Revisiting Supersaturation of a Biopharmaceutical Classification System IIB Drug: Evaluation via a Multi-Cup Dissolution Approach and Molecular Dynamic Simulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
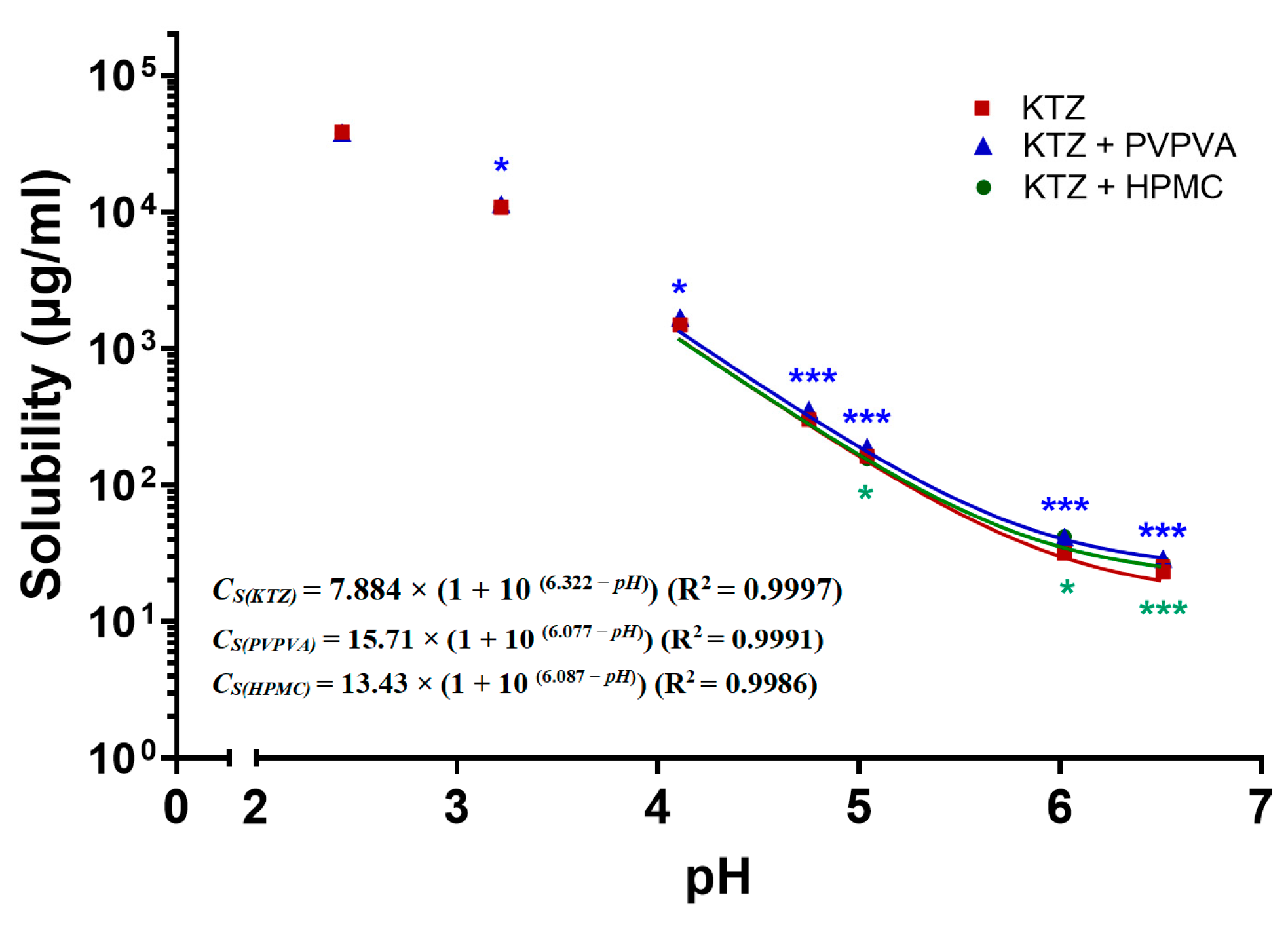
2.1. pH-Dependent Solubility
2.2. In Vitro Supersaturation–Precipitation and Absorption Assay
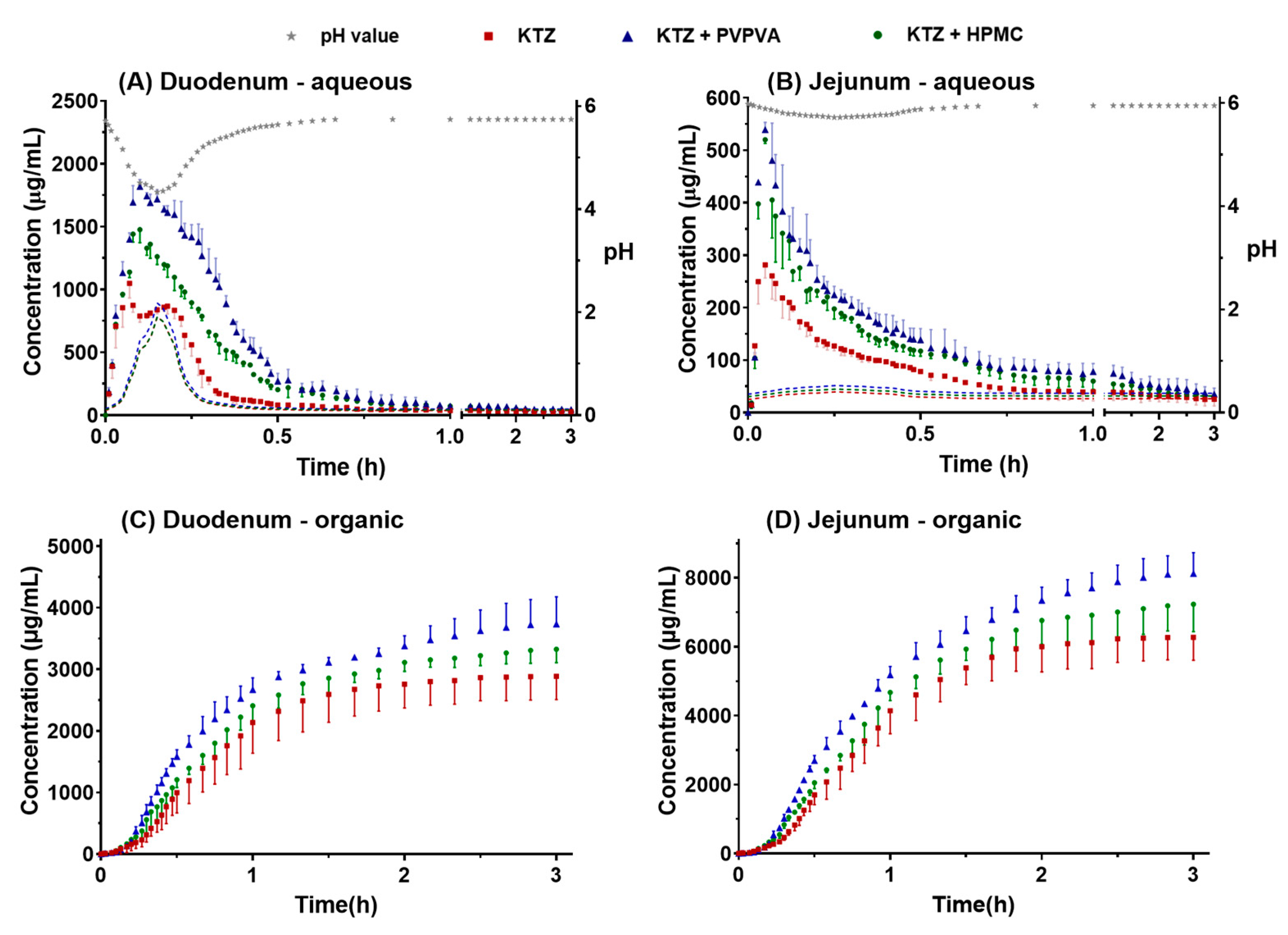
2.2.1. Supersaturation–Precipitation and Absorption in the DGIM
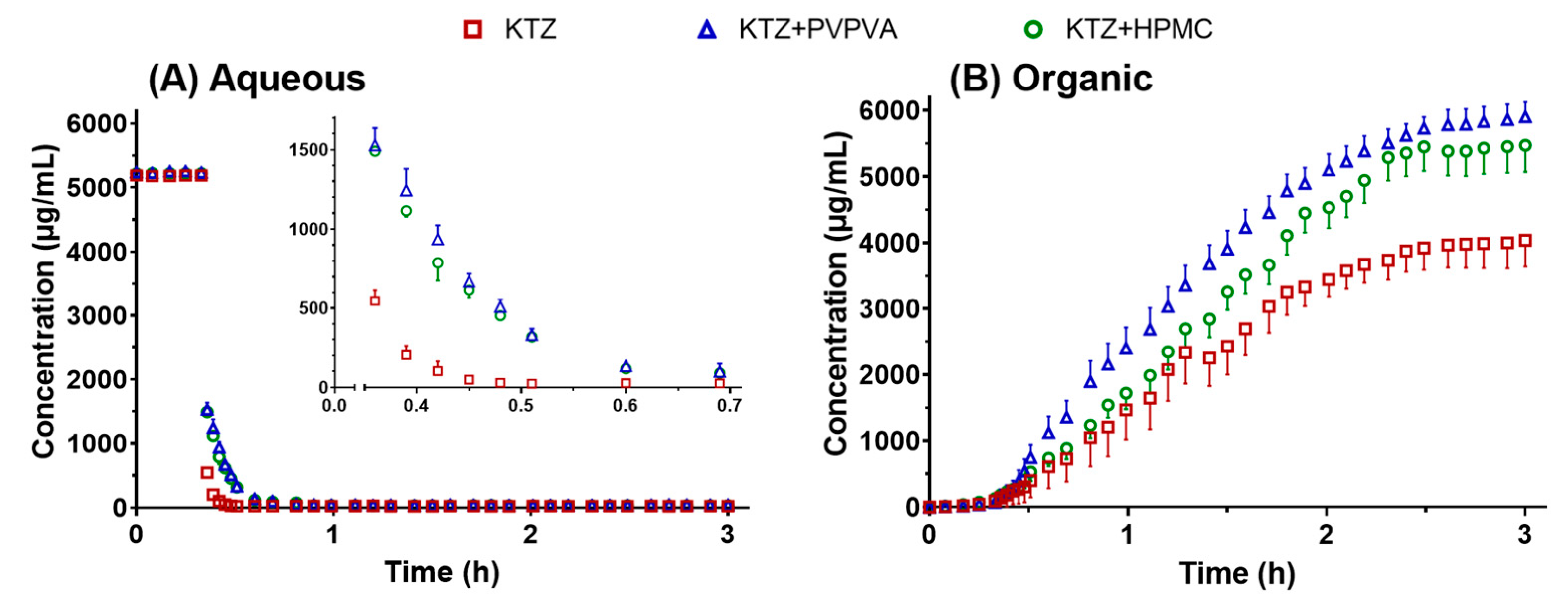
2.2.2. Supersaturation and Absorption in the USP II
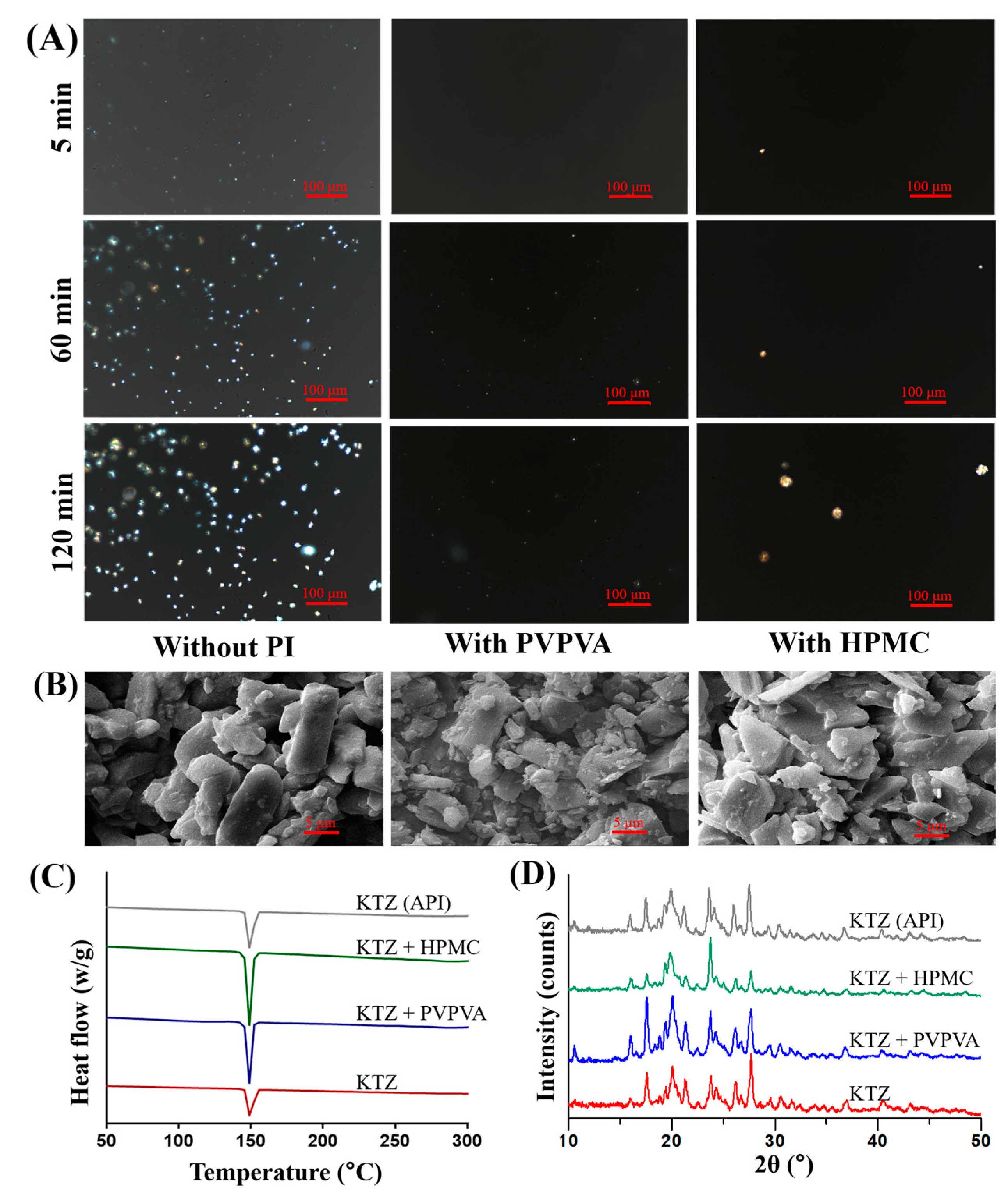
2.3. Solid State Characterizations
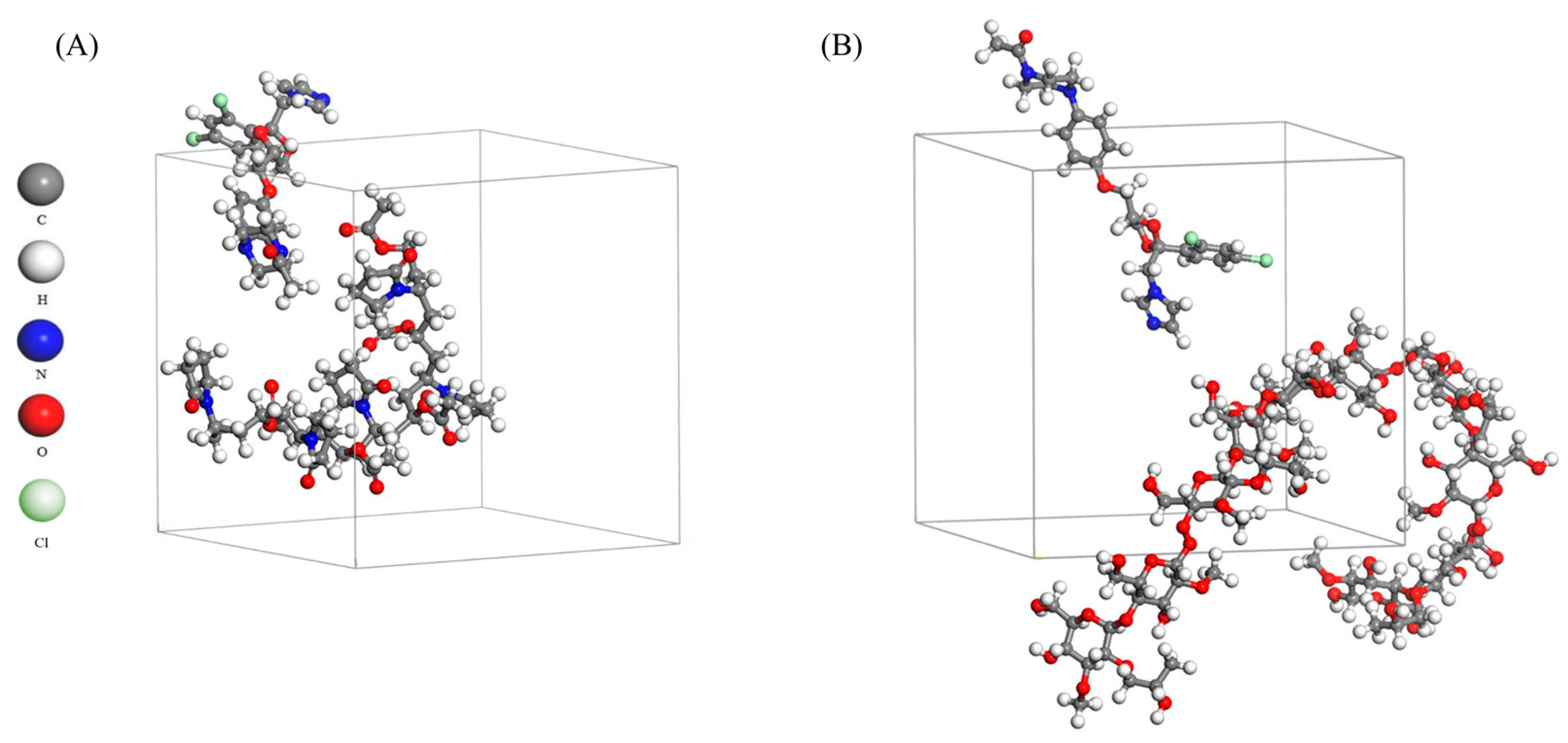
2.4. Molecular Dynamic Simulation
2.5. In Vivo Pharmacokinetics
2.6. IVIVC
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. pH-Dependent Solubility Measurements
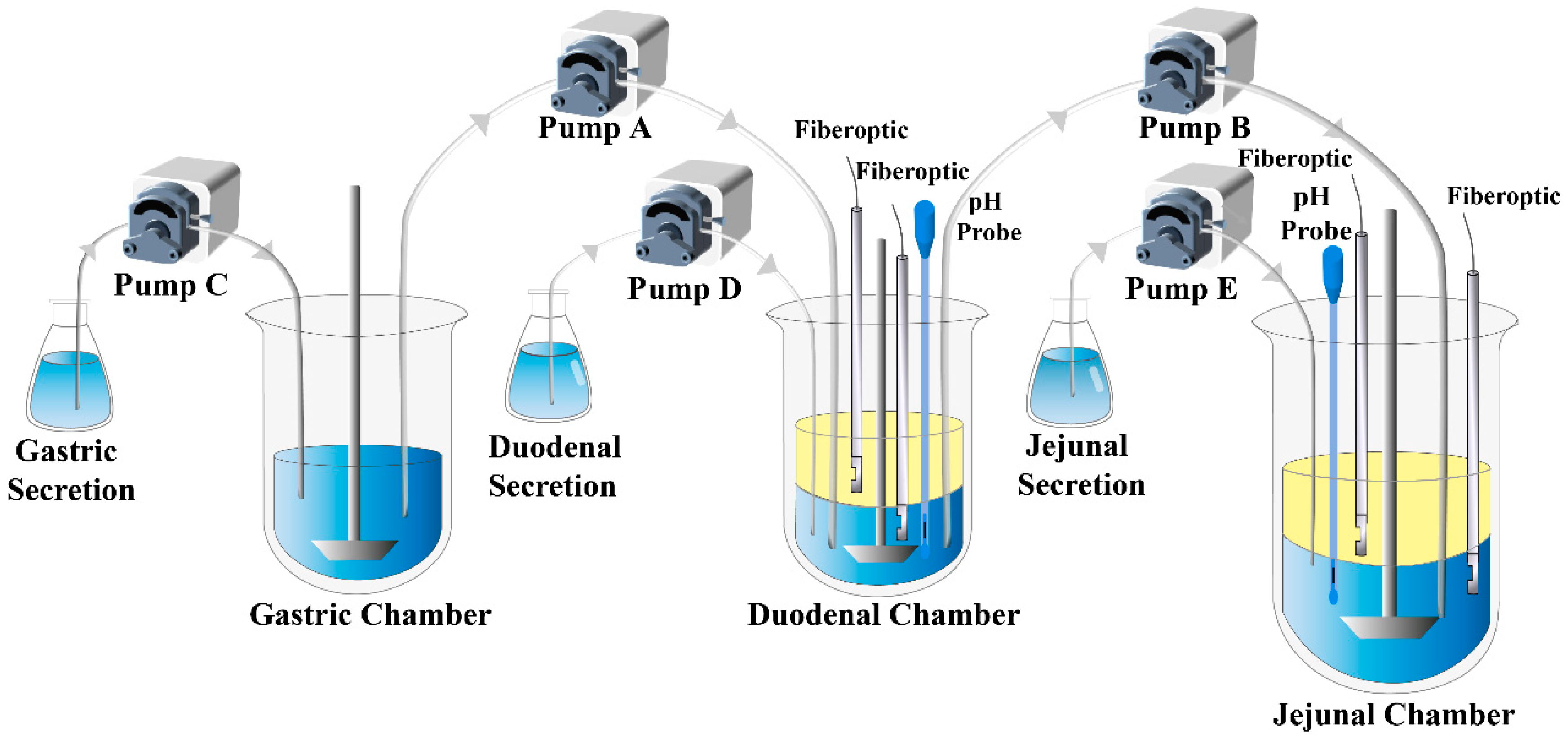
3.3. In Vitro Supersaturation–Precipitation and Absorption Assay
3.3.1. Supersaturation–Precipitation and Absorption in the DGIM
3.3.2. Supersaturation–Precipitation and Absorption in the USP II
3.4. Solid State Characterizations
3.4.1. Polarizing Microscopy
3.4.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.4.3. X-ray Powder Diffraction
3.4.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
3.5. Molecular Dynamic Simulation
3.6. Pharmacokinetic Study
3.7. In Vitro–In Vivo Correlation
3.8. Statistics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Sharma, A.; Arora, K.; Mohapatra, H.; Sindhu, R.K.; Bulzan, M.; Cavalu, S.; Paneshar, G.; Elansary, H.O.; El-Sabrout, A.M.; Mahmoud, E.A.; et al. Supersaturation-Based Drug Delivery Systems: Strategy for Bioavailability Enhancement of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs. Molecules 2022, 27, 2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzmán, H.; Tawa, M.; Zhang, Z.; Ratanabanangkoon, P.; Shaw, P.; Mustonen, P.; Gardner, C.; Chen, H.; Moreau, J.-P.; Almarsson, O.; et al. Spring and parachute approach to designing solid celecoxib formulations having enhanced oral absorption. AAPS J. 2004, 6, T2189. [Google Scholar]
- Tsume, Y.; Mudie, D.M.; Langguth, P.; Amidon, G.E.; Amidon, G.L. The Biopharmaceutics Classification System: Subclasses for in vivo predictive dissolution (IPD) methodology and IVIVC. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 57, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bevernage, J.; Brouwers, J.; Brewster, M.E.; Augustijns, P. Evaluation of gastrointestinal drug supersaturation and precipitation: Strategies and issues. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinarov, Z.; Abrahamsson, B.; Artursson, P.; Batchelor, H.; Berben, P.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A.; Butler, J.; Ceulemans, J.; Davies, N.; Dupont, D.; et al. Current challenges and future perspectives in oral absorption research: An opinion of the UNGAP network. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 171, 289–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, A.; Fadda, H.M. Effect of surfactants, gastric emptying, and dosage form on supersaturation of dipyridamole in an in vitro model simulating the stomach and duodenum. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 2835–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, K.; Tsume, Y.; Amidon, G.E.; Amidon, G.L. In Vitro Dissolution of Fluconazole and Dipyridamole in Gastrointestinal Simulator (GIS), Predicting in Vivo Dissolution and Drug-Drug Interaction Caused by Acid-Reducing Agents. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 2418–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hens, B.; Bermejo, M.; Cristofoletti, R.; Amidon, G.E.; Amidon, G.L. Application of the Gastrointestinal Simulator (GIS) Coupled with In Silico Modeling to Measure the Impact of Coca-Cola(®) on the Luminal and Systemic Behavior of Loratadine (BCS Class 2b). Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, K.; Tsume, Y.; Amidon, G.E.; Amidon, G.L. The Evaluation of In Vitro Drug Dissolution of Commercially Available Oral Dosage Forms for Itraconazole in Gastrointestinal Simulator With Biorelevant Media. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2804–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsume, Y.; Patel, S.; Wang, M.; Hermans, A.; Kesisoglou, F. The Introduction of a New Flexible In Vivo Predictive Dissolution Apparatus, GIS-Alpha (GIS-α), to Study Dissolution Profiles of BCS Class IIb Drugs, Dipyridamole and Ketoconazole. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 109, 3471–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berben, P.; Ashworth, L.; Beato, S.; Bevernage, J.; Bruel, J.L.; Butler, J.; Dressman, J.; Schafer, K.; Hutchins, P.; Klumpp, L.; et al. Biorelevant dissolution testing of a weak base: Interlaboratory reproducibility and investigation of parameters controlling in vitro precipitation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 140, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsume, Y.; Matsui, K.; Searls, A.L.; Takeuchi, S.; Amidon, G.E.; Sun, D.; Amidon, G.L. The impact of supersaturation level for oral absorption of BCS class IIb drugs, dipyridamole and ketoconazole, using in vivo predictive dissolution system: Gastrointestinal Simulator (GIS). Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 102, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsume, Y.; Igawa, N.; Drelich, A.J.; Amidon, G.E.; Amidon, G.L. The combination of GIS and biphasic to better predict in vivo dissolution of BCS class IIb drugs, ketoconazole and raloxifene. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 107, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsume, Y.; Igawa, N.; Drelich, A.J.; Ruan, H.; Amidon, G.E.; Amidon, G.L. The in vivo predictive dissolution for immediate release dosage of donepezil and danazol, BCS class IIc drugs, with the GIS and the USP II with biphasic dissolution apparatus. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 100920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, D.; Zhang, H.; Baak, J.P.; Luo, L.; Xia, Y.; Wang, J.; Ke, X.; Sun, P. Evaluating supersaturation in vitro and predicting its performance in vivo with Biphasic gastrointestinal Simulator: A case study of a BCS IIB drug. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 578, 119043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Baak, J.P.A.; Chen, T.; Ye, H.; Liao, W.; Lv, H.; Wen, C.; Zheng, S. Supersaturation and Precipitation Applicated in Drug Delivery Systems: Development Strategies and Evaluation Approaches. Molecules 2023, 28, 2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Sun, M.; Zhao, Y.; Song, X.; He, Z.; Wang, J.; Sun, J. Molecular mechanism of polymer-assisting supersaturation of poorly water-soluble loratadine based on experimental observations and molecular dynamic simulations. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2017, 7, 738–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hens, B.; Bermejo, M.; Tsume, Y.; Gonzalez-Alvarez, I.; Ruan, H.; Matsui, K.; Amidon, G.E.; Cavanagh, K.L.; Kuminek, G.; Benninghoff, G.; et al. Evaluation and optimized selection of supersaturating drug delivery systems of posaconazole (BCS class 2b) in the gastrointestinal simulator (GIS): An in vitro-in silico-in vivo approach. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 115, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, E.L.; Basit, A.W.; Murdan, S. Measurements of rat and mouse gastrointestinal pH, fluid and lymphoid tissue, and implications for in-vivo experiments. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2008, 60, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Guidance for Industry: Extended Release Oral Dosage Forms: Development, Evaluation, and Application of In Vitro/In Vivo Correlations; US Department of Health and Human Services, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER): Rockville, MD, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Indulkar, A.S.; Box, K.J.; Taylor, R.; Ruiz, R.; Taylor, L.S. pH-Dependent Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation of Highly Supersaturated Solutions of Weakly Basic Drugs. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 2365–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, M.; Hinatsu, Y.; Kusamori, K.; Katsumi, H.; Sakane, T.; Nakatani, M.; Wada, K.; Yamamoto, A. Improved dissolution and absorption of ketoconazole in the presence of organic acids as pH-modifiers. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 76, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestieau, A.; Evrard, B. In vitro biphasic dissolution tests and their suitability for establishing in vitro-in vivo correlations: A historical review. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 102, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plum, J.; Bavnhøj, C.; Palmelund, H.; Pérez-Alós, L.; Müllertz, A.; Rades, T. Comparison of induction methods for supersaturation: pH shift versus solvent shift. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 573, 118862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bren, U.; Oostenbrink, C. Cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibition by ketoconazole: Tackling the problem of ligand cooperativity using molecular dynamics simulations and free-energy calculations. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 1573–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deutsch, P.H.; Quintiliani, R. Ketoconazole. Conn. Med. 1984, 48, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patel, V.; Liaw, B.; Oh, W. The role of ketoconazole in current prostate cancer care. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2018, 15, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psachoulias, D.; Vertzoni, M.; Goumas, K.; Kalioras, V.; Beato, S.; Butler, J.; Reppas, C. Precipitation in and supersaturation of contents of the upper small intestine after administration of two weak bases to fasted adults. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 3145–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukiage, M.; Suzuki, K.; Matsuda, M.; Nishida, Y.; Oikawa, M.; Fujita, T.; Kawakami, K. Inhibition of Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation for Breaking the Solubility Barrier of Amorphous Solid Dispersions to Improve Oral Absorption of Naftopidil. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares-Morales, A.; Ghosh, A.; Aarons, L.; Rostami-Hodjegan, A. Development of a Novel Simplified PBPK Absorption Model to Explain the Higher Relative Bioavailability of the OROS® Formulation of Oxybutynin. AAPS J. 2016, 18, 1532–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madabushi, R.; Seo, P.; Zhao, L.; Tegenge, M.; Zhu, H. Review: Role of Model-Informed Drug Development Approaches in the Lifecycle of Drug Development and Regulatory Decision-Making. Pharm. Res. 2022, 39, 1669–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Han, H.; Wang, J.; Wei, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, J. Model Informed Drug Development and Regulation in China: Challenges and Opportunities. CPT Pharmacomet. Syst. Pharmacol. 2019, 8, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, M.A.; Flanagan, T.; Brewster, M.; Kesisoglou, F.; Beato, S.; Biewenga, J.; Crison, J.; Holm, R.; Li, R.; Mannaert, E.; et al. A survey on IVIVC/IVIVR development in the pharmaceutical industry—Past experience and current perspectives. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 102, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanbhogue, M.H.; Thirumaleshwar, S.; Tegginamath, P.K.; Somareddy, H.K. Artificial Intelligence in Pharmaceutical Field–A Critical Review. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2021, 18, 1456–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Kwong, C.F.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Z. A Novel Artificial Intelligence System in Formulation Dissolution Prediction. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 8640115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bein, A.; Shin, W.; Jalili-Firoozinezhad, S.; Park, M.H.; Sontheimer-Phelps, A.; Tovaglieri, A.; Chalkiadaki, A.; Kim, H.J.; Ingber, D.E. Microfluidic Organ-on-a-Chip Models of Human Intestine. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 5, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Su, W.; Zhu, Y.; Tao, T.; Li, D.; Peng, X.; Qin, J. Drug absorption related nephrotoxicity assessment on an intestine-kidney chip. Biomicrofluidics 2017, 11, 034114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Choi, N.; Sung, J.H. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic insights from microfluidic intestine-on-a-chip models. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2019, 15, 1005–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portela, R.M.C.; Varsakelis, C.; Richelle, A.; Giannelos, N.; Pence, J.; Dessoy, S.; von Stosch, M. When Is an In Silico Representation a Digital Twin? A Biopharmaceutical Industry Approach to the Digital Twin Concept. Adv. Biochem. Eng./Biotechnol. 2021, 176, 35–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schütt, M.; O’Farrell, C.; Stamatopoulos, K.; Hoad, C.L.; Marciani, L.; Sulaiman, S.; Simmons, M.J.H.; Batchelor, H.K.; Alexiadis, A. Simulating the Hydrodynamic Conditions of the Human Ascending Colon: A Digital Twin of the Dynamic Colon Model. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schütt, M.; Stamatopoulos, K.; Batchelor, H.K.; Simmons, M.J.H.; Alexiadis, A. Development of a digital twin of a tablet that mimics a real solid dosage form: Differences in the dissolution profile in conventional mini-USP II and a biorelevant colon model. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 179, 106310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
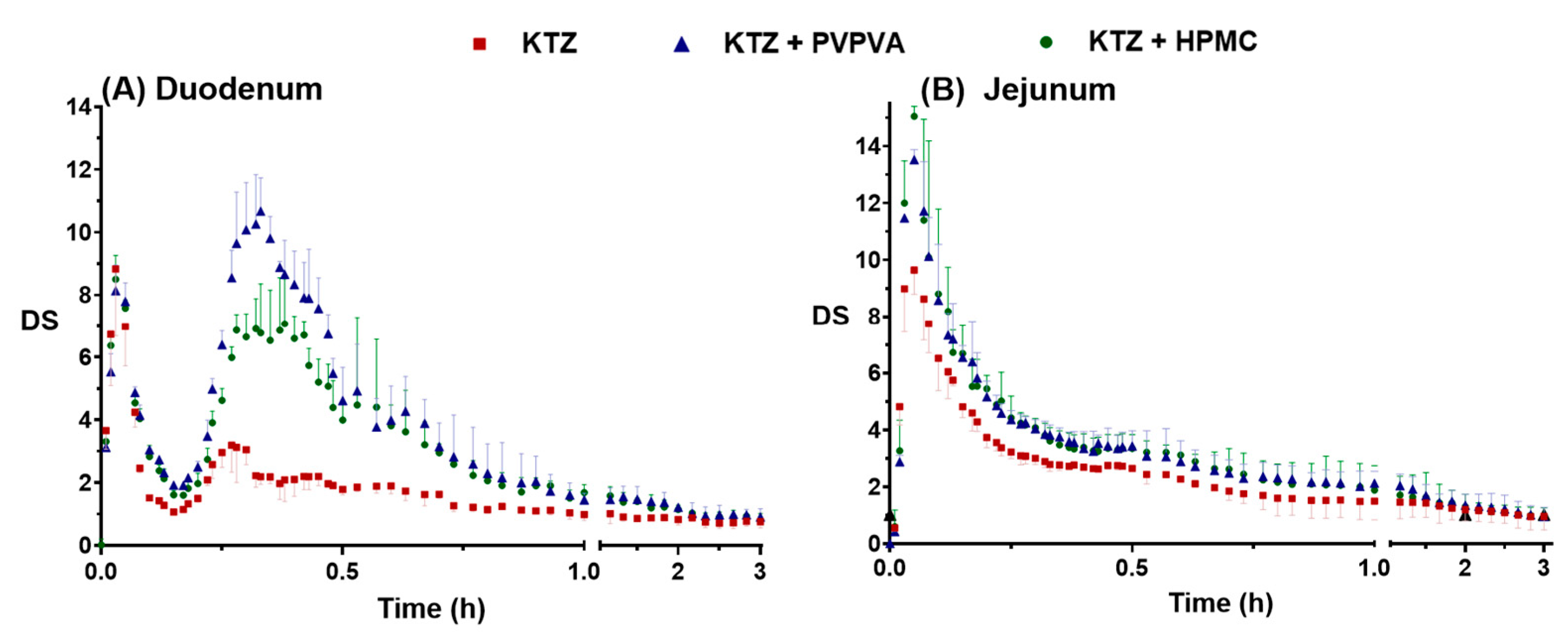


| Group | Duodenal | Jejunal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSmax | DSAUC | DSmax | DSAUC | |
| Control | 8.837 | 3.715 | 9.643 | 5.452 |
| PVPVA | 10.68 | 6.988 | 13.53 | 6.859 |
| HPMC | 8.507 | 6.095 | 15.05 | 6.660 |
| DGIM | USP II | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | PVPVA | HPMC | Mean | Control | PVPVA | HPMC | Mean | ||
| Cmax (ng·mL−1) | Observation | 41,300 | 48,100 | 45,400 | 41,300 | 48,100 | 45,400 | ||
| Prediction | 45,529 | 54,269 | 48,488 | 45,702 | 58,480 | 57,044 | |||
| PE (%) | 10.24 | 12.83 | 6.80 | 9.96 | 10.66 | 21.58 | 25.65 | 19.3 | |
| AUC (h·ng·mL−1) | Observation | 112,853 | 146,143 | 135,015 | 112,853 | 146,144 | 135,015 | ||
| Prediction | 114,652 | 144,456 | 135,032 | 108,727 | 149,731 | 126,032 | |||
| PE (%) | 1.59 | −1.16 | 0.01 | 0.92 | −3.66 | 2.45 | −6.65 | 4.25 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gan, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hu, H.; Xiao, W.; Yu, Z.; Sun, T.; Zhang, J.; Wen, C.; Zheng, S. Revisiting Supersaturation of a Biopharmaceutical Classification System IIB Drug: Evaluation via a Multi-Cup Dissolution Approach and Molecular Dynamic Simulation. Molecules 2023, 28, 6962. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196962
Gan Y, Xu Y, Zhang X, Hu H, Xiao W, Yu Z, Sun T, Zhang J, Wen C, Zheng S. Revisiting Supersaturation of a Biopharmaceutical Classification System IIB Drug: Evaluation via a Multi-Cup Dissolution Approach and Molecular Dynamic Simulation. Molecules. 2023; 28(19):6962. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196962
Chicago/Turabian StyleGan, Yanxiong, Yaxin Xu, Xue Zhang, Huiling Hu, Wenke Xiao, Zheng Yu, Tao Sun, Jinming Zhang, Chuanbiao Wen, and Shichao Zheng. 2023. "Revisiting Supersaturation of a Biopharmaceutical Classification System IIB Drug: Evaluation via a Multi-Cup Dissolution Approach and Molecular Dynamic Simulation" Molecules 28, no. 19: 6962. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196962
APA StyleGan, Y., Xu, Y., Zhang, X., Hu, H., Xiao, W., Yu, Z., Sun, T., Zhang, J., Wen, C., & Zheng, S. (2023). Revisiting Supersaturation of a Biopharmaceutical Classification System IIB Drug: Evaluation via a Multi-Cup Dissolution Approach and Molecular Dynamic Simulation. Molecules, 28(19), 6962. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196962






