Enhanced Sorption Performance of Natural Zeolites Modified with pH-Fractionated Humic Acids for the Removal of Methylene Blue from Water
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. HA Characterization
2.2. Sorption Kinetics of MB
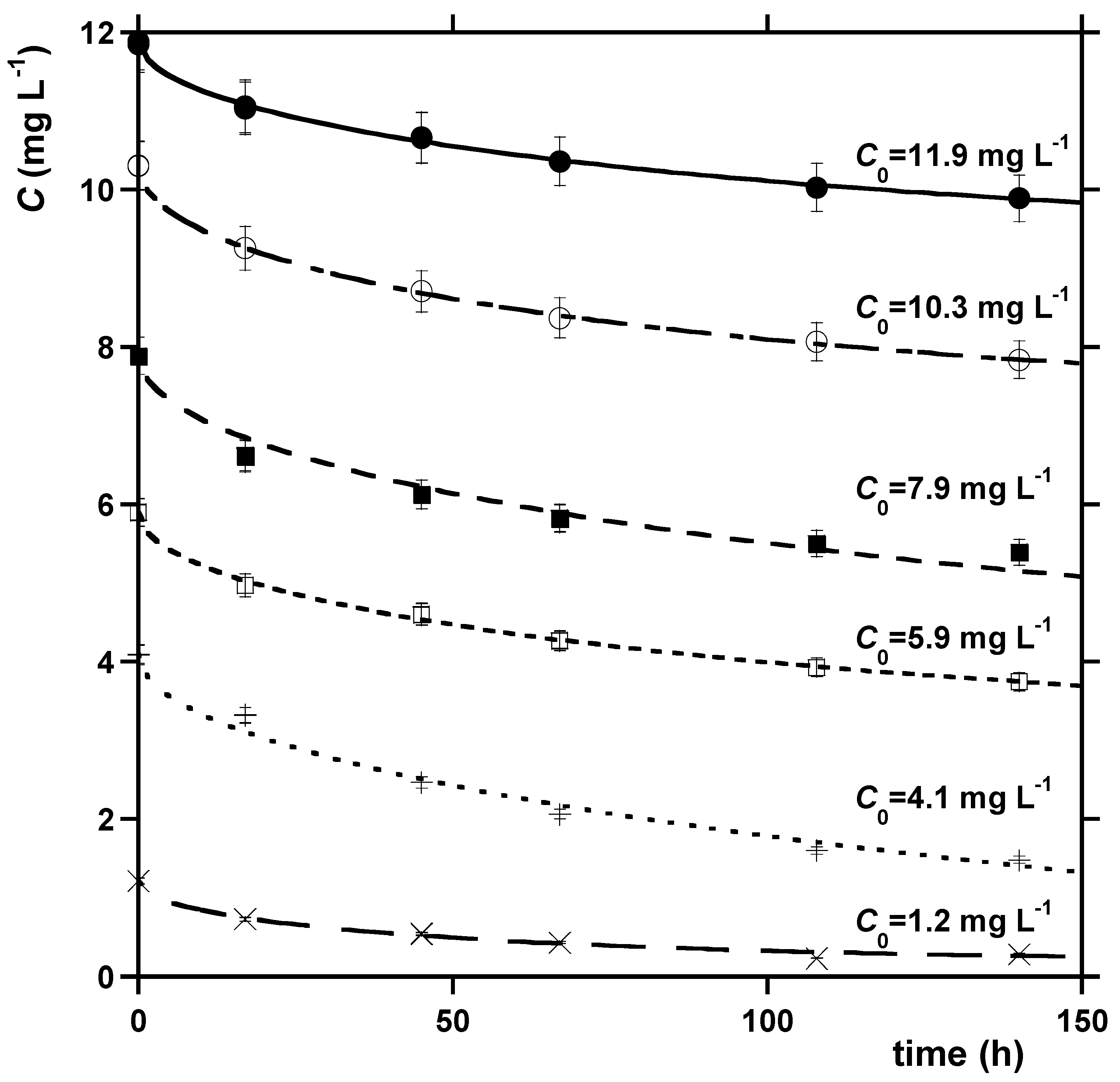
2.2.1. MB Sorption Kinetics on NYT
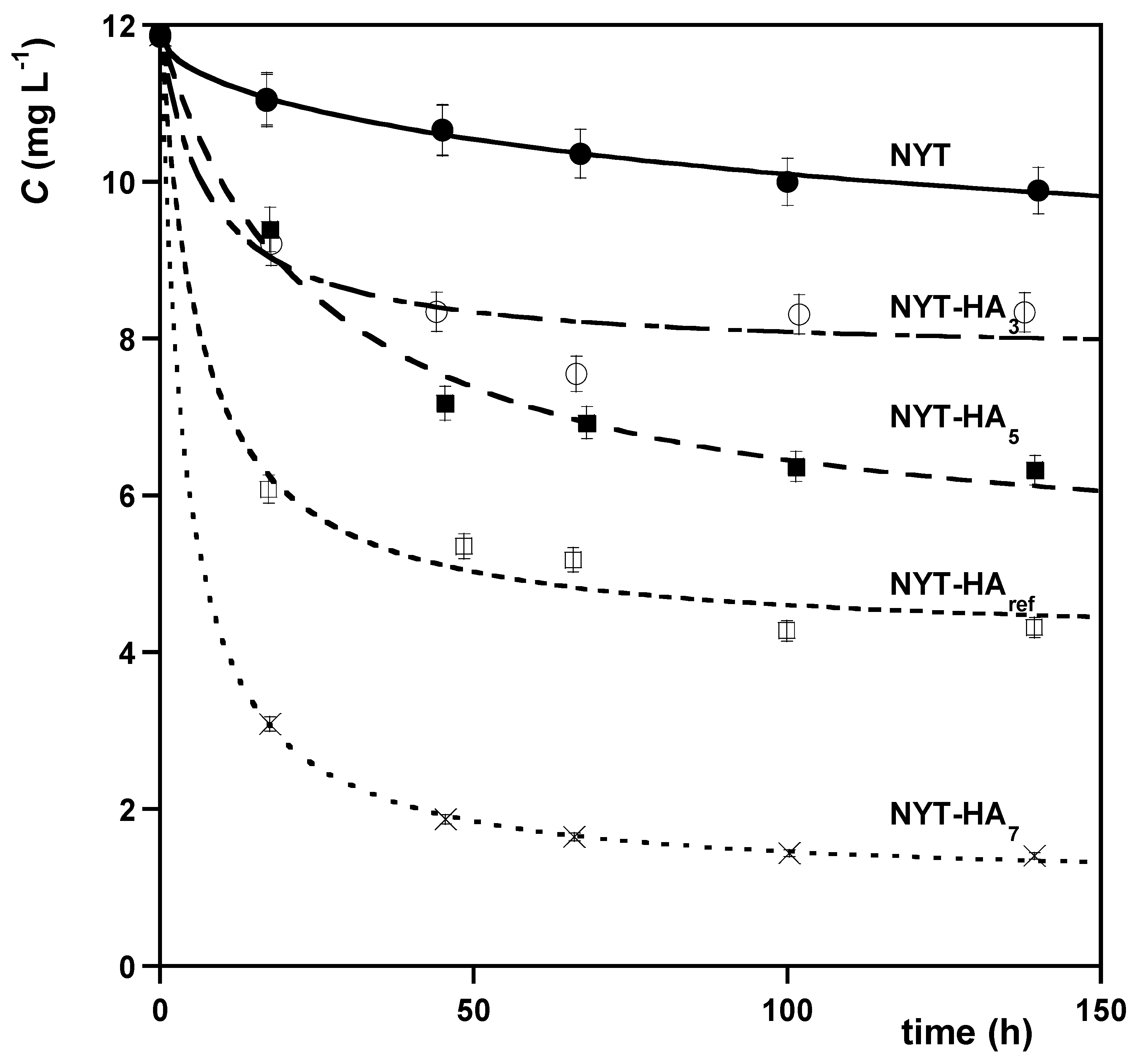
2.2.2. MB Sorption Kinetics on NYT-HA
2.3. Sorption Equilibrium
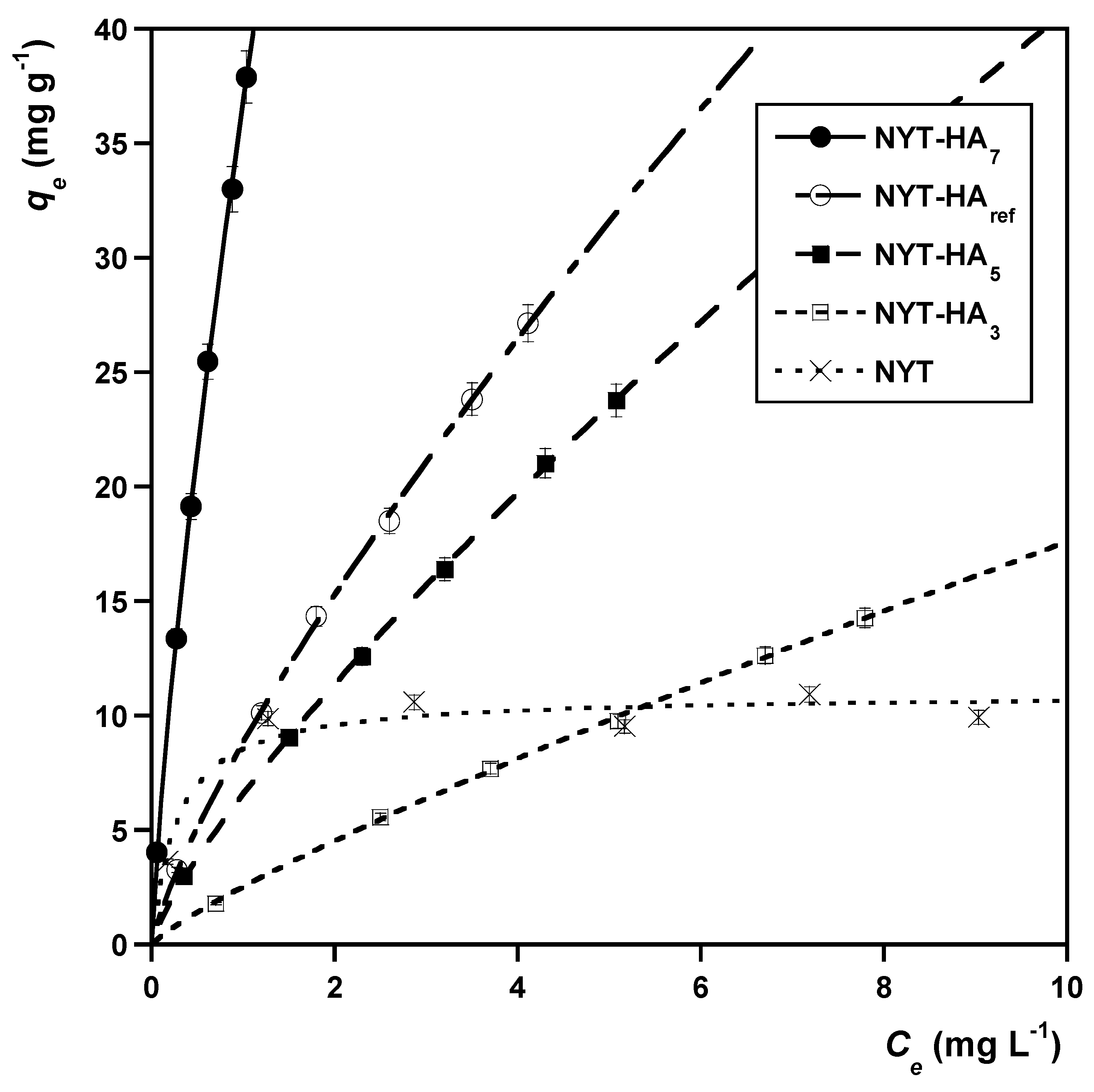
2.3.1. Isotherms of the Sorption of MB onto Natural Zeolite and Natural Zeolite–Humic Acids Adducts: Effect of pH Fractionation
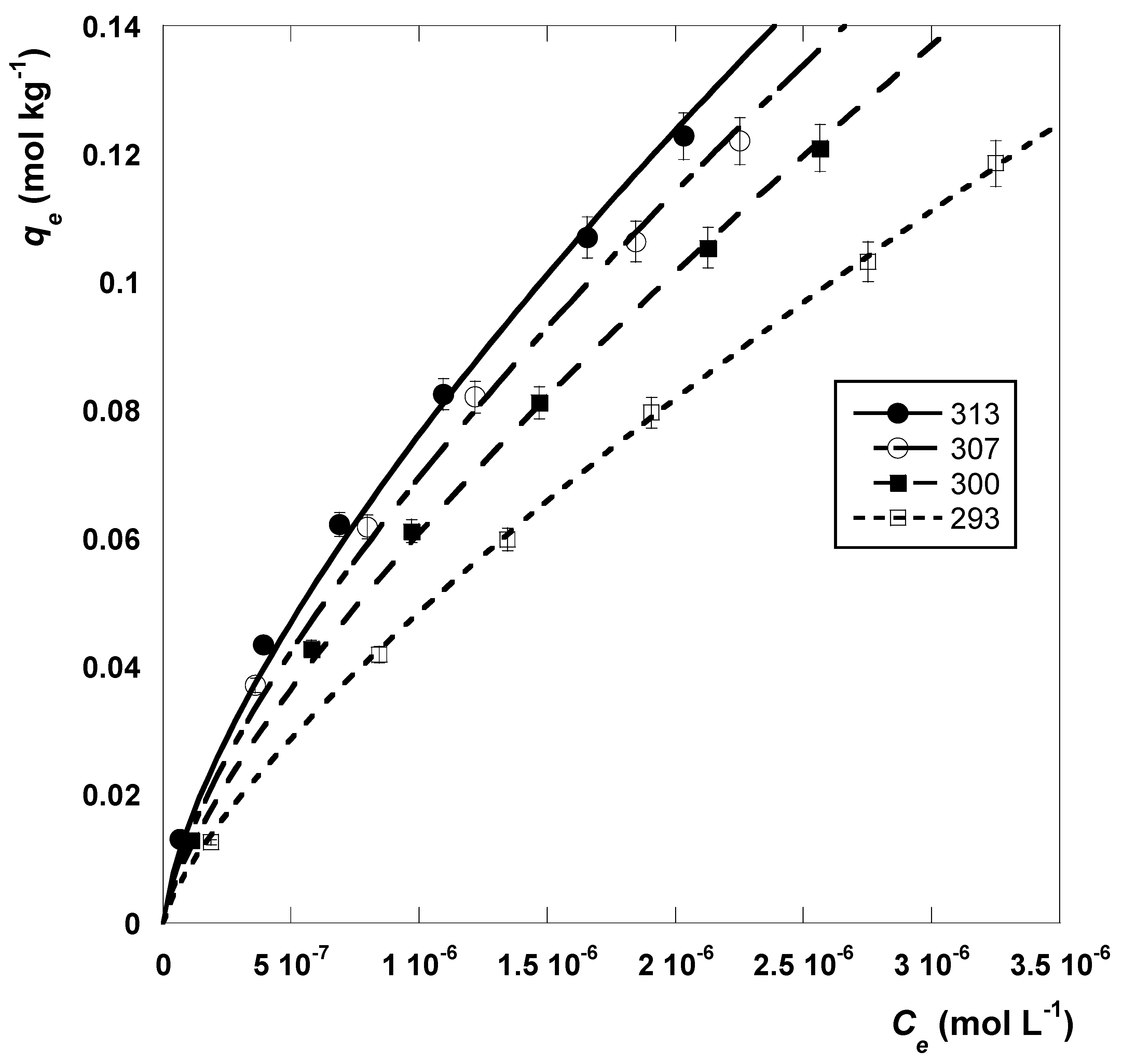
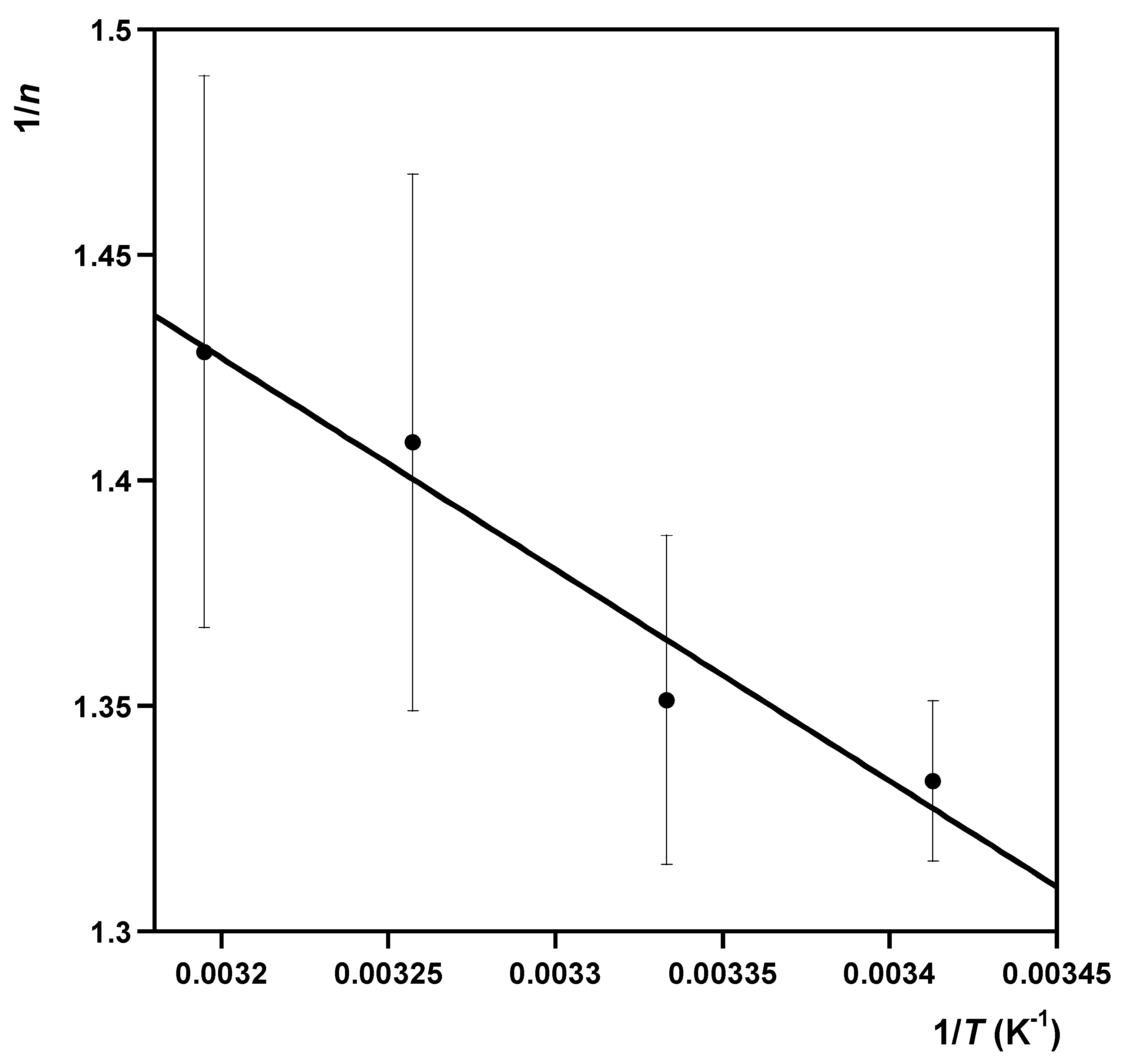
2.3.2. Sorption Thermodynamics
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Natural Zeolite Sample
3.3. Extraction of Humic Acids from Vegetable Compost, pH Fractionation, and Characterization
3.3.1. HA Extraction
3.3.2. pH-Fractionation of HA
3.3.3. HA Characterization
3.4. Preparation of the Humic Acids—Zeolitic Tuff Sorbents and Point-of-Zero-Charge Measurements
3.5. MB Spectrophotometric Measurements and Calibration Curve
3.6. MB Sorption Experiments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Singh, J.; Yadav, P.; Pal, A.K.; Mishra, V. Water Pollutants: Origin and Status. In Sensors in Water Pollutants Monitoring: Role of Material; Pooja, D., Kumar, P., Singh, P., Patil, S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 5–20. ISBN 978-981-15-0670-3. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Z.; Jia, X.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, X.; Ge, M.; Liu, D.; Wang, C.; He, Z. A Review on Application of Biochar in the Removal of Pharmaceutical Pollutants through Adsorption and Persulfate-Based AOPs. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.D.; Singh, H.; Varjani, S.; Awasthi, M.K.; Giri, B.S.; Pandey, A. A critical review on biochar-based catalysts for the abatement of toxic pollutants from water via advanced oxidation processes (AOPs). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 849, 157831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Wang, B.; Gao, B.; Cheng, N.; Feng, Q.; Chen, M.; Wang, S. Degradation of organic pollutants from water by biochar-assisted advanced oxidation processes: Mechanisms and applications. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 442, 130075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Zhao, R. Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) in Wastewater Treatment. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2015, 1, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Wu, L.; Han, C.; Zhang, D.; Li, M.; Wei, R. Preparation of auto-suspending hollow silica microfiber derived from biotemplate and its highly selective adsorption for organic dyes. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 34, 105437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaria, G.; Calisto, V.; Esteves, V.I.; Otero, M. Overview of relevant economic and environmental aspects of waste-based activated carbons aimed at adsorptive water treatments. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 344, 130984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atugoda, T.; Gunawardane, C.; Ahmad, M.; Vithanage, M. Mechanistic interaction of ciprofloxacin on zeolite modified seaweed (Sargassum crassifolium) derived biochar: Kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamics. Chemosphere 2021, 281, 130676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, J.; Javanbakht, V. Alginate beads impregnated with magnetic Chitosan@Zeolite nanocomposite for cationic methylene blue dye removal from aqueous solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 1426–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamd, A.; Dryaz, A.R.; Shaban, M.; Almohamadi, H.; Abu Al-Ola, K.A.; Soliman, N.K.; Ahmed, S.A. Fabrication and application of zeolite/acanthophora spicifera nanoporous composite for adsorption of congo red dye from wastewater. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dryaz, A.R.; Shaban, M.; AlMohamadi, H.; Al-Ola, K.A.A.; Hamd, A.; Soliman, N.K.; Ahmed, S.A. Design, characterization, and adsorption properties of Padina gymnospora/zeolite nanocomposite for Congo red dye removal from wastewater. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, R.S. Applications of surfactant-modified zeolites to environmental remediation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2003, 61, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Bai, R. Mechanisms and kinetics of humic acid adsorption onto chitosan-coated granules. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 264, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milićević, S.; Matović, L.; Petrović, Đ.; Đukić, A.; Milošević, V.; Đokić, D.; Kumrić, K. Surfactant modification and adsorption properties of clinoptilolite for the removal of pertechnetate from aqueous solutions. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2016, 310, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelletti, P.; Colella, A.; Langella, A.; Mercurio, M.; Catalanotti, L.; Monetti, V.; de Gennaro, B. Use of surface modified natural zeolite (SMNZ) in pharmaceutical preparations Part 1. Mineralogical and technological characterization of some industrial zeolite-rich rocks. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 250, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chianese, S.; Fenti, A.; Iovino, P.; Musmarra, D.; Salvestrini, S. Sorption of Organic Pollutants by Humic Acids: A Review. Molecules 2020, 25, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, V.; Canzano, S.; Iovino, P.; Salvestrini, S.; Capasso, S. A novel organo-zeolite adduct for environmental applications: Sorption of phenol. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Melo, B.A.G.; Motta, F.L.; Santana, M.H.A. Humic acids: Structural properties and multiple functionalities for novel technological developments. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 62, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonebayashi, K.; Hattori, T. Chemical and biological studies on environmental humic acids. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2012, 34, 571–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abakumov, E.V.; Cajthaml, T.; Brus, J.; Frouz, J. Humus accumulation, humification, and humic acid composition in soils of two post-mining chronosequences after coal mining. J. Soils Sediments 2013, 13, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Shi, Y.; Lin, C. Characterization of humic acids extracted from the sediments of the various rivers and lakes in China. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 1294–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, V.; Iovino, P.; Salvestrini, S.; Capasso, S. Sorption of non-ionic organic pollutants onto a humic acids-zeolitic tuff adduct: Thermodynamic aspects. Chemosphere 2014, 95, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Gowthaman, S.; Nakashima, K.; Kawasaki, S. Influence of humic acid on microbial induced carbonate precipitation for organic soil improvement. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 15230–15240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, L. Ultrafiltration performance of EfOM and NOM under different MWCO membranes: Comparison with fluorescence spectroscopy and gel filtration chromatography. Desalination 2014, 344, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yuan, L.; Li, W.; Lin, Z.; Li, Y.; Hu, S.; Zhao, B. Characterization of pH-fractionated humic acids derived from Chinese weathered coal. Chemosphere 2017, 166, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglieri, A.; Vindrola, D.; Gennari, M.; Negre, M. Chemical and spectroscopic characterization of insoluble and soluble humic acid fractions at different pH values. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2014, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, R.; Lee, N.Y. Adsorptive removal of organic pollutant methylene blue using polysaccharide-based composite hydrogels. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Zekker, I.; Zhang, B.; Hendi, A.H.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, S.; Zada, N.; Ahmad, H.; Shah, L.A.; et al. Review on Methylene Blue: Its Properties, Uses, Toxicity and Photodegradation. Water 2022, 14, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, D.; Chin, Y.P.; Weber, W.J. Structural and behavioral characteristics of a commercial humic acid and natural dissolved aquatic organic matter. Chemosphere 1990, 21, 1181–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Huang, X.; Pan, X.; Li, N.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, X. Hyperbranched Polycaprolactone through RAFT Polymerization of 2-Methylene-1,3-dioxepane. Polymers 2019, 11, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.T.; Lee, C.H.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Chen, T.C.; Jien, S.H. Using Fluorescence Spectroscopy to Assess Compost Maturity Degree during Composting. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloster, N.; Brigante, M.; Zanini, G.; Avena, M. Aggregation kinetics of humic acids in the presence of calcium ions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 427, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doskočil, L.; Burdíková-Szewieczková, J.; Enev, V.; Kalina, L.; Wasserbauer, J. Spectral characterization and comparison of humic acids isolated from some European lignites. Fuel 2018, 213, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.H.; Shin, H.S.; Park, H. Characterization of humic substances present in landfill leachates with different landfill ages and its implications. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4023–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Yuan, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, B. Characterization of ultrafiltration-fractionated HUMIC acid derived from Chinese weathered coal by spectroscopic techniques. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvestrini, S. Analysis of the Langmuir rate equation in its differential and integrated form for adsorption processes and a comparison with the pseudo first and pseudo second order models. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2018, 123, 455–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Chen, T. A film-diffusion-based adsorption kinetic equation and its application. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2017, 119, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crank, J. The Mathematics of Diffusion; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Vermeulen, T. Theory for Irreversible and Constant-Pattern Solid Diffusion. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2002, 45, 1664–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magesh, N.; Renita, A.A.; Siva, R.; Harirajan, N.; Santhosh, A. Adsorption behavior of fluoroquinolone(ciprofloxacin) using zinc oxide impregnated activated carbon prepared from jack fruit peel: Kinetics and isotherm studies. Chemosphere 2022, 290, 133227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamoudi, S.; Srasra, E. Adsorption of organic dyes by HDPy+-modified clay: Effect of molecular structure on the adsorption. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1193, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashentseva, A.A.; Aimanova, N.A.; Parmanbek, N.; Temirgaziyev, B.S.; Barsbay, M.; Zdorovets, M.V. Serratula coronata L. Mediated Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles and Their Application for the Removal of Alizarin Yellow R by Photocatalytic Degradation and Adsorption. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiol, N.; Villaescusa, I. Determination of sorbent point zero charge: Usefulness in sorption studies. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2009, 7, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Qin, P.; Lei, M.; Zeng, Q.; Song, H.; Yang, J.; Shao, J.; Liao, B.; Gu, J. Modifying Fe3O4 nanoparticles with humic acid for removal of Rhodamine B in water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 209–210, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yin, D.; Zhu, S.; Hu, X. Adsorption of cadmium(II) on humic acid coated titanium dioxide. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 367, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iovino, P.; Leone, V.; Salvestrini, S.; Capasso, S. Sorption of non-ionic organic pollutants onto immobilized humic acid. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 56, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, H.; Suzuki, A. Adsorption of heavy metal ions onto insolubilized humic acid. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1995, 171, 490–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, T.H.; Nguyen, V.T.; Dung, N.Q.; Chu, M.N.; Van Kiet, D.; Ngan, T.T.K.; Van Tan, L. Study on methylene blue adsorption of activated carbon made from Moringa oleifera leaf. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 38, 3405–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Ji, L.; Guo, J.; Ge, S.; Lu, W.; Cai, L.; Wang, Y.; Song, W.; Zhang, H. Magnetic activated biochar nanocomposites derived from wakame and its application in methylene blue adsorption. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 302, 122842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Wen, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, X.; Shao, W. A Double cross-linked strategy to construct graphene aerogels with highly efficient methylene blue adsorption performance. Chemosphere 2021, 265, 129169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zhang, M.; Gong, K.; Su, L.; Guo, Z.; Mao, L. Adsorption of methylene blue dye onto carbon nanotubes: A route to an electrochemically functional nanostructure and its layer-by-layer assembled nanocomposite. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 3457–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Shuang, S.; Dong, C.; Pan, J. Study on the interaction of methylene blue with cyclodextrin derivatives by absorption and fluorescence spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2003, 59, 2935–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. Über die Adsorption in Lösungen. Zeitschrift Phys. Chemie 1907, 57U, 385–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigdorowitsch, M.; Pchelintsev, A.; Tsygankova, L.; Tanygina, E. Freundlich isotherm: An adsorption model complete framework. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debord, J.; Chu, K.H.; Harel, M.; Salvestrini, S.; Bollinger, J.C. Yesterday, Today, and Tomorrow. Evolution of a Sleeping Beauty: The Freundlich Isotherm. Langmuir 2023, 39, 3062–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchelkia, N.; Tahraoui, H.; Amrane, A.; Belkacemi, H.; Bollinger, J.C.; Bouzaza, A.; Zoukel, A.; Zhang, J.; Mouni, L. Jujube stones based highly efficient activated carbon for methylene blue adsorption: Kinetics and isotherms modeling, thermodynamics and mechanism study, optimization via response surface methodology and machine learning approaches. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 170, 513–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouni, L.; Belkhiri, L.; Bollinger, J.C.; Bouzaza, A.; Assadi, A.; Tirri, A.; Dahmoune, F.; Madani, K.; Remini, H. Removal of Methylene Blue from aqueous solutions by adsorption on Kaolin: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 153, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheikh, S.; Bollinger, J.-C.; Belkhiri, L.; Tiri, A.; Bouzaza, A.; El, J.; Assadi, A.; Amrane, A.; Mouni, A.; Waste, L.Z.; et al. Zeolite Waste Characterization and Use as Low-Cost, Ecofriendly, and Sustainable Material for Malachite Green and Methylene Blue Dyes Removal: Box–Behnken Design, Kinetics, and Thermodynamics. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Xu, F.; Chen, M.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, Z. Adsorption behavior of methylene blue on carbon nanotubes. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 3040–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, S.; Roy, D.; Saha, P.; Gopakumar, D.; Thomas, S. Rapid methylene blue adsorption using modified lignocellulosic materials. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 107, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banat, F.; Al-Asheh, S.; Al-Makhadmeh, L. Evaluation of the use of raw and activated date pits as potential adsorbents for dye containing waters. Process Biochem. 2003, 39, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Tao, X.; Yang, Z.; Li, K.; Yang, H.; Li, A.; Cheng, R. Effects of the oxidation degree of graphene oxide on the adsorption of methylene blue. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 268, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juzsakova, T.; Salman, A.D.; Abdullah, T.A.; Rasheed, R.T.; Zsirka, B.; Al-Shaikhly, R.R.; Sluser, B.; Cretescu, I. Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution by Mixture of Reused Silica Gel Desiccant and Natural Sand or Eggshell Waste. Materials 2023, 16, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bestani, B.; Benderdouche, N.; Benstaali, B.; Belhakem, M.; Addou, A. Methylene blue and iodine adsorption onto an activated desert plant. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 8441–8444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, S. Adsorption of Methylene Blue in Water onto Activated Carbon by Surfactant Modification. Water 2020, 12, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhong, H.; Jiang, Y.; Li, H.; Tang, P.; Li, D.; Feng, Y. Porous ZnCl2-Activated Carbon from Shaddock Peel: Methylene Blue Adsorption Behavior. Materials 2022, 15, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvestrini, S.; Ambrosone, L.; Kopinke, F.D. Some mistakes and misinterpretations in the analysis of thermodynamic adsorption data. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 352, 118762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Wen, C.; He, J.; Gan, F.; Ho, Y.S. Adsorption thermodynamics of Methylene Blue onto bentonite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 630–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.A.; Mohamad Yusop, M.F.; Zakaria, R.; Karim, J.; Yahaya, N.K.E.M.; Mohamed Yusoff, M.A.; Hashim, N.H.F.; Abdullah, N.S. Adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution by peanut shell based activated carbon. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 47, 1246–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottet, L.; Almeida, C.A.P.; Naidek, N.; Viante, M.F.; Lopes, M.C.; Debacher, N.A. Adsorption characteristics of montmorillonite clay modified with iron oxide with respect to methylene blue in aqueous media. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 95, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.; Tan, H.; Liu, K.; Gao, W. Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution by Bone Char. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Cui, C.; Wang, P. Pomelo Peel Modified with Citrate as a Sustainable Adsorbent for Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution. Molecules 2018, 23, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuhara, S.; Pradhan, S.; Zakaria, Y.; Shetty, A.R.; McKay, G. Removal of Methylene Blue from Water Using Magnetic GTL-Derived Biosolids: Study of Adsorption Isotherms and Kinetic Models. Molecules 2023, 28, 1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkins, P.; de Paula, J.; Keeler, J. Atkins’ Physical Chemistry; OUP Oxford: Oxford, UK, 2017; ISBN 978-0198769866. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, H.N.; Bollinger, J.-C.; Salvestrini, S.; Chu, K.H.; Juang, R.-S. Critical Review and Discussion of the Nonlinear Form of Radke–Prausnitz Model in Adsorption Solid–Liquid Phases. J. Environ. Eng. 2022, 149, 03122006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvestrini, S. New insights into the interaction mechanism of humic acids with phillipsite. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2017, 120, 735–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooney, D.O. Adsorption Design for Wastewater Treatment; Lewis Publishers: Ririe, ID, USA, 1999; ISBN 1566703336. [Google Scholar]
- Colella, A.; de Gennaro, B.; Salvestrini, S.; Colella, C. Surface interaction of humic acids with natural and synthetic phillipsite. J. Porous Mater. 2015, 22, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csicsor, A.; Tombácz, E. Screening of Humic Substances Extracted from Leonardite for Free Radical Scavenging Activity Using DPPH Method. Molecules 2022, 27, 6334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalmár, J.; Lente, G.; Fábián, I. Kinetics and mechanism of the adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution on the surface of a quartz cuvette by on-line UV–Vis spectrophotometry. Dye. Pigment. 2016, 127, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, N.T.; Vo, L.N.H.; Tran, N.T.T.; Phan, T.D.; Nguyen, D.B. Enhancing the removal efficiency of methylene blue in water by fly ash via a modified adsorbent with alkaline thermal hydrolysis treatment. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 20292–20302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawafta, R.; Shahwan, T. A comparative study of the removal of methylene blue by iron nanoparticles from water and water-ethanol solutions. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 273, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Pérez, A.; Valdés-Solís, T.; Marbán, G. Visible light spectroscopic analysis of Methylene Blue in water; the resonance virtual equilibrium hypothesis. Dye. Pigment. 2019, 161, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, W.; Sutter, J.R. Kinetic study of the monomer-dimer equilibrium of methylene blue in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. 1979, 83, 1573–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| HA Type | E2/E3 | E4/E6 |
|---|---|---|
| HAref | 1.7 | 4.0 |
| HA3 | 1.9 | 4.4 |
| HA5 | 1.8 | 4.1 |
| HA7 | 1.6 | 3.6 |
| Model | k1 (h−1) | k2 (g mg−1 h−1) | B (h−1) | kD (h−1) | Res. Sum of Squares | AICc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFO | 0.023 ± 0.003 | - | - | - | 1.087 | −8.23 |
| PSO | - | 0.0027 ± 0.0005 | - | - | 0.533 | −14.63 |
| Boyd | - | - | 0.0036 ± 0.0009 | - | 0.093 | −30.36 |
| Vermeulen | - | - | - | 0.0048 ± 0.0008 | 0.094 | −30.25 |
| Model | k1 (h−1) | k2 (g mg−1 h−1) | B (h−1) | kD (h−1) | Res. Sum of Squares | AICc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFO | 0.108 ± 0.008 | - | - | - | 1.241 | 23.03 |
| PSO | - | 0.0066 ± 0.0003 | - | - | 0.085 | 9.65 |
| Boyd | - | - | 0.077 ± 0.006 | - | 0.728 | 20.36 |
| Vermeulen | - | - | - | 0.070 ± 0.005 | 0.616 | 19.53 |
| Sorbent | pHPZC |
|---|---|
| NYT | 7.2 |
| NYT-HAref | 5.0 |
| NYT-HA3 | 4.1 |
| NYT-HA5 | 4.9 |
| NYT-HA7 | 4.8 |
| Sorbent | (mg g−1) | (L mg−1) | Res. Sum of Squares | AICc | (mg1-n g−1 Ln) | Res. Sum of Squares | AICc | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NYT | 10.9 ± 0.5 | 4 ± 1 | 2.930 | 13.70 | 8 ± 1 | 0.18 ± 0.08 | 11.781 | 22.04 |
| NYT-HAref | 70 ± 10 | 0.14 ± 0.03 | 1.794 | 10.76 | 8.8 ± 0.1 | 0.79 ± 0.01 | 0.190 | −2.73 |
| NYT-HA3 | 44 ± 8 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.477 | 2.81 | 2.52 ± 0.07 | 0.84 ± 0.02 | 0.078 | −8.08 |
| NYT-HA5 | 70 ± 10 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 1.159 | 8.14 | 6.56 ± 0.08 | 0.79 ± 0.01 | 0.076 | −8.19 |
| NYT-HA7 | 110 ± 10 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 1.319 | 8.91 | 36.7 ± 0.2 | 0.77 ± 0.01 | 0.255 | −0.95 |
| Sorbent | (mg g−1) | pH a | Sorbent Dosage (g L−1) | T (K) | Fitting Model | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NYT-HA7 | 37 | 7.4 (buff.) | 0.3 | 293 | Freundlich | This work |
| Jujube-stone-based activated carbon | 23 | 7.0 | 1 | 298 | Langmuir | [57] |
| Kaolin | 19 | 2.0 | 0.5 | 298 | Langmuir | [58] |
| Zeolite waste | 8 | free | 1 | 298 | Langmuir | [59] |
| Carbon nanotubes | 8 | 7.0 | 0.3 | 298 | Langmuir | [60] |
| Modified lignocellulosic materials | 39 | 6.0 | 10 | 298 | Langmuir | [61] |
| Row date pits | 11 | 8.0 | 5 | 298 | Langmuir | [62] |
| Graphene oxide | 191 | 7.0 | 0.5 | 298 | Langmuir | [63] |
| Silica gel/eggshell powder | 16 | 7.0 | 0.25 | 298 | Freundlich | [64] |
| Magnetic activated biochar nanocomposites derived from wakame | 183 | n.d. | 1 | 293 | Langmuir | [49] |
| Commercial activated carbon | 24 | 6.9 | 4 | 297 | Langmuir | [65] |
| Surfactant-modified activated carbon | 106 | 5.0 | 0.15 | 298 | Langmuir | [66] |
| ZnCl2-Activated Carbon | 642 | free | 0.5 | 303 | Langmuir | [67] |
| T (K) | (mol1−n kg−1 Ln) | (kJ mol−1) | (kJ mol−1) | (J K−1 mol−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 293 | 1600 ± 300 | 0.75 ± 0.01 | −3.25 ± 0.04 | 3.9 ± 0.6 | 24 ± 2 |
| 300 | 1600 ± 400 | 0.74 ± 0.02 | −3.37 ± 0.09 | ||
| 307 | 1400 ± 600 | 0.71 ± 0.03 | −3.6 ± 0.2 | ||
| 313 | 1200 ± 500 | 0.70 ± 0.03 | −3.7 ± 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salvestrini, S.; Debord, J.; Bollinger, J.-C. Enhanced Sorption Performance of Natural Zeolites Modified with pH-Fractionated Humic Acids for the Removal of Methylene Blue from Water. Molecules 2023, 28, 7083. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28207083
Salvestrini S, Debord J, Bollinger J-C. Enhanced Sorption Performance of Natural Zeolites Modified with pH-Fractionated Humic Acids for the Removal of Methylene Blue from Water. Molecules. 2023; 28(20):7083. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28207083
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalvestrini, Stefano, Jean Debord, and Jean-Claude Bollinger. 2023. "Enhanced Sorption Performance of Natural Zeolites Modified with pH-Fractionated Humic Acids for the Removal of Methylene Blue from Water" Molecules 28, no. 20: 7083. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28207083
APA StyleSalvestrini, S., Debord, J., & Bollinger, J.-C. (2023). Enhanced Sorption Performance of Natural Zeolites Modified with pH-Fractionated Humic Acids for the Removal of Methylene Blue from Water. Molecules, 28(20), 7083. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28207083







