Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Salvia verticillata and Filipendula ulmaria Extracts: Optimization of Synthesis, Biological Activities, and Catalytic Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
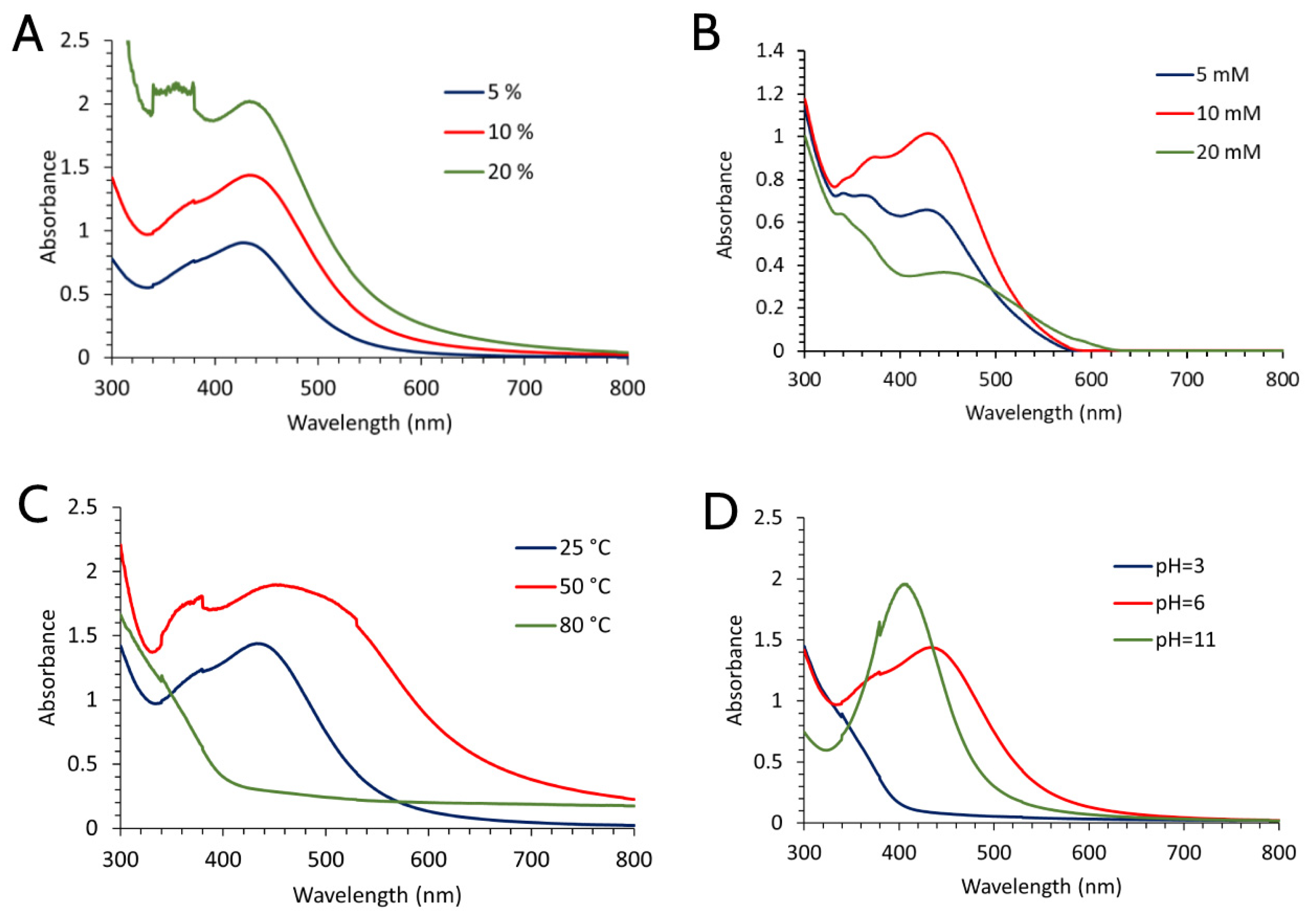
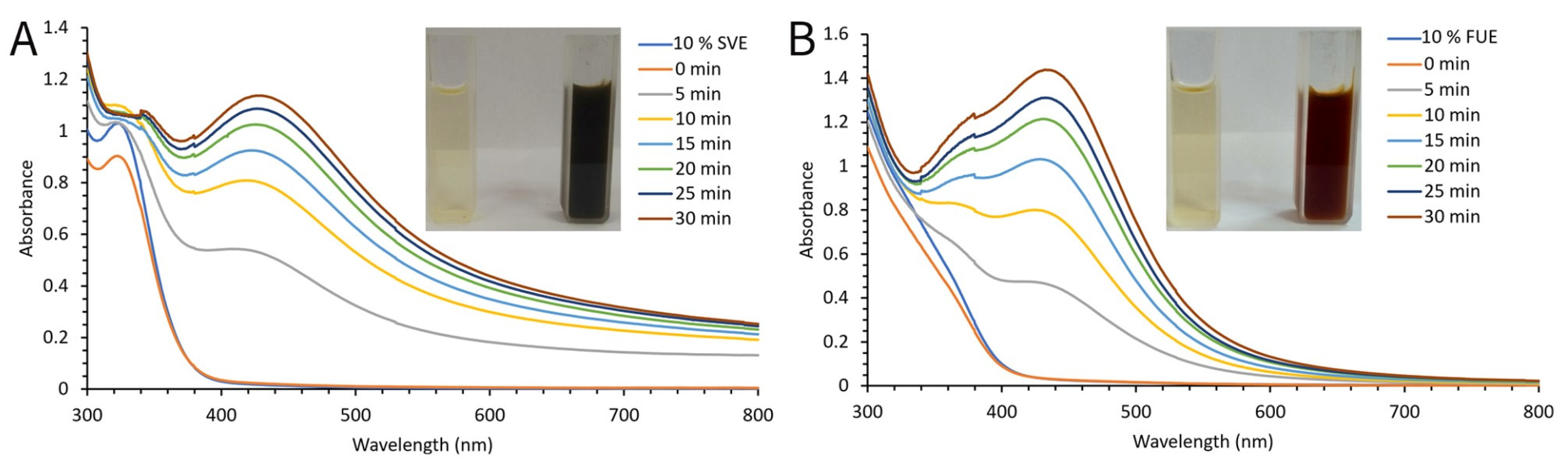
2.1. Optimization Conditions and Synthesis of SVAgNP and FUAgNP
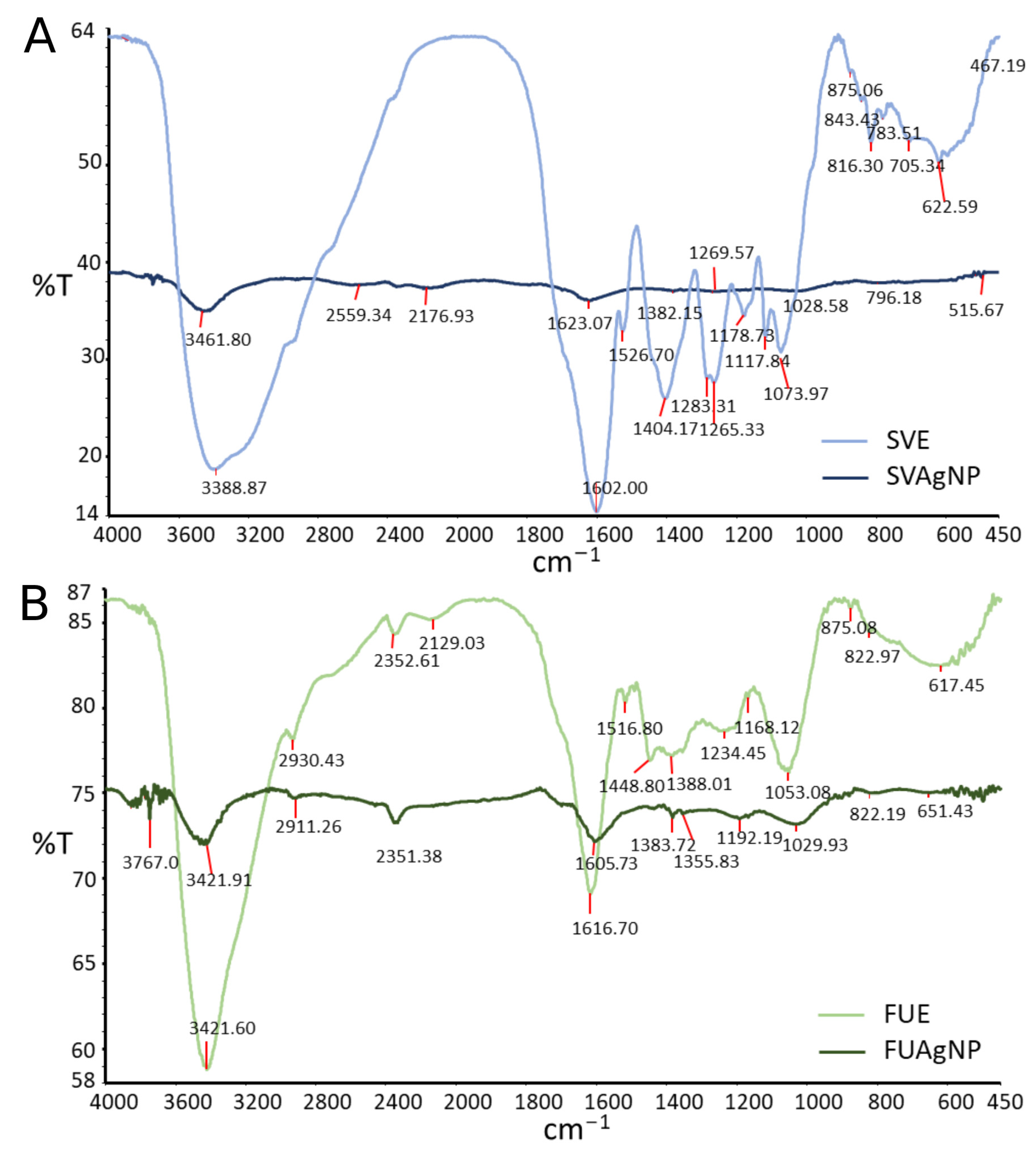
2.2. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
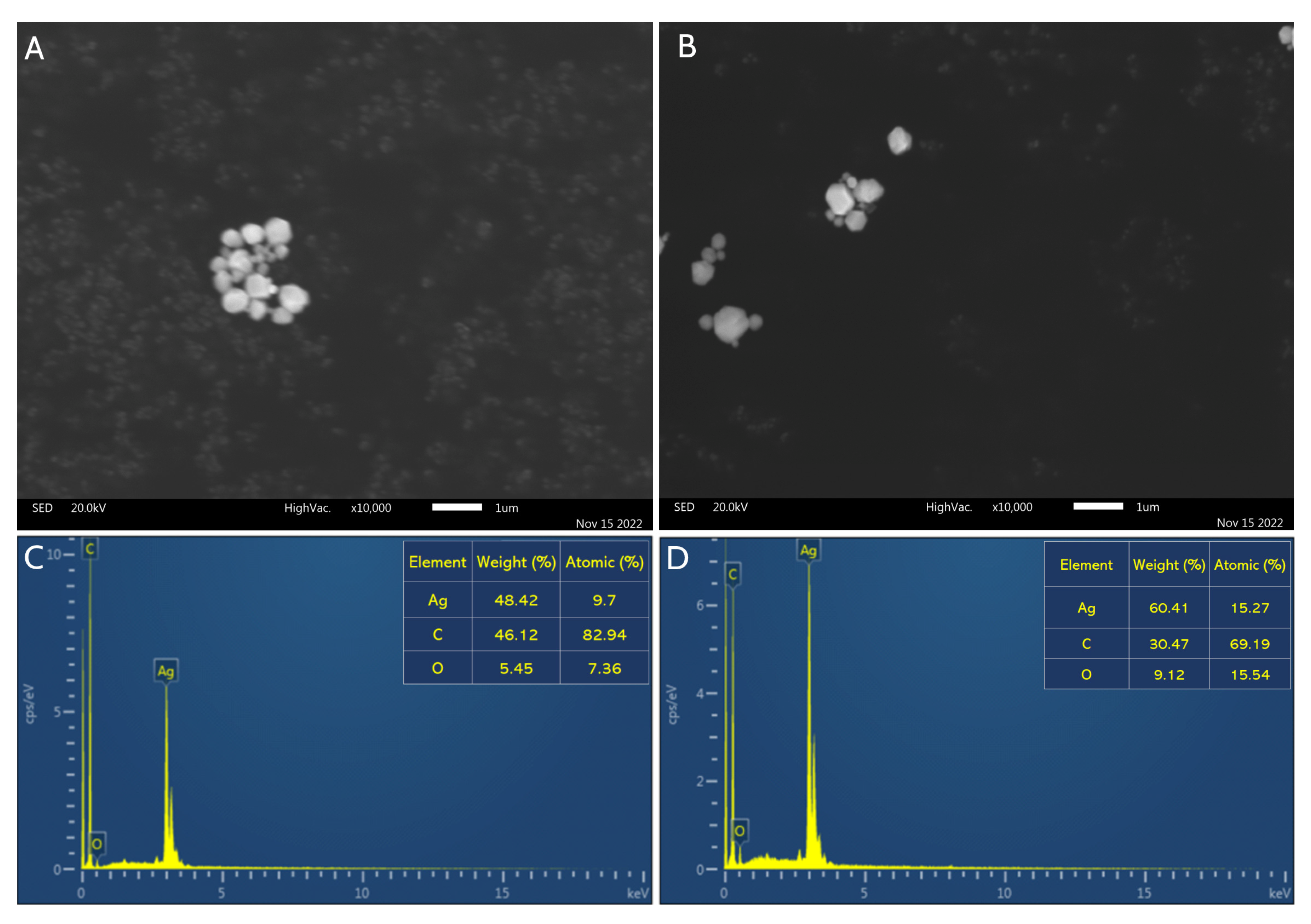
2.3. SEM/EDX Analysis
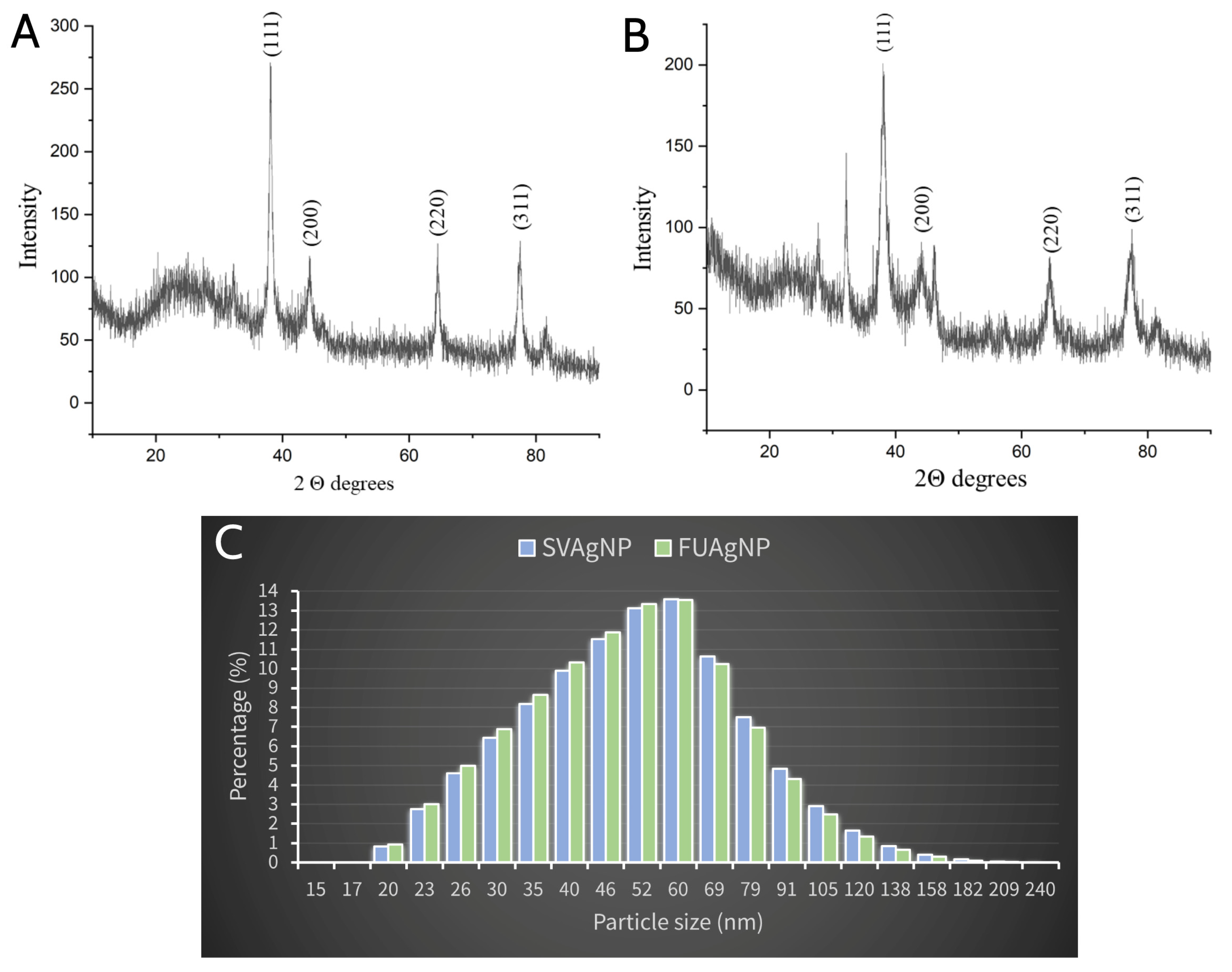
2.4. XRPD Analysis
2.5. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Analysis
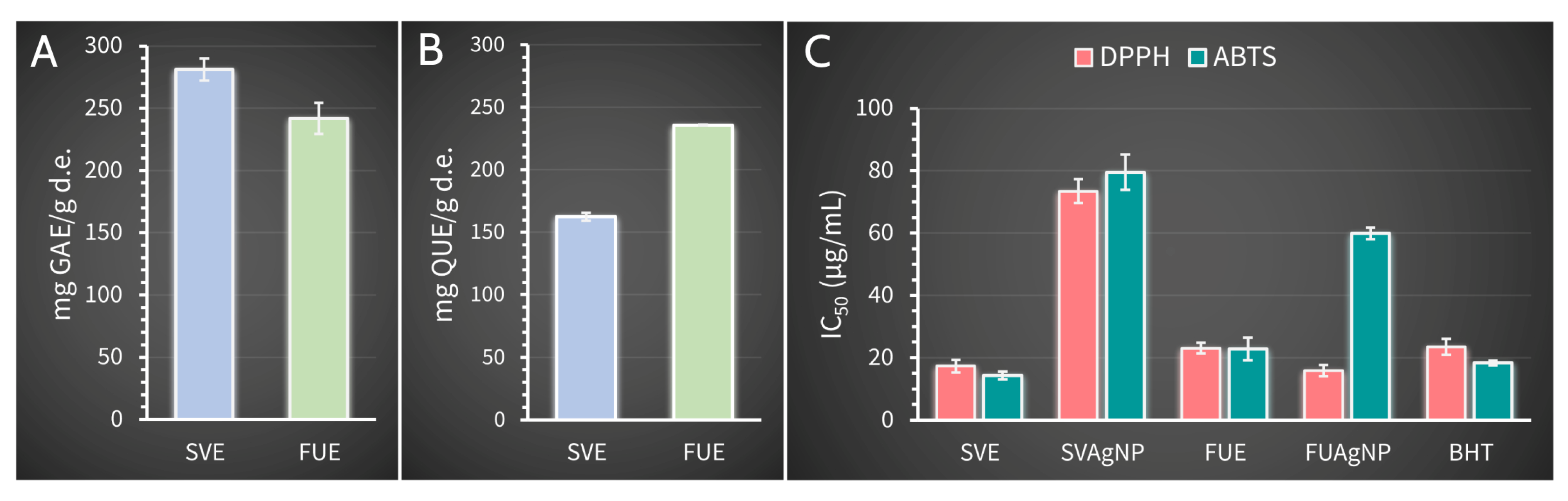
2.6. Phenolic Content in Extracts and Antioxidant Activity of Synthesized Nanoparticles
2.7. Antimicrobial Activity
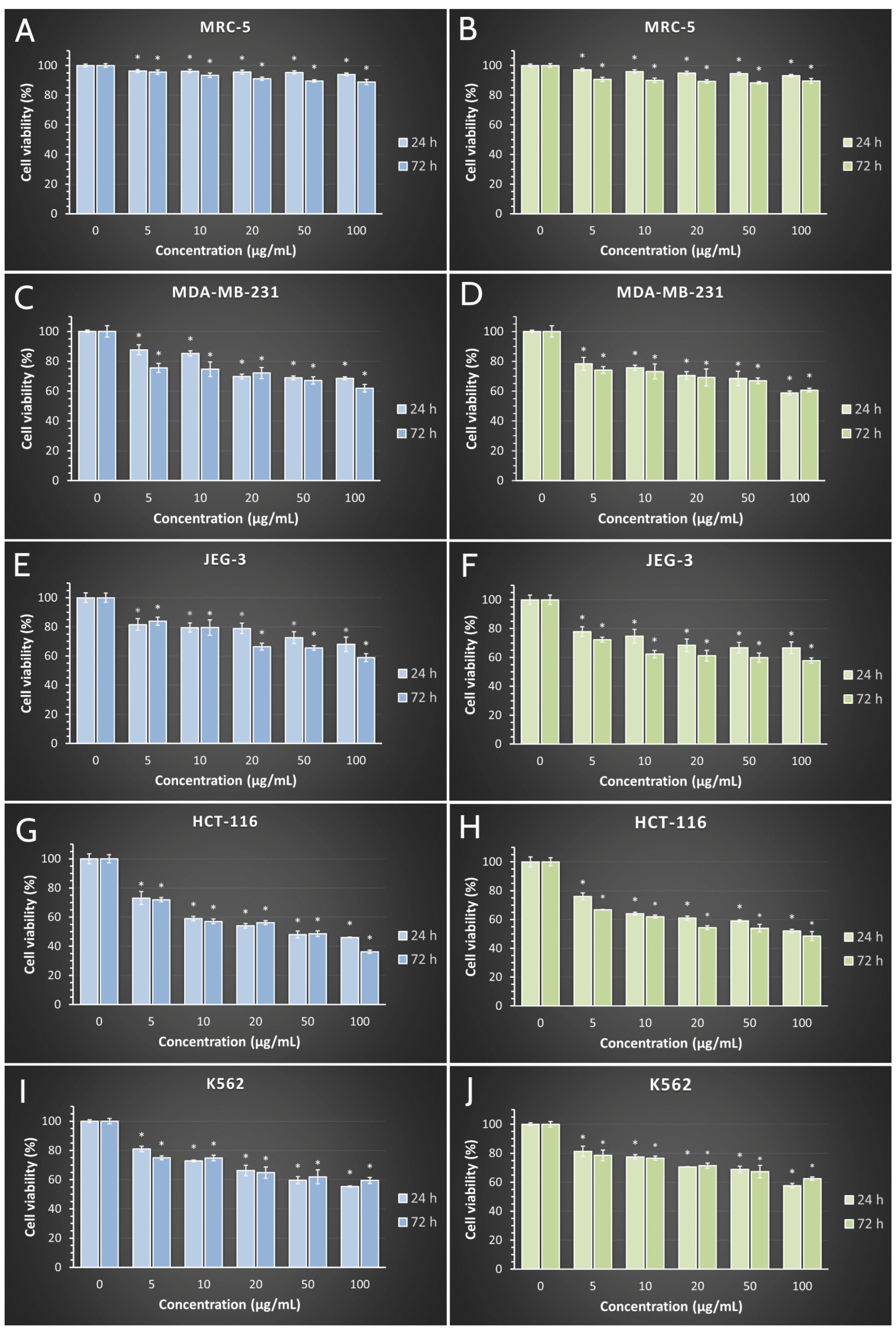
2.8. Cytotoxic Activity/The Effects on Cell Viability
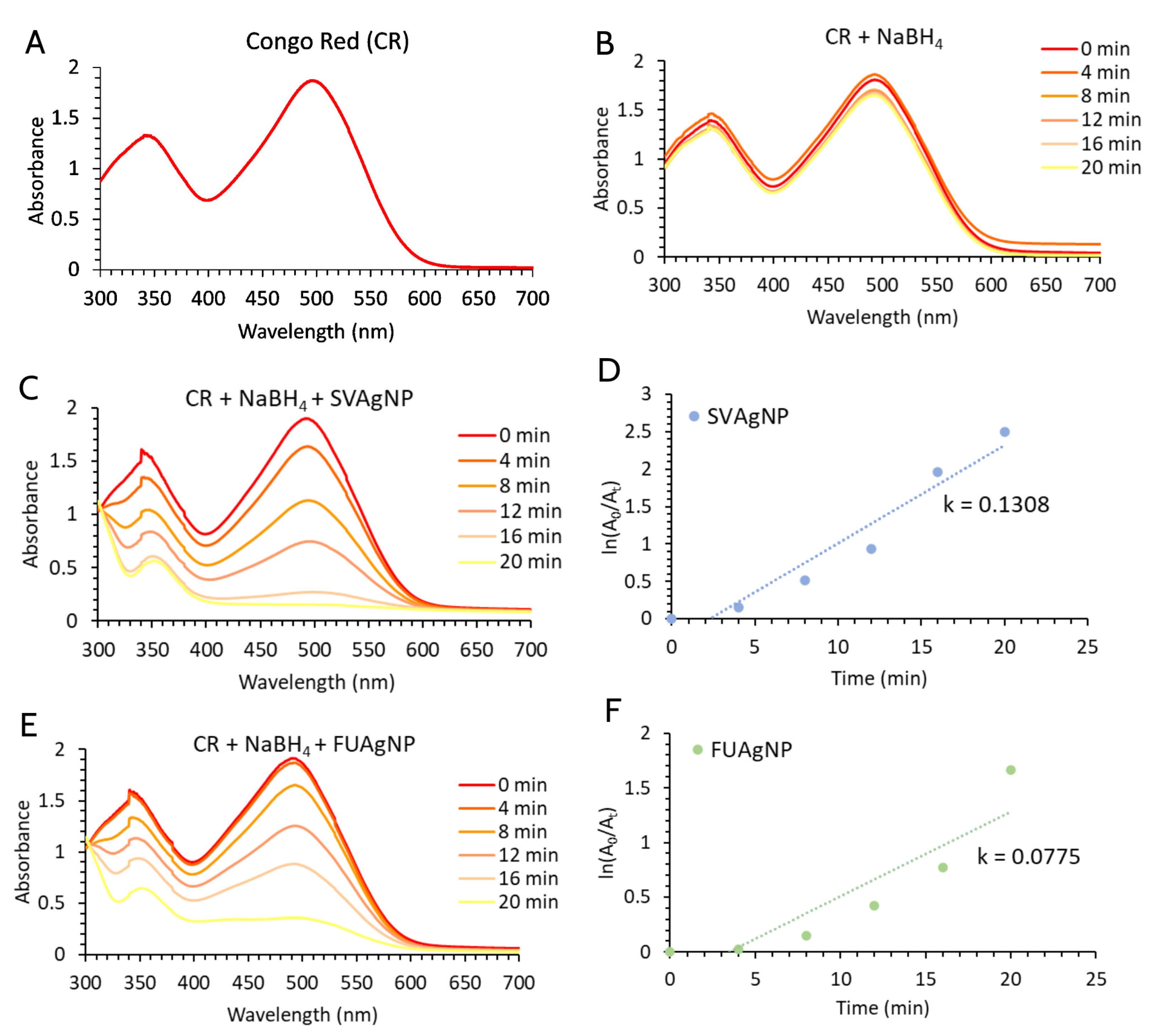
2.9. Catalytic Potential of SVAgNP and FUAgNP
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. The Extract Preparation
3.3. Green Synthesis of AgNPs
3.4. Characterization of Synthesized AgNPs
3.5. Determination of Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity
3.6. Antimicrobial Activity
3.7. MTT Cell Viability Assay
3.8. Catalytic Degradation of Congo Red
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Ijaz, I.; Bukhari, A.; Gilani, E.; Nazir, A.; Zain, H.; Saeed, R.; Hussain, S.; Hussain, T.; Bukhari, A.; Naseer, Y.; et al. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Different Plants Parts and Biological Organisms, Characterization and Antibacterial Activity. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2022, 18, 100704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, D.; Modi, A.; Narayan, G.; Rai, S.P. Green and Cost Effective Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Endangered Medicinal Plant Withania coagulans and Their Potential Biomedical Properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 100, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadaf, S.J.; Jadhav, N.R.; Naikwadi, H.S.; Savekar, P.L.; Sapkal, I.D.; Kambli, M.M.; Desai, I.A. Green Synthesis of Gold and Silver Nanoparticles: Updates on Research, Patents, and Future Prospects. OpenNano 2022, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihailovic, V.; Katanic Stankovic, J.S.; Selakovic, D.; Rosic, G. An Overview of the Beneficial Role of Antioxidants in the Treatment of Nanoparticle-Induced Toxicities. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 2021, 7244677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Shariq, M.; Asif, M.; Siddiqui, M.A.; Malan, P.; Ahmad, F. Green Nanotechnology: Plant-Mediated Nanoparticle Synthesis and Application. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolae-Maranciuc, A.; Chicea, D.; Chicea, L.M. Ag Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications—Synthesis and Characterization—A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashin, I.; Fouda, A.; Gobouri, A.A.; Azab, E.; Mohammedsaleh, Z.M.; Makharita, R.R. Antimicrobial and in vitro Cytotoxic Efficacy of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) Fabricated by Callus Extract of Solanum incanum L. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouda, A.; Eid, A.M.; Abdelkareem, A.; Said, H.A.; El-Belely, E.F.; Alkhalifah, D.H.M.; Alshallash, K.S.; Hassan, S.E.D. Phyco-Synthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Marine Macroalgae, Ulva fasciata Delile, Characterization, Antibacterial Activity, Photocatalysis, and Tanning Wastewater Treatment. Catalysts 2022, 12, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, A.M.; Fouda, A.; Eid, A.M.; Fahmy, N.M.; Elsayed, A.M.; Khalil, A.M.A.; Alzahrani, O.M.; Ahmed, A.F.; Soliman, A.M. Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Their Activity against Pathogenic Microbes and Common House Mosquito, Culex pipiens. Materials 2021, 14, 6983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouda, A.; Eid, A.M.; Abdel-Rahman, M.A.; EL-Belely, E.F.; Awad, M.A.; Hassan, S.E.D.; AL-Faifi, Z.E.; Hamza, M.F. Enhanced Antimicrobial, Cytotoxicity, Larvicidal, and Repellence Activities of Brown Algae, Cystoseira crinita-Mediated Green Synthesis of Magnesium Oxide Nanoparticles. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maťátková, O.; Michailidu, J.; Miškovská, A.; Kolouchová, I.; Masák, J.; Čejková, A. Antimicrobial Properties and Applications of Metal Nanoparticles Biosynthesized by Green Methods. Biotechnol. Adv. 2022, 58, 107905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katanić, J.; Boroja, T.; Mihailović, V.; Nikles, S.; Pan, S.P.; Rosić, G.; Selaković, D.; Joksimović, J.; Mitrović, S.; Bauer, R. In vitro and in vivo Assessment of Meadowsweet (Filipendula ulmaria) as Anti-Inflammatory Agent. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 193, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samardžić, S.; Arsenijević, J.; Božić, D.; Milenković, M.; Tešević, V.; Maksimović, Z. Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory and Gastroprotective Activity of Filipendula ulmaria (L.) Maxim. and Filipendula vulgaris Moench. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 213, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katanić, J.; Boroja, T.; Stanković, N.; Mihailović, V.; Mladenović, M.; Kreft, S.; Vrvić, M.M. Bioactivity, Stability and Phenolic Characterization of Filipendula ulmaria (L.) Maxim. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 1164–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maksimović, Z.; Petrović, S.; Pavlović, M.; Kovačević, N.; Kukić, J. Antioxidant Activity of Filipendula hexapetala Flowers. Fitoterapia 2007, 78, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, M.J.; Sousa, D.; Lima, R.T.; Carvalho, A.M.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Vasconcelos, M.H. Flower Extracts of Filipendula ulmaria (L.) Maxim Inhibit the Proliferation of the NCI-H460 Tumour Cell Line. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 59, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boziaris, I.S.; Proestos, C.; Kapsokefalou, M.; Komaitis, M. Antimicrobial Effect of Filipendula ulmaria Plant Extract Against Selected Foodborne Pathogenic and Spoilage Bacteria in Laboratory Media, Fish Flesh and Fish Roe Product. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2011, 49, 263–270. [Google Scholar]
- Fecka, I. Qualitative and Quantitative Determination of Hydrolysable Tannins and Other Polyphenols in Herbal Products from Meadowsweet and Dog Rose. Phytochem. Anal. 2009, 20, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijttebier, S.; van der Auwera, A.; Voorspoels, S.; Noten, B.; Hermans, N.; Pieters, L.; Apers, S. A First Step in the Quest for the Active Constituents in Filipendula ulmaria (Meadowsweet): Comprehensive Phytochemical Identification by Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Quadrupole-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry. Planta Med. 2016, 82, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katanić, J.; Matić, S.; Pferschy-Wenzig, E.M.; Kretschmer, N.; Boroja, T.; Mihailović, V.; Stanković, V.; Stanković, N.; Mladenović, M.; Stanić, S.; et al. Filipendula ulmaria Extracts Attenuate Cisplatin-Induced Liver and Kidney Oxidative Stress in Rats: In vivo Investigation and LC-MS Analysis. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 99, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matkowski, A.; Zielińska, S.; Oszmiański, J.; Lamer-Zarawska, E. Antioxidant Activity of Extracts from Leaves and Roots of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge, S. Przewalskii Maxim., and S. verticillata L. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 7892–7896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tepe, B.; Eminagaoglu, O.; Akpulat, H.A.; Aydin, E. Antioxidant Potentials and Rosmarinic Acid Levels of the Methanolic Extracts of Salvia verticillata (L.) Subsp. verticillata and S. verticillata (L.) Subsp. amasiaca (Freyn & Bornm.) Bornm. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 985–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katanić Stanković, J.S.; Srećković, N.; Mišić, D.; Gašić, U.; Imbimbo, P.; Monti, D.M.; Mihailović, V. Bioactivity, Biocompatibility and Phytochemical Assessment of Lilac Sage, Salvia verticillata L. (Lamiaceae)—A Plant Rich in Rosmarinic Acid. Ind. Crops. Prod. 2020, 143, 111932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çadirci, E.; Süleyman, H.; Gürbüz, P.; Uz, A.K.; Güvenalp, Z.; Demirezer, L.Ö. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Different Extracts from Three Salvia Species. Turk. J. Biol. 2012, 36, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zengin, G.; Llorent-Martínez, E.J.; de Córdova, M.L.F.; Bahadori, M.B.; Mocan, A.; Locatelli, M.; Aktumsek, A. Chemical Composition and Biological Activities of Extracts from Three Salvia Species: S. blepharochlaena, S. euphratica Var. leiocalycina, and S. verticillata Subsp. amasiaca. Ind. Crops. Prod. 2018, 111, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathishkumar, M.; Sneha, K.; Yun, Y.S. Immobilization of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Curcuma Longa Tuber Powder and Extract on Cotton Cloth for Bactericidal Activity. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 7958–7965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srećković, N.Z.; Nedić, Z.P.; Liberti, D.; Monti, D.M.; Mihailović, N.R.; Katanić Stanković, J.S.; Dimitrijević, S.; Mihailović, V.B. Application Potential of Biogenically Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles Using: Lythrum salicaria L. Extracts as Pharmaceuticals and Catalysts for Organic Pollutant Degradation. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 35585–35599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konai, N.; Raidandi, D.; Pizzi, A.; Meva’a, L. Characterization of Ficus sycomorus Tannin Using ATR-FT MIR, MALDI-TOF MS and 13C NMR Methods. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2017, 75, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzolin, M.R.; dos Santoa Courrol, D.; de Oliveira Silva, F.R.; Courrol, L.C. Antimicrobial Activity of Silver and Gold Nanoparticles Prepared by Photoreduction Process with Leaves and Fruit Extracts of Plinia cauliflora and Punica granatum. Molecules 2022, 27, 6860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufail, S.; Liaqat, I.; Ali, S.; Ulfat, M.; Shafi, A.; Sadiqa, A.; Ahsan, F. Bacillus licheniformis (MN900686) Mediated Synthesis, Characterization and Antimicrobial Potential of Silver Nanoparticles. J. Oleo. Sci. 2022, 71, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranović, G.; Šegota, S. Infrared Spectroscopy of Flavones and Flavonols. Reexamination of the Hydroxyl and Carbonyl Vibrations in Relation to the Interactions of Flavonoids with Membrane Lipids. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 192, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benelli, G.; Kadaikunnan, S.; Alharbi, N.S.; Govindarajan, M. Biophysical Characterization of Acacia Caesia-Fabricated Silver Nanoparticles: Effectiveness on Mosquito Vectors of Public Health Relevance and Impact on Non-Target Aquatic Biocontrol Agents. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 10228–10242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, A.; Vanlalveni, C.; Adhikari, P.P.; Lalfakzuala, R.; Rokhum, L. Green Biosynthesis, Characterisation and Antimicrobial Activities of Silver Nanoparticles Using Fruit Extract of Solanum viarum. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 12, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corciovă, A.; Mircea, C.; Burlec, A.F.; Fifere, A.; Moleavin, I.T.; Sarghi, A.; Tuchiluș, C.; Ivănescu, B.; Macovei, I. Green Synthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles Using a Lythrum salicaria Extract and in vitro Exploration of Their Biological Activities. Life 2022, 12, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirtarighat, S.; Ghannadnia, M.; Baghshahi, S. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using the Plant Extract of Salvia spinosa Grown in vitro and Their Antibacterial Activity Assessment. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautela, A.; Rani, J.; Debnath, M. Das, Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Tectona grandis Seeds Extract: Characterization and Mechanism of Antimicrobial Action on Different Microorganisms. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, A.A.; Al-Ghobashy, M.A.; Fawzy, M.; Mohamed, M.B.; Abdel-Mottaleb, M.M.S.A. Phytosynthesis of Au, Ag, and Au-Ag Bimetallic Nanoparticles Using Aqueous Extract of Sago Pondweed (Potamogeton pectinatus L.). ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 1520–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albeladi, S.S.R.; Malik, M.A.; Al-Thabaiti, S.A. Facile Biofabrication of Silver Nanoparticles Using Salvia officinalis Leaf Extract and Its Catalytic Activity towards Congo Red Dye Degradation. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 10031–10044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erjaee, H.; Rajaian, H.; Nazifi, S. Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Silver Nanoparticles Using Chamaemelum nobile Extract for Antibacterial Application. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 025004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anigol, L.B.; Charantimath, J.S.; Gurubasavaraj, P.M. Effect of Concentration and pH on the Size of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by Green Chemistry. Org. Med. Chem. Int. J. 2017, 3, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathishkumar, M.; Sneha, K.; Won, S.W.; Cho, C.W.; Kim, S.; Yun, Y.S. Cinnamon zeylanicum Bark Extract and Powder Mediated Green Synthesis of Nano-Crystalline Silver Particles and Its Bactericidal Activity. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2009, 73, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stankovic, J.S.K.; Selakovic, D.; Mihailovic, V.; Rosic, G. Antioxidant Supplementation in the Treatment of Neurotoxicity Induced by Platinum-Based Chemotherapeutics—A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chouke, P.B.; Shrirame, T.; Potbhare, A.K.; Mondal, A.; Chaudhary, A.R.; Mondal, S.; Thakare, S.R.; Nepovimova, E.; Valis, M.; Kuca, K.; et al. Bioinspired Metal/Metal Oxide Nanoparticles: A Road Map to Potential Applications. Mater. Today Adv. 2022, 16, 100314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moges, A.; Goud, V.V. Optimization, Characterization, and Evaluation of Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activities of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized from Hippophae salicifolia D. Don. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 146, 110086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuda, F.; Jamil, M.; Ali Khan Khalil, A.; Ullah, R.; Ullah, N.; Naureen, F.; Abbas, M.; Shafiq Khan, M.; Ali, S.; Muhammad Umer Farooqi, H.; et al. Assessment of Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Potential of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized from Root Extract of Reynoutria japonica Houtt. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufail, S.; Zeeshan, M.; Hanif, S.; Sajjad, A.; Zia, M. Synthesis and Morphological & Biological Characterization of Campsis radicans and Cascabela thevetia Petals Derived Silver Nanoparticles. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2022, 105, 104526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Sun, P.; Lei, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Guo, W.; Wu, Y.; Morovvati, H.; Goorani, S. Introducing a Novel Chemotherapeutic Supplement Prepared by Silver Nanoparticles Green-Formulated by Salvia officinalis Leaf Aqueous Extract to Treat the Human Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 146, 110161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siakavella, I.K.; Lamari, F.; Papoulis, D.; Orkoula, M.; Gkolfi, P.; Lykouras, M.; Avgoustakis, K.; Hatziantoniou, S. Effect of Plant Extracts on the Characteristics of Silver Nanoparticles for Topical Application. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balčiūnaitienė, A.; Liaudanskas, M.; Puzerytė, V.; Viškelis, J.; Janulis, V.; Viškelis, P.; Griškonis, E.; Jankauskaitė, V. Eucalyptus globulus and Salvia officinalis Extracts Mediated Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Application as an Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Agent. Plants 2022, 11, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flieger, J.; Franus, W.; Panek, R.; Szymańska-Chargot, M.; Flieger, W.; Flieger, M.; Kołodziej, P. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Natural Extracts with Proven Antioxidant Activity. Molecules 2021, 26, 4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, G.; Sundaramoorthy, A.; Shanmugam, N. Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Leaf Extract of Salvia coccinea and Its Effects of Anti-Inflammatory Potential in Human Monocytic THP-1 Cells. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 8433–8442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gecer, E.N. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Salvia aethiopis L. and Their Antioxidant Activity. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2021, 31, 4402–4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, N.; Pathak, A.; Anupam, R.; Jain, N.; Singh, J.; Upadhyaya, C.P. A Rapid and Efficient Biosynthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles Using Aqueous Extract of Chia (Salvia hispanica L.) Seeds. J. Bionanosci. 2019, 9, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Kuk, E.; Yu, K.N.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.J.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.H.; Park, Y.K.; Park, Y.H.; Hwang, C.Y.; et al. Antimicrobial Effects of Silver Nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 2007, 3, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macovei, I.; Luca, S.V.; Skalicka-Woźniak, K.; Sacarescu, L.; Pascariu, P.; Ghilan, A.; Doroftei, F.; Ursu, E.L.; Rimbu, C.M.; Horhogea, C.E.; et al. Phyto-Functionalized Silver Nanoparticles Derived from Conifer Bark Extracts and Evaluation of Their Antimicrobial and Cytogenotoxic Effects. Molecules 2022, 27, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, P.; Meyer, S.; Madiehe, A.; Meyer, M. Antibacterial Activity of Biogenic Silver and Gold Nanoparticles Synthesized from Salvia africana-Lutea and Sutherlandia frutescens. J. Nanotechnol. 2020, 31, 505607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pungle, R.; Nile, S.H.; Makwana, N.; Singh, R.; Singh, R.P.; Kharat, A.S. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using the Tridax procumbens Plant Extract and Screening of Its Antimicrobial and Anticancer Activities. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 9671594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouda, A.; Awad, M.A.; Al-Faifi, Z.E.; Gad, M.E.; Al-Khalaf, A.A.; Yahya, R.; Hamza, M.F. Aspergillus flavus-Mediated Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Evaluation of Their Antibacterial, Anti-Candida, Acaricides, and Photocatalytic Activities. Catalysts 2022, 12, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, M.F.; Hamad, D.M.; Hamad, N.A.; Abdel-Rahman, A.A.H.; Fouda, A.; Wei, Y.; Guibal, E.; El-Etrawy, A.A.S. Functionalization of Magnetic Chitosan Microparticles for High-Performance Removal of Chromate from Aqueous Solutions and Tannery Effluent. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 428, 131775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouda, A.; Al-Otaibi, W.A.; Saber, T.; AlMotwaa, S.M.; Alshallash, K.S.; Elhady, M.; Badr, N.F.; Abdel-Rahman, M.A. Antimicrobial, Antiviral, and in-vitro Cytotoxicity and Mosquitocidal Activities of Portulaca oleracea-Based Green Synthesis of Selenium Nanoparticles. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Han, J.W.; Eppakayala, V.; Jeyaraj, M.; Kim, J.H. Cytotoxicity of Biologically Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles in MDA-MB-231 Human Breast Cancer Cells. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 535796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, H.I.O.; Martins, C.S.M.; Prior, J.A.V.; Taglietti, M. Silver Nanoparticles as Carriers of Anticancer Drugs for Efficient Target Treatment of Cancer Cells. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiani, Z.; Aramjoo, H.; Chamani, E.; Siami-Aliabad, M.; Mortazavi-Derazkola, S. In vitro Cytotoxicity against K562 Tumor Cell Line, Antibacterial, Antioxidant, Antifungal and Catalytic Activities of Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles Using Sophora pachycarpa Extract. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 103677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Kang, M.H.; Qasim, M.; Kim, J.H. Nanoparticle-Mediated Combination Therapy: Two-in-One Approach for Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendran, R.; Pullani, S.; Thavamurugan, S.; Radhika, R.; Prabha, A.L. Green Fabrication of Silver Nanoparticles from Salvia Species Extracts: Characterization and Anticancer Activities against A549 Human Lung Cancer Cell Line. Appl. Nanosci. 2022, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okaiyeto, K.; Hoppe, H.; Okoh, A.I. Plant-Based Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Aqueous Leaf Extract of Salvia officinalis: Characterization and Its Antiplasmodial Activity. J. Clust. Sci. 2021, 32, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataria, N.; Garg, V.K. Removal of Congo Red and Brilliant Green Dyes from Aqueous Solution Using Flower Shaped ZnO Nanoparticles. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 5420–5428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunger, K.; Mischke, P.; Rieper, W.; Raue, R.; Kunde, K.; Engel, A. Azo Dyes. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, K.; Farooqi, Z.H.; Begum, R.; Irfan, A. Removal of Congo Red Dye from Aqueous Medium by Its Catalytic Reduction Using Sodium Borohydride in the Presence of Various Inorganic Nano-Catalysts: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 187, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, V.K.; Amita, M.; Kumar, R.; Gupta, R. Basic Dye (Methylene Blue) Removal from Simulated Wastewater by Adsorption Using Indian Rosewood Sawdust: A Timber Industry Waste. Dyes Pigm. 2004, 63, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolya, H.; Maiti, P.; Pandey, A.; Tripathy, T. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles with Antimicrobial and Azo Dye (Congo Red) Degradation Properties Using Amaranthus gangeticus Linn Leaf Extract. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markus, J.; Wang, D.; Kim, Y.J.; Ahn, S.; Mathiyalagan, R.; Wang, C.; Yang, D.C. Biosynthesis, Characterization, and Bioactivities Evaluation of Silver and Gold Nanoparticles Mediated by the Roots of Chinese Herbal Angelica pubescens Maxim. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouda, A.; Awad, M.A.; Eid, A.M.; Saied, E.; Barghoth, M.G.; Hamza, M.F.; Awad, M.F.; Abdelbary, S.; Hassan, S.E.D. An Eco-Friendly Approach to the Control of Pathogenic Microbes and Anopheles Stephensi Malarial Vector Using Magnesium Oxide Nanoparticles (Mg-NPs) Fabricated by Penicillium chrysogenum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srećković, N.; Katanić Stanković, J.S.; Matić, S.; Mihailović, N.R.; Imbimbo, P.; Monti, D.M.; Mihailović, V. Lythrum salicaria L. (Lythraceae) as a Promising Source of Phenolic Compounds in the Modulation of Oxidative Stress: Comparison between Aerial Parts and Root Extracts. Ind. Crops. Prod. 2020, 155, 112781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumarasamy, Y.; Byres, M.; Cox, P.J.; Jaspars, M.; Nahar, L.; Sarker, S.D. Screening Seeds of Some Scottish Plants for Free Radical Scavenging Activity. Phytother. Res. 2007, 21, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant Activity Applying an Improved ABTS Radical Cation Decolorization Assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarker, S.D.; Nahar, L.; Kumarasamy, Y. Microtitre Plate-Based Antibacterial Assay Incorporating Resazurin as an Indicator of Cell Growth, and Its Application in the in vitro Antibacterial Screening of Phytochemicals. Methods 2007, 42, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CLSI. Serving the World’ s Medical Science Community Through Voluntary Consensus. In Reference Method for Broth Dilution Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Yeasts, 2nd ed.; Approved Standard; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Berwyn, PA, USA, 2008; Volume 22. [Google Scholar]
- NCCLS. NCCLS Document M27-A2. In Reference Method for Broth Dilution Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Yeasts, 2nd ed.; Approved Standard; National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards: Wayne, PA, USA, 2002; Volume 22, ISBN 1-56238-469-4. [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid Colorimetric Assay for Cellular Growth and Survival: Application to Proliferation and Cytotoxicity Assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umamaheswari, C.; Lakshmanan, A.; Nagarajan, N.S. Green Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Degradation Studies of Gold Nanoparticles against Congo Red and Methyl Orange. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2018, 178, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Microorganisms | MIC (µg/mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FUAgNP | SVAgNP | Ciprofloxacin/ Clotrimazole a | ||
| Bacterial Strains | ||||
| S. aureus S. epidermidis B. cereus B. subtilis E. faecalis M. lysodeikticus E. coli S. typhimurium S. enteritidis K. pneumoniae P. aeruginosa | G+ | ˂39.1 | 78.1 | 2.5 |
| G+ | 625.0 | 156.2 | 2.5 | |
| G+ | ˂39.1 | ˂39.1 | 20 | |
| G+ | ˂39.1 | 78.1 | 10 | |
| G+ | ˂39.1 | ˂39.1 | ˂0.3125 | |
| G+ | 625.0 | 156.2 | ˂0.3125 | |
| G− | 625.0 | 2500 | ˂0.3125 | |
| G− | 78.1 | 78.1 | 5 | |
| G− | ˂39.1 | ˂39.1 | ˂0.3125 | |
| G− | ˂39.1 | ˂39.1 | ˂0.3125 | |
| G− | ˂39.1 | 78.1 | ˂0.3125 | |
| Fungal Strains | ||||
| C. albicans | 312.5 | 312.5 | 10 | |
| A. brasiliensis | ˃10 × 103 | ˃10 × 103 | 1.25 | |
| P. canescens | ˂78.1 | ˂78.1 | 2.5 | |
| P. cyclopium | ˂78.1 | ˂78.1 | ˂0.0391 | |
| T. lougibrachiatum | ˂78.1 | 312.5 | 20 | |
| T. harzianum | 1250 | 1250 | 40 | |
| F. oxysporum | ˃10 × 103 | ˃10 × 103 | ˂0.0391 | |
| D. stemonitis | 5 × 103 | 5 × 103 | 0.625 | |
| A. alternata | ˃10 × 103 | ˃10 × 103 | ˂0.0391 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mihailović, V.; Srećković, N.; Nedić, Z.P.; Dimitrijević, S.; Matić, M.; Obradović, A.; Selaković, D.; Rosić, G.; Katanić Stanković, J.S. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Salvia verticillata and Filipendula ulmaria Extracts: Optimization of Synthesis, Biological Activities, and Catalytic Properties. Molecules 2023, 28, 808. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020808
Mihailović V, Srećković N, Nedić ZP, Dimitrijević S, Matić M, Obradović A, Selaković D, Rosić G, Katanić Stanković JS. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Salvia verticillata and Filipendula ulmaria Extracts: Optimization of Synthesis, Biological Activities, and Catalytic Properties. Molecules. 2023; 28(2):808. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020808
Chicago/Turabian StyleMihailović, Vladimir, Nikola Srećković, Zoran P. Nedić, Silvana Dimitrijević, Miloš Matić, Ana Obradović, Dragica Selaković, Gvozden Rosić, and Jelena S. Katanić Stanković. 2023. "Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Salvia verticillata and Filipendula ulmaria Extracts: Optimization of Synthesis, Biological Activities, and Catalytic Properties" Molecules 28, no. 2: 808. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020808
APA StyleMihailović, V., Srećković, N., Nedić, Z. P., Dimitrijević, S., Matić, M., Obradović, A., Selaković, D., Rosić, G., & Katanić Stanković, J. S. (2023). Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Salvia verticillata and Filipendula ulmaria Extracts: Optimization of Synthesis, Biological Activities, and Catalytic Properties. Molecules, 28(2), 808. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020808







