Effect of Side-Chain Functional Groups in the Immunogenicity of Bacterial Surface Glycans
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Naturally Occurring Side-Chain Functional Groups in the Glycans on the Bacterial Surface
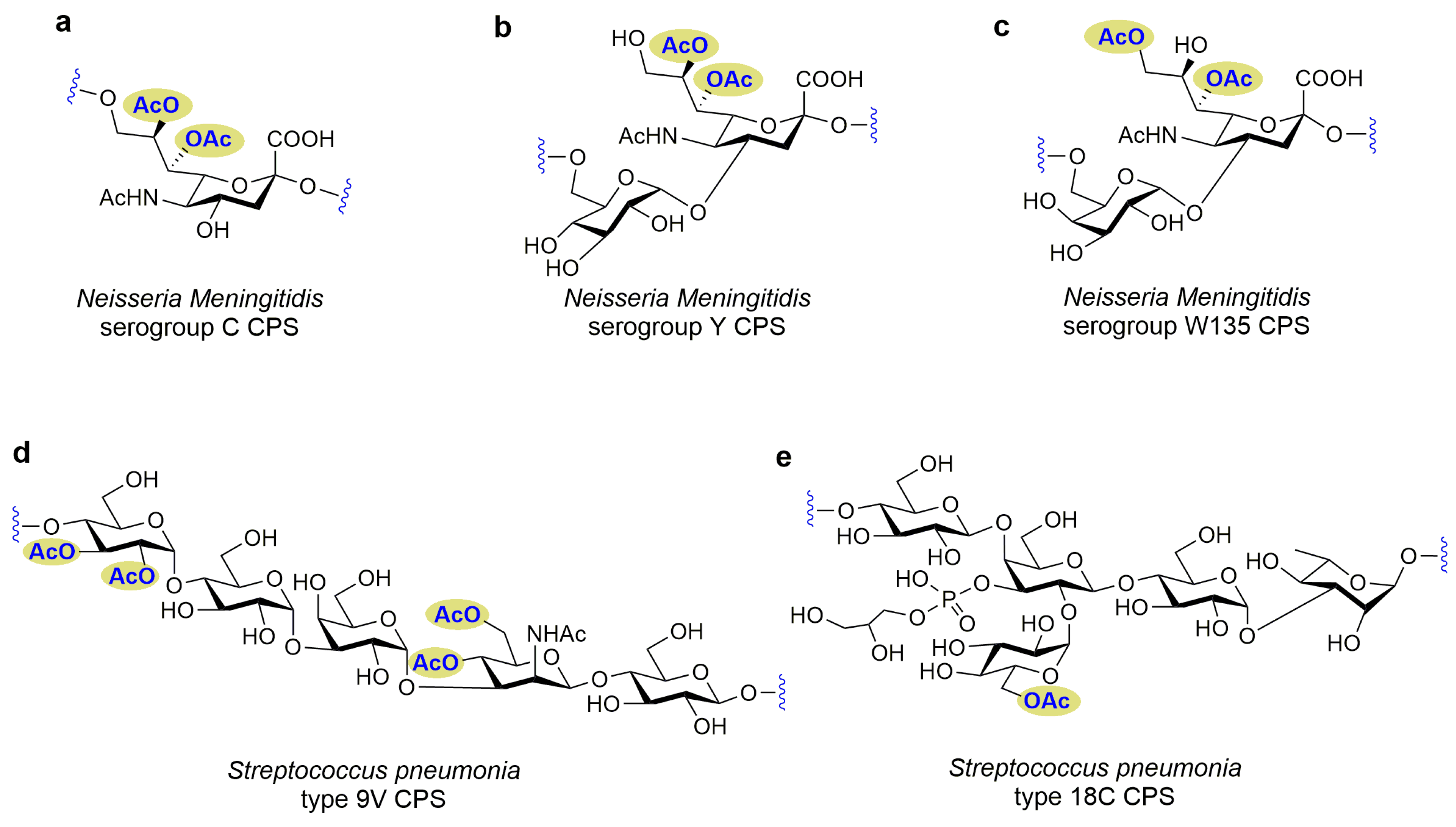
2.1. Bacterial Glycans’ O-Modified Side-Chain Functional Groups
2.2. Bacterial Glycans’ N-Modified Side-Chain Functional Groups
2.3. Bacterial Glycans’ Carboxyl-Linked Side-Chain Functional Groups
3. The Biological Activity of Bacterial Surface Glycans’ Functional Groups
3.1. Functional Groups in Bacterial Glycans as Essential Determinants for Immunogenicity
3.2. Functional Groups in Glycans on the Bacterial Surface Are Not Essential for Inducing Functional Antibody Responses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rohokale, R.; Guo, Z. Development in the concept of bacterial polysaccharide repeating unit-based antibacterial conjugate vaccines. ACS Infect. Dis. 2023, 9, 178–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo, F.D.; Duda, K.A.; Lanzetta, R.; Silipo, A.; Castro, C.D.; Molinaro, A. A journey from structure to function of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 15767–15821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeberger, P.H. Discovery of semi- and fully-synthetic carbohydrate vaccines against bacterial infections using a medicinal chemistry approach. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 3598–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vella, M.; Pace, D. Glycoconjugate vaccines: An update. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2015, 15, 529–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.L.; Geissner, A.; Anish, C.; Seeberger, P.H. Chemical synthesis elucidates the immunological importance of a pyruvate modification in the capsular polysaccharide of Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 4. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 10016–10019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berti, F.; Ricco, D.R.; Rappuoli, R. Role of O-acetylation in the immunogenicity of bacterial polysaccharide vaccines. Molecules 2018, 23, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, S.G. Bacterial lipopolysaccharides—Themes and variations. Prog. Lipid Res. 1996, 35, 283–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, J. Bacterial exopolysaccharides: Chemical structures, gene clusters and genetic engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 173, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, R.N.; Liu, L.; Boons, G.J. 4,6-O-Pyruvyl ketal modified N-acetylmannosamine of the secondary cell wall polysaccharide of Bacillus anthracis is the anchoring residue for its surface layer proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 17079–17085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michon, F.; Huang, C.H.; Farley, E.K.; Hronowski, L.; Fusco, P.C. Structure activity studies on group C meningococcal polysaccharide-protein conjugate vaccines: Effect of O-acetylation on the nature of the protective epitope. Dev. Biol. 2000, 103, 151–160. [Google Scholar]
- Fusco, P.C.; Farley, E.K.; Huang, C.H.; Moore, S.; Michon, F. Protective meningococcal capsular polysaccharide epitopes and the role of O acetylation. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2007, 14, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Li, L.; Tian, G.; Ding, M.; Zhu, S.; Song, W.; Hu, J.; Seeberger, P.H.; Yin, J. Chemical synthesis and antigenicity evaluation of Shigella dysenteriae serotype 10 O-antigen tetrasaccharide containing a (S)-4,6-O-pyruvyl ketal. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 21068–21079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, L.L.; Perry, M.B.; Crump, E.M.; Kay, W.W. Structural characterization of the lipopolysaccharide O-polysaccharide antigen produced by Flavobacterium columnare ATCC 43622. Eur. J. Biochem. 2003, 270, 3440–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knirel, Y.A.; Kochetkov, N.K. The structure of lipopolysaccharides of Gram-negative bacteria. III. The structure of O-antigens. Biochemistry 1994, 59, 1325–1383. [Google Scholar]
- Jansson, P.E.; Lnngren, J.; Widmalm, G.; Leontein, K.; Tiller, P.R. Structural studies of the O-antigen polysaccharides of Klebsiella O5 and Escherichia coli O8. Carbohydr. Res. 1985, 145, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Knirel, Y.A.; Feng, L.; Perepelov, A.V.; Senchenkova, S.Y.N.; Wang, Q.; Reeves, P.R.; Wang, L. Structure and genetics of Shigella O antigens. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 32, 627–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knirel, Y.A.; Paramonov, N.A.; Vinogradov, E.V.; Shashkov, A.S.; Kochetkov, N.K.; Sidorczyk, Z.; Swierzko, A. Structure of the O-specific polysaccharide of Proteus penneri 62 containing 2-acetamido-3-O-[(S)-1-carboxyethyl]-2-deoxy-D-glucose (N-acetylisomuramic acid). Carbohydr. Res. 1992, 235, C19–C23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashkov, A.S.; Kocharova, N.A.; Toukach, F.V.; Kachala, V.V.; Knirel, Y.A. 2,4-Dihydroxypentanoic acids: New non-sugar components of bacterial polysaccharides. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2008, 3, 1625–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenyon, J.J.; Speciale, I.; Hall, R.M.; De Castro, C. Structure of repeating unit of the capsular polysaccharide from Acinetobacter baumannii D78 and assignment of the K4 gene cluster. Carbohydr. Res. 2016, 434, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashkov, A.S.; Senchenkova, S.N.; Vinogradov, E.V.; Zatonsky, G.V.; Knirel, Y.A.; Literacka, E.; Kaca, W. Full structure of the O-specific polysaccharide of Proteus mirabilis O24 containing 3,4-O-[(S)-1-carboxyethylidene]-d-galactose. Carbohydr. Res. 2000, 329, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.; Currie, F.; Forster, M.J. Nmr and conformational analysis of the capsular polysaccharide from Streptococcus pneumoniae type 4. Carbohydr. Res. 1991, 221, 95–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolaev, A.V.; Botvinko, I.V.; Ross, A.J. Natural phosphoglycans containing glycosyl phosphate units: Structural diversity and chemical synthesis. Carbohydr. Res. 2007, 342, 297–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, U.; Lycknert, K.; Stenutz, R.; Weintraub, A.; Widmalm, G. Structural analysis of the O-antigen polysaccharide from Escherichia coli O152. Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 340, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, N.M.; Kreisman, L.S.C.; Stupak, J.; MacLean, L.L.; Cobb, B.A.; Richards, J.C. Structural characterization and MHCII-dependent immunological properties of the zwitterionic O-chain antigen of Morganella morganii. Glycobiology 2011, 21, 1266–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanowska, E. Immunochemical aspects of Hafnia alvei O antigens. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2000, 27, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenne, L.; Lindberg, B.; Petersson, K.; Katzenellenbogen, E.; Romanowska, E. Structural studies of the O-specific side-chains of the Shigella sonnei phase I lipopolysaccharide. Carbohydr. Res. 1980, 78, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Ding, M.; Tian, G.; Zou, X.; Fu, J.; Hu, J.; Yin, J. Chemical approaches towards installation of rare functional groups in bacterial surface glycans. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2022, 20, 401–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzianabos, A.; Wang, J.Y.; Kaspera, D.L. Biological chemistry of immunomodulation by zwitterionic polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Res. 2003, 338, 2531–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Perepelov, A.V.; Quan, W.; Senchenkova, S.N.; Liu, B.; Shevelev, S.D.; Guo, X.; Shashkov, A.S.; Chen, W.; Wang, L. Structural and genetic characterization of the O-antigen of Escherichia coli O161 containing a derivative of a higher acidic diamino sugar, legionaminic acid. Carbohydr. Res. 2010, 345, 1581–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbatsky, N.P.; Shashkov, A.S.; Widmalm, G.; Knirel, Y.A.; Zych, K.; Sidorczyk, Z. Structure of the O-specific polysaccharide of Proteus penneri strain 25 containing N-(L-alanyl) and multiple O-acetyl groups in a tetrasaccharide repeating unit. Carbohydr. Res. 1997, 298, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, M.; Asai, Y.; Jinno, T.; Adachi, S.; Kusumoto, S.; Ogawa, T. Structural elucidation of polysaccharide part of glycoconjugate from Treponema medium ATCC 700293. Eur. J. Biochem. 2003, 270, 2671–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocharova, N.A.; Senchenkova, S.N.; Kondakova, A.N.; Gremyakov, A.I.; Zatonsky, G.V.; Shashkov, A.S.; Knirel, Y.A.; Kochetkov, N.K. D- and L-Aspartic acids: New non-sugar components of bacterial polysaccharides. Biochemistry 2004, 69, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitriev, B.A.; Lvov, V.; Tochtamysheva, N.V.; Shashkov, A.S.; Jann, K. Cell-wall lipopolysaccharide of Escherichia coli O114:H2. Structure of the polysaccharide chain. Eur. J. Biochem. 1983, 134, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komandrova, N.A.; Isakov, V.V.; Tomshich, S.V.; Romanenko, L.A.; Shashkov, A.S. Structure of an acidic O-specific polysaccharide of the marine bacterium Pseudoalteromonas agarivorans KMM 232 (R-form). Biochemistry 2010, 75, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perepelov, A.V.; Kocharova, N.A.; Knirel, Y.A.; Jansson, P.E.; Weintraub, A. Structure of the O-polysaccharide of Vibrio cholerae O43 containing a new monosaccharide derivative, 4-(N-acetyl-L-allothreonyl) amino-4,6-dideoxy-D-glucose. Carbohydr. Res. 2011, 346, 430–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eguchi, H.; Kaya, S.; Araki, Y.; Kojima, N.; Yokota, S.I. Structure of the O-polysaccharide chain of the lipopolysaccharide of Vibrio anguillarum V-123. Carbohydr. Res. 1992, 231, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedziela, T.; Dag, S.; Lukasiewicz, J.; Dzieciatkowska, M.; Jachymek, W.; Lugowski, C.; Kenne, L. Complete lipopolysaccharide of Plesiomonas shigelloides O74:H5 (strain CNCTC 144/92). 1. Structural analysis of the highly hydrophobic lipopolysaccharide, including the O-antigen, its biological repeating unit, the core oligosaccharide, and the linkage between them. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 10422–10433. [Google Scholar]
- Hermansson, K.; Jansson, P.E.; Holme, T.; Gustavsson, B. Structural studies of the Vibrio cholerae O: 5 O-antigen polysaccharide. Carbohydr. Res. 1993, 248, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejewska, A.; Lukasiewicz, J.; Niedziela, T.; Szewczuk, Z.; Lugowski, C. Structural analysis of the O-specific polysaccharide isolated from Plesiomonas shigelloides O51 lipopolysaccharide. Carbohydr. Res. 2009, 344, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieretti, G.; Corsaro, M.M.; Lanzetta, R.; Parrilli, M.; Canals, R.; Merino, S.; Tomás, J.M. Structural studies of the O-chain polysaccharide from Plesiomonas shigelloides strain 302–73 (serotype O1). Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 2008, 3149–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, L.L.; Vinogradov, E.; Crump, E.M.; Perry, M.B.; Kay, W.W. The structure of the lipopolysaccharide O-antigen produced by Flavobacterium psychrophilum (259-93). Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 2710–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valueva, O.A.; Zdorovenko, E.L.; Varbanets, L.D.; Shubchinskiy, V.V.; Shashkov, A.S.; Knirel, Y.A. Structural studies of the O-polysaccharide of Pragia fontium 97U124 containing 2-acetamido-2,4,6-trideoxy-4-(D-glyceroyl)amino-D-glucose. Carbohydr. Res. 2012, 355, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondakova, A.N.; Lindner, B.; Fudala, R.; Senchenkova, S.N.; Moll, H.; Shashkov, A.S.; Kaca, W.; Zähringer, U.; Knirel, Y.A. New stuctures of the O-specific polysaccharides of Proteus. Part 4. Polysaccharides containing unusual acidic N-acyl derivatives of 4-amino-4,6-dideoxy-D-glucose. Biochemistry 2004, 69, 1034–1043. [Google Scholar]
- Kilcoyne, M.; Shashkov, A.S.; Knirel, Y.A.; Gorshkova, R.P.; Nazarenko, E.L.; Ivanova, E.P.; Gorshkova, N.M.; Senchenkova, S.N.; Savage, A.V. The structure of the O-polysaccharide of the Pseudoalteromonas rubra ATCC 29570T lipopolysaccharide containing a keto sugar. Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 340, 2369–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caroff, M.; Brisson, J.-R.; Martin, A.; Karibian, D. Structure of the Bordetella pertussis 1414 endotoxin. FEBS Lett. 2000, 477, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.D.; Kocíncová, D.; Westman, E.L.; Lam, J.S. Lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Innate Immun. 2009, 15, 261–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torzewska, A.; Kocharova, N.A.; Zatonsky, G.V.; Aleksandra, B.; Bystrova, O.V.; Shashkov, A.S.; Knirel, Y.A.; Antoni, R. Structure of the O-polysaccharide and serological cross-reactivity of the Providencia stuartii O33 lipopolysaccharide containing 4-(N-acetyl-D-aspart-4-yl)amino-4,6-dideoxy-D-glucose. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2004, 41, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovchinnikova, O.G.; Valueva, O.A.; Kocharova, N.A.; Arbatsky, N.P.; Maszewska, A.; Zablotni, A.; Shashkov, A.S.; Rozalski, A.; Knirel, Y.A. Structure of the O-polysaccharide of Providencia alcalifaciens O35 containing an N-[(S)-1-carboxyethyl]-L-alanine (alanopine) derivative of 4-amino-4, 6-dideoxyglucose. Carbohydr. Res. 2013, 375, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perepelov, A.V.; Liu, B.; Shevelev, S.D.; Senchenkova, S.N.; Shashkov, A.S.; Lu, F.; Knirel, Y.A.; Lei, W. Relatedness of the O-polysaccharide structures of Escherichia coli O123 and Salmonella enterica O58, both containing 4,6-dideoxy-4-{N-[(S)-3-hydroxybutanoyl]-D-alanyl}amino-D-glucose; revision of the E. coli O123 O-polysaccharide structure. Carbohydr. Res. 2010, 345, 825–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindberg, B. Components of bacterial polysaccharides. Adv. Carbohydr. Chem. Biochem. 1990, 48, 279–318. [Google Scholar]
- Knirel, Y.A.; Vinogradov, E.V.; Shashkov, A.S.; Dmitriev, B.A.; Kochetkov, N.K.; Stanislavsky, E.S.; Mashilova, G.M. Somatic antigens of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The structure of the O-specific polysaccharide chains of lipopolysaccharides of P. aeruginosa serogroup O4 (Lányi) and related serotype O6 (Habs) and immunotype 1 (Fisher). Eur. J. Biochem. 1985, 150, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branefors-Helander, P.; Kenne, L.; Lindberg, B.; Petersson, K.; Unger, P. Structural studies of the capsular polysaccharide elaborated by Haemopltilus influenzae type d. Carbohydr. Res. 1981, 97, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradov, E.V.; Krajewska-Pietrasik, D.; Kaca, W.; Shashkov, A.S.; Kochetkov, N.K. Structure of Proteus mirabilis O27 O-specific polysaccharide containing amino acids and phosphoethanolamine. Eur. J. Biochem. 1989, 185, 645–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radziejewska-Lebrecht, J.; Shashkov, A.S.; Vinogradov, E.V.; Grosskurth, H.; Bartodziejska, B.; Rozalski, A.; Kaca, W.; Kononov, L.O.; Chernyak, A.Y.; Mayer, H.; et al. Structure and epitope characterisation of the O-specific polysaccharide of Proteus mirabilis O28 containing amides of D-galacturonic acid with L-serine and L-lysine. Eur. J. Biochem. 1995, 230, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salimath, P.V.; Tharanathan, R.N.; Weckesser, J.; Mayer, H. The structure of the polysaccharide moiety of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides ATCC 17023 lipopolysaccharide. Eur. J. Biochem. 1984, 144, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenutz, R.; Weintraub, A.; Widmalm, G. The structures of Escherichia coli O-polysaccharide antigens. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 30, 382–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansson, P.E.; Lindberg, B.; Widmalm, G.; Dutton, G.G.S.; Lim, A.V.S.; Sutherland, I.W. Structural studies of the capsular polysaccharides from Klebsiella types 8 and 82, a reinvestigation. Carbohydr. Res. 1988, 175, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocharova, N.A.; Zatonsky, G.V.; Torzewska, A.; Macieja, Z.; Bystrova, O.V.; Shashkov, A.S.; Knirel, Y.A.; Rozalski, A. Structure of the O-specific polysaccharide of Providencia rustigianii O14 containing Nε-[(S)-1-carboxyethyl]-Nα-(D-galacturonoyl)-L-lysine. Carbohydr. Res. 2003, 338, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudlavalleti, S.K.; Datta, A.K.; Tzeng, Y.L.; Noble, C.; Carlson, R.W.; Stephens, D.S. The Neisseria meningitidis serogroup A capsular polysaccharide O-3 and O-4 acetyltransferase. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 42765–42773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, D.S.; Lynn, F.; Lee, C.H.; Frasch, C.E.; Bash, M.C. Effect of O acetylation of Neisseria meningitidis serogroup A capsular polysaccharide on development of functional immune responses. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 3707–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardotti, A.; Averani, G.; Berti, F.; Berti, S.; Carinci, V.; D’Ascenzi, S.; Fabbri, B.; Giannini, S.; Giannozzi, A.; Magagnoli, C. Physicochemical characterisation of glycoconjugate vaccines for prevention of meningococcal diseases. Vaccine 2008, 26, 2284–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiebig, T.; Freiberger, F.; Pinto, V.; Romano, M.R.; Black, A.; Litschko, C.; Bethe, A.; Yashunsky, D.; Adamo, R.; Nikolaev, A.; et al. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of components of the capsule biosynthesis complex of Neisseria meningitidis serogroup A: Toward in vitro vaccine production. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 19395–19407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, P.; Dello Iacono, L.; Gimeno, A.; Biolchi, A.; Romano, M.R.; Arda, A.; Bernardes, G.J.L.; Jimenez-Barbero, J.; Berti, F.; Rappuoli, R.; et al. Structure of a protective epitope reveals the importance of acetylation of Neisseria meningitidis serogroup A capsular polysaccharide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 29795–29802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarvis, F.G.; Mesenko, M.T.; Martin, D.G.; Perrine, T.D. Physiochemical properties of the Vi antigen before and after mild alkaline hydrolysis. J. Bacteriol. 1967, 94, 1406–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szewczyk, B.; Taylor, A. Immunochemical properties of Vi antigen from Salmonella typhi Ty2: Presence of two antigenic determinants. Infect. Immun. 1980, 29, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szu, S.C.; Li, X.R.; Stone, A.L.; Robbins, J.B. Relation between structure and immunologic properties of the Vi capsular polysaccharide. Infect. Immun. 1991, 59, 4555–4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitri, K.; Kuttel, M.M.; De Benedetto, G.; Lockyer, K.; Gao, F.; Hansal, P.; Rudd, T.R.; Beamish, E.; Rijpkema, S.; Ravenscroft, N.; et al. O-acetylation of typhoid capsular polysaccharide confers polysaccharide rigidity and immunodominance by masking additional epitopes. Vaccine 2019, 37, 3866–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C. Revised structures for the capsular polysaccharides from Staphylococcus aureus Types 5 and 8 components of novel glycoconjugate vaccines. Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 340, 1097–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, I.L.; Pavliak, V.; Timofeyeva, Y.; Liu, Y.; Singer, C.; Anderson, A.S. O-acetylation is essential for functional antibody generation against Staphylococcus aureus capsular polysaccharide. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2018, 14, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattom, A.; Matalon, A.; Buerkert, J.; Taylor, K.; Damaso, S.; Boutriau, D. Efficacy profile of a bivalent Staphylococcus aureus glycoconjugated vaccine in adults on hemodialysis: Phase III randomized study. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2015, 11, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinefield, H.; Black, S.; Fattom, A.; Horwith, G.; Rasgon, S.; Ordonez, J.; Yeoh, H.; Law, D.; Robbins, J.B.; Schneerson, R.; et al. Use of a Staphylococcus aureus conjugate vaccine in patients receiving hemodialysis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.; Lemercinier, X. Full NMR assignment and revised structure for the capsular polysaccharide from Streptococcus pneumoniae type 15B. Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 340, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajam, G.; Carlone, G.M.; Romero-Steiner, S. Functional antibodies to the O-acetylated Pneumococcal serotype 15B capsular polysaccharide have low cross-reactivities with serotype 15C. Clin. Vaccin. Immunol. 2007, 14, 1223–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calix, J.J.; Nahm, M.H.; Zartler, E.R. Elucidation of structural and antigenic properties of pneumococcal serotype 11A, 11B, 11C, and 11F polysaccharide capsules. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 5271–5278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.X.; Duda, K.A.; Elverdal, P.L.; Skovsted, I.C.; Kjeldsen, C.; Teze, D.; Duus, J.Ø. Structural, biosynthetic and serological cross-reactive elucidation of capsular polysaccharides from Streptococcus pneumoniae serogroup 28. Carbohyd. Polym. 2021, 254, 117323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frasa, H.; Procee, J.; Torensma, R.; Verbruggen, A.; Algra, A.; Rozenberg-Arska, M.; Kraaijeveld, K.; Verhoef, J. Escherichia coli in bacteremia: O-acetylated K1 strains appear to be more virulent than non-O-acetylated K1 strains. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1993, 31, 3174–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugowski, C.; Jennings, H.J. Structural determination of the capsular polysaccharide of Streptococcus pneumoniae type 18C (56). Carbohydr. Res. 1984, 131, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Serrano, Y.; Garrido, R.; Rodríguez, L.M.; Pedroso, J.; Cardoso, F.; Valdés, Y.; García, D.; Fernández-Santana, V.; Verez-Bencomo, V. Relevance of O-acetyl and phosphoglycerol groups for the antigenicity of Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 18C capsular polysaccharide. Vaccine 2012, 30, 7090–7096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganeshapillai, J.; Vinogradov, E.; Rousseau, J.; Weese, J.S.; Monteiro, M.A. Clostridium difficile cell-surface polysaccharides composed of pentaglycosyl and hexaglycosyl phosphate repeating units. Carbohydr. Res. 2008, 343, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danieli, E.; Lay, L.; Proietti, D.; Berti, F.; Costantino, P.; Adamo, R. First synthesis of C. difficile PS-II Cell wall polysaccharide repeating unit. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamo, R.; Romano, M.R.; Berti, F.; Leuzzi, R.; Tontini, M.; Danieli, E.; Cappelletti, E.; Cakici, O.S.; Swennen, E.; Pinto, V.; et al. Phosphorylation of the synthetic hexasaccharide repeating unit is essential for the induction of antibodies to Clostridium difficile PSII cell wall polysaccharide. ACS Chem. Biol. 2012, 7, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C.; Currie, F. The pneumococcal polysaccharide S4: A structural reassessment. Carbohydr. Res. 1988, 184, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higginbotham, J.D.; Heidelberger, M.; Gotschlich, E.C. Degradation of a Pneumococcal type-specific polysaccharide with exposure of group-specificity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1970, 67, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perepelov, A.V.; Senchenkova, S.N.; Shashkov, A.S.; Knirel, Y.A.; Lu, B.; Feng, L.; Wang, L. A completed structure of the O-polysaccharide from Shigella dysenteriae type 10. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2009, 35, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemercinier, X.; Jones, C. Full 1H NMR assignment and detailed O-acetylation patterns of capsular polysaccharides from Neisseria meningitidis used in vaccine production. Carbohydr. Res. 1996, 296, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glode, M.P.; Lewin, E.B.; Ann, S.; Le, C.T.; Gotschlich, E.C.; Robbins, J.B. Comparative immunogenicity of vaccines prepared from capsular polysaccharides of group C Neisseria meningitidis O-acetyl-positive and O-acetyl-negative variants and Escherichia coli K92 in adult volunteers. J. Infect. Dis. 1979, 139, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltola, H.; Safary, A.; Käyhty, H.; Karanko, V.; André, F.E. Evaluation of two tetravalent (ACYW135) meningococcal vaccines in infants and small children: A clinical study comparing immunogenicity of O-acetyl-negative and O-acetyl-positive group C polysaccharides. Pediatrics 1985, 76, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhoff, M.C.; Lewin, E.B.; Gotschlich, E.C.; Robbins, J.B. Group C Neisseria meningitidis variant polysaccharide vaccines in children. Infect. Immun. 1981, 34, 144–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, A.K.; Jennings, H.J.; Kenny, C.P.; Martin, A.; Smith, I.C. Structural determination of the polysaccharide antigens of Neisseria meningitidis serogroups Y, W-135, and BO1. Can. J. Biochem. 1976, 54, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Requirement for meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine (Requirements for Biological substances No.23) Addendum 1980, TRS 658, Annexure 6. 1980. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/meningococcal-polysaccharide-vaccine-annex-6-trs-no-658 (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Gudlavalleti, S.K.; Lee, C.H.; Norris, S.E.; Paul-Satyaseela, M.; Vann, W.F.; Frasch, C.E. Comparison of Neisseria meningitidis serogroup W135 polysaccharide-tetanus toxoid conjugate vaccines made by periodate activation of O-acetylated, non-O-acetylated and chemically de-O-acetylated polysaccharide. Vaccine 2007, 46, 7972–7980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Bohach, G.A.; Shiloach, J.; Norris, S.E.; Freedberg, D.I.; Deobald, C.; Coxon, B.; Robbins, J.B.; Schneerson, R. Conjugates of group A and W135 capsular polysaccharides of Neisseria meningitidis bound to recombinant Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin C1: Preparation, physicochemical characterization, and immunological properties in mice. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 7887–7893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, M.B.; Daoust, V.; Carlo, D.J. The specific capsular polysaccharide of Streptococcus pneumoniae type 9V. Can. J. Biochem. 1981, 59, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNeely, T.B.; Staub, J.M.; Rusk, C.M.; Blum, M.J.; Donnelly, J.J. Antibody responses to capsular polysaccharide backbone and O-acetate side groups of Streptococcus pneumoniae type 9V in humans and rhesus macaques. Infect. Immun. 1998, 66, 3705–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, C.J.; Edwards, M.S. Group B streptococcal conjugate vaccines. Arch. Dis. Child. 2003, 88, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.L.; Nizet, V.; Varki, A. Discovery and characterization of sialic acid O-acetylation in group B Streptococcus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11123–11128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiman, S.; Uchiyama, S.; Lin, F.Y.; Chaffin, D.; Varki, A.; Nizet, V.; Lewis, A.L. O-acetylation of sialic acid on group B Streptococcus inhibits neutrophil suppression and virulence. Biochem. J. 2010, 428, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pannaraj, P.S.; Edwards, M.S.; Ewing, K.T.; Lewis, A.L.; Rench, M.A.; Baker, C.J. Group B streptococcal conjugate vaccines elicit functional antibodies independent of strain O-acetylation. Vaccine 2009, 27, 4452–4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| O-Modified Groups | Representative Bacterial Polysaccharides | Glycan | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| acetyl | →4)-β-D-GlcpNAc3RA-(1→4)-α-L-FucpNAm3R-(1→3)-α-D-Sugp-(1→ | Flavobacterium columnare ATCC 43622 O-antigen | [13] |
| propanoyl | β-L-Quip3NAc-(1-[→4)-β-L-Quip3NAc-(1→4)-[α-D-QuipNAc3/4R-(1→2)]-β-L-Quip3NAc-(1-]→ | Vibrio anguillarum O-antigen | [14] |
| methyl | α-D-Manp3OR-(1-[→3)-β-D-Manp-(1→2)-α-D-Manp-(1→2)-α-D-Manp-(1-]→ | Klebsiella O5 and Escherichia coli O8 O-antigen | [15] |
| (S)-1-carboxyethyl | →3)-β-D-GlcpNAc6OAc-(1→6)-β-D-GlcpNAc3OR-(1→3)-α-D-Galp-(1→ | Proteus penneri 62 O-antigen | [17] |
| 2,4-dihydroxypentanoic acid 2-ethers | →4)-β-D-GalpNAc-(1→3)-β-D-GalpNAc-(1→3)-[β-D-Manp4OR-(1→4)]-α-D-Galp-(1→ | Providencia alcalifaciens O31 O-antigen | [18] |
| 4,6-O-pyruvate ketal | →3)-α-D-QuipNAc-(1→4)-[α-D-GalpNAc4,6R-(1→6)]-α-D-GalpNAc-(1→4)-α-D-GalpNAcA-(1→ | Acinetobacter baumannii D78 CPS | [19] |
| 3,4-O-pyruvate ketal | →3)-β-D-GlcpNAc-(1→4)-[β-D-Galp3,4R-(1→3)]-β-D-GalpNAc-(1→4)-β-D-GlcpNAc-(1→ | P. mirabilis O24 O-antigen | [20] |
| 2,3-O-pyruvate ketal | →3)-β-D-ManpNAc-(1→3)-α-L-FucpNAc-(1→3)-α-D-GalpNAc-(1→4)-α-D-Galp2,3R-(1→ | Streptococcus pneumoniae ST4 CPS | [21] |
| phosphoric ester | →6)-α-D-Glcp-(1→2)-β-D-Glcp-(1→3)-β-D-GlcpNAc-(1→3)-[β-L-Rhap-(1→4)]-α-D-GlcpNAc-(1-PO3H→ | E. coli O152 O-antigen | [23] |
| glycerol-P- and choline-P- | →4)-[α-D-GalpN-(1→3)]-β-D-Galp2PCho-(1→3)-β-D-GalpNAc6OAc-(1→3)-Gro-1-P-(O→ | Morganella morganii O-antigen | [24] |
| N-Modified Groups | Representative Bacterial Polysaccharides | Glycan | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| free amino | →4)-α-L-AltpNAcA-(1→3)-β-D-FucpNAc4N-(1→ | Shigella sonnei phase I O-antigen | [26] |
| acetyl | →4)-α-D-GalpNR-(1→4)-β-D-GlcpNR3NRA-D-(1→3)-α-D-FucpNR-(1→3)-α-D-QuipNR-(1→ | Pseudomonas aeruginosa O1 O-antigen | [46] |
| formyl | →4)-α-Psep4OAc5NAc7NR-(2→4)-β-D-Xylp-(1→3)-α-D-FucpNAc-(1→ | Pseudomonas aeruginosa O8 O-antigen | [46] |
| acetimidoyl | →4)-β-D-ManpNAc3NRA-(1→4)-β-D-ManpNAc3NAcA-(1→3)-α-D-FucpNAc-(1→ | Pseudomonas aeruginosa O5 O-antigen | [46] |
| D-alanyl | →8)-α-Legp5NAc7NR-(2→4)-β-D-GlcpA-(1→3)-β-D-GlcpNAc-(1→ | E. coli O161 O-antigen | [29] |
| L-alanyl | →4)-β-D-GlcpA-(1→3)-β-D-GlcpNAc-(1→6)-[α-D-GlcpA-(1→4)]-β-D-GlcpNR-(1→ | Proteus penneri 25 O-antigen | [30] |
| D-aspartyl | →4)-β-D-GlcpNAc3NAcA-(1→4)-β-D-ManpNAc3NA(L-ornithine)-(1→3)-β-D-GlcpNAc-(1→3)-α-D-Fucp4NR(1→ | Treponema medium ATCC 700293 glycoconjugate | [31] |
| N-acetyl-glycyl | →3)-β-D-Quip4NR-(1→4)-α-D-GalpNAc3OAcAN-(1→4)-α-D-GalpNAcA-(1→3)-α-D-GlcpNAc-(1→ | S. dysenteriae D7 O-antigen | [15] |
| N-acetyl-D-aspartyl | →6)-α-D-GlcpNAc-(1→4)-α-D-GalpA-(1→3)-α-D-GlcpNAc-(1→3)-β-D-Quip4NR-(1→ | Providencia stuartii O33 O-antigen | [47] |
| N-acetyl-L-aspartyl | →3)-β-D-GlcpNAc-(1→3)-[β-D-Quip4NR-(1→4)]-β-D-Galp-(1→6)-β-D-GlcpNAc-(1→3)-β-D-Galp-(1→ | Providencia alcalifaciens O4 O-antigen | [32] |
| N-acetyl-L-seryl | →3)-α-D-GlcpNAc-(1→4)-β-D-Quip3NR-(1→3)-β-D-Ribf-(1→4)-β-D-Gal-(1→ | Escherichia coli O114 O-antigen | [33] |
| N-acetyl-L-threonyl | →3)-α-D-FucpNR-(1→3)-[β-D-ManpNAcA-(1→4)]-α-D-GalpNAc-(1→3)-α-L-Rhap-(1→ | Pseudoalteromonas agarivorans KMM 232 O-antigen | [34] |
| N-acetyl-L-allothreonyl | →3)-β-D-Quip4NR-(1→3)-α-D-GalpNAcA-(1→4)-α-D-GalpNAc-(1→3)-α-D-QuipNAc-(1→ | V. cholerae O43 O-antigen | [35] |
| (2S,4S)-N-[1-carboxyethyl]-alanyl | →4)-[β-D-Quip4NR-(1→6)]-α-D-GalpNAc-(1→6)-α-D-Glcp-(1→4)-β-D-GlcpA-(1→3)-β-D-GalpNAc-(1→ | P. alcalifaciens O35 O-antigen | [48] |
| N-[(S)-3-hydroxybutyryl]-D-alanyl | →3)-β-D-Quip4NR-(1→6)-α-D-GlcpNAc-(1→3)-α-L-QuipNAc-(1→3)-α-D-GlcpNAc3OAc-(1→ | E. coli O123 O-antigen | [49] |
| 2,4-dihydroxy-3,3,4-trimethylpyroglutamoyl | →3)-α-D-GalpNAcAN-(1→4)-α-D-GalpNFoA-(1→3)-α-D-QuipNAc-(1→3)-β-D-ViopNR-(1→ | Vibrio anguillarum V-123 O-antigen | [36] |
| 3-hydroxy-2,3-dimethyl-5-oxoprolyl | →2)-β-D-Quip3NR-(1→3)-α-L-Rhap2OAc-(1→3)-α-D-FucpNAc-(1→ | P. shigelloides O74 O-antigen | [37] |
| (R,R)-3-hydroxy-3-Methyl-5-oxoprolyl | →3)-β-D-QuipNAc4NAc-(1→4)-[α-D-Fucp3NR-(1→3)]-β-D-ManpNAcA-(1→ | Vibrio cholerae O5 O-antigen | [38] |
| (R)-3-hydroxybutyryl | →4)-β-D-GlcpNAc3NRA-(1→4)-α-L-FucpNAm3OAc-(1→3)-α-D-QuipNAc-(1→ | P. shigelloides O51 O-antigen | [39] |
| (S)-3-hydroxybutyryl | →3)-α-L-PnepNAc4OAc-(1→4)-α-L-FucpNAc-(1→4)-α-L-FucpNAc-(1→4)-α-L-FucpNAc-(1→3)-β-D-QuipNAc4NR(1→ | Plesiomonas shigelloides O1 O-antigen | [40] |
| (3S,5S)-3,5-dihydroxyhexanoyl | →4)-α-L-FucpNAc-(1→3)-α-D-Quip2NAc4NR-(1→2)-α-L-Rhap-(1→ | Flavobacterium psychrophilum 259-93 O-antigen | [41] |
| D-glyceroyl | →3)-α-L-FucpNAc-(1→3)-α-L-FucpNAc-(1→3)-β-D-QuipNAc4NR-(→ | Pragia fontium 97U124 O-antigen | [42] |
| L-maloyl | →4)-α-L-GalpNAm3OAcA-(1→3)-α-Sugp-(1→4)-β-D-GlcpNAc3NRA-(1→ | Pseudoalteromonas rubra ATCC 29570T O-antigen | [44] |
| methyl | α-D-GlcpNAc-(1→4)-β-D-Man2NAc3AcA-(1→3)-β-L-Fucp2NAc4NR-(1→6)-[α-LD-Hepp-(1→4)]-α-D-GlcpNAc-(1→ | Bordetella pertussis LPS | [45] |
| Carboxyl-Modified Groups | Representative Bacterial Polysaccharides | Glycan | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| carboxamide | →3)-α-L-Rhap-(1→4)-α-D-GalpNAc3OAcAR-(1→4)-α-D-GalpN(formyl)A-(1→3)-α-D-QuipNAc-(1→ | P. aeruginosa O6 O-antigen | [51] |
| 2-aminopropane-1,3-diol | →3)-β-D-GlcpNAc-(1→2)-β-D-Galp3OAc4OAcA6NR-(1→3)-β-D-GalpNAc-(1→4)-β-D-GlcpA-(1→ | Shigella boydii O8 O-antigen | [50] |
| L-alanine/L-serine/L-threonine (2:2:1) | →4)-β-D-GlcpNAc-(1→3)-β-D-ManpNAcA6NR-(1→ | Haemophilus influenzae type d CPS | [52] |
| R1 = L-lysine, R2 = L-alanine | →3)-[β-D-GlcpNAc-(1→4)]-β-D-GlcpA6NR1-(1→3)-α-D-GalpA6NR2-(1→3)-β-D-GlcpNAc-(1→ | Proteus mirabilis O27 O-antigen | [53] |
| R1 = L-serine, R2 = L-lysine | →4)-α-D-GalpA6NR2-(1→4)-α-D-Galp-(1→3)-α-D-Galp4OAcA6NR1-β-D-GlcpNAc-(1→ | Proteus mirabilis O28 O-antigen | [54] |
| L-threonine | →4)-α-D-GlcpA6NR-(1→4)-α-D-GlcpA-(1→4)-α-D-GlcpA-(1→ | Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides ATCC 17023 LPS | [55] |
| D-allothreonine | →4)-α-D-GalpA6NR-(1→2)-α-L-Rhap-(1→2)-β-D-Ribf-(1→4)-β-D-Galp-(1→3)-β-D-GalpNAc-(1→ | Hafni. alvei 1206 O-antigen | [23] |
| L-ornithine | →4)-β-D-GlcpNAc3NAcA-(1→4)-β-D-ManpNAc3NA6NR-(1→3)-β-D-GlcpNAc-(1→3)-α-D-Fucp4NAsp(1→ | Treponema medium ATCC 700293 glycoconjugate | [31] |
| glycine | →4)-α-D-Quip3NAcyl-(1→4)-β-D-Galp-(1→4)-β-D-GlcpNAc-(1→4)-β-D-GlcpA6NR-(1→3)-β-D-GlcpNAc-(1→ | E. coli O91 O-antigen | [56] |
| L-glutamic acid | →3)-β-D-Glcp-(1→3)-[β-D-GlcpA6NR-(1→4)]-β-D-Galp2OAc-(l→3)-α-D-Galp-(l→ | Klebsiella K82 CPS | [57] |
| Nε-[(S)-1-carboxyethyl]-L-lysine | →4)-α-D-GalpNAc-(1→3)-α-D-GlcpNAc-(1→3)-α-D-GalpA6NR-(1→ | Providencia rustigianii O14 O-antigen | [58] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, G.; Qin, C.; Hu, J.; Zou, X.; Yin, J. Effect of Side-Chain Functional Groups in the Immunogenicity of Bacterial Surface Glycans. Molecules 2023, 28, 7112. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28207112
Tian G, Qin C, Hu J, Zou X, Yin J. Effect of Side-Chain Functional Groups in the Immunogenicity of Bacterial Surface Glycans. Molecules. 2023; 28(20):7112. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28207112
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Guangzong, Chunjun Qin, Jing Hu, Xiaopeng Zou, and Jian Yin. 2023. "Effect of Side-Chain Functional Groups in the Immunogenicity of Bacterial Surface Glycans" Molecules 28, no. 20: 7112. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28207112
APA StyleTian, G., Qin, C., Hu, J., Zou, X., & Yin, J. (2023). Effect of Side-Chain Functional Groups in the Immunogenicity of Bacterial Surface Glycans. Molecules, 28(20), 7112. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28207112







