Solid-Phase Microextraction Techniques and Application in Food and Horticultural Crops
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Optimizing SMPE Analyte Extraction
2.1. Effect of Ionic Strength on Analyte Extraction from Samples
2.2. Effect of Extraction Efficiency on pH
3. Flavors and Aromas (Volatile Organic Compounds) in Foods Using HS-SPME
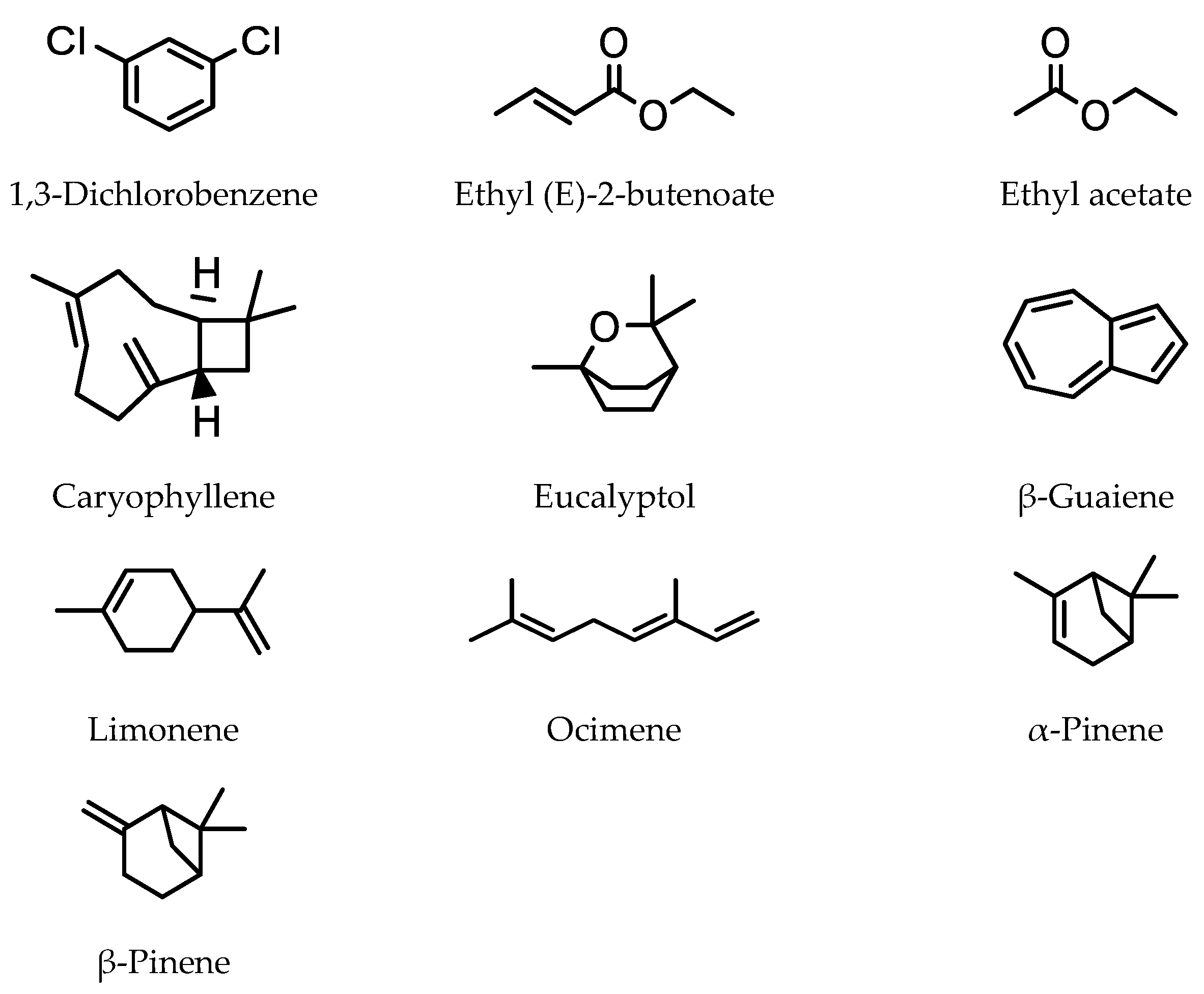
3.1. Volatile Organic Compounds in Fruit/Fruit Juice
3.2. Volatile Organic Compound Profile in Oranges Correlated with Farming Practice
3.3. Volatile Organic Compounds and Wine Quality
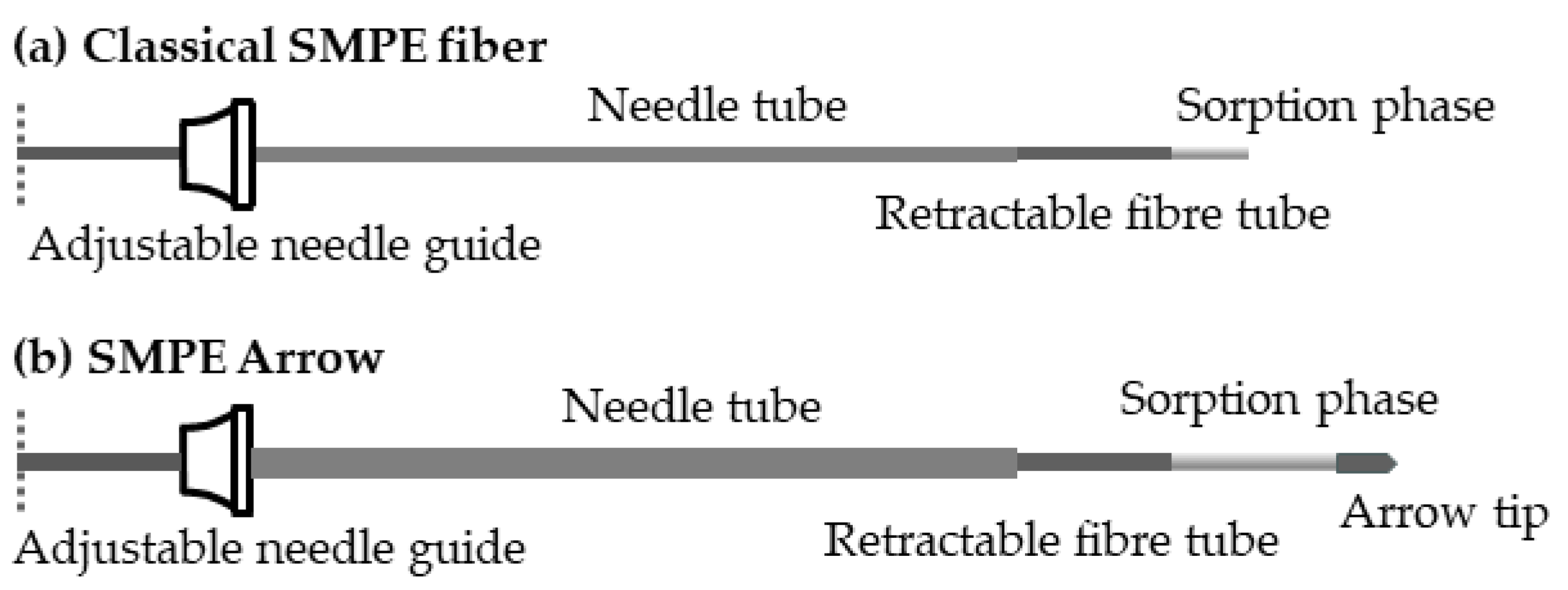
4. HS-SMPE Arrow Applications in Food Analysis
5. Applications of SPME and HPLC in Agricultural Products
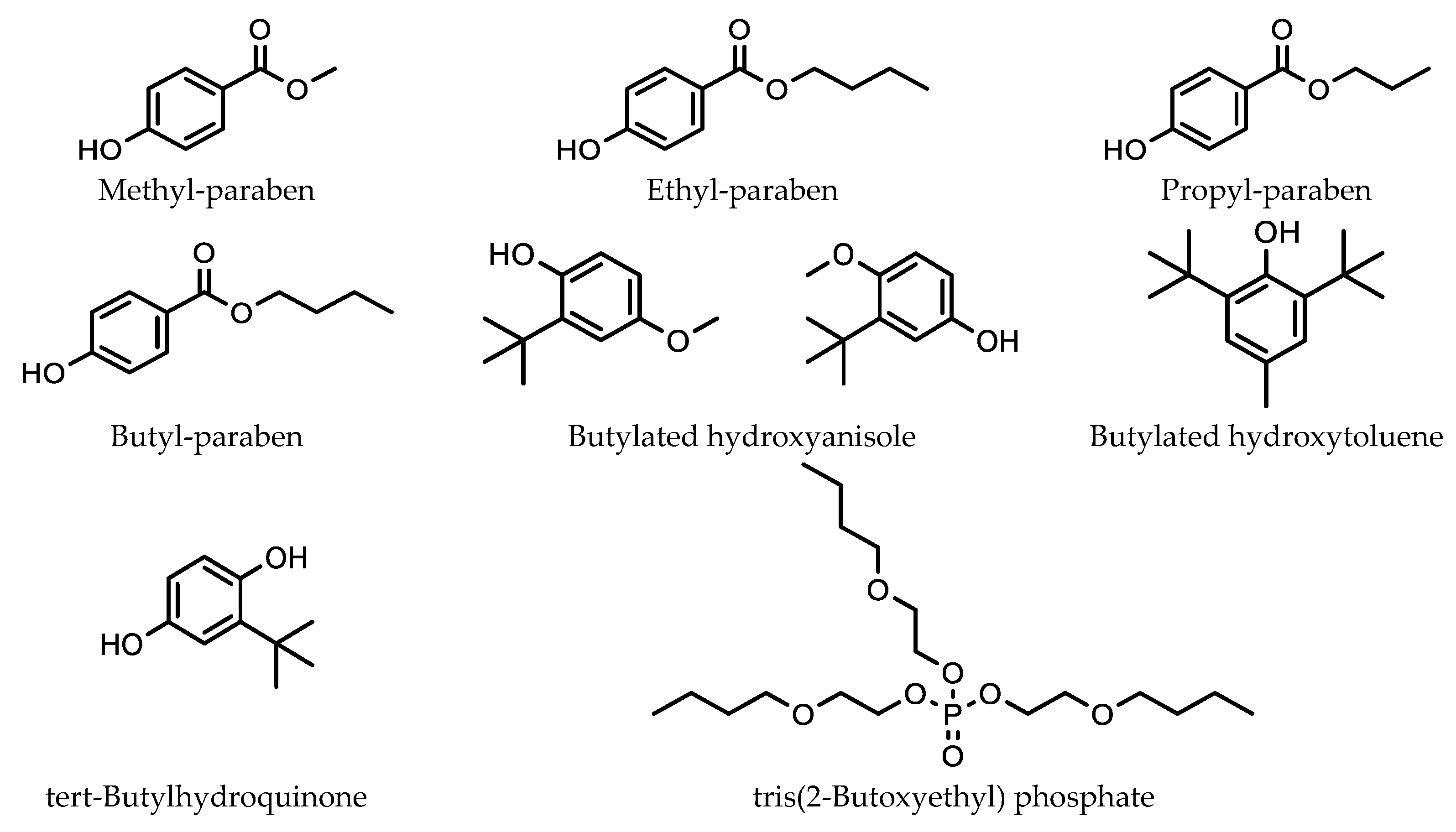
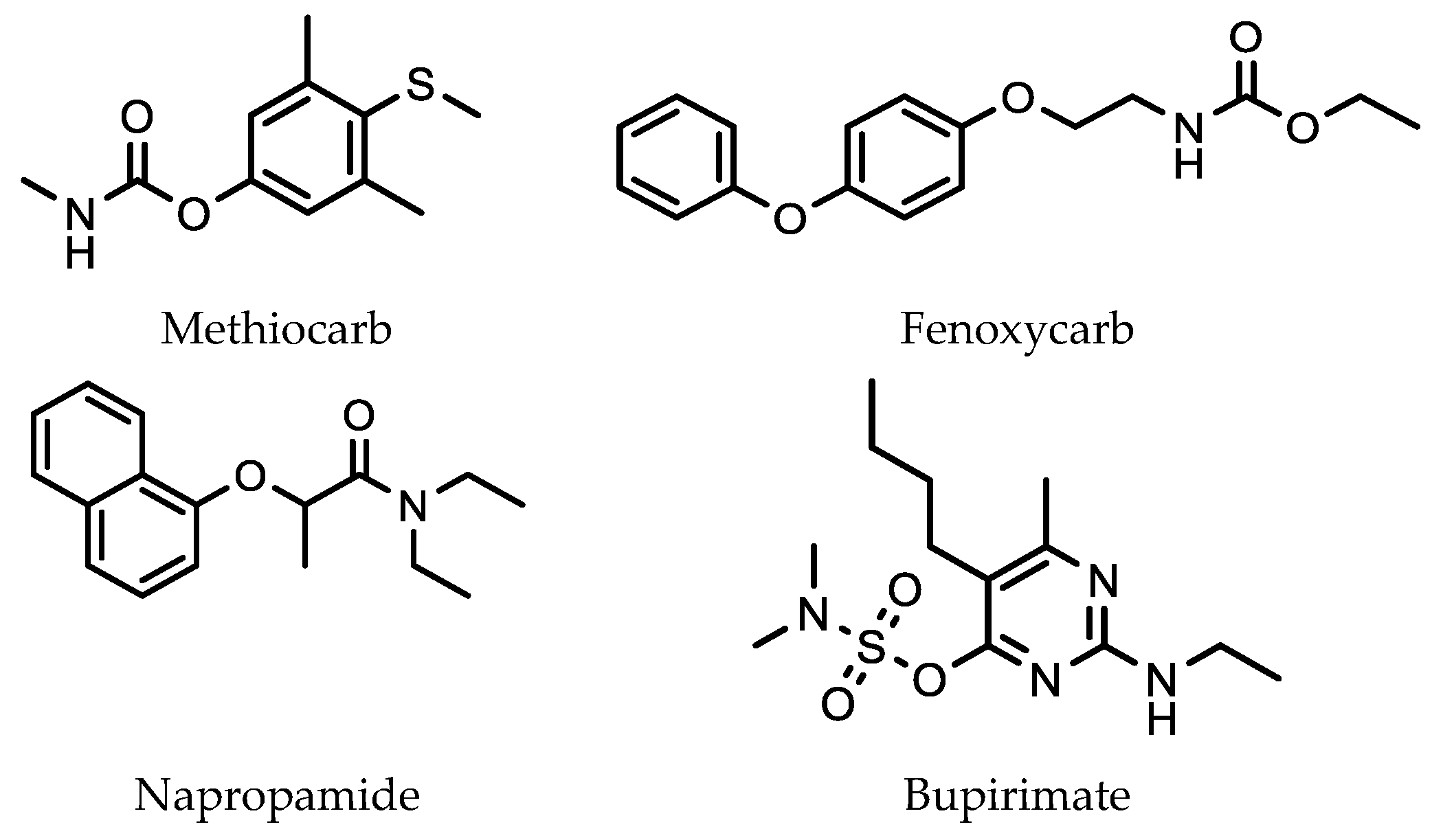
5.1. Analysis of Pesticides, Herbicides and Environmental Pollutants in Agricultural Products Using SMPE and HPLC
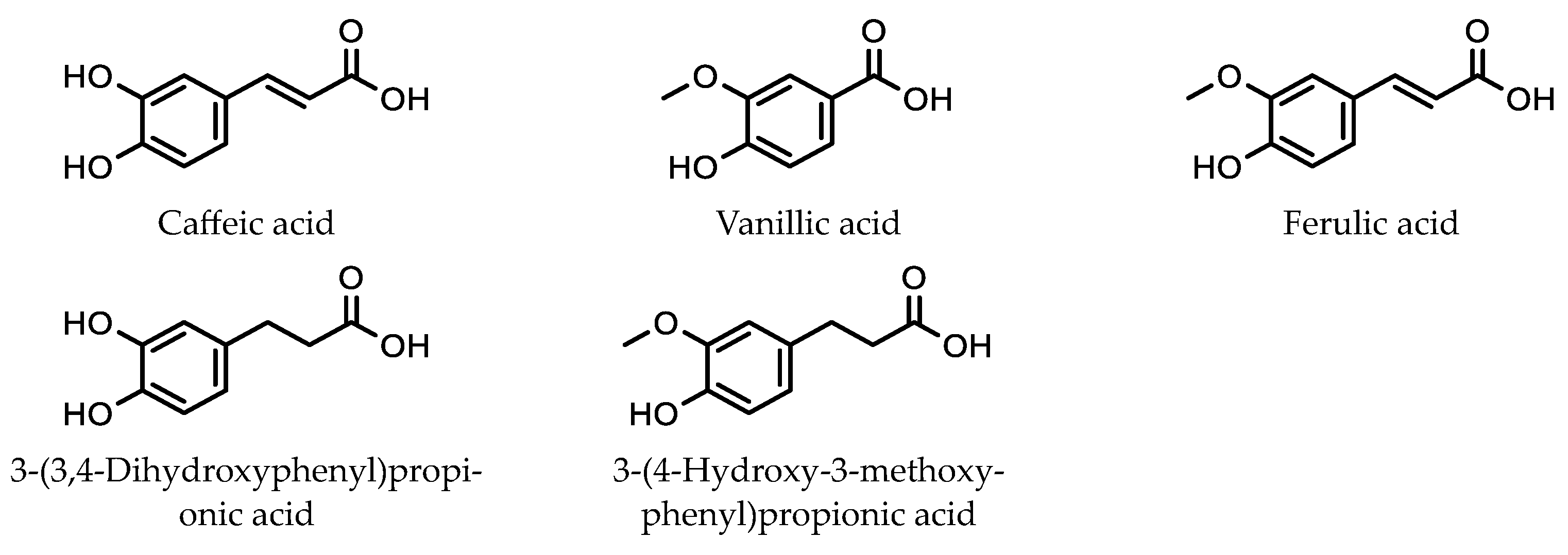
5.2. Analysis of Phenolic Acids in Orange Juice Using SMPE and HPLC
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lambropoulou, D.A.; Albanis, T.A. Methods of sample preparation for determination of pesticide residues in food matrices by chromatography-mass spectrometry-based techniques: A review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 389, 1663–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vas, G.; Vékey, K. Solid-phase microextraction: A powerful sample preparation tool prior to mass spectrometric analysis. J. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 39, 233–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthur, C.L.; Pawliszyn, J. Solid phase microextraction with thermal desorption using fused silica optical fibers. Anal. Chem. 1990, 62, 2145–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belardi, R.P.; Pawliszyn, J.B. The application of chemically modified fused silica fibers in the extraction of organics from water matrix samples and their rapid transfer to capillary columns. Water Qual. Res. J. Canada 1989, 24, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawliszyn, J. (Ed.) Unified Theory of Extraction. In Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; Volume 37, pp. 253–278. [Google Scholar]
- Reyes-Garcés, N.; Gionfriddo, E.; Gómez-Ríos, G.A.; Alam, M.N.; Boyacı, E.; Bojko, B.; Singh, V.; Grandy, J.; Pawliszyn, J. Advances in solid phase microextraction and perspective on future directions. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 302–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzi-Achkouty, S.; Estephan, N.; Ouaini, N.; Rutledge, D.N. Headspace solid-phase microextraction for wine volatile analysis. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 2009–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balkir, P.; Kemahlioglu, K.; Yucel, U. Foodomics: A new approach in food quality and safety. Trends Food Sci. 2021, 108, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalilia, V.; Barkhordari, A.; Ghiasvand, A. A comprehensive look at solid-phase microextraction technique: A review of reviews. Microchem. J. 2020, 152, 104319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza-Silva, É.A.; Gionfriddo, E.; Pawliszyn, J. A critical review of the state of the art of solid-phase microextraction of complex matrices II. Food analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 71, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piri-Moghadam, H.; Ahmadi, F.; Pawliszyn, J. A critical review of solid phase microextraction for analysis of water samples. TrAC, Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 85, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BBojko, B.; Reyes-Garcés, N.; Bessonneau, V.; Goryński, K.; Mousavi, F.; Silva, E.A.S.; Pawliszyn, J. Solid-phase microextraction in metabolomics. TrAC, Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 61, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenessov, B.; Koziel, J.A.; Bakaikina, N.V.; Orazbayeva, D. Perspectives and challenges of on-site quantification of organic pollutants in soils using solid-phase microextraction. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 85, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyacı, Á.; Rodríguez-Lafuente, Á.; Gorynski, K.; Mirnaghi, F.; Souza-Silva, É.A.; Hein, D.; Pawliszyn, J. Sample preparation with solid phase microextraction and exhaustive extraction approaches: Comparison for challenging cases. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 873, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremser, A.; Jochmann, M.A.; Schmidt, T.C. PAL SPME Arrow—Evaluation of a novel solid-phase microextraction device for freely dissolved PAHs in water. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prosen, H.; Zupancíicí-Kralj, L. Solid-phase microextraction. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 1999, 18, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirey, R.E. SPME Commercial Devices and Fibre Coatings. In Handbook of Solid Phase Microextraction; Pawliszyn, J., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 99–133. [Google Scholar]
- van Hout, M.W.J.; Niederländer, H.A.G.; de Zeeuw, R.A.; de Jong, G.J. New Developments in Integrated Sample Preparation for Bioanalysis. In Bioanalytical Separations; Wilson, I.D., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Gaurava; Malik, A.K.; Tewary, D.K.; Singh, B. A review on development of solid phase microextraction fibers by sol–gel methods and their applications. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 610, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, F.; Sandra, P. Stir bar sorptive extraction for trace analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1152, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardencki, W.; Curyło, J.; Namieśnik, J. Trends in solventless sample preparation techniques for environmental analysis. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2007, 70, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrubini, G.; Dugheri, S.; Cappelli, G.; Arcangeli, G.; Mucci, N.; Appelblad, P.; Melzi, C.; Speltini, A. Experimental designs for solid-phase microextraction method development in bioanalysis: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1119, 77–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risticevic, S.; Lord, H.; Górecki, T.; Arthur, C.L.; Pawliszyn, J. Protocol for solid-phase microextraction method development. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 122–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SMPE for GC Analysis; Merck KGaA: Darmstadt, Germany, 2020.
- Žnideršič, L.; Mlakara, A.; Prosen, H. Development of a SPME-GC-MS/MS method for the determination of some contaminants from food contact material in beverages. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 134, 110829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jové, P.; Pareras, A.; De Nadal, R.; Verdum, M. Development and optimization of a quantitative analysis of main odorants causing off flavours in cork stoppers using headspace solid-phase microextraction gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 2021, 56, e4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipowska, W.; Jaskula-Goiris, B.; Ditrych, M.; Schlich, J.; De Rouck, G.; Aerts, G.; De Cooman, L. Determination of optimal sample preparation for aldehyde extraction from pale malts and their quantification via headspace solid-phase microextraction followed by gas chromatography and mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1612, 460647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorini, D.; Pacetti, D.; Gabbianelli, R.; Gabrielli, S.; Ballini, R. A salting out system for improving the efficiency of the headspace solid-phase microextraction of short and medium chain free fatty acids. J. Chromatog. A 2015, 1409, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kataoka, H.; Lord, H.L.; Pawliszyn, J. Applications of solid-phase microextraction in food analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 880, 35–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chammui, Y. Rapid analysis of some endocrine disruptor chemicals leaching from baby milk feeding bottles Using SPME and SDME techniques. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 2607–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regueiro, J.; Negreira, N.; Simal-Gandara, J. Challenges in relating concentrations of aromas and tastes with flavor features of foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 2112–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steingass, C.B.; Glock, M.P.; Lieb, V.M.; Carle, R. Light-induced alterations of pineapple (Ananas comosus [L.] Merr.) juice volatiles during accelerated ageing and mass spectrometric studies into their precursors. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facundo, H.V.d.V.; Garruti, D.S.; Cordenunsi, B.R.; Lajolo, F.M. Isolation of volatiles compounds in banana by HS-SPME: Optimization for the whole fruit and pulp. Int. J. Biosci. Biochem. Bioinform. 2013, 3, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.; Matsukawa, T.; Kanematsu, R.; Itoh, K.; Kanzaki, S.; Shigeoka, S.; Kajiyama, S.i. Volatile profiling of fruits of 17 mango cultivars by HS-SPME-GC/MS combined with principal component analysis. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2021, 85, 1789–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanabria, G.G.R.; Garcia, A.J.C.; Lima, A.W.O.; Alejandra, B.-M.M.; Narain, N. HS-SPME-GC-MS detection of volatile compounds in Myrciaria jabuticaba Fruit. Sci. Agropecu. 2018, 9, 319–327. [Google Scholar]
- Cuevas, F.J.; Moreno-Rojas, J.M.; Ruiz-Moreno, M.J. Assessing a traceability technique in fresh oranges (Citrus sinensis L. Osbeck) with an HS-SPME-GC-MS method. Towards a volatile characterisation of organic oranges. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 1930–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panighel, A.; Flamini, R. Applications of solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (SPME-GC/MS) in the study of grape and wine volatile compounds. Molecules 2014, 19, 21291–21309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pati, S.; Tufariello, M.; Crupi, P.; Coletta, A.; Grieco, F.; Losito, I. Quantification of volatile compounds in wines by HS-SPME-GC/MS: Critical issues and use of multivariate statistics in method optimization. Processes 2021, 9, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, L.; Foschi, M.; Biancolillo, A.; Maggi, M.A.; D’Archivio, A.A. Optimization of HS-SPME-GC/MS analysis of wine volatiles supported by chemometrics for the aroma profiling of trebbiano d’abruzzo and pecorino white wines produced in Abruzzo (Italy). Molecules 2023, 28, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, S.; Ramalheira, V.; Barros, A.; Delgadillo, I.; Coimbra, M.A. Headspace solid phase microextraction (SPME) analysis of flavor compounds in wines. Effect of the matrix volatile composition in the relative response factors in a wine model. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 49, 5142–5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Choi, Y.-S.; Sung, J.-M.; Jang, H.W. Comparison of different types of SPME Arrow sorbents to analyze volatile compounds in Cirsium setidens Nakai. Foods 2020, 9, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, T.G.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, B.-K.; Song, N.-E.; Jang, H.W. Analyzing volatiles in brown rice vinegar by headspace solid-phase microextraction (SPME)–Arrow: Optimizing the extraction conditions and comparisons with conventional SPME. Int. J. Food Prop. 2019, 22, 1195–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Kao, T.-H.; Inbaraj, B.S.; Chen, B.-H. Improved analytical method for determination of furan and its derivatives in commercial foods by HS-SPME Arrow combined with gas chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 7762–7772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotti, M.S.; Granby, K.; Rozowski, J.; Pedreschi, F. Furan: A critical heat induced dietary contaminant. Food Funct. 2013, 4, 1001–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, H.; Piri-Moghadam, H.; Naderi, M. Towards greater mechanical, thermal and chemical stability in solid-phase microextraction. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 34, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambonin, C.; Aresta, A. Recent applications of solid phase microextraction coupled to liquid chromatography. Separations 2021, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulakh, J.S.; Malik, A.K.; Kaur, V.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P. A Review on solid phase micro extraction-high performance liquid chromatography (SPME-HPLC) analysis of pesticides. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2005, 35, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hennion, B.; Urruty, L.; Montury, M. Solid-phase microextraction coupled with high performance liquid chromatography: A complementary technique to solid-phase microextraction-gas chromatography for the analysis of pesticide residues in strawberries. Food Addit. Contam. 2000, 17, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamora-León, P. Are the Effects of DES Over? A Tragic Lesson from the Past. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, J.; Shi, Y.-P. Determination of diethylstilbestrol in milk using carbon nanotube-reinforced hollow fiber solid-phase microextraction combined with high-performance liquid chromatography. Talanta 2012, 97, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, A.; Aguiar, A.; Mansilha, C.; Pinho, O.; Ferreira, I.M. Optimisation of a solid-phase microextraction/HPLC/Diode Array method for multiple pesticide screening in lettuce. Food Chem. 2012, 130, 1090–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Ma, P.; Piao, H.; Qin, Z.; Tao, S.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Song, D. Solid-phase microextraction of triazine herbicides via cellulose paper coated with a metal-organic framework of type MIL-101(Cr), and their quantitation by HPLC-MS. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Férey, G.; Mellot-Draznieks, C.; Serre, C.; Millange, F.; Dutour, J.; Surblé, S.; Margiolaki, I. A chromium terephthalate-based solid with unusually large pore volumes and surface area. Science 2005, 309, 2040–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Song, X.; Huang, X. Development of magnetism-assisted in-tube solid phase microextraction of phenolic acids in fruit juices prior to high-performance liquid chromatography quantification. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 3418–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portillo-Castillo, O.J.; Castro-Ríos, R.; Chávez-Montes, A.; González-Horta, A.; Cavazos-Rocha, N.; de Torres, N.H.W.; Garza-Tapia, M. Developments of solid-phase microextraction fiber coatings for environmental pharmaceutical and personal care products analysis. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2018, 37, 20170018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Agatonovic-Kustrin, S.; Gegechkori, V.; Kobakhidze, T.; Morton, D. Solid-Phase Microextraction Techniques and Application in Food and Horticultural Crops. Molecules 2023, 28, 6880. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196880
Agatonovic-Kustrin S, Gegechkori V, Kobakhidze T, Morton D. Solid-Phase Microextraction Techniques and Application in Food and Horticultural Crops. Molecules. 2023; 28(19):6880. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196880
Chicago/Turabian StyleAgatonovic-Kustrin, Snezana, Vladimir Gegechkori, Tamara Kobakhidze, and David Morton. 2023. "Solid-Phase Microextraction Techniques and Application in Food and Horticultural Crops" Molecules 28, no. 19: 6880. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196880
APA StyleAgatonovic-Kustrin, S., Gegechkori, V., Kobakhidze, T., & Morton, D. (2023). Solid-Phase Microextraction Techniques and Application in Food and Horticultural Crops. Molecules, 28(19), 6880. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196880






