The Inhibitory Effect of Magnolol on the Human TWIK1 Channel Is Related to G229 and T225 Sites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. TWIK1 Is Activated by High K+ and High NH4+ Extracellular Solution
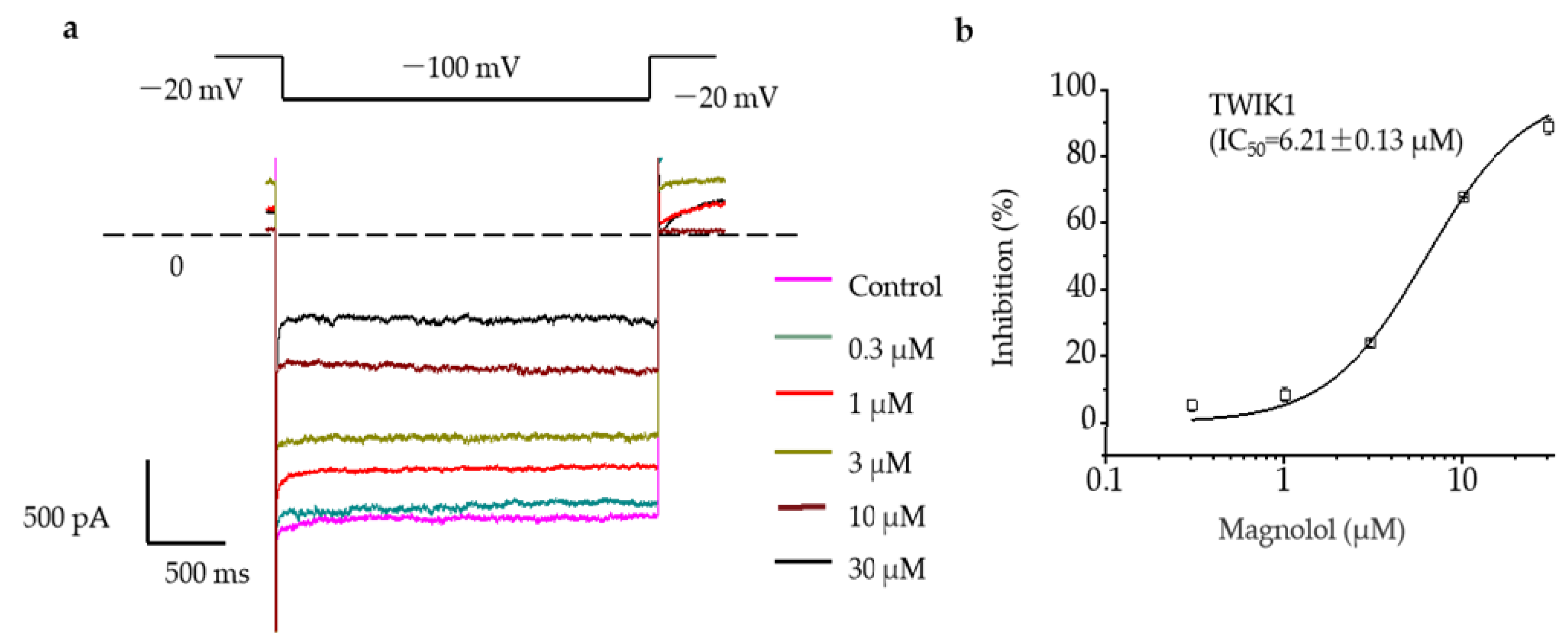
2.2. Magnolol Significantly Inhibited the Activation Current of TWIK1
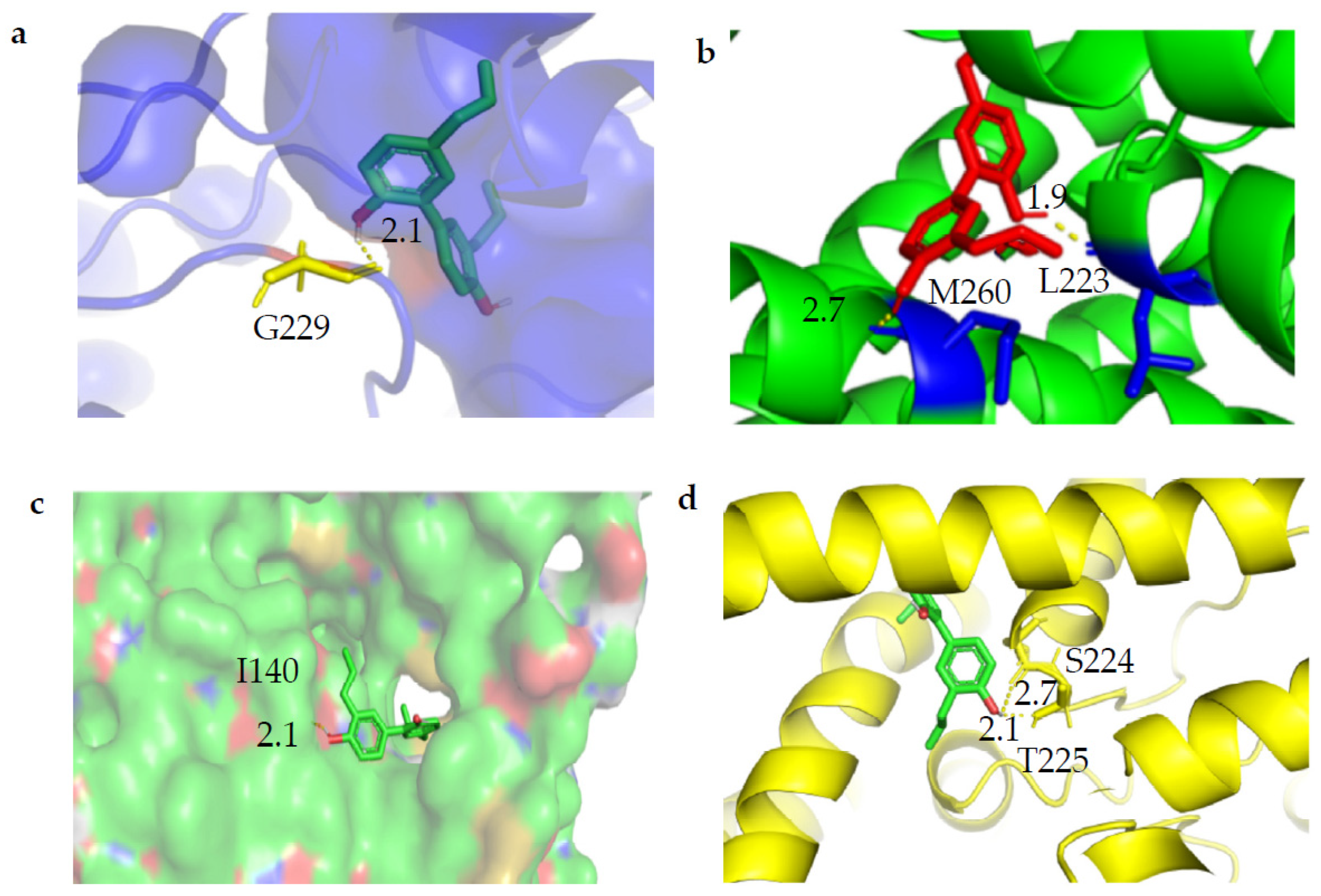
2.3. Molecular Docking of Magnolol with TWIK1
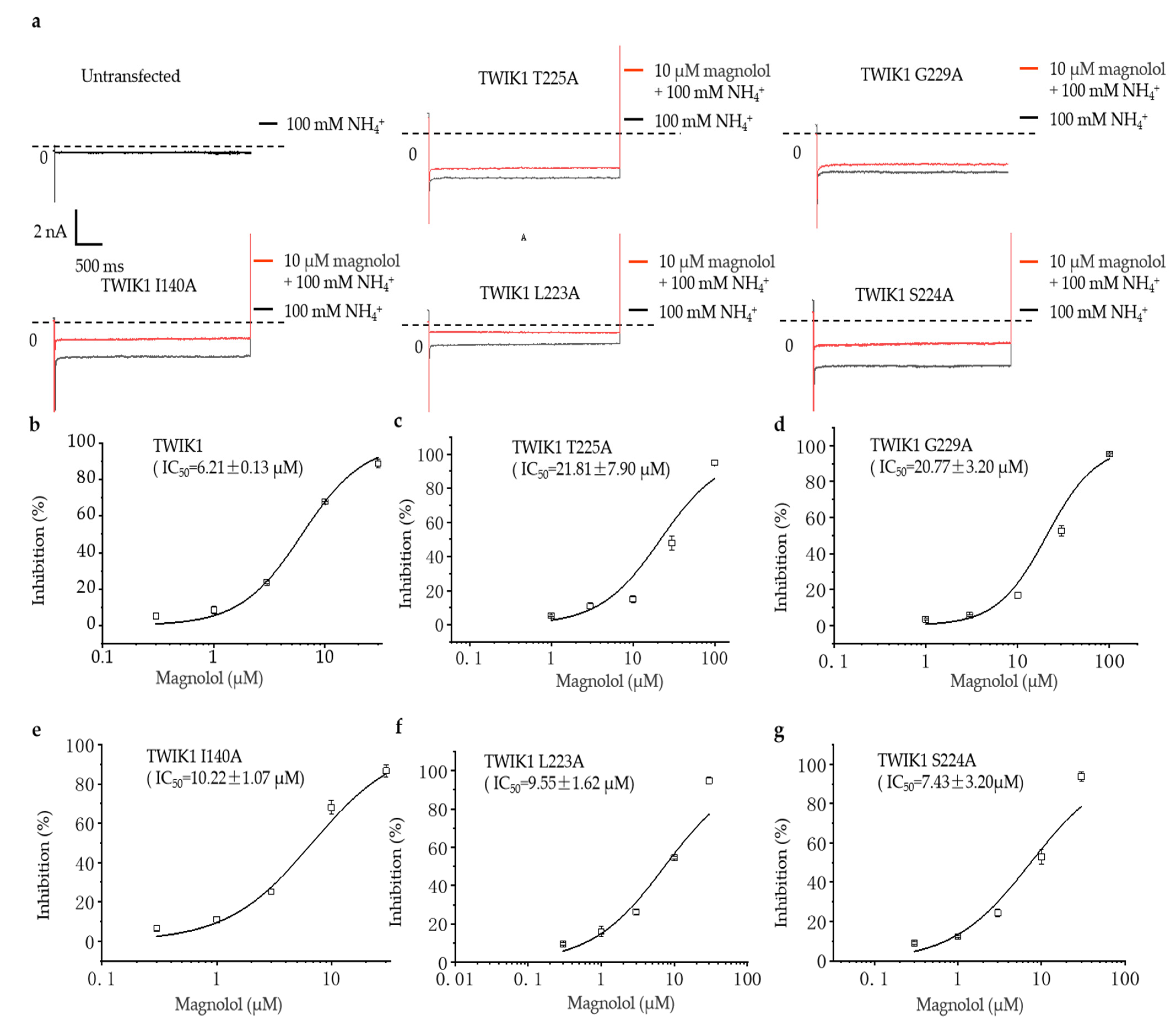
2.4. The Comparison of the Inhibitory Effect of Magnolol on Wild-Type and Different Mutation TWIK1
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. T225A, G229A, L223A, S224A and I140A Mutations
4.3. Cell-Line Preparation
4.4. Magnolol Preparation
4.5. Electrophysiology
4.6. Molecular Docking
4.7. Data Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Nomenclature
| AKT | protein kinase B |
| CHO | Chinese hamster ovary cell |
| ERK | extracellular regulated protein kinases |
| MAPK | mitogen-protein kinase |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| PEG2 | prostaglandin E2 |
| PPAR-γ | peroxisome proliferators activated receptors |
| RXRα | retinoid X receptor α |
| TLR4 | Toll-like receptor 4 |
| HIF-1α | hypoxia inducible factor-1α |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
| TWIK | the tandem of pore domains in a weak inward rectifying K+ channel |
| TASK | TWIK-related acid-sensitive K+ channel |
| TALK | TWIK-related alkaline pH-activated K+ channel |
| THIK | tandem pore domain halothane-inhibited K+ channel |
| TRAAK | TWIK-related arachidonic acid-stimulated K+ channel |
| TREK | TWIK-related K+ channel |
References
- Lin, Y.; Li, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Tian, B.; Qu, X.; Yuan, Q.; Song, Y. Pharmacology, Toxicity, Bioavailability, and Formulation of Magnolol: An Update. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 632767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhang, N.; Liu, Z.; Liang, D.; Li, F.; Cao, Y.; Feng, X.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Z. Magnolol inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response by interfering with TLR4 mediated NF-κB and MAPKs signaling pathways. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 145, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.H.; Chen, M.C.; Chen, T.H.; Chang, H.Y.; Chou, T.C.L. Magnolol ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats through PPAR-γ-dependent inhibition of NF-κB activation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 28, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.S.; Lai, Y.S.; Kuo, D.H.; Wu, C.H.; Ho, C.T.; Pan, H. Magnolol potently suppressed lipopolysaccharide-induced iNOS and COX-2 expression via downregulating MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. J. Funct. Foods 2011, 3, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Chang, C.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Chou, C.Y.; Chou, T.C. Magnolol ameliorates pneumonectomy and monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension in rats through inhibition of angiotensin II and endothelin-1 expression. Phytomedicine 2018, 51, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.C.; Lee, C.F.; Huang, W.H.; Chou, T.C. Magnolol suppresses hypoxia-induced angiogenesis via inhibition of HIF-1α/VEGF signaling pathway in human bladder cancer cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 85, 1278–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.M.; Huang, H.M.; Hsieh, M.T.; Chen, C.S.; Yeh, F.T.; Kuo, J.S. Anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects of Magnolol in chemical hypoxia in rat cultured cortical cells in hypoglycemic media. Chin. J. Physiol. 2000, 43, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, X.; Chen, L.; Chen, J.; Hu, L.; Jiang, H.; Shen, X. Molecular determinants of Magnolol targeting both RXRα and PPARγ. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Wang, J.S.; Shan, S.M.; Wang, X.B.; Luo, J.; Yang, M.H.; Kong, L.Y. Chemical constituents from Trichilia connaroides and their nitric oxide production and α-glucosidase inhibitory activities. Planta Med. 2013, 79, 1767–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatelain, F.C.; Bichet, D.; Douguet, D.; Feliciangeli, S.; Bendahhou, S.; Reichold, M.; Warth, R.; Barhanin, J.; Lesage, F. TWIK1, a unique background channel with variable ion selectivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5499–5504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesage, F.; Guillemare, E.; Fink, M.; Duprat, F.; Lazdunski, M.; Romey, G.; Barhanin, J. TWIK-1, a ubiquitous human weakly inward rectifying K+ channel with a novel structure. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fink, M.; Duprat, F.; Lesage, F.; Reyes, R.; Romey, G.; Heurteaux, C.; Lazdunski, M. Cloning, functional expression and brain localization of a novel unconventional outward rectifier K+ channel. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 6854–6862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duprat, F.; Lesage, F.; Fink, M.; Reyes, R.; Heurteaux, C.; Lazdunski, M. TASK, a human background K+ channel to sense external pH variations near physiological pH. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 5464–5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajan, S.; Wischmeyer, E.; Karschin, C.; Preisig-Müller, R.; Grzeschik, K.H.; Daut, J.; Karschin, A.; Derst, C. THIK-1 and THIK-2, a novel subfamily of tandem pore domain K+ channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 7302–7311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, R.; Duprat, F.; Lesage, F.; Fink, M.; Salinas, M.; Farman, N.; Lazdunski, M. Cloning and expression of a novel pH-sensitive two pore domain K+ channel from human kidney. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 30863–30869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sano, Y.; Inamura, K.; Miyake, A.; Mochizuki, S.; Kitada, C.; Yokoi, H.; Nozawa, K.; Okada, H.; Matsushime, H.; Furuichi, K. A novel two-pore domain K+ channel, TRESK, is localized in the spinal cord. J Biol Chem. 2003, 278, 27406–27412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrighi, I.; Lesage, F.; Scimeca, J.C.; Carle, G.F.; Barhanin, J. Structure, chromosome localization, and tissue distribution of the mouse TWIK K+ channel gene. FEBS Lett. 1998, 425, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesage, F.; Lauritzen, I.; Duprat, F.; Reyes, R.; Fink, M.; Heurteaux, C.; Lazdunski, M. The structure, function and distribution of the mouse TWIK-1 K+ channel. FEBS Lett. 1997, 402, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Kiyoshi, C.M.; Du, Y.; Ma, B.; Alford, C.C.; Chen, H.; Zhou, M. mGluR3 Activation Recruits Cytoplasmic TWIK-1 Channels to Membrane that Enhances Ammonium Uptake in Hippocampal Astrocytes. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 6169–6182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, S.; Plant, L.D.; Rabin, M.L.; Butler, M.H.; Goldstein, S.A. Sumoylation silences the plasma membrane leak K+ channel K2P1. Cell 2005, 121, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliciangeli, S.; Bendahhou, S.; Sandoz, G.; Gounon, P.; Reichold, M.; Warth, R.; Lazdunski, M.; Barhanin, J.; Lesage, F. Does sumoylation control K2P1/TWIK1 background K+ channels? Cell 2007, 130, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feliciangeli, S.; Tardy, M.P.; Sandoz, G.; Chatelain, F.C.; Warth, R.; Barhanin, J.; Bendahhou, S.; Lesage, F. Potassium channel silencing by constitutive endocytosis and intracellular sequestration. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 4798–4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aryal, P.; Abd-Wahab, F.; Bucci, G.; Sansom, M.S.; Tucker, S.J. A hydrophobic barrier deep within the inner pore of the TWIK1 K2P potassium channel. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Xie, Y.P.; Zhou, M.; Chen, H. Silent TWIK-1 potassium channels conduct monovalent cation currents. Biophys. J. 2012, 102, L34–L36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H. TWIK-1 two-pore domain potassium channels change ion selectivity and conduct inward leak sodium currents in hypokalemia. Sci. Signal. 2011, 4, ra37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, M.; Chen, H. Acid-sensitive TWIK and TASK two-pore domain potassium channels change ion selectivity and become permeable to sodium in extracellular acidification. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 37145–37153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chatelain, F.C.; Lesage, F. Altered and dynamic ion selectivity of K+ channels in cell development and excitability. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 35, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.Y.; Pike, A.C.; Mackenzie, A.; McClenaghan, C.; Aryal, P.; Dong, L.; Quigley, A.; Grieben, M.; Goubin, S.; Carpenter, E.P. K2P channel gating mechanisms revealed by structures of TREK-2 and a complex with Prozac. Science 2015, 347, 1256–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rödström, K.E.; Kiper, A.K.; Zhang, W.; Rinne, S.; Pike, A.C.; Goldstein, M.; Conrad, L.J.; Delbeck, M.; Hahn, M.G.; Carpenter, E.P. A lower X-gate in TASK channels traps inhibitors within the vestibule. Nature 2020, 582, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakes, V.; Furini, S.; Pryde, D.; Domene, C. Exploring the Dynamics of the TWIK1 Channel. Biophys. J. 2016, 111, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, C.; Darré, L.; Oakes, V.; Torella, R.; Pryde, D.; Domene, C. Lateral Fenestrations in K (+)-Channels Explored Using Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 2263–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nematian-Ardestani, E.; Abd-Wahab, F.; Chatelain, F.C.; Sun, H.; Schewe, M.; Baukrowitz, T.; Tucker, S.J. Selectivity filter instability dominates the low intrinsic activity of the TWIK-1 K2P K+ channel. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhao, W.; Pan, L.; Zhang, A.; Chen, Q.; Xu, K.; Lu, H.; Chen, Y. Peimine, a main active ingredient of Fritillaria, exhibits anti-inflammatory and pain suppression properties at the cellular level. Fitoterapia 2016, 111, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Sun, Z.; Zou, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, X.; Pan, L.; Stalin, A.; Zhao, W.; Chen, Y. The Inhibitory Effect of Magnolol on the Human TWIK1 Channel Is Related to G229 and T225 Sites. Molecules 2023, 28, 6815. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196815
Wang J, Liu H, Sun Z, Zou X, Zhang Z, Wei X, Pan L, Stalin A, Zhao W, Chen Y. The Inhibitory Effect of Magnolol on the Human TWIK1 Channel Is Related to G229 and T225 Sites. Molecules. 2023; 28(19):6815. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196815
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jintao, Huan Liu, Zhuolin Sun, Xinyi Zou, Zixuan Zhang, Xiaofeng Wei, Lanying Pan, Antony Stalin, Wei Zhao, and Yuan Chen. 2023. "The Inhibitory Effect of Magnolol on the Human TWIK1 Channel Is Related to G229 and T225 Sites" Molecules 28, no. 19: 6815. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196815
APA StyleWang, J., Liu, H., Sun, Z., Zou, X., Zhang, Z., Wei, X., Pan, L., Stalin, A., Zhao, W., & Chen, Y. (2023). The Inhibitory Effect of Magnolol on the Human TWIK1 Channel Is Related to G229 and T225 Sites. Molecules, 28(19), 6815. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28196815





