; Rastorgueva, A.A.; Kobzeva, I.V.; Usupzhanova, D.Y.; et al. Biodistribution of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Labeled with [89Zr]Zr-Oxine in Local Radiation Injuries in Laboratory Animals. Molecules 2023, 28, 7169. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28207169
Astrelina TA, Brunchukov VA, Kodina GE, Bubenshchikov VB, Larenkov AA, Lunev AS, Petrosova KA, Rastorgueva AA, Kobzeva IV, Usupzhanova DY, et al. Biodistribution of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Labeled with [89Zr]Zr-Oxine in Local Radiation Injuries in Laboratory Animals. Molecules. 2023; 28(20):7169. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28207169
Chicago/Turabian StyleAstrelina, Tatiana A., Vitaliy A. Brunchukov, Galina E. Kodina, Viktor B. Bubenshchikov, Anton A. Larenkov, Aleksandr S. Lunev, Kristina A. Petrosova, Anna A. Rastorgueva, Irina V. Kobzeva, Daria Y. Usupzhanova, and et al. 2023. "Biodistribution of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Labeled with [89Zr]Zr-Oxine in Local Radiation Injuries in Laboratory Animals" Molecules 28, no. 20: 7169. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28207169
APA StyleAstrelina, T. A., Brunchukov, V. A., Kodina, G. E., Bubenshchikov, V. B., Larenkov, A. A., Lunev, A. S., Petrosova, K. A., Rastorgueva, A. A., Kobzeva, I. V., Usupzhanova, D. Y., Nikitina, V. A., Malsagova, K. A., Kulikova, L. I., Samoilov, A. S., & Pustovoyt, V. I. (2023). Biodistribution of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Labeled with [89Zr]Zr-Oxine in Local Radiation Injuries in Laboratory Animals. Molecules, 28(20), 7169. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28207169






