Photo-Induced, Phenylhydrazine-Promoted Transition-Metal-Free Dehalogenation of Aryl Fluorides, Chlorides, Bromides, and Iodides
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Information
4.2. Procedure for the Deiodination of 4-chloro-1,1′-biphenyl
4.3. General Procedure for the Reduction of C−X Bond
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Fukuzumi, S.; Kotani, H.; Ohkubo, K.; Ogo, S.; Tkachenko, N.V.; Lemmetyinen, H. Electron-transfer state of 9-mesityl-10-methylacridinium ion with a much longer lifetime and higher energy than that of the natural photosynthetic reaction center. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 1600–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowsky, D.; McNeill, K.; Cramer, C.J. Dehalogenation of aromatics by nucleophilic aromatic substitution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 10904–10906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrad, S.; Robson, M.; Hazrati, S.; Baxter-Plant, V.S.; Deplanche, K.; Redwood, M.D.; Macaskie, L.E. Dehalogenation of polychlorinated biphenyls and polybrominated diphenyl ethers using a hybrid bioinorganic catalyst. J. Environ. Monit. 2007, 9, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mitoma, Y.; Nagashima, S.; Simion, C.; Simion, A.M.; Yamada, T.; Mimura, K.; Ishimoto, K.; Tashiro, M. Dehalogenation of aromatic halides using metallic calcium in ethanol. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 4145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hites, R.A. Environmental behavior of chlorinated dioxins and furans. Acc. Chem. Res. 1990, 23, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjya, A.; Klumphu, P.; Lipshutz, B. Ligand-Free, Palladium-Catalyzed Dihydrogen Generation from TMDS: Dehalogenation of aryl halides on water. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyo, A.; Kim, S.; Kumar, M.R.; Byeun, A.; Eom, M.S.; Han, M.S.; Lee, S. Palladium-catalyzed hydrodehalogenation of aryl halides using paraformaldehyde as the hydride source: High-throughput screening by paper-based colorimetric iodide sensor. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawisza, A.M.; Muzart, J. Pd-catalyzed reduction of aryl halides using dimethylformamide as the hydride source. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 6738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Hou, F. Transition-metal-free dehalogenation of aryl halides promoted by phenanthroline/potassium tert-butoxide. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, R.; Shimizu, T.; Shirakawa, E. Reduction of aryl halides into arenes with 2-propanol promoted by a substoichiometric amount of a tert-butoxy radical source. Synlett 2016, 27, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, D.Y.; Tejo, C.; Xu, K.; Hirao, H.; Chiba, S. Hydrodehalogenation of haloarenes by a sodium hydride–iodide composite. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewanji, A.; Mück-Lichtenfeld, C.; Studer, A. Radical hydrodeiodination of aryl, alkenyl, alkynyl, and alkyl iodides with an alcoholate as organic chain reductant through electron catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 6749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, D.-W.; Yan, C.-X.; Zhou, P.-P.; Zeng, H.-Y.; Li, C.-J. Hydrogen bonding promoted simple and clean photo-induced reduction of C–X bond with isopropanol. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuyama, T.; Fujita, Y.; Miyoshi, H.; Ryu, I.; Kao, S.-C.; Wu, Y.-K. Electron transfer-induced reduction of organic halides with amines. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 5582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Bak, J.R.; Loópez-Delgado, F.J.; Jørgensen, K.A. Practical metal-and additive-free methods for radical-mediated reduction and cyclization reactions. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, T.; Ryu, I. Radical reactions of borohydrides. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 9733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dichiarante, V.; Fagnoni, M.; Albini, A. Eco-friendly hydrodehalogenation of electron-rich aryl chlorides and fluorides by photochemical reaction. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 942–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gair, J.J.; Grey, R.L.; Giroux, S.; Brodney, M.A. Palladium catalyzed hydrodefluorination of fluoro-(hetero) arenes. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, J.H.; Kim, D.; Teets, T.S. Photoredox catalysis on unactivated substrates with strongly reducing iridium photosensitizers. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 4069–4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.S.; Tang, W.X.; Chen, X.Y. Electron donor–acceptor complex enabled cascade reaction of unprotected o-anilide aryl chlorides for heterocycle synthesis. Org. Chem. Front. 2023, 10, 1219–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dam, B.; Sahoo, A.K.; Patel, B.K. Visible-light-mediated synthesis of β-keto sulfones using g-C3N 4 as a recyclable photocatalyst under sustainable conditions. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 7122–7130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäsing, F.; Nu, H.; Klingauf, J.; Studer, A. Light mediated preparation of palladium nanoparticles as catalysts for alkyne cis-semihydrogenation. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 2658. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Wang, J.C.; Dong, G.B. Modular entry to functionalized tetrahydrobenzo[b]azepines via the palladium/norbornene cooperative catalysis enabled by a C7-modified norbornene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 9991–10004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Studer, A.; Curran, D.P. Catalysis of radical reactions: A radical chemistry perspective. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Studer, A.; Curran, D.P. The electron is a catalyst. Nat. Chem. 2014, 6, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studer, A.; Curran, D.P. Organocatalysis and C-H activation meet radica- and electron-transfer reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drapeau, M.P.; Fabre, I.; Grimaud, L.; Ciofini, I.; Ollevier, T.; Taillefer, M. Transition-metal-free α-arylation of enolizable aryl ketones and mechanistic evidence for a radical process. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 10587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, W.J., Jr.; Bunnett, J.F. Relative reactivities of methanol and methoxide ion as hydrogen atom donors to the p-nitrophenyl radical. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1974, 96, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, T.; Sato, A.; Ryu, I. Photoinduced aminocarbonylation of aryl iodides. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 14764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäsing, F.; Mardyukov, A.; Doerenkamp, C.; Eckert, H.; Malkus, U.; Nüsse, H.; Klingauf, J.; Studer, A. Controlled light-mediated preparation of gold nanoparticles by a norrish type i reaction of photoactive polymers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 12612. [Google Scholar]
- Mäsing, F.; Wang, X.; Nüsse, H.; Klingauf, J.; Studer, A. Facile light-mediated preparation of small polymer-coated palladium-nanoparticles and their application as catalysts for alkyne semi-hydrogenation. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 6014. [Google Scholar]
- MacKenzie, I.A.; Wang, L.; Onuska, N.P.R.; Williams, O.F.; Begam, K.; Moran, A.M.; Dunietz, B.D.; Nicewicz, D.A. Discovery and characterization of an acridine radical photoreductant. Nature 2020, 580, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venditto, N.J.; Liang, Y.S.; El Mokadem, R.K.; Nicewicz, D.A. Ketone–olefin coupling of aliphatic and aromatic carbonyls catalyzed by excited-state acridine radicals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 11888–11896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wu, C.; Hou, J.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, M.; Huang, X.; He, W. Ferrocene-mediated photocatalytic annulation of n-sulfonyl ketimines on a polycrystalline wse2 semiconductor photocatalyst. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 13071–13076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Li, X.; Ma, J.; Zuo, J.; Song, X.; Lv, J.; Yang, D. Visible-light-induced synthesis of thioethers through three-component reactions of α-diazoesters, thiols, and cyclic ethers. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 108403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Xiao, F.; Jiang, J.; Wu, C.; Ji, H.; Lu, Y.; Wang, K.; He, W. External photocatalyst-free CH alkylation of N-sulfonyl ketimines with alkanes under visible light. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 108509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Liu, Y.; Ge, Y.; Dong, S.; Song, S.; Yang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Qu, L. Visible-light-induced regioselective ortho-c—h phosphonylation of β-naphthols with diarylphosphine oxides. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 12, 4738–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Zhu, H.; Wang, R.; Yuan, X.; Sun, K.; Qu, L.; Chen, X.; Yu, B. Bismuth vanadate: A versatile heterogeneous catalyst for photocatalytic functionalization of C(sp2)-H bonds. Chin. J. Catal. 2023, 46, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



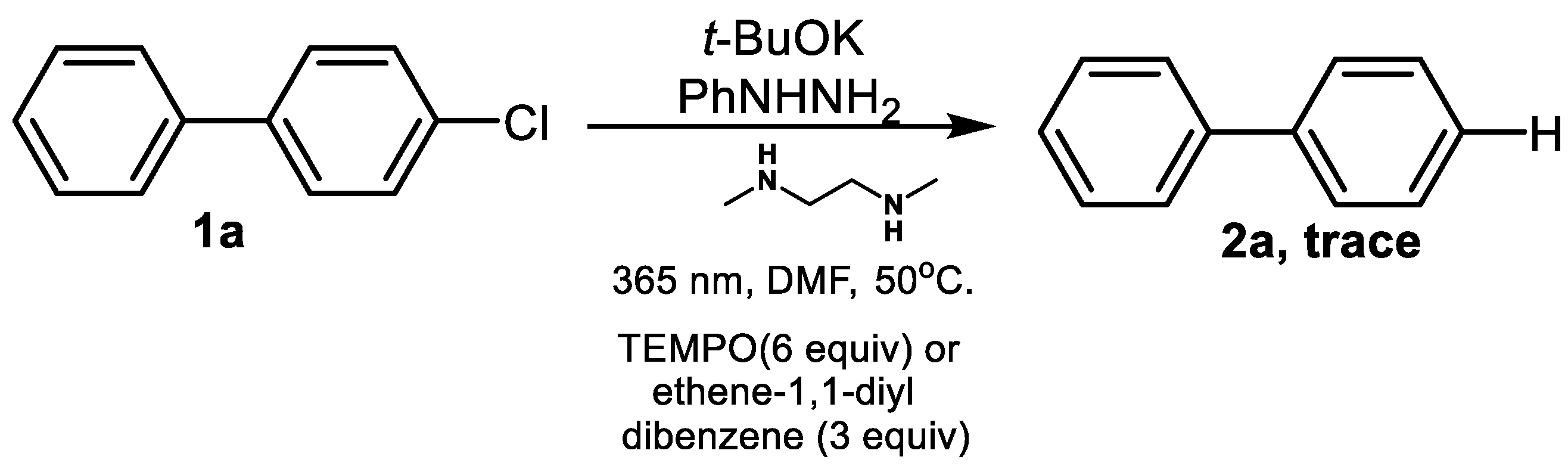

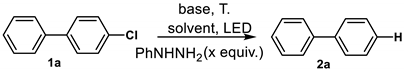
| Entry | x | Light Source | T (°C) | Base | Solvent | Yield (%) b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 365 nm | 50 | 4eq. t-BuOK + 8eq. Et3N | DMF | 6 |
| 2 | 1 | 365 nm | 50 | 4eq. t-BuOK + 8eq. Et3N | DMF | 13 |
| 3 | 2 | 365 nm | 50 | 4eq. t-BuOK + 8eq. Et3N | DMF | 29 |
| 4 | 4 | 365 nm | 50 | 4eq. t-BuOK + 8eq. Et3N | DMF | 83 |
| 5 | 6 | 365 nm | 50 | 4eq. t-BuOK + 8eq. Et3N | DMF | 72 |
| 6 | 4 | 365 nm | 50 | 4eq. t-BuOK + 8eq. Et3N | MeCN | 38 |
| 7 | 4 | 365 nm | 50 | 4eq. t-BuOK + 8eq. Et3N | 1,4-Dioxane | 15 |
| 8 | 4 | 365 nm | 50 | 4eq. t-BuOK + 8eq. Et3N | t-BuOH | 19 |
| 9 | 4 | 254 nm | 50 | 4eq. t-BuOK + 8eq. Et3N | DMF | 21 |
| 10 | 4 | 395 nm | 50 | 4eq. t-BuOK + 8eq. Et3N | DMF | 42 |
| 11 | 4 | 405 nm | 50 | 4eq. t-BuOK + 8eq. Et3N | DMF | 62 |
| 12 | 4 | 455 nm | 50 | 4eq. t-BuOK + 8eq. Et3N | DMF | 35 |
| 13 | 4 | 485 nm | 50 | 4eq. t-BuOK + 8eq. Et3N | DMF | 38 |
| 14 | 4 | Dark | 50 | 4eq. t-BuOK + 8eq. Et3N | DMF | 7 |
| 15 | 4 | 365 nm | 50 | 4eq. t-BuOK | DMF | 26 |
| 16 | 4 | 365 nm | 50 | 8eq. Et3N | DMF | 8 |
| 17 | 4 | 365 nm | 50 | 8eq. t-BuOK + 16eq. Et3N | DMF | 88 |
| 18 | 4 | 365 nm | 50 | 8eq. t-BuOK + 16eq. N,N,N′,N′-Tetramethylethylenediamine | DMF | 92 |
| 19 | 4 | 365 nm | 50 | 8eq. t-BuOK + 16eq. N,N′-Dimethyl-1,2-ethanediamine | DMF | 95 |
| 20 | 4 | 365 nm | 35 | 8eq. t-BuOK + 16eq. N,N′-Dimethyl-1,2-ethanediamine | DMF | 42 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Sun, H.; Ding, J. Photo-Induced, Phenylhydrazine-Promoted Transition-Metal-Free Dehalogenation of Aryl Fluorides, Chlorides, Bromides, and Iodides. Molecules 2023, 28, 6915. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196915
Zhu Y, Wu Z, Sun H, Ding J. Photo-Induced, Phenylhydrazine-Promoted Transition-Metal-Free Dehalogenation of Aryl Fluorides, Chlorides, Bromides, and Iodides. Molecules. 2023; 28(19):6915. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196915
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yiwei, Zhimin Wu, Hongcai Sun, and Junjun Ding. 2023. "Photo-Induced, Phenylhydrazine-Promoted Transition-Metal-Free Dehalogenation of Aryl Fluorides, Chlorides, Bromides, and Iodides" Molecules 28, no. 19: 6915. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196915
APA StyleZhu, Y., Wu, Z., Sun, H., & Ding, J. (2023). Photo-Induced, Phenylhydrazine-Promoted Transition-Metal-Free Dehalogenation of Aryl Fluorides, Chlorides, Bromides, and Iodides. Molecules, 28(19), 6915. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196915





