Steroidal Alkaloids from the Roots of Veratrum mengtzeanum Loes. with Their Anti-Inflammatory Activities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation and Structural Assessment
2.2. Structural Assessment of Known Constituents
2.3. Biological Studies
2.3.1. Anti-Inflammatory Property through the Suppression of LPS-Induced NO Formation
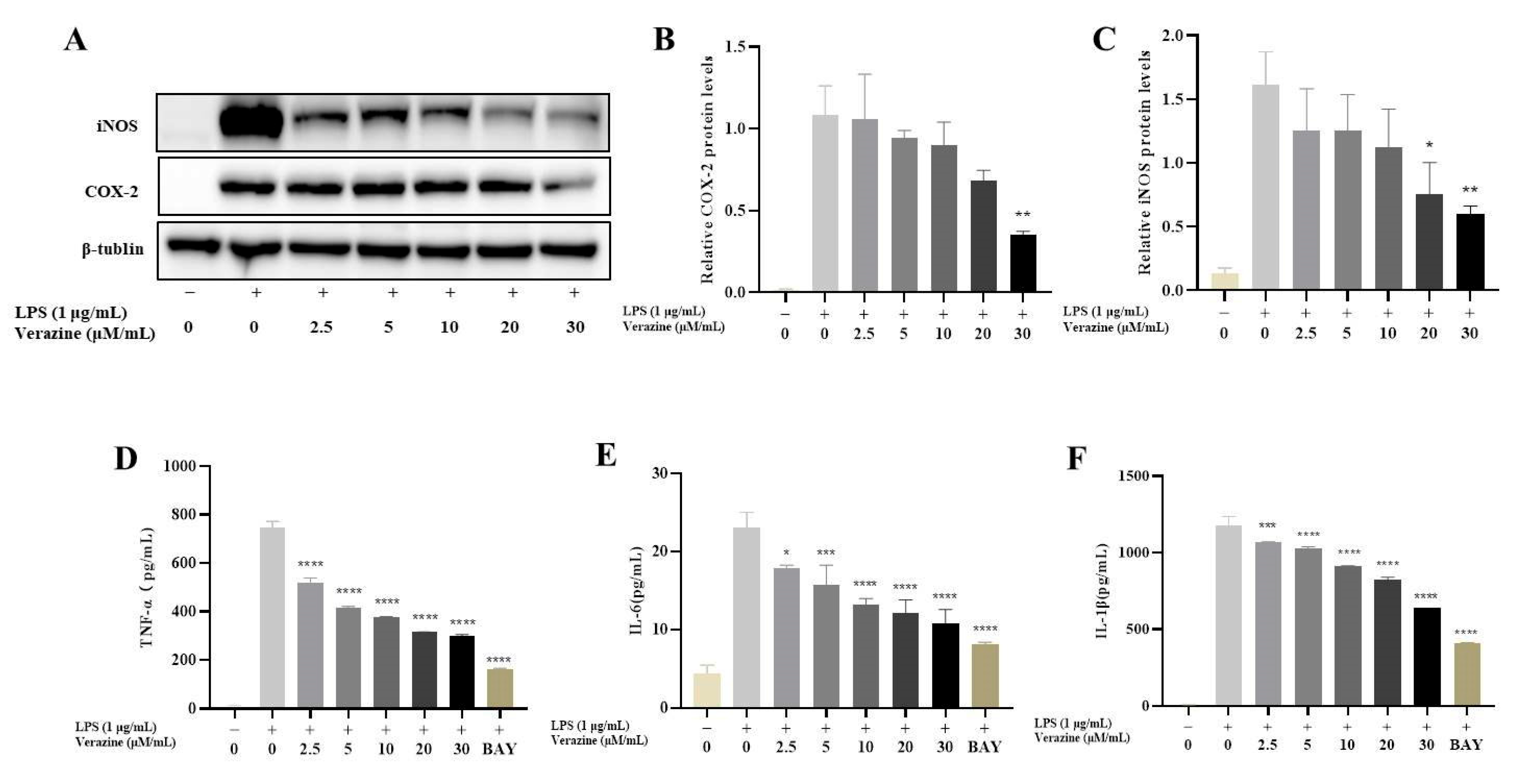
2.3.2. Verazine Inhibits the Release of TNFα, IL1β, and IL6, and Suppresses the Production of iNOS and COX2
2.3.3. Verazine Suppresses the Triggering of NF-κB Signaling
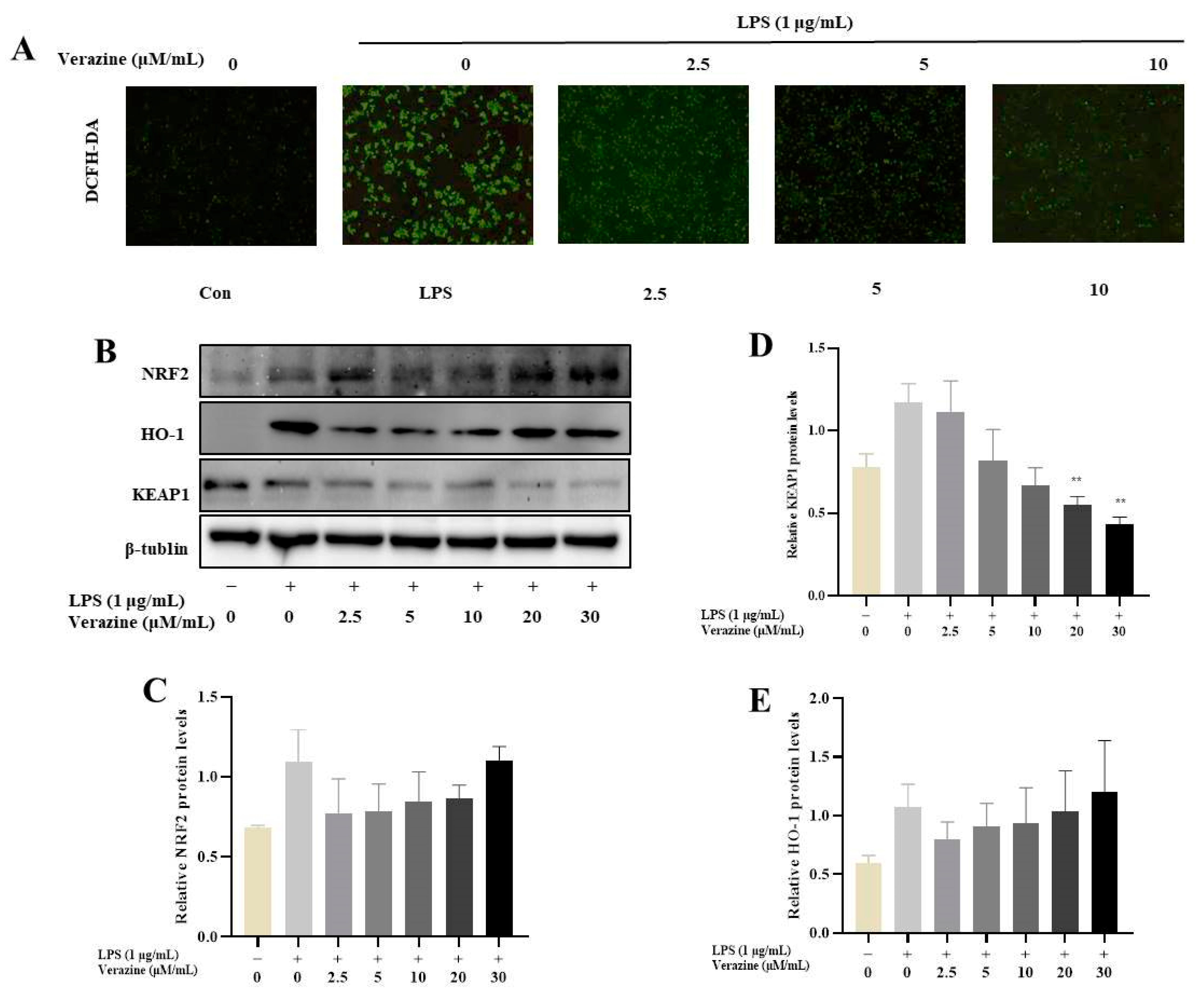
2.3.4. Verazine Activates Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling to Alleviate Oxidative Stress in LPS-Induced RAW264.7 Macrophages
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
Chemicals
3.2. Plants
3.3. Extraction Process
3.3.1. Mengtzeanines A (1)
3.3.2. Mengtzeanines A (2)
3.4. Cell Culture
3.5. MTT Assays
3.6. NO Inhibition Assays
3.7. ELISA
3.8. Western Blot
3.9. ROS Analysis of Annexin V Expression
3.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the nearly four decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 770–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Yang, K.X.; Zhao, Y.L.; Qin, X.J.; Yang, X.W.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.P.; Luo, X.D. Potent anti-inflammatory and analgesic steroidal alkaloids from Veratrum taliense. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 179, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Yaseen, A.; Li, F.; Chen, B.; Shen, X.-F.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, G.-L.; Wang, M.-K. Steroidal alkaloids from the bulbs of Fritillaria pallidiflora Schrenk and their anti-inflammatory activity. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 112, 104845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, T.Z.; Luo, L.; Zhao, Y.L.; Li, H.; Xiang, M.L.; Qin, X.J.; He, Y.J.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Dai, Z.; Wang, Z.J.; et al. Steroidal alkaloids with a potent analgesic effect based on N-type calcium channel inhibition. Org. Lett. 2021, 24, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhao, Y.L.; Long, C.B.; Zhu, P.F.; Liu, Y.P.; Luo, X.D. Seven new veratramine-type alkaloids with potent analgesic effect from Veratrum taliense. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 244, 112137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rehaily, A.J.; Ahmad, M.S.; Mustafa, J.; Al-Oqail, M.M.; Hassan, W.H.; Khan, S.I.; Khan, I.A. Solanopubamine, a rare steroidal alkaloid from Solanum schimperianum: Synthesis of some new alkyl and acyl derivatives, their anticancer and antimicrobial evaluation. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2013, 17, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.-N.; Ge, X.-L.; Dong, T.T.; Gao, H.-Y.; Sun, B.-H. Antibacterial steroidal alkaloids from Holarrhena antidysenteriaca. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2017, 15, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Y.; Yang, Y.K.; Wang, J.N.; Ren, J.G. Steroidal alkaloids from Solanum nigrum and their cytotoxic activities. Phytochemistry 2022, 202, 113317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.J.; Zhang, M.Z.; Li, X.Y.; Huang, W.K.; Xu, S.F.; Ye, Y.P. Steroidal alkaloids isolated from Veratrum grandiflorum Loes. as novel Smoothened inhibitors with anti-proliferation effects on DAOY medulloblastoma cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2021, 39, 116166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, N.U.; Kifayatullah, M.; Amin, F.; Rahim, H.; Abbas, S.; Mohani, S.N.U.H.; Aman, S.; Raza, M. Antioxidant and Cytotoxic activity of Steroidal Alkaloids Isolated from Sarcococca saligna against DPPH and HeLa Cell Lines. Indian J. Pharm. Educ. Res. 2022, 56, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumlu, F.A.; Aydin, T.; Odabasoglu, F.; Berktas, O.A.; Kutlu, Z.; Erol, H.S.; Halici, M.B.; Cadirci, E.; Cakir, A. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of jervine, a sterodial alkaloid from rhizomes of Veratrum album. Phytomedicine 2019, 55, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, A.; Serly, J.; Christov, V.; Stamboliyska, B.; Molnar, J. Alkaloids derived from genus Veratrum and Peganum of Mongolian origin as multidrug resistance inhibitors of cancer cells. Fitoterapia 2011, 82, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirks, M.L.; Seale, J.T.; Collins, J.M.; McDougal, O.M. Veratrum californicum alkaloids. Molecules 2021, 26, 5934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seale, J.T.; McDougal, O.M. Veratrum parviflorum: An Underexplored Source for Bioactive Steroidal Alkaloids. Molecules 2022, 27, 5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Xie, H.; Zhang, J. A preliminary study of biological characteristics of Veratrum nigrum. Yunnan J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Mat. Med. 2014, 4, 54–57. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Shao, S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Yuan, H.; Gao, Y. Neurotoxicity of Veratrum nigrum L. and the molecular mechanism of veratridine toxicity. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2018, 11, 6547–6559. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Tsao, R. Dietary polyphenols, oxidative stress and antioxidant and anti- inflammatory effects. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2016, 8, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Jang, H.J.; Han, Y.K.; Su, X.D.; Lee, S.W.; Rho, M.C.; Wang, H.S.; Yang, S.Y.; Kim, Y.H. Alkaloids from Tetrastigma hemsleyanum and their anti-inflammatory effects on LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells. Molecules 2018, 23, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosser, D.M. The many faces of macrophage activation. J. Leucoc. Biol. 2003, 73, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellheim, A.; Brekke, O.-L.; Espevik, T.; Harboe, M.; Mollnes, T.E. Innate immune responses to danger signals in systemic inflammatory response syndrome and sepsis. Scand. J. Immunol. 2009, 69, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.Y.; Cesari, M.; Anton, S.; Marzetti, E.; Giovannini, S.; Seo, A.Y.; Carter, C.; Yu, B.P.; Leeuwenburgh, C. Molecular inflammation: Underpinnings of aging and age-related diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 2009, 8, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Tang, J.; Zuo, Y.; Yu, Y.; Luo, P.; Yao, X.; Dong, Y.; Wang, P.; Liu, L.; Zhou, H. Stauntoside B inhibits macrophage activation by inhibiting NF-κB and ERK MAPK signalling. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 111, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, P.P.; Xia, Q.; Hwang, H.M.; Ray, P.C.; Yu, H. Mechanisms of nanotoxicity: Generation of reactive oxygen species. J. Food Drug Anal. 2014, 22, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzaei, S.; Mohammadi, A.T.; Gholami, M.H.; Hashemi, F.; Zarrabi, A.; Zabolian, A.; Hushmandi, K.; Makvandi, P.; Samec, M.; Liskova, A.; et al. Nrf2 signaling pathway in cisplatin chemotherapy: Potential involvement in organ protection and chemoresistance. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 167, 105575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, A.M.; Alam, J. Heme oxygenase-1: Function, regulation, and implication of a novel stress-inducible protein in oxidant-induced lung injury. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1996, 15, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paine, A.; Eiz-Vesper, B.; Blasczyk, R.; Immenschuh, S. Signaling to heme oxygenase-1 and its anti-inflammatory therapeutic potential. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 1895–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terazawa, R.; Akimoto, N.; Kato, T.; Itoh, T.; Fujita, Y.; Hamada, N.; Deguchi, T.; Iinuma, M.; Noda, M.; Nozawa, Y.; et al. A kavalactone derivative inhibits lipopolysaccharide- stimulated iNOS induction and NO production through activation of Nrf2 signaling in BV2 microglial cells. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 71, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, P.-Z.; Hu, Z.-X.; Gu, Y.-C.; Ye, J.; Hao, X.-J. Two new steroidal alkaloids from the rhizomes of Veratrum nigrum L. and their anti-TYLCV activity. Fitoterapia 2019, 147, 104731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanyonyi, A.W.; Chhabra, S.C.; Mkoji, G.; Eilert, U.; Njue, W.M. Bioactive steroidal alkaloid glycosides from Solanum aculeastrum. Phytochemistry 2002, 59, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Chen, F.; Li, X.; Xu, S.; Huang, W.; Ye, Y. Three new alkaloids from Veratrum grandiflorum Loes. with inhibition activities on Hedgehog pathway. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 4735–4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Li, H.L.; Shen, Y.H.; Jin, H.Z.; Yan, S.K.; Liu, R.H.; Zhang, W.D. Four new germine esters from Veratrum dahuricum. Helv. Chim. Acta 2007, 90, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanfar, M.A.; El Sayed, K.A. The Veratrum alkaloids jervine, veratramine, and their analogues as prostate cancer migration and proliferation inhibitors: Biological evaluation and pharmacophore modeling. Med. Chem. Res. 2013, 22, 4775–4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Kader, M.S.; Bahler, B.D.; Malone, S.; Werkhoven, M.C.M.; van Troon, F.; Wisse, D.J.H.; Bursuker, I.; Neddermann, K.M.; Mamber, S.W.; Kingston, D.G.I. DNA Damaging Steroidal Alkaloids from Eclipta alba from the Suriname Rain Forest. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lü, Y.F.; Chen, K.Y.; Li, H.L.; Pei, Y.H.; Liu, R.H.; Zhang, W.D. Biotransformation of vermitaline by Cunninghamella echinulata. Helv. Chim. Acta 2008, 91, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.X.; Tan, R.X.; Ye, W.C.; Min, Z.D. Steroidal alkaloids from Veratrum taliense. Planta Med. 1999, 65, 480–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oatis, J.E.; Brunsfeld, P.; Rushing, J.W.; Moeller, P.D.; Bearden, D.W.; Gallien, T.N.; Cooper, G. Isolation, purification, and full NMR assignments of cyclopamine from Veratrum californicum. Chem. Cent. J. 2008, 2, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezuka, Y.; Kikuchi, T.; Zhao, W.; Chen, J.; Guo, Y. Two New Steroidal Alkaloids, 20-Isoveratramine and Verapatuline, from the Roots and Rhizomes of Veratrum patulum. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 1078–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refaey, M.S.; Abouelela, M.E.; El-Shoura, E.A.M.; Alkhalidi, H.M.; Fadil, S.A.; Elhady, S.S.; Abdelhameed, R.F.A. In vitro anti-Inflammatory activity of Cotula anthemoides essential oil and in silico molecular docking of its bioactives. Molecules 2022, 27, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Qiu, F.; Chen, L.; Liu, R.; Chang, M.; Wang, X. Identification and in vitro anti-inflammatory activity of different forms of phenolic compounds in Camellia oleifera oil. Food Chem. 2021, 344, 128660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

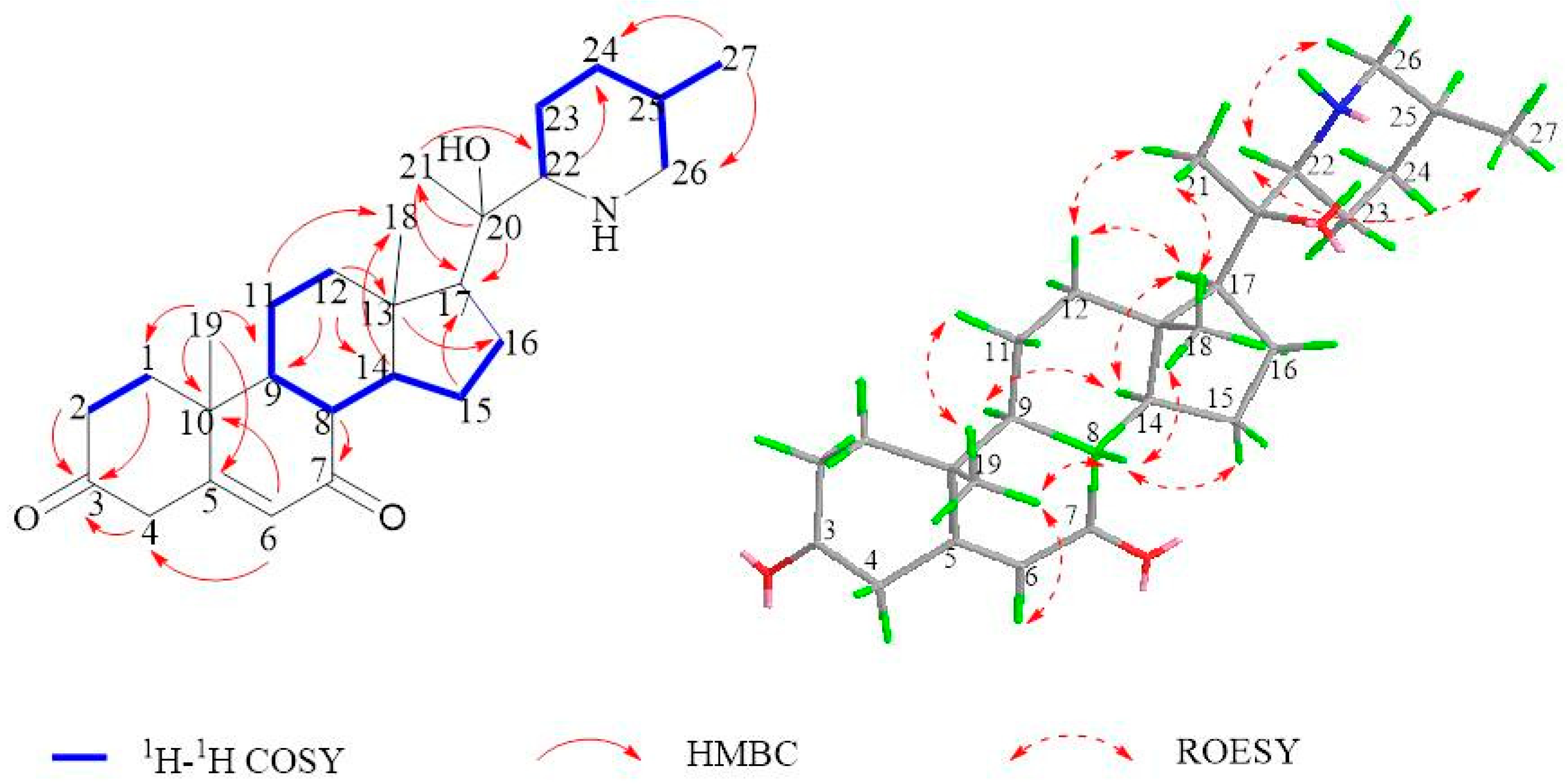
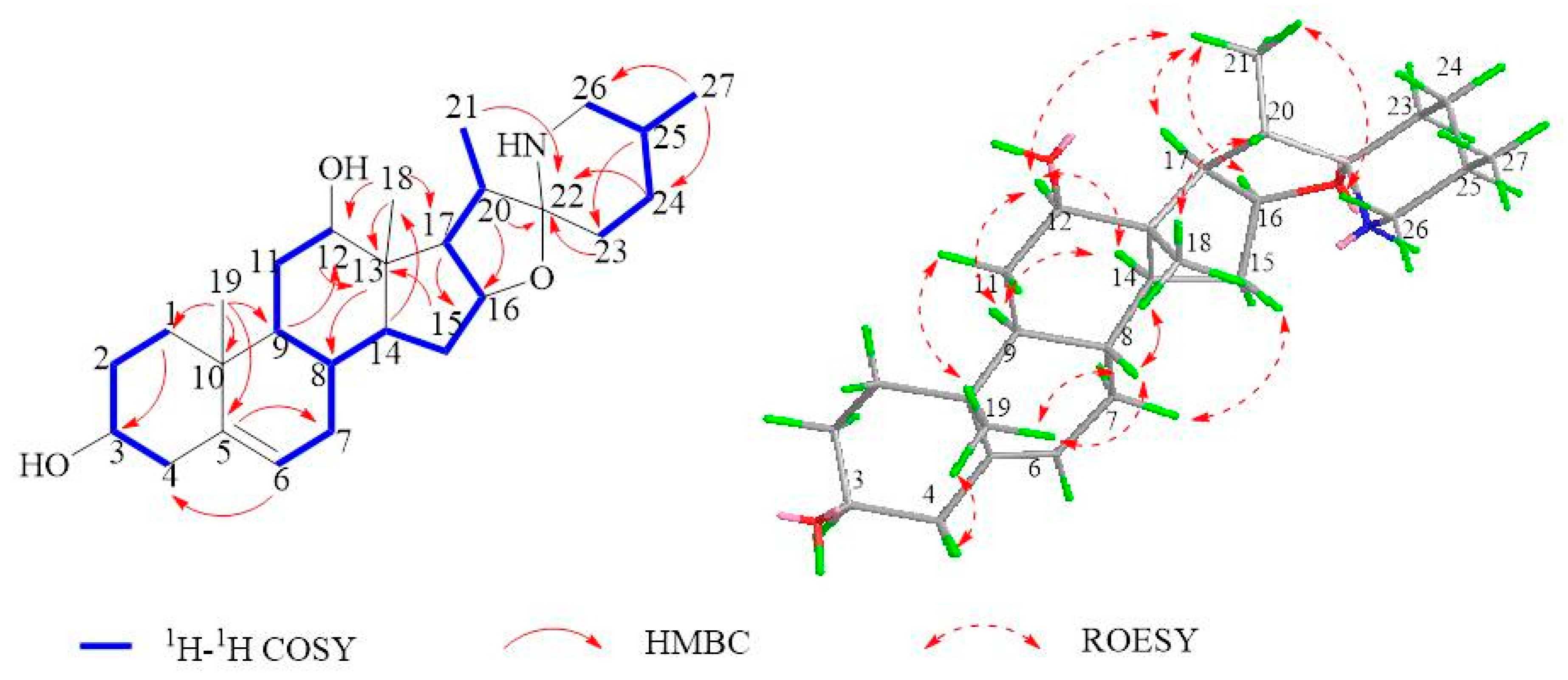


| Position | δC a | δH b | Position | δC a | δH b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1a | 37.1 | 1.79 (1H, m) | 14 | 47.4 | 1.59 (1H, m) |
| 1b | 1.09 (1H, m) | 15a | 26.6 | 1.70 (1H, m) | |
| 2a | 31.8 | 2.02 (1H, m) | 15b | 1.36 (1H, m) | |
| 2b | 1.69 (1H, m) | 16 | 77.9 | 4.12 (1H, m) | |
| 3 | 71.6 | 3.52 (1H, m) | 17 | 52.8 | 2.30 (1H, m) |
| 4a | 42.2 | 2.30 (1H, m) | 18 | 17.4 | 0.87 (3H, s) |
| 4b | 2.23 (1H, m) | 19 | 19.3 | 1.01 (3H, s) | |
| 5 | 140.6 | 20 | 43.1 | 1.62 (1H, m) | |
| 6 | 121.5 | 5.34 (1H, d, 6.4) | 21 | 15.7 | 0.98 (3H, d, 8.4) |
| 7a | 32.5 | 2.03 (1H, m) | 22 | 99.2 | |
| 7b | 1.33 (1H, m) | 23a | 28.5 | 1.54 (1H, m) | |
| 8 | 31.4 | 1.63 (1H, m) | 23b | 1.36 (1H, m) | |
| 9 | 43.9 | 1.30 (1H, m) | 24a | 28.7 | 1.78 (1H, m) |
| 10 | 36.3 | 24b | 1.54 (1H, m) | ||
| 11a | 31.5 | 1.83 (1H, m) | 25 | 31.0 | 1.60 (1H, m) |
| 11b | 1.49 (1H, m) | 26a | 50.2 | 2.72 (1H, m) | |
| 12 | 72.3 | 3.75 (1H, m) | 26b | 1.57 (1H, m) | |
| 13 | 44.7 | 27 | 19.4 | 0.85 (3H, d, 7.8) |
| Position | δC a | δH b | Position | δC a | δH b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1a | 34.0 | 2.38 (1H, m) | 15a | 23.9 | 1.62 (1H, m) |
| 1b | 1.59 (1H, m) | 15b | 1.46 (1H, m) | ||
| 2a | 32.8 | 2.56 (1H, m) | 16a | 27.1 | 1.75 (1H, m) |
| 2b | 2.34 (1H, m) | 16b | 1.58 (1H, m) | ||
| 3 | 214.1 | 17 | 55.1 | 1.55 (1H, m) | |
| 4a | 40.3 | 2.21 (1H, m) | 18 | 13.4 | 0.92 (3H, s) |
| 4b | 1.35 (1H, m) | 19 | 17.3 | 1.19 (3H, s) | |
| 5 | 171.3 | 20 | 80.0 | ||
| 6 | 123.8 | 5.73 (1H, m) | 21 | 24.7 | 1.43 (3H, brs) |
| 7 | 199.6 | 22 | 56.0 | 1.05 (1H, m) | |
| 8 | 55.1 | 1.73 (1H, m) | 23a | 20.9 | 1.54 (1H, m) |
| 9 | 53.8 | 0.94 (1H, m) | 23b | 1.15 (1H, m) | |
| 10 | 38.6 | 24a | 31.9 | 2.27 (1H, d, 12.8 Hz) | |
| 11a | 22.1 | 1.56 (1H, m) | 24b | 1.83 (1H, m) | |
| 11b | 1.18 (1H, m) | 25 | 35.0 | 1.57 (1H, m) | |
| 12a | 35.7 | 2.03 (1H, m) | 26a | 67.7 | 3.47 (1H, d, 5.9 Hz) |
| 12b | 1.70 (1H, m) | 26b | 1.57 (1H, m) | ||
| 13 | 43.8 | 27 | 16.5 | 0.93 (3H, d, 3.4 Hz) | |
| 14 | 56.0 | 1.20 (1H, m) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, W.; Ma, J.; Liu, X.; Zi, C.; Xi, Y.; Shen, X.; Li, G.; Sheng, J.; Wang, X. Steroidal Alkaloids from the Roots of Veratrum mengtzeanum Loes. with Their Anti-Inflammatory Activities. Molecules 2023, 28, 7116. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28207116
Yuan W, Ma J, Liu X, Zi C, Xi Y, Shen X, Li G, Sheng J, Wang X. Steroidal Alkaloids from the Roots of Veratrum mengtzeanum Loes. with Their Anti-Inflammatory Activities. Molecules. 2023; 28(20):7116. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28207116
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Wenjuan, Jinrong Ma, Xinlan Liu, Chengting Zi, Yongkai Xi, Xiaojing Shen, Guodong Li, Jun Sheng, and Xuanjun Wang. 2023. "Steroidal Alkaloids from the Roots of Veratrum mengtzeanum Loes. with Their Anti-Inflammatory Activities" Molecules 28, no. 20: 7116. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28207116
APA StyleYuan, W., Ma, J., Liu, X., Zi, C., Xi, Y., Shen, X., Li, G., Sheng, J., & Wang, X. (2023). Steroidal Alkaloids from the Roots of Veratrum mengtzeanum Loes. with Their Anti-Inflammatory Activities. Molecules, 28(20), 7116. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28207116







