Rapid Discrimination of Panax quinquefolium and Panax ginseng Using the Proofman-Duplex-LMTIA Technique
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Sequence Analysis and Primer Design for 18S rDNA of P. quinquefolium and P. ginseng
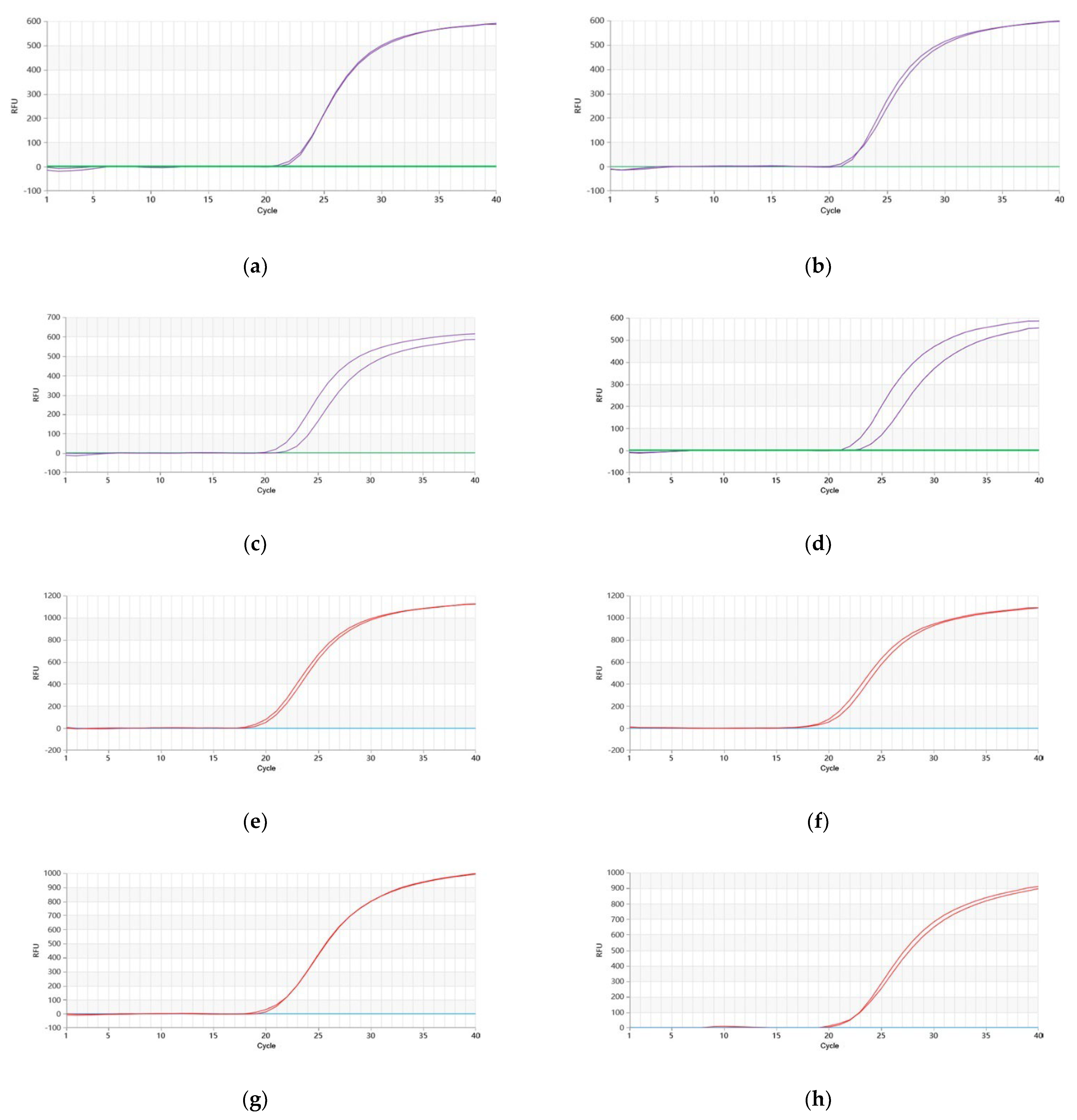
2.2. Optimization of Single-plex Proofman-LMTIA Reaction Temperature for P. quinquefolium and P. ginseng
2.3. Single-Plex Proofma-LMTIA Sensitivity Assay for P. quinquefolium and P. ginseng
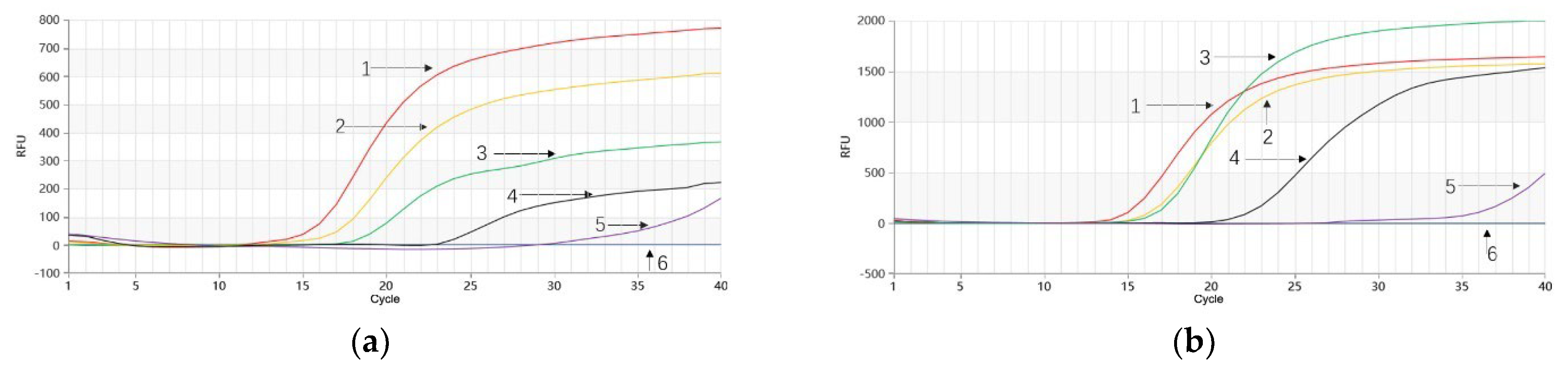
2.4. Single-Plex Proofman-LMTIA Specificity Test for P. quinquefolium and P. ginseng
2.5. Single-Plex Simulated Adulteration Test for P. quinquefolium and P. ginseng
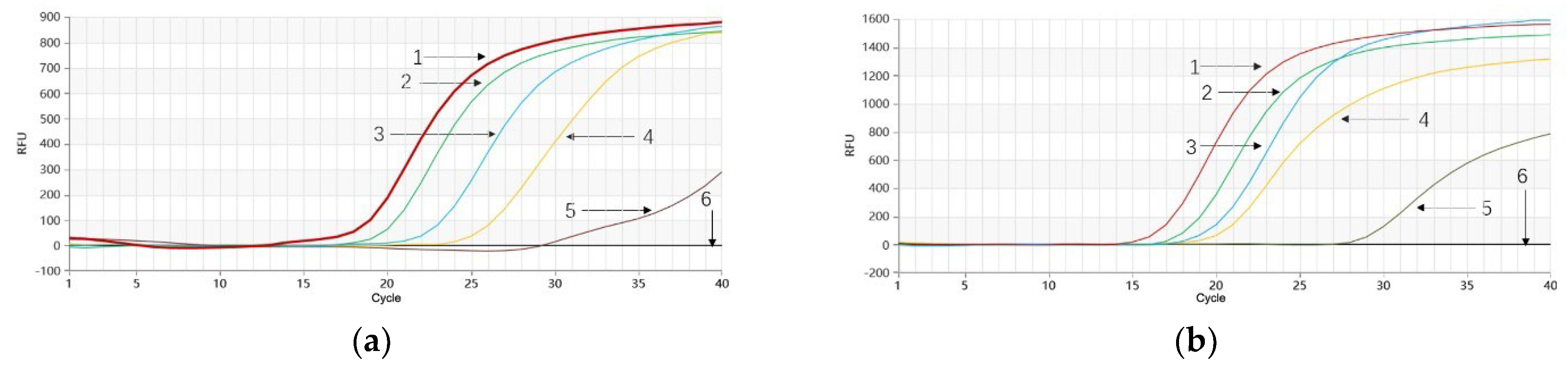
2.6. Optimization of Proofman-Duplex-LMTIA Reaction Temperature for P. quinquefolium and P. ginseng
2.7. Sensitivity Test for Proofman-Duplex-LMTIA Detection of P. quinquefolium and P. ginseng
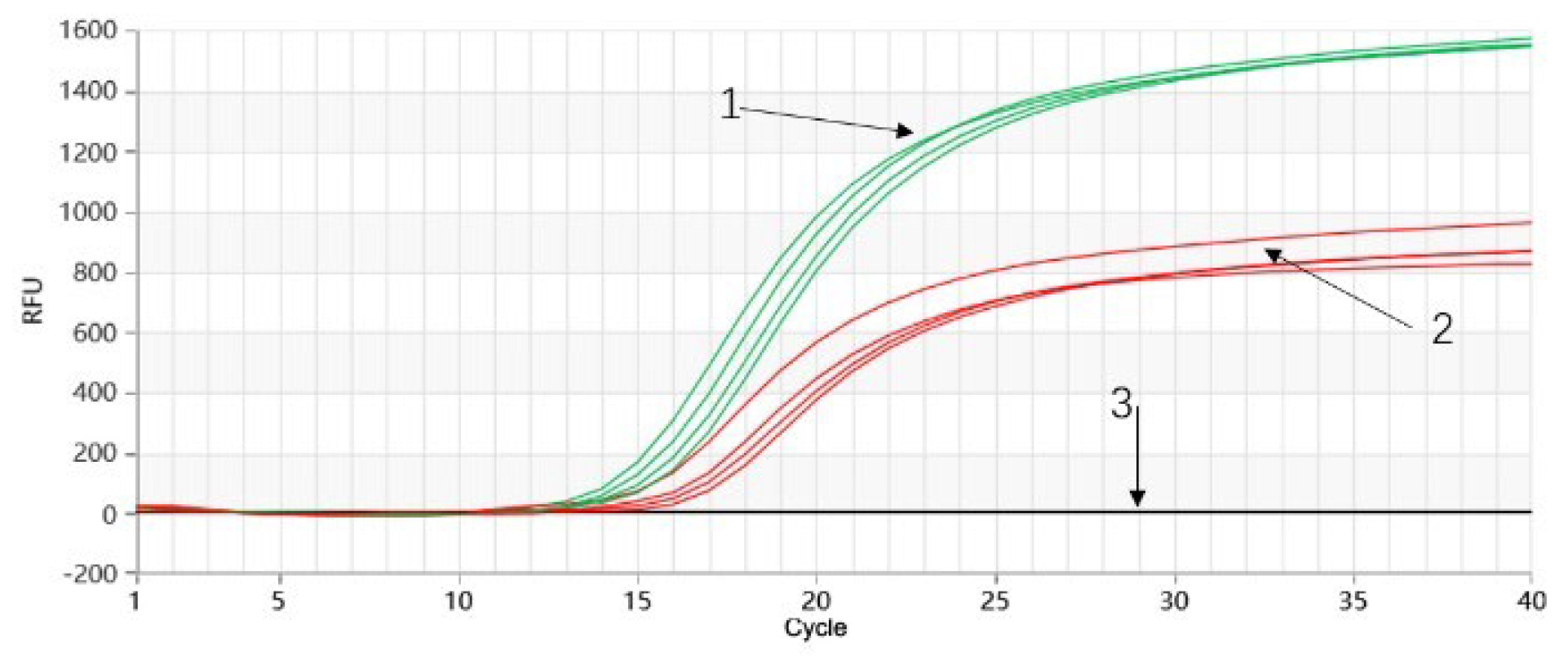
2.8. Stability Test for Proofman-Duplex-LMTIA Detection of P. quinquefolium and P. ginseng
2.9. Results of Proofman-Duplex-LMTIA Detection of Marketed Slices of P. quinquefolium and P. ginseng
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. LMTIA Primer Design
4.2.2. DNA Extraction
4.2.3. Reaction System Determination
4.2.4. Temperature Optimization Experiment
4.2.5. Temperature Sensitivity Determination Experiment
4.2.6. Specificity Experiment
4.2.7. Simulated Adulteration Experiment
4.2.8. Temperature Optimization Experiment for Simultaneous Detection of P. quinquefolium and P. ginseng Using Proofman-Duplex-LMTIA
4.2.9. Sensitivity Testing Experiment for Simultaneous Detection of P. quinquefolium and P. ginseng Using Proofman-Duplex-LMTIA
4.2.10. Stability Experiment for Simultaneous Detection of P. quinquefolium and P. ginseng Using Proofman-Duplex-LMTIA
4.2.11. Proofman-Duplex-LMTIA Detection of Market P. quinquefolium and P. ginseng Slices
4.2.12. Data Processing
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- National Pharmacopoeia Committee. Chinese Pharmacopoeia; China Medical Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2020; Volume 1, pp. 8, 136. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tian, X.; Lv, S.; Tian, H.; Wang, R.; Wang, H. Development of an accurate and reliable DNA method for botanical origin authentication of ginseng food products. J. Food Compost. Anal. 2020, 87, 103419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Cheng, C.; Cheng, Q.; Lao, C.; Cui, H.; Tang, Z.; Ouyang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhou, H. Novel SNP markers on ginsenosides biosynthesis functional gene for authentication of ginseng herbs and commercial products. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2020, 18, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.; Cao, H.; Ren, H.; Yao, L. Seeds identification of Panax ginseng and Panax quinquefolium using ITS2 DNA barcordes. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2019, 50, 2188–2193. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Handy, S.M.; Zhang, N.; Quan, Z.; Xu, Q.; Ambrose, M.; Giancaspro, G.; Sarma, N.D. Development and validation of a species-specific PCR method for the identification of ginseng species using orthogonal approaches. Planta Med. 2021, 88, 1004–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Sun, L.; Li, M. Development and evaluation of a PCR kit for authentication of Panax quinquefolius L. with PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism. J. Anal. Test. 2022, 6, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Tiao, X.; Qi, M.; Chen, A.; Wang, H. Identification of Panax ginseng and Panax quinquefolius by mitochondrial Cox II intron. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Form. 2020, 26, 163–167. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Song, C.; Xiao, F.; Ping, Y.; Pan, C.; Hu, Y.; et al. Ladder-shape melting temperature isothermal amplification of nucleic acids. BioTechniques 2021, 71, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notomi, T.; Mori, Y.; Tomita, N.; Kanda, H. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): Principle, features, and future prospects. J. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, K.; Shi, L.; Zhang, M.; Yu, J.; Liu, Y. Detection of cassava component in sweet potato noodles by real-time loop-mediated isothermal amplification (Real-time LAMP) method. Molecules 2019, 24, 2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Xu, D.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D. Development of a ladder-shape melting temperature isothermal amplification (LMTIA) assay for detection of African swine fever virus (ASFV). J. Vet. Sci. 2022, 23, e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, D. Detection of Listeria monocytogenes in food using the Proofman-LMTIA assay. Molecules 2023, 28, 5457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, F.; Gu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xian, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Ding, C.; Zhang, G.; Wang, D. Detection of soybean-derived components in dairy products using proofreading enzyme-mediated probe cleavage coupled with ladder-shape melting temperature isothermal amplification (Proofman-LMTIA). Molecules 2023, 28, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S. Standard DNA Barcodes of Chinese Materia Medica in Chinese Pharmacopoeia; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2015; pp. 56–57, 202–203. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Oberc, C.; Sojoudi, P.; Li, P.C. Nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT) conducted in a microfluidic chip to differentiate between various ginseng species. Analyst 2023, 148, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Yao, H.; Han, J.; Xin, Y.; Pang, X.; Shi, L.; Luo, K.; Song, J.; Hou, D.; Shi, S. Principles for molecular identification of traditional Chinese materia medica using DNA barcoding. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2013, 38, 141–148. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sayers, E.W.; Cavanaugh, M.; Clark, K.; Ostell, J.; Pruitt, K.D.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Primer Name | Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|
| Shen-F1 | CTCATTCCAATTACCATTTTACGGGGAGGTAGTGACAATA |
| Shen-B1 | TGGTAATTGGAATGAGTTTTACCAGACTTGCCCTCCAATG |
| Shen-F2 | ATTCCAATTACCAGACTTTTACGGGGAGGTAGTGACAATA |
| Shen-B2 | TAATTGGAATGAGTACTTTTACCAGACTTGCCCTCCAATG |
| Shen-R-LF | BHQ1-GACTGAATT-JOE |
| Shen-X-LF | BHQ1-GACTCACTA-FAM |
| Shen-LB | AATCTAAATCCCTTAACG |
| Number | Scientific Name | Source | Number | Scientific Name | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pg1 | P. ginseng | White Mountain, Jilin, China | pq5 | P. quinquefolium | America |
| pg2 | P. ginseng | Tonghua, Jilin, China | Pq6 | P. quinquefolium | Bozhou, Anhui, China |
| pg3 | P. ginseng | Jixi, Heilongjiang, China | pq7 | P. quinquefolium | Bozhou, Anhui, China |
| pg4 | P. ginseng | Bozhou, Anhui, China | pq8 | P. quinquefolium | Tonghua, Jilin, China |
| pg5 | P. ginseng | Yanbian, Jilin, China | pq9 | P. quinquefolium | Tonghua, Jilin, China |
| pg6 | P. ginseng | America | pq10 | P. quinquefolium | Yanbian, Jilin, China |
| pq1 | P. quinquefolium | White Mountain, Jilin, China | pq11 | P. quinquefolium | Fushun, Liaoning, China |
| pq2 | P. quinquefolium | White Mountain, Jilin, China | Pg-S | P. ginseng | White Mountain, Jilin, China |
| pq3 | P. quinquefolium | America | Pq-S | P. quinquefolium | White Mountain, Jilin, China |
| pq4 | P. quinquefolium | Canada |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, D.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, F.; Wang, D. Rapid Discrimination of Panax quinquefolium and Panax ginseng Using the Proofman-Duplex-LMTIA Technique. Molecules 2023, 28, 6872. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196872
Zhang X, Li Z, Zhang Y, Xu D, Zhang L, Xiao F, Wang D. Rapid Discrimination of Panax quinquefolium and Panax ginseng Using the Proofman-Duplex-LMTIA Technique. Molecules. 2023; 28(19):6872. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196872
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaodong, Zongding Li, Yaoxuan Zhang, Dandan Xu, Liang Zhang, Fugang Xiao, and Deguo Wang. 2023. "Rapid Discrimination of Panax quinquefolium and Panax ginseng Using the Proofman-Duplex-LMTIA Technique" Molecules 28, no. 19: 6872. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196872
APA StyleZhang, X., Li, Z., Zhang, Y., Xu, D., Zhang, L., Xiao, F., & Wang, D. (2023). Rapid Discrimination of Panax quinquefolium and Panax ginseng Using the Proofman-Duplex-LMTIA Technique. Molecules, 28(19), 6872. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196872






