Ebselen Inhibits the Growth of Lung Cancer Cells via Cell Cycle Arrest and Cell Death Accompanied by Glutathione Depletion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
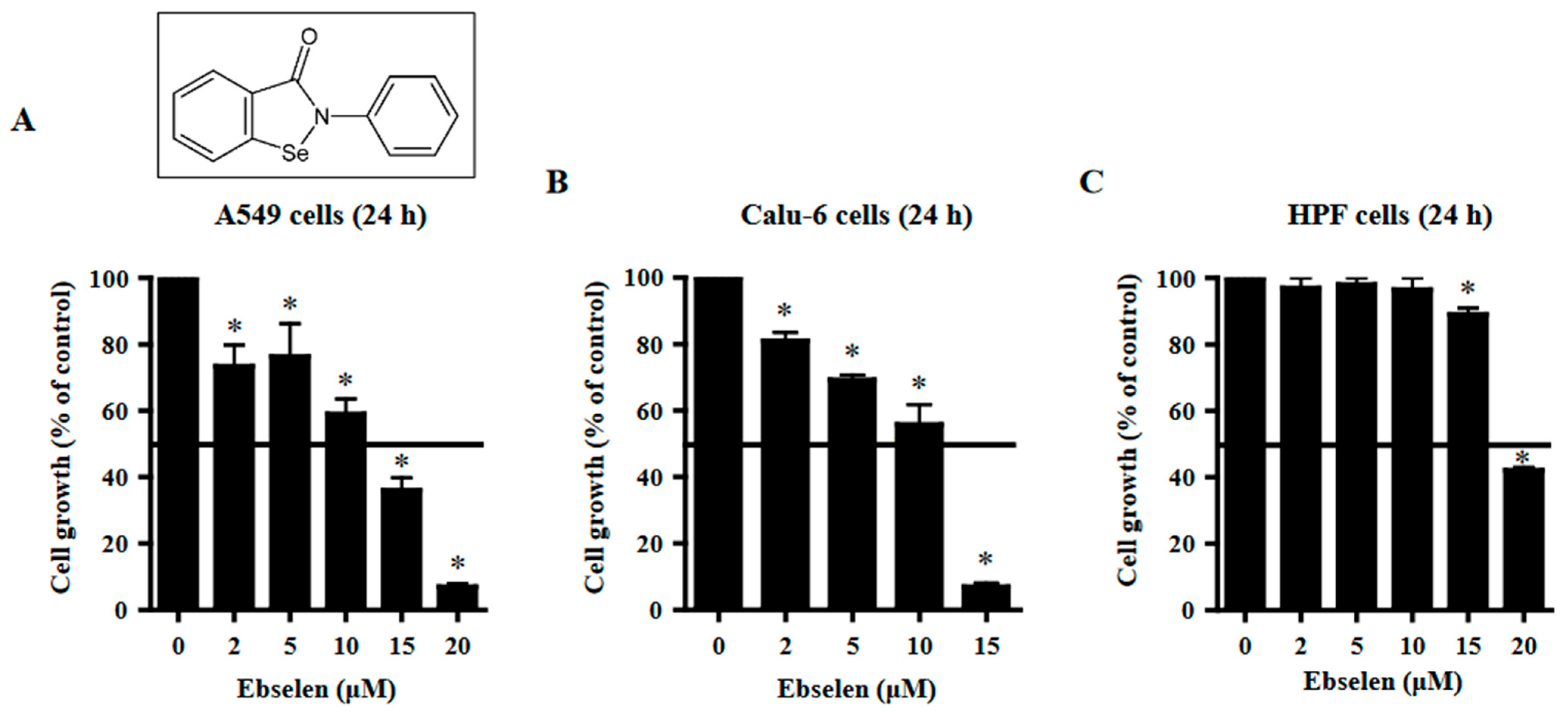
2.1. Effects of Ebselen on Lung Cancer and Normal Cell Growth
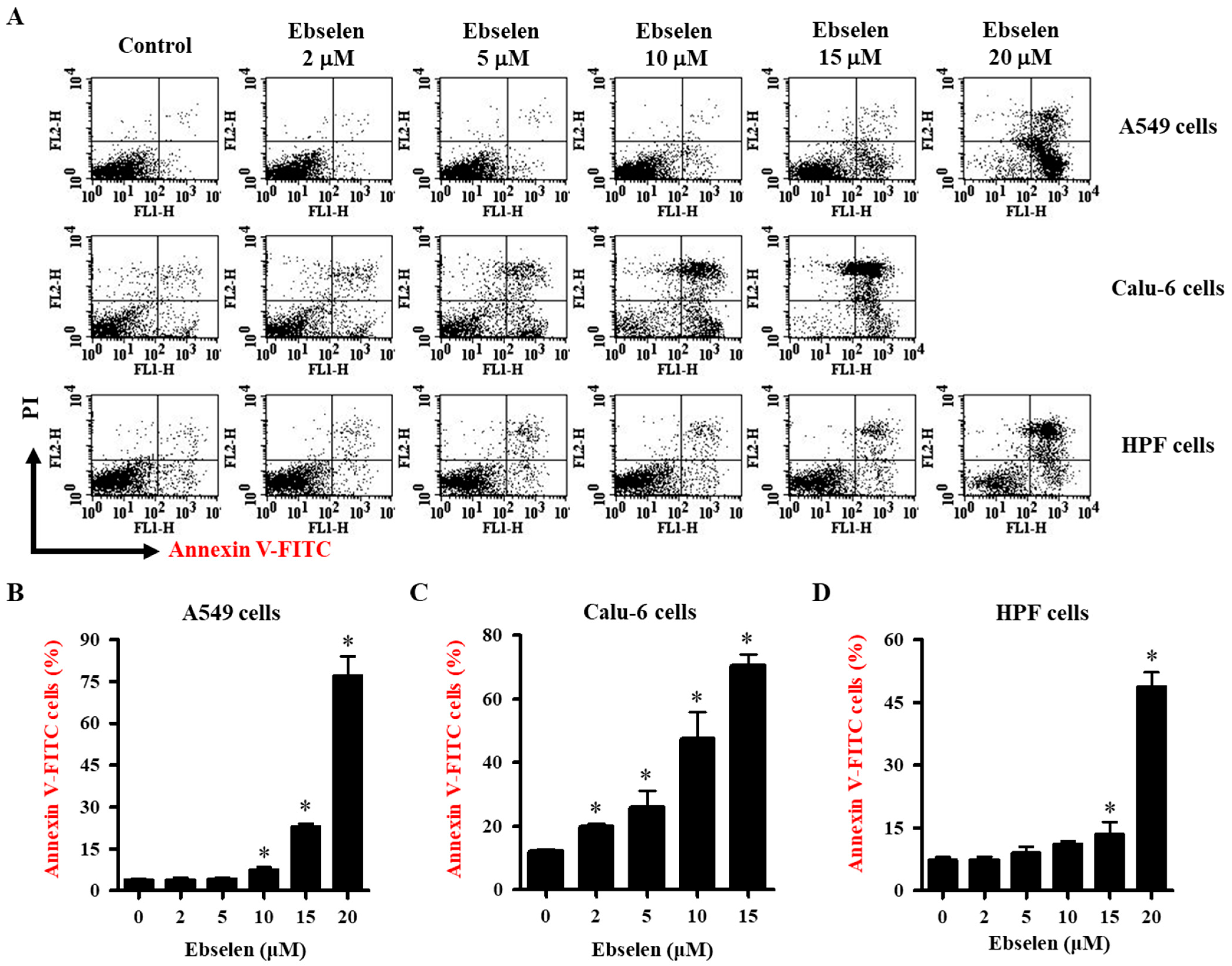
2.2. Effects of Ebselen on Apoptosis of Lung Cancer and HPF Cells
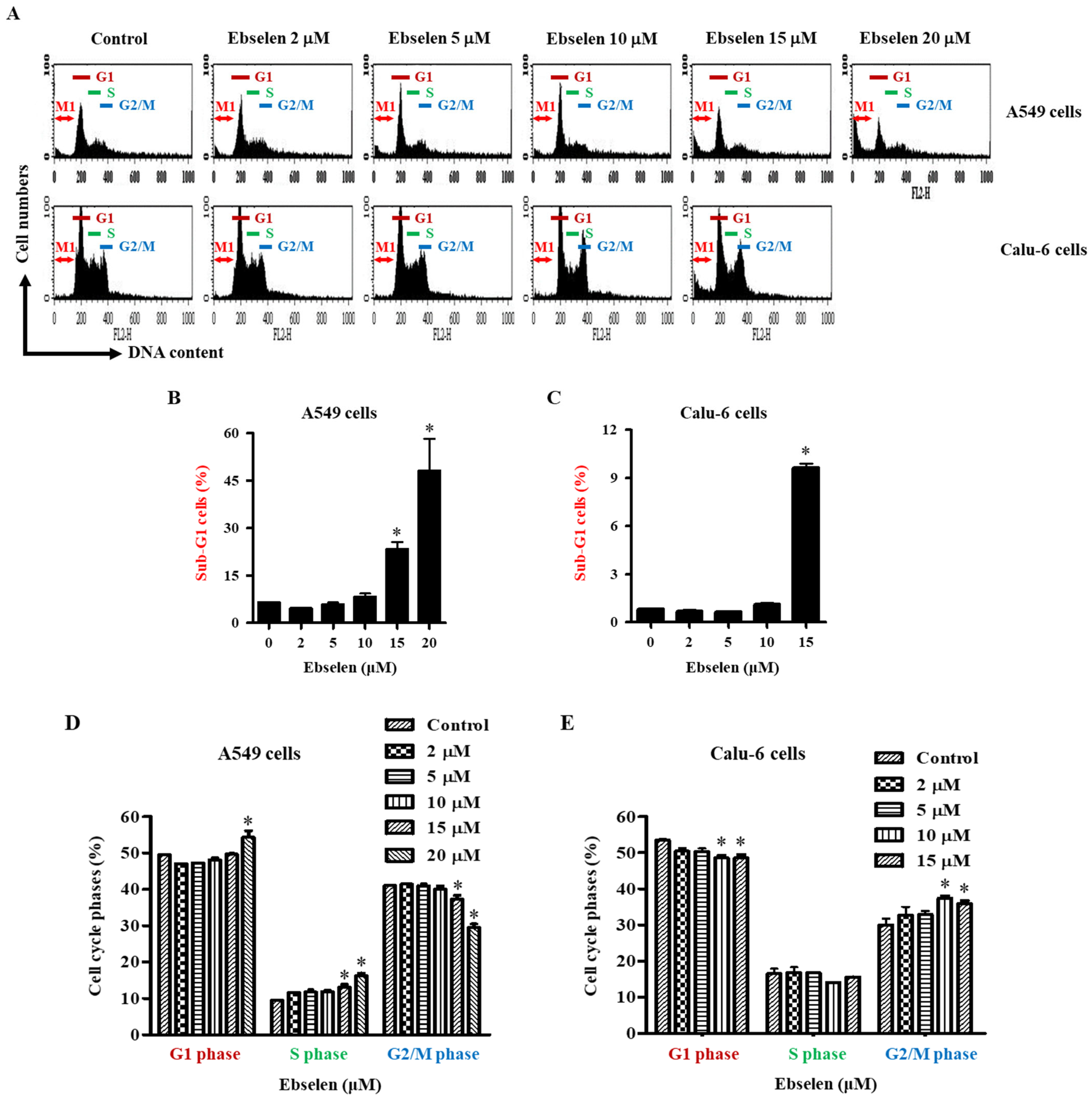
2.3. Effects of Ebselen on Sub-G1 and Cell Cycle Distributions in Lung Cancer Cells
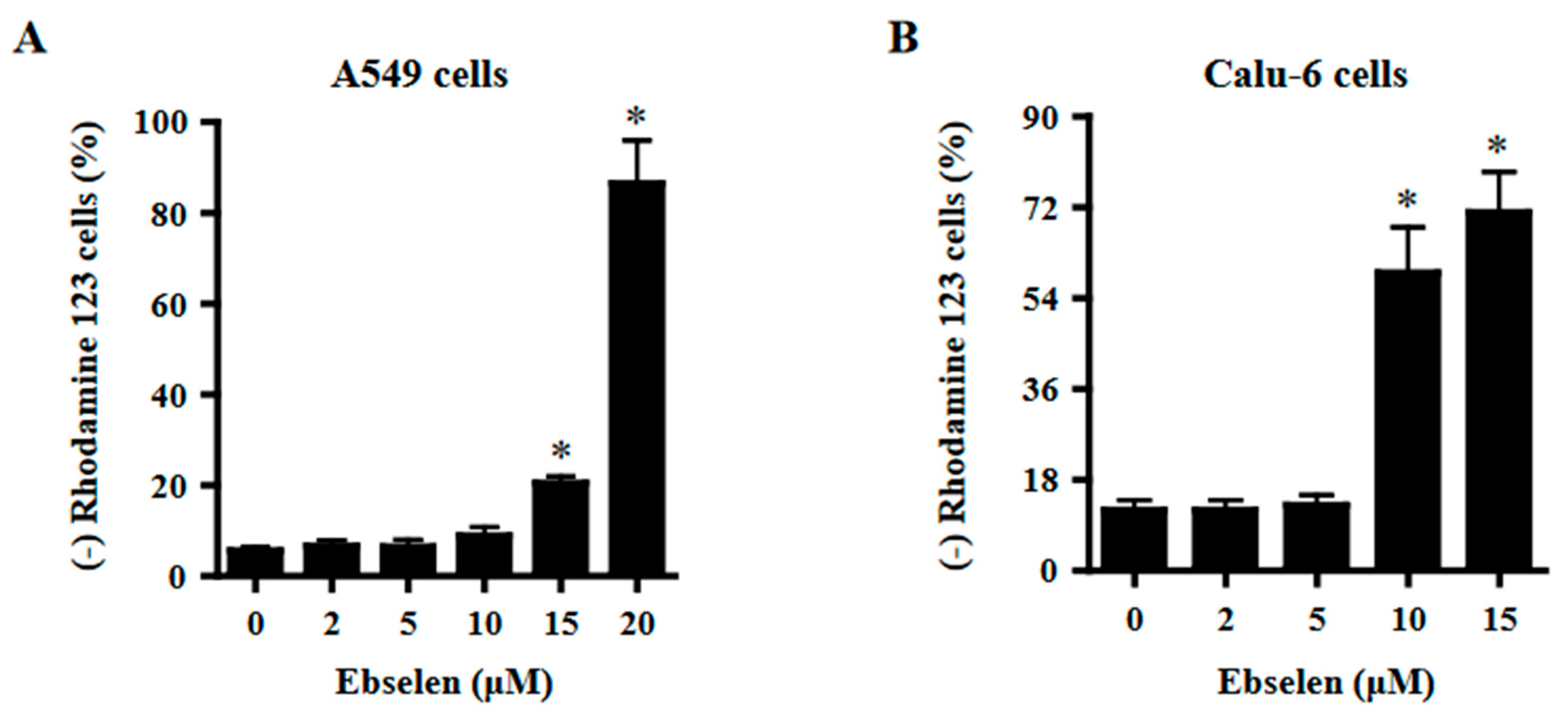
2.4. Effects of Ebselen on Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (MMP; ΔΨm) in Lung Cancer Cells
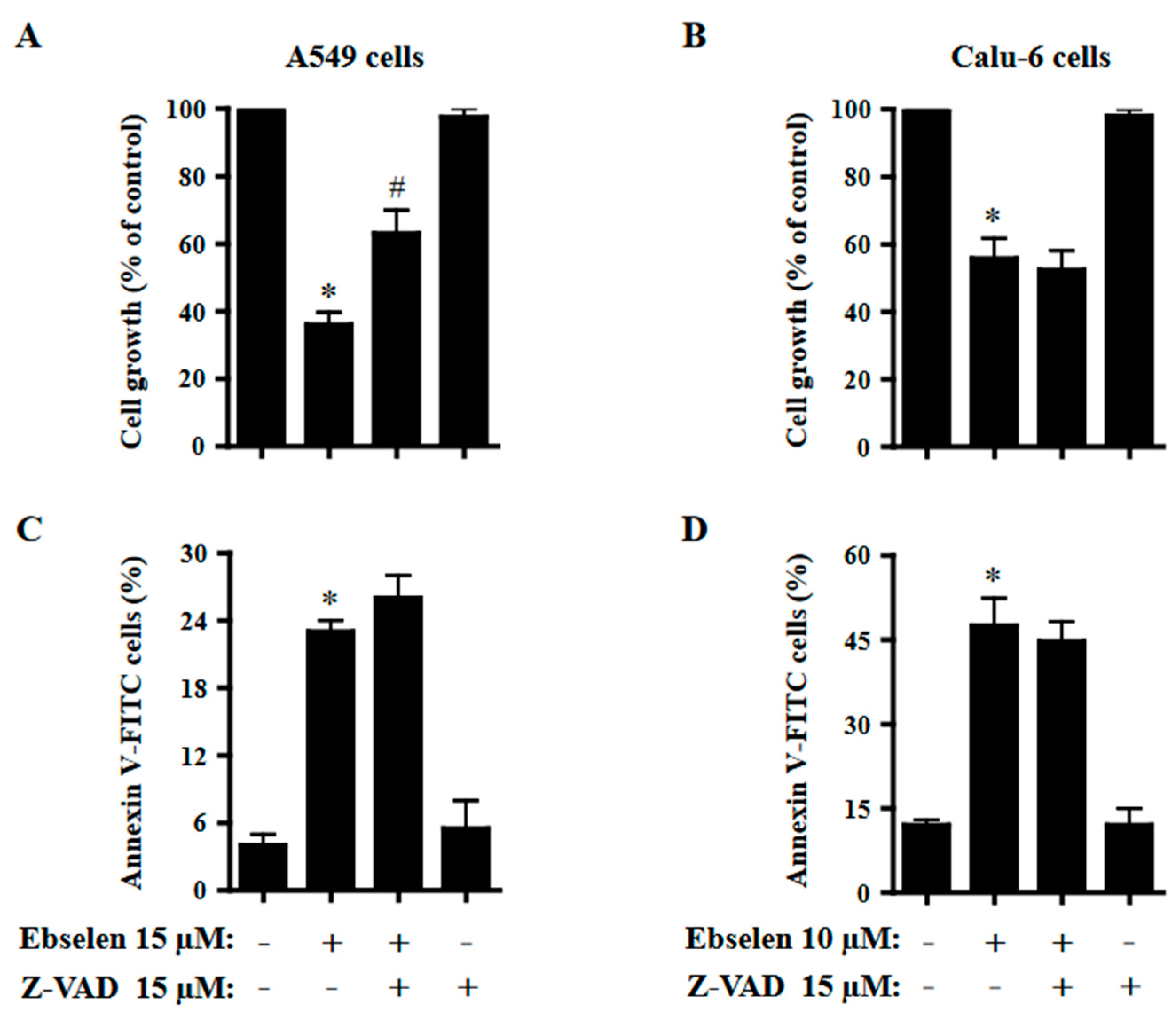
2.5. Effects of Z-VAD on Cell Growth and Cell Death in Ebselen-Treated Lung Cancer Cells
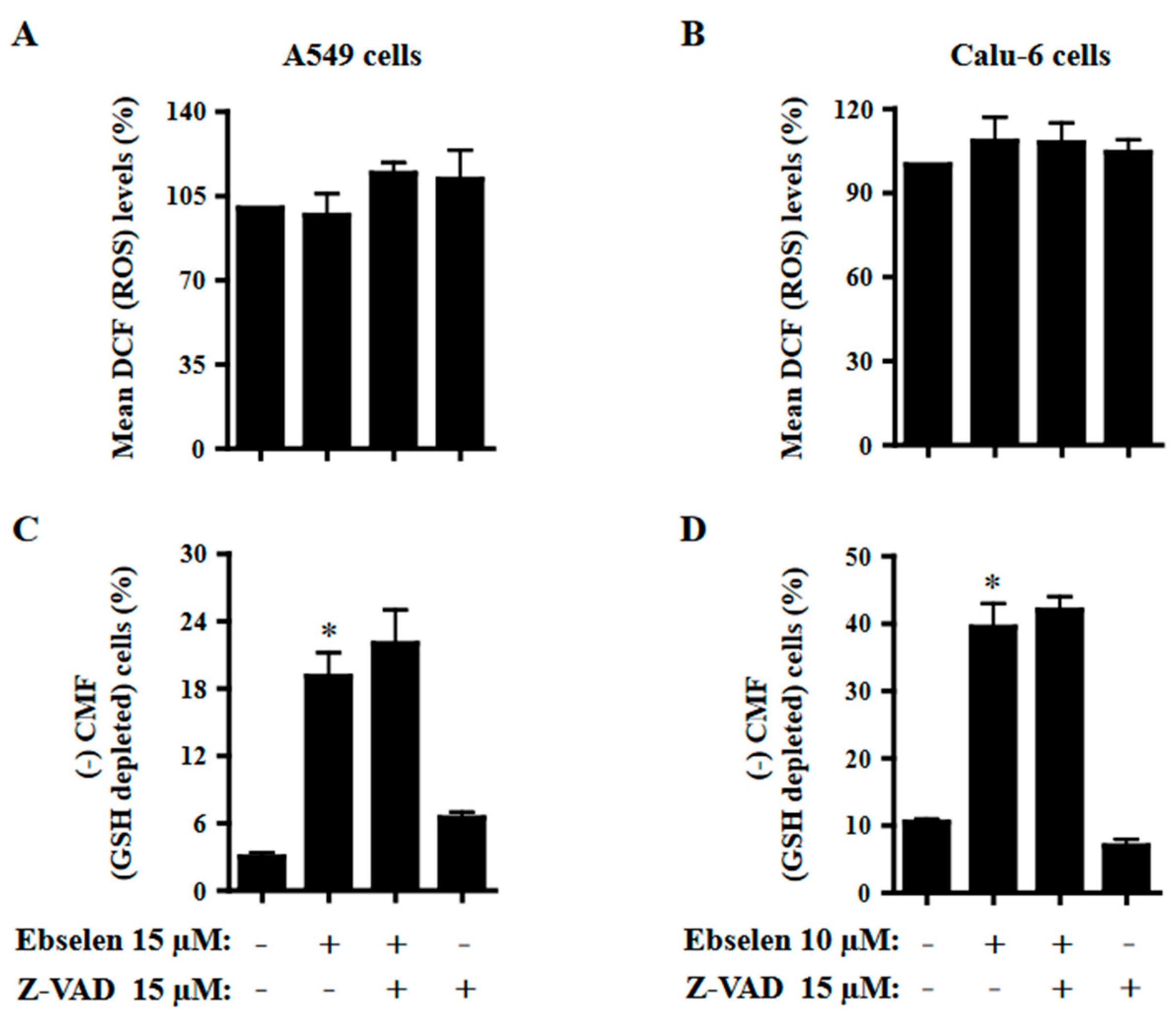
2.6. Effects of Z-VAD on ROS and GSH Levels in Ebselen-Treated Lung Cancer Cells
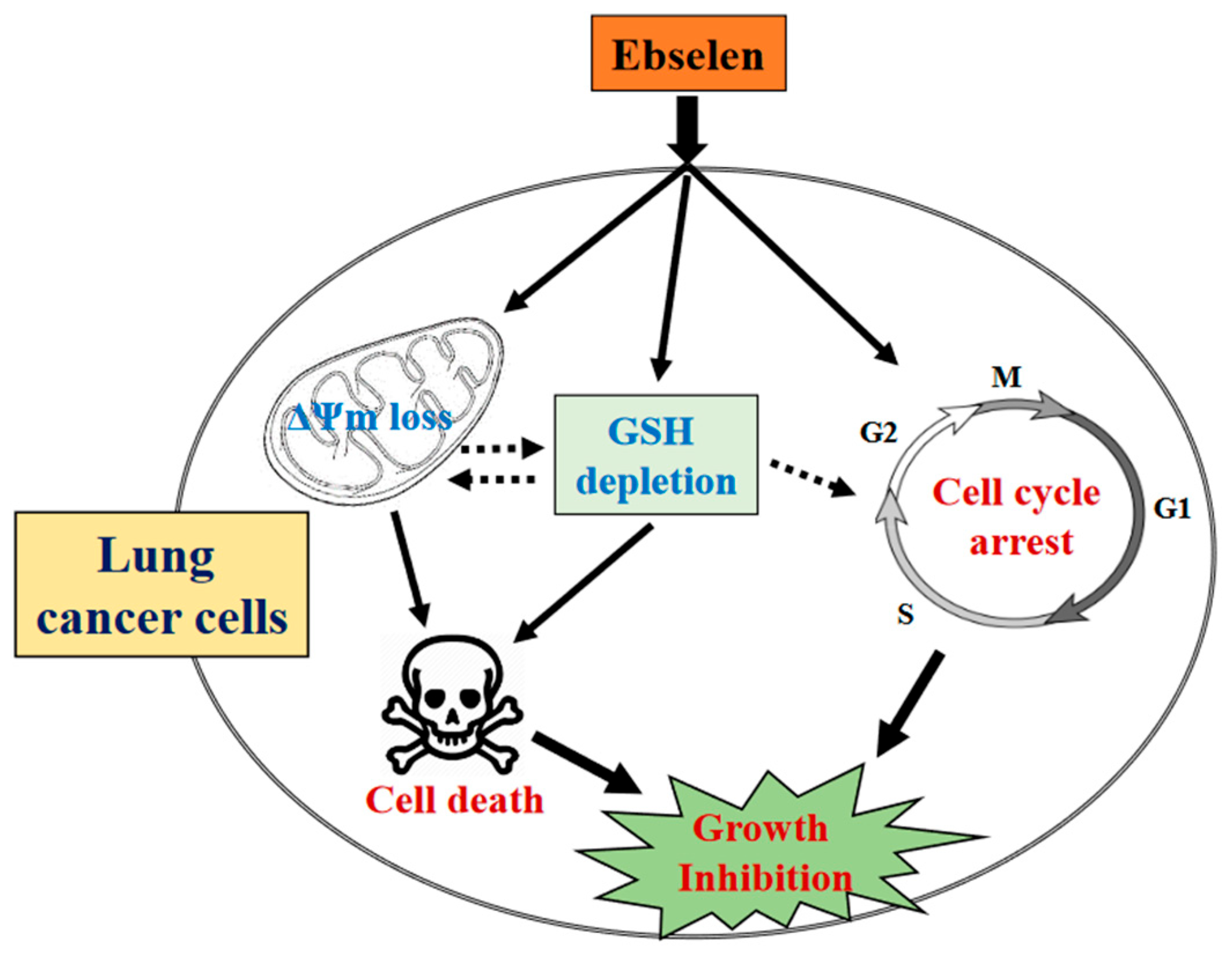
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Reagents
4.3. Cell Growth Inhibition Assay
4.4. Annexin V-Fluorescein Isothiocyanate Staining (FITC) and Propidium Iodide (PI) Staining for Apoptotic Cell Detection
4.5. Cell Cycle and Sub-G1 Cell Analysis
4.6. Measurement of MMP (ΔΨm)
4.7. Determination of Intracellular ROS Levels
4.8. Detection of Intracellular GSH Levels
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Hinz, B.; Phan, S.H.; Thannickal, V.J.; Prunotto, M.; Desmouliere, A.; Varga, J.; De Wever, O.; Mareel, M.; Gabbiani, G. Recent developments in myofibroblast biology: Paradigms for connective tissue remodeling. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 180, 1340–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.S.; Wynn, T.A. Pulmonary fibrosis: Pathogenesis, etiology and regulation. Mucosal. Immunol. 2009, 2, 103–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Li, M.; Chen, Z.; Zhan, C.; Lin, Z.; Wang, Q. Advances in clinical trials of targeted therapy and immunotherapy of lung cancer in 2018. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 1091–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi-Rad, R.; Li, R.; Paul, M.K.; Dubinett, S.M.; Liu, B. The Biology of Lung Cancer: Development of More Effective Methods for Prevention, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Clin. Chest Med. 2020, 41, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huska, J.D.; Lamb, H.M.; Hardwick, J.M. Overview of BCL-2 Family Proteins and Therapeutic Potentials. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 1877, pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, C. Restoring the switch for cancer cell death: Targeting the apoptosis signaling pathway. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2018, 75, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Alonso, D.; Malumbres, M. Mammalian cell cycle cyclins. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 107, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, S. Linking the Cell Cycle to Cell Fate Decisions. Trends Cell. Biol. 2015, 25, 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorov, D.B.; Juhaszova, M.; Sollott, S.J. Mitochondrial ROS-induced ROS release: An update and review. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1757, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, C.S. Reactive oxygen species: Roles in blood pressure and kidney function. Curr. Hypertens Rep. 2002, 4, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauterburg, B.H. Analgesics and glutathione. Am. J. Ther. 2002, 9, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onodera, T.; Momose, I.; Kawada, M. Potential Anticancer Activity of Auranofin. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 67, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Zou, L.; Lu, J.; Holmgren, A. Selenocysteine in mammalian thioredoxin reductase and application of ebselen as a therapeutic. Free Radic Biol. Med. 2018, 127, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassalle, C.; Maltinti, M.; Sabatino, L. Targeting Oxidative Stress for Disease Prevention and Therapy: Where Do We Stand, and Where Do We Go from Here. Molecules 2020, 25, 2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, J.D.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Tew, K.D. Oxidative Stress in Cancer. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 167–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, N. Ebselen, a useful tool for understanding cellular redox biology and a promising drug candidate for use in human diseases. Arch. Biochem. Biophys 2016, 595, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christison, J.; Sies, H.; Stocker, R. Human blood cells support the reduction of low-density-lipoprotein-associated cholesteryl ester hydroperoxides by albumin-bound ebselen. Biochem. J. 1994, 304 Pt 2, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, N.; Gotoh, N.; Niki, E. Effects of ebselen and probucol on oxidative modifications of lipid and protein of low density lipoprotein induced by free radicals. Biochim. Biophys Acta 1994, 1213, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, A.; Cadenas, E.; Graf, P.; Sies, H. A novel biologically active seleno-organic compound--I. Glutathione peroxidase-like activity in vitro and antioxidant capacity of PZ 51 (Ebselen). Biochem. Pharmacol. 1984, 33, 3235–3239. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Parnham, M.J.; Kindt, S. A novel biologically active seleno-organic compound--III. Effects of PZ 51 (Ebselen) on glutathione peroxidase and secretory activities of mouse macrophages. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1984, 33, 3247–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Masayasu, H.; Holmgren, A. Ebselen: A substrate for human thioredoxin reductase strongly stimulating its hydroperoxide reductase activity and a superfast thioredoxin oxidant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 8579–8584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, H.C.; Yu, J.J.; Guentzel, M.N.; Chambers, J.P.; Cap, A.P.; Arulanandam, B.P. Repurposing Auranofin, Ebselen, and PX-12 as Antimicrobial Agents Targeting the Thioredoxin System. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 336. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mahadevan, J.; Parazzoli, S.; Oseid, E.; Hertzel, A.V.; Bernlohr, D.A.; Vallerie, S.N.; Liu, C.Q.; Lopez, M.; Harmon, J.S.; Robertson, R.P. Ebselen treatment prevents islet apoptosis, maintains intranuclear Pdx-1 and MafA levels, and preserves beta-cell mass and function in ZDF rats. Diabetes 2013, 62, 3582–3588. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yun, J.W.; Lei, X.G. Glutathione peroxidase mimic ebselen improves glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in murine islets. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2014, 20, 191–203. [Google Scholar]
- Klann, I.P.; Martini, F.; Rosa, S.G.; Nogueira, C.W. Ebselen reversed peripheral oxidative stress induced by a mouse model of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 2205–2215. [Google Scholar]
- Yagasaki, H.; Takekoshi, S.; Kitatani, K.; Kato, C.; Yamasaki, H.; Shioyama, K.; Tsuboi, T.; Matsuzaki, T.; Inagaki, Y.; Masuda, R.; et al. Protective effect of ebselen on bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis: Analysis of the molecular mechanism of lung fibrosis mediated by oxidized diacylglycerol. Free Radic Res. 2022, 56, 473–482. [Google Scholar]
- Brassington, K.; Chan, S.M.H.; De Luca, S.N.; Dobric, A.; Almerdasi, S.A.; Mou, K.; Seow, H.J.; Oseghale, O.; Bozinovski, S.; Selemidis, S.; et al. Ebselen abolishes vascular dysfunction in influenza A virus-induced exacerbations of cigarette smoke-induced lung inflammation in mice. Clin. Sci. 2022, 136, 537–555. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.H.; Park, W.H. Proteasome inhibitor MG132 reduces growth of As4.1 juxtaglomerular cells via caspase-independent apoptosis. Arch. Toxicol. 2010, 84, 689–698. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Bhalla, K.; Kim, C.N.; Ibrado, A.M.; Cai, J.; Peng, T.I.; Jones, D.P.; Wang, X. Prevention of apoptosis by Bcl-2: Release of cytochrome c from mitochondria blocked. Science 1997, 275, 1129–1132. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ham, J.; Lim, W.; Park, S.; Bae, H.; You, S.; Song, G. Synthetic phenolic antioxidant propyl gallate induces male infertility through disruption of calcium homeostasis and mitochondrial function. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 845–856. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.K.; Han, B.R.; Park, W.H. Combination of Arsenic Trioxide and Valproic Acid Efficiently Inhibits Growth of Lung Cancer Cells via G2/M-Phase Arrest and Apoptotic Cell Death. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2649. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, W.H. Hydrogen peroxide inhibits the growth of lung cancer cells via the induction of cell death and G1phase arrest. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 1787–1794. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- You, B.R.; Shin, H.R.; Park, W.H. PX-12 inhibits the growth of A549 lung cancer cells via G2/M phase arrest and ROS-dependent apoptosis. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 44, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.H.; Park, W.H. MG132, a proteasome inhibitor decreased the growth of Calu-6 lung cancer cells via apoptosis and GSH depletion. Toxicol. Vitr. Int. J. Publ. Assoc. BIBRA 2010, 24, 1237–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.H.; Park, W.H. Growth inhibition in antimycin A treated-lung cancer Calu-6 cells via inducing a G1 phase arrest and apoptosis. Lung Cancer 2009, 65, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Holmgren, A. A novel antioxidant mechanism of ebselen involving ebselen diselenide, a substrate of mammalian thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 39456–39462. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.H.; Kim, S.Z.; Kim, S.H.; Park, W.H. Induction of apoptosis in arsenic trioxide-treated lung cancer A549 cells by buthionine sulfoximine. Mol. Cells 2008, 26, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, W.H.; Han, B.R.; Park, H.K.; Kim, S.Z. Arsenic trioxide induces growth inhibition and death in human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells accompanied by mitochondrial O2*- increase and GSH depletion. Environ. Toxicol. 2018, 33, 833–840. [Google Scholar]
- You, B.R.; Park, W.H. The levels of HDAC1 and thioredoxin1 are related to the death of mesothelioma cells by suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 2197–2204. [Google Scholar]
- Kroemer, G.; Dallaporta, B.; Resche-Rigon, M. The mitochondrial death/life regulator in apoptosis and necrosis. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1998, 60, 619–642. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, H.J.; Park, W.H. Butylated hydroxyanisole inhibits the growth of HeLa cervical cancer cells via caspase-dependent apoptosis and GSH depletion. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2011, 349, 179–186. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.H.; Park, W.H. Propyl gallate inhibits the growth of HeLa cells via regulating intracellular GSH level. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2009, 47, 2531–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, W.H.; Han, Y.W.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, S.H.; Cho, K.W.; Kim, S.Z. Antimycin A induces apoptosis in As4.1 juxtaglomerular cells. Cancer Lett. 2007, 251, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, W.H. Ebselen Inhibits the Growth of Lung Cancer Cells via Cell Cycle Arrest and Cell Death Accompanied by Glutathione Depletion. Molecules 2023, 28, 6472. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186472
Park WH. Ebselen Inhibits the Growth of Lung Cancer Cells via Cell Cycle Arrest and Cell Death Accompanied by Glutathione Depletion. Molecules. 2023; 28(18):6472. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186472
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Woo Hyun. 2023. "Ebselen Inhibits the Growth of Lung Cancer Cells via Cell Cycle Arrest and Cell Death Accompanied by Glutathione Depletion" Molecules 28, no. 18: 6472. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186472
APA StylePark, W. H. (2023). Ebselen Inhibits the Growth of Lung Cancer Cells via Cell Cycle Arrest and Cell Death Accompanied by Glutathione Depletion. Molecules, 28(18), 6472. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28186472





