Anti-Colorectal Cancer Activity of Solasonin from Solanum nigrum L. via Histone Deacetylases-Mediated p53 Acetylation Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
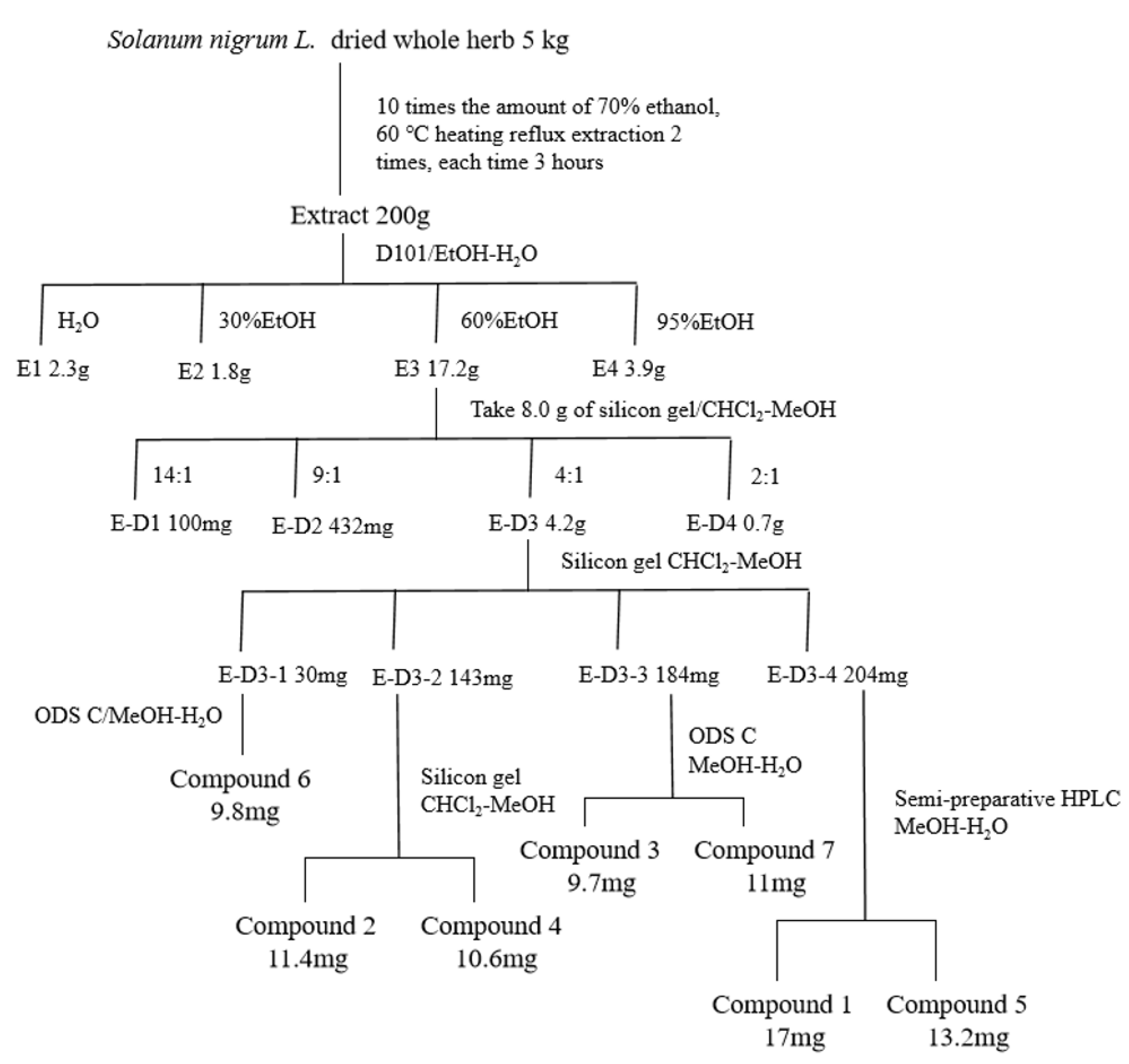
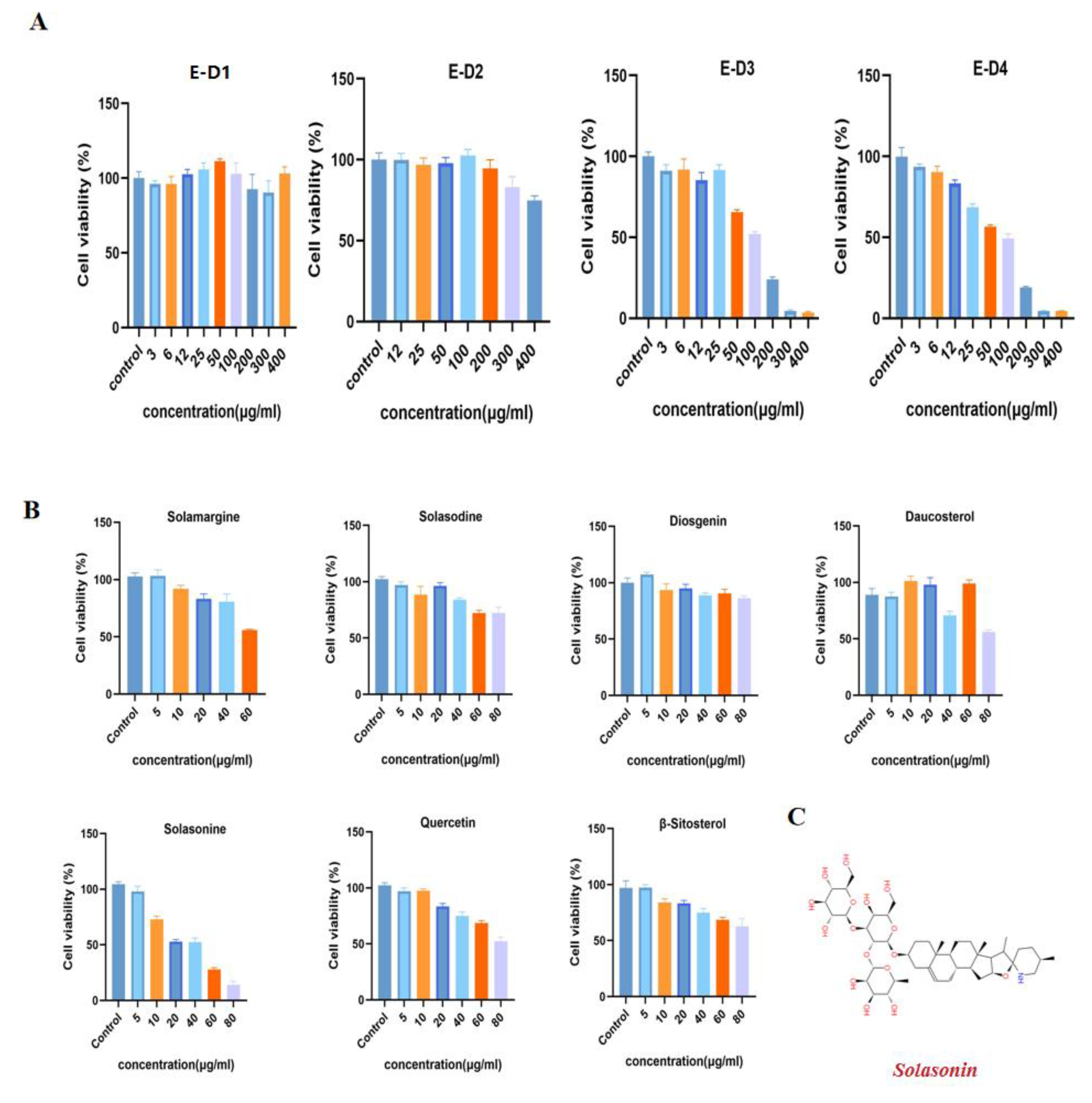
2.1. Anti-CRC Activity-Guided Isolation and Purification of Solanum nigrum L.
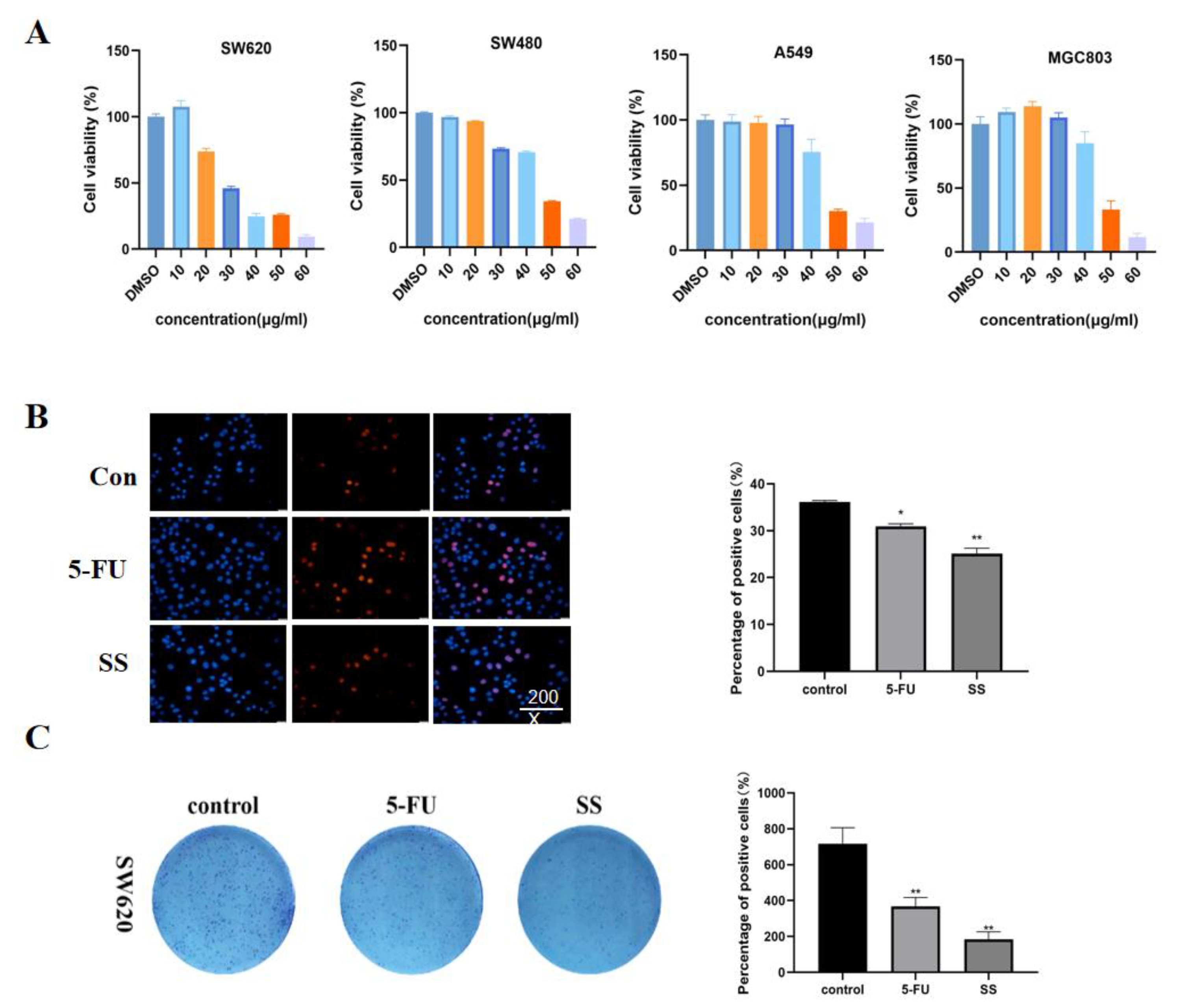
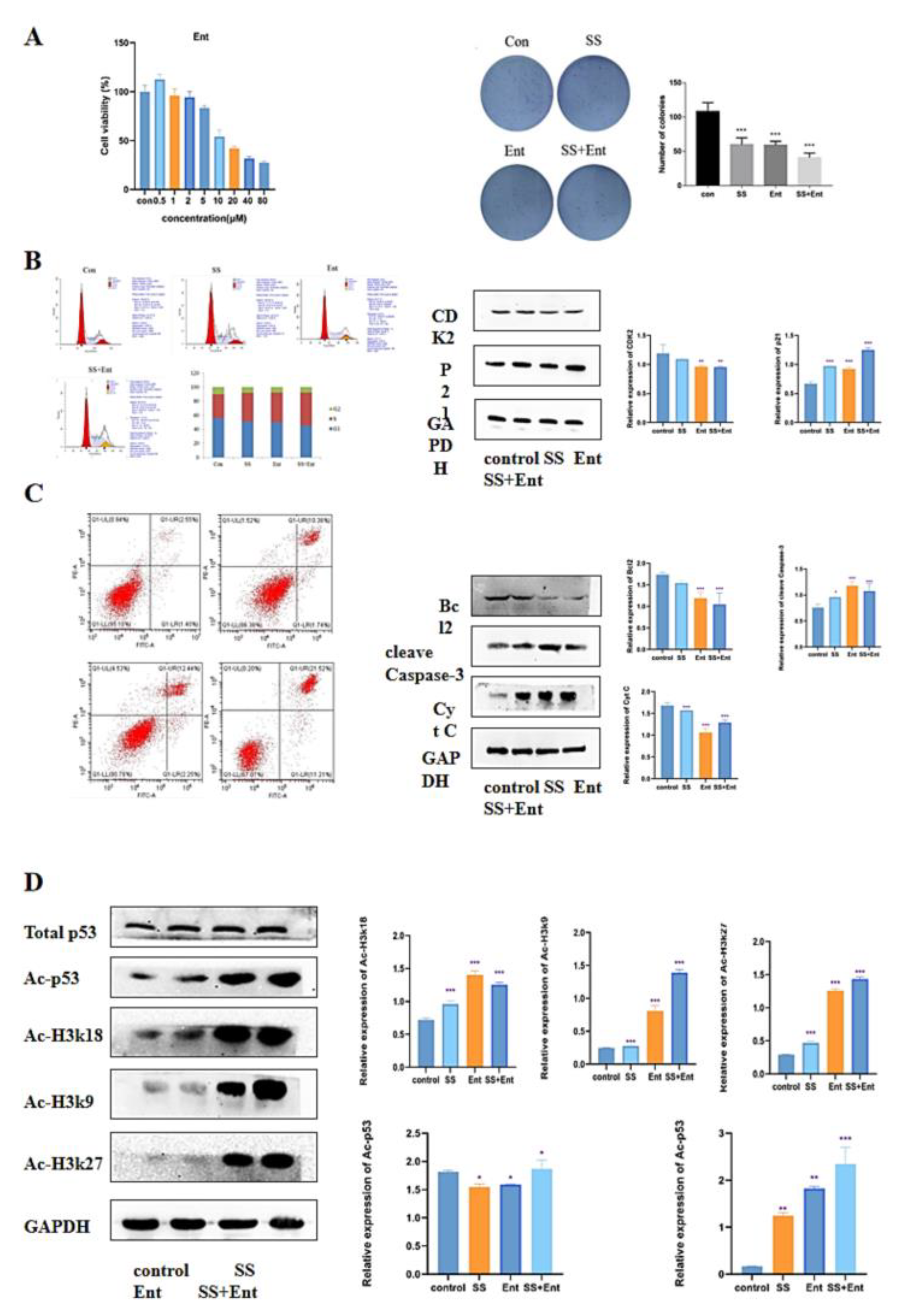
2.2. SS Inhibited the Proliferation of CRC Cells
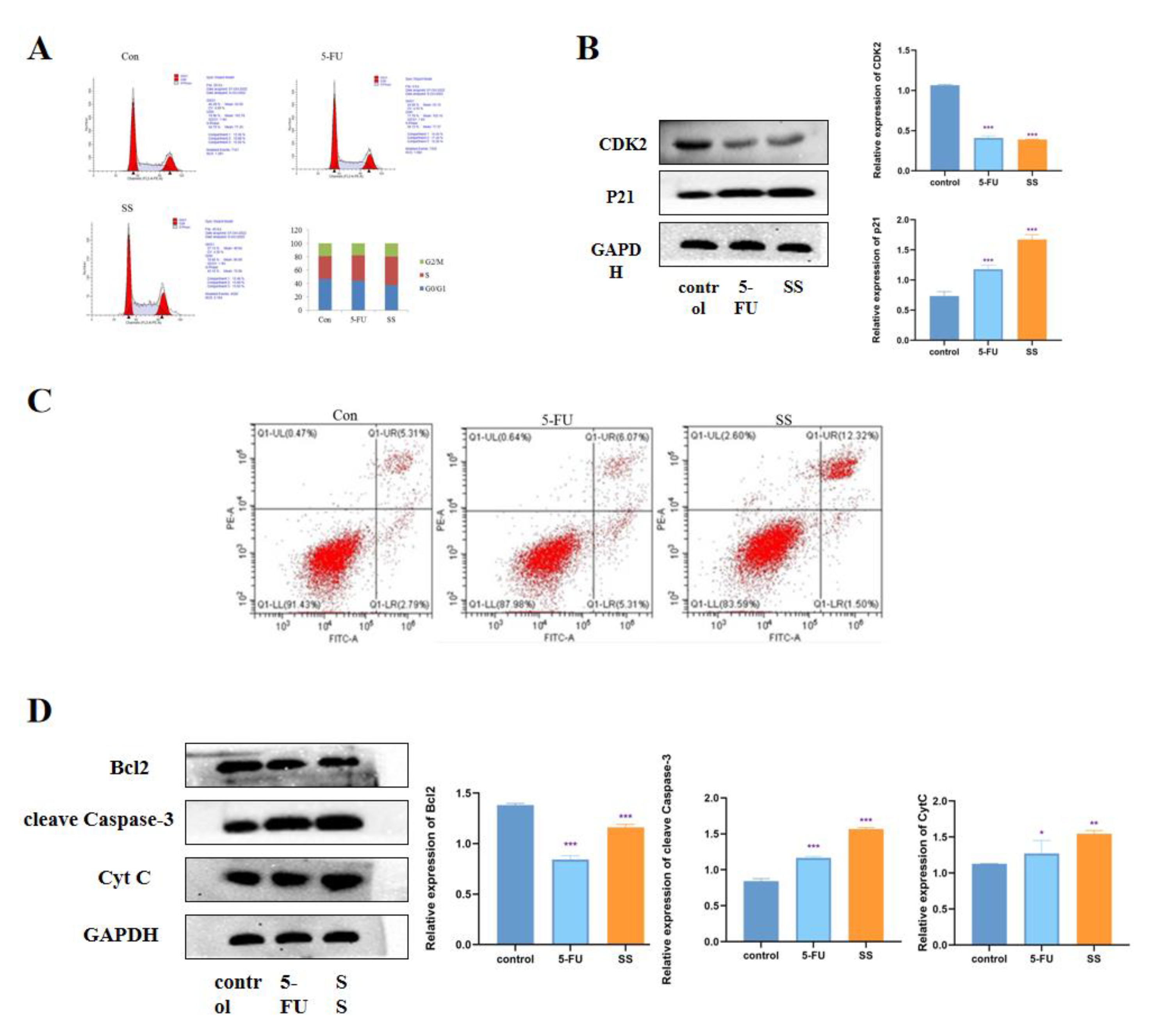
2.3. SS Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in CRC Cells
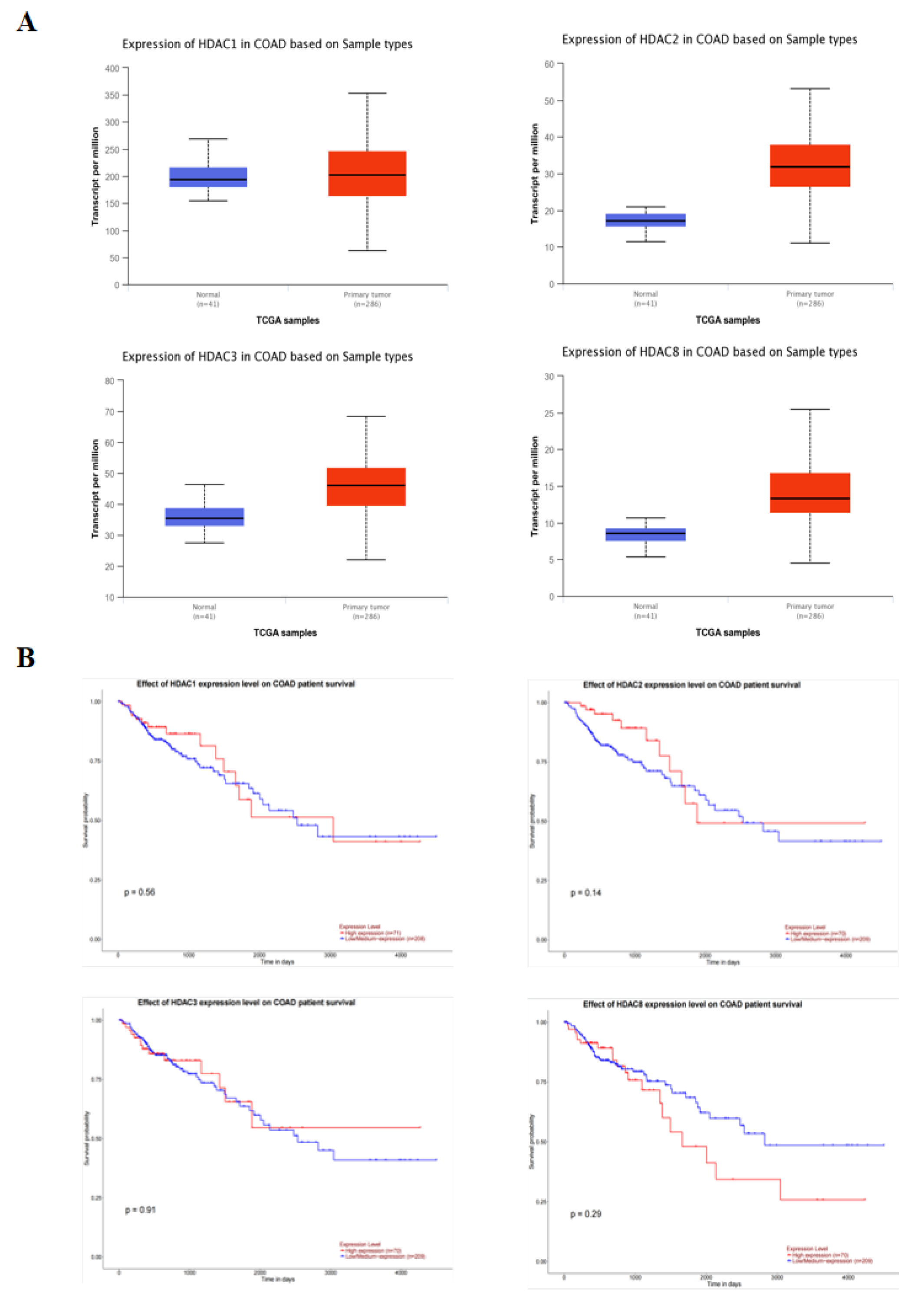
2.4. Class I HDAC Is Highly Expressed in CRC Cells
2.5. Downregulation of Class I HDAC Is Involved in SS-Mediated Anti-CRC Effects
2.6. SS Acts through Class I HDAC-Induced P53 Acetylation
2.7. SS Inhibited the Growth of SW620 Xenograft Mouse Model
2.8. SS Evaluation of Docking with Class I HDACs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Collection of Plants and Preparation of Extracts
4.3. Cell Line
4.4. Animals
4.5. MTT Assay
4.6. Cell Count Kit-8 (CCK-8) Assay
4.7. EdU Assay
4.8. Colony Formation Assay
4.9. Cell Cycle Assay
4.10. Apoptosis Detection Assay
4.11. Network Target Verification
4.12. Western Blot Assay
4.13. Xenograft Tumor Growth Experiments
4.14. Immunochemistry
4.15. Molecular Docking
4.16. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Abbreviations
References
- Morgan, E.; Arnold, M.; Gini, A.; Lorenzoni, V.; Cabasag, C.J.; Laversanne, M.; Vignat, J.; Ferlay, J.; Murphy, N.; Bray, F. Global burden of colorectal cancer in 2020 and 2040: Incidence and mortality estimates from GLOBOCAN. Gut 2022, 72, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuipers, E.J.; Grady, W.M.; Lieberman, D.; Seufferlein, T.; Sung, J.J.; Boelens, P.G.; de Velde, C.J.H.V.; Watanabe, T. Colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 521, 15065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.S.; Karuniawati, H.; Jairoun, A.A.; Urbi, Z.; Ooi, D.J.; John, A.; Lim, Y.C.; Kibria, K.M.K.; Mohiuddin, A.K.M.; Ming, L.C.; et al. Colorectal Cancer: A Review of Carcinogenesis, Global Epidemiology, Current Challenges, Risk Factors, Preventive and Treatment Strategies. Cancers 2022, 14, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanasov, A.G.; Zotchev, S.B.; Dirsch, V.M.; Supuran, C.T. Natural products in drug discovery: Advances and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 200–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-C.; Wang, S.; Yang, X.-X.; Li, T.-J.; Gu, J.-X.; Zhao, L.; Bao, Y.-R.; Meng, X.-S. Patrinia villosa treat colorectal cancer by activating PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 309, 116264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Liang, D.; Zheng, Q.; Zhao, M.; Lv, R.; Tang, J.; Chen, N. Berbamine dihydrochloride suppresses the progression of colorectal cancer via RTKs/Akt axis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 303, 116025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, X.; Dong, X.; Han, Q. Study on numerical classification of Chinese Nightshade. Plant Res. 1999, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; He, X.; Zhou, G.; Ye, W.; Yao, X. Study on chemical constituents of saponins from whole sunflower. Chin. Herb. Med. 2006, 1618–1621. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J. Flora of China. Harv. Pap. Bot. 2007, 13, 301–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Mei, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, Q. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Nightshade. Pharm. Today 2011, 21, 713–715. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Xu, J.W.; Wang, Y.H.; Xiang, L.M.; He, X.J. Total steroidal saponins from black nightshade (Solanum nigrum L.) overcome tumor multidrug resistance by inducing autophagy-mediated cell death in vivo and in vitro. Phytother. Res. 2023, 37, 3009–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Dai, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, L.; He, X.; Gong, G. Solanum nigrum Linn.: An Insight into Current Research on Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacology. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 918071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, G.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gong, H. Solasonine inhibits gastric cancer proliferation and enhances chemosensitivity through microRNA-486-5p. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 3522–3530. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.Y.; Luo, Y.B.; Ju, X.D.; Zhang, B.; Cui, Y.J.; Pan, Y.B.; Tian, J.H.; Teng, W.J.; Wu, J.; Li, Y. Solasonine Causes Redox Imbalance and Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress of Ferroptosis in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 874900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Shi, C.; Li, T.; Wu, Y.; Hu, C.; Huang, G. Solasonine promotes ferroptosis of hepatoma carcinoma cells via glutathione peroxidase 4-induced destruction of the glutathione redox system. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 129, 110282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.R.; Kozukue, N.; Han, J.S.; Park, J.H.; Chang, E.Y.; Baek, E.J.; Chang, J.S.; Friedman, M. Glycoalkaloids and metabolites inhibit the growth of human colon (HT29) and liver (HepG2) cancer cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 2832–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crea, F.; Nobili, S.; Paolicchi, E.; Perrone, G.; Napoli, C.; Landini, I.; Danesi, R.; Mini, E. Epigenetics and chemoresistance in colorectal cancer: An opportunity for treatment tailoring and novel therapeutic strategies. Drug Resist. Updates 2011, 14, 280–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Chen, Y.; Fang, J.-Y. Influence of the microbiota on epigenetics in colorectal cancer. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2019, 6, 1138–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberland, M.; Montgomery, R.L.; Olson, E.N. The many roles of histone deacetylases in development and physiology: Implications for disease and therapy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacroix, M.; Riscal, R.; Arena, G.; Linares, L.K.; Le Cam, L. Metabolic functions of the tumor suppressor p53: Implications in normal physiology, metabolic disorders, and cancer. Mol. Metab. 2020, 33, 2–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-L.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Z.-R.; Chng, W.-J. p53 mutations in colorectal cancer- molecular pathogenesis and pharmacological reactivation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.L.; La, M.T.; Shin, M.W.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, H.K. A novel HDAC1 inhibitor, CBUD-1001, exerts anticancer effects by modulating the apoptosis and EMT of colorectal cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 57, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomicic, M.T.; Dawood, M.; Efferth, T. Epigenetic Alterations Upstream and Downstream of p53 Signaling in Colorectal Carcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahalakshmi, R.; Husayn Ahmed, P.; Mahadevan, V. HDAC inhibitors show differential epigenetic regulation and cell survival strategies on p53 mutant colon cancer cells. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2018, 36, 938–955. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, Y.; Xu, P. Global colorectal cancer burden in 2020 and projections to 2040. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 101174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Hu, C.; Han, M.; Liu, C.; Sun, X.; Yu, K.; Gu, H.; Zhang, J. Solasonine Inhibits Pancreatic Cancer Progression with Involvement of Ferroptosis Induction. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 834729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.C.; Chen, N.J.; Chen, Y.Y.; He, B.J.; Zhou, Z.F. Solasonine induces apoptosis of the SGC-7901 human gastric cancer cell line in vitro via the mitochondria-mediated pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 3387–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Li, S.Y.; Shen, M.X.; Qiu, R.Z.; Fan, H.W.; Li, Y.B. Anti-tumor effects of Solanum nigrum L. extraction on C6 high-grade glioma. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 274, 114034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.F.; Wu, S.W.; Shi, Z.M.; Qu, Y.J.; Ding, M.R.; Hu, B. Exploring the components and mechanism of Solanum nigrum L. for colon cancer treatment based on network pharmacology and molecular docking. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1111799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celesia, A.; Franzo, M.; Di Liberto, D.; Lauricella, M.; Carlisi, D.; D’Anneo, A.; Notaro, A.; Allegra, M.; Giuliano, M.; Emanuele, S. Oncogenic BRAF and p53 Interplay in Melanoma Cells and the Effects of the HDAC Inhibitor ITF2357 (Givinostat). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Gou, S. Discovery of phthalazino 1,2-b -quinazolinone derivatives as multi-target HDAC inhibitors for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma via activating the p53 signal pathway. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 229, 114058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, J.B.; Zhao, J.; Keith, M.C.L.; Amraotkar, A.R.; Wysoczynski, M.; Hong, K.U.; Bolli, R. The Epigenetic Regulator HDAC1 Modulates Transcription of a Core Cardiogenic Program in Human Cardiac Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Through a p53-Dependent Mechanism. Stem Cells 2016, 34, 2916–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-M.; Liou, J.-P. An updated patent review of histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors in cancer (2020-present). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2023, 33, 349–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yenigul, M.; Akcok, E.B.G. Histone Deacetylase Inhibition and Autophagy Modulation Induces a Synergistic Antiproliferative Effect and Cell Death in Cholangiocarcinoma Cells. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 21755–21768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garmpis, N.; Damaskos, C.; Dimitroulis, D.; Kouraklis, G.; Garmpi, A.; Sarantis, P.; Koustas, E.; Patsouras, A.; Psilopatis, I.; Antoniou, E.A.; et al. Clinical Significance of the Histone Deacetylase 2 (HDAC-2) Expression in Human Breast Cancer. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheshmazar, N.; Hamzeh-Mivehroud, M.; Charoudeh, H.N.; Hemmati, S.; Melesina, J.; Dastmalchi, S. Current trends in development of HDAC-based chemotherapeutics. Life Sci. 2022, 308, 120946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| HDAC1 | HDAC2 | HDAC3 | HDAC8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solasonin | −6.4 | −8.09 | −7.31 | −6.59 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lan, X.; Lu, M.; Fang, X.; Cao, Y.; Sun, M.; Shan, M.; Gao, W.; Wang, Y.; Yu, W.; Luo, H. Anti-Colorectal Cancer Activity of Solasonin from Solanum nigrum L. via Histone Deacetylases-Mediated p53 Acetylation Pathway. Molecules 2023, 28, 6649. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186649
Lan X, Lu M, Fang X, Cao Y, Sun M, Shan M, Gao W, Wang Y, Yu W, Luo H. Anti-Colorectal Cancer Activity of Solasonin from Solanum nigrum L. via Histone Deacetylases-Mediated p53 Acetylation Pathway. Molecules. 2023; 28(18):6649. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186649
Chicago/Turabian StyleLan, Xintian, Meng Lu, Xiaoxue Fang, Yiming Cao, Mingyang Sun, Mengyao Shan, Wenyi Gao, Yuchen Wang, Wenbo Yu, and Haoming Luo. 2023. "Anti-Colorectal Cancer Activity of Solasonin from Solanum nigrum L. via Histone Deacetylases-Mediated p53 Acetylation Pathway" Molecules 28, no. 18: 6649. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186649
APA StyleLan, X., Lu, M., Fang, X., Cao, Y., Sun, M., Shan, M., Gao, W., Wang, Y., Yu, W., & Luo, H. (2023). Anti-Colorectal Cancer Activity of Solasonin from Solanum nigrum L. via Histone Deacetylases-Mediated p53 Acetylation Pathway. Molecules, 28(18), 6649. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186649






