Unprecedented Neoverrucosane and Cyathane Diterpenoids with Anti-Neuroinflammatory Activity from Cultures of the Culinary-Medicinal Mushroom Hericium erinaceus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
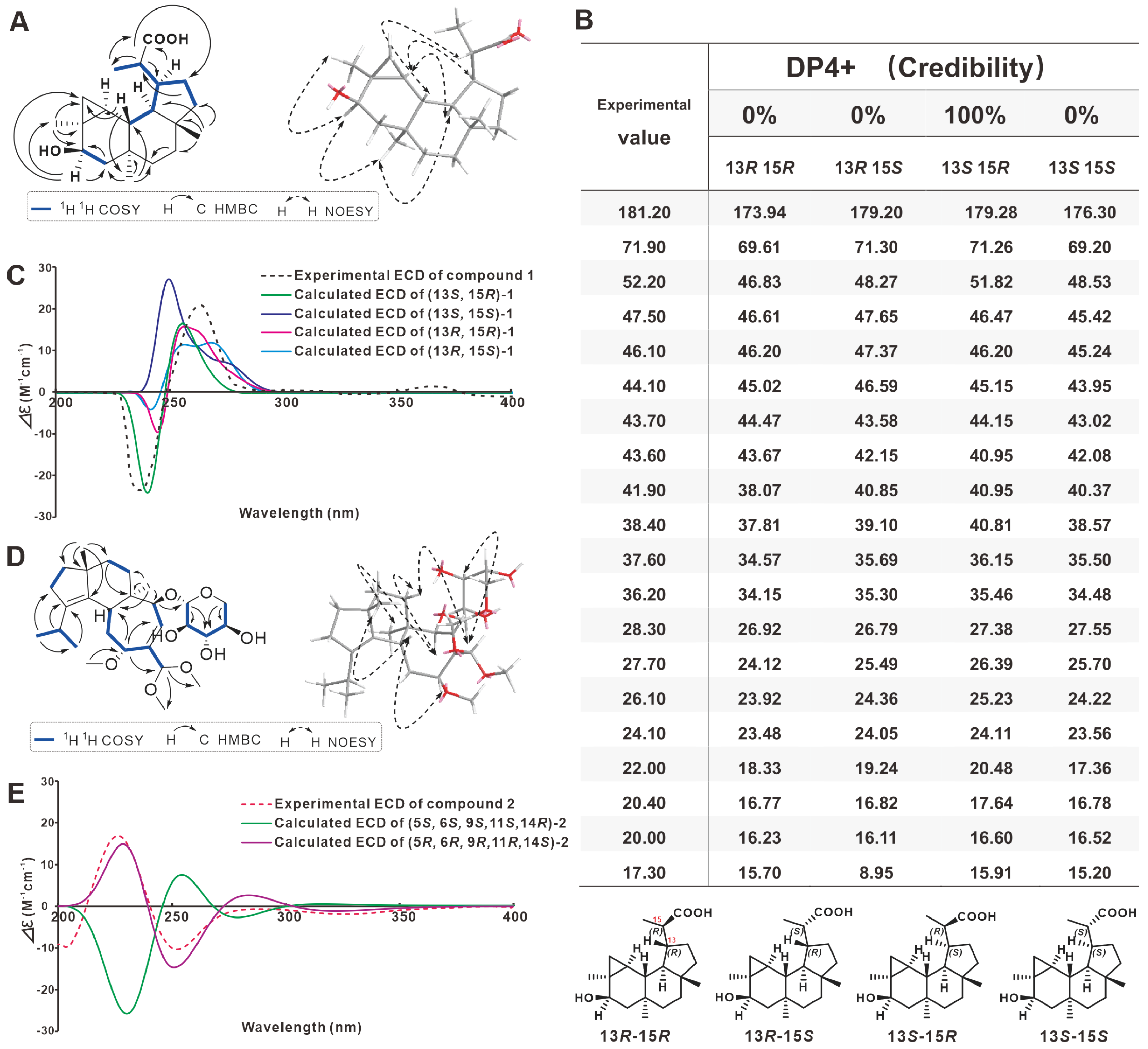
2.1. Structure Elucidation for 1 and 2
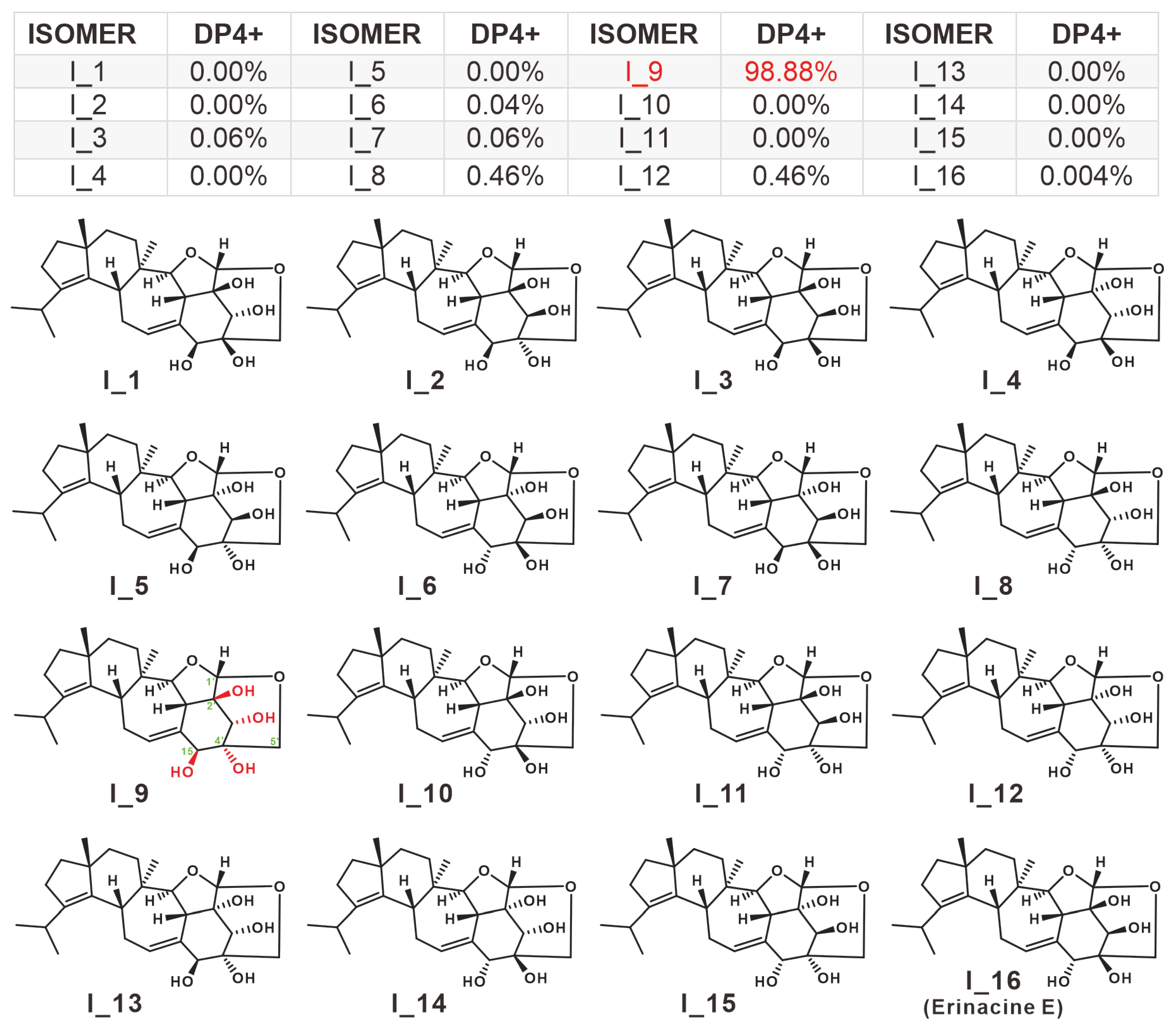
2.2. Structure Revision for 5
2.3. Neurotrophic Activity
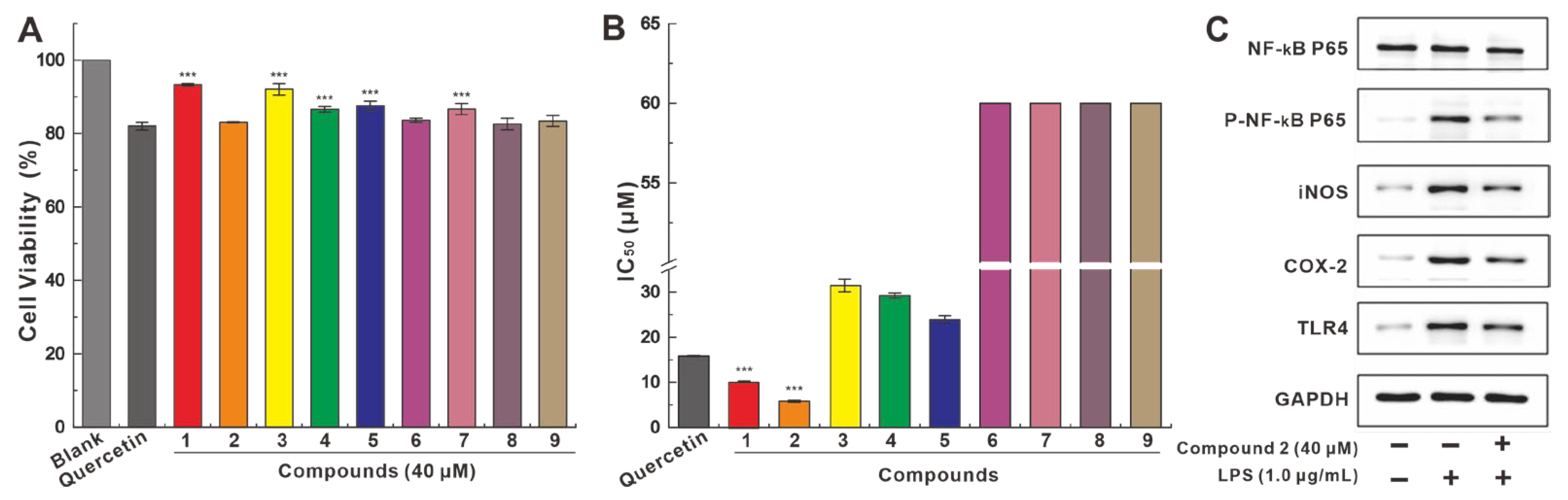
2.4. Anti-Neuroinflammatory Activities
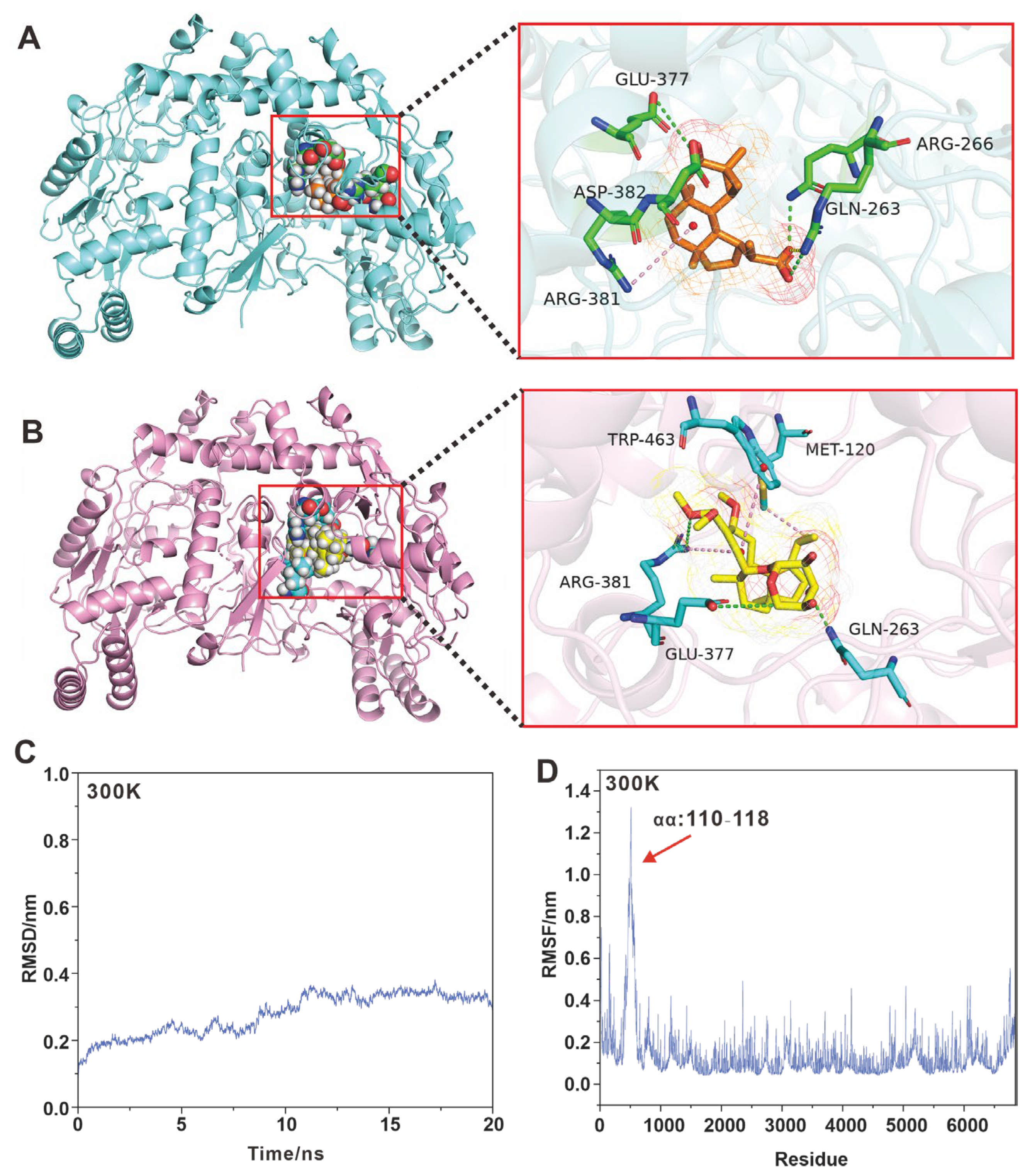
2.5. Molecular Docking Simulation of iNOS Inhibition
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Experimental Procedures
4.2. Fungal Material
4.3. Extraction, Isolation and Purification
4.4. Structural Identification and Quantum Chemistry Calculations
4.5. Spectroscopic Data
4.5.1. Novel Compounds
4.5.2. Known Compounds
4.6. Biological Activity Assay
4.6.1. Evaluation of Neurotrophic Activity
4.6.2. Evaluation of Anti-Neuroinflammatory Activity
4.7. Molecular Docking and Dynamics Simulation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sandargo, B.; Chepkirui, C.; Cheng, T.; Chaverra-Muñoz, L.; Thongbai, B.; Stadler, M.; Hüttel, S. Biological and chemical diversity go hand in hand: Basidiomycota as source of new pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 107344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.X.; Feng, X.L.; Liu, C.; Gao, J.M.; Qi, J. Diverse Metabolites and Pharmacological Effects from the Basidiomycetes Inonotus hispidus. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.-G.; Wang, Z.-X.; Feng, X.-L.; Zhang, R.-Q.; Shen, D.-Y.; Du, S.; Gao, J.-M.; Qi, J. Chromosome-Level Genome Sequences, Comparative Genomic Analyses, and Secondary-Metabolite Biosynthesis Evaluation of the Medicinal Edible Mushroom Laetiporus sulphureus. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0243922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawagishi, H.; Shimada, A.; Shirai, R.; Okamoto, K.; Ojima, F.; Sakamoto, H.; Ishiguro, Y.; Furukawa, S. Erinacines A, B and C, strong stimulators of nerve growth factor (NGF)-synthesis, from the mycelia of Hericium erinaceum. Tetrahedron Lett. 1994, 35, 1569–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawagishi, H.; Shimada, A.; Hosokawa, S.; Mori, H.; Sakamoto, H.; Ishiguro, Y.; Sakemi, S.; Bordner, J.; Kojima, N.; Furukawa, S. Erinacines E, F, and G, stimulators of nerve growth factor (NGF)-synthesis, from the mycelia of Hericium erinaceum. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 7399–7402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirokazu, K.; Ayano, M.; Shinji, T.; Tomoyuki, N. Erinacines J and K from the mycelia of Hericium erinaceum. Tetrahedron 2006, 62, 8463–8466. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, M. Chemistry, Nutrition, and Health-Promoting Properties of Hericium erinaceus (Lion’s Mane) Mushroom Fruiting Bodies and Mycelia and Their Bioactive Compounds. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 7108–7123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailly, C.; Gao, J.M. Erinacine A and related cyathane diterpenoids: Molecular diversity and mechanisms underlying their neuroprotection and anticancer activities. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 159, 104953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupcic, Z.; Rascher, M.; Kanaki, S.; Köster, R.W.; Stadler, M.; Wittstein, K. Two New Cyathane Diterpenoids from Mycelial Cultures of the Medicinal Mushroom Hericium erinaceus and the Rare Species, Hericium flagellum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Gao, Y.-Q.; Kang, S.-j.; Liu, C.; Gao, J.-M. Secondary Metabolites of Bird’s Nest Fungi: Chemical Structures and Biological Activities. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 6513–6524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allbutt, A.D.; Ayer, W.A.; Brodie, H.J.; Johri, B.N.; Taube, H. Cyathin, a new antibiotic complex produced by Cyathus helenae. Can. J. Microbiol. 1971, 17, 1401–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johri, B.N.; Brodie, H.J. The physiology of production of the antibiotic cyathin by Cyathus helenae. Can. J. Microbiol. 1971, 17, 1243–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.-W.; Liu, L.; Gao, J.-M.; Zhang, A.-L. Cyathane diterpenes from Chinese mushroom Sarcodon scabrosus and their neurite outgrowth-promoting activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 3112–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, S.-T.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.-H.; Li, B.; Liu, J.-K. Cyathane Diterpenoids and Nitrogenous Terphenyl Derivative from the Fruiting Bodies of Basidiomycete Phellodon niger. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 58, 1176–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudalungu, C.M.; Richter, C.; Wittstein, K.; Abdalla, M.A.; Matasyoh, J.C.; Stadler, M.; Süssmuth, R.D. Laxitextines A and B, Cyathane Xylosides from the Tropical Fungus Laxitextum incrustatum. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 894–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sum, W.C.; Mitschke, N.; Schrey, H.; Wittstein, K.; Kellner, H.; Stadler, M.; Matasyoh, J.C. Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Cyathane-Xylosides from Cultures of the Basidiomycete Dentipellis fragilis. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, A.; Nozaki, H.; Nakayama, M.; Hayashi, S.; Takaoka, D. Structure of (–)-2,9-dihydroxyverrucosane, a novel carbon skeletal diterpenoid from the liverwort Mylia verrucosa. Chem. Commun. 1978, 5, 198–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, S.; Matsuo, A.; Nakayama, M.; Takaoka, D.; Hayashi, S. Mass Spectra of Some Diterpenoids with the Novel Carbon Skeletons Verrucosane, Neoverrucosane and Homoverrucosane. J. Mass Spectrom. Soc. Jpn. 1982, 30, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakawa, Y.; Masuya, T.; Tori, M.; Fukuyama, Y. 13-Epi-neo- and 13-epi-homoverrucosane diterpenoids from the liverwort Schistochila nobilis. Phytochemistry 1988, 27, 3509–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grammes, C.; Burkhardt, G.; Veith, M.; Huch, V.; Becker, H. Epi-neoverrucosane- and epi-homoverrucosane-type diterpenoids from Fossombronia alaskana. Phytochemistry 1997, 44, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimogawa, H.; Teruya, T.; Suenaga, K.; Kigoshi, H. Isolation of Two 13-epi-Neoverrucosane-Type Diterpenoids from a Marine Sponge Axinyssa tethyoides. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2005, 78, 1345–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuyama, Y.; Masuya, T.; Tori, M.; Kido, M.; Wakamatsu, M.; Asakawa, Y. Verrucosane diterpene from the liverwort Plagiochila stephensoniana. Phytochemistry 1988, 27, 1797–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyere, A.; Rowley, D.C.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. New Neoverrucosane Diterpenoids Produced by the Marine Gliding Bacterium Saprospira grandis. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.-l.; Zhang, S.; Ma, K.; Xu, Y.; Tao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J.; Guo, S.; Ren, J.; Wang, W.; et al. Discovery and Characterization of a New Family of Diterpene Cyclases in Bacteria and Fungi. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 4749–4752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenreich, W.; Rieder, C.; Grammes, C.; Heßler, G.; Adam, K.P.; Becker, H.; Arigoni, D.; Bacher, A. Biosynthesis of a Neo-epi-verrucosane Diterpene in the Liverwort Fossombronia alaskana. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 36312–36320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, H.-J.; Wu, C.-L.; Becker, H.; Zapp, J. Sesquiterpenoids and diterpenoids from the Chilean liverwort Lepicolea ochroleuca. Phytochemistry 2000, 53, 845–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamada, T.; Johanis, M.L.; Ng, S.Y.; Phan, C.S.; Suleiman, M.; Vairappan, C.S. A New Epi-neoverrucosane-type Diterpenoid from the Liverwort Pleurozia subinflata in Borneo. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2020, 10, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.J.; Dattelbaum, J.D.; Field, J.J.; Smart, Z.; Woolly, E.F.; Barber, J.M.; Heathcott, R.; Miller, J.H.; Northcote, P.T. Structurally diverse hamigerans from the New Zealand marine sponge Hamigera tarangaensis: NMR-directed isolation, structure elucidation and antifungal activity. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 8041–8051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yao, J.-N.; Chen, H.-P.; Zhao, Z.-Z.; Li, Z.-H.; Feng, T.; Liu, J.-K. Hericinoids A–C, cyathane diterpenoids from culture of mushroom Hericium erinaceus. Phytochem. Lett. 2018, 27, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chobot, V.; Opletal, L.; Jáhodář, L.; Patel, A.V.; Dacke, C.G.; Blunden, G. Ergosta-4,6,8,22-tetraen-3-one from the edible fungus, Pleurotus ostreatus (oyster fungus). Phytochemistry 1997, 45, 1669–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Wang, L. Chemical Constituents of the Fruits of Cassia Agnes Brenan. Chin. J. Mod. Appl. Pharm. 2014, 31, 1355–1359. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Ali, M.; Alam, M.S.; Niwa, M.; Sakai, T. Isolation and Characterization of a Dihydroxysterol from Lawsonia inermis. Nat. Prod. Lett. 1994, 4, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, H.; Nakamura, E.; Okuyama, E.; Ishibashi, M. Six Immunosuppressive Features from an Ascomycete, Zopfiella longicaudata, Found in a Screening Study Monitored by Immunomodulatory Activity. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 52, 1005–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asiri, I.A.M.; Badr, J.M.; Youssef, D.T.A. Penicillivinacine, antimigratory diketopiperazine alkaloid from the marine-derived fungus Penicillium vinaceum. Phytochem. Lett. 2015, 13, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rosa, S.; Mitova, M.; Tommonaro, G. Marine bacteria associated with sponge as source of cyclic peptides. Biomol. Eng. 2003, 20, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.N.; Li, S.W.; Ying, J.Z.; Chong, R.Y. Chemical Constituents of Acroscyphus sphaerophoroides. Plant Sci. J. 2011, 29, 234–237. [Google Scholar]
- Hirotani, M.; Sai, K.; Hirotani, S.; Yoshikawa, T. Blazeispirols B, C, E and F, des-A-ergostane-type compounds, from the cultured mycelia of the fungus Agaricus blazei. Phytochemistry 2001, 59, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongklang, N.; Thongbai, B.; Chamyuang, S.; Callac, P.; Chukeatirote, E.; Hyde, K.D.; Wittstein, K.; Stadler, M. Blazeispirol A, a chemotaxonomic marker from mycelia of the medicinal mushroom Agaricus subrufescens. Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2017, 44, 298–308. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.; Feng, X.-L.; Wang, Z.-X.; Qi, J. The First Whole Genome Sequencing of Agaricus bitorquis and Its Metabolite Profiling. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo-Sanchez, L.T.; López-Peña, D.; Torres-Moreno, H.; Gutiérrez, A.; Gaitán-Hernández, R.; Esqueda, M. Biosynthesis, Gene Expression, and Pharmacological Properties of Triterpenoids of Ganoderma Species (Agaricomycetes): A Review. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2022, 24, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.-q.; Feng, X.-L.; Wang, Z.-X.; Xie, T.-C.; Duan, Y.; Liu, C.; Gao, J.-M.; Qi, J. Genomic and Metabolomic Analyses of the Medicinal Fungus Inonotus hispidus for Its Metabolite’s Biosynthesis and Medicinal Application. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.-K.; Yun, B.-S. Styrylpyrone-class compounds from medicinal fungi Phellinus and Inonotus spp., and their medicinal importance. J. Antibiot. 2011, 64, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Xu, Y.Z.; Wang, W.W.; Yang, Z.; Liu, B.; Stadler, M.; Liu, L.L.; Gao, J.M. Cyathane Diterpenes from Cultures of the Bird’s Nest Fungus Cyathus hookeri and Their Neurotrophic and Anti-neuroinflammatory Activities. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 1599–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousuf, S.; Choudhary, M.I.; Atta-ur, R. Chapter 7—Lichens: Chemistry and Biological Activities. In Studies in Natural Products Chemistry; Atta-ur, R., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 43, pp. 223–259. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, C.-Y.; Zhang, C.-C.; Shi, X.-W.; Li, D.; Cao, W.; Yin, X.; Gao, J.-M. Sarcodonin G Derivatives Exhibit Distinctive Effects on Neurite Outgrowth by Modulating NGF Signaling in PC12 Cells. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 1607–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, K.; Sakai, T.; Shimada, A.; Shirai, R.; Sakamoto, H.; Yoshida, S.; Ojima, F.; Ishiguro, Y.; Kawagishi, H. Antimicrobial chlorinated orcinol derivatives from mycelia of Hericium erinaceum. Phytochemistry 1993, 34, 1445–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Tokunaga, T.; Kondo, M.; Ishigami, K.; Tokuyama, S.; Suzuki, T.; Choi, J.-H.; Hirai, H.; Kawagishi, H. Erinaceolactones A to C, from the Culture Broth of Hericium erinaceus. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, K.; Kodani, S.; Kubo, M.; Masuno, K.; Sekiya, A.; Nagai, K.; Kawagishi, H. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Stress-Suppressive Compounds from Scrap Cultivation Beds of the Mushroom Hericium erinaceum. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2009, 73, 1908–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewick, P.M. The biosynthesis of C5–C25 terpenoid compounds. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2002, 19, 181–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Li, B.X.; Takagi, T.; Wang, C.; Miyamoto, K.; Uchiyama, M. DFT Study on the Biosynthesis of Verrucosane Diterpenoids and Mangicol Sesterterpenoids: Involvement of Secondary-Carbocation-Free Reaction Cascades. JACS Au 2021, 1, 1231–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mincer, T.J.; Spyere, A.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. Phylogenetic Analyses and Diterpenoid Production by Marine Bacteria of the Genus Saprospira. Curr. Microbiol. 2004, 49, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Chen, F. Multiwfn: A multifunctional wavefunction analyzer. J. Comput. Chem. 2012, 33, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimblat, N.; Zanardi, M.M.; Sarotti, A.M. Beyond DP4: An Improved Probability for the Stereochemical Assignment of Isomeric Compounds using Quantum Chemical Calculations of NMR Shifts. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 12526–12534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hei, Y.; Zhang, H.; Tan, N.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, X.; Hu, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Qi, J.; Gao, J.-M. Antimicrobial activity and biosynthetic potential of cultivable actinomycetes associated with Lichen symbiosis from Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 244, 126652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Wang, D.; Yin, X.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, J.-M. New Metabolite With Inhibitory Activity Against α-Glucosidase and α-Amylase From Endophytic Chaetomium globosum. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2020, 15, 1934578X20941338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
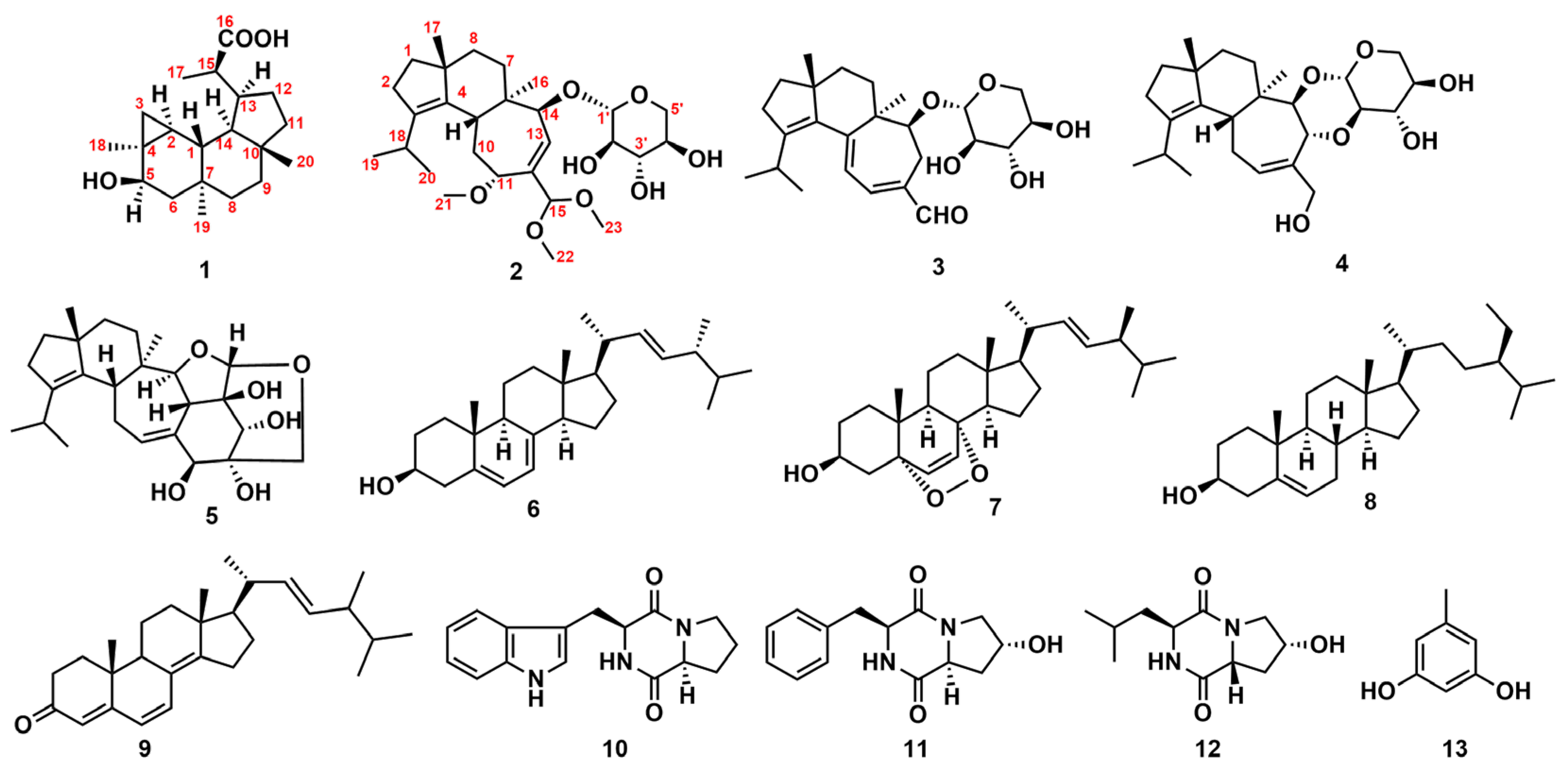

| 1 (CD3OD) | 2 (CDCl3) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position | δC | δH (m, J in Hz) | δC | δH (m, J in Hz) |
| 1 | 46.1 | 1.29 | 37.1 | 1.52 t (7.4) 2H |
| 2 | 28.3 | 0.68 m | 28.6 | 2.30 dt (7.8,1.4) 2H |
| 3 | 22.0 | 0.96 m 2H | 138.6 | |
| 4 | 24.1 | 140.3 | ||
| 5 | 71.9 | 4.00 dd (10.8, 7.3) | 34.0 | 3.27 m |
| 6 | 47.5 | 1.62 m H-6a 0.74 m H-6b | 43.7 | |
| 7 | 38.4 | 34.2 | 1.00 td (13.4,4.2) H-7a 2.06 dt (12.9,4.8) H-7b | |
| 8 | 36.2 | 1.23 m H-8a 1.07 m H-8b | 36.1 | 1.45 m 2H |
| 9 | 37.6 | 1.41 m H-9a 1.32 m H-9b | 49.7 | |
| 10 | 44.1 | 30.0 | 2.30 m H-10a 1.92 t (13.6) H-10b | |
| 11 | 41.9 | 1.50 m H-11a 1.21 m H-11b | 75.1 | 3.88 d (5.8) |
| 12 | 27.7 | 1.92 m H-12a 1.67 m H-12b | 141.4 | |
| 13 | 43.6 | 2.35 m | 132.0 | 6.13 d (8.0) |
| 14 | 52.2 | 1.59 m | 85.0 | 3.48 m |
| 15 | 43.7 | 2.88 m | 106.6 | 4.55 s |
| 16 | 181.2 | 17.4 | 0.78 s | |
| 17 | 20.0 | 1.26 d (7.0) | 24.2 | 1.08 s |
| 18 | 26.1 | 1.18 s | 27.2 | 2.98 p |
| 19 | 17.3 | 0.80 s | 21.4 | 0.96 d (4.6) |
| 20 | 20.4 | 0.83 s | 22.3 | 0.97 d (4.6) |
| 21 | 57.0 | 3.29 s | ||
| 22 | 54.7 | 3.36 s | ||
| 23 | 53.4 | 3.32 s | ||
| 1′ | 103.7 | 4.78 s | ||
| 2′ | 68.5 | 3.80 m | ||
| 3′ | 68.9 | 3.82 m | ||
| 4′ | 70.0 | 3.75 m | ||
| 5′ | 60.8 | 4.26 d (13.2) 3.47 m | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, J.; Li, J.-y.; Feng, X.-l.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, X.; Hui, H.; Xue, X.; Qi, J. Unprecedented Neoverrucosane and Cyathane Diterpenoids with Anti-Neuroinflammatory Activity from Cultures of the Culinary-Medicinal Mushroom Hericium erinaceus. Molecules 2023, 28, 6380. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176380
Wei J, Li J-y, Feng X-l, Zhang Y, Hu X, Hui H, Xue X, Qi J. Unprecedented Neoverrucosane and Cyathane Diterpenoids with Anti-Neuroinflammatory Activity from Cultures of the Culinary-Medicinal Mushroom Hericium erinaceus. Molecules. 2023; 28(17):6380. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176380
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Jing, Jia-yao Li, Xi-long Feng, Yilin Zhang, Xuansheng Hu, Heping Hui, Xiaodong Xue, and Jianzhao Qi. 2023. "Unprecedented Neoverrucosane and Cyathane Diterpenoids with Anti-Neuroinflammatory Activity from Cultures of the Culinary-Medicinal Mushroom Hericium erinaceus" Molecules 28, no. 17: 6380. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176380
APA StyleWei, J., Li, J.-y., Feng, X.-l., Zhang, Y., Hu, X., Hui, H., Xue, X., & Qi, J. (2023). Unprecedented Neoverrucosane and Cyathane Diterpenoids with Anti-Neuroinflammatory Activity from Cultures of the Culinary-Medicinal Mushroom Hericium erinaceus. Molecules, 28(17), 6380. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176380






